What a Modern Physician Should Know About microRNAs in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Diabetic Kidney Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. MiRNA Biosynthesis
MiRNA—Mechanism of Action
3. MiRNAs in DKD
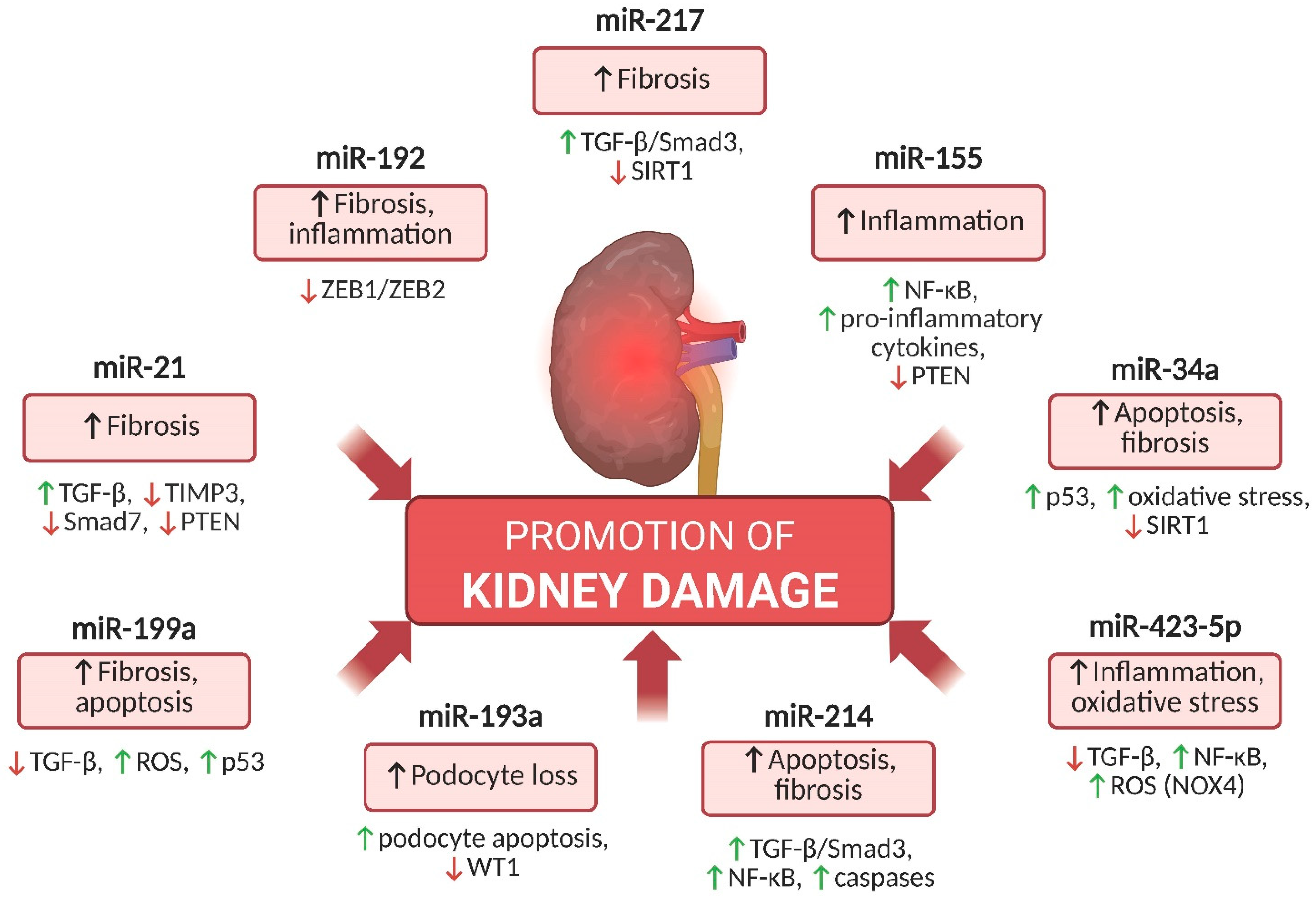
4. Key miRNAs Involved in DKD Pathogenesis That Promote Kidney Injury
4.1. miR-21
4.2. miR-192
4.3. miR-155
4.4. miR-34a
4.5. miR-217
4.6. miR-423-5p
4.7. mir-214
4.8. miR-199a
4.9. miR-193a
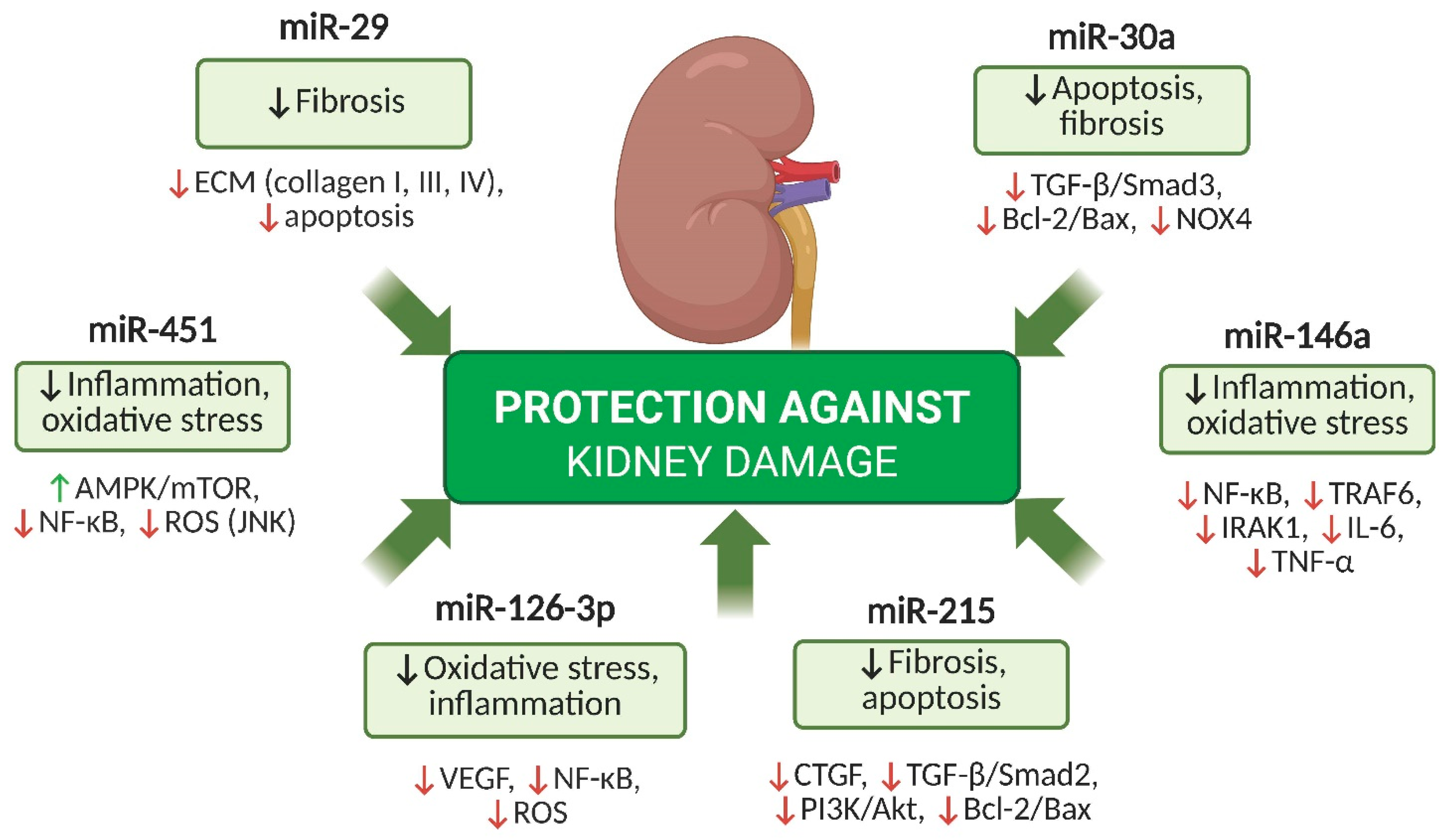
5. Key miRNAs with Protective Potential in DKD
5.1. miR-126-3p
5.2. miR-29
5.3. miR-451
5.4. miR-30a
5.5. miR-146a
5.6. miR-215
6. MiRNAs as Potential Biomarkers in DKD
7. Preclinical Models and Functional Validation of miRNAs in DKD
8. MiRNAs as Therapeutic Targets in DKD: Perspectives and Challenges
9. The Impact of Commonly Available Drugs and Dietary Compounds on miRNA Modulation in DKD
9.1. SGLT2 Inhibitors
9.2. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
9.3. Statins
9.4. Metformin
9.5. Polyphenols
9.6. Sulforaphane
9.7. The Role of Gut Microbiota in miRNA Modulation in DKD
10. Summary
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.N.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallon, V.; Thomson, S.C. The tubular hypothesis of nephron filtration and diabetic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 317–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Diabetes Work Group. KDIGO 2022 Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2022, 102 (Suppl. S5), S1–S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubara, Y.; Sawa, N.; Yamanouchi, M.; Kono, K.; Ohashi, K. New interpretation of diabetic nephropathy or diabetic kidney disease from kidney biopsy: Review article. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2025, 29, 875–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: From microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D155–D162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S. Serum VEGF as a predictive marker of glycemic control and diabetic nephropathy in Chinese older adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1274025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margaritis, K.; Margioula-Siarkou, G.; Giza, S.; Tsakoumaki, F.; Goulis, D.G.; Koliakos, G.; Kotanidou, E.P. Micro-RNA implications in type 1 diabetes mellitus: A review of literature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, P.T.B.; Clark, I.M.; Le, L.T.T. MicroRNA-based diagnosis and therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Wang, Q. Non-coding RNA and diabetic kidney disease. DNA Cell Biol. 2021, 40, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alles, J.; Fehlmann, T.; Fischer, U.; Backes, C.; Galata, V.; Minet, M.; Hart, M.; Abu-Halima, M.; Grässer, F.A.; Lenhof, H.-P.; et al. An estimate of the total number of true human miRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 3353–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Liao, J.; Lai, H.; Zhang, S.; Cui, J.; Chen, C. Roles of microRNA-192 in diabetic nephropathy: The clinical applications and mechanisms of action. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1179161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wu, W.; Liao, J.; Tang, F.; Gao, G.; Peng, J.; Fu, X.; Zhan, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xu, W.; et al. MicroRNA-21: A critical pathogenic factor of diabetic nephropathy. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 895010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhas, Y.; Arshad, N.; Biswas, N.; Jones, L.D.; Ashili, S. MicroRNA-21 silencing in diabetic nephropathy: Insights on therapeutic strategies. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Wei, G.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, X.; Wang, Q. The mechanism of miR-192 in regulating high glucose-induced MCP-1 expression in rat glomerular mesangial cells. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2019, 19, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; He, F.; Zhang, C. Molecular therapeutics for diabetic kidney disease: An update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Xu, M.; Gao, H.; Fang, Y.; Sun, W. Epigenetic modification in diabetic kidney disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1133970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankauskas, S.S.; Gambardella, J.; Sardu, C.; Lombardi, A.; Santulli, G. Functional role of miR-155 in the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Noncoding RNA 2021, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, I.; Jimenez-Castilla, L.; Lazaro, I.; Bernal-Uribe, S.; Lopez-Sanz, L.; Flores-Muñoz, M.; Egido, J.; Lopez-Franco, O.; Gomez-Guerrero, C. MiR-155/SOCS1 regulatory loop influences diabetic kidney disease by JAK/STAT pathway modulation. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36 (Suppl. S1), gfab143.004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, I.; Kavanagh, M.; Jimenez-Castilla, L.; Pardines, M.; Lazaro, I.; Herrero del Real, I.; Flores-Muñoz, M.; Egido, J.; Lopez-Franco, O.; Gomez-Guerrero, C. Amutual regulatory loop between miR-155 and SOCS1 influences renal inflammation and diabetic kidney disease. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2023, 34, 102041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Qi, Q.; Liu, S.; Huang, R.; Shen, J.; Zhu, Y.; Chai, J.; Zheng, H.; Wu, H.; Liu, H. MicroRNA-34a: A Novel Therapeutic Target in Fibrosis. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 895242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Hu, C.; Zhao, D.; Li, X. SIRT1–SIRT7 in diabetic kidney disease: Biological functions and molecular mechanisms. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1151378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.; Lv, C.; Wu, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Q. miR-217 promotes inflammation and fibrosis in high glucose cultured rat glomerular mesangial cells via Sirt1/HIF-1α signaling pathway. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2016, 32, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, X. Long non-coding RNA XIST promoted cell proliferation and suppressed apoptosis by miR-423-5p/HMGA2 axis in diabetic nephropathy. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2021, 476, 4517–4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Fan, D.; Chen, B. LncRNA NEAT1 accelerates the proliferation, oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrosis and suppresses the apoptosis through the miR-423-5p/GLIPR2 axis in diabetic nephropathy. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2022, 79, 342–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fan, L.; He, X. miR-423-5p suppresses high-glucose-induced podocyte injury by targeting Nox4. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 505, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Li, L.; Livingston, M.J.; Zhang, D.; Mi, Q.; Zhang, M.; Ding, H.F.; Huo, Y.; Mei, C.; Dong, Z. p53/microRNA-214/ULK1 axis impairs renal tubular autophagy in diabetic kidney disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 5011–5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szostak, J.; Gorący, A.; Durys, D.; Dec, P.; Modrzewski, A.; Pawlik, A. The role of microRNA in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Fei, X.; Lu, Y.; Xu, B.; Ma, Y.; Wan, H. miRNA-214 suppresses oxidative stress in diabetic nephropathy via the ROS/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway and uncoupling protein 2. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 17, 3530–3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Mamuti, D.; Zhou, W.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Z. METTL3 aggravates renal fibrogenesis in obstructive nephropathy by promoting the maturation of pri-miR-199a-3p. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 943, 175628. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.; Xu, X.; Li, H.; Chen, J.; Xiang, X.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, D. p53 induces miR-199a-3p to suppress SOCS7 for STAT3 activation in renal fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43409. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Yang, J.; Dai, S.; Gao, P.; Qi, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y. miRNA-193a-mediated WT1 suppression triggers podocyte injury through activation of the EZH2/β-catenin/NLRP3 pathway in children with diabetic nephropathy. Exp. Cell Res. 2024, 442, 114238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, H.; Kaneko, S.; Yanai, K.; Aomatsu, A.; Hirai, K.; Ookawara, S.; Ishibashi, K.; Morishita, Y. MicroRNAs in podocyte injury in diabetic nephropathy. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, N.P.; Tingle, S.J.; Shuttleworth, V.G.; Cooke, K.; Redgrave, R.E.; Singh, E.; Glover, E.K.; Tajuddin, H.B.A.; Kirby, J.A.; Arthur, H.M.; et al. MiR-126-3p is dynamically regulated in endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition during fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assmann, T.S.; Recamonde-Mendoza, M.; Costa, A.R.; de Souza, B.M.; Bauer, A.C.; Crispim, D. MicroRNAs and diabetic kidney disease: Systematic review and bioinformatic analysis. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2018, 32, 848–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Gao, H.; Dai, L.; Han, Y.; Lei, Z.; Wang, X.; Chang, H.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Tong, H.; et al. miR-126 regulates angiogenesis in myocardial ischemia by targeting HIF-1α. Exp. Cell Res. 2021, 409, 112925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.-Y.; Liu, X.-S.; Huang, X.-R.; Yu, X.-Q.; Lan, H.-Y. Diverse role of TGF-β in kidney disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluba-Sagr, A.; Franczyk, B.; Rysz-Górzyńska, M.; Rysz, J. The role of miRNA in renal fibrosis leading to chronic kidney disease. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, M.; Mohan, A.; Ecelbarger, C.M.; Saxena, A.; Gupta, A.; Prasad, N.; Tiwari, S. miR-451 loaded exosomes are released by the renal cells in response to injury and associated with reduced kidney function in human. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 234. [Google Scholar]
- Garmaa, G.; Bunduc, S.; Kóti, T.; Hegyi, P.; Csupor, D.; Ganbat, D.; Dembrovszky, F.; Meznerics, F.A.; Nasirzadeh, A.; Barbagallo, C.; et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of microRNA profiling studies in chronic kidney diseases. Noncoding RNA 2024, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, G.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J. Exosome miR-30a-5p regulates glomerular endothelial cells’ EndMT and angiogenesis by modulating Notch1/VEGF signaling pathway. Curr. Gene Ther. 2024, 24, 159–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Huang, F. LncRNA H19: A novel player in the regulation of diabetic kidney disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1238981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilyazova, I.; Asadullina, D.; Kagirova, E.; Sikka, R.; Mustafin, A.; Ivanova, E.; Bakhtiyarova, K.; Gilyazova, G.; Gupta, S.; Khusnutdinova, E.; et al. MiRNA-146a—A key player in immunity and diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, M.; Wang, M.; Chen, Z.; Bhatt, K.; Oh, H.J.; Lanting, L.; Deshpande, S.; Jia, Y.; Lai, J.Y.C.; O’Connor, C.L.; et al. An endoplasmic reticulum stress-regulated lncRNA hosting a microRNA megacluster induces early features of diabetic nephropathy. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohandes, S.; Doke, T.; Hu, H.; Mukhi, D.; Dhillon, P.; Susztak, K. Molecular pathways that drive diabetic kidney disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e165654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negeem, Z.R.; Abdel Moneim, A.A.; Mahmoud, B.; Ahmed, A.E.; Hasona, N.A. Association of microRNA-192, pentraxin-3, and transforming growth factor β1 with diabetic nephropathy: A case-control study. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2023, 22, 123–131. [Google Scholar]
- Sasso, C.V.; Lhamyani, S.; Hevilla, F.; Padial, M.; Blanca, M.; Barril, G.; Jiménez-Salcedo, T.; Sanz Martínez, E.; Nogueira, Á.; Lago-Sampedro, A.M.; et al. Modulation of miR-29a and miR-29b expression and their target genes related to inflammation and renal fibrosis by an oral nutritional supplement with probiotics in malnourished hemodialysis patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theofilis, P.; Oikonomou, E.; Vogiatzi, G.; Sagris, M.; Antonopoulos, A.S.; Siasos, G.; Iliopoulos, D.C.; Perrea, D.; Vavouranakis, M.; Tsioufis, K.; et al. The Role of MicroRNA-126 in Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2023, 30, 1902–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, K.; Lanting, L.L.; Jia, Y.; Yadav, S.; Reddy, M.A.; Magilnick, N.; Boldin, M.; Natarajan, R. Anti-inflammatory role of microRNA-146a in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 2277–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, J.; Maxwell, A.P.; Simpson, D.A.; McKay, G.J. Differential expression of urinary exosomal microRNAs miR-21-5p and miR-30b-5p in individuals with diabetic kidney disease. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-C.; Chen, C.-C.; Hsu, C.-K.; Chen, Y.-T.; Chen, C.-Y.; Yang, K.-J.; Hung, M.-J.; Wu, I.-W. Urinary microRNA in diabetic kidney disease: A literature review. Medicina 2023, 59, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapała, B.; Kamińska, A.; Piwowar, M.; Paziewska, A.; Gala-Błądzińska, A.; Stępień, E.Ł. miRNA signature of urine extracellular vesicles shows the involvement of inflammatory and apoptotic processes in diabetic chronic kidney disease. Pharm. Res. 2023, 40, 817–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satake, E.; Krolewski, B.; Kobayashi, H.; Md Dom, Z.I.; Ricca, J.; Wilson, J.M.; Hoon, D.S.B.; Duffin, K.L.; Pezzolesi, M.G.; Krolewski, A.S. Preanalytical considerations in quantifying circulating miRNAs that predict progression to end-stage kidney disease in diabetes. JCI Insight 2024, 9, e174153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, P.H.; Hsu, Y.C.; Chen, T.H.; Lin, C.L. Recent advances in diabetic kidney diseases: From kidney injury to kidney fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Miao, C.; Wang, J. LncRNA ZEB1-AS1 inhibits renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy by regulating the miR-217/MAFB axis. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 30389–30397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.Y.; Lu, F.H.; Huang, X.R.; Meng, X.M.; Lan, H.Y. Non-coding RNAs as biomarkers and therapeutic targets for diabetic kidney disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 583528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, B.; Xue, H.; Zhou, Q.Q.; Peng, L. miR-217 is a useful diagnostic biomarker and regulates human podocyte cells apoptosis via targeting TNFSF11 in membranous nephropathy. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 2168767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C. Advances in the study of miRNAs in chronic kidney disease with cardiovascular complications. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1283597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kölling, M.; Kaucsar, T.; Schauerte, C.; Hübner, A.; Dettling, A.; Park, J.K.; Busch, M.; Wulff, X.; Meier, M.; Scherf, K.; et al. Therapeutic miR-21 silencing ameliorates diabetic kidney disease in mice. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyhan, A.A. Trials and tribulations of microRNA therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tang, J.-Y.; Chen, J.; Li, G.-Q.; Feng, B.; Mu, J. MiR-29a-3p inhibits fibrosis of diabetic kidney disease in diabetic mice via downregulation of DNA methyl transferase 3A and 3B. World J. Diabetes 2024, 15, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, P.; Chacko, L.; Dua, T.K.; Chakraborty, P.; Paul, U.; Phulchand, V.V.; Jha, N.K.; Jha, S.K.; Kandimalla, R.; Dewanjee, S. Nanomedicines for the management of diabetic nephropathy: Present progress and prospects. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1236686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluitt, M.B.; Mohit, N.; Gambhir, K.K.; Nunlee-Bland, G. To the future: The role of exosome-derived microRNAs as markers, mediators, and therapies for endothelial dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Res. 2022, 2022, 5126968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putta, S.; Lanting, L.; Sun, G.; Lawson, G.; Kato, M.; Natarajan, R. Inhibiting microRNA-192 ameliorates renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Ha, X.; Yang, S.; Tian, X.; Jiang, H. Advances in understanding and treating diabetic kidney disease: Focus on tubulointerstitial inflammation mechanisms. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1232790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, S.; Wu, X.; Shen, X.; Tao, L. MiR-126-loaded immunoliposomes against vascular endothelial inflammation: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Xu, C.; Jin, Y. The role of exosomes in the pathogenesis and management of diabetic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1398382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Huo, Z.; He, X.; Liu, F.; Liang, J.; Wu, L.; Yang, D. The role of miR-29 in the mechanism of fibrosis. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2023, 23, 1846–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, D.M.; Han, P.; Mangala, L.S.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Sood, A.K.; Liu, J.; Kriegel, A.J.; Usa, K.; Widlansky, M.E.; Liang, M. Broad-acting therapeutic effects of miR-29b-chitosan on hypertension and diabetic complications. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2022, 29, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klen, J.; Dolžan, V. SGLT2 inhibitors in the treatment of diabetic kidney disease: More than just glucose regulation. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.-C.; Chen, J.-X.; Zou, R.; Liang, X.-B.; Tang, J.-X.; Yao, C.-W. Role and mechanisms of SGLT-2 inhibitors in the treatment of diabetic kidney disease. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1213473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawanami, D.; Takashi, Y. GLP-1 receptor agonists in diabetic kidney disease: From clinical outcomes to mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Górriz, J.L.; Soler, M.J.; Navarro-González, J.F.; García-Carro, C.; Puchades, M.J.; D’Marco, L.; Martínez Castelao, A.; Fernández-Fernández, B.; Ortiz, A.; Górriz-Zambrano, C.; et al. GLP-1 receptor agonists and diabetic kidney disease: A call of attention to nephrologists. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, X.; Wang, D.; Chen, R.; Tan, W.; Liang, L.; Shi, M.; Zhang, F.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Atorvastatin restores PPARα inhibition of lipid metabolism disorders by downregulating miR-21 expression to improve mitochondrial function and alleviate diabetic nephropathy progression. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 819787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Ma, X.-Y.; Han, J.-Y.; Yang, M.; Lv, C.; Shao, Y.; Wang, Y.-L.; Kang, J.-Y.; Wang, Q.-Y. Metformin regulates inflammation and fibrosis in diabetic kidney disease through TNC/TLR4/NF-κB/miR-155-5p inflammatory loop. World J. Diabetes 2021, 12, 19–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.A.; Stroebel, B.; Zhang, L.; Aouizerat, B.; Mattis, A.; Flowers, E. MicroRNAs associated with metformin treatment in the diabetes prevention program. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudrapal, M.; Khairnar, S.J.; Khan, J.; Dukhyl, A.B.; Ansari, M.A.; Alomary, M.N.; Alshabrmi, F.M.; Palai, S.; Deb, P.K.; Devi, R. Dietary polyphenols and their role in oxidative stress-induced human diseases: Insights into protective effects, antioxidant potentials and mechanism(s) of action. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 806470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabbir, U.; Rubab, M.; Daliri, E.B.; Oh, D.H.; Paik, H.D. Curcumin, quercetin, catechins and metabolic diseases: The role of gut microbiota. Nutrients 2021, 13, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cione, E.; La Torre, C.; Cannataro, R.; Caroleo, M.C.; Plastina, P.; Gallelli, L. Quercetin, epigallocatechin gallate, curcumin, and resveratrol: From dietary sources to human microRNA modulation. Molecules 2019, 25, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; He, W.; Shi, W. Sulforaphane (Sul) reduces renal interstitial fibrosis (RIF) by controlling the inflammation and TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2024, 67, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.H.; Gao, Z.X.; Liu, D.W.; Liu, Z.S.; Wu, P. Gut microbiota and its metabolites—Molecular mechanisms and management strategies in diabetic kidney disease. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1124704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Yang, J. The role and mechanism of the gut microbiota in the development and treatment of diabetic kidney disease. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1166685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Q.; Liu, N.; Zheng, B.; Guo, F.; Zeng, X.; Huang, X.; Ouyang, D. Roles of gut microbial metabolites in diabetic kidney disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 636175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Yang, L.; Wei, W.; Fu, P. Efficacy of probiotics/synbiotics supplementation in patients with chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1434613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Li, C.; Lv, M.; Hu, Q.; Guo, L.; Xiong, D. Correlation between alterations of gut microbiota and miR-122-5p expression in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Xu, M.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, H. probiotics and nutrients in cardiovascular and kidney disease. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paquette, S.; Thomas, S.C.; Venkataraman, K.; Appanna, V.D.; Tharmalingam, S. The effects of oral probiotics on type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM): A clinical trial systematic literature review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matz, L.M.; Geesala, R.; Gaddam, R.R.; Shi, X.Z. Editorial: Understanding the role of gut hormones, microbiota, and miRNAs in metabolic regulation and glucose homeostasis in obesity and type-2-diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1255942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| miRNA | Biomarker Function | Clinical Application in Diagnostic DKD |
|---|---|---|
| miR-192 | Regulator of fibrosis | High expression in early stages; marker for early kidney damage; potential therapeutic target |
| miR-21 | Regulator of fibrosis and inflammation | Indicator of disease progression and fibrosis; potential therapeutic target |
| miR-29 | Anti-fibrotic activity | Decreases with disease progression; potential early-stage marker |
| miR-126-3p | Endothelial function and vascular health marker | Associated with vascular complications and endothelial health; potential indicator of vascular damage in DKD |
| miR-146a | Anti-inflammatory function | Reduced levels in advanced DKD; potential therapeutic target |
| miR-215 | Fibrosis regulator | Promising early-stage biomarker; indicator of disease progression |
| miR-217 | Cell apoptosis regulator | Associated with various DKD stages; potential marker for cellular health and disease progression |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodzoń-Norwicz, M.; Kogut, P.; Sowa-Kućma, M.; Gala-Błądzińska, A. What a Modern Physician Should Know About microRNAs in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Diabetic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6662. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146662
Rodzoń-Norwicz M, Kogut P, Sowa-Kućma M, Gala-Błądzińska A. What a Modern Physician Should Know About microRNAs in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Diabetic Kidney Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6662. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146662
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodzoń-Norwicz, Małgorzata, Patryk Kogut, Magdalena Sowa-Kućma, and Agnieszka Gala-Błądzińska. 2025. "What a Modern Physician Should Know About microRNAs in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Diabetic Kidney Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6662. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146662
APA StyleRodzoń-Norwicz, M., Kogut, P., Sowa-Kućma, M., & Gala-Błądzińska, A. (2025). What a Modern Physician Should Know About microRNAs in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Diabetic Kidney Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6662. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146662






