From Control to Cure: Insights into the Synergy of Glycemic and Antibiotic Management in Modulating the Severity and Outcomes of Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pathophysiology of Diabetic Foot Ulcers
2.1. Neuropathy, Peripheral Arterial Disease, and Ischemia
2.2. Hyperglycemia, Infection, and Inflammation
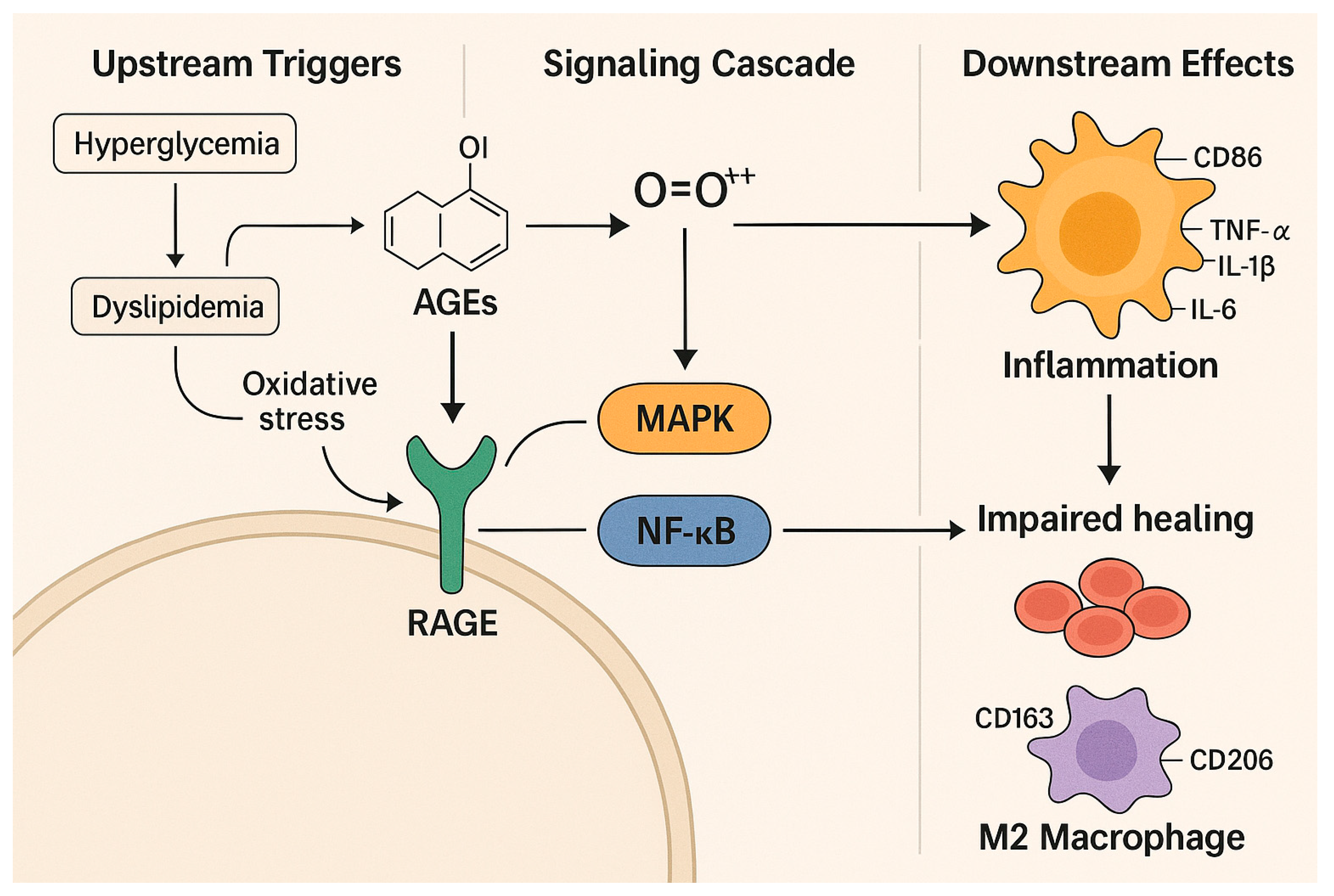
2.3. From Hyperglycemia to Impaired Healing: Molecular Insights into DFU Pathogenesis
3. The Synergy of Glycemic Control and Antibiotic Therapy in DFU Management
3.1. Innovations in Glycemic Monitoring and Control
3.2. Glycemic Control Target
3.3. Bacteria and Antibiotic Resistance in DFUs
3.4. Association Between Antibiotics and the Severity of DFU in Patients with T2DM
3.5. Antibiotic Regimen in the Management of DFU
3.6. Role and Molecular Mechanism of Glycemic Control and Antibiotic Therapy in DFU Management
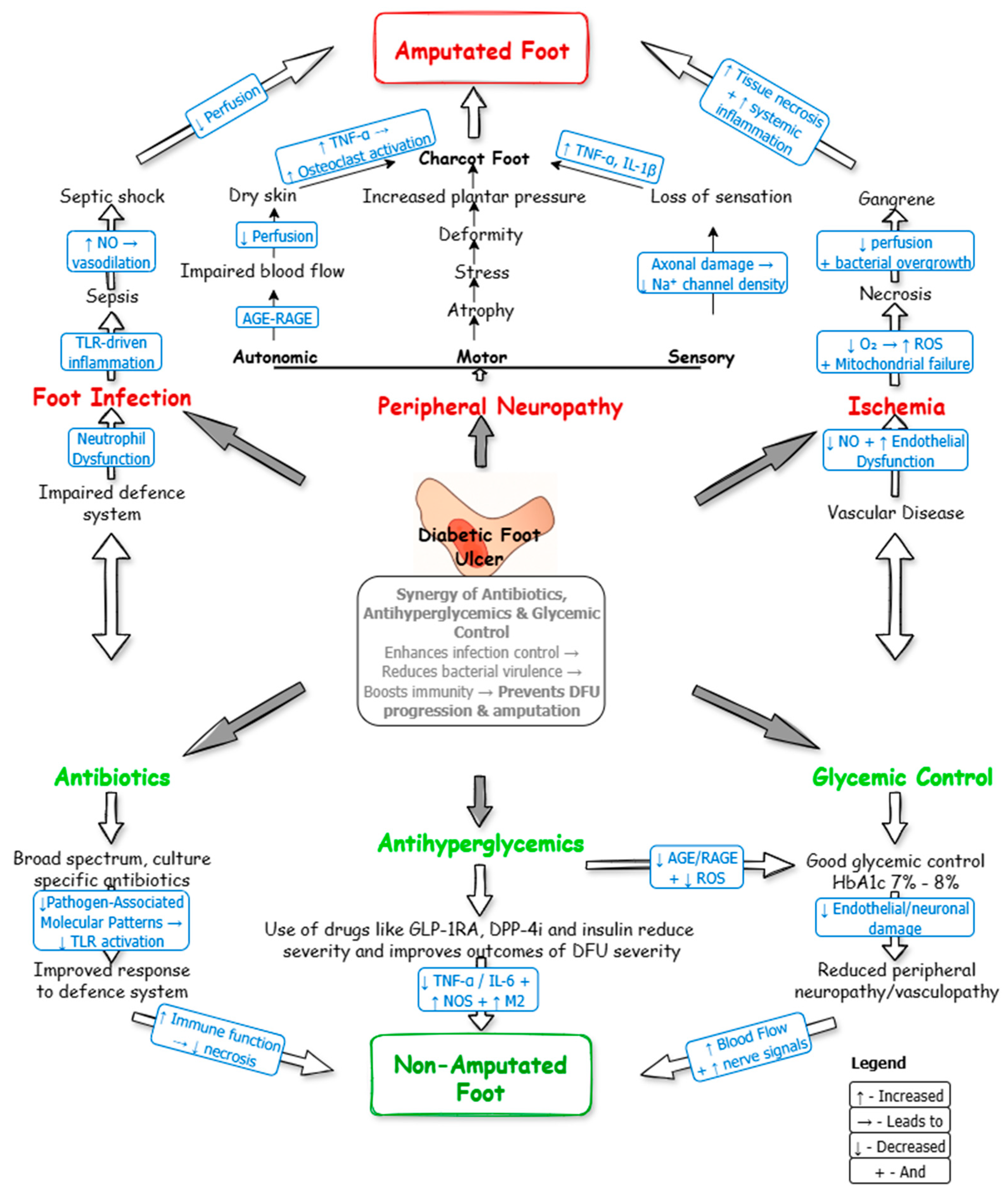
3.6.1. Therapeutic Targeting of DFU Pathophysiology
3.6.2. Synergy of Glycemic Control and Antibiotics
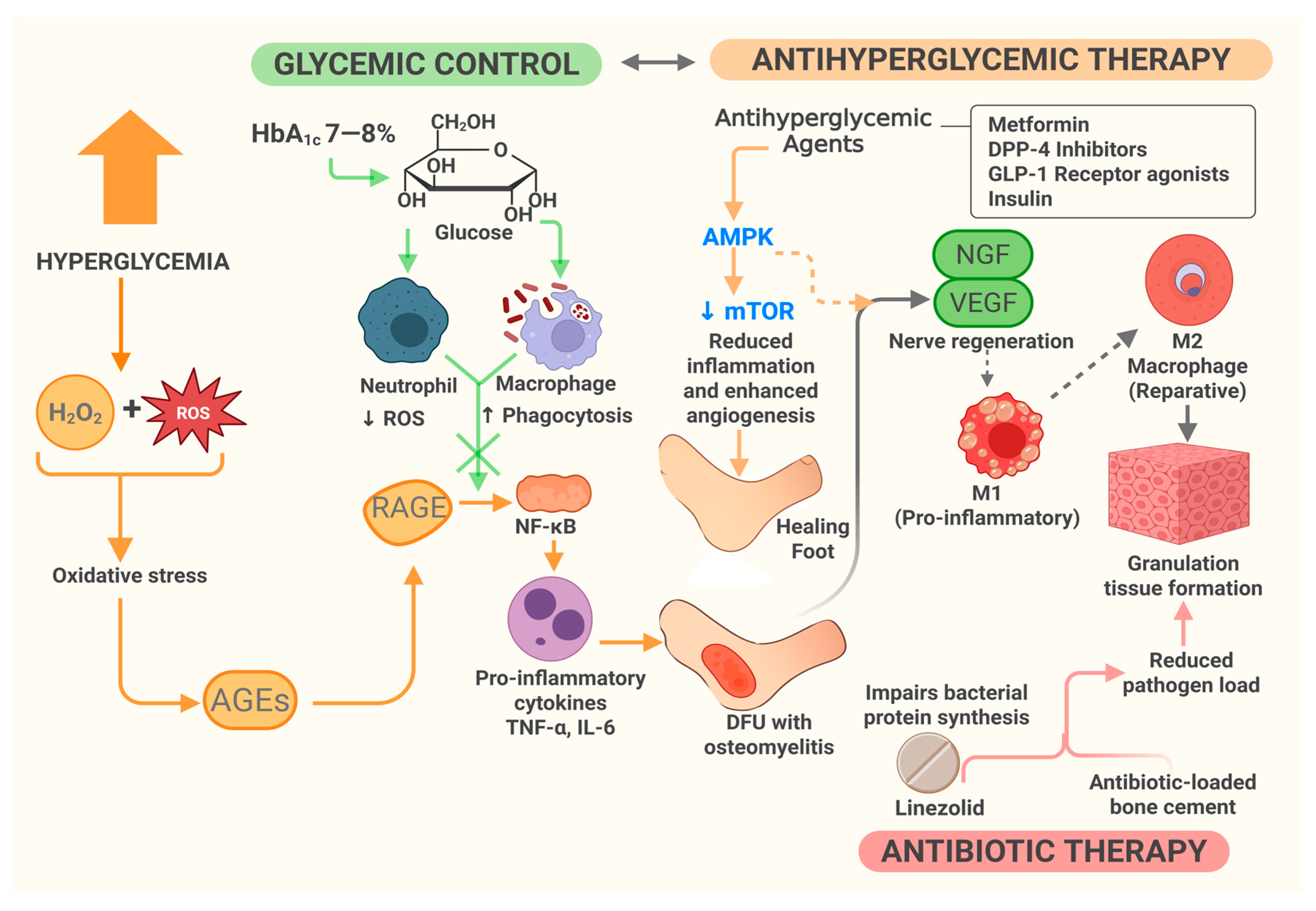
3.6.3. Molecular Mechanism of Combined Therapy
3.6.4. Clinical Staging and Therapeutic Applications
3.7. Real-World Challenges and Recommendations for Improving the Outcomes in DFU and DFI
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGE | Advanced Glycation End-product |
| AMPK | AMP-Activated Protein Kinase |
| BGM | Blood Glucose Monitor |
| CGM | Continuous Glucose Monitoring |
| CKD | Chronic Kidney Disease |
| COVID–19 | Coronavirus Disease 2019 |
| DFI | Diabetic Foot Infections |
| DFU | Diabetic Foot Ulcer |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic Acid |
| DPP4i | Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 enzyme inhibitors |
| eGFR | Glomerular Filtration Rate |
| ERK | Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase |
| GLP1 | Glucagon-like Peptide 1 receptor agonists |
| GMI | Glucose Management Indicator |
| HbA1c | Glycated Hemoglobin |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1 Beta |
| IV | Intravenous |
| JAK | Janus Kinase |
| MAPK | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase |
| MMP | Matrix Metalloproteinase |
| MRSA | Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
| mTOR | Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin |
| NADPH | Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor-Kappa B |
| NGF | Nerve Growth Factor |
| NOX-1 | NADPH Oxidase-1 |
| PAD | Peripheral Arterial Disease |
| PKC | Protein Kinase C |
| PO | Per Oral |
| RAGE | Receptors of Advanced Glycation End-products |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| T2DM | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus |
| TGF-α | Transforming Growth Factor-Alpha |
| TLR | Toll-Like Receptor |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha |
| VEGF | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
References
- Dickson, M.C.; Skrepnek, G.H. Hospitalization and health resource utilization in emergency department cases of diabetic foot infections in the U.S from 2012 to 2021: A nationally representative analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogbeide, O.A.; Okeleke, S.I.; Okorie, J.C.; Mandong, J.; Ajiboye, A.; Olawale, O.O.; Salifu, F. Evolving trends in the management of diabetic foot ulcers: A narrative review. Cureus 2024, 16, e65095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.X.; Niu, S.N.; Mai, L.F.; Liu, X.Z.; Yang, C. Factors associated with infection severity of diabetic foot ulcers: A cross-sectional study. Int. J. Low. Extrem. Wounds 2022, 15347346221140164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maity, S.; Leton, N.; Nayak, N.; Jha, A.; Anand, N.; Thompson, K.; Boothe, D.; Cromer, A.; Garcia, Y.; Al Islam, A.; et al. A systematic review of diabetic foot infections: Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management strategies. Front. Clin. Diabetes Healthc. 2024, 5, 1393309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Shao, T.; Deng, X.; Cao, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, C. Oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation: Prospective associations between ferroptosis and delayed wound healing in diabetic ulcers. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 898657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olamoyegun, M.A.; Alare, K.; Afolabi, S.A.; Aderinto, N.; Adeyemi, T. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence and risk factors of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Nigeria. Clin. Diabetes Endocrinol. 2024, 10, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Pan, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Role of advanced glycation end products in diabetic vascular injury: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Liu, A.; Liu, B.; Huang, W.; Jiang, Z.; Bai, X.; Hu, L.; Zheng, S.; Guo, S.; Wu, J.; et al. Natural biologics accelerate healing of diabetic foot ulcers by regulating oxidative stress. Front. Biosci. 2022, 27, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Mashayamombe, M.; Walsh, T.P.; Kuang, B.K.P.; Pena, G.N.; Vreugde, S.; Cooksley, C.; Carda Diéguez, M.; Mira, A.; Jesudason, D.; et al. The bacteriology of diabetic foot ulcers and infections and incidence of staphylococcus aureus small colony variants. J. Med. Microbiol. 2023, 72, e001716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satpathy, A.S.; Patnaik, B.; Mohapatra, K.C. Prospective observational study of microbiology of infected diabetic foot ulcers in a tertiary care hospital. Cureus 2024, 16, e71705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranuve, M.S.; Mohammadnezhad, M. Healthcare workers’ perceptions on diabetic foot ulcers (DFU) and foot care in Fiji: A qualitative study. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e060896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Nuntaboot, K.; Liu, J.; Long, S. Perceptions of delay in seeking medical help among people with diabetic foot ulcers in rural southwest China. Pac. Rim Int. J. Nurs. Res. 2024, 28, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunlana, M.O.; Govender, P.; Oyewole, O.O.; Odole, A.C.; Falola, J.L.; Adesina, O.F.; Akindipe, J.A. Qualitative exploration into reasons for delay in seeking medical help with diabetic foot problems. Int. J. Qual. Stud. Health Well Being 2021, 16, e1945206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, I.G.; Tregunno, D.; Camargo Plazas, P. Patients’ perceptions of reasons contributing to delay in seeking help at the onset of a diabetic foot ulcer: A grounded theory study. J. Wound Ostomy Cont. Nurs. 2022, 49, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, R.; Bhadada, S.K. AGEs accumulation with vascular complications, glycemic control, and metabolic syndrome: A narrative review. Bone 2023, 176, 116884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zeng, G.; Hu, J.; Li, M.; Tian, M.; Lei, T.; Huang, R. Advanced glycation end products regulate macrophage apoptosis and influence the healing of diabetic foot wound through miR 361 3p/CSF1R and PI3K/AKT pathway. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.; Xu, H.; Liu, Q. Effects of advanced glycation end products on neutrophil migration and aggregation in diabetic wounds. Aging 2021, 13, 12143–12159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Sahoo, J.P.; Mennon, A.; Ghosh, A.; Jha, S.; Bal, A. Intensive glycemic control for diabetic foot ulcer healing: A multicentric, randomised, parallel arm, single blind, controlled study protocol (INGLOBE Study). Int. J. Low. Extrem. Wounds 2020, 21, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berlanga Acosta, J.; Garcia del Barco, D.; Cibrian Vera, D.; Savigne, W.; Lopez-Saura, P.; Guillen Nieto, G.; Schultz Acosta, J.B.; Barco, D. The pro-inflammatory environment in recalcitrant diabetic foot wounds. Int. Wound J. 2008, 5, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, C.; Lima, M.J.; Fernandes, R. Modulation of oxidative stress and Nrf2 pathway in diabetic wound healing. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Wei, H.; Zhang, T.; Li, Z.; Chi, X.; Liu, D.; Chang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Q. A potent weighted risk model for evaluating the occurrence and severity of diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2021, 13, e00711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndosi, M.; Wright Hughes, A.; Brown, S.; Backhouse, M.; Lipsky, B.A.; Bhogal, M.; Reynolds, C.; Vowden, P.; Jude, E.B.; Nixon, J.; et al. Prognosis of the infected diabetic foot ulcer: A 12-month prospective observational study. Diabet. Med. 2018, 35, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayate, A.S.; Nagoba, B.S.; Mumbre, S.S.; Mavani, H.B.; Gavkare, A.M.; Deshpande, A.S. Current scenario of traditional medicines in management of diabetic foot ulcers: A review. World J. Diabetes 2023, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDermott, K.; Fang, M.; Boulton, A.J.M.; Selvin, E.; Hicks, C.W. Etiology, epidemiology, and disparities in the burden of diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, 209–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.Z.; Al Hajri, N.; Kanbour, S.; Ahmadzada, M.; Borovoy, A.; Abusamaan, M.S.; Canner, J.K.; Nass, C.; Sherman, R.L.; Hines, K.F.; et al. Glycemic control in diabetic foot ulcers: A comparative analysis of wound and wound-free periods in adults with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Can. J. Diabetes 2024, 48, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgetto, J.V.; Oggiam, D.S.; Gamba, M.A.; Kusahara, D.M. Factors associated with changes in plantar pressure of people with peripheral diabetic neuropathy. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2022, 21, 1577–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nativel, M.; Potier, L.; Alexandre, L.; Baillet Blanco, L.; Ducasse, E.; Velho, G.; Marre, M.; Roussel, R.; Rigalleau, V.; Mohammedi, K. Lower extremity arterial disease in patients with diabetes: A contemporary narrative review. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, B.; Liu, H.; Chang, Q. Microenvironmental dynamics of diabetic wounds and insights for hydrogel-based therapeutics. J. Tissue Eng. 2024, 15, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J. The pathophysiology of diabetic foot: A narrative review. J. Yeungnam Med. Sci. Yeungnam Univ. Sch. Med. 2023, 40, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mieczkowski, M.; Mrozikiewicz Rakowska, B.; Kowara, M.; Kleibert, M.; Czupryniak, L. The problem of wound healing in diabetes—From molecular pathways to the design of an animal model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, F.; Liu, C.; Hu, H.; Zhang, Q. Advanced glycation end products and diabetes and other metabolic indicators. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2022, 14, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brownlee, M. Biochemistry and molecular cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature 2001, 414, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.W.; Hung, C.M.; Chen, W.J.; Chen, J.C.; Huang, W.Y.; Lu, C.S.; Kuo, M.L.; Chen, S.G. New horizons of macrophage immunomodulation in the healing of diabetic foot ulcers. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Wang, Q.; Huang, X.; Feng, J.; Wang, Y.; Shao, T.; Deng, X.; Cao, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhou, M.; et al. Wounds under diabetic milieu: The role of immune cellar components and signaling pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 157, 114052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Wu, T.; Zhang, J.; Liang, Z.; Shao, W.; Wang, D.; Li, L.; Zuo, D.; Zhou, J. D-mannose promotes diabetic wound healing through inhibiting advanced glycation end products formation in keratinocytes. Mol. Med. 2025, 31, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasi, A.T. Neural control system for continuous glucose monitoring and maintenance. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.13852. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Health (Malaysia). Clinical Practice Guideline: Management of Diabetic Foot, 2nd ed.; Ministry of Health: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2018; pp. 50–51.
- Yin, X.; Zhu, W.; Liu, C.; Yao, H.; You, J.; Chen, Y.; Ying, X.; Li, L. Association of continuous glucose monitoring-derived time in range with major amputation risk in diabetic foot osteomyelitis patients undergoing amputation. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 13, e21099337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, T.; Beck, R.W.; Bailey, R.; Ruedy, K.J.; Calhoun, P.; Peters, A.L.; Pop Busui, R.; Philis Tsimikas, A.; Bao, S.; Umpierrez, G.; et al. Effect of continuous glucose monitoring on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with basal insulin: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2021, 326, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldocsda, R. Non-invasive glucose monitoring: Pioneering the future of diabetes care. J. Dia. Med. Care 2024, 7, 234–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunsanya, A.O.; Daramola, D.O. Design and development of a non-invasive glucometer system. West Indian J. Eng. 2022, 44, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felgueiras, H.P. Emerging antimicrobial and immunomodulatory fiber-based scaffolding systems for treating diabetic foot ulcers. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of medical care in diabetes. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, S15–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, J.; Wang, S.; He, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhang, S.; Tang, Z. Reasonable glycemic control would help wound healing during the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetes Ther. 2019, 10, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fesseha, B.K.; Abularrage, C.J.; Hines, K.F.; Sherman, R.; Frost, P.; Langan, S.; Canner, J.; Likes, K.C.; Hosseini, S.M.; Jack, G.; et al. Association of hemoglobin A1c and wound healing in diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 1478–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, K.L.; Abusamaan, M.S.; Voss, B.F.; Thurber, E.G.; Al Hajri, N.; Gopakumar, S.; Le, J.T.; Gill, S.; Blanck, J.; Prichett, L.; et al. Glycemic control and diabetic foot ulcer outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2020, 34, e107638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanathan, B.; Duraisamy, R.; Venkatramanasami, B.T.D.; Abbas, M.K.; Balamurugan, A. Association of glycemic status and outcomes in diabetic foot problems: Retrospective evidence from south India. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2022, 33, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Aroda, V.R.; Bannuru, R.R.; Brown, F.M.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Hilliard, M.E.; Isaacs, D.; Johnson, E.L.; et al. Glycemic targets: Standards of care in diabetes. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, S97–S110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. Glycemic targets: Standards of medical care in diabetes. Diabetes Care 2021, 45, S83–S96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, K.B.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, Y.K. Factors influencing wound healing in diabetic foot patients. Medicina 2024, 60, e50723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makeri, D.; Odoki, M.; Eilu, E.; Agwu, E. Update on prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from diabetic foot ulcers in Africa: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2023, 47, e01119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heravi, F.S.; Zakrzewski, M.; Vickery, K.; Armstrong, D.G.; Hu, H. Bacterial diversity of diabetic foot ulcers: Current status and future prospects. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Złoch, M.; Maślak, E.; Kupczyk, W.; Pomastowski, P. Multi-instrumental analysis toward exploring the diabetic foot infection microbiota. Curr. Microbiol. 2023, 80, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, D.M.; Rao, V.I.; Moosabba, M.S.; MubarakAli, D.; Manzoor, M. Antimicrobial resistance and prevalence of β-lactamase genes among multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from infected diabetic foot ulcers. Bacteria 2025, 4, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.; Moursi, S.A.; Altamimi, T.N.A.; Alharbi, M.S.; Alaskar, A.M.; Hammam, S.A.H.; Rakha, E.; Syed Muhammad, O.I.; Almalaq, H.A.; Alshammari, M.N.; et al. Prevalence and molecular characterisation of car-bapenemase-producing multidrug-resistant bacteria in diabetic foot ulcer infections. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barwell, N.D.; Devers, M.C.; Kennon, B.; Hopkinson, H.E.; McDougall, C.; Young, M.J.; Robertson, H.M.A.; Stang, D.; Dancer, S.J.; Seaton, A.; et al. Diabetic foot infection: Antibiotic therapy and good practice recommendations. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2017, e13006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regis, E.; Hao, Z.; Baiwen, Q.; Aixi, Y. Application and clinical effectiveness of antibiotic-loaded bone cement to promote soft tissue granulation in neuropathic diabetic foot ulcers complicated by osteomyelitis: A randomised controlled trial. J. Diabetes Res. 2021, 2021, 9911072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mougakou, E.; Mastrogianni, E.; Kyziroglou, M.; Tziomalos, K. The role of novel antibiotics in the management of diabetic foot infection. Diabetes Ther. 2023, 14, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jm, R.; Ma, M.; Kayali, S.; Khouzam, A.; Efeovbokhan, N. Diabetic foot ulcer: A comprehensive review of pathophysiology and management modalities. World J. Clin. Cases 2023, 11, 1684–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, K.; Anastasio, A.T.; Krez, A.; Siewny, L.; Adams, S.B. Charcot neuroarthropathy of the foot and ankle in the acute setting: An illustrative case report and targeted review. West. J. Emerg. Med. 2023, 24, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matheson, E.M.; Bragg, S.W.; Blackwelder, R.S. Diabetes related foot infections: Diagnosis and treatment. Am. Fam. Phys. 2021, 104, 386–394. [Google Scholar]
- Kuthati, Y.; Davuluri, V.N.G.; Wong, C.S. Therapeutic effects of GLP 1 receptor agonists and DPP 4 inhibitors in neuropathic pain: Mechanisms and clinical implications. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wu, T.; Ren, N. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists for the management of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1268619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegazy, W.A.H.; Rajab, A.A.H.; Abu Lila, A.S.; Abbas, H.A. Anti diabetics and antimicrobials: Harmony of mutual inter-play. World J. Diabetes 2021, 12, 1832–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khayat, M.T.; Abbas, H.A.; Ibrahim, T.S.; Elbaramawi, S.S.; Khayyat, A.N.; Alharbi, M.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Yehia, F.A.Z. Synergistic benefits: Exploring the anti-virulence effects of metformin/vildagliptin antidiabetic combination against Pseudomonas aeruginosa via controlling quorum sensing systems. Biomedicines 2023, 11, e11051442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christman, A.L.; Selvin, E.; Margolis, D.J.; Lazarus, G.S.; Garza, L.A. Hemoglobin A1c predicts healing rate in diabetic wounds. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 2121–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecube, A.; Pachón, G.; Petriz, J.; Hernández, C.; Simó, R. Phagocytic activity is impaired in type 2 diabetes mellitus and increases after metabolic improvement. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.; Jaggers, R.M.; Gopalkrishna, S.; Dahdah, A.; Murphy, A.J.; Hanssen, N.M.J.; Nagareddy, P.R. Oxidative stress in neutrophils: Implications for diabetic cardiovascular complications. Antioxid. Redox. Signal. 2022, 36, 652–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlou, S.; Lindsay, J.; Ingram, R.; Xu, H.; Chen, M. Sustained high glucose exposure sensitises macrophage responses to cytokine stimuli but reduces their phagocytic activity. BMC Immunol. 2018, 19, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Cai, L.; de Haan, J.B.; Giacconi, R. Targeting oxidative stress in diabetic complications: New insights. J. Diabetes Res. 2018, 1909675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, H.; Guo, X.; Li, P. The effect of topical insulin therapy on diabetic foot ulcers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Tissue Viability 2025, 34, 100932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, A.K.; Seikh, O.; Elamurugan, T.P.; Ali, M. Effect of topical insulin on wound healing in diabetic foot ulcer—A prospective randomized controlled trial. Surg. Chron. 2022, 27, 91–94. [Google Scholar]
- Abdraimova, N.K.; Shitikov, E.A.; Bespiatykh, D.A.; Gorodnichev, R.B.; Klimina, K.M.; Veselovsky, V.A.; Boldyreva, D.I.; Bogdanova, A.S.; Klinov, D.V.; Kornienko, M.A. Response of Staphylococcus aureus to combination of virulent bacteriophage vB_SauM-515A1 and linezolid. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1519312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miceli, G.; Basso, M.G.; Pennacchio, A.R.; Cocciola, E.; Pintus, C.; Cuffaro, M.; Profita, M.; Rizzo, G.; Sferruzza, M.; Tut-tolomondo, A. The potential impact of SGLT2 I in diabetic foot prevention: Promising pathophysiologic implications, state of the art, and future perspectives—A narrative review. Medicina 2024, 60, 1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werkman, N.C.C.; Driessen, J.H.M.; Klungel, O.H.; Schaper, N.S.; Souverein, P.C.; Stehouwer, C.D.A.; Nielen, J.T.H. Incretin-based therapy and the risk of diabetic foot ulcers and related events. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2024, 26, 3764–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Rong, G.C.; Wu, Q.N. Diabetic foot ulcer: Challenges and future. World J. Diabetes 2022, 13, 1014–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panou, T.; Gouveri, E.; Popovic, D.S.; Papazoglou, D.; Papanas, N. The therapeutic potential of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Diabetes Ther. 2025, 16, 1077–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Bai, L.; Fan, B.; Ding, H.; Ding, H.; Hou, L.; Ma, H.; Xing, N.; Wang, F. Effect of SGLT2 inhibitors versus DPP4 inhibitors or GLP 1 agonists on diabetic foot related extremity amputation in patients with T2DM: A meta-analysis. Prim. Care Diabetes 2022, 16, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, M.B.; Powell, W.R.; Kaiksow, F.; Kramer, J.; Liu, Y.; Kind, A.J.H.; Bartels, C.M. Association of race, ethnicity, and rurality with major leg amputation or death among medicare beneficiaries hospitalized with diabetic foot ulcers. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e228399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, G.; Feldman, G.; Dimri, I.; Shapiro, A.; Rozen, N. Effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on the outcome and mortality of patients with diabetic foot ulcers. Int. Wound J. 2022, 19, e13837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalilian, M.; Sarbarzeh, P.A.; Oubari, S. Factors related to the severity of diabetic foot ulcer: A systematic review. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2020, 13, 1835–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Singh, S.K.; Agrawal, N.K.; Kumar, U.; Kumar, S.C.S.; Bishnoi, A. The prevalence of anemia in hospitalized patients with diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) and the relationship between the severity of anaemia and the severity of DFU. Cureus 2023, 15, e41922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershater, M.A.; Apelqvist, J. Elderly individuals with diabetes and foot ulcer have a probability for healing despite extensive comorbidity and dependency. Expert Rev. Pharmacoecon. Outcomes Res. 2021, 21, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnet, J.B.; Sultan, A. Narrative review of the relationship between CKD and diabetic foot ulcer. Kidney Int. Rep. 2022, 7, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elghoneimy, Y.A.; Alkabah, A.A.; Alalsayedsalih, H.M.; Almanyan, A.J.; Alibrahim, H.A.; Albokamsin, M.H.; Alshammary, S.A.; Makhdom, F.A. Risk factors and surgical outcomes of diabetic foot in diabetic patients at King Fahad University Hospital. Cureus 2022, 14, e32457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mader, J.K.; Haas, W.; Aberer, F.; Boulgaropoulos, B.; Baumann, P.; Pandis, M.; Horvath, K.; Aziz, F.; Köhler, G.; Pieber, T.R.; et al. Patients with healed diabetic foot ulcer represent a cohort at highest risk for future fatal events. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, e46961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uçkay, I.; Schöni, M.; Berli, M.C.; Niggli, F.; Noschajew, E.; Lipsky, B.A.; Waibel, F.W.A. The association of chronic, enhanced immunosuppression with outcomes of diabetic foot infections. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2022, 5, e298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Nomkhondorj, O.; An, C.Y.; Choi, Y.C.; Cho, J. Management of diabetic foot ulcers: A narrative review. J. Yeungnam Med. Sci. 2023, 40, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, T.W.; Crocker, R.M.; Palmer, K.N.B.; Gomez, C.; Armstrong, D.G.; Marrero, D.G. A qualitative study of barriers to care seeking for diabetic foot ulceration across multiple levels of the healthcare system. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2022, 15, e00561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piragine, E.; Petri, D.; Martelli, A.; Calderone, V.; Lucenteforte, E. Adherence to oral antidiabetic drugs in patients with type 2 diabetes: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, M.; Schindler, C. Clinically and pharmacologically relevant interactions of antidiabetic drugs. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 7, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivadas, A.; Sahana, S.; Jolly, B.; Bhoyar, R.C.; Jain, A.; Sharma, D.; Imran, M.; Senthivel, V.; Divakar, M.K.; Mishra, A.; et al. Landscape of pharmacogenetic variants associated with non-insulin antidiabetic drugs in the Indian population. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2024, 12, e003769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Omotosho, I.A.; Shamsuddin, N.; Zaman Huri, H.; Chong, W.L.; Rehman, I.U. From Control to Cure: Insights into the Synergy of Glycemic and Antibiotic Management in Modulating the Severity and Outcomes of Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6909. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146909
Omotosho IA, Shamsuddin N, Zaman Huri H, Chong WL, Rehman IU. From Control to Cure: Insights into the Synergy of Glycemic and Antibiotic Management in Modulating the Severity and Outcomes of Diabetic Foot Ulcers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6909. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146909
Chicago/Turabian StyleOmotosho, Idris Ajibola, Noorasyikin Shamsuddin, Hasniza Zaman Huri, Wei Lim Chong, and Inayat Ur Rehman. 2025. "From Control to Cure: Insights into the Synergy of Glycemic and Antibiotic Management in Modulating the Severity and Outcomes of Diabetic Foot Ulcers" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6909. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146909
APA StyleOmotosho, I. A., Shamsuddin, N., Zaman Huri, H., Chong, W. L., & Rehman, I. U. (2025). From Control to Cure: Insights into the Synergy of Glycemic and Antibiotic Management in Modulating the Severity and Outcomes of Diabetic Foot Ulcers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6909. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146909






