Abstract
We aimed to examine the effect of zonulin and zonulin inhibition on gastrointestinal (GI) motility and the mRNA expression of zonulin and the protease-activated receptor 2 (par2), the primary receptor for zonulin, under conditions of inflammation by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) injection. The experimental models included zonulin transgenic mice (ztm), par2 knockout ztm (ztm-par2 −/−), ztm exposed to the zonulin inhibitor AT1001 (ztm-AT1001), and wildtype mouse controls. GI transit was measured by fluorescein isothiocyanate-dextran and mRNA expression by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction in whole, and in epithelial and non-epithelial tissues of all GI segments. There were no differences in the GI transit between mouse groups at baseline. After the LPS injection, ztm mice had an attenuated slowing of the GI transit compared to wildtype mice. The zonulin-inhibited mice had motility patterns similar to wildtype mice. zonulin upregulation was noted in GI segments of the ztm, ztm-par2 −/−, and ztm-AT1001 after the LPS injection. Differences in motility patterns between ztm and zonulin inhibition models despite zonulin expression in GI segments of all mouse groups supports that PAR2 is key for zonulin’s effect on motility under conditions of inflammation. However, the findings from the epithelial and non-epithelial compartments suggest that the pathway of activity is complex and likely indirect.
1. Introduction
The epithelial barrier lining the gastrointestinal (GI) tract plays a vital role in maintaining physiological homeostasis by regulating bidirectional signaling across the barrier. Gastrointestinal functions such as nutrient absorption, energy regulation, immune tolerance, endocrine signaling and motility can all be impacted by changes in the transepithelial signaling of the GI tract [1,2,3,4,5]. Transepithelial trafficking increases, particularly under conditions of inflammation, thereby contributing to GI dysfunction under acute or chronic conditions of systemic inflammation [6,7,8,9,10]. Understanding the relationship between transepithelial barrier trafficking and other GI functions, such as motility, is key to restoring GI homeostasis when the epithelial barrier is disrupted, particularly under inflammatory conditions.
Zonulin is a protein that reversibly disrupts the epithelial barrier, allowing for an increase in transepithelial trafficking and thereby potentially impacting multiple GI functions beyond the epithelial barrier [11,12,13]. Zonulin is increased under conditions of local or systemic inflammation [14,15,16]. Increases in zonulin have been associated with multiple inflammatory conditions including obesity, celiac disease, critical illness and COVID-19-associated multisystem inflammatory syndrome [14,15,17,18,19]. Multiple aspects of GI homeostasis are impacted in these conditions, including motility, supporting a role for zonulin-mediated transepithelial trafficking in the development of dysmotility.
We have previously shown an association between systemic levels of zonulin and post-operative gastric dysmotility in a cohort of pediatric patients undergoing surgery and requiring critical care [19]. In a mouse model of inflammation, we demonstrated differences in the motility patterns in the small intestine of zonulin transgenic mice (ztm) compared to wildtype (wt) [19]. The mechanism by which zonulin is associated with dysmotility, however, is unclear. The primary receptor by which zonulin acts is the protease-activated receptor 2 (PAR2) [12]. Four PARs have been described, with the unique ability to self-activate by a protease-mediated cleavage of a tethered ligand or directly by external agonists [20,21]. PAR2 is present on diverse cell types throughout the GI tract in both the epithelial and non-epithelial layers, such as epithelial, immune and neuronal cells [20,22]. PAR2 activation by native and synthetic proteases in the GI tract has been found to impact GI motility by influencing intestinal contractility [23,24,25].
We have demonstrated that PAR2 is key for zonulin to exert its effect on the epithelial barrier; however, whether PAR2 also contributes to the effects of zonulin on GI motility is not clear. The effect of zonulin on motility may be direct or indirect. A direct mechanism may be that zonulin binds on PAR2 on key downstream cells in the non-epithelial compartment, such as neuronal or muscular cells that subsequently regulate and trigger contractility. An indirect mechanism may be that zonulin binds to PAR2 on epithelial cells on the epithelial compartment of the GI tract, driving transepithelial trafficking and the trafficking of microbial products, metabolites, etc., which impacts downstream cells that regulate motility such as enteroendocrine or immune cells.
To address this gap, this study aimed to examine the relationship between zonulin, PAR2 and motility under conditions of inflammation. Our approach included two models of zonulin inhibition. The first was employing a PAR2 knockout mouse and crossing it with ztm. The second mode of inhibition exposed ztm to AT1001, a zonulin inhibitor, prior to triggering inflammation [26]. zonulin and par2 differences on whole tissue and epithelial and non-epithelial tissue from individual GI segments, among the diverse zonulin expressing mouse models, were examined using quantitative real-time PCR.
2. Results
2.1. GI Motility
GI motility was examined by the transit of FITC-dextran, with faster transit being represented by FITC-dextran reaching segments farther in the GI tract. Under baseline conditions, (wt), ztm, ztm-par2 −/− and ztm-AT1001 mice all had a similar pattern of FITC-dextran transit, with a peak %FITC in the ileum ((wt): 59.7 ± 27% FITC, ztm: 59.8 ± 35.6% FITC, ztm-par2 −/−: 54.7 ± 20.6% FITC, ztm-AT1001: 54 ± 33% FITC) (Figure 1). ztm and ztm-par2 −/− mice also had significant differences in %FITC in the jejunum and cecum/colon, respectively, compared to (wt), (jejunum-ztm: 4.8 ± 5% versus (vs) (wt): 18.5 ± 9.8% FITC, p = 0.04; cecum/colon-ztm-par2 −/−: 31.5 ± 23.8%, (wt): 16.7 ± 26.8%, p = 0.003) (Supplementary Table S1).
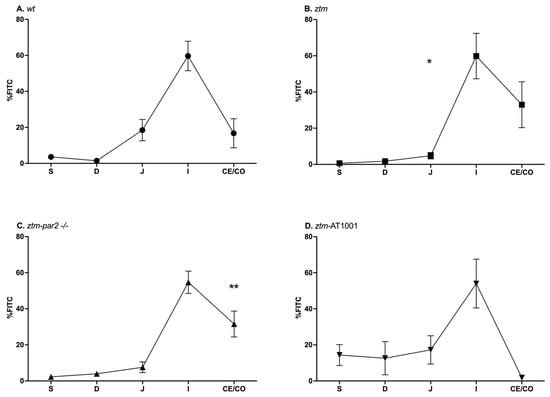
Figure 1.
Gastrointestinal (GI) transit by FITC-dextran distribution in PBS-injected mice. Panel (A) depicts GI transit for wildtype (wt) mice (closed circles) which serves as control for statistical analysis of all experimental mouse groups; Panel (B) depicts GI transit for zonulin transgenic mice (ztm) (closed squares). ztm had less %FITC than (wt) in the jejunum, * p-value < 0.05; Panel (C) depicts GI transit for ztm-protease activated receptor 2 knockout (ztm-par2 −/−) mice (closed upward-facing triangle). ztm-par2 −/− had greater %FITC in the cecum/colon than (wt) ** p-value < 0.01: Panel (D) depicts GI transit for ztm exposed to AT1001 (ztm-AT1001) (downward-facing triangle). S: stomach; D: duodenum; J: jejunum; I: ileum; Ce: cecum; and Co: colon. Each symbol represents the mean %FITC for that segment and the standard mean error. n = 6–12, male and female mice; Dirichlet regression performed to compare %FITC between mouse groups and GI segments with (wt) serving as control.
Upon LPS exposure, all mouse groups had significant slowing in their transit, represented by the retention of FITC in the proximal segments of the GI tract, i.e., stomach and duodenum. The ztm had less %FITC in the jejunum (ztm: 21 ± 25.5%, (wt): 23.3 ± 20.5%) and more %FITC in the ileum, cecum, and colon than the (wt) control (ileum + cecum + colon: ztm: 18.3 ± 29.4%, (wt): 8.6% ± 16.2%), reflecting faster transit (Figure 2A,B). Inhibiting zonulin reduced the %FITC in the ileum, cecum, and colon in the ztm-par2 −/− and ztm-AT1001 compared to ztm, thereby reverting the phenotype back to the (wt) (ileum + cecum + colon: ztm-par2 −/−: 10.4 ± 13.9%, ztm-AT1001: 3.1% ± 2.1%, (wt): 8.6% ± 16.2%) (Figure 2C,D).
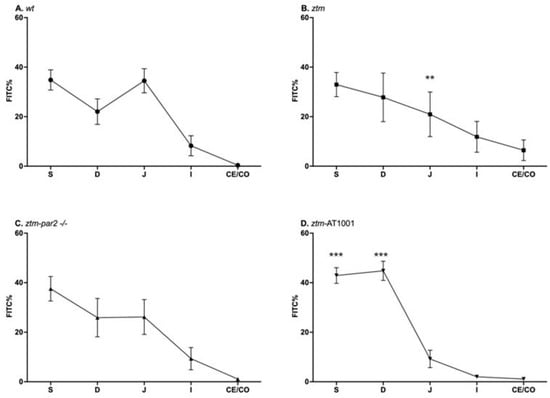
Figure 2.
Gastrointestinal (GI) transit by FITC-dextran of LPS-injected mice. Panel (A) depicts GI transit for wildtype (wt) mice (open circles) which serves as control for statistical analysis of all experimental mouse groups; Panel (B) depicts GI transit for zonulin transgenic mice (ztm) (open squares). ztm had less %FITC than (wt) in the jejunum, ** p-value < 0.01; Panel (C) depicts GI transit for ztm-protease activated receptor 2 knockout (ztm-par2 −/−) mice (open upward-facing triangle): Panel (D) depicts GI transit for ztm exposed to AT1001 (ztm-AT1001) (open downward-facing triangle). ztm-AT1001 had more %FITC in the stomach and duodenum than (wt), *** p-value < 0.001. S: stomach; D: duodenum; J: jejunum; I: ileum; Ce: cecum; and Co: colon. Each symbol represents the mean %FITC for that segment and the standard mean error. n = 6–16, male and female mice; Dirichlet regression performed to compare %FITC between mouse groups and GI segments with (wt) serving as control.
Analyzing these %FITC values between GI segments and mouse groups using a Dirichlet regression identified a lower %FITC in the jejunum of the ztm compared to (wt) [OR = 0.24, 95% CI (0.11, 0.54), p < 0.001] and a higher %FITC in the stomach and duodenum of ztm-AT1001 compared to (wt) [stomach-OR = 3.16, 95% CI (1.66, 5.99), p < 0.001; duodenum-OR = 5.75, 95% CI (3, 11.99), p < 0.001] (Supplementary Table S2).
2.2. zonulin mRNA Expression—Whole Tissue
We examined zonulin mRNA expression in all GI tissues of ztm, ztm-par2 −/−and ztm-AT1001 mice at baseline and under inflammatory conditions. zonulin mRNA expression was greater with LPS-injection compared to PBS in the stomach, duodenum, jejunum and colon of ztm, the duodenum, ileum and colon of the ztm-par2 −/− and the colon of ztm-AT1001 mice (Figure 3).
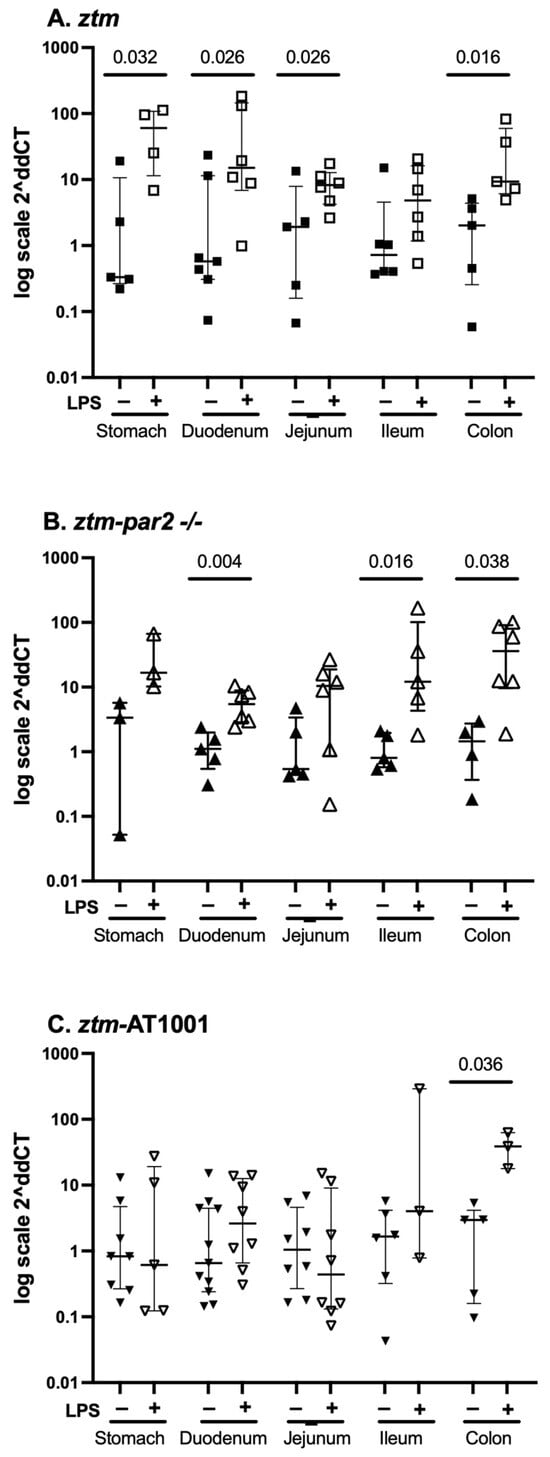
Figure 3.
zonulin mRNA expression throughout the gastrointestinal tract. Panel (A) depicts data from PBS-(closed squares) and LPS (open squares)-injected zonulin-transgenic mice (ztm). LPS-injected ztm had more zonulin expression in the stomach, duodenum, jejunum and colon than PBS-injected ztm, p < 0.05; Panel (B) depicts data from PBS-(closed upward-facing triangles) and LPS (open upward-facing triangles)-injected protease-activated receptor 2 knockout ztm (ztm-par2 −/−) mice. LPS-injected ztm-par2 −/− had more zonulin expression in the duodenum, ileum and colon than PBS-injected ztm-par2 −/− mice, p < 0.05; Panel (C) depicts data from PBS-(closed downward-facing triangles) and LPS (open downward-facing triangles)-injected ztm exposed to AT1001 (ztm-AT1001). LPS-injected ztm-AT1001 mice had more zonulin expression in the colon than PBS-injected ztm-AT1001, p < 0.05. Data are summarized as median (25th, 75th); Kruskal–Wallis test controlled for multiple comparisons between mouse groups within each gastrointestinal tissue represented here, statistical significance set at p-value < 0.05. Data are presented as 2−ΔΔCT based on the delta cycle threshold (Ct) [dCt = target gene Ct − housekeeping gene Ct (18S)] of individual data − the mean of the PBS dCt within each mouse group.
We also examined zonulin mRNA expression for each GI segment between mouse groups (e.g., zonulin mRNA expression in the stomach of ztm, ztm-par2 −/− and ztm-AT1001) and between each GI segment within individual mouse groups (e.g., stomach, duodenum, jejunum, etc., for ztm) (Table 1). Under baseline conditions, ztm-AT1001 had more zonulin mRNA expression in the duodenum than ztm, [median (25th, 75th) Ct zonulin-18S: ztm 18.36 (15.99, 21.52) versus ztm-AT1001 14.23 (12.07, 16.23), Kruskal–Wallis test p = 0.021], whereas the ztm had more zonulin mRNA expression than ztm-par2 −/− in the colon, [median (25th, 75th) Ct zonulin-18S: ztm 14.77 (13.12, 15.49) versus ztm-par2 −/− 17.59 (16.33, 18.08), Kruskal–Wallis test p = 0.013]. There were no differences in zonulin mRNA expression between mouse groups within each GI segment under inflammatory conditions (Table 1).

Table 1.
zonulin mRNA expression in whole tissue of GI segments.
Differences in zonulin mRNA expression between tissues within mouse groups were noted under baseline conditions for ztm and ztm-AT1001 and under inflammatory conditions for ztm-par2 −/− (Table 1).
2.3. par2 mRNA Expression—Whole Tissue
Given that zonulin acts via PAR2 and that the ztm-par2 −/− versus ztm-AT1001 inhibition models demonstrated different motility patterns, we examined par2 mRNA expression in ztm and ztm-AT1001 mice in all GI segments under baseline and inflammatory conditions. There was an overall pattern of par2 mRNA expression downregulation under inflammatory conditions compared to the baseline for ztm and ztm-AT1001 in all GI segments (Figure 4). Downregulation after LPS-injection was statistically significant in the ileum of ztm [median (25th, 75th) Ct par2-18S: PBS-10.28 (8.99, 11.52) versus LPS-12.80 (11.88, 15.17), Mann–Whitney U Test p = 0.03; jejunum of the ztm-AT1001 [PBS 10.10 (9.74, 11.19) versus LPS 11.49 (11.09, 12.57), Mann–Whitney U test p = 0.011] (Figure 4). When comparing par2 expression within GI segments between mouse groups, ztm-AT1001 mice had less par2 mRNA expression in the ileum and colon and more in the jejunum than ztm under baseline conditions (Table 2). Under inflammatory conditions, par2 mRNA expression was lower in the ileum and colon of ztm-AT1001 than ztm (Table 2). ztm-AT1001 had differences in par2 mRNA expression in individual GI segments under both baseline and inflammatory conditions (Table 2).
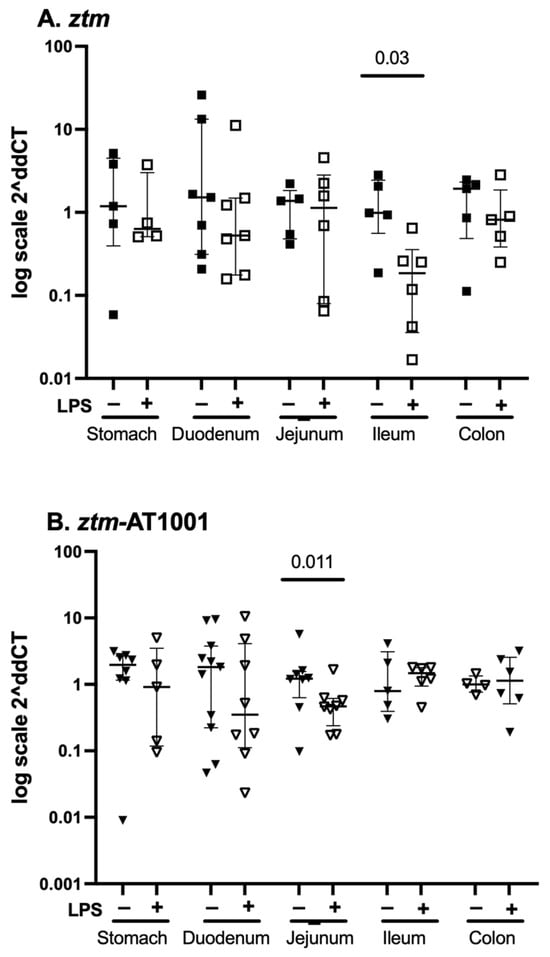
Figure 4.
par2 mRNA expression throughout the gastrointestinal tract. Panel (A) depicts data from PBS-(closed squares) and LPS (open squares)-injected zonulin transgenic mice (ztm). LPS-injected ztm had less par2 expression in the ileum than PBS-injected ztm, p < 0.05. Panel (B) depicts data from PBS-(closed downward-facing triangles) and LPS (open downward-facing triangles)-injected, ztm exposed to AT1001 (ztm-AT1001). LPS-injected ztm-AT1001 had less par2 expression in the jejunum than PBS-injected ztm-AT1001, p < 0.05. Data are summarized as median (25th, 75th); Mann–Whitney U test between mouse groups within gastrointestinal tissue. Data are presented as 2−ΔΔCT based on the delta cycle threshold (Ct) [dCt = target gene Ct − housekeeping gene Ct (18S)] of individual data − the mean of the PBS dCt within each mouse group.

Table 2.
par2 mRNA expression in whole tissue of GI segments.
2.4. zonulin mRNA Expression in Epithelial Versus Non-Epithelial Compartments
zonulin can be expressed in cells within the epithelial and non-epithelial compartments of the GI tract; therefore, we examined zonulin mRNA expression within these two compartments in all GI segments and zonulin-producing mouse groups. Table 3 and Table 4 depict median (25th, 75th) Ct zonulin-18S mRNA expression in the epithelial and non-epithelial compartments of ztm, ztm-par2 −/− and ztm-AT1001 under baseline and inflammatory conditions, respectively.

Table 3.
zonulin mRNA expression in PBS-injected mouse groups across the epithelial and non-epithelial compartments of GI segments.

Table 4.
zonulin mRNA expression in LPS-injected mouse groups across the epithelial and non-epithelial compartments of GI segments.
2.4.1. Baseline Conditions
Median zonulin mRNA expression under baseline conditions for all mouse groups was greater in the non-epithelial tissues compared to the epithelial tissues [epithelial vs. non-epithelial—median (25th, 75th) Ct Ct zonulin-18S: ztm 19.96 (18.75, 20.91) vs. 17.10 (14.65, 18.92), ztm-par2 −/− 20.11 (18.51, 21.46) vs. 16.87 (15.27, 19.00), ztm-AT1001 22.30 (21.46, 23.27) vs. 19.19 (16.43, 20.95)] (Table 3). In the epithelial compartment of the stomach, ztm-par2 −/− had more zonulin expression than ztm-AT1001 mice (median (25th, 75th) median Ct zonulin-18S stomach: ztm-par 2 −/− 15.90 (15.17, 18.08) versus ztm-AT1001 21.66 (20.26, 22.25), Kruskal–Wallis test, p = 0.028) (Table 3). In the non-epithelial compartment, there was no difference in zonulin mRNA expression between mouse groups (Table 3). When examining expression between GI segments and within a mouse group in the epithelial compartment, zonulin mRNA expression was greater in the stomach compared to the jejunum in ztm and ztm-par2 −/− [median (25th, 75th) Ct zonulin-18S, stomach versus jejunum, ztm 18.01 (16.52, 18.60) versus 21.70 (20.91, 21.88), Kruskal–Wallis test p = 0.005, and ztm-par2 −/− 15.90 (15.17, 18.08) versus 24.29 (20.94, 24.55), Kruskal–Wallis test p = 0.048] (Table 3). In the non-epithelial compartment for all mouse groups, there was no difference in the zonulin mRNA expression among GI tissues within a mouse group (Table 3).
2.4.2. Inflammatory Conditions
Median zonulin mRNA expression under inflammatory conditions for all mouse groups was greater in the non-epithelial compartment compared to the epithelial compartment [median (25th, 75th) Ct zonulin-18S, epithelial vs. non-epithelial: ztm 17.65 (15.87, 19.87) vs. 15.72 (12.73, 17.85), ztm-par2-/- 18.60 (18.30, 19.88) vs. 14.06 (13.35, 16.22), ztm-AT1001 19.19 (16.49, 21.11) vs. 15.19 (14.14, 16.56)] (Table 4). There was no difference in zonulin mRNA expression between mouse groups within GI segments in either compartment (Table 4). When examining expression between GI segments and within individual mouse groups in the epithelial compartment, ztm had more zonulin mRNA expression in the stomach and colon than the duodenum, [Ct zonulin-18S: stomach 14.29 (12.62, 17.56) versus duodenum 19.88 (18.97, 21.45), Kruskal–Wallis test p = 0.012 and duodenum 19.88 (18.97, 21.45) versus colon 15.64 (14.41, 18.25), Kruskal–Wallis test p = 0.016] (Table 4). In the non-epithelial compartment, ztm-par2 -/- mice had more zonulin mRNA expression in the stomach than the duodenum, [median (25th, 75th) Ct zonulin-18S ztm-par 2-/- stomach 11.54 (10.71, 14.15) versus duodenum 17.44 (16.36, 19.48), Kruskal–Wallis test p = 0.016] (Table 4).
2.5. par2 mRNA Expression in Epithelial Versus Non-Epithelial Compartment
par2 mRNA expression was examined in the epithelial and non-epithelial compartments of all GI segments of zonulin- and par2-producing mouse groups, ztm and ztm-AT1001. Table 5 and Table 6 depict median (25th, 75th) Ct par2-18S mRNA expression in the epithelial and non-epithelial compartments of ztm and ztm-AT1001 under baseline and inflammatory conditions, respectively.

Table 5.
par2 mRNA expression in PBS-injected mouse groups across the epithelial and non-epithelial compartments of GI segments.

Table 6.
par2 mRNA expression in LPS-injected mouse groups across the epithelial and non-epithelial compartments of GI segments.
2.5.1. Baseline Conditions
Median par2 mRNA expression under baseline conditions was similar in the epithelial and non-epithelial compartments [median (25th, 75th) Ct par2-18S epithelial versus (vs) non-epithelial: ztm 13.46 (12.29, 15.03) vs. 14.16 (12.40, 16.92), ztm-AT1001 14.19 (12.88, 15.65) vs. 14.98 (14.06, 16.34)] (Table 5). Within the stomach, ztm had more par2 expression than ztm-AT1001 [median (25th, 75th) Ct par2-18S: ztm 12.66 (11.79, 13.16) versus ztm-AT1001 13.86 (13.52, 13.98, Mann–Whitney U test p = 0.016] (Table 5). There was no difference in par2 expression between ztm and ztm-AT1001 in the other GI segments. There was no difference in par2 expression between GI segments for ztm. There was more par2 mRNA expression in the ileum than the duodenum of ztm-AT1001, [median (25th, 75th) Ct par2-18S: ileum 12.30 (11.10, 12.66) versus duodenum 16.86 (15.45, 18.78), Kruskal–Wallis test, p = 0.012].
2.5.2. Inflammatory Conditions
Median par2 mRNA expression under inflammatory conditions was similar in the epithelial vs. non-epithelial compartments for ztm and ztm-AT1001 mice [median (25th, 75th) Ct par2-18S, epithelial vs. non-epithelial: ztm 13.17 (11.47, 16.02) vs. 14.45 (12.15, 16.87), ztm-AT1001 13.57 (12.24, 15.30) vs. 13.99 (12.87, 16.23)] (Table 6). There were no differences in par2 expression between ztm and ztm-AT1001 in any of the GI segments in the epithelial and non-epithelial compartment (Table 6). The only difference between GI segments within mouse groups was noted in the epithelial compartment between the duodenum and colon of ztm-AT1001, [median (25th, 75th) Ct par2-18S, duodenum 15.38 (14.84, 17.80) versus colon 10.18 (8.50, 13.08), Kruskal–Wallis test p = 0.015] (Table 6).
3. Discussion
We have examined the relationship between zonulin and PAR2 on motility under inflammatory conditions, leveraging two models of zonulin inhibition and comprehensively examining gene expression in three tissue levels and all GI segments. We have demonstrated that under baseline conditions, motility follows similar patterns in zonulin expression and inhibition models to the (wt) control. However, triggering inflammation elicited distinct phenotypes, specifically with the ztm having faster small intestinal transit and zonulin inhibition reverting the phenotype back to the (wt) motility pattern. Differences in zonulin and par2 mRNA expression were primarily noted when examining whole tissue between baseline and inflammatory conditions within mouse groups. Differences in zonulin and par2 expression between mouse groups within GI segments and between GI segments within mouse groups in whole, epithelial and non-epithelial tissues were noted and support a complex and indirect role for zonulin on motility under conditions of inflammation.
An overall increase in zonulin under conditions of inflammation has been described for multiple diseases and in experimental models [14,16,17,27]. However, a comprehensive characterization of zonulin expression including multiple levels of GI tissue and segments, and in the context of motility, has not been described. In this study, ztm mice exhibited significantly increased zonulin expression after LPS injection across multiple GI segments, with the most pronounced upregulation observed in the stomach and proximal small intestine compared to baseline levels. This aligns with previous data reported on ztm by this group, including an increase in the zonulin mRNA expression of the stomach after LPS injection and an increase in zonulin expression in the duodenum and jejunum after dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) exposure [16,19]. It is this change in zonulin expression, as opposed to absolute zonulin expression, that drives the changes in motility after LPS injection, since the ztm had a similar motility pattern to (wt) mice under baseline conditions despite having zonulin expression and a different pattern of motility under conditions of inflammation when zonulin expression levels were increased in most GI segments. Furthermore, the GI segments with greatest dysmotility in the ztm were the segments with the greatest upregulation in zonulin expression. This is also supported by the mRNA expression for par2 in the ztm. Zonulin acts via PAR2 and, therefore, differences in par2 expression across GI segments could influence the effect of zonulin on GI function across tissues. However, par2 mRNA expression was not different across GI segments under baseline or inflammatory conditions. The effect of zonulin on motility across GI tissues under conditions of inflammation, therefore, does not appear to be modulated by differences in par2 itself, but rather the change in zonulin expression.
Although par2 expression may not influence the differences in motility across GI segments in ztm, PAR2 is critical for the overall effect of zonulin. Both of our zonulin inhibition models block the PAR2 signaling pathway, ztm-par2 −/−, by a whole body receptor knockout and in ztm-AT1001 by the binding of a competitive peptide, AT1001, on PAR2 [12,13,26]. These two models of inhibition had dysmotility patterns more akin to the (wt) mouse after LPS injection, with minimal to no FITC reaching the distal small intestine, cecum or colon. This reversion to the (wt) motility phenotype in the inhibition models was present despite differences in the upregulation of zonulin, with increased expression in most GI segments for ztm-par2 −/− and some for ztm-AT1001. This confirms that inhibiting PAR2 blocked the effect of zonulin and its effect on motility, under conditions of inflammation. Previous models of intestinal inflammation have shown that AT1001 blocks the effect of zonulin, resulting in changes in GI physiology—specifically, an epithelial barrier leak [16]. No models of ztm-par2 −/−, however, have been previously reported and we noted differences between the two inhibition models regarding the degree of dysmotility and zonulin mRNA expression. The ztm-par 2 −/− had a dysmotility pattern that was almost identical to that of (wt) mice, whereas the ztm-AT1001 had an exaggerated dysmotility pattern after LPS injection. In effect, a mouse from the ztm-par 2 −/− group phenotypically resembles a (wt) mouse, since despite zonulin expression, it has no receptor for zonulin to affect at any time in its development and life cycle. However, the ztm-AT1001 mouse has zonulin and PAR2 throughout its development with the abrupt inhibition of this pathway, resulting in potential compensatory mechanisms that contributed to the exaggerated phenotype. The ztm has been described to have differences in its microbiome and immune cell composition compared to (wt) under baseline conditions [28]. Specifically, ztm has an overall pro-inflammatory microbial composition with a reduced abundance of Akkermansia and increased abundance of Rikinella bacterial species. Furthermore, it has a pro-inflammatory immune profile that is microbiome-independent, since alteration of the microbiome did not reverse this phenotype. The sudden inhibition of zonulin in ztm by the AT1001 peptide likely changes transepithelial trafficking of ztm’s altered microbiome which then impacts immune composition and, therefore, GI physiology. Future experiments will examine changes in the microbiome and immune profile to understand how the different approaches to zonulin inhibition impact GI physiology.
The role of PAR2 has been examined in various models of motility [23,24,25]. In a mouse model, intraperitoneal injection of PAR2 agonists resulted in faster transit, measured by the distance traversed of a marker within the small intestine [23]. Another study examined the role of PAR2 in motility after GI injury in a mouse model and demonstrated that PAR2 activation after injury accelerated transit compared to the sham [29]. The motility phenotype demonstrated in the GI injury model parallels that of our ztm model of inflammation, whereby ztm has attenuated dysmotility under conditions of inflammation compared to (wt), but no difference in transit at the baseline despite ztm having zonulin expression and, therefore, PAR2 activation. Similarly, par2 mRNA expression was different between ztm and ztm-AT1001 under baseline conditions when the GI motility phenotype was the same. These findings support an interaction between inflammation and PAR2 for PAR2 to have a role in motility. These findings also emphasize the importance of PAR2 as the receptor for zonulin to have its effect, but do not support an independent role for PAR2 on motility since absolute changes in PAR2 were not associated with the phenotype.
In summary, ztm has attenuated dysmotility, particularly in the small intestine. This appears to be due to changes in zonulin expression and zonulin activity on PAR2, as evidenced by the reversal of the phenotype in the zonulin inhibition models. Although zonulin and PAR2 are present in multiple cell populations across the GI tissue, our findings suggest that the effect of zonulin and PAR2 on motility is mediated primarily via the epithelial compartment. We identified few differences in zonulin and par2 expression among mouse groups only in the epithelial compartment and under baseline conditions. However, effector cells that impact motility are in the non-epithelial compartment of the GI tissue (e.g., resident macrophages and enteric neurons), which supports an indirect role for zonulin on motility. As previously described, zonulin increases epithelial barrier leak, particularly under conditions of inflammation, and ztm has an altered microbiome [11,12,13,28]. An increase in transepithelial trafficking in ztm of intraluminal factors, including metabolites and microbial products, can impact downstream cell populations that regulate motility, whether under baseline or inflammatory conditions. Such cell populations include immune cells, particularly macrophages, and enteroendocrine cells [30,31]. Therefore, we postulate that zonulin impacts motility due to the differential priming of downstream cell populations under baseline conditions, which influences the inflammatory response of these cells. This relationship between transepithelial trafficking secondary to zonulin and motility is pertinent to inflammatory diseases where therapies to improve an epithelial barrier leak could negatively impact motility.
This study was unique in its use of two zonulin inhibition models which have not been widely studied. We also performed a comprehensive gene expression analysis of zonulin and par2 in multiple tissue levels of the GI tract and within all GI segments. This allowed for an examination of the effect of zonulin and par2 on motility at a segment-specific level and allowed for an exploration of how zonulin may modulate motility, whether directly or indirectly. Subsequent studies will examine in depth the potential indirect pathways by which transepithelial trafficking from an increase in zonulin mRNA expression may modulate dysmotility under conditions of inflammation. Furthermore, the regulation of motility, like many GI functions, is multifactorial and, therefore, more than one of its regulatory mechanisms were likely impacted under conditions of inflammation.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
Experiments were performed in adult (8–12 week-old) male and female mice for all included genotypes and experimental groups. All mice were in a C57Bl/6 background and bred and maintained in an in-house colony at the Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH). Mice included (a) (wt) mice, which do not produce zonulin, as control, (b) ztm, which produce zonulin, (c) ztm-par2 −/−, which produce zonulin and lack the primary receptor for zonulin activity, PAR2, and (d) ztm exposed to AT1001, a zonulin inhibitor, so designated ztm-AT1001. The ztm was donated by Dr. Andrew Levy and its construct has been previously published [32]. The ztm-par2 −/− mice were generated by breeding ztm with commercially available par2 −/− mice. All mice were bred and housed under the same standard conditions per MGH regulations. Separate cohorts of mice were utilized for GI transit testing and for tissue isolation for mRNA expression. This animal protocol was approved by the MGH Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) and all procedures were performed in accordance with the MGH IACUC. All mice were euthanized per IACUC guidelines with isoflurane anesthetic overdose (5% isoflurane with secondary physical method). ARRIVE guidelines were followed. Weights were obtained 24–48 h prior to the experiment. All mouse experiments were run at a minimum in triplicate.
4.2. Experimental Conditions
4.2.1. Inflammation
Inflammation was triggered by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) injection as previously published [33]. Mice were injected with 10 mg/kg of LPS or 1% Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS) as vehicle control. The LPS utilized in these experiments was Escherichia Coli LPS O111:B4 (L3012, Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA), which was reconstituted in sterile 1% PBS. Mice were weighed 24–48 h prior to an experiment and injected 6 h prior to GI motility testing or euthanasia for tissue isolation [19]. We have previously shown this protocol to elicit significant inflammation with cytokine changes and the use of a sepsis score [19]. We confirmed inflammation in these experiments by the use of the sepsis score 6 h after injection [34]. Mice were excluded if they did not show signs and symptoms of inflammation by the sepsis score. Mice were fasted from standard chow at the time of injection and from water at the time of gavage. Mice within the same genotype were distributed randomly to be injected with vehicle control or LPS. Blinding from inflammatory conditions was not possible given the explicit changes in behavior as a result of LPS injection.
4.2.2. Zonulin Inhibition by AT1001
AT1001 is an eight-amino-acid peptide, GGVLVQPG, that blocks zonulin activity by binding to PAR2. [26] AT1001 was produced by GenScript (Piscataway, NJ, USA) with a >98% purity. The ztm was exposed to 1 mg/mL of AT1001 in water for one week prior to completion of GI transit or tissue isolation. The AT1001 water was changed every other day and water intake (mL) was tracked. Animal weight was also tracked to ensure there were no adverse effects from AT1001.
4.3. Gastrointestinal Transit Testing
70 kDa of non-digestible fluorescein isothiocyanate-dextran (FITC-dextran) was purchased from MilliporeSigma, Burlington, MA, USA (MilliporeSigma FD70). Mice were gavaged with 6 mg/kg of FITC-dextran using a standard oral gavage needle 1 h prior to GI transit testing. GI tissue was isolated, including the stomach, small intestine, cecum and colon. Given the limitations of flushing the stomach and cecum, both tissues were cut open and then flushed with 2 mL of PBS. The small intestine was measured and divided into 10 equal segments; each segment was flushed with 2 mL of PBS. Lastly, the colon was flushed in total with 2 mL of PBS. The small intestine was further subdivided into the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. Based on the average length of each segment, the first three (1–3) segments were determined to be the duodenum, the second three (4–6) segments, the jejunum and the last four (7–10) segments, the ileum. Each flush was diluted PBS at a 1:100 ratio and loaded in duplicates for measurement of FITC fluorescence using the Synergy-2 spectrophoto fluorimetry from BioTek, Santa Clara, CA, USA at 485/535 nm wavelengths. Given that the volume of FITC-dextran gavaged was dependent on individual mouse weight, FITC nanogram/mL measurements per GI segment were converted to percent based on total GI tract FITC measurement to allow for comparison among mouse groups and conditions.
4.4. Real-Time Quantitative-Polymerase Chain Reaction (q-PCR)
Stomach, duodenum, jejunum, ileum and colon tissue were isolated and processed whole and also divided into epithelial and non-epithelial compartments. The epithelial compartment was isolated from the non-epithelial compartment by scraping dissected tissue sections. All subsequent procedures were performed the same in whole tissue and epithelial versus non-epithelial tissue. The mRNA expression of zonulin and par2 was examined by quantitative-Polymerase Chain Reaction (q-PCR), as previously published [19]. A 0.5 cm frozen piece of each segment, or scrape and residual tissue for the epithelial and non-epithelial compartments, from all mouse groups were collected and immediately placed in 1 mL of TRIzolTM Reagent (Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA) and homogenized. mRNA was extracted using the Direct-zol RNA mini prep Kit (Zymo Research, Irvine, CA, USA) following manufacturer’s instructions. RNA concentrations and A260/A280 and A260/A230 ratios were measured with the NanoDrop spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) to ensure the quality of the extracted mRNA. Target A260/A280 and A260/A230 ratios were ~2 and ~2–2.0. Any tissue that did not meet these criteria was discarded and mRNA extraction was performed with a new piece of tissue. Then, 1 µg of mRNA was used to perform the removal of genomic DNA, conversion to cDNA and the q-PCR. To ensure all genomic DNA was removed, we completed the DNAse step of the Direct-zol RNA mini prep kit and upon completion of mRNA extraction, also ran the DNA freeTM Kit (Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA) per manufacturer’s instructions. mRNA was reverse-transcribed using random hexamer primers and Maxima universal first-strand cDNA synthesis kit #1661 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) according to manufacturers’ instructions.
Quantitative real-time PCR was performed using PerfeCTa SYBR® Green SuperMix (Quantabio, Beverly, MA, USA) using in-house-designed primers based on NIH’s Primer Blast and obtained from Integrated DNA Technologies (Coralville, IA, USA) [18S-Primers 5′ Oligo AGAAACGGCTACCACATCCA 3′ Oligo CCCTCCAATGGATCCTCGTT, zonulin-Primers 5′ Oligo GAATGTGAGGCAGATGACAG, 3′ Oligo GTGTTCACCCATTGCTTCTC; par2-Primers 5′ Oligo TCTGTCATCTGGTTCCCCCT, 3′ Oligo CGATCACCCAGTACCTCTGC]. For this, 1 uL (=1 µg) of cDNA was run per well and samples were run in duplicate; <20% difference between duplicates was ensured. If the difference was >20%, the samples were rerun. PerfeCTa SYBR® Green SuperMix (Quantabio, Waltham, MA, USA) plus the primers but without the cDNA samples were run as blanks to ensure no contamination in our master mix. The delta cycle threshold (dCt), target gene Ct—housekeeping gene Ct, was calculated for all statistical analyses. The primary mRNA expression analysis was the difference between LPS and PBS conditions within each mouse group. Therefore, only Figure 3 and Figure 4 showing zonulin and par2 mRNA expression under PBS and LPS conditions, show the 2−ΔΔCT, where individual LPS dCt values were controlled for the mean dCt of PBS samples within the same mouse group. Controlling for the PBS mean dCt would not apply to subsequent analyses and, therefore, 2−ΔΔCT figures would misrepresent the relationship between data. Therefore, all secondary analyses considering differences between mouse groups or between GI tissues within mouse groups were performed using the dCt data and are represented in tabular format (Table 3, Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6).
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Motility data were analyzed using R version 4.2.1 by the R Foundation for Statistical Computing (Vienna, Austria). Motility data are presented as mean and standard deviation. q-PCR statistical analyses were completed using GraphPad Prism Version 8, GraphPad Software La Jolla, California. In the setting of large biological variability, q-PCR data are presented as median (25th, 75th).
Male and female mice were analyzed in aggregate. Sample size was calculated based on previous mouse GI transit data and to identify a minimum 10% difference in GI transit between our primary experimental group, LPS-injected ztm and control with 80% power. A minimum sample size of 8 mice per study group, under baseline and inflammatory conditions, was selected to mitigate the inherent variance of the assay. GI transit between mouse groups was analyzed using Dirichlet regression. The outcome—FITC percentage across five intestinal segments (duodenum, jejunum, ileum, cecum and colon)—is compositional and adds up to 100%. Using a Dirichlet regression, all parts of the composition are modeled together, which preserves the internal correlation structure inherent in such datasets. Mouse groups were treated as independent variables, with the (wt) group as the reference and the distribution of FITC across the segments as the dependent variables (Figure 1 and Figure 2). Results are presented as odds ratio and 95% confidence interval (Supplementary Tables S1 and S2). All qPCR data were analyzed using Mann–Whitney U test or Kruskal–Wallis test, as applicable (Figure 3 and Figure 4, Table 1, Table 2, Table 3, Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6). All data from mice that exhibited expected inflammation post-LPS injection were included.
5. Conclusions
In the ztm model, we have demonstrated that changes in zonulin expression under conditions of inflammation are associated with distinct motility patterns and that PAR2 is necessary for zonulin to have its effect on motility. Zonulin and PAR2 within the epithelial compartment appear to be driving these differences in the phenotype, supporting a complex and indirect relationship between zonulin and downstream effector cell populations that modulate motility.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijms26136381/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: E.E.M. and A.F.; Methodology: E.E.M., J.L. and A.F.; Validation: E.E.M., J.D.P., K.M.R.H. and A.F.; Formal analysis: E.E.M. and J.D.P.; Investigation: E.E.M., J.D.P., J.L. and K.M.R.H.; Resources: E.E.M. and J.L.; Data curation: E.E.M., J.D.P. and K.M.R.H.; Writing—original draft: E.E.M. and J.D.P. Writing—review and editing: E.E.M., J.D.P., J.L., K.M.R.H. and A.F.; Visualization: E.E.M. and J.D.P.; Supervision: E.E.M. and A.F.; Project administration: E.E.M. and A.F.; Funding acquisition: E.E.M. and A.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
E.E.M. was supported by NIH K23DK128634. A.F. was supported by NIH grants DK104344 and P30DK040561.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This protocol was approved by the Massachusetts General Hospital Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC), protocol number 2013N000013.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original data presented in the study are openly available in Harvard Dataverse at https://doi.org/10.7910/DVN/CJXYGL.
Conflicts of Interest
A.F. is co-founder and stockholder at Alba Therapeutics. All other authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Abbreviations
Fluorescein–isothiocyanate, FITC; gastrointestinal, GI; lipopolysaccharide, LPS; protease-activated receptor 2, PAR2; quantitative-polymerase chain reaction, qPCR; zonulin transgenic mouse, ztm; ztm-par2 knockout, ztm-par2 −/−; ztm and AT1001 exposed, ztm-AT1001; wildtype, (wt); zonulin and par2 are presented in lowercase and italics when when referring to mRNA or the mouse models.
References
- Peterson, L.W.; Artis, D. Intestinal epithelial cells: Regulators of barrier function and immune homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bubeck, M.; Becker, C.; Patankar, J.V. Guardians of the gut: Influence of the enteric nervous system on the intestinal epithelial barrier. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1228938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colgan, S.P.; Curtis, V.F.; Lanis, J.M.; Glover, L.E. Metabolic regulation of intestinal epithelial barrier during inflammation. Tissue Barriers 2015, 3, e970936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philpott, J.D.; Hovnanian, K.M.R.; Stefater-Richards, M.; Mehta, N.M.; Martinez, E.E. The enteroendocrine axis and its effect on gastrointestinal function, nutrition, and inflammation. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2024, 30, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, E.E.; Mehta, N.M.; Fasano, A. The Zonulin Pathway as a Potential Mediator of Gastrointestinal Dysfunction in Critical Illness. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 23, e424–e428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, A.; Turner, J.R. Cell Biology of Tight Junction Barrier Regulation and Mucosal Disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a029314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michielan, A.; D’Inca, R. Intestinal Permeability in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Pathogenesis, Clinical Evaluation, and Therapy of Leaky Gut. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 628157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoni, L.; Nuding, S.; Wehkamp, J.; Stange, E.F. Intestinal barrier in inflammatory bowel disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 1165–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita, K.; Kabashima, K. Tight junctions in the development of asthma, chronic rhinosinusitis, atopic dermatitis, eosinophilic esophagitis, and inflammatory bowel diseases. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 107, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, C.; Fornai, M.; D’Antongiovanni, V.; Antonioli, L.; Bernardini, N.; Derkinderen, P. The intestinal barrier in disorders of the central nervous system. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudry, B.; Fasano, A.; Ketley, J.; Kaper, J.B. Cloning of a gene (zot) encoding a new toxin produced by Vibrio cholerae. Infect. Immun. 1992, 60, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, A.; Lammers, K.M.; Goldblum, S.; Shea-Donohue, T.; Netzel-Arnett, S.; Buzza, M.S.; Antalis, T.M.; Vogel, S.N.; Zhao, A.; Yang, S.; et al. Identification of human zonulin, a physiological modulator of tight junctions, as prehaptoglobin-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 16799–16804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldblum, S.E.; Rai, U.; Tripathi, A.; Thakar, M.; De Leo, L.; Di Toro, N.; Not, T.; Ramachandran, R.; Puche, A.C.; Hollenberg, M.D.; et al. The active Zot domain (aa 288–293) increases ZO-1 and myosin 1C serine/threonine phosphorylation, alters interaction between ZO-1 and its binding partners, and induces tight junction disassembly through proteinase activated receptor 2 activation. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapone, A.; de Magistris, L.; Pietzak, M.; Clemente, M.G.; Tripathi, A.; Cucca, F.; Lampis, R.; Kryszak, D.; Carteni, M.; Generoso, M.; et al. Zonulin upregulation is associated with increased gut permeability in subjects with type 1 diabetes and their relatives. Diabetes 2006, 55, 1443–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonker, L.M.; Gilboa, T.; Ogata, A.F.; Senussi, Y.; Lazarovits, R.; Boribong, B.P.; Bartsch, Y.C.; Loiselle, M.; Rivas, M.N.; Porritt, R.A.; et al. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children is driven by zonulin-dependent loss of gut mucosal barrier. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e149633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturgeon, C.; Lan, J.; Fasano, A. Zonulin transgenic mice show altered gut permeability and increased morbidity/mortality in the DSS colitis model. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2017, 1397, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drago, S.; El Asmar, R.; Di Pierro, M.; Grazia Clemente, M.; Tripathi, A.; Sapone, A.; Thakar, M.; Iacono, G.; Carroccio, A.; D’Agate, C.; et al. Gliadin, zonulin and gut permeability: Effects on celiac and non-celiac intestinal mucosa and intestinal cell lines. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 41, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaus, D.A.; Motal, M.C.; Burger-Klepp, U.; Marschalek, C.; Schmidt, E.M.; Lebherz-Eichinger, D.; Krenn, C.G.; Roth, G.A. Increased plasma zonulin in patients with sepsis. Biochem. Medica 2013, 23, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, E.E.; Lan, J.; Konno, T.; Miranda-Ribera, A.; Fiorentino, M.; Mehta, N.M.; Fasano, A. Novel role of zonulin in the pathophysiology of gastro-duodenal transit: A clinical and translational study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuberger, D.M.; Schuepbach, R.A. Protease-activated receptors (PARs): Mechanisms of action and potential therapeutic modulators in PAR-driven inflammatory diseases. Thromb. J. 2019, 17, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peach, C.J.; Edgington-Mitchell, L.E.; Bunnett, N.W.; Schmidt, B.L. Protease-activated receptors in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2023, 103, 717–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergnolle, N. Review article: Proteinase-activated receptors—Novel signals for gastrointestinal pathophysiology. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2000, 14, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawabata, A.; Kuroda, R.; Nagata, N.; Kawao, N.; Masuko, T.; Nishikawa, H.; Kawai, K. In vivo evidence that protease-activated receptors 1 and 2 modulate gastrointestinal transit in the mouse. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 133, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawabata, A.; Matsunami, M.; Sekiguchi, F. Gastrointestinal roles for proteinase-activated receptors in health and disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153 (Suppl. S1), S230–S240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiguchi, F.; Hasegawa, N.; Inoshita, K.; Yonezawa, D.; Inoi, N.; Kanke, T.; Saito, N.; Kawabata, A. Mechanisms for modulation of mouse gastrointestinal motility by proteinase-activated receptor (PAR)-1 and -2 in vitro. Life Sci. 2006, 78, 950–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pierro, M.; Lu, R.; Uzzau, S.; Wang, W.; Margaretten, K.; Pazzani, C.; Maimone, F.; Fasano, A. Zonula occludens toxin structure-function analysis. Identification of the fragment biologically active on tight junctions and of the zonulin receptor binding domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 19160–19165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, T.; Berti, I.; Sapone, A.; Gerarduzzi, T.; Not, T.; Zielke, R.; Fasano, A. Role of the intestinal tight junction modulator zonulin in the pathogenesis of type I diabetes in BB diabetic-prone rats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 2916–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda-Ribera, A.; Ennamorati, M.; Serena, G.; Cetinbas, M.; Lan, J.; Sadreyev, R.I.; Jain, N.; Fasano, A.; Fiorentino, M. Exploiting the Zonulin Mouse Model to Establish the Role of Primary Impaired Gut Barrier Function on Microbiota Composition and Immune Profiles. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaruzza, F.; Cenac, N.; Barocelli, E.; Impicciatore, M.; Hyun, E.; Vergnolle, N.; Sternini, C. Protective effect of proteinase-activated receptor 2 activation on motility impairment and tissue damage induced by intestinal ischemia/reperfusion in rodents. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 169, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, P.A.; Koscso, B.; Rajani, G.M.; Stevanovic, K.; Berres, M.L.; Hashimoto, D.; Mortha, A.; Leboeuf, M.; Li, X.M.; Mucida, D.; et al. Crosstalk between muscularis macrophages and enteric neurons regulates gastrointestinal motility. Cell 2014, 158, 300–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selleri, S.; Palazzo, M.; Deola, S.; Wang, E.; Balsari, A.; Marincola, F.M.; Rumio, C. Induction of pro-inflammatory programs in enteroendocrine cells by the Toll-like receptor agonists flagellin and bacterial LPS. Int. Immunol. 2008, 20, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, A.P.; Levy, J.E.; Kalet-Litman, S.; Miller-Lotan, R.; Levy, N.S.; Asaf, R.; Guetta, J.; Yang, C.; Purushothaman, K.R.; Fuster, V.; et al. Haptoglobin genotype is a determinant of iron, lipid peroxidation, and macrophage accumulation in the atherosclerotic plaque. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlinski, R.; Pedersen, B.; Schabbauer, G.; Tencati, M.; Holscher, T.; Boisvert, W.; Andrade-Gordon, P.; Frank, R.D.; Mackman, N. Role of tissue factor and protease-activated receptors in a mouse model of endotoxemia. Blood 2004, 103, 1342–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrum, B.; Anantha, R.V.; Xu, S.X.; Donnelly, M.; Haeryfar, S.M.; McCormick, J.K.; Mele, T. A robust scoring system to evaluate sepsis severity in an animal model. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).