Exploring the Interplay Between Gut Microbiota and the Melatonergic Pathway in Hormone Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical Characteristics of the Study Groups
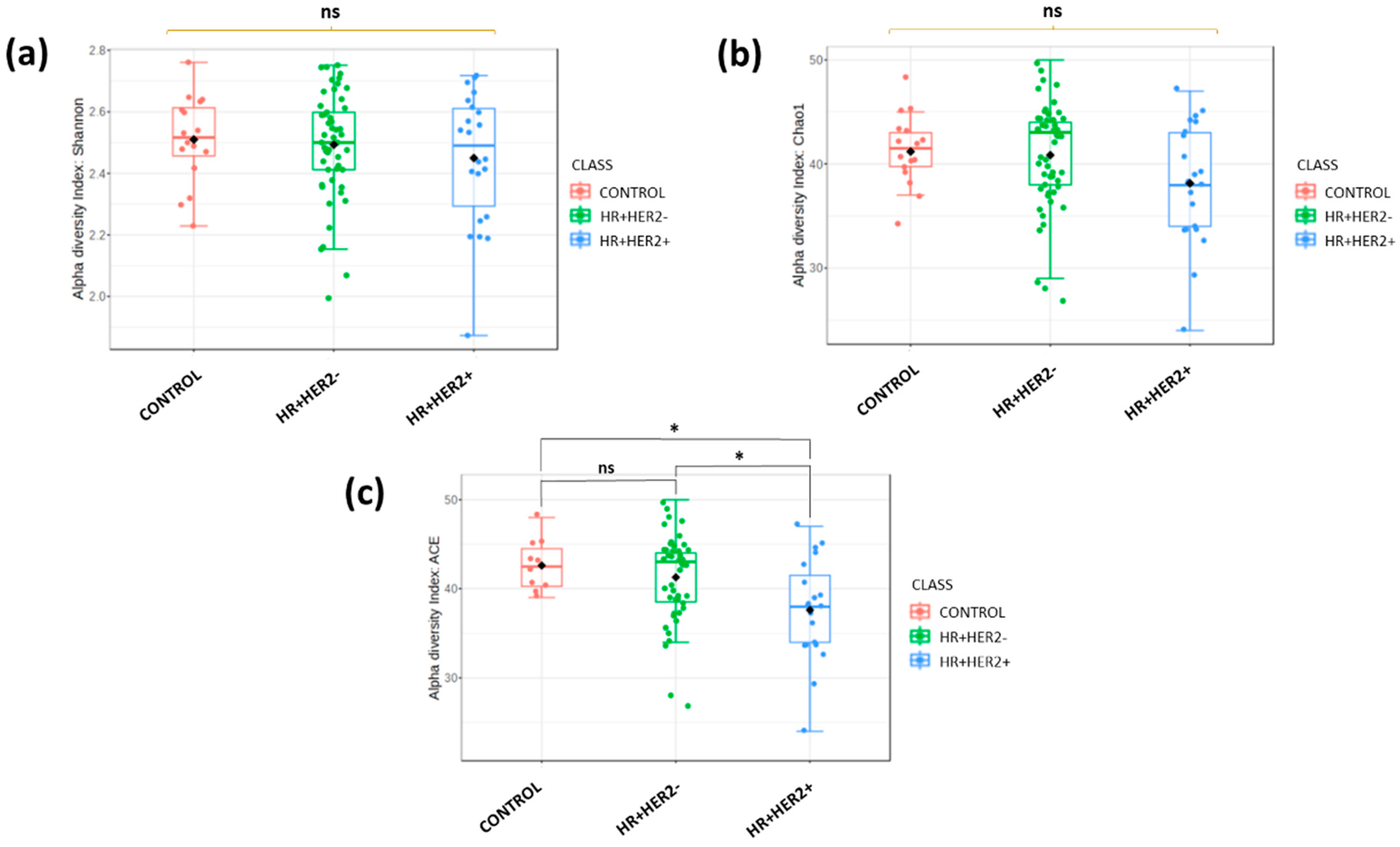
2.2. Differences in Fecal Microbiota Richness and Diversity Between Breast Cancer Patients and Healthy Controls
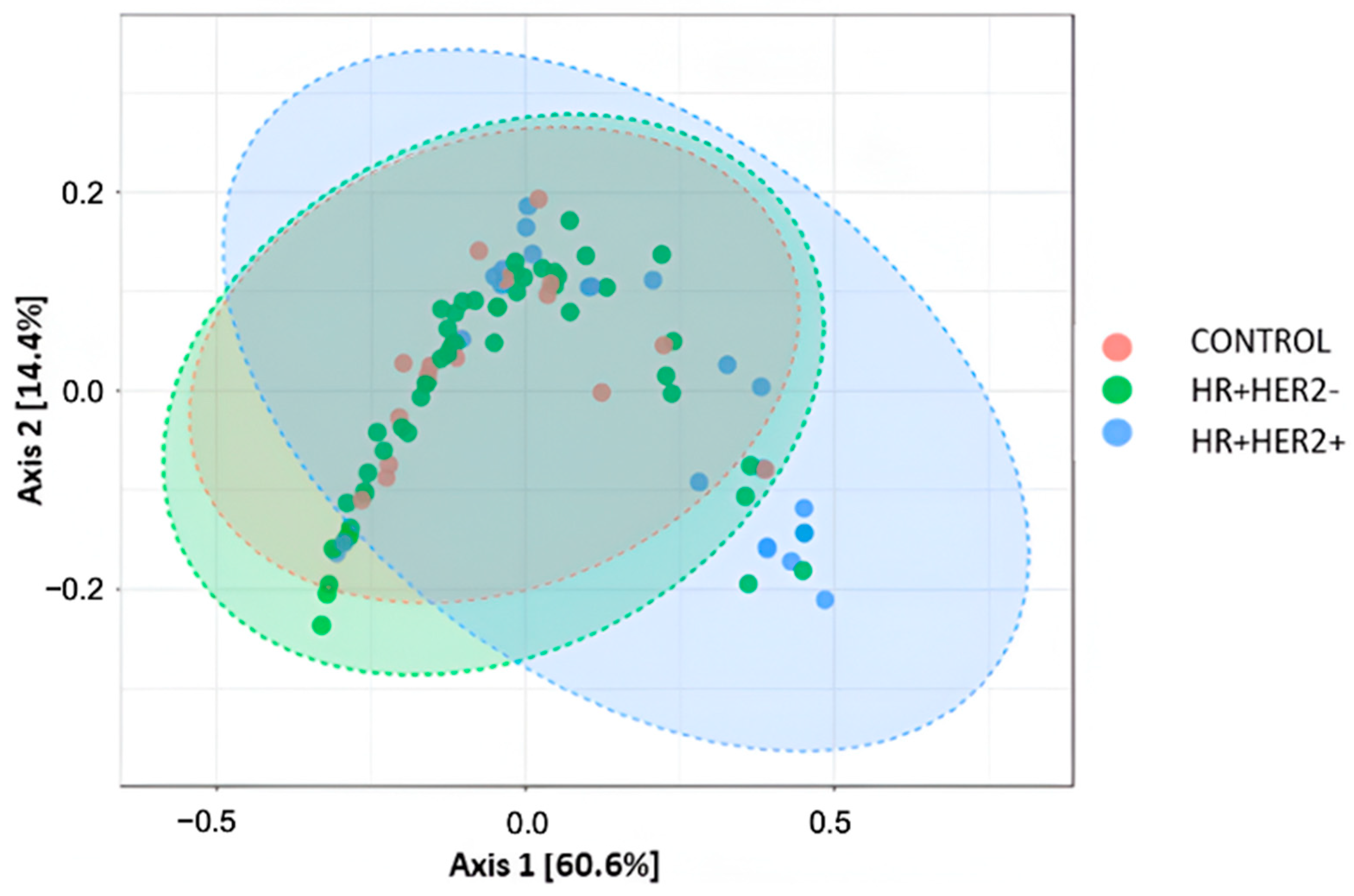
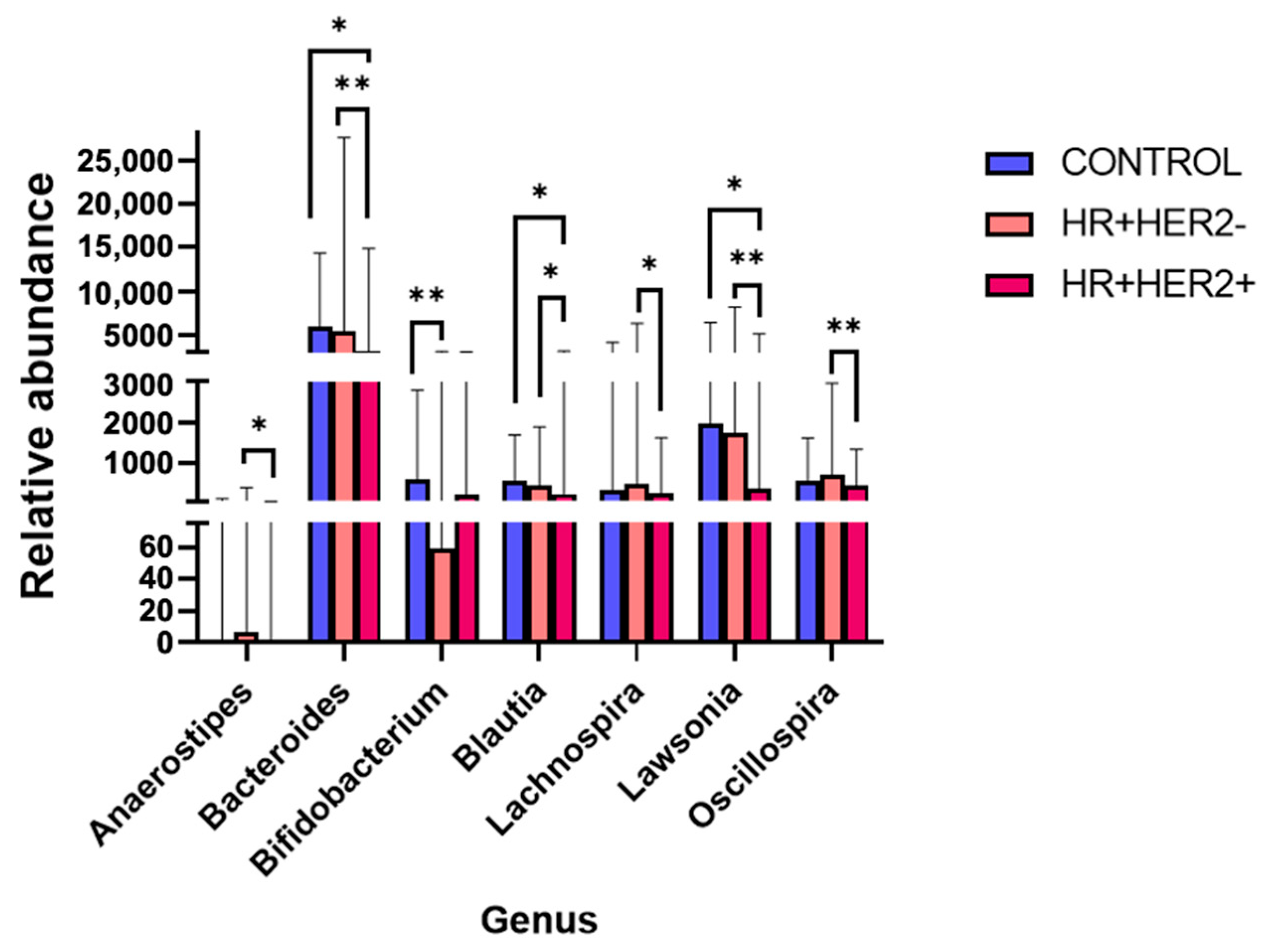
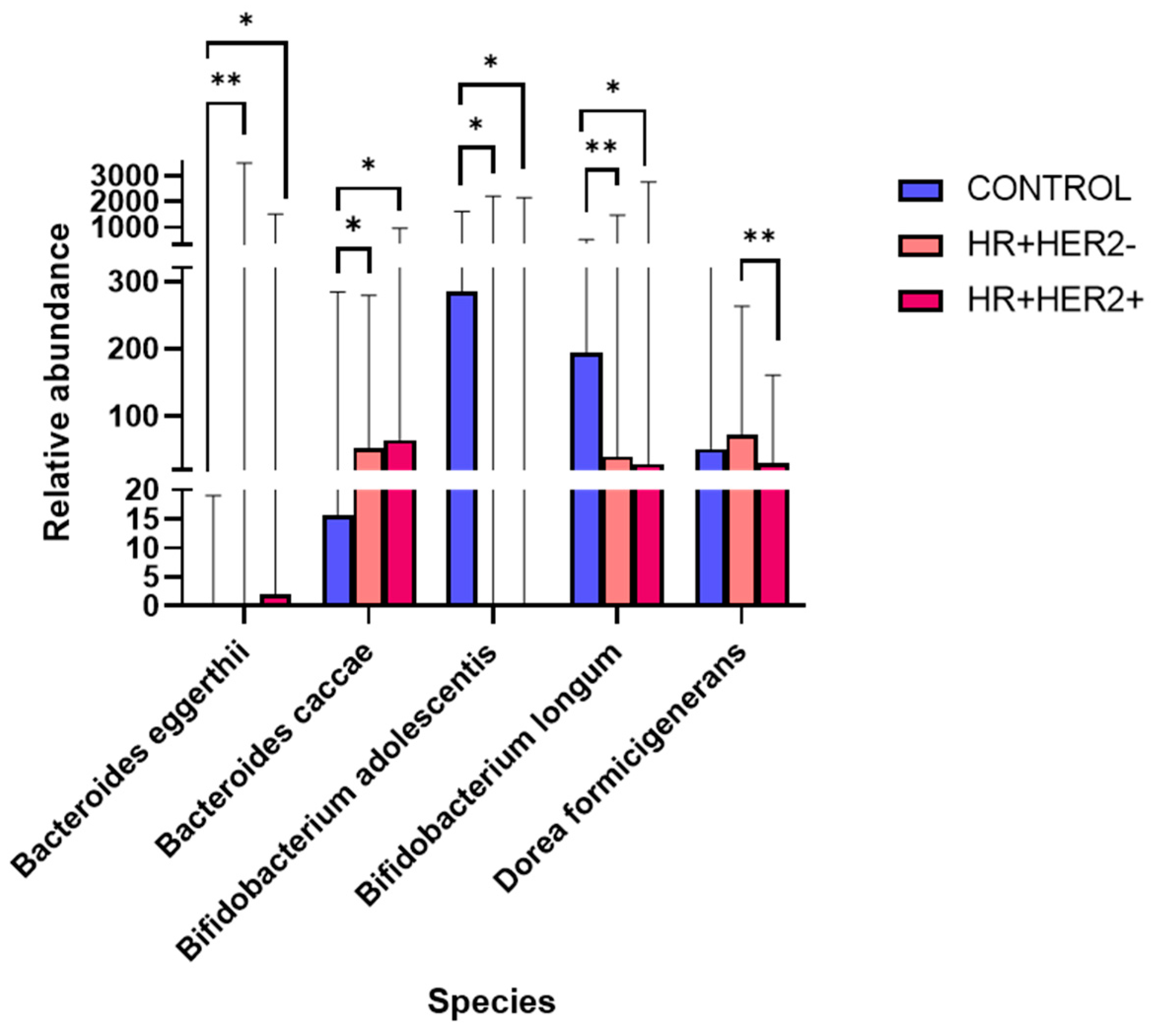
2.3. Variations in the Taxonomic Composition of the Fecal Microbiota Between Study Groups
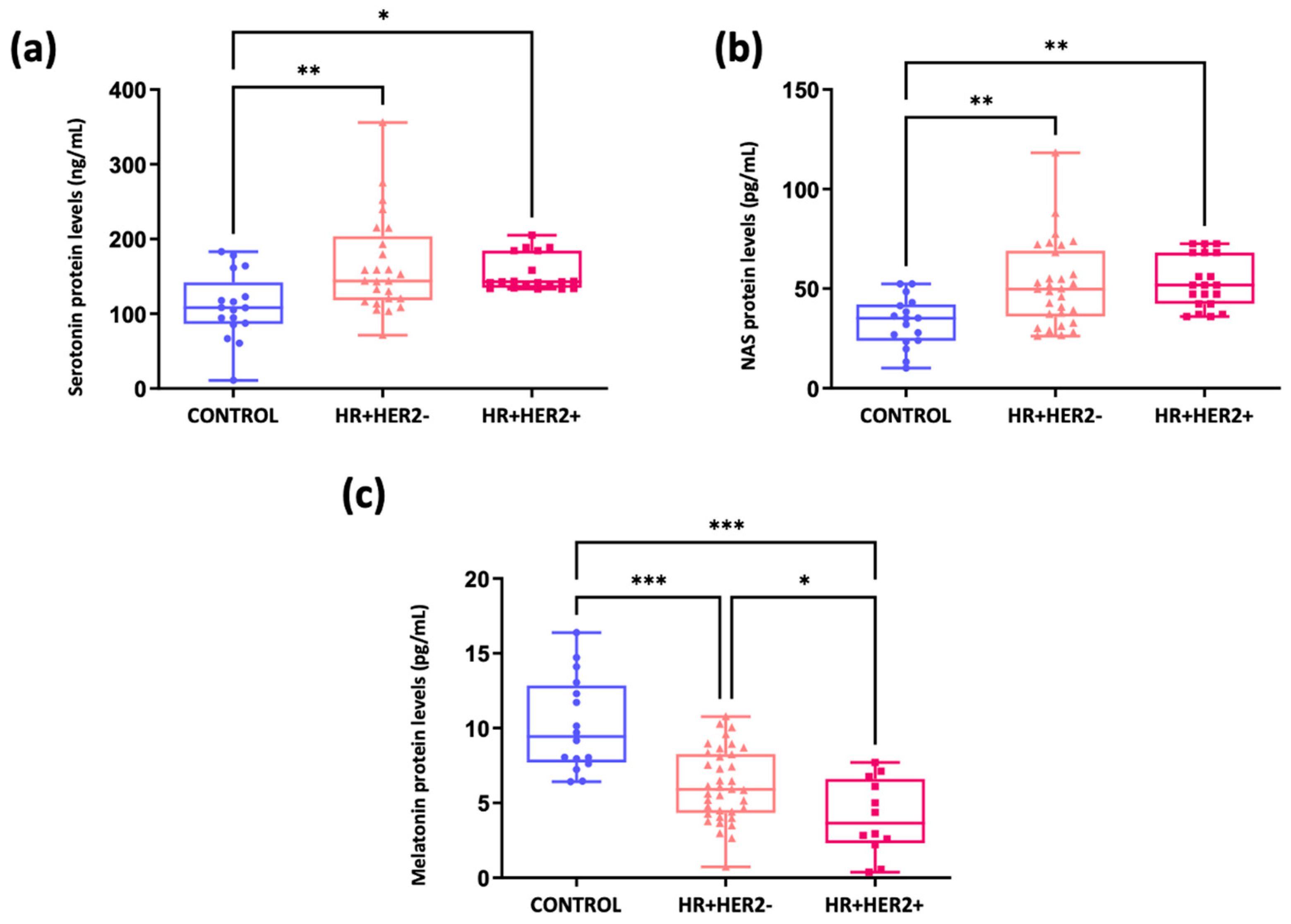
2.4. Analysis of the Melatonergic Pathway in Breast Cancer Patients and Healthy Controls
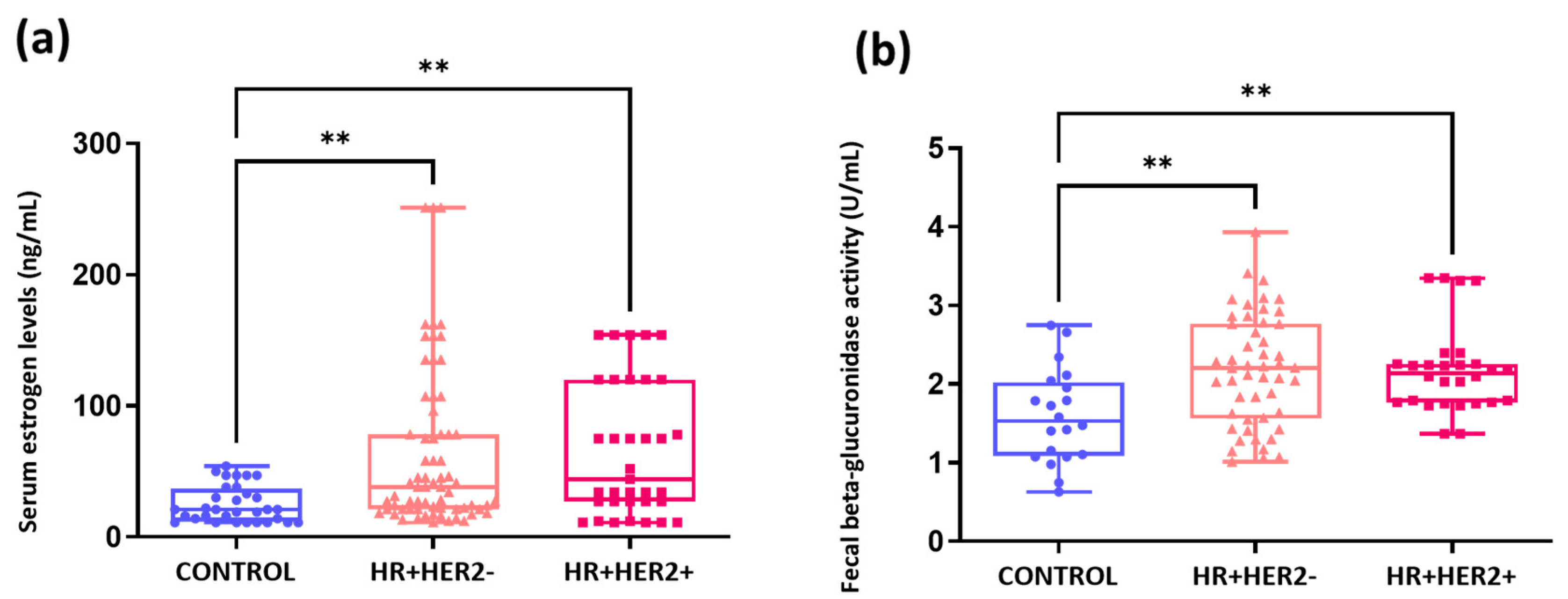
2.5. Elevated Serum Estrogen Levels and Fecal Beta-Glucuronidase Activity in Breast Cancer Patients Compared to Healthy Controls
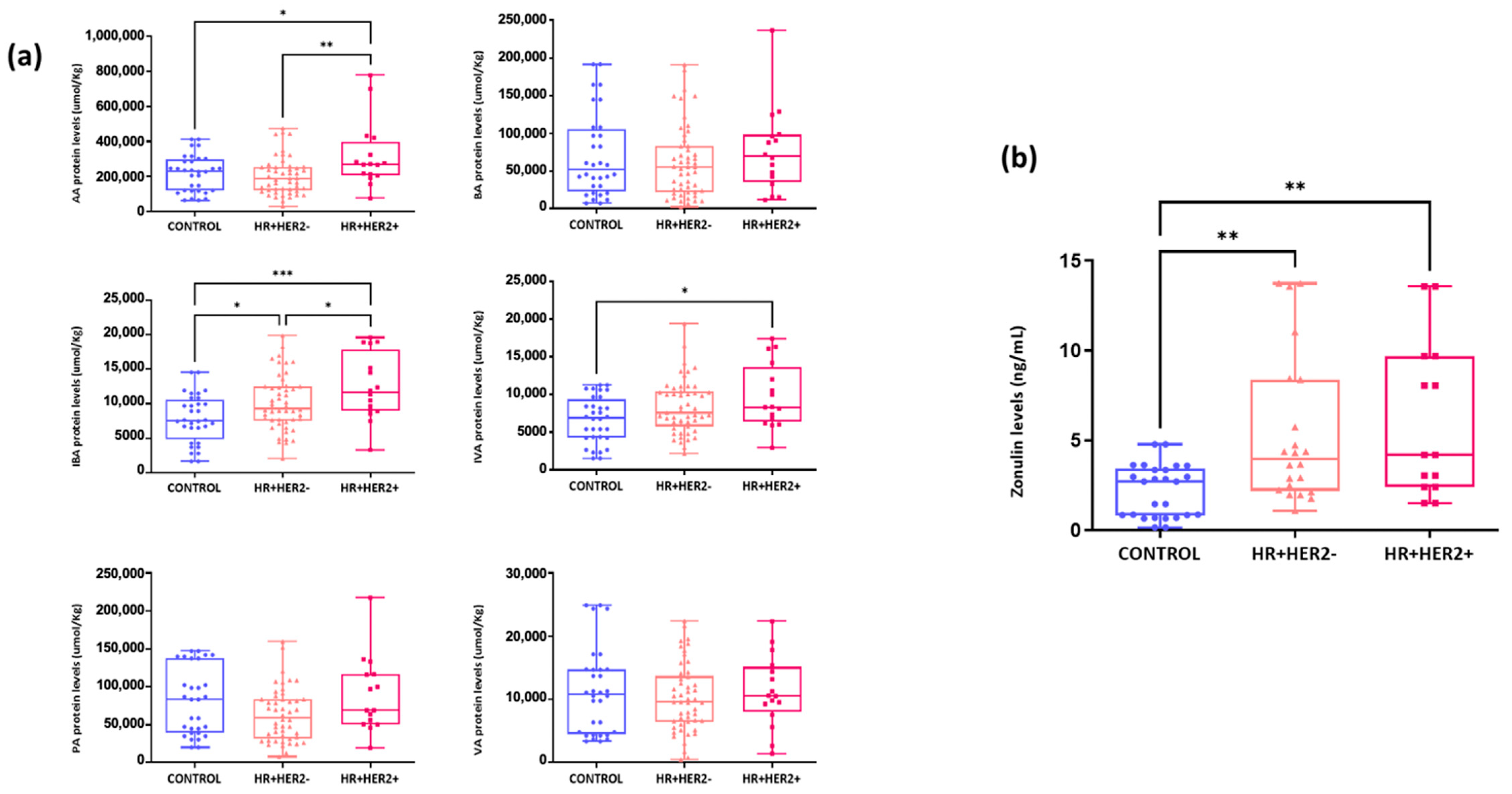
2.6. Differences in the Fecal Levels of Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs) and Serum Zonulin Levels Between Study Groups
2.7. Associations Between the Fecal Microbiota and the Serotonin–NAS–Melatonin Axis and Fecal Beta-Glucuronidase Activity
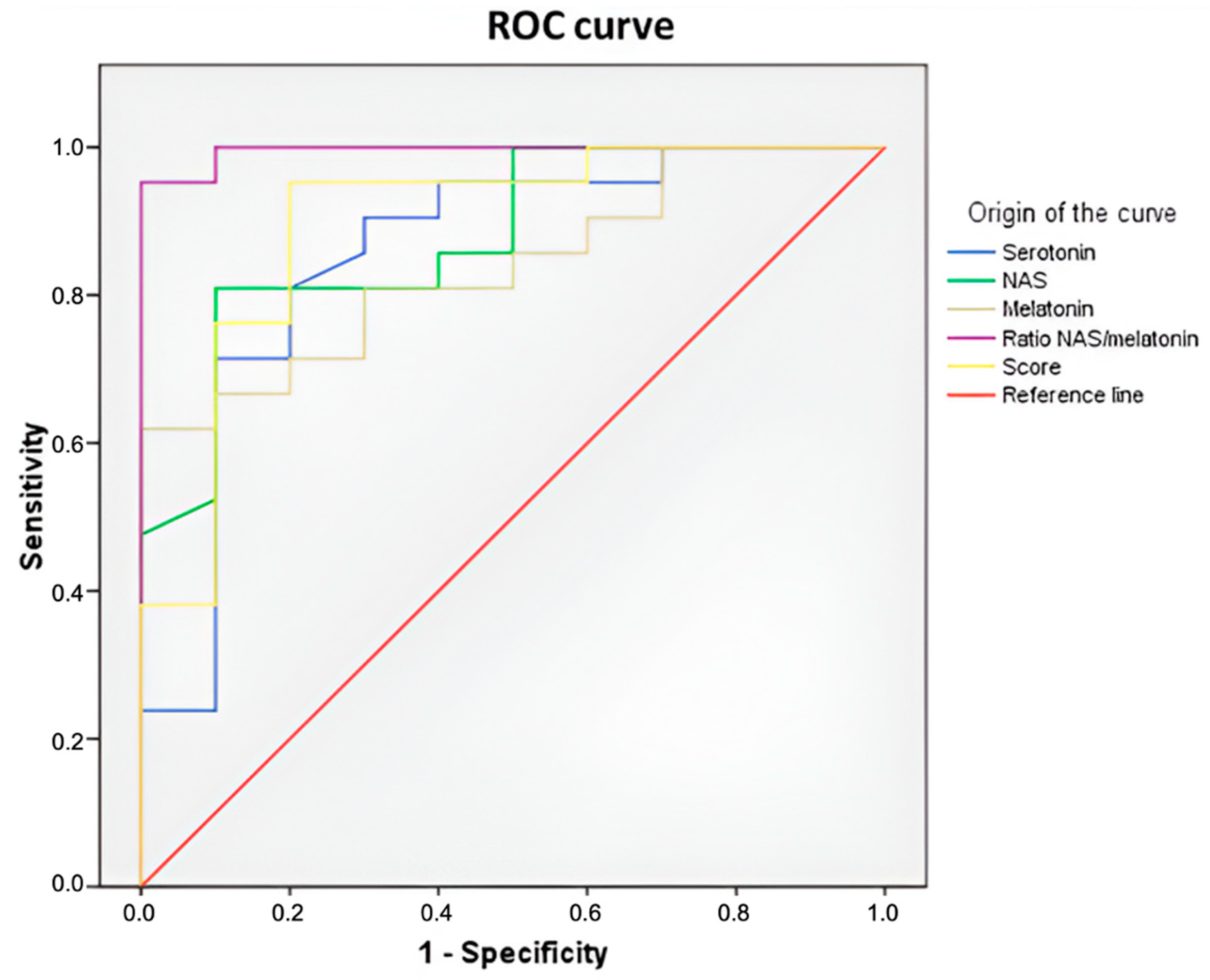
2.8. Serum Levels of Serotonin, N-Acetylserotonin, and Melatonin as Biomarkers for Breast Cancer Risk
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Participants
4.2. Fecal Sample Processing, DNA Extraction, and Gut Microbiota Sequencing
4.3. Bioinformatics Analysis
4.4. Analysis of Serum Serotonin, N-Acetylserotonin, and Melatonin Levels by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Tandem Mass Spectrometry (HPLC–MS/MS)
4.5. Determination of Serum Protein Levels of AANAT, ASMT, and 14-3-3 Involved in Melatonin Synthesis by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.6. Measurement of Fecal Beta-Glucuronidase Activity
4.7. Intestinal Permeability Analysis
4.8. Analysis of Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs) in Fecal Samples Was Conducted Using Gas Chromatography Coupled to Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry (GC–MS/MS)
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 14-3-3 Pro | 14-3-3 Protein |
| AA | Acetic acid |
| AANAT | Arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase |
| ASMT | Acetylserotonin-O-methyltransferase |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| BA | Butyric acid |
| BC | Breast cancer |
| βGD | Beta-glucuronidase |
| COS | Center for Omic Sciences |
| CQS Lab | Chemical Sanitary Consulting |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| ER | Estrogen receptor |
| EST | Estrogen sulfotransferase |
| FDR | False discovery rate |
| GC–MS/MS | Gas chromatography coupled to triple quadrupole mass spectrometry |
| HPLC–MS/MS | High-performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry |
| HR | Hormonal receptor |
| IBA | Isobutyric acid |
| IDC | Invasive ductal carcinoma |
| ILC | Invasive lobular carcinoma |
| IS | Internal standard |
| IVA | Isovaleric acid |
| MRM | Multiple reaction monitoring |
| NAS | N-acetylserotonin |
| OTUs | Operational taxonomic units: |
| PA | Propionic acid |
| PCoA | Principal coordinate analysis |
| PR | Progesterone receptor |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| SCFAs | Short-chain fatty acids |
| SNPs | Single nucleotide polymorphisms |
| STS | Sulfatase |
| Tph2 | Tryptophan hydroxylase 2 |
| VA | Valeric acid |
References
- Laborda-Illanes, A.; Sanchez-Alcoholado, L.; Dominguez-Recio, M.E.; Jimenez-Rodriguez, B.; Lavado, R.; Comino-Méndez, I.; Alba, E.; Queipo-Ortuño, M.I. Breast and Gut Microbiota Action Mechanisms in Breast Cancer Pathogenesis and Treatment. Cancers 2020, 12, 2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parida, S.; Sharma, D. The Microbiome–Estrogen Connection and Breast Cancer Risk. Cells 2019, 8, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, S. Melatonin: A Potential Antineoplastic Agent in Breast Cancer. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2022, 41, 55–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Q.; Diao, L.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Jin, J. A Protective Effect of Melatonin on Intestinal Permeability Is Induced by Diclofenac via Regulation of Mitochondrial Function in Mice. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2011, 32, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hao, Y.; Fan, F.; Zhang, B. The Role of Microbiome in Insomnia, Circadian Disturbance and Depression. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reigstad, C.S.; Salmonson, C.E.; Rainey, F.R., III; Szurszewski, J.H.; Linden, D.R.; Sonnenburg, J.L.; Farrugia, G.; Kashyap, P.C. Gut Microbes Promote Colonic Serotonin Production through an Effect of Short-Chain Fatty Acids on Enterochromaffin Cells. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelrod, J.; Weissbach, H. Purification and Properties of Hydroxyindole-O-Methyl Transferase. J. Biol. Chem. 1961, 236, 211–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cos, S.; Sánchez-Barceló, E.J. Melatonin and Mammary Pathological Growth. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2000, 21, 133–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.-W.; Liu, X.; Pradoldej, S.; Tosini, G.; Chang, Q.; Iuvone, P.M.; Ye, K. N-Acetylserotonin Activates TrkB Receptor in a Circadian Rhythm. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 3876–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laborda-Illanes, A.; Sánchez-Alcoholado, L.; Boutriq, S.; Plaza-Andrades, I.; Peralta-Linero, J.; Alba, E.; González-González, A.; Queipo-Ortuño, M.I. A New Paradigm in the Relationship between Melatonin and Breast Cancer: Gut Microbiota Identified as a Potential Regulatory Agent. Cancers 2021, 13, 3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavartkiladze, A.A.; Potskhoraia, T.; Revazishvili, P.; Maisuradze, M.; Japaridze, T.; Tavartkiladze, L. 63P The Impact of Disruption of Melatonin Secretion on the Structural-Functional Changes of the Microbiome and the Role of the Melatonin-Microbiome Axis in the Initiation of Carcinogenesis. ESMO Open 2023, 8, 101873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iesanu, M.I.; Zahiu, C.D.M.; Dogaru, I.-A.; Chitimus, D.M.; Pircalabioru, G.G.; Voiculescu, S.E.; Isac, S.; Galos, F.; Pavel, B.; O’Mahony, S.M.; et al. Melatonin-Microbiome Two-Sided Interaction in Dysbiosis-Associated Conditions. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannino, G.; Caradonna, F.; Cruciata, I.; Lauria, A.; Perrone, A.; Gentile, C. Melatonin Reduces Inflammatory Response in Human Intestinal Epithelial Cells Stimulated by Interleukin-1β. J. Pineal Res. 2019, 67, e12598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, Y.; Yang, D.; Bai, F.; Zhang, C.; Qin, C.; Li, D.; Wang, L.; Yang, M.; Chen, Z.; Li, J. Melatonin Treatment Alleviates Spinal Cord Injury-Induced Gut Dysbiosis in Mice. J. Neurotrauma 2019, 36, 2646–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.S.; Kim, S.H.; Park, J.W.; Kho, Y.; Seok, P.R.; Shin, J.-H.; Choi, Y.J.; Jun, J.-H.; Jung, H.C.; Kim, E.K. Melatonin in the Colon Modulates Intestinal Microbiota in Response to Stress and Sleep Deprivation. Intest. Res. 2020, 18, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.-W.; Zhao, B.-C.; Yang, X.; Lei, S.-H.; Jiang, Y.-M.; Liu, K.-X. Relationships of Sleep Disturbance, Intestinal Microbiota, and Postoperative Pain in Breast Cancer Patients: A Prospective Observational Study. Sleep Breath. 2020, 25, 1655–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G. Breast Cancer: Occluded Role of Mitochondria N-Acetylserotonin/Melatonin Ratio in Co-Ordinating Pathophysiology. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 168, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veres-Székely, A.; Szász, C.; Pap, D.; Szebeni, B.; Bokrossy, P.; Vannay, Á. Zonulin as a Potential Therapeutic Target in Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis Disorders: Encouraging Results and Emerging Questions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, D.; Lim, S.H. Bidirectional Interaction between Intestinal Microbiome and Cancer: Opportunities for Therapeutic Interventions. Biomark. Res. 2020, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonmati-Carrion, M.-A.; Tomas-Loba, A. Melatonin and Cancer: A Polyhedral Network Where the Source Matters. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthakumaran, T.; Moen, A.E.F.; Tannæs, T.M.; Endres, A.; Brackmann, S.A.; Rounge, T.B.; Bemanian, V.; Tunsjø, H.S. Microbial Dynamics with CRC Progression: A Study of the Mucosal Microbiota at Multiple Sites in Cancers, Adenomatous Polyps, and Healthy Controls. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 42, 305–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Fan, L.; Lin, Y.; Qi, Y.; Xu, C.; Ge, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Jia, D.; Wang, L.; et al. Bifidobacterium Adolescentis Orchestrates CD143+ Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts to Suppress Colorectal Tumorigenesis by Wnt Signaling-Regulated GAS1. Cancer Commun. 2023, 43, 1027–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y.; Isoda, K.; Taira, Y.; Taira, I.; Kondoh, M.; Ishida, I. Anti-Tumor Effect of a Recombinant Bifidobacterium Strain Secreting a Claudin-Targeting Molecule in a Mouse Breast Cancer Model. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 887, 173596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisa, A.; Roya, G.; Mahdi, R.; Shabnam, R.; Maryam, E.; Malihe, T. Anti-Cancer Effects of Bifidobacterium Species in Colon Cancer Cells and a Mouse Model of Carcinogenesis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karmakar, S.; Lal, G. Role of Serotonin Receptor Signaling in Cancer Cells and Anti-Tumor Immunity. Theranostics 2021, 11, 5296–5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.-E.; Du, X.; Wang, M.; Xie, F.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Y. Identification of Serotonin as a Predictive Marker for Breast Cancer Patients. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 1939–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, V.P.; Marshall, A.M.; Hernandez, L.L.; Buckley, A.R.; Horseman, N.D. Altered Serotonin Physiology in Human Breast Cancers Favors Paradoxical Growth and Cell Survival. Breast Cancer Res. 2009, 11, R81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, J.; Tavares, C.D.J.; Ebelt, N.D.; Lodi, A.; Edupuganti, R.; Xie, X.; Devkota, A.K.; Kaoud, T.S.; Van Den Berg, C.L.; Anslyn, E.V.; et al. Serotonin Analogues as Inhibitors of Breast Cancer Cell Growth. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 1072–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishna, P.; George, S.; Hatoum, H.; Mukherjee, S. Serotonin Pathway in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Ghai, K.; Sompol, P.; Liu, X.; Cao, X.; Iuvone, P.M.; Ye, K. N-Acetyl Serotonin Derivatives as Potent Neuroprotectants for Retinas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3540–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehlert, S.; Clanton, M.; on behalf of the Shift Work and Breast Cancer Strategic Advisory Group. Shift Work and Breast Cancer. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubatka, P.; Zubor, P.; Busselberg, D.; Kwon, T.K.; Adamek, M.; Petrovic, D.; Opatrilova, R.; Gazdikova, K.; Caprnda, M.; Rodrigo, L.; et al. Melatonin and Breast Cancer: Evidences from Preclinical and Human Studies. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2018, 122, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, V.; Spence, D.W.; Pandi-Perumal, S.R.; Trakht, I.; Esquifino, A.I.; Cardinali, D.P.; Maestroni, G.J. Melatonin, Environmental Light, and Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2008, 108, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, A.; Cos, S.; Martinez-Campa, C.; Alonso-Gonzalez, C.; Sanchez-Mateos, S.; Mediavilla, M.D.; Sanchez-Barcelo, E.J. Selective Estrogen Enzyme Modulator Actions of Melatonin in Human Breast Cancer Cells. J. Pineal Res. 2008, 45, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurunathan, S.; Qasim, M.; Kang, M.-H.; Kim, J.-H. Role and Therapeutic Potential of Melatonin in Various Type of Cancers. Onco Targets Ther. 2021, 14, 2019–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Summers, W.; Xiang, S.; Yuan, L.; Dauchy, R.T.; Reynolds, A.; Wren-Dail, M.A.; Pointer, D.; Frasch, T.; Blask, D.E.; et al. Melatonin Represses Metastasis in Her2 -Postive Human Breast Cancer Cells by Suppressing RSK2 Expression. Mol. Cancer Res. 2016, 14, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, Q.H.; Than, V.T.; Luu, P.L.; Clarke, D.; Lam, H.N.; Nguyen, T.-G.T.; Nguyen, D.-T.; Duy, P.Q.; Phung, D.; Nguyen, M.N. A Novel Signature Predicts Recurrence Risk and Therapeutic Response in Breast Cancer Patients. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 148, 2848–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zienolddiny, S.; Haugen, A.; Lie, J.-A.S.; Kjuus, H.; Anmarkrud, K.H.; Kjærheim, K. Analysis of Polymorphisms in the Circadian-Related Genes and Breast Cancer Risk in Norwegian Nurses Working Night Shifts. Breast Cancer Res. 2013, 15, R53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, Y.P.; Bernardi, A.; Frozza, R.L. The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids From Gut Microbiota in Gut-Brain Communication. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Lu, T.; Chen, Z.; Liu, B.; Fan, D.; Li, C.; Wu, J.; He, L.; Zhu, X.; Du, Y.; et al. 5-Hydroxytryptamine Produced by Enteric Serotonergic Neurons Initiates Colorectal Cancer Stem Cell Self-Renewal and Tumorigenesis. Neuron 2022, 110, 2268–2282.E4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.-X.; Yuan, X.; Cui, Y.-Y.; Liu, J.; Shen, J.; Jin, B.-Y.; Feng, B.-C.; Zhai, Y.-J.; Zheng, M.-Q.; Kou, G.-J.; et al. Melatonin Mitigates Oxazolone-Induced Colitis in Microbiota-Dependent Manner. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 783806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.K.; Jang, S.; Baek, E.H.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, K.S.; Shin, H.S.; Chung, M.J.; Kim, J.E.; Lee, K.O.; Ha, N.J. Lactic Acid Bacteria Affect Serum Cholesterol Levels, Harmful Fecal Enzyme Activity, and Fecal Water Content. Lipids Health Dis. 2009, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candeliere, F.; Raimondi, S.; Ranieri, R.; Musmeci, E.; Zambon, A.; Amaretti, A.; Rossi, M. β-Glucuronidase Pattern Predicted From Gut Metagenomes Indicates Potentially Diversified Pharmacomicrobiomics. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 826994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripodi, L.; Passariello, M.; D’Argenio, V.; Leggiero, E.; Vitale, M.; Colicchio, R.; Salvatore, P.; Cerullo, V.; De Lorenzo, C.; Pastore, L. Evaluation of the Antiproliferative Effect of Bifidobacterium Longum BB-536 in Solid Tumor Cell Lines, Co-Cultured with Murine Splenocytes. Biochim. Clin. 2021, 45, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, P.; Goli, H.R.; Abediankenari, S.; Chandani, S.R.; Jafari, N.; Ghasemi, M.; Ahanjan, M. Anti-Tumor Effects of Bacteroides fragilis and Bifidobacterium bifidum Culture Supernatants on Mouse Breast Cancer. Gene Rep. 2023, 33, 101815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, J.; Cai, K.; Xiao, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Deng, S.; Pei, C.; Chen, Y.; Xie, Z.; et al. Bifidobacterium Longum Subsp. Longum XZ01 Delays the Progression of Colon Cancer in Mice through the Interaction between the Microbial Spatial Distribution and Tumour Immunity. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 150, 114283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziarski, R.; Park, S.Y.; Kashyap, D.R.; Dowd, S.E.; Gupta, D. Pglyrp-Regulated Gut Microflora Prevotella Falsenii, Parabacteroides Distasonis and Bacteroides Eggerthii Enhance and Alistipes Finegoldii Attenuates Colitis in Mice. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H. Intestinal Permeability Regulation by Tight Junction: Implication on Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Intest. Res. 2015, 13, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G. Endometriosis Pathoetiology and Pathophysiology: Roles of Vitamin A, Estrogen, Immunity, Adipocytes, Gut Microbiome and Melatonergic Pathway on Mitochondria Regulation. Biomol. Concepts 2019, 10, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G.; Carbone, A.; Mazzoccoli, G. Tryptophan Metabolites and Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome, Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) Pathophysiology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G.; Reiter, R.J. Glioblastoma: Role of Mitochondria N-Acetylserotonin/Melatonin Ratio in Mediating Effects of miR-451 and Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor and in Coordinating Wider Biochemical Changes. Int. J. Tryptophan Res. 2019, 12, 1178646919855942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benabou, M.; Rolland, T.; Leblond, C.; Millot, G.; Huguet, G.; Delorme, R.; Leboyer, M.; Pagan, C.; Callebert, J.; Maronde, E.; et al. Heritability of the Melatonin Synthesis Variability in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagan, C.; Delorme, R.; Callebert, J.; Goubran-Botros, H.; Amsellem, F.; Drouot, X.; Boudebesse, C.; Le Dudal, K.; Ngo-Nguyen, N.; Laouamri, H.; et al. The Serotonin-N-Acetylserotonin–Melatonin Pathway as a Biomarker for Autism Spectrum Disorders. Transl. Psychiatry 2014, 4, e479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takada, A.; Shimizu, F.; Masuda, J. Measurement of Plasma Tryptophan Metabolites: Clinical and Experimental Application for Depression and Stress States Assessment; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; ISBN 978-1-78984-505-1. [Google Scholar]
- Simonneaux, V.; Ribelayga, C. Generation of the Melatonin Endocrine Message in Mammals: A Review of the Complex Regulation of Melatonin Synthesis by Norepinephrine, Peptides, and Other Pineal Transmitters. Pharmacol. Rev. 2003, 55, 325–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, Interactive, Scalable and Extensible Microbiome Data Science Using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calgaro, M.; Romualdi, C.; Waldron, L.; Risso, D.; Vitulo, N. Assessment of Statistical Methods from Single Cell, Bulk RNA-Seq, and Metagenomics Applied to Microbiome Data. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slominski, A.T.; Kim, T.-K.; Kleszczyński, K.; Semak, I.; Janjetovic, Z.; Sweatman, T.; Skobowiat, C.; Steketee, J.D.; Lin, Z.; Postlethwaite, A.; et al. Characterization of Serotonin and N-Acetylserotonin Systems in the Human Epidermis and Skin Cells. J. Pineal Res. 2020, 68, e12626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliannan, K.; Donnell, S.O.; Murphy, K.; Stanton, C.; Kang, C.; Wang, B.; Li, X.-Y.; Bhan, A.K.; Kang, J.X. Decreased Tissue Omega-6/Omega-3 Fatty Acid Ratio Prevents Chemotherapy-Induced Gastrointestinal Toxicity Associated with Alterations of Gut Microbiome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.H.; Onyeaghala, G.C.; Rashidi, A.; Holtan, S.G.; Khoruts, A.; Israni, A.; Jacobson, P.A.; Staley, C. Fecal β-Glucuronidase Activity Differs between Hematopoietic Cell and Kidney Transplantation and a Possible Mechanism for Disparate Dose Requirements. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2108279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotti, C.; Rubert, J.; Fava, F.; Tuohy, K.; Mattivi, F.; Vrhovsek, U. Development of a Fast and Cost-Effective Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Method for the Quantification of Short-Chain and Medium-Chain Fatty Acids in Human Biofluids. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 5555–5567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Controls n = 16 | BC Patients n = 76 | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (Years) Average (range) | 62 (47–85) | 64 (44–85) |
| HORMONAL STATUS | ||
| Perimenopausal | 2 (12.5%) | 9 (11.84%) |
| Postmenopausal | 14 (87.5%) | 67 (88.15%) |
| ESTROGEN STATUS | Not applicable | |
| Positive | 73 (96.05%) | |
| Negative | 3 (3.95%) | |
| PROGESTERONE STATUS | Not applicable | |
| ≥20% | 60 (78.95%) | |
| <20% | 7 (9.21%) | |
| Negative | 9 (11.84%) | |
| HER2 STATUS | Not applicable | |
| Positive | 20 (26.32%) | |
| Negative | 56 (73.68%) | |
| SUBTYPE CLASSIFICATION | Not applicable | |
| HR+HER2- | 56 (73.68%) | |
| HR+HER2+ | 20 (26.32%) | |
| AFFECTED AXILAR LYMPH NODE | Not applicable | |
| N0 | 52 (68.42%) | |
| N1 | 17 (22.37%) | |
| N2 | 7 (9.21%) | |
| TUMOR SIZE (cm) | Not applicable | |
| <2 | 32 (42.11%) | |
| 2 to 5 | 35 (46.05%) | |
| >5 | 9 (11.84%) | |
| TUMOR TYPE | Not applicable | |
| IDC (invasive ductal carcinoma) | 61 (80.26%) | |
| ILC (invasive lobular carcinoma) | 11 (14.47%) | |
| Papillary carcinoma | 2 (2.63%) | |
| Mucinous carcinoma | 2 (2.64%) | |
| HISTOLOGICAL GRADE | Not applicable | |
| Grade 1 | 7 (9.21%) | |
| Grade 2 | 43 (56.58%) | |
| Grade 3 | 26 (34.21%) |
| Analyte | Retention Time (min) | Quantitative Transition (m/z) | Qualitative Transition (m/z) | CE (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA | 6.62 | 60→45 | 60→43 | 10/5 |
| PA | 7.49 | 73→55 | 74→55 | 5/10 |
| IBA | 7.77 | 88→73 | 88→55 | 10/15 |
| BA | 8.27 | 60→42 | 73→55 | 10/5 |
| IVA | 8.56 | 60→42 | 60→45 | 10/10 |
| VA | 9.00 | 60→42 | 73→55 | 10/5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laborda-Illanes, A.; Boutriq, S.; Aranega-Martín, L.; Castellano-Castillo, D.; Sánchez-Alcoholado, L.; Plaza-Andrades, I.; Peralta-Linero, J.; Alba, E.; Fernández-García, J.C.; González-González, A.; et al. Exploring the Interplay Between Gut Microbiota and the Melatonergic Pathway in Hormone Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6801. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146801
Laborda-Illanes A, Boutriq S, Aranega-Martín L, Castellano-Castillo D, Sánchez-Alcoholado L, Plaza-Andrades I, Peralta-Linero J, Alba E, Fernández-García JC, González-González A, et al. Exploring the Interplay Between Gut Microbiota and the Melatonergic Pathway in Hormone Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6801. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146801
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaborda-Illanes, Aurora, Soukaina Boutriq, Lucía Aranega-Martín, Daniel Castellano-Castillo, Lidia Sánchez-Alcoholado, Isaac Plaza-Andrades, Jesús Peralta-Linero, Emilio Alba, José Carlos Fernández-García, Alicia González-González, and et al. 2025. "Exploring the Interplay Between Gut Microbiota and the Melatonergic Pathway in Hormone Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6801. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146801
APA StyleLaborda-Illanes, A., Boutriq, S., Aranega-Martín, L., Castellano-Castillo, D., Sánchez-Alcoholado, L., Plaza-Andrades, I., Peralta-Linero, J., Alba, E., Fernández-García, J. C., González-González, A., & Queipo-Ortuño, M. I. (2025). Exploring the Interplay Between Gut Microbiota and the Melatonergic Pathway in Hormone Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6801. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146801






