Sensitivity of Pancreatic Cancer Cell Lines to Clinically Approved FAK Inhibitors: Enhanced Cytotoxicity Through Combination with Oncolytic Coxsackievirus B3
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. FAKi Induce Dephosphorylation at Tyr-397 of FAK in Pancreatic Tumor Cells
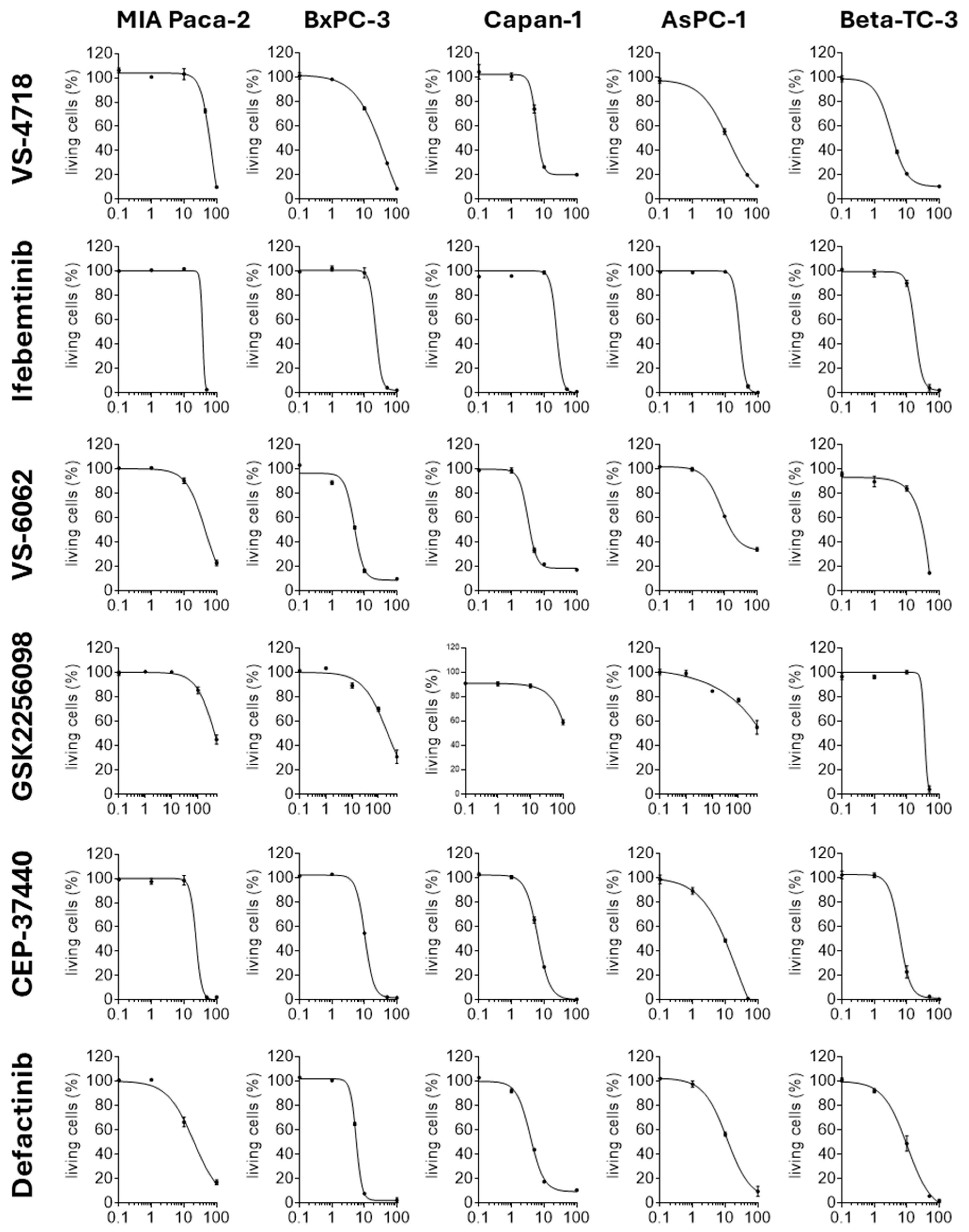
2.2. FAKi Have Different Oncolytic Activity in Pancreatic Tumor Cells
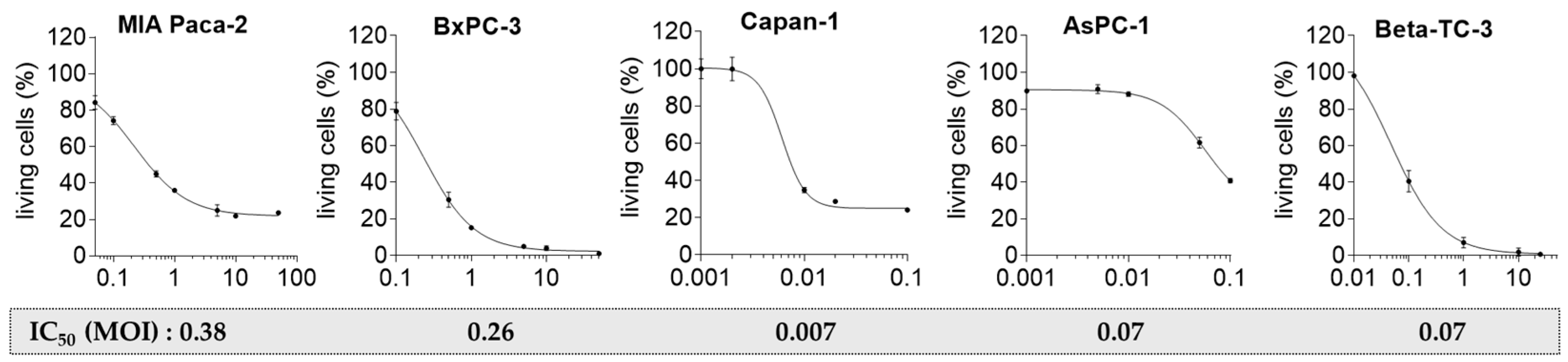
2.3. Pancreatic Tumor Cells Exhibit Different Sensitivity to the Oncolytic CVB3 PD-H
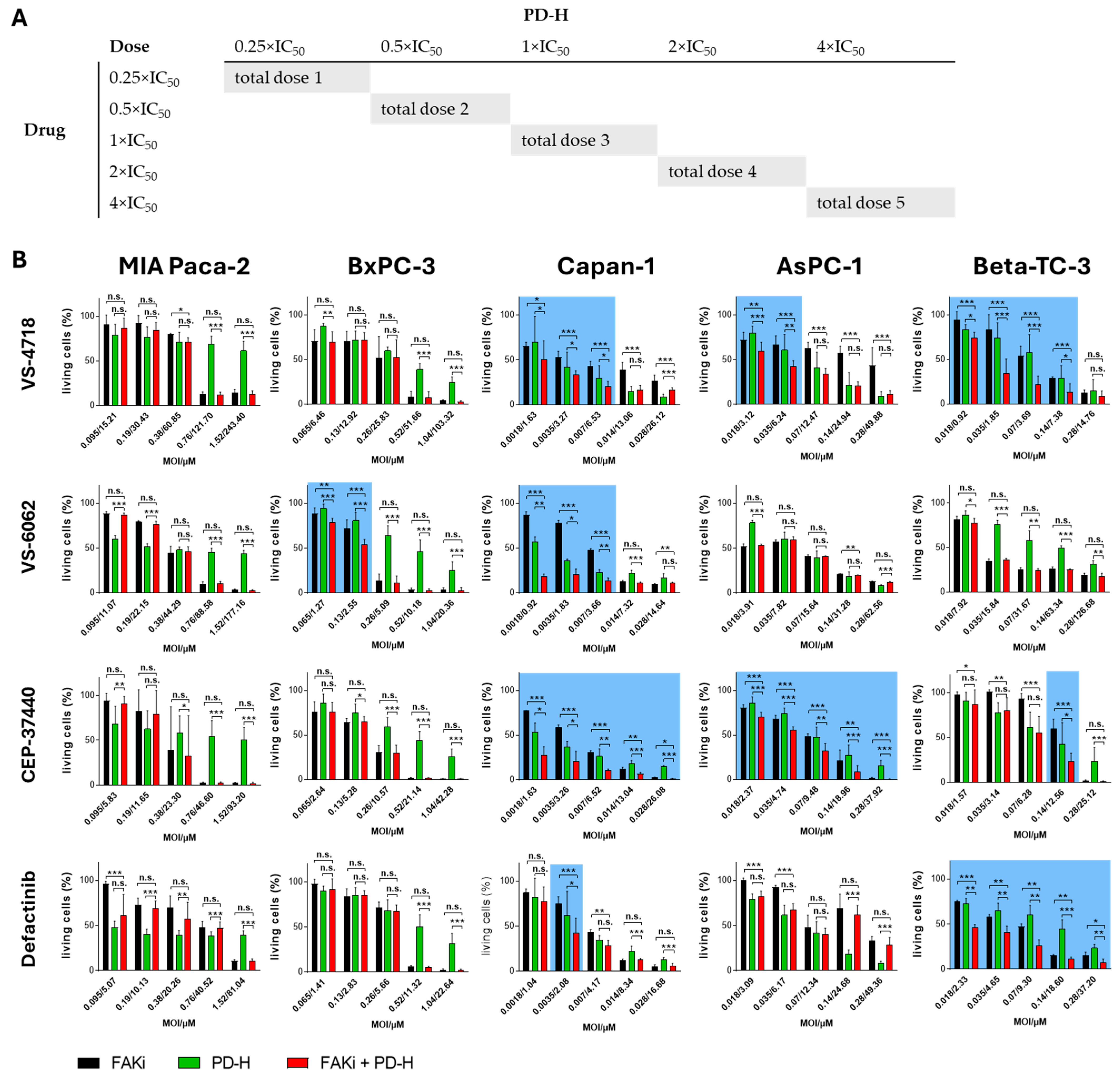
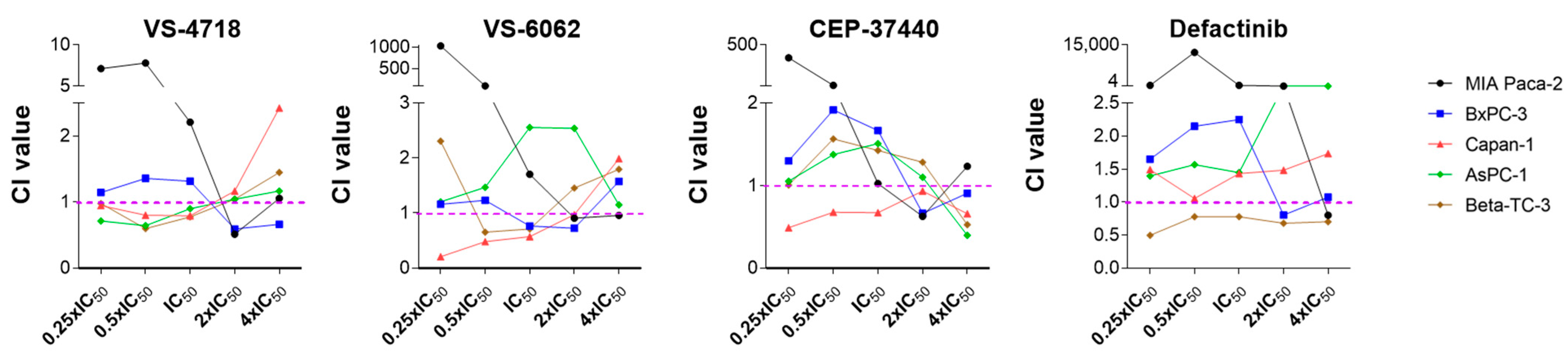
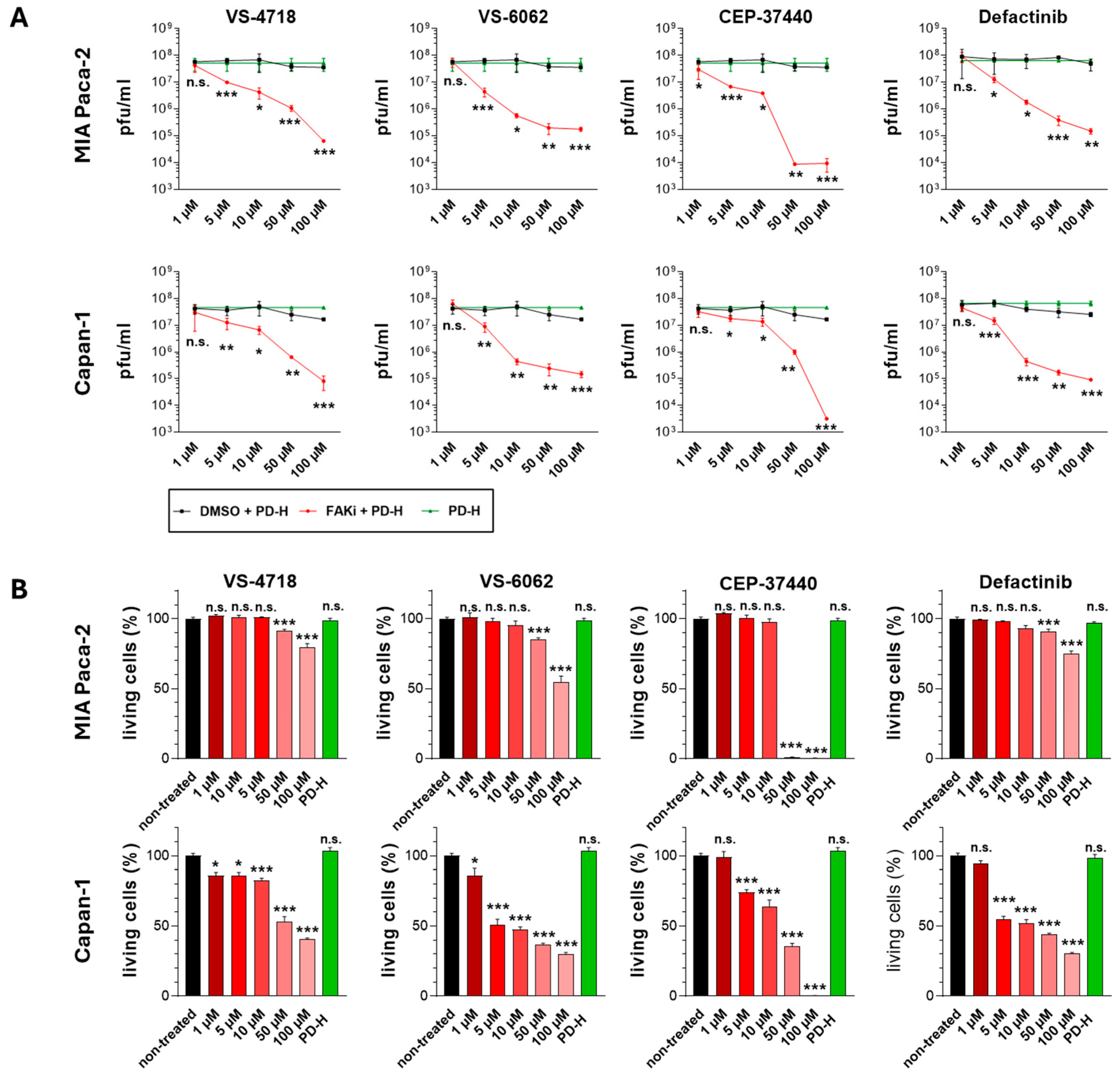
2.4. The Combination of FAKi and PD-H Can Induce a Higher Cytotoxicity in Pancreatic Tumor Cells than Treatment with Either Agent Alone
2.5. Treatment of Pancreatic Tumor Cells with FAKi Inhibits PD-H Replication
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Virus
4.3. FAKi
4.4. Cell Viability Assay
4.5. Determination of IC50 of FAKi
4.6. Determination of IC50 of PD-H
4.7. Determination of the Combination Index Using the Chou–Talalay Constant Ratio Approach
4.8. Virus Growth Curves
4.9. Virus Plaque Assay
4.10. Western Blot
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kan, C.; Liu, N.; Zhang, K.; Wu, D.; Liang, Y.; Cai, W.; Jing, Q.; Han, F.; Xing, S.; Sun, X. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Pancreatic Cancer, 1990–2019: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Ann. Glob. Health 2023, 89, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Siegel, R.L.; Ferlay, J.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saiki, Y.; Horii, A. Molecular Pathology of Pancreatic Cancer. Pathol. Int. 2014, 64, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potievskiy, M.B.; Nekrasova, L.A.; Korobov, I.V.; Bykova, E.A.; Moshurov, R.I.; Sokolov, P.V.; Shatalov, P.A.; Falaleeva, N.A.; Petrov, L.O.; Trifanov, V.S.; et al. Prognostic Impact of Phenotypic and Genetic Features of Pancreatic Malignancies. Life 2025, 15, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.; Letson, J.; Furuta, S. Fibrous Stroma: Driver and Passenger in Cancer Development. Sci. Signal 2022, 15, eabg3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazan-Peregrino, M.; Garcia-Carbonero, R.; Laquente, B.; Álvarez, R.; Mato-Berciano, A.; Gimenez-Alejandre, M.; Morgado, S.; Rodríguez-García, A.; Maliandi, M.V.; Riesco, M.C.; et al. VCN-01 Disrupts Pancreatic Cancer Stroma and Exerts Antitumor Effects. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e003254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakkera, M.; Foote, J.B.; Farran, B.; Nagaraju, G.P. Breaking the Stromal Barrier in Pancreatic Cancer: Advances and Challenges. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2024, 1879, 189065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulart, M.R.; Stasinos, K.; Fincham, R.E.A.; Delvecchio, F.R.; Kocher, H.M. T Cells in Pancreatic Cancer Stroma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 7956–7968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, M.; Haghnejad, V.; Schaefer, M.; Gauchotte, G.; Caron, B.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Bronowicki, J.-P.; Neuzillet, C.; Lopez, A. The Immune Landscape of Human Pancreatic Ductal Carcinoma: Key Players, Clinical Implications, and Challenges. Cancers 2022, 14, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hingorani, S.R.; Zheng, L.; Bullock, A.J.; Seery, T.E.; Harris, W.P.; Sigal, D.S.; Braiteh, F.; Ritch, P.S.; Zalupski, M.M.; Bahary, N.; et al. HALO 202: Randomized Phase II Study of PEGPH20 Plus Nab-Paclitaxel/Gemcitabine Versus Nab-Paclitaxel/Gemcitabine in Patients with Untreated, Metastatic Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, S.R.; Quaranta, V.; Linford, A.; Emeagi, P.; Rainer, C.; Santos, A.; Ireland, L.; Sakai, T.; Sakai, K.; Kim, Y.-S.; et al. Macrophage-Secreted Granulin Supports Pancreatic Cancer Metastasis by Inducing Liver Fibrosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 18, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, Y.-L.; Chen, L.-C.; Shen, T.-L. Emerging Roles of Focal Adhesion Kinase in Cancer. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 690690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.Y.; Timpson, P.; Horvath, L.G.; Daly, R.J. FAK Signaling in Human Cancer as a Target for Therapeutics. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 146, 132–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, J.M.; Rodriguez, Y.A.R.; Jeong, K.; Ahn, E.-Y.E.; Lim, S.-T.S. Targeting Focal Adhesion Kinase in Cancer Cells and the Tumor Microenvironment. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Hochwald, S.N. The Role of FAK in Tumor Metabolism and Therapy. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 142, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Hegde, S.; Knolhoff, B.L.; Zhu, Y.; Herndon, J.M.; Meyer, M.A.; Nywening, T.M.; Hawkins, W.G.; Shapiro, I.M.; Weaver, D.T.; et al. Targeting Focal Adhesion Kinase Renders Pancreatic Cancers Responsive to Checkpoint Immunotherapy. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulzmaier, F.J.; Jean, C.; Schlaepfer, D.D. FAK in Cancer: Mechanistic Findings and Clinical Applications. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 598–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, K.J.; Zhu, J.; Trpceski, M.; Pereira, B.A.; Timpson, P.; Herrmann, D. Focal Adhesion Kinase Priming in Pancreatic Cancer, Altering Biomechanics to Improve Chemotherapy. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2022, 50, 1129–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, H.-H.; Zhen, Y.-Y.; Tsai, Y.-C.; Chuang, C.-H.; Hsiao, M.; Huang, M.-S.; Yang, C.-J. FAK in Cancer: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokes, J.B.; Adair, S.J.; Slack-Davis, J.K.; Walters, D.M.; Tilghman, R.W.; Hershey, E.D.; Lowrey, B.; Thomas, K.S.; Bouton, A.H.; Hwang, R.F.; et al. Inhibition of Focal Adhesion Kinase by PF-562,271 Inhibits the Growth and Metastasis of Pancreatic Cancer Concomitant with Altering the Tumor Microenvironment. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 2135–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soria, J.C.; Gan, H.K.; Blagden, S.P.; Plummer, R.; Arkenau, H.T.; Ranson, M.; Evans, T.R.J.; Zalcman, G.; Bahleda, R.; Hollebecque, A.; et al. A Phase I, Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Study of GSK2256098, a Focal Adhesion Kinase Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 2268–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.F.; Siu, L.L.; Bendell, J.C.; Cleary, J.M.; Razak, A.R.A.; Infante, J.R.; Pandya, S.S.; Bedard, P.L.; Pierce, K.J.; Houk, B.; et al. A Phase I Study of VS-6063, a Second-Generation Focal Adhesion Kinase Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Investig. New Drugs 2015, 33, 1100–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jonge, M.J.A.; Steeghs, N.; Lolkema, M.P.; Hotte, S.J.; Hirte, H.W.; van der Biessen, D.A.J.; Abdul Razak, A.R.; De Vos, F.Y.F.L.; Verheijen, R.B.; Schnell, D.; et al. Phase I Study of BI 853520, an Inhibitor of Focal Adhesion Kinase, in Patients with Advanced or Metastatic Nonhematologic Malignancies. Targ. Oncol. 2019, 14, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerber, D.E.; Camidge, D.R.; Morgensztern, D.; Cetnar, J.; Kelly, R.J.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Spigel, D.R.; Jeong, W.; Scaglioni, P.P.; Zhang, S.; et al. Phase 2 Study of the Focal Adhesion Kinase Inhibitor Defactinib (VS-6063) in Previously Treated Advanced KRAS Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer 2020, 139, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, T.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Shitara, K.; Naito, Y.; Cheng, A.-L.; Sarashina, A.; Pronk, L.C.; Takeuchi, Y.; Lin, C.-C. Phase I Study of the Focal Adhesion Kinase Inhibitor BI 853520 in Japanese and Taiwanese Patients with Advanced or Metastatic Solid Tumors. Target. Oncol. 2019, 14, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, T.; Tateishi, R.; Iwai, M.; Tanaka, M.; Ijichi, H.; Sano, M.; Koike, K.; Todo, T. Overcoming Resistance of Stroma-Rich Pancreatic Cancer with Focal Adhesion Kinase Inhibitor Combined with G47Δ and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2023, 28, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coma, S.; Liu, X.; Pieper, N.L.; Chang, W.-H.; Bryant, K.L.; Der, C.J.; DeNardo, D.G.; Pachter, J.A. Abstract A091: The RAF/MEK Clamp Avutometinib as the Backbone of Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer: Novel Combinations with Standard of Care Chemotherapy, FAK Inhibitors, KRAS G12D Inhibitors and/or Autophagy Inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2024, 84, A091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osipov, A.; B. Blair, A.; Liberto, J.; Wang, J.; Li, K.; Herbst, B.; Xu, Y.; Li, S.; Niu, N.; Rashid, R.; et al. Inhibition of Focal Adhesion Kinase Enhances Antitumor Response of Radiation Therapy in Pancreatic Cancer through CD8+ T Cells. Cancer Biol. Med. 2021, 18, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez-Arreguín, K.; Kaur, B. Triple Combination Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer Remodels Stroma and Improves Survival. Mol. Ther-Oncolytics 2023, 29, 15–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musher, B.L.; Rowinsky, E.K.; Smaglo, B.G.; Abidi, W.; Othman, M.; Patel, K.; Jawaid, S.; Jing, J.; Brisco, A.; Leen, A.M.; et al. LOAd703, an Oncolytic Virus-Based Immunostimulatory Gene Therapy, Combined with Chemotherapy for Unresectable or Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer (LOKON001): Results from Arm 1 of a Non-Randomised, Single-Centre, Phase 1/2 Study. Lancet Oncol. 2024, 25, 488–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, A.B.; Wang, J.; Davelaar, J.; Baker, A.; Li, K.; Niu, N.; Wang, J.; Shao, Y.; Funes, V.; Li, P.; et al. Dual Stromal Targeting Sensitizes Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma for Anti-Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 Therapy. Gastroenterology 2022, 163, 1267–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang-Gillam, A.; Lim, K.-H.; McWilliams, R.; Suresh, R.; Lockhart, A.C.; Brown, A.; Breden, M.; Belle, J.I.; Herndon, J.; Bogner, S.J.; et al. Defactinib, Pembrolizumab, and Gemcitabine in Patients with Advanced Treatment Refractory Pancreatic Cancer: A Phase I Dose Escalation and Expansion Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 5254–5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, H.L.; Kohlhapp, F.J.; Zloza, A. Oncolytic Viruses: A New Class of Immunotherapy Drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 642–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andtbacka, R.H.; Kaufman, H.L.; Collichio, F.; Amatruda, T.; Senzer, N.; Chesney, J.; Delman, K.A.; Spitler, L.E.; Puzanov, I.; Agarwala, S.S.; et al. Talimogene Laherparepvec Improves Durable Response Rate in Patients with Advanced Melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2780–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Fang, H. Clinical Trials with Oncolytic Adenovirus in China. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2007, 7, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.; Shimada., H.; Hiroshima, K.; Tada, Y.; Suzuki, N.; Tagawa, M. Gene Medicine for Cancer Treatment: Commercially Available Medicine and Accumulated Clinical Data in China. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2009, 2, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Todo, T.; Ino, Y.; Ohtsu, H.; Shibahara, J.; Tanaka, M. A Phase I/II Study of Triple-Mutated Oncolytic Herpes Virus G47∆ in Patients with Progressive Glioblastoma. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazini, A.; Dieringer, B.; Klingel, K.; Pryshliak, M.; Geisler, A.; Kobelt, D.; Daberkow, O.; Kurreck, J.; Linthout, S.V.; Fechner, H. Application Route and Immune Status of the Host Determine Safety and Oncolytic Activity of Oncolytic Coxsackievirus B3 Variant PD-H. Viruses 2021, 13, 1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazini, A.; Pryshliak, M.; Brückner, V.; Klingel, K.; Sauter, M.; Pinkert, S.; Kurreck, J.; Fechner, H. Heparan Sulfate Binding Coxsackievirus B3 Strain PD: A Novel Avirulent Oncolytic Agent Against Human Colorectal Carcinoma. Hum. Gene Ther. 2018, 29, 1301–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geisler, A.; Dieringer, B.; Elsner, L.; Klopfleisch, R.; Kurreck, J.; Fechner, H. Oncolytic Coxsackievirus B3 Strain PD-H Is Effective Against a Broad Spectrum of Pancreatic Cancer Cell Lines and Induces a Growth Delay in Pancreatic KPC Cell Tumors In Vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girod, M.; Geisler, A.; Hinze, L.; Elsner, L.; Dieringer, B.; Beling, A.; Kurreck, J.; Fechner, H. Combination of FOLFOXIRI Drugs with Oncolytic Coxsackie B3 Virus PD-H Synergistically Induces Oncolysis in the Refractory Colorectal Cancer Cell Line Colo320. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toutant, M.; Costa, A.; Studler, J.-M.; Kadaré, G.; Carnaud, M.; Girault, J.-A. Alternative Splicing Controls the Mechanisms of FAK Autophosphorylation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 7731–7743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolasco-Quiroga, M.; Rosas-Díaz, M.; Moreno, J.; Godínez-Aguilar, R.; López-Ibarra, M.J.; Piña-Sánchez, P.; Alvarado-Cabrero, I.; Vázquez-Gómez, G.; Rocha-Zavaleta, L.; Arenas-Aranda, D.; et al. Increased Expression of FAK Isoforms as Potential Cancer Biomarkers in Ovarian Cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 4779–4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, T.-C. Drug Combination Studies and Their Synergy Quantification Using the Chou-Talalay Method. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, S.; Elbahesh, H. Targeting the Proviral Host Kinase, FAK, Limits Influenza a Virus Pathogenesis and NFkB-Regulated pro-Inflammatory Responses. Virology 2019, 534, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brastianos, P.K.; Twohy, E.L.; Gerstner, E.R.; Kaufmann, T.J.; Iafrate, A.J.; Lennerz, J.; Jeyapalan, S.; Piccioni, D.E.; Monga, V.; Fadul, C.E.; et al. Alliance A071401: Phase II Trial of Focal Adhesion Kinase Inhibition in Meningiomas with Somatic NF2 Mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 618–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; He, D.-H.; Zajac-Kaye, M.; Hochwald, S.N. A Small Molecule FAK Kinase Inhibitor, GSK2256098, Inhibits Growth and Survival of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cells. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 3143–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, G.R.; Cheng, M.; Learn, K.S.; Wagner, J.; Gingrich, D.E.; Lisko, J.G.; Curry, M.; Mesaros, E.F.; Ghose, A.K.; Quail, M.R.; et al. Discovery of Clinical Candidate CEP-37440, a Selective Inhibitor of Focal Adhesion Kinase (FAK) and Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK). J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 7478–7496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duong, H.-Q.; Than, V.T.; Nguyen, H.-T.; Nguyen, P.-T.; Thi, H.T.H.; Bui, T.N.H.; Dang, V.P.L.; Dinh, T.-T.; You, K.S.; Dang, T.-H.; et al. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Inhibitor NVP-TAE684 Suppresses the Proliferation of Human Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Cells. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 45, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Chen, G.; Zhang, D.H.; Zhang, J.; Kuan, S.-F.; Hu, W.; Esni, F.; Gao, X.; Guan, J.-L.; Chu, E.; et al. PYK2 Is Involved in Premalignant Acinar Cell Reprogramming and Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Maintenance by Phosphorylating β-CateninY654. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 8, 561–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, T.-C. Theoretical Basis, Experimental Design, and Computerized Simulation of Synergism and Antagonism in Drug Combination Studies. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 621–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| FAKi | Clinical Trial/Phase | Targeted Kinases | Structural Formula | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VS-4718 (PND-1186) | Acute Myeloid Leukemia, non-hematologic cancers, metastatic cancer, advanced PDAC | NCT01849744: I NCT02215629: I NCT02651727: I | FAK PYK2 |  |
| Ifebemtinib (BI-853520; IN-10018) | non-hematologic malignancies, various advanced or metastatic solid tumors | 16 in sum: I (5), I/II (9), II (2) | FAK FER/FES | 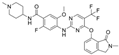 |
| VS-6062 (PF-00562271) | advanced solid tumors | NCT00666926: I | FAK PYK2 | 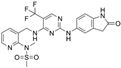 |
| GSK2256098 | PDAC, advanced solid tumors, progressive meningiomas | NCT02428270: II NCT00996671: I NCT02551653: I NCT01938443: I NCT01138033: I NCT02523014: II | FAK | 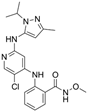 |
| CEP-37440 | advanced or metastatic tumors | NCT01922752: I | FAK ALK |  |
| Defactinib (VS-6063; PF-04554878) | advanced solid cancer, lung cancer, non-hematologic cancers, ovarian cancer, glioblastoma, mesothelioma, PDAC | 36 in sum: I (11), I/II (6), II (18), III (1) | FAK PYK2 | 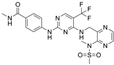 |
| Pancreatic Tumor Cell Line | IC50 [µM] VS-4718 | IC50 [µM] Ifebemtinib | IC50 [µM] VS-6062 | IC50 [µM] GSK2256098 | IC50 [µM] CEP-37440 | IC50 [µM] Defactinib |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIA Paca-2 | 60.85 | 36.99 | 44.29 | 422.95 | 23.30 | 20.26 |
| BxPC-3 | 25.83 | 22.47 | 5.09 | 222.16 | 10.57 | 5.66 |
| Capan-1 | 6.53 | 24.15 | 3.66 | 123.78 | 6.52 | 4.17 |
| AsPC-1 | 12.47 | 27.47 | 15.64 | 740.58 | 9.48 | 12.34 |
| Beta-TC-3 | 3.69 | 18.65 | 31.67 | 35.36 | 6.28 | 9.30 |
| Average IC50 [µM] | 21.87 | 25.95 | 20.07 | 308.97 | 11.23 | 10.35 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geisler, A.; Dieringer, B.; Elsner, L.; Girod, M.; Van Linthout, S.; Kurreck, J.; Fechner, H. Sensitivity of Pancreatic Cancer Cell Lines to Clinically Approved FAK Inhibitors: Enhanced Cytotoxicity Through Combination with Oncolytic Coxsackievirus B3. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146877
Geisler A, Dieringer B, Elsner L, Girod M, Van Linthout S, Kurreck J, Fechner H. Sensitivity of Pancreatic Cancer Cell Lines to Clinically Approved FAK Inhibitors: Enhanced Cytotoxicity Through Combination with Oncolytic Coxsackievirus B3. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146877
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeisler, Anja, Babette Dieringer, Leslie Elsner, Maxim Girod, Sophie Van Linthout, Jens Kurreck, and Henry Fechner. 2025. "Sensitivity of Pancreatic Cancer Cell Lines to Clinically Approved FAK Inhibitors: Enhanced Cytotoxicity Through Combination with Oncolytic Coxsackievirus B3" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146877
APA StyleGeisler, A., Dieringer, B., Elsner, L., Girod, M., Van Linthout, S., Kurreck, J., & Fechner, H. (2025). Sensitivity of Pancreatic Cancer Cell Lines to Clinically Approved FAK Inhibitors: Enhanced Cytotoxicity Through Combination with Oncolytic Coxsackievirus B3. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146877





