Amine-Modified Diatomaceous Earth Syringe Platform (DeSEI) for Efficient and Cost-Effective EV Isolation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
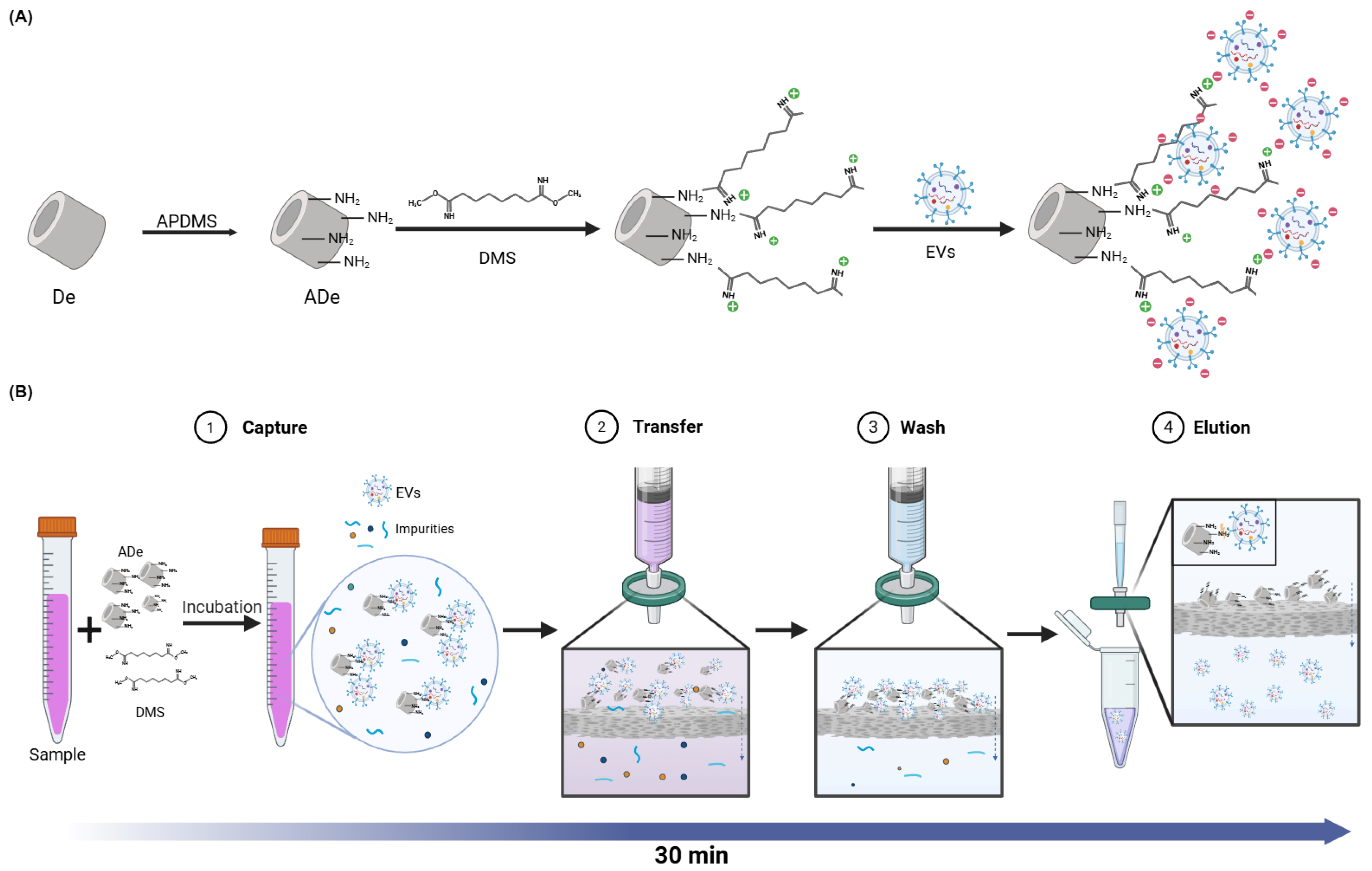
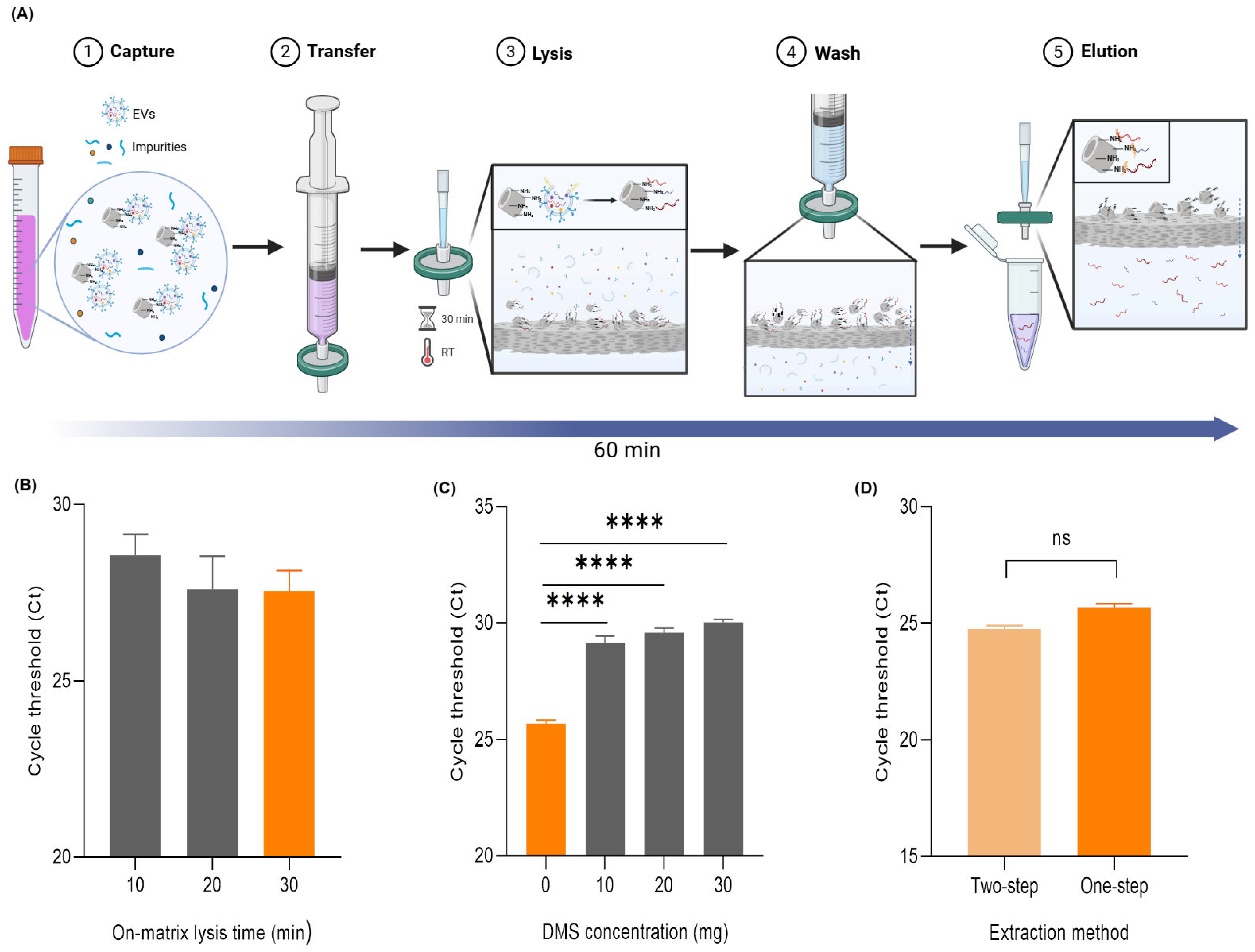
2.1. The Principle and Workflow of the DeSEI
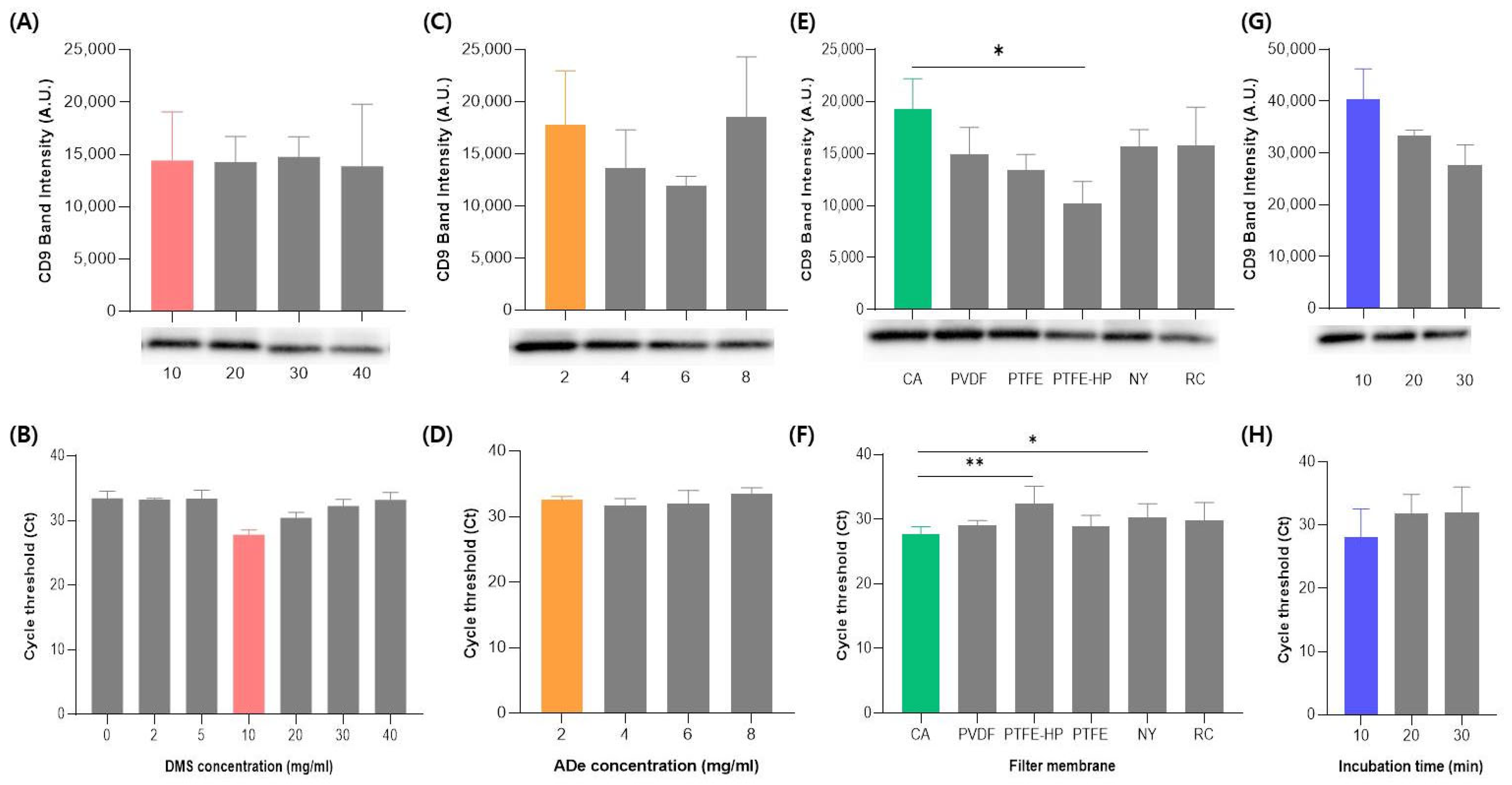
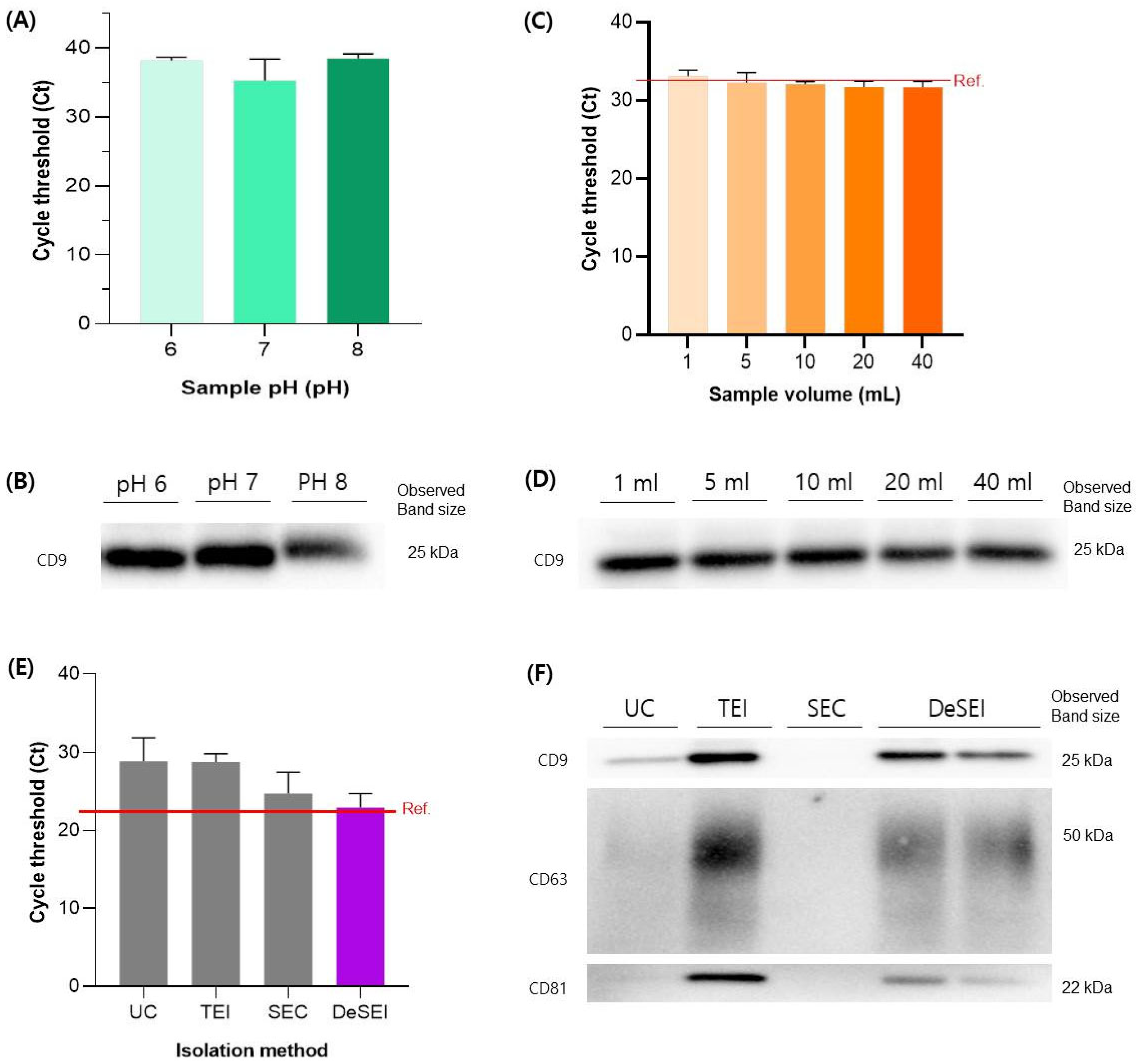
2.2. The Optimization of the DeSEI Protocol
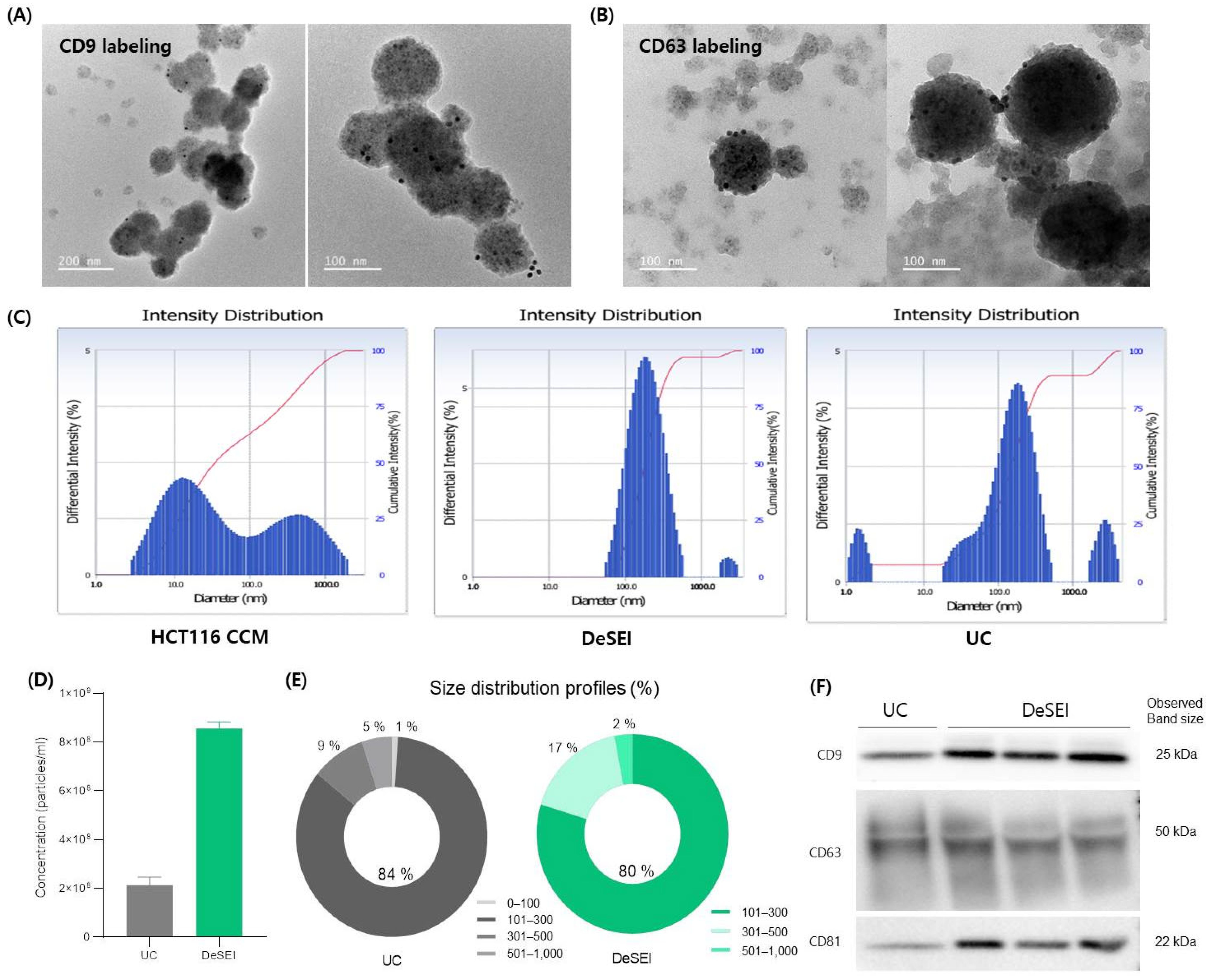
2.3. The Validation and Comparison of the DeSEI
2.4. One-Step DeSEI Protocol for Direct EV-Derived miRNA Extraction
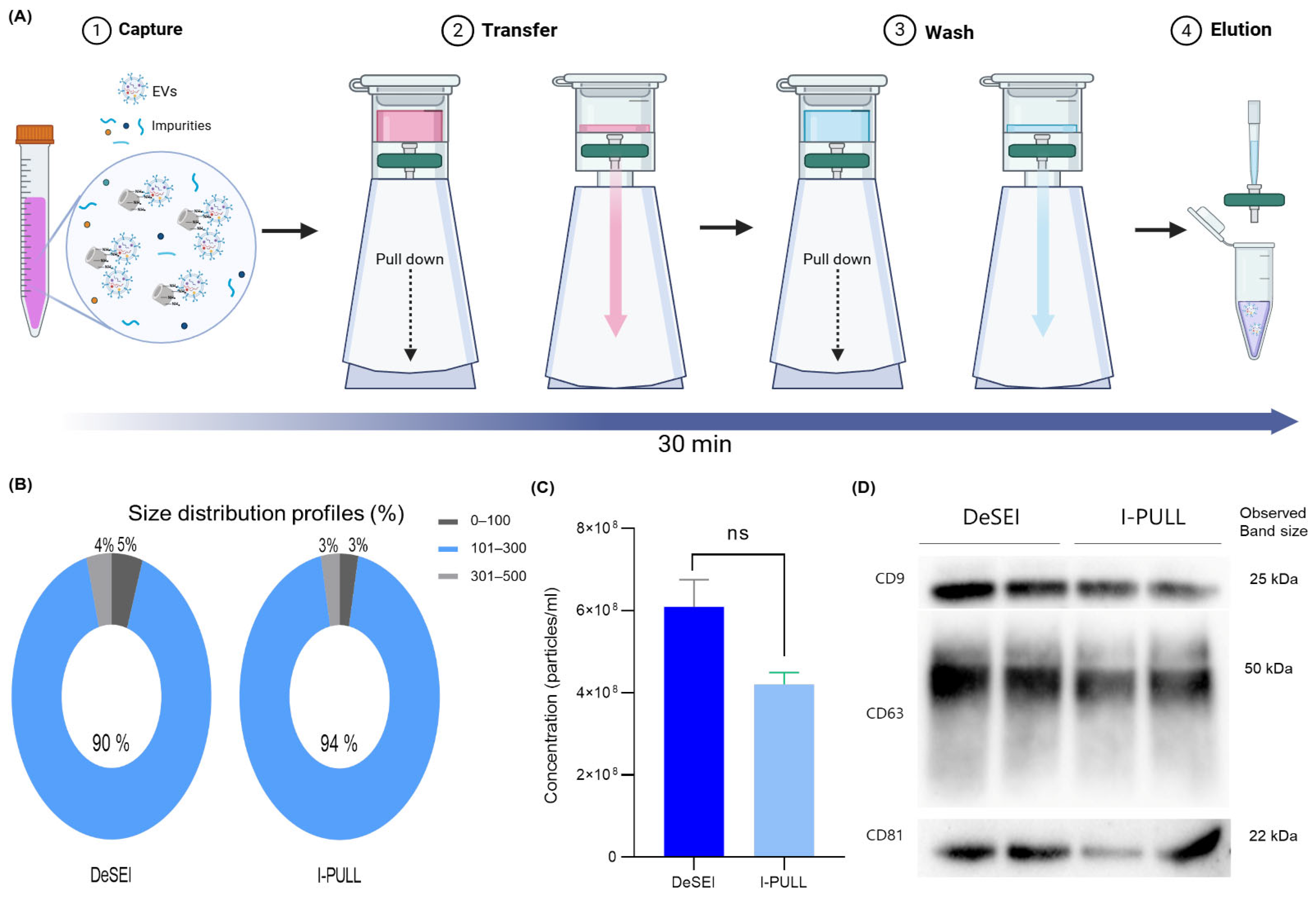
2.5. User-Friendly Cartridge System (I-PULL) with DeSEI
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Media Collection
4.2. Synthesis of Amine-Functionalized Diatomaceous Earth (ADe)
4.3. EV Isolation and EV-Derived miRNA Extraction Using DeSEI
4.4. EV Isolation Using Conventional Methods
4.5. Characterization of Isolated EVs
4.6. EV-Derived miRNA Extraction and RT-qPCR
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DeSEI | Amine-functionalized Diatomaceous earth Syringe platform for EV Isolation |
| DE | Diatomaceous earth |
| ADe | Amine-functionalized Diatomaceous earth |
| EVs | Extracellular vesicles |
| UC | Ultracentrifugation |
| TEI | Total exosome isolation kit |
| SEC | Size exclusion chromatography |
| SPE | Solid-phase extraction |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| DLS | Dynamic light scattering |
| NTA | Nanoparticle tracking analysis |
| miRNAs | MicroRNAs |
| Ct | Cycle threshold |
| CCM | Cell culture media |
| APDMS | 3-Aminopropyl(diethoxy)methylsilane |
| DMS | Dimethyl suberimidate dihydrochloride |
| RIPA | Radioimmunoprecipitation assay |
| TBS | Tris-buffered saline |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified eagle medium |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| DW | Distilled water |
References
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, 6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 200, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanez-Mo, M.; Siljander, P.R.; Andreu, Z.; Zavec, A.B.; Borras, F.E.; Buzas, E.I.; Buzas, K.; Casal, E.; Cappello, F.; Carvalho, J.; et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Niel, G.; D’Angelo, G.; Raposo, G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Lyon, C.J.; Hu, T. A Panorama of Extracellular Vesicle Applications: From Biomarker Detection to Therapeutics. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 9784–9797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurunathan, S.; Kang, M.H.; Jeyaraj, M.; Qasim, M.; Kim, J.H. Review of the Isolation, Characterization, Biological Function, and Multifarious Therapeutic Approaches of Exosomes. Cells 2019, 8, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Hurley, J.; Roberts, D.; Chakrabortty, S.K.; Enderle, D.; Noerholm, M.; Breakefield, X.O.; Skog, J.K. Exosome-based liquid biopsies in cancer: Opportunities and challenges. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palakurthi, S.S.; Shah, B.; Kapre, S.; Charbe, N.; Immanuel, S.; Pasham, S.; Thalla, M.; Jain, A.; Palakurthi, S. A comprehensive review of challenges and advances in exosome-based drug delivery systems. Nanoscale Adv. 2024, 6, 5803–5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, S.R.; Shah, K.M. Prospects and Current Challenges of Extracellular Vesicle-Based Biomarkers in Cancer. Biology 2024, 13, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Greening, D.W.; Zhu, H.J.; Takahashi, N.; Simpson, R.J. Extracellular vesicle isolation and characterization: Toward clinical application. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 1152–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thery, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konoshenko, M.Y.; Lekchnov, E.A.; Vlassov, A.V.; Laktionov, P.P. Isolation of Extracellular Vesicles: General Methodologies and Latest Trends. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 8545347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.; Fernandez-Rhodes, M.; Law, A.; Peacock, B.; Lewis, M.P.; Davies, O.G. Comparison of extracellular vesicle isolation processes for therapeutic applications. J. Tissue Eng. 2023, 14, 20417314231174609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furi, I.; Momen-Heravi, F.; Szabo, G. Extracellular vesicle isolation: Present and future. Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thery, C.; Amigorena, S.; Raposo, G.; Clayton, A. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2006, 30, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Peng, L.; Zhu, X.; Chu, T.; Yang, C.; Zhou, B.; Sun, X.; Gao, T.; Zhang, M.; Chen, P.; et al. Isolation, identification, and challenges of extracellular vesicles: Emerging players in clinical applications. Apoptosis 2025, 30, 422–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, L.; Wang, S.; Cai, J.; Xu, J.; Shi, M.; Ruan, L.; Zhu, Q.; et al. Highly Selective Purification of Plasma Extracellular Vesicles Using Titanium Dioxide Microparticles for Depicting the Metabolic Signatures of Diabetic Retinopathy. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 14099–14108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xu, Q.; Cai, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, D. Biological particle separation techniques based on microfluidics. Interdiscip. Med. 2024, 2, e20240003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennion, M.C. Solid-phase extraction: Method development, sorbents, and coupling with liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1999, 856, 3–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majors, R. Advanced topics in solid-phase extraction: Chemistries. LCGC N. Am. 2007, 25, 16–32. [Google Scholar]
- Badawy, M.E.I.; El-Nouby, M.A.M.; Kimani, P.K.; Lim, L.W.; Rabea, E.I. A review of the modern principles and applications of solid-phase extraction techniques in chromatographic analysis. Anal. Sci. 2022, 38, 1457–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, K.K.; Powell, R.R.; Bruce, T.F.; Marcus, R.K. Solid-phase extraction of exosomes from diverse matrices via a polyester capillary-channeled polymer (C-CP) fiber stationary phase in a spin-down tip format. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 4713–4724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, K.K.; Powell, R.R.; Bruce, T.F.; Marcus, R.K. Rapid isolation of extracellular vesicles from diverse biofluid matrices via capillary-channeled polymer fiber solid-phase extraction micropipette tips. Analyst 2021, 146, 4314–4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, B.; Kim, Y.I.; Lee, M.; Lim, S.B.; Shin, Y. Enhanced Early Detection of Colorectal Cancer via Blood Biomarker Combinations Identified Through Extracellular Vesicle Isolation and Artificial Intelligence Analysis. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2025, 14, e70088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.H.; Tieu, A.K.; Tran, B.H.; Wan, S.; Zhu, H.; Pham, S.T. Porosity-induced mechanically robust superhydrophobicity by the sintering and silanization of hydrophilic porous diatomaceous earth. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2021, 589, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, F.; Hu, M.; Deng, S.; Wang, K.; Sun, W.; Peng, H.; Liu, J. Designing transition metal-based porous architectures for supercapacitor electrodes: A review. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 11482–11512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appiah, E.S.; Mensah-Darkwa, K.; Andrews, A.; Agyemang, F.O.; Nartey, M.A.; Makgopa, K.; Hou, Y.; Aggrey, P.; Quansah, D.A. Tailoring a hierarchical porous carbon electrode from carbon black via 3D diatomite morphology control for enhanced electrochemical performance. Nanoscale Adv. 2024, 6, 6265–6277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, K.; Foegeding, P.M.; Swaisgood, H.E. Isolation of RNA and DNA fragments using diatomaceous earth. Biotechnol. Tech. 1998, 12, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qodah, Z.; Lafi, W.; Al-Anber, Z.; Al-Shannag, M.; Harahsheh, A. Adsorption of methylene blue by acid and heat treated diatomaceous silica. Desalination 2007, 217, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Koo, B.; Liu, H.; Eun Jin, C.; Shin, Y. A single-tube approach for in vitro diagnostics using diatomaceous earth and optical sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 99, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Lee, E.Y.; Noh, G.S.; Shin, J.; Liu, H.; Qiao, Z.; Shin, Y. A robust, hand-powered, instrument-free sample preparation system for point-of-care pathogen detection. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Lee, E.Y.; Shin, Y. Improved Reversible Cross-Linking-Based Solid-Phase RNA Extraction for Pathogen Diagnostics. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 1725–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.G.; Kim, S.; Jang, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, N.; Yu, Y.; Kim, A.R.; Lim, S.; Bae, M.; Shin, Y. Highly Sensitive Molecular Diagnostic Platform for Scrub Typhus Diagnosis Using O. tsutsugamushi Enrichment and Nucleic Acid Extraction. Biosensors 2024, 14, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uthappa, U.; Sriram, G.; Brahmkhatri, V.; Kigga, M.; Jung, H.-Y.; Altalhi, T.; Neelgund, G.M.; Kurkuri, M.D. Xerogel modified diatomaceous earth microparticles for controlled drug release studies. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 11964–11971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilarska, A.A.; Pilarski, K.; Adamski, M.; Zaborowicz, M.; Cais-Sokolińska, D.; Wolna-Maruwka, A.; Niewiadomska, A. Eco-friendly and effective diatomaceous earth/peat (DEP) microbial carriers in the anaerobic biodegradation of food waste products. Energies 2022, 15, 3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlikova, M.; Rovnanikova, P.; Zaleska, M.; Pavlik, Z. Diatomaceous Earth-Lightweight Pozzolanic Admixtures for Repair Mortars-Complex Chemical and Physical Assessment. Matser 2022, 15, 6881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiee, N.; Khatami, M.; Jamalipour Soufi, G.; Fatahi, Y.; Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. Diatoms with Invaluable Applications in Nanotechnology, Biotechnology, and Biomedicine: Recent Advances. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 3053–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisson, A.R.; Tan, S.; Linares, R.; Gounou, C.; Arraud, N. Extracellular vesicles from activated platelets: A semiquantitative cryo-electron microscopy and immuno-gold labeling study. Platelets 2017, 28, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klymiuk, M.C.; Balz, N.; Elashry, M.I.; Heimann, M.; Wenisch, S.; Arnhold, S. Exosomes isolation and identification from equine mesenchymal stem cells. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arraud, N.; Linares, R.; Tan, S.; Gounou, C.; Pasquet, J.M.; Mornet, S.; Brisson, A.R. Extracellular vesicles from blood plasma: Determination of their morphology, size, phenotype and concentration. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 12, 614–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hon, K.W.; Ab-Mutalib, N.S.; Abdullah, N.M.A.; Jamal, R.; Abu, N. Extracellular Vesicle-derived circular RNAs confers chemoresistance in Colorectal cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Guo, J.; Fang, L.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Pang, X.; Peng, Y. Quality and efficiency assessment of five extracellular vesicle isolation methods using the resistive pulse sensing strategy. Anal. Methods 2024, 16, 5536–5544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.Y.; Chen, C.C. Toward characterizing extracellular vesicles at a single-particle level. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvey, H.E.; Chang, A.; Adler, J.; Del Tatto, M.; Perez, K.; Quesenberry, P.J.; Chatterjee, D. Extracellular vesicle-mediated phenotype switching in malignant and non-malignant colon cells. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, N.H.; Lee, E.H.; Yoon, Y.S.; Jeong, Y.J.; Lee, B.C.; Koo, B.; Jang, Y.O.; Kim, S.H.; Kang, Y.A.; et al. Multicenter Testing of a Simple Molecular Diagnostic System for the Diagnosis of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. Biosensors 2023, 13, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.J.; Lee, J.; Kim, N.; Shin, Y. Amine-Modified Diatomaceous Earth Syringe Platform (DeSEI) for Efficient and Cost-Effective EV Isolation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6843. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146843
Lee HJ, Lee J, Kim N, Shin Y. Amine-Modified Diatomaceous Earth Syringe Platform (DeSEI) for Efficient and Cost-Effective EV Isolation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6843. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146843
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hyo Joo, Jinkwan Lee, Namheon Kim, and Yong Shin. 2025. "Amine-Modified Diatomaceous Earth Syringe Platform (DeSEI) for Efficient and Cost-Effective EV Isolation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6843. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146843
APA StyleLee, H. J., Lee, J., Kim, N., & Shin, Y. (2025). Amine-Modified Diatomaceous Earth Syringe Platform (DeSEI) for Efficient and Cost-Effective EV Isolation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6843. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146843






