Galectin-3—Insights from Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
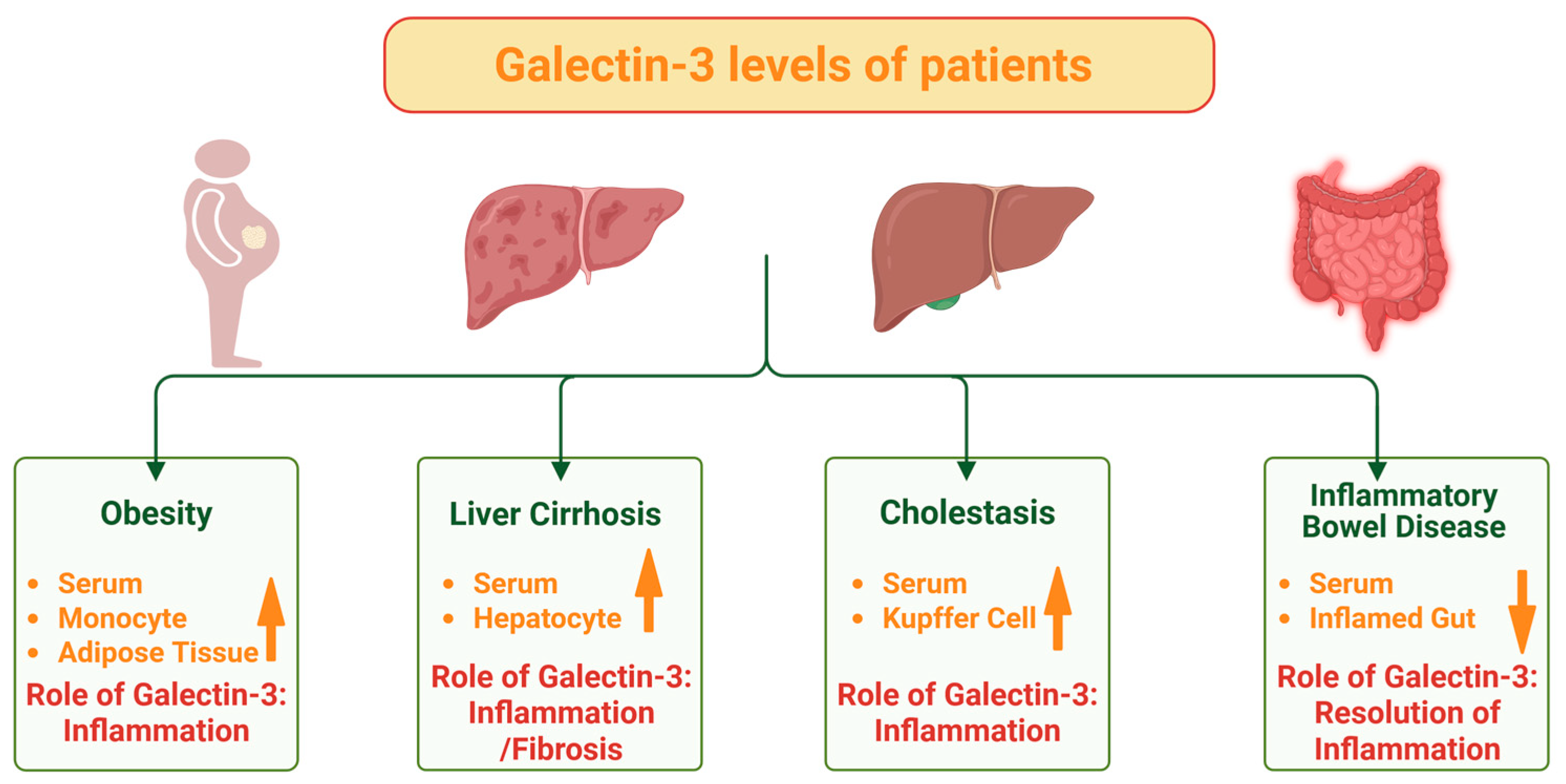
2. IBD, Obesity and Galectin-3
Galectin-3 and Obesity-Associated Disease
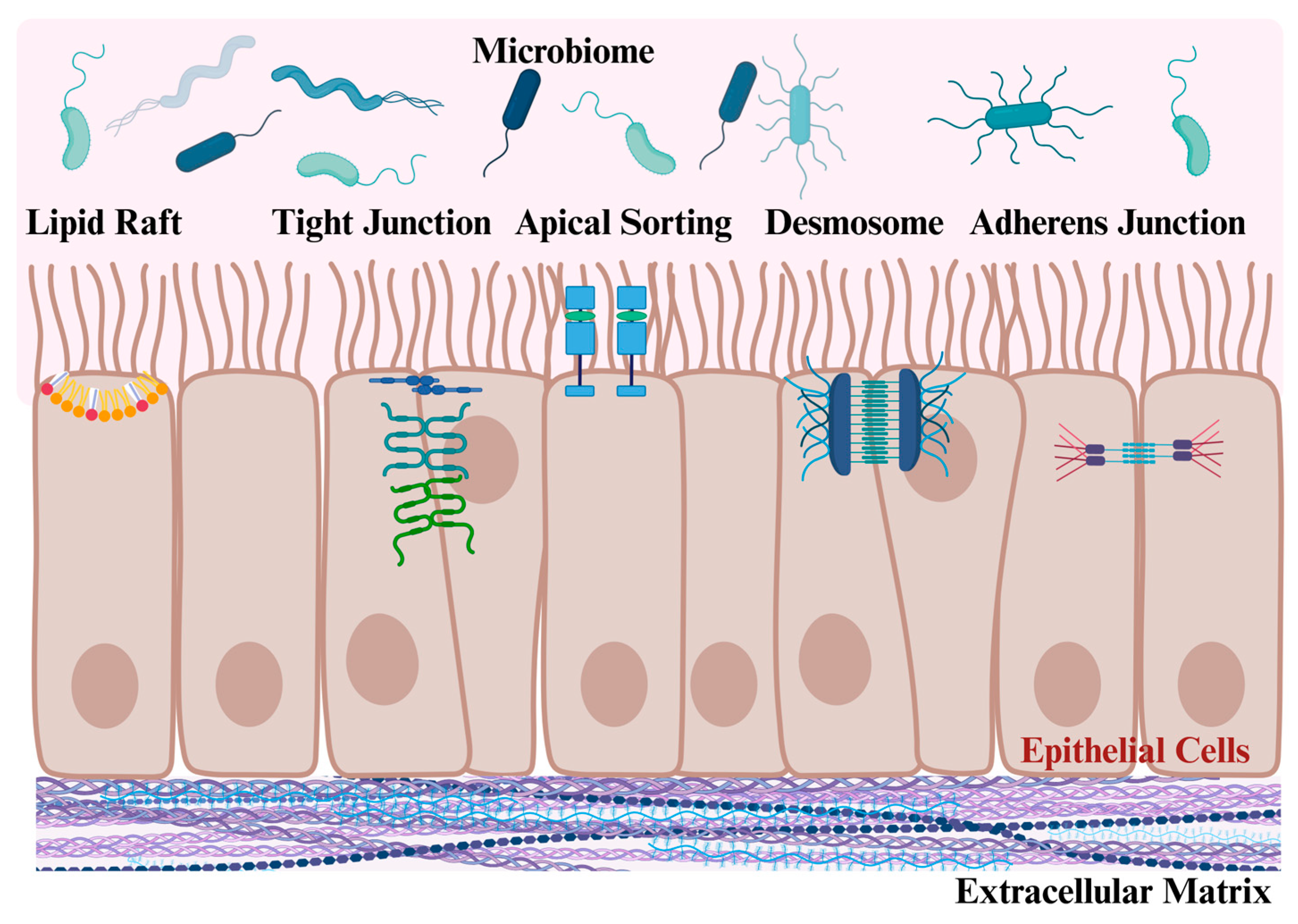
3. Galectin-3 Regulates Intestinal Epithelial Cell Junctions
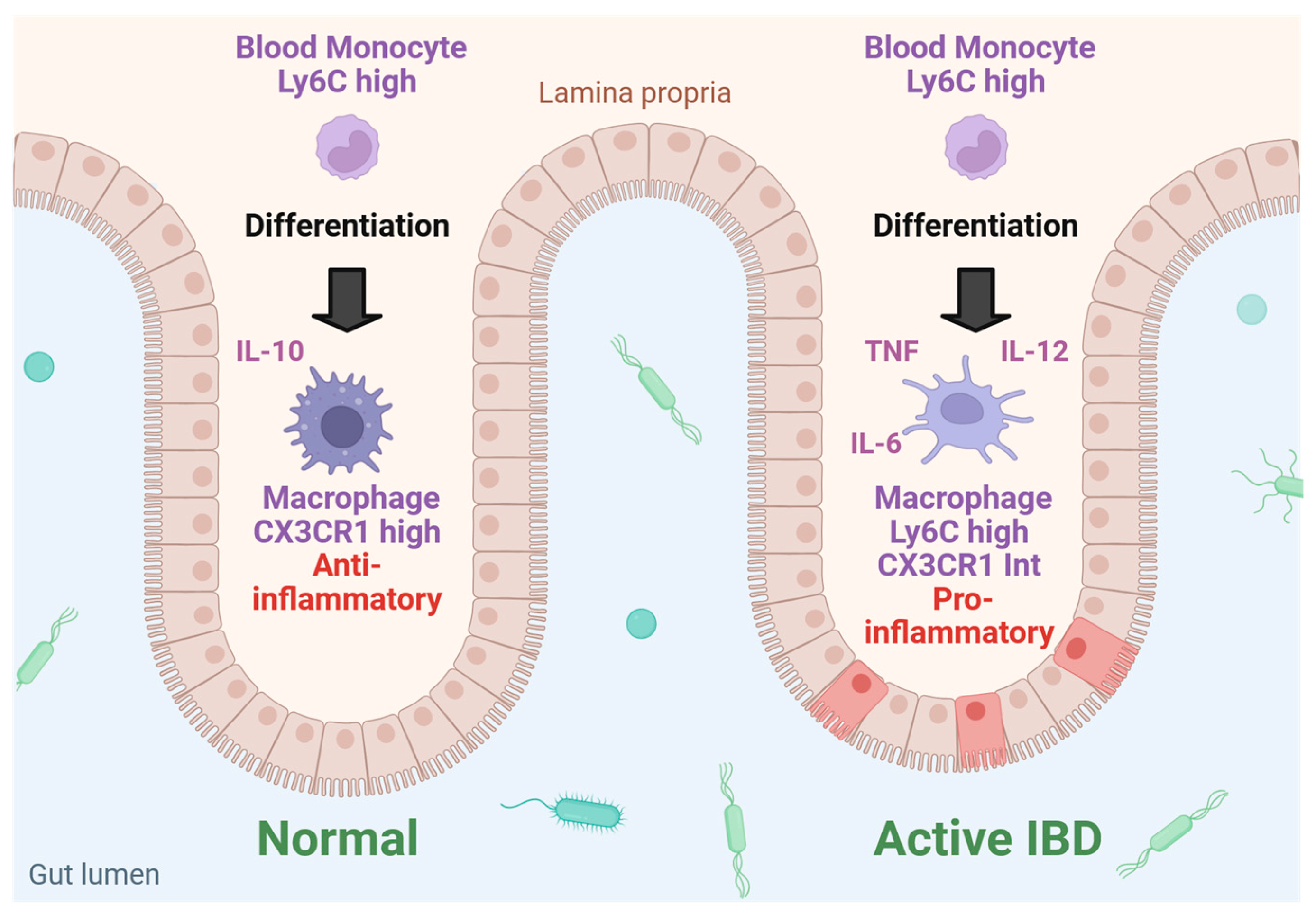
4. Macrophage, Neutrophil and T-Cell Function Is Regulated by Galectin-3
The Multiple Roles of Galectin-3 in Inflamed Intestinal Epithelium
5. Galectin-3 in Experimental IBD
6. Serum, Urinary and Fecal Galectin-3 in IBD
7. Tissue Expression of Galectin-3 in IBD
8. Galectin-3 in Liver Diseases and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
9. Drugs Affecting Galectin-3 and Galectin-3 Antagonists for Liver Fibrosis
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CD | Crohn’s disease |
| CRD | Carbohydrate recognition domain |
| CX3CR1 | CX3C motif chemokine receptor 1 |
| E-cadherin | Epithelial cadherin |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| DSS | Dextran sodium sulfate |
| IBD | Inflammatory bowel disease |
| IL | Interleukin |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| Ly6C | Lymphocyte antigen 6 complex |
| MAFLD | Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease |
| NLRP3 | NOD-like receptor family, pyrin domain containing 3 |
| Th | T helper |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor |
| UC | Ulcerative colitis |
| PSC | Primary sclerosing cholangitis |
References
- Brown, S.J.; Mayer, L. The immune response in inflammatory bowel disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 102, 2058–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.H. The genetics and immunopathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlhamer, J.M.; Zammitti, E.P.; Ward, B.W.; Wheaton, A.G.; Croft, J.B. Prevalence of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Among Adults Aged ≥ 18 Years—United States, 2015. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2016, 65, 1166–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, C.; Obermeier, F.; Thieler, S.; Kemptner, D.; Bauer, A.; Scholmerich, J.; Rogler, G.; Timmer, A. The incidence of inflammatory bowel disease in a rural region of Southern Germany: A prospective population-based study. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 20, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, M.; Christensen, H.S.; Bogsted, M.; Colombel, J.F.; Jess, T.; Allin, K.H. The Rising Burden of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Denmark Over Two Decades: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Gastroenterology 2022, 163, 1547–1554.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2017 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Collaborators. The global, regional, and national burden of inflammatory bowel disease in 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Kwon, J.E.; Cho, M.L. Immunological pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Intest. Res. 2018, 16, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, H.S.; Fiocchi, C. Immunopathogenesis of IBD: Current state of the art. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obermeier, F.; Hofmann, C.; Falk, W. Inflammatory bowel diseases: When natural friends turn into enemies-the importance of CpG motifs of bacterial DNA in intestinal homeostasis and chronic intestinal inflammation. Int. J. Inflam. 2010, 2010, 641910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Scholmerich, J. Inflammatory bowel disease: Pandora’s box, present and future. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1072, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavricka, S.R.; Rogler, G. New insights into the pathogenesis of Crohn’s disease: Are they relevant for therapeutic options? Swiss Med. Wkly. 2009, 139, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, D.; Ye, S.; He, Y.; Wang, S.; Xiao, Y.; Xiang, X.; Deng, M.; Luo, W.; Chen, X.; Wang, X. Fatty acids and lipid mediators in inflammatory bowel disease: From mechanism to treatment. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1286667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajendran, M.; Loganathan, P.; Catinella, A.P.; Hashash, J.G. A comprehensive review and update on Crohn’s disease. Dis. Mon. 2018, 64, 20–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajendran, M.; Loganathan, P.; Jimenez, G.; Catinella, A.P.; Ng, N.; Umapathy, C.; Ziade, N.; Hashash, J.G. A comprehensive review and update on ulcerative colitis. Dis. Mon. 2019, 65, 100851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedian, S.S.; Nokhostin, F.; Malamir, M.D. A review of the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment methods of inflammatory bowel disease. J. Med. Life 2019, 12, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghoul, Z.; Yang, C.; Merlin, D. The Current Status of Molecular Biomarkers for Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.T.; Zhang, Y.; She, Y.; Goyal, H.; Wu, Z.Q.; Xu, H.G. Diagnostic Utility of Non-invasive Tests for Inflammatory Bowel Disease: An Umbrella Review. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 920732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, R.; Xiao, Y.L.; Gao, X.; Chen, B.L.; He, Y.; Yang, L.; Hu, P.J.; Chen, M.H. Fecal calprotectin in predicting relapse of inflammatory bowel diseases: A meta-analysis of prospective studies. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2012, 18, 1894–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Huang, C.; Xu, J.; Xu, H.; Liu, L.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J.; Huang, W.; Peng, W.; Chen, Y.; et al. Gut Microbiota Is a Potential Biomarker in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 818902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rheenen, P.F.; Van de Vijver, E.; Fidler, V. Faecal calprotectin for screening of patients with suspected inflammatory bowel disease: Diagnostic meta-analysis. BMJ 2010, 341, c3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.M.; Kim, J.; Lee, Y.J.; Bae, S.U.; Lee, H.W. Inflammatory bowel disease-associated intestinal fibrosis. J. Pathol. Transl. Med. 2023, 57, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pehrsson, M.; Alexdottir, M.S.; Karsdal, M.A.; Thakker, P.; Mortensen, J.H. Novel fibro-inflammatory biomarkers associated with disease activity in patients with Crohn’s disease. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 17, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domislovic, V.; Hog Mortensen, J.; Lindholm, M.; Kaarsdal, M.A.; Brinar, M.; Barisic, A.; Manon-Jensen, T.; Krznaric, Z. Inflammatory Biomarkers of Extracellular Matrix Remodeling and Disease Activity in Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, J.H.; Godskesen, L.E.; Jensen, M.D.; Van Haaften, W.T.; Klinge, L.G.; Olinga, P.; Dijkstra, G.; Kjeldsen, J.; Karsdal, M.A.; Bay-Jensen, A.C.; et al. Fragments of Citrullinated and MMP-degraded Vimentin and MMP-degraded Type III Collagen Are Novel Serological Biomarkers to Differentiate Crohn’s Disease from Ulcerative Colitis. J. Crohns Colitis 2015, 9, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Wei, F.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.; Duan, B.; Shi, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, W.; Mu, W. Measurement of hydroxyproline in collagen with three different methods. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 1157–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belostotsky, R.; Frishberg, Y. Catabolism of Hydroxyproline in Vertebrates: Physiology, Evolution, Genetic Diseases and New siRNA Approach for Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huss, M.; Elger, T.; Loibl, J.; Kandulski, A.; Binder, B.; Stoeckert, P.; Mester, P.; Müller, M.; Buechler, C.; Tews, H.C. Urinary Hydroxyproline as an Inflammation-Independent Biomarker of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterol. Insights 2024, 15, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsen, T.H.; Folseraas, T.; Thorburn, D.; Vesterhus, M. Primary sclerosing cholangitis—A comprehensive review. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 1298–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertz, A.; Nguyen, N.A.; Katsanos, K.H.; Kwok, R.M. Primary sclerosing cholangitis and inflammatory bowel disease comorbidity: An update of the evidence. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2019, 32, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floreani, A.; De Martin, S. Treatment of primary sclerosing cholangitis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2021, 53, 1531–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weismuller, T.J.; Lankisch, T.O. Medical and endoscopic therapy of primary sclerosing cholangitis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2011, 25, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dave, M.; Elmunzer, B.J.; Dwamena, B.A.; Higgins, P.D. Primary sclerosing cholangitis: Meta-analysis of diagnostic performance of MR cholangiopancreatography. Radiology 2010, 256, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schramm, C.; Eaton, J.; Ringe, K.I.; Venkatesh, S.; Yamamura, J.; MRI Working Group of the IPSCSG. Recommendations on the use of magnetic resonance imaging in PSC-A position statement from the International PSC Study Group. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1675–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackinnon, A.C.; Tonev, D.; Jacoby, B.; Pinzani, M.; Slack, R.J. Galectin-3: Therapeutic targeting in liver disease. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2023, 27, 779–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouffette, S.; Botez, I.; De Ceuninck, F. Targeting galectin-3 in inflammatory and fibrotic diseases. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 44, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochieng, J.; Furtak, V.; Lukyanov, P. Extracellular functions of galectin-3. Glycoconj. J. 2002, 19, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshminarayan, R.; Wunder, C.; Becken, U.; Howes, M.T.; Benzing, C.; Arumugam, S.; Sales, S.; Ariotti, N.; Chambon, V.; Lamaze, C.; et al. Galectin-3 drives glycosphingolipid-dependent biogenesis of clathrin-independent carriers. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 16, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Zhang, M.; Hu, Q.; Zheng, S.; Soh, A.; Zheng, Y.; Yuan, H. Galectin-3 as a novel biomarker for disease diagnosis and a target for therapy (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 599–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krautbauer, S.; Eisinger, K.; Hader, Y.; Buechler, C. Free fatty acids and IL-6 induce adipocyte galectin-3 which is increased in white and brown adipose tissues of obese mice. Cytokine 2014, 69, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigert, J.; Neumeier, M.; Wanninger, J.; Filarsky, M.; Bauer, S.; Wiest, R.; Farkas, S.; Scherer, M.N.; Schaffler, A.; Aslanidis, C.; et al. Systemic chemerin is related to inflammation rather than obesity in type 2 diabetes. Clin. Endocrinol. 2010, 72, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutin, L.; Depret, F.; Gayat, E.; Legrand, M.; Chadjichristos, C.E. Galectin-3 in Kidney Diseases: From an Old Protein to a New Therapeutic Target. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Alvarez, L.; Ortega, E. The Many Roles of Galectin-3, a Multifaceted Molecule, in Innate Immune Responses against Pathogens. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 9247574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, A.; Niwa, M.; Noguchi, K.; Kanayama, T.; Niwa, A.; Matsuo, M.; Hatano, Y.; Tomita, H. Galectin-3 as a Next-Generation Biomarker for Detecting Early Stage of Various Diseases. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.T.; Hsu, D.K. The role of galectin-3 in promotion of the inflammatory response. Drug News Perspect. 2007, 20, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menini, S.; Iacobini, C.; Blasetti Fantauzzi, C.; Pesce, C.M.; Pugliese, G. Role of Galectin-3 in Obesity and Impaired Glucose Homeostasis. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 9618092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slack, R.J.; Mills, R.; Mackinnon, A.C. The therapeutic potential of galectin-3 inhibition in fibrotic disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2021, 130, 105881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Xu, S.; Liu, Y.; Xu, X.; Philips, C.A.; Chen, J.; Mendez-Sanchez, N.; Guo, X.; Qi, X. Role of Galectins in the Liver Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 744518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumic, J.; Dabelic, S.; Flogel, M. Galectin-3: An open-ended story. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1760, 616–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Dulai, P.S.; Zarrinpar, A.; Ramamoorthy, S.; Sandborn, W.J. Obesity in IBD: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, disease course and treatment outcomes. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Sultana, H.; Refat, M.N.H.; Farhana, Z.; Kamil, A.A.; Rahman, M.M. The global burden of overweight-obesity and its association with economic status, benefiting from STEPs survey of WHO member states: A meta-analysis. Prev. Med. Rep. 2024, 46, 102882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, P.; Su, S.; Zech, J.; Nobel, Y.; Luk, L.; Economou, I.; Shen, B.; Lewis, J.D.; Freedberg, D.E. Visceral Adiposity Independently Predicts Time to Flare in Inflammatory Bowel Disease but Body Mass Index Does Not. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2024, 30, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarur, A.J.; Bruss, A.; Moosreiner, A.; Beniwal-Patel, P.; Nunez, L.; Berens, B.; Colombel, J.F.; Targan, S.R.; Fox, C.; Melmed, G.Y.; et al. Higher Intra-Abdominal Visceral Adipose Tissue Mass Is Associated with Lower Rates of Clinical and Endoscopic Remission in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Initiating Biologic Therapy: Results of the Constellation Study. Gastroenterology 2023, 165, 963–975.E5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, G.; Schaffler, A.; Neumeier, M.; Furst, A.; Bataillle, F.; Buechler, C.; Muller-Ladner, U.; Scholmerich, J.; Rogler, G.; Herfarth, H. Profiling adipocytokine secretion from creeping fat in Crohn’s disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2006, 12, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, C.W.Y.; Martin, A.; Sepich-Poore, G.D.; Shi, B.; Wang, Y.; Gouin, K.; Humphrey, G.; Sanders, K.; Ratnayake, Y.; Chan, K.S.L.; et al. Translocation of Viable Gut Microbiota to Mesenteric Adipose Drives Formation of Creeping Fat in Humans. Cell 2020, 183, 666–683.E17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaglio, A.E.; Magro, D.O.; Imbrizi, M.; De Oliveira, E.C.; Di Stasi, L.C.; Sassaki, L.Y. Creeping fat and gut microbiota in Crohn’s disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2025, 31, 102042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buechler, C.; Wanninger, J.; Neumeier, M. Adiponectin, a key adipokine in obesity related liver diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 2801–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, M.R.; Pockros, P.J.; Harrison, S.A. Impact of obesity on treatment of chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2006, 43, 1177–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Shen, J.; Sun, T.T.; Zhang, X.; Wong, N. Obesity, insulin resistance, NASH and hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2013, 23, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakhari, S. Bermuda Triangle for the liver: Alcohol, obesity, and viral hepatitis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 28 (Suppl. 1), 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolph, T.E.; Grander, C.; Grabherr, F.; Tilg, H. Adipokines and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Multiple Interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.; Anstee, Q.M.; Marietti, M.; Hardy, T.; Henry, L.; Eslam, M.; George, J.; Bugianesi, E. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: Trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maresca, R.; Mignini, I.; Varca, S.; Calvez, V.; Termite, F.; Esposto, G.; Laterza, L.; Scaldaferri, F.; Ainora, M.E.; Gasbarrini, A.; et al. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Piecing a Complex Puzzle Together. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulamhusein, A.; Reid, D.; Eksteen, B. Increased BMI is associated rapid progression of fibrosis in Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC). Hepatology 2014, 60, 341A–342A. [Google Scholar]
- Rowan, C.R.; McManus, J.; Boland, K.; O’Toole, A. Visceral adiposity and inflammatory bowel disease. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2021, 36, 2305–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigert, J.; Neumeier, M.; Wanninger, J.; Bauer, S.; Farkas, S.; Scherer, M.N.; Schnitzbauer, A.; Schaffler, A.; Aslanidis, C.; Scholmerich, J.; et al. Serum galectin-3 is elevated in obesity and negatively correlates with glycosylated hemoglobin in type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 1404–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.; Sporrer, D.; Weigert, J.; Wanninger, J.; Neumeier, M.; Wurm, S.; Stögbauer, F.; Kopp, A.; Bala, M.; Schäffler, A.; et al. Adiponectin downregulates galectin-3 whose cellular form is elevated whereas its soluble form is reduced in type 2 diabetic monocytes. FEBS Lett. 2013, 583, 3718–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jiang, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Li, P. Galectin-3 in metabolic disorders: Mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Trends Mol. Med. 2025, 31, 424–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, T.; Zhou, Z.; Xiao, Y. Emerging roles of Galectin-3 in diabetes and diabetes complications: A snapshot. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2022, 23, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.H.; Kim, S.J.; Kang, H.G.; Lee, H.W.; Kim, J.H.; Hwang, K.A.; Song, J.; Chun, K.H. Galectin-3 activates PPARgamma and supports white adipose tissue formation and high-fat diet-induced obesity. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejnovic, N.N.; Pantic, J.M.; Jovanovic, I.P.; Radosavljevic, G.D.; Milovanovic, M.Z.; Nikolic, I.G.; Zdravkovic, N.S.; Djukic, A.L.; Arsenijevic, N.N.; Lukic, M.L. Galectin-3 deficiency accelerates high-fat diet-induced obesity and amplifies inflammation in adipose tissue and pancreatic islets. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1932–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeftic, I.; Miletic-Kovacevic, M.; Jovicic, N.; Pantic, J.; Arsenijevic, N.; Lukic, M.; Pejnovic, N. Galectin-3 Deletion Enhances Visceral Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Dysregulates Glucose Metabolism in Mice on a High-Fat Diet. Exp. Appl. Biomed. Res. (EABR) 2016, 17, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Iacobini, C.; Menini, S.; Ricci, C.; Scipioni, A.; Sansoni, V.; Cordone, S.; Taurino, M.; Serino, M.; Marano, G.; Federici, M.; et al. Accelerated lipid-induced atherogenesis in galectin-3-deficient mice: Role of lipoxidation via receptor-mediated mechanisms. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009, 29, 831–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKinnon, A.C.; Liu, X.; Hadoke, P.W.; Miller, M.R.; Newby, D.E.; Sethi, T. Inhibition of galectin-3 reduces atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Glycobiology 2013, 23, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanninger, J.; Weigert, J.; Wiest, R.; Bauer, S.; Karrasch, T.; Farkas, S.; Scherer, M.N.; Walter, R.; Weiss, T.S.; Hellerbrand, C.; et al. Systemic and hepatic vein galectin-3 are increased in patients with alcoholic liver cirrhosis and negatively correlate with liver function. Cytokine 2011, 55, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, R.; Watanabe, M. Role of epithelial cells in the pathogenesis and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldars-Garcia, L.; Chaparro, M.; Gisbert, J.P. Systematic Review: The Gut Microbiome and Its Potential Clinical Application in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D. Human gut microbiome: Hopes, threats and promises. Gut 2018, 67, 1716–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederreiter, L.; Adolph, T.E.; Tilg, H. Food, microbiome and colorectal cancer. Dig. Liver Dis. 2018, 50, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, A.M.; Khadka, S.; Sato, F.; Omura, S.; Fujita, M.; Hsu, D.K.; Liu, F.T.; Tsunoda, I. Galectin-3 as a Therapeutic Target for NSAID-Induced Intestinal Ulcers. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 550366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechuga, S.; Ivanov, A.I. Disruption of the epithelial barrier during intestinal inflammation: Quest for new molecules and mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2017, 1864, 1183–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, S.; Nijhuis, A.; Kumagai, T.; Lindsay, J.; Silver, A. Defects in the adherens junction complex (E-cadherin/ beta-catenin) in inflammatory bowel disease. Cell Tissue Res. 2015, 360, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakai, D.; Miyake, M. Intestinal Membrane Function in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Pharmaceutics 2023, 16, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, L.; Hatzfeld, M.; Keil, R. Desmosomes as Signaling Hubs in the Regulation of Cell Behavior. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 745670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argueso, P.; Mauris, J.; Uchino, Y. Galectin-3 as a regulator of the epithelial junction: Implications to wound repair and cancer. Tissue Barriers 2015, 3, e1026505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Nelson, C.M. New insights into the regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tissue fibrosis. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 294, 171–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudino, V.; Bartolome-Casado, R.; Salas, A. Single-cell omics in inflammatory bowel disease: Recent insights and future clinical applications. Gut 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.X.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, H.Y.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, Y. Higenamine improves DSS-induced ulcerative colitis in mice through the Galectin-3/TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway. Tissue Cell 2023, 82, 102111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Merlin, D. Unveiling Colitis: A Journey through the Dextran Sodium Sulfate-induced Model. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2024, 30, 844–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Rankin, C.R.; Nava, P.; Sumagin, R.; Kamekura, R.; Stowell, S.R.; Feng, M.; Parkos, C.A.; Nusrat, A. Galectin-3 regulates desmoglein-2 and intestinal epithelial intercellular adhesion. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 10510–10517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscher, C.; Zheng, Y.Z.; Lakshminarayan, R.; Johannes, L.; Dennis, J.W.; Foster, L.J.; Nabi, I.R. Galectin-3 protein regulates mobility of N-cadherin and GM1 ganglioside at cell-cell junctions of mammary carcinoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 32940–32952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauris, J.; Woodward, A.M.; Cao, Z.; Panjwani, N.; Argueso, P. Molecular basis for MMP9 induction and disruption of epithelial cell-cell contacts by galectin-3. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 3141–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, M.; Feng, C.; Zong, G.; Wang, L.X.; Vasta, G.R. Galectin-3 disrupts tight junctions of airway epithelial cell monolayers by inducing expression and release of matrix metalloproteinases upon influenza A infection. Glycobiology 2025, 35, cwae093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowie, R.V.; Donatello, S.; Lyes, C.; Owens, M.B.; Babina, I.S.; Hudson, L.; Walsh, S.V.; O’Donoghue, D.P.; Amu, S.; Barry, S.P.; et al. Lipid rafts are disrupted in mildly inflamed intestinal microenvironments without overt disruption of the epithelial barrier. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 302, G781–G793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, D.K.; Chernyavsky, A.I.; Chen, H.Y.; Yu, L.; Grando, S.A.; Liu, F.T. Endogenous galectin-3 is localized in membrane lipid rafts and regulates migration of dendritic cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, J.; Boscher, C.; Nabi, I.R. Caveolin-1, galectin-3 and lipid raft domains in cancer cell signalling. Membr. Nanodomains 2015, 57, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delacour, D.; Cramm-Behrens, C.I.; Drobecq, H.; Le Bivic, A.; Naim, H.Y.; Jacob, R. Requirement for galectin-3 in apical protein sorting. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honig, E.; Ringer, K.; Dewes, J.; von Mach, T.; Kamm, N.; Kreitzer, G.; Jacob, R. Galectin-3 modulates the polarized surface delivery of beta1-integrin in epithelial cells. J. Cell Sci. 2018, 131, jcs213199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lee, D.W.; Jeong, E.K.; Lee, H.C.; Park, Y.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Chung, C.P.; Park, Y.J. Nipep-Ibd; a Synthetic Peptide Targeting Novel Molecule, Integrin Beta 1, to Restitute Intestinal Epithelial Cells for Inflammatory Bowel Disease (Ibd) Treatment. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, S64–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, R.; Invernizzi, P.; Mousa, H. Innate immune cells in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease—From microbial metabolites to immune modulation. Front. Gastroenterol. 2024, 3, 1452430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smythies, L.E.; Sellers, M.; Clements, R.H.; Mosteller-Barnum, M.; Meng, G.; Benjamin, W.H.; Orenstein, J.M.; Smith, P.D. Human intestinal macrophages display profound inflammatory anergy despite avid phagocytic and bacteriocidal activity. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelink, P.J.; Bloemendaal, F.M.; Li, B.; Westera, L.; Vogels, E.W.M.; van Roest, M.; Gloudemans, A.K.; van‘t Wout, A.B.; Korf, H.; Vermeire, S.; et al. Anti-TNF therapy in IBD exerts its therapeutic effect through macrophage IL-10 signalling. Gut 2020, 69, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keubler, L.M.; Buettner, M.; Hager, C.; Bleich, A. A Multihit Model: Colitis Lessons from the Interleukin-10-deficient Mouse. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 1967–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desalegn, G.; Pabst, O. Inflammation triggers immediate rather than progressive changes in monocyte differentiation in the small intestine. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivollier, A.; He, J.; Kole, A.; Valatas, V.; Kelsall, B.L. Inflammation switches the differentiation program of Ly6Chi monocytes from antiinflammatory macrophages to inflammatory dendritic cells in the colon. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Mayer, E.P.; Nachtigal, M. Galectin-3 expression in macrophages is signaled by Ras/MAP kinase pathway and up-regulated by modified lipoproteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1641, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippert, E.; Gunckel, M.; Brenmoehl, J.; Bataille, F.; Falk, W.; Scholmerich, J.; Obermeier, F.; Rogler, G. Regulation of galectin-3 function in mucosal fibroblasts: Potential role in mucosal inflammation. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2008, 152, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciacchitano, S.; Lavra, L.; Morgante, A.; Ulivieri, A.; Magi, F.; De Francesco, G.P.; Bellotti, C.; Salehi, L.B.; Ricci, A. Galectin-3: One Molecule for an Alphabet of Diseases, from A to Z. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotshenker, S. Galectin-3 (MAC-2) controls phagocytosis and macropinocytosis through intracellular and extracellular mechanisms. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2022, 16, 949079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaspyridonos, M.; McNeill, E.; de Bono, J.P.; Smith, A.; Burnand, K.G.; Channon, K.M.; Greaves, D.R. Galectin-3 is an amplifier of inflammation in atherosclerotic plaque progression through macrophage activation and monocyte chemoattraction. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwabara, I.; Liu, F.T. Galectin-3 promotes adhesion of human neutrophils to laminin. J. Immunol. 1996, 156, 3939–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elad-Sfadia, G.; Haklai, R.; Balan, E.; Kloog, Y. Galectin-3 augments K-Ras activation and triggers a Ras signal that attenuates ERK but not phosphoinositide 3-kinase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 34922–34930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takenaka, Y.; Fukumori, T.; Yoshii, T.; Oka, N.; Inohara, H.; Kim, H.R.; Bresalier, R.S.; Raz, A. Nuclear export of phosphorylated galectin-3 regulates its antiapoptotic activity in response to chemotherapeutic drugs. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 24, 4395–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, W.; Kidoya, H.; Yamakawa, D.; Naito, H.; Takakura, N. Galectin-3 accelerates M2 macrophage infiltration and angiogenesis in tumors. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 182, 1821–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sano, H.; Hsu, D.K.; Yu, L.; Apgar, J.R.; Kuwabara, I.; Yamanaka, T.; Hirashima, M.; Liu, F.T. Human galectin-3 is a novel chemoattractant for monocytes and macrophages. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 2156–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabelic, S.; Novak, R.; Goreta, S.S.; Dumic, J. Galectin-3 expression in response to LPS, immunomodulatory drugs and exogenously added galectin-3 in monocyte-like THP-1 cells. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Anim. 2012, 48, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, M.J.; Strasser, A.; Metcalf, D. Selective up-regulation of macrophage function in granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor transgenic mice. J. Immunol. 1991, 147, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Komai-Koma, M.; Gilchrist, D.S.; Hsu, D.K.; Liu, F.T.; Springall, T.; Xu, D. Galectin-3 is a negative regulator of lipopolysaccharide-mediated inflammation. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 2781–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuberi, R.I.; Hsu, D.K.; Kalayci, O.; Chen, H.Y.; Sheldon, H.K.; Yu, L.; Apgar, J.R.; Kawakami, T.; Lilly, C.M.; Liu, F.T. Critical role for galectin-3 in airway inflammation and bronchial hyperresponsiveness in a murine model of asthma. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 165, 2045–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Pozo, V.; Rojo, M.; Rubio, M.L.; Cortegano, I.; Cardaba, B.; Gallardo, S.; Ortega, M.; Civantos, E.; Lopez, E.; Martin-Mosquero, C.; et al. Gene therapy with galectin-3 inhibits bronchial obstruction and inflammation in antigen-challenged rats through interleukin-5 gene downregulation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamias, G.; Zampeli, E.; Domenech, E. Targeting neutrophils in inflammatory bowel disease: Revisiting the role of adsorptive granulocyte and monocyte apheresis. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 16, 721–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Cong, Y. Exploring Colitis through Dynamic T Cell Adoptive Transfer Models. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2023, 29, 1673–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuffrida, P.; Di Sabatino, A. Targeting T cells in inflammatory bowel disease. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 159, 105040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strober, W.; Fuss, I.J. Proinflammatory cytokines in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 1756–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powrie, F.; Leach, M.W.; Mauze, S.; Caddle, L.B.; Coffman, R.L. Phenotypically distinct subsets of CD4+ T cells induce or protect from chronic intestinal inflammation in C. B-17 scid mice. Int. Immunol. 1993, 5, 1461–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asseman, C.; Mauze, S.; Leach, M.W.; Coffman, R.L.; Powrie, F. An essential role for interleukin 10 in the function of regulatory T cells that inhibit intestinal inflammation. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 190, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedke, T.; Stumme, F.; Tomczak, M.; Steglich, B.; Jia, R.; Bohmann, S.; Wittek, A.; Kempski, J.; Goke, E.; Bottcher, M.; et al. Protective function of sclerosing cholangitis on IBD. Gut 2024, 73, 1292–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilson, R.C.; Gunasinghe, S.D.; Johannes, L.; Gaus, K. Galectin-3 modulation of T-cell activation: Mechanisms of membrane remodelling. Prog. Lipid Res. 2019, 76, 101010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, T.; Nguyen, M.K.L.; Buechler, C. Cholesterol and COVID-19-therapeutic opportunities at the host/virus interface during cell entry. Life Sci. Alliance 2024, 7, e202302453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demotte, N.; Bigirimana, R.; Wieers, G.; Stroobant, V.; Squifflet, J.L.; Carrasco, J.; Thielemans, K.; Baurain, J.F.; Van Der Smissen, P.; Courtoy, P.J.; et al. A short treatment with galactomannan GM-CT-01 corrects the functions of freshly isolated human tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocklenburg, F.; Moharregh-Khiabani, D.; Geffers, R.; Janke, V.; Pfoertner, S.; Garritsen, H.; Groebe, L.; Klempnauer, J.; Dittmar, K.E.; Weiss, S.; et al. UBD, a downstream element of FOXP3, allows the identification of LGALS3, a new marker of human regulatory T cells. Lab. Investig. 2006, 86, 724–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroca-Crevillen, A.; Vicanolo, T.; Ovadia, S.; Hidalgo, A. Neutrophils in Physiology and Pathology. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2024, 19, 227–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wera, O.; Lancellotti, P.; Oury, C. The Dual Role of Neutrophils in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yui, S.; Nakatani, Y.; Mikami, M. Calprotectin (S100A8/S100A9), an inflammatory protein complex from neutrophils with a broad apoptosis-inducing activity. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 26, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jukic, A.; Bakiri, L.; Wagner, E.F.; Tilg, H.; Adolph, T.E. Calprotectin: From biomarker to biological function. Gut 2021, 70, 1978–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokama, A.; Mizoguchi, E.; Mizoguchi, A. Roles of galectins in inflammatory bowel disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 5133–5137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.I.; Choi, M.E. TGF-beta-activated kinase-1: New insights into the mechanism of TGF-beta signaling and kidney disease. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2012, 31, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simovic Markovic, B.; Nikolic, A.; Gazdic, M.; Bojic, S.; Vucicevic, L.; Kosic, M.; Mitrovic, S.; Milosavljevic, M.; Besra, G.; Trajkovic, V.; et al. Galectin-3 Plays an Important Pro-inflammatory Role in the Induction Phase of Acute Colitis by Promoting Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasome and Production of IL-1beta in Macrophages. J. Crohns Colitis 2016, 10, 593–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Wang, H.; Zheng, Z.; Huang, X.; Yang, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Y. Pectic polysaccharide from Smilax china L. ameliorated ulcerative colitis by inhibiting the galectin-3/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 277, 118864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volarevic, V.; Zdravkovic, N.; Harrell, C.R.; Arsenijevic, N.; Fellabaum, C.; Djonov, V.; Lukic, M.L.; Simovic Markovic, B. Galectin-3 Regulates Indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase-Dependent Cross-Talk between Colon-Infiltrating Dendritic Cells and T Regulatory Cells and May Represent a Valuable Biomarker for Monitoring the Progression of Ulcerative Colitis. Cells 2019, 8, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.F.; Wu, C.S.; Chen, Y.L.; Liao, H.J.; Chyuan, I.T.; Hsu, P.N. Galectin-3 suppresses mucosal inflammation and reduces disease severity in experimental colitis. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 94, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptiste, T.A.; James, A.; Saria, M.; Ochieng, J. Mechano-transduction mediated secretion and uptake of galectin-3 in breast carcinoma cells: Implications in the extracellular functions of the lectin. Exp. Cell Res. 2007, 313, 652–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippert, E.; Stieber-Gunckel, M.; Dunger, N.; Falk, W.; Obermeier, F.; Kunst, C. Galectin-3 Modulates Experimental Colitis. Digestion 2015, 92, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippert, E.; Falk, W.; Bataille, F.; Kaehne, T.; Naumann, M.; Goeke, M.; Herfarth, H.; Schoelmerich, J.; Rogler, G. Soluble galectin-3 is a strong, colonic epithelial-cell-derived, lamina propria fibroblast-stimulating factor. Gut 2007, 56, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez-Huergo, S.P.; Hockl, P.F.; Stupirski, J.C.; Maller, S.M.; Morosi, L.G.; Pinto, N.A.; Beron, A.M.; Musuruana, J.L.; Nasswetter, G.G.; Cavallasca, J.A.; et al. Clinical Relevance of Galectin-1 and Galectin-3 in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: Differential Regulation and Correlation with Disease Activity. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frol’ova, L.; Smetana, K., Jr.; Borovska, D.; Kitanovicova, A.; Klimesova, K.; Janatkova, I.; Malickova, K.; Lukas, M.; Drastich, P.; Benes, Z.; et al. Detection of galectin-3 in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases: New serum marker of active forms of IBD? Inflamm. Res. 2009, 58, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.B.; Dodd, S.; Yu, L.G.; Subramanian, S. Serum galectins as potential biomarkers of inflammatory bowel diseases. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cibor, D.; Szczeklik, K.; Brzozowski, B.; Mach, T.; Owczarek, D. Serum galectin 3, galectin 9 and galectin 3-binding proteins in patients with active and inactive inflammatory bowel disease. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 70, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajraktari, G.; Elger, T.; Huss, M.; Loibl, J.; Albert, A.; Kandulski, A.; Muller, M.; Tews, H.C.; Buechler, C. Serum Galectin-3 as a Non-Invasive Marker for Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tews, H.C.; Elger, T.; Grewal, T.; Weidlich, S.; Vitali, F.; Buechler, C. Fecal and Urinary Adipokines as Disease Biomarkers. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijers, W.C.; Schroten, N.F.; Ruifrok, W.P.; Assa, S.; Dokter, M.M.; Damman, K.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Van Gilst, W.H.; Sillje, H.H.; De Boer, R.A. Urinary and plasma galectin-3 in heart failure—Insights in renal handling. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, P4243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.M.; Tsai, M.T.; Chen, H.Y.; Li, F.A.; Lee, K.H.; Tseng, W.C.; Chang, F.P.; Lin, Y.P.; Yang, R.B.; Tarng, D.C. Urinary Galectin-3 as a Novel Biomarker for the Prediction of Renal Fibrosis and Kidney Disease Progression. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, T.; Rao, V.; Chunara, Z.; Mahoney, D.; Jackson, K.; Hodson, D.; Tarleton, C.; Thomas, D.; Chen, M.; Jacoby, D.; et al. Urine Galectin-3 Levels Identify High Risk Renal Dysfunction in Patients with Heart Failure. J. Card. Fail. 2017, 23, S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, K.; Vasudevamurthy, R.; Venkateshaiah, S.U.; Thomas, A.; Vishweshwara, A.; Dharmesh, S.M. Galectin-3 in urine of cancer patients: Stage and tissue specificity. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 135, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambruzs, J.M.; Larsen, C.P. Renal Manifestations of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 44, 699–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dincer, M.T.; Dincer, Z.T.; Bakkaloglu, O.K.; Yalin, S.F.; Trabulus, S.; Celik, A.F.; Seyahi, N.; Altiparmak, M.R. Renal Manifestations in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Cohort Study During the Biologic Era. Med. Sci. Monit. 2022, 28, e936497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminska, J.; Dymicka-Piekarska, V.; Tomaszewska, J.; Matowicka-Karna, J.; Koper-Lenkiewicz, O.M. Diagnostic utility of protein to creatinine ratio (P/C ratio) in spot urine sample within routine clinical practice. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2020, 57, 345–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, M.; Molne, J.; Leffler, H.; Borjesson, L.; Breimer, M.E. Immunohistochemical Studies on Galectin Expression in Colectomised Patients with Ulcerative Colitis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 5989128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, S.; Rai, V.; Rubin, D.T. Pouchitis in inflammatory bowel disease: A review of diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment. Intest. Res. 2021, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazowski, E.; Dotan, I.; Tulchinsky, H.; Filip, I.; Eisenthal, A. Galectin-3 expression in pouchitis in patients with ulcerative colitis who underwent ileal pouch-anal anastomosis (IPAA). Pathol. Res. Pract. 2009, 205, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen-Jarolim, E.; Gscheidlinger, R.; Oberhuber, G.; Neuchrist, C.; Lucas, T.; Bises, G.; Radauer, C.; Willheim, M.; Scheiner, O.; Liu, F.T.; et al. The constitutive expression of galectin-3 is downregulated in the intestinal epithelia of Crohn’s disease patients, and tumour necrosis factor alpha decreases the level of galectin-3-specific mRNA in HCT-8 cells. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2002, 14, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, S.; Schaffer, T.; Flogerzi, B.; Fleetwood, A.; Weimann, R.; Schoepfer, A.M.; Seibold, F. Galectin-3 modulates T cell activity and is reduced in the inflamed intestinal epithelium in IBD. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2006, 12, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butscheid, M.; Hauptvogel, P.; Fritz, P.; Klotz, U.; Alscher, D.M. Hepatic expression of galectin-3 and receptor for advanced glycation end products in patients with liver disease. J. Clin. Pathol. 2007, 60, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimonishi, T.; Miyazaki, K.; Kono, N.; Sabit, H.; Tuneyama, K.; Harada, K.; Hirabayashi, J.; Kasai, K.; Nakanuma, Y. Expression of endogenous galectin-1 and galectin-3 in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2001, 32, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudowska, M.; Gruszewska, E.; Cylwik, B.; Panasiuk, A.; Rogalska, M.; Flisiak, R.; Szmitkowski, M.; Chrostek, L. Galectin-3 Concentration in Liver Diseases. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2015, 45, 669–673. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, D.K.; Dowling, C.A.; Jeng, K.C.; Chen, J.T.; Yang, R.Y.; Liu, F.T. Galectin-3 expression is induced in cirrhotic liver and hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 1999, 81, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, N.C.; Mackinnon, A.C.; Farnworth, S.L.; Poirier, F.; Russo, F.P.; Iredale, J.P.; Haslett, C.; Simpson, K.J.; Sethi, T. Galectin-3 regulates myofibroblast activation and hepatic fibrosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 5060–5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes-Alvarez, E.; Limon-de la Rosa, N.; Vilatoba, M.; Perez-Monter, C.; Hurtado-Gomez, S.; Martinez-Cabrera, C.; Argemi, J.; Alatorre-Arenas, E.; Yarza-Regalado, S.; Tejeda-Dominguez, F.; et al. Galectin-3 is overexpressed in advanced cirrhosis and predicts post-liver transplant infectious complications. Liver Int. 2022, 42, 2260–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacigalupo, M.L.; Manzi, M.; Rabinovich, G.A.; Troncoso, M.F. Hierarchical and selective roles of galectins in hepatocarcinogenesis, liver fibrosis and inflammation of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 8831–8849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsenijevic, A.; Milovanovic, M.; Milovanovic, J.; Stojanovic, B.; Zdravkovic, N.; Leung, P.S.; Liu, F.T.; Gershwin, M.E.; Lukic, M.L. Deletion of Galectin-3 Enhances Xenobiotic Induced Murine Primary Biliary Cholangitis by Facilitating Apoptosis of BECs and Release of Autoantigens. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsenijevic, A.; Milovanovic, J.; Stojanovic, B.; Djordjevic, D.; Stanojevic, I.; Jankovic, N.; Vojvodic, D.; Arsenijevic, N.; Lukic, M.L.; Milovanovic, M. Gal-3 Deficiency Suppresses Novosphyngobium aromaticivorans Inflammasome Activation and IL-17 Driven Autoimmune Cholangitis in Mice. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeftic, I.; Jovicic, N.; Pantic, J.; Arsenijevic, N.; Lukic, M.L.; Pejnovic, N. Galectin-3 Ablation Enhances Liver Steatosis, but Attenuates Inflammation and IL-33-Dependent Fibrosis in Obesogenic Mouse Model of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Mol. Med. 2015, 21, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Yang, G.; Chen, H.Y.; Hsu, D.K.; Tomilov, A.; Olson, K.A.; Dehnad, A.; Fish, S.R.; Cortopassi, G.; Zhao, B.; et al. Galectin-3 regulates inflammasome activation in cholestatic liver injury. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 4202–4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomir, A.C.; Sun, R.; Choi, H.; Laskin, J.D.; Laskin, D.L. Role of galectin-3 in classical and alternative macrophage activation in the liver following acetaminophen intoxication. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 5934–5941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKinnon, A.C.; Farnworth, S.L.; Hodkinson, P.S.; Henderson, N.C.; Atkinson, K.M.; Leffler, H.; Nilsson, U.J.; Haslett, C.; Forbes, S.J.; Sethi, T. Regulation of alternative macrophage activation by galectin-3. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 2650–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.H.; Fritzler, M.J.; Swain, M.G. A Review on Biomarkers for the Evaluation of Autoimmune Cholestatic Liver Diseases and Their Overlap Syndromes. Front. Mol. Med. 2022, 2, 914505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersten, R.; Trampert, D.C.; Hubers, L.M.; Tolenaars, D.; Vos, H.R.; van de Graaf, S.F.J.; Beuers, U. Galectin-3 and prohibitin 1 are autoantigens in IgG4-related cholangitis without clear-cut protective effects against toxic bile acids. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1251134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanovic, M.; Simovic Markovic, B.; Gajovic, N.; Jurisevic, M.; Djukic, A.; Jovanovic, I.; Arsenijevic, N.; Lukic, A.; Zdravkovic, N. Metabolic syndrome attenuates ulcerative colitis: Correlation with interleukin-10 and galectin-3 expression. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 6465–6482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardizzone, S.; Cassinotti, A.; Manes, G.; Porro, G.B. Immunomodulators for all patients with inflammatory bowel disease? Therap Adv. Gastroenterol. 2010, 3, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabelic, S.; Supraha, S.; Dumic, J. Galectin-3 in macrophage-like cells exposed to immunomodulatory drugs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1760, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, J.C.; Desai, A.A.; Kochhar, G.S.; Crosby, S.K.; Kinnucan, J.A.; Picco, M.F.; Hashash, J.G.; Farraye, F.A. Metformin Is Associated with Improved Inflammatory Bowel Disease Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Propensity-Matched Cohort Study. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2024, 31, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rena, G.; Hardie, D.G.; Pearson, E.R. The mechanisms of action of metformin. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1577–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villumsen, M.; Schelde, A.B.; Jimenez-Solem, E.; Jess, T.; Allin, K.H. GLP-1 based therapies and disease course of inflammatory bowel disease. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 37, 100979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchaava, K.; Gegeshidze, N.; Shavdia, M.; Ninashvili, N.; Shervashidze, T. Change in Galectin-3 (Marker of Fibrosis) During Empagliflozin Therapy. Am. Heart J. 2022, 254, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knopf, H.C.; Busch, M.A.; Du, Y.; Truthmann, J.; Schienkiewitz, A.; Scheidt-Nave, C. Changes in the prevalence of statin use in Germany—Findings from national health interview and examination surveys 1997–1999 and 2008–2011. Z Evidenz Fortbild. Qual. Gesundhwes. 2017, 122, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuncez, A.; Altunkeser, B.B.; Ozturk, B.; Ates, M.S.; Tezcan, H.; Aydogan, C.; Kirik, E.C.; Yalcin, U.; Aygul, N.; Demir, K.; et al. Comparative effects of atorvastatin 80 mg and rosuvastatin 40 mg on the levels of serum endocan, chemerin, and galectin-3 in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2019, 22, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Crohn’s Disease | Ulcerative Colitis | |
|---|---|---|
| Serum Galectin-3 | Increased | Increased |
| Serum Galectin-3 | Reduced | |
| Serum Galectin-3 | Increased | Increased |
| Serum Galectin-3 | Normal | Normal |
| Serum Galectin-3 | Normal | Normal |
| Colonic tissue | Reduced | Normal |
| Intestinal macrophages | Reduced | Normal |
| Colonic tissue | Trend to lower levels | |
| Intestinal epithelial cells | Reduced | |
| Colonic tissue | Increased | |
| Endoscopic biopsies | Reduced in IBD | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grewal, T.; Tews, H.C.; Buechler, C. Galectin-3—Insights from Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6101. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136101
Grewal T, Tews HC, Buechler C. Galectin-3—Insights from Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6101. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136101
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrewal, Thomas, Hauke Christian Tews, and Christa Buechler. 2025. "Galectin-3—Insights from Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6101. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136101
APA StyleGrewal, T., Tews, H. C., & Buechler, C. (2025). Galectin-3—Insights from Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6101. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136101








