The Role of GPX Enzymes, Lipid Profiles, and Iron Accumulation in Necrotizing Enterocolitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
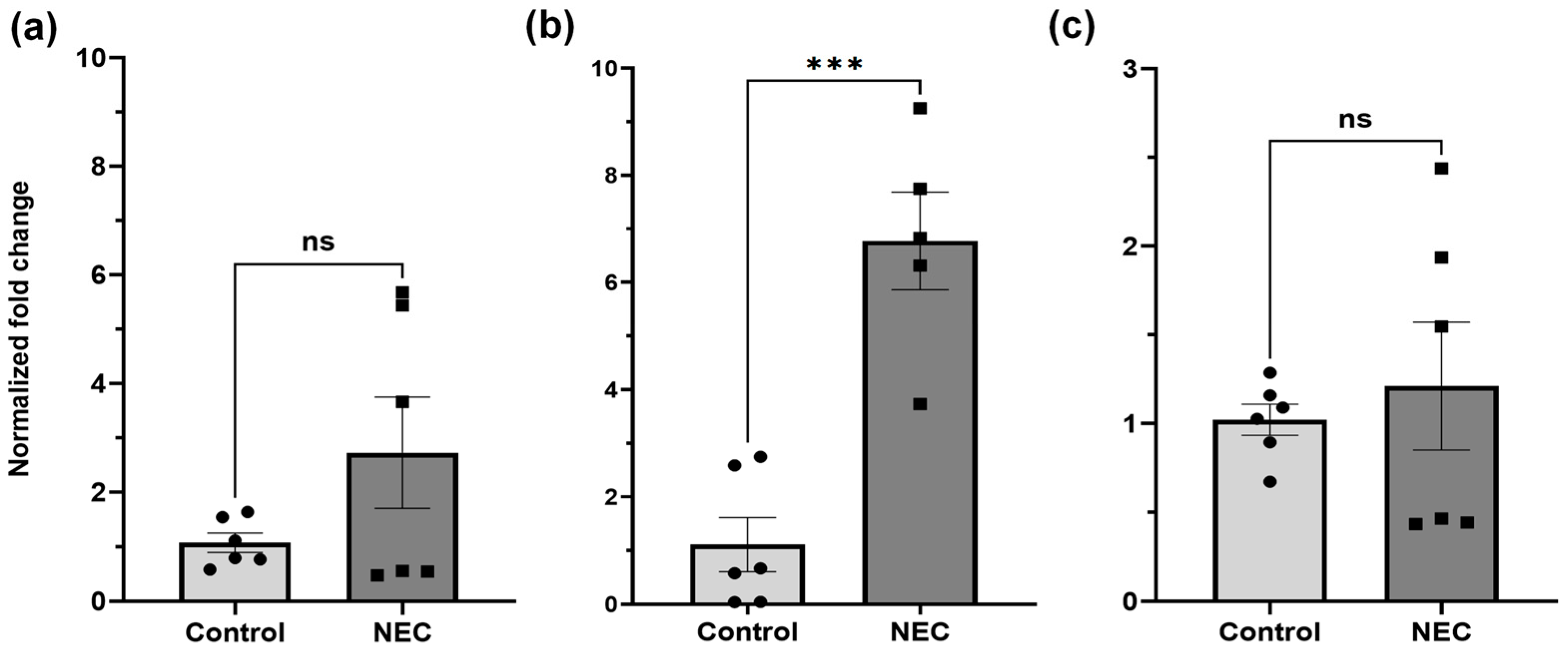
2.1. GPX1, 2, and GSS DNA Expression
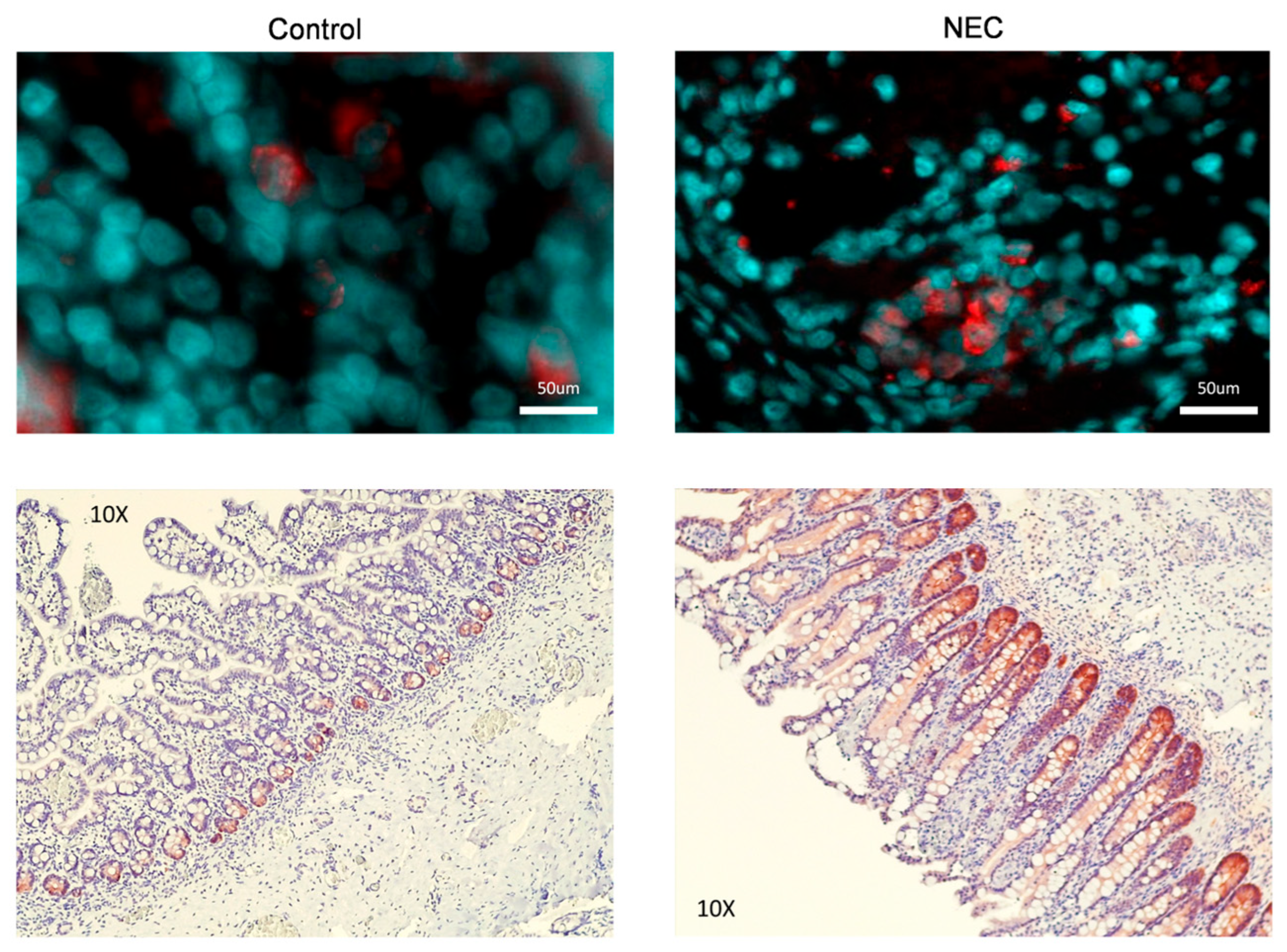
2.2. GPX2 Immunofluorescence and Immunohistochemistry
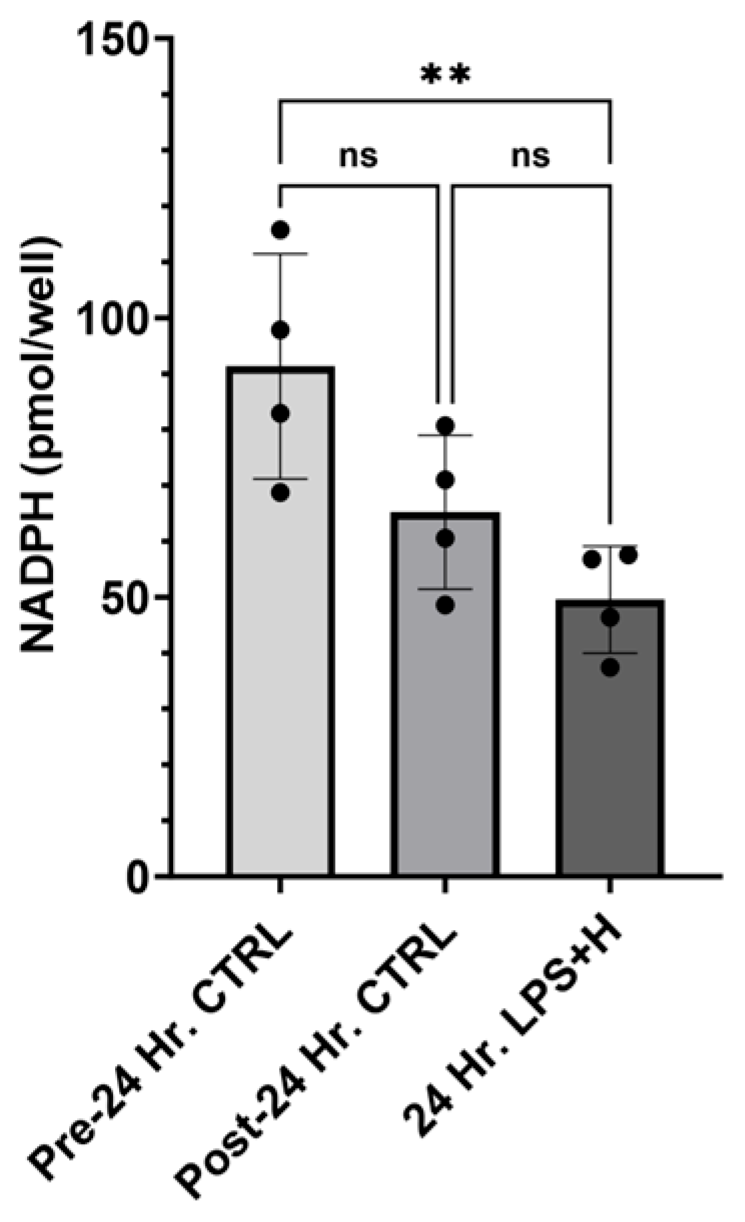
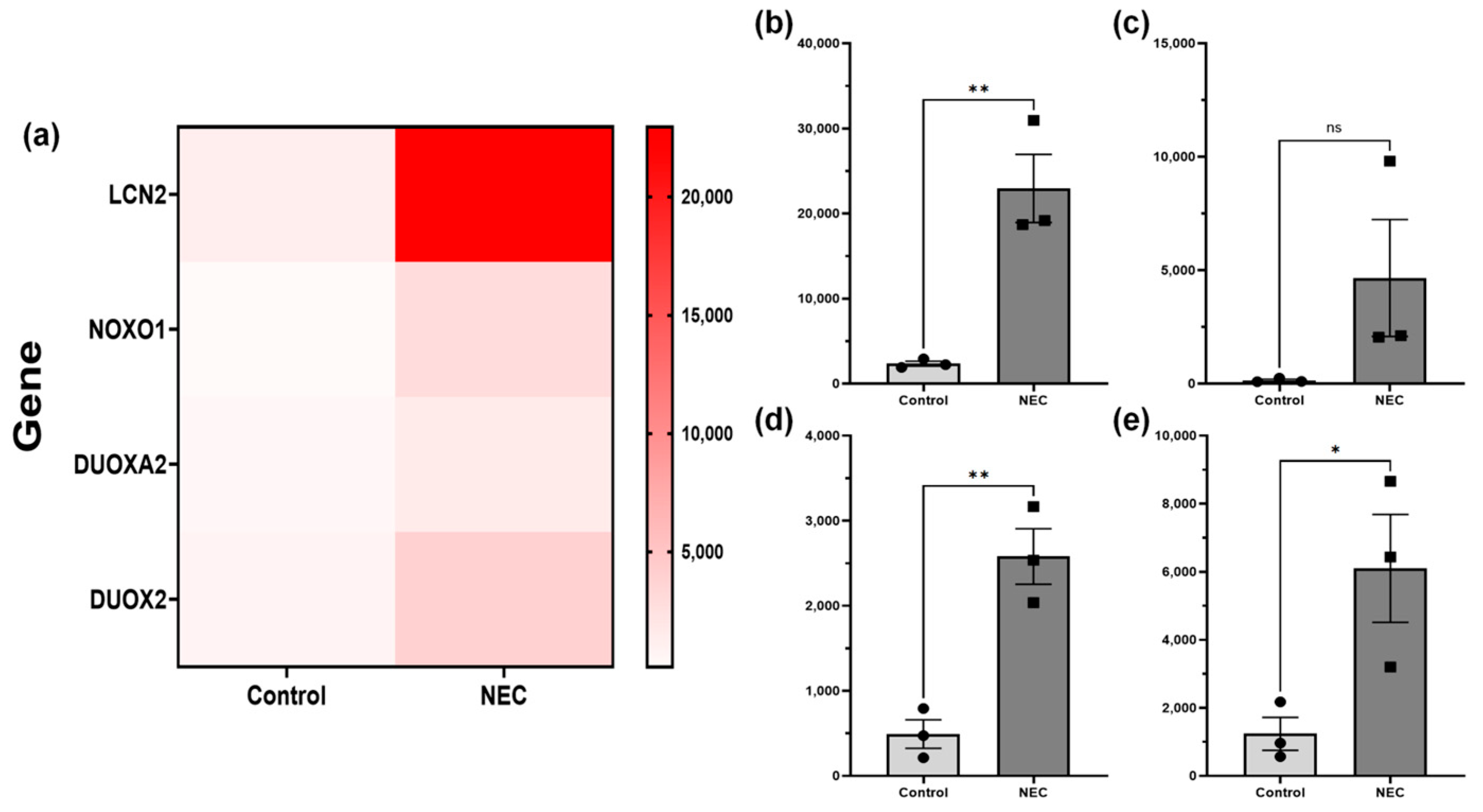
2.3. NADPH Concentration, and ReDox Gene RNA-Sequencing
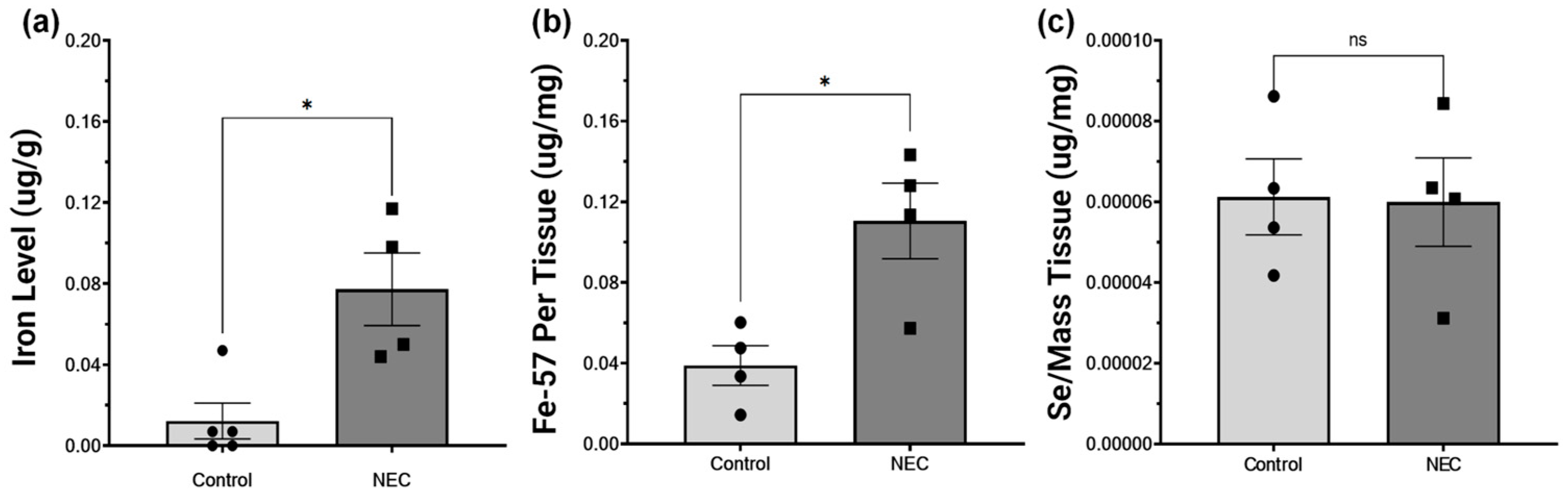
2.4. NEC Increases Intestinal Iron Concentration and Is Not Deficient in Selenium
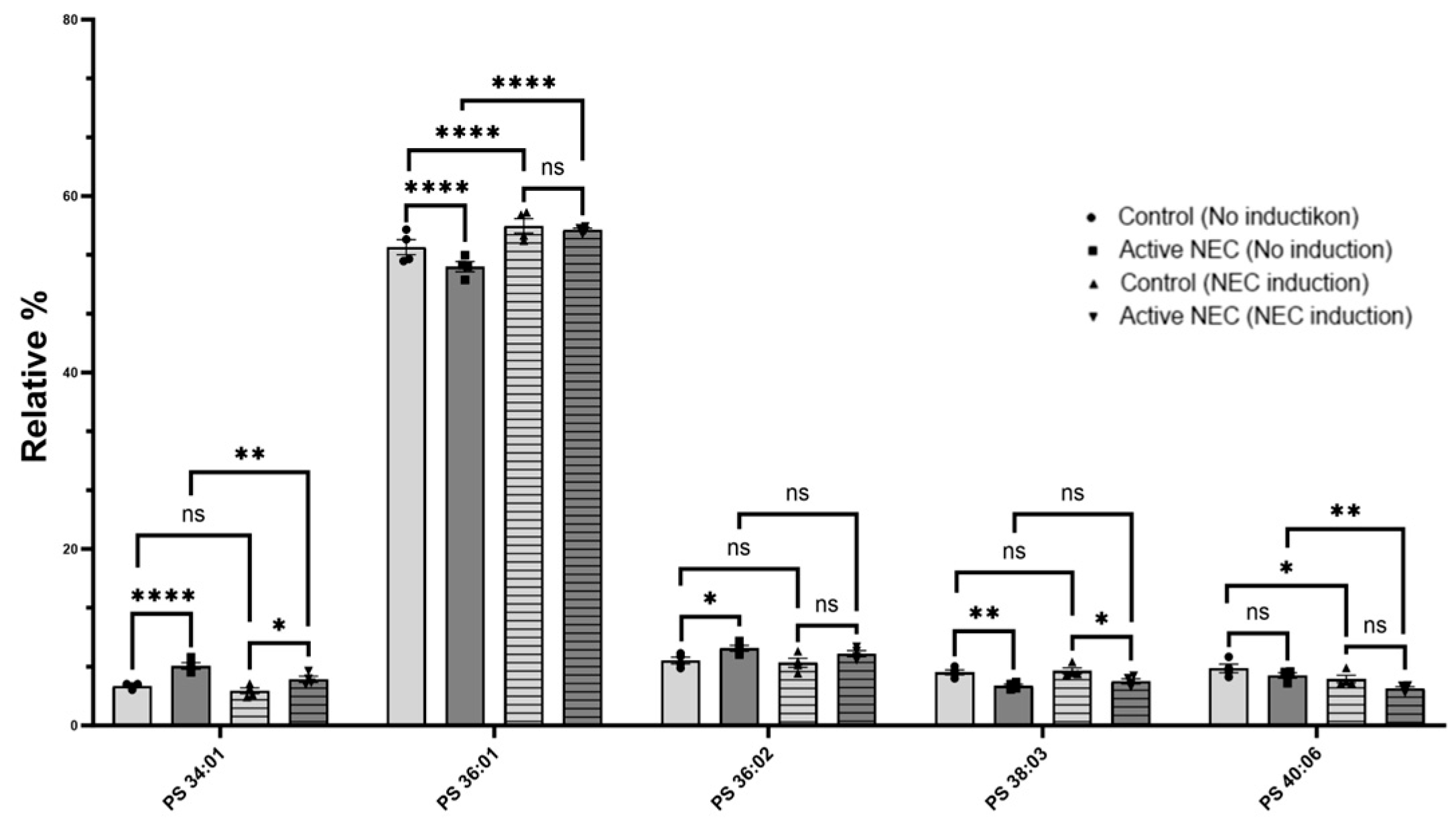
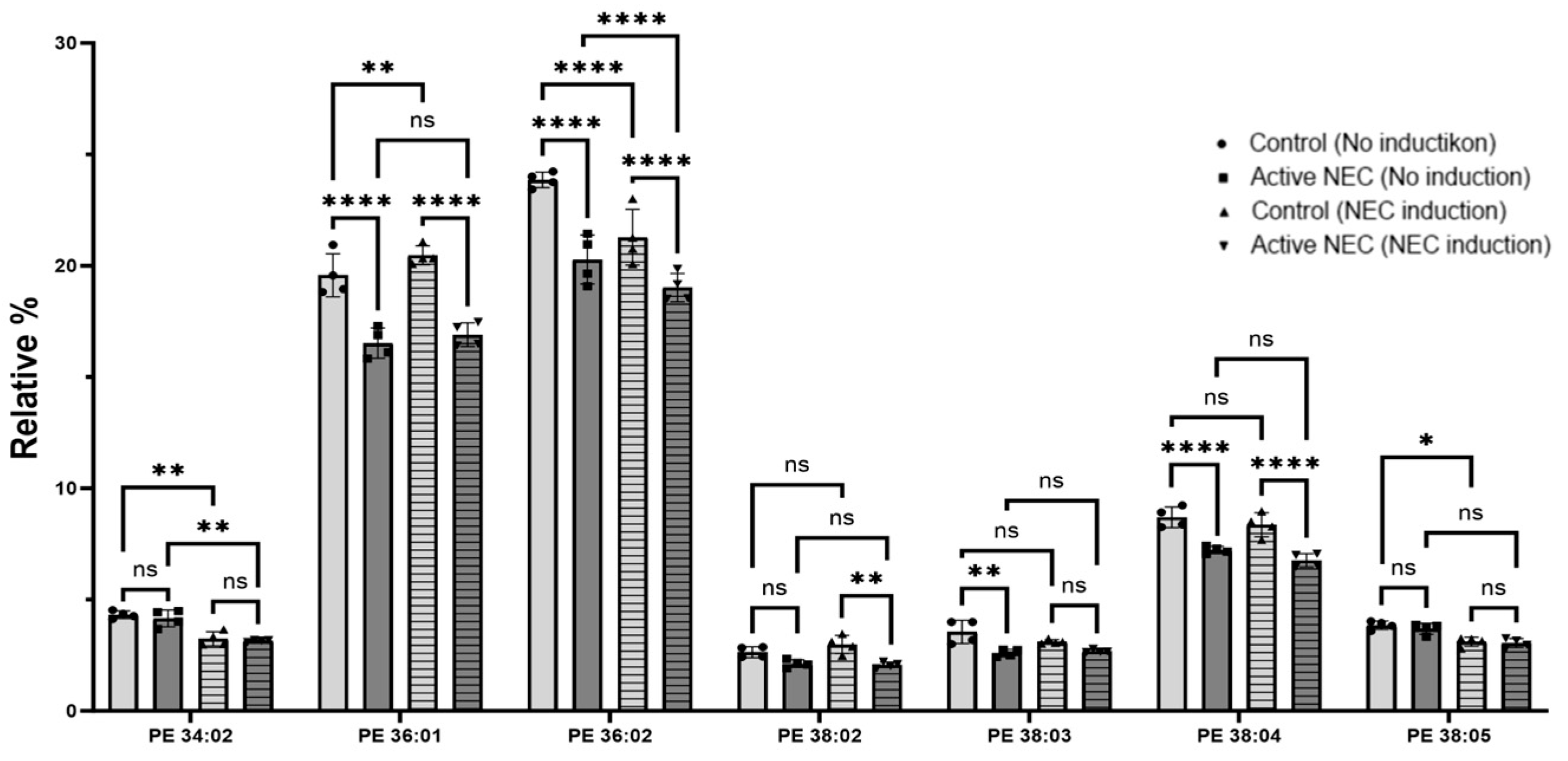
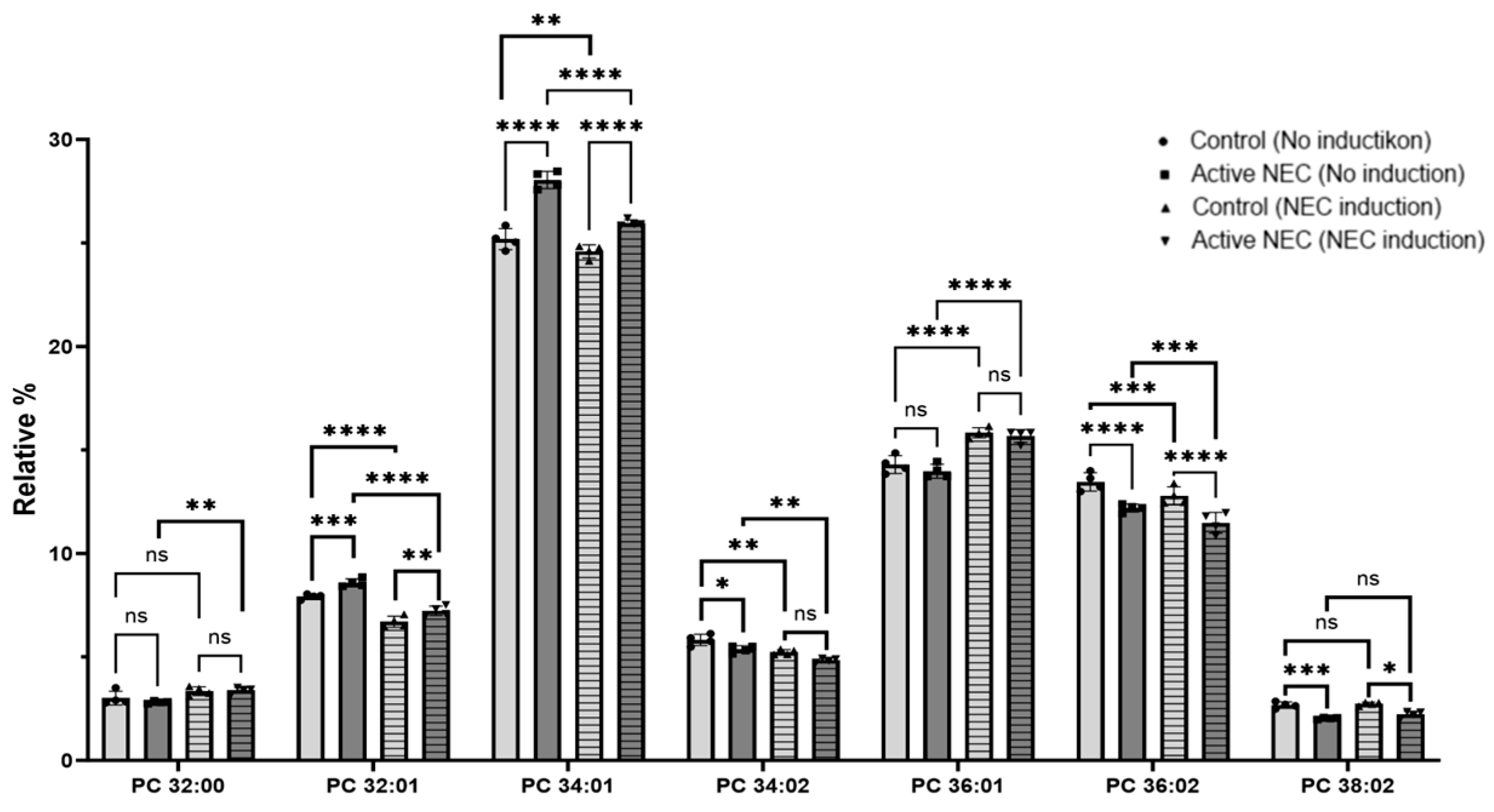
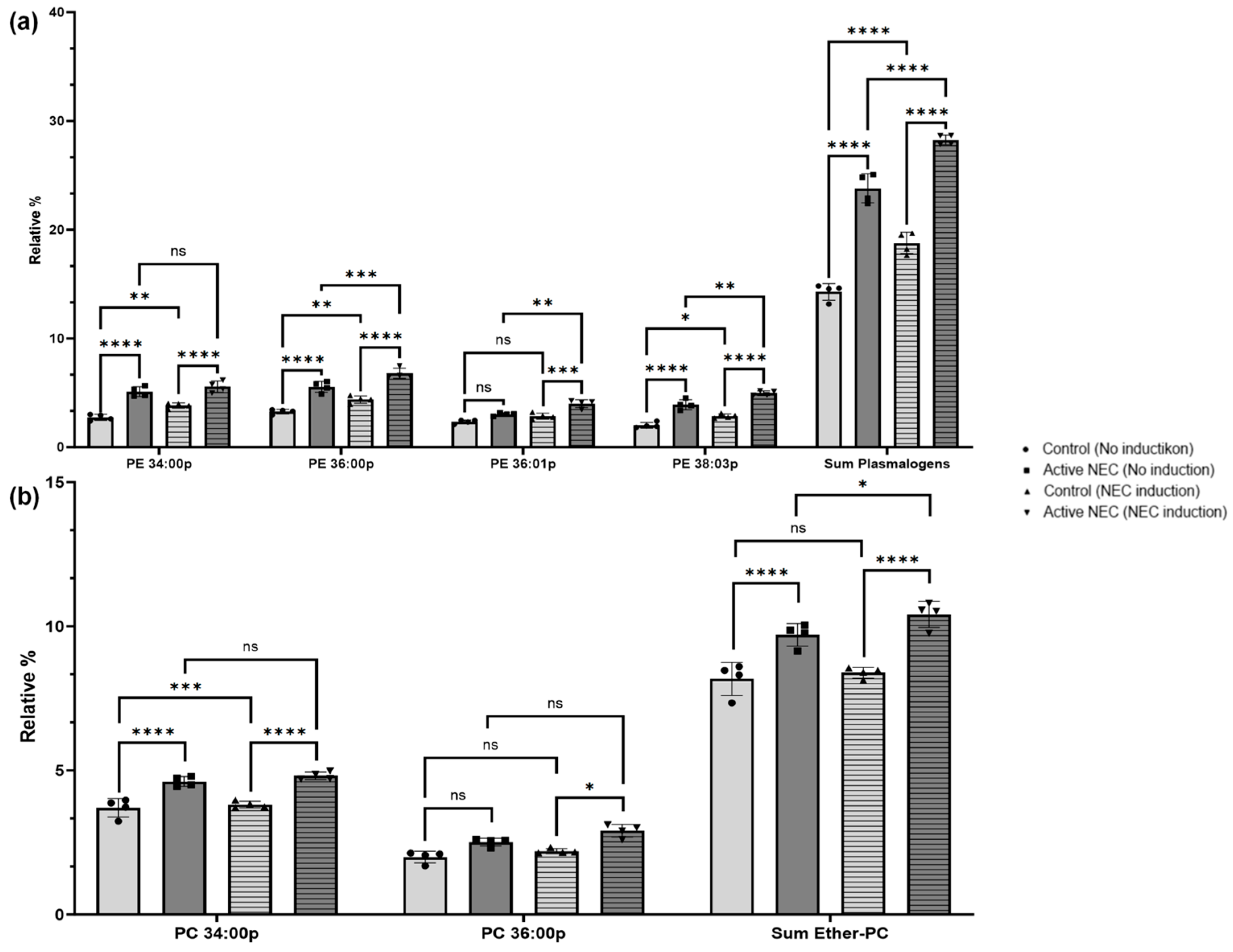
2.5. Lipids Profiling
2.6. Profile of Plasmalogen-Containing Lipids
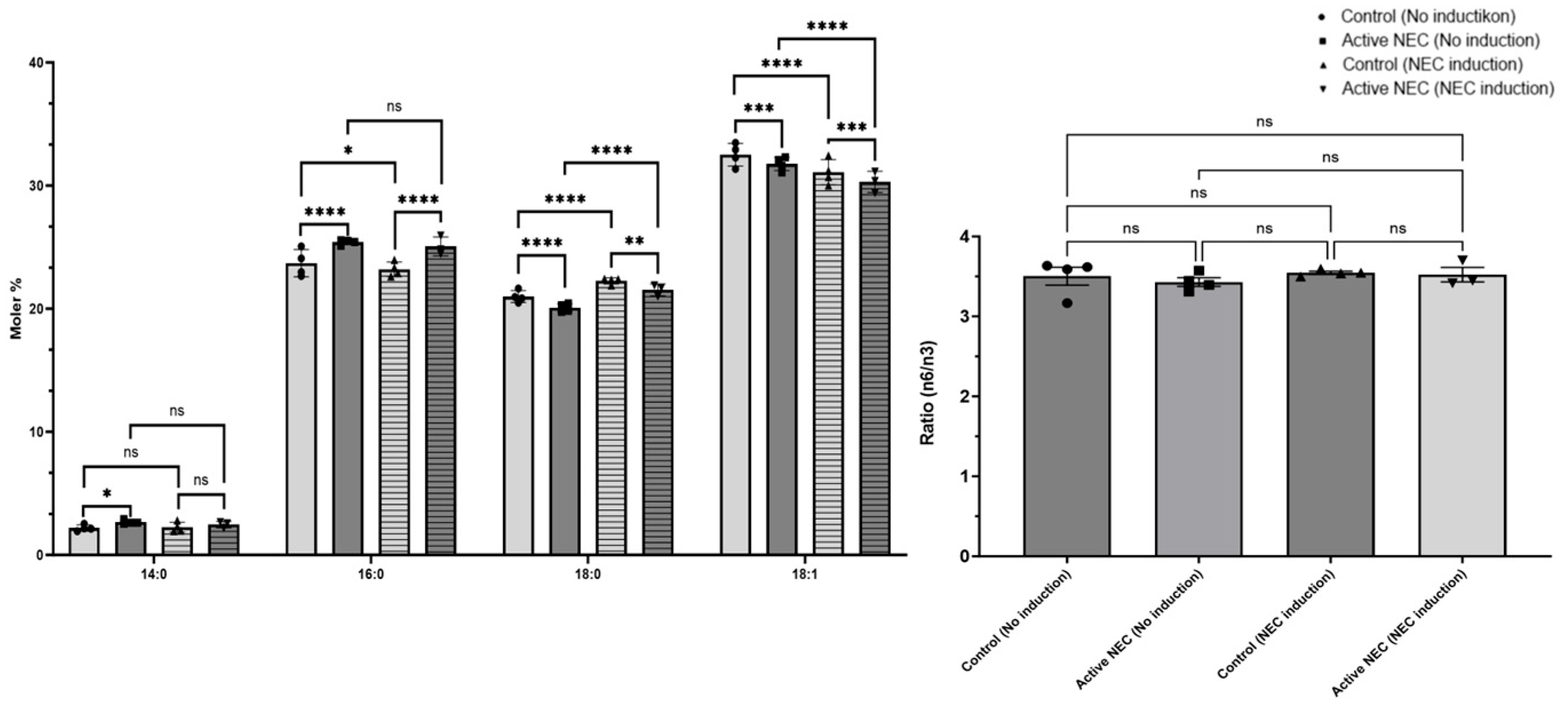
2.7. Changes in Fatty Acid Composition
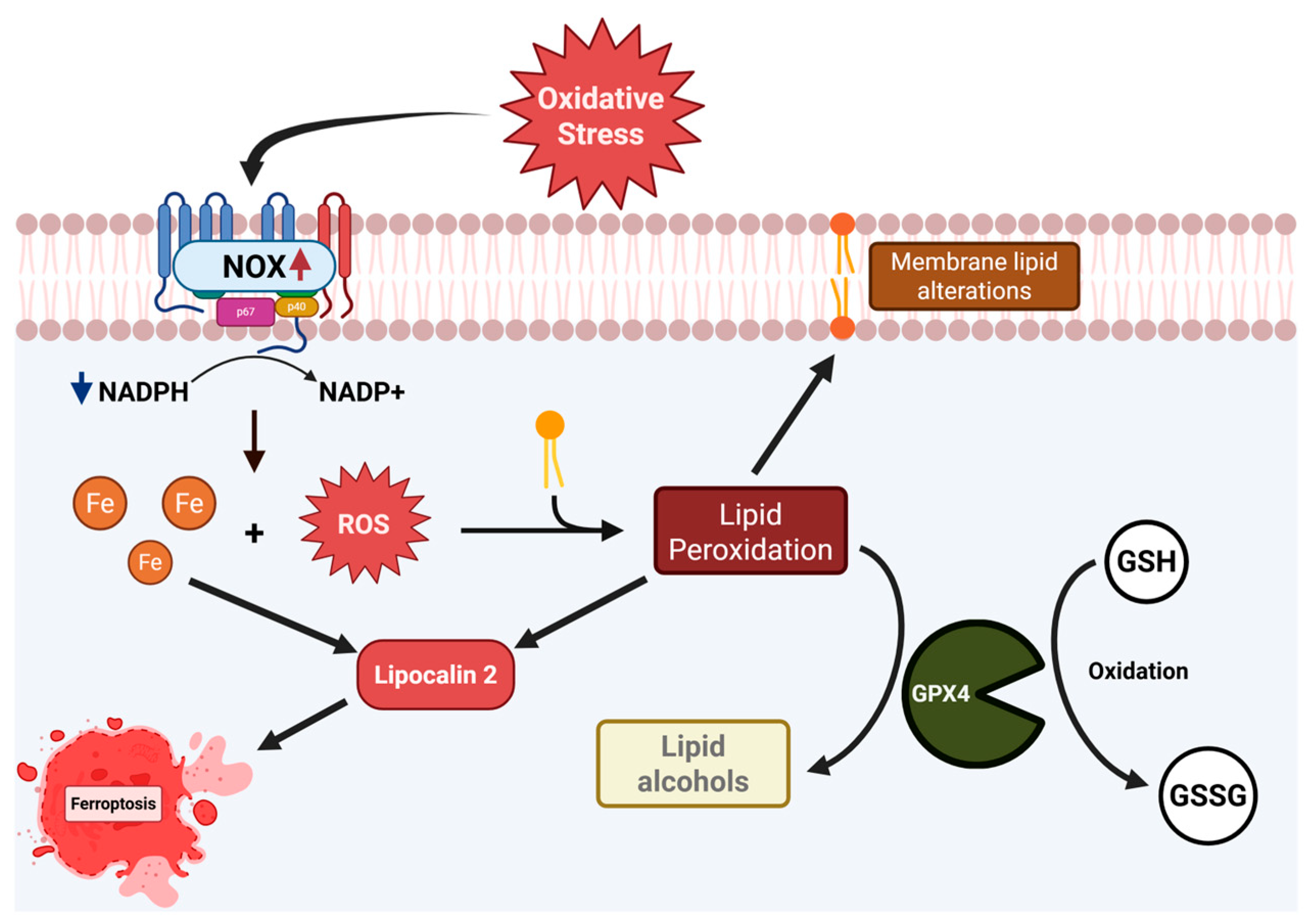
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Human Intestinal Sample Collection
4.2. Human Neonatal Enteroid Cultures
4.3. Enteroid NEC Induction
4.4. RNA Isolation, Reverse Transcription, and RTqPCR
4.5. NADPH Assay
4.6. Illumina RNA-Sequencing Methodology
4.7. Immunofluorescence
4.8. Immunohistochemistry
4.9. Bathophenathroline Colorimetric Assay
- : Absorbance of test sample
- : Absorbance of acid blank
- : Absorbance of standard
- : Iron concentration of working iron solution (µg Fe/mL)
- : Weight of dry tissue (g)
- : Sample volume
- : Final volume of the acid mixture after overnight incubation
- : Volume of iron standard
- : Final reaction volume
4.10. Iron Quantification by ICP-MS
4.11. Lipidomics and Fatty Acid Analyses
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NEC | Necrotizing enterocolitis |
| NICU | Neonatal intensive care unit |
| VLBW | Very low birth weight |
| ROP | Retinopathy of prematurity |
| BPD | Bronchopulmonary dysplasia |
| PVL | Periventricular leukomalacia |
| OS | Oxidative stress |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| PUFA | Polyunsaturated fatty acid |
| GPX# | Glutathione peroxidase # |
| 4-HNE | 4-hdroxy-2-nonenal |
| 4-HHE | 4-hydroxy-2-hexenal |
| ICP-MS | Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry |
| LCN2 | Lipocalin 2 |
| DUOX2 | Dual Oxidase 2 |
| DUOXA2 | Dual Oxidase maturation factor 2 |
| NOXO1 | NADPH oxidase organizer 1 |
| FA | Fatty acids |
| AA | Arachidonic acid |
| DHA | Docosahexaenoic acid |
| IF | Immunofluorescent |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| PC | Phosphatidylcholine |
| PS | Phosphatidylserine |
| PE | Phosphatidylethanolamine |
| IBD | Inflammatory bowel disease |
References
- Zozaya, C.; García González, I.; Avila-Alvarez, A.; Oikonomopoulou, N.; Sánchez Tamayo, T.; Salguero, E.; Saenz de Pipaón, M.; García-Muñoz Rodrigo, F.; Couce, M.L. Incidence, Treatment, and Outcome Trends of Necrotizing Enterocolitis in Preterm Infants: A Multicenter Cohort Study. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, I.H.; Hall, N.J. Contemporary Outcomes for Infants with Necrotizing Enterocolitis—A Systematic Review. J. Pediatr. 2020, 220, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, K.B.; Calkins, C.L.; Golubkova, A.; Leiva, T.; Schlegel, C.; Hunter, C.J. Despite Recovery from Necrotizing Enterocolitis Infants Retain a Hyperinflammatory Response to Injury. J. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 17, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinci, M.; Piccolo, C.L.; Pallottino, A.A.; Esposito, F.; Zeccolini, M.; Miele, V. Necrotizing Enterocolitis. In Imaging Non-Traumatic Abdominal Emergencies in Pediatric Patients; Miele, V., Trinci, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 53–72. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, K.B.; Hunter, C.J. The leaky gut: A narrative review on the role of epithelial cell permeability in necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatr. Med. 2023, 7, 22–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuffrè, M.; Rizzo, M.; Scaturro, G.; Pitruzzella, A.; Gammazza, A.M.; Cappello, F.; Corsello, G.; Li Volti, G. Oxidative stress markers at birth: Analyses of a neonatal population. Acta Histochem. 2015, 117, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceti, A.; Beghetti, I.; Martini, S.; Faldella, G.; Corvaglia, L. Oxidative Stress and Necrotizing Enterocolitis: Pathogenetic Mechanisms, Opportunities for Intervention, and Role of Human Milk. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 7397659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, L.; Ilene Sosenko, R.S. Development of lung antioxidant enzyme system in late gestation: Possible implications for the prematurely born infant. J. Pediatr. 1987, 110, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yan, Y.; Niu, F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Su, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Qian, L.; Liu, P.; et al. Ferroptosis: A cell death connecting oxidative stress, inflammation and cardiovascular diseases. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubkova, A.; Leiva, T.; Snyder, K.; Schlegel, C.; Bonvicino, S.M.; Agbaga, M.-P.; Brush, R.S.; Hansen, J.M.; Vitiello, P.F.; Hunter, C.J. Response of the Glutathione (GSH) Antioxidant Defense System to Oxidative Injury in Necrotizing Enterocolitis. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Pan, X.; Wei, G.; Hua, Y. Research progress of glutathione peroxidase family (GPX) in redoxidation. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1147414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedard, K.; Krause, K.-H. The NOX Family of ROS-Generating NADPH Oxidases: Physiology and Pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 245–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, B.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Liao, S.; Zhou, Z.; He, Q.; Zhou, Y. NOX Family: Regulators of Reactive Oxygen Species Balance in Tumor Enteroids. Faseb. J. 2025, 39, e70565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bánfi, B.; Clark, R.A.; Steger, K.; Krause, K.-H. Two Novel Proteins Activate Superoxide Generation by the NADPH Oxidase NOX1. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 3510–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Deken, X.; Corvilain, B.; Dumont, J.E.; Miot, F. Roles of DUOX-Mediated Hydrogen Peroxide in Metabolism, Host Defense, and Signaling. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 20, 2776–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esworthy, R.S. Enzymatic Oxidants, Antioxidants, and Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Appl. Biosci. 2025, 4, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, X.F.; Wen, D.T.; Xu, Z.; Du, T.T.; Fan, Z.F.; Zhu, F.F.; Xiao, J. Identification and validation of ferroptosis-related prognostic gene signature in patients with cervical cancer. Transl. Cancer Res. 2024, 13, 3382–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Moon, J.S. Molecular Roles of NADPH Oxidase-Mediated Oxidative Stress in Alzheimer’s Disease: Isoform-Specific Contributions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Liao, Y.; Zhu, C.; Zou, Z. GPX4, ferroptosis, and diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 174, 116512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, S.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; He, J.; Li, G.; Li, D.; Wei, Z.; Chen, J. Identification and validation of a ferroptosis-related gene signature for predicting survival in skin cutaneous melanoma. Cancer Med. 2022, 11, 3529–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, L.; Gao, H.; Yang, J. Development and Validation of a Ferroptosis-Related Gene Signature for Overall Survival Prediction in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 684259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, D.; Lou, Y.; Liu, X.; Huang, P.; Jin, M.; Huang, G. Regulatory mechanism of α-hederin upon cisplatin sensibility in NSCLC at safe dose by destroying GSS/GSH/GPX2 axis–mediated glutathione oxidation-reduction system. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 150, 112927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigelius-Flohé, R.; Kipp, A.P. Physiological functions of GPx2 and its role in inflammation-triggered carcinogenesis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1259, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florian, S.; Krehl, S.; Loewinger, M.; Kipp, A.; Banning, A.; Esworthy, S.; Chu, F.-F.; Brigelius-Flohé, R. Loss of GPx2 increases apoptosis, mitosis, and GPx1 expression in the intestine of mice. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 1694–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Kan, X.-F.; Ma, C.; Chen, L.-L.; Cheng, T.-T.; Zou, Z.-W.; Li, Y.; Cao, F.-J.; Zhang, W.-J.; Yao, J.; et al. GPX2 overexpression indicates poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317700410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esworthy, R.S.; Yang, L.; Frankel, P.H.; Chu, F.-F. Epithelium-Specific Glutathione Peroxidase, Gpx2, Is Involved in the Prevention of Intestinal Inflammation in Selenium-Deficient Mice1. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 740–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, W. NAD+/NADH and NADP+/NADPH in cellular functions and cell death: Regulation and biological consequences. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2008, 10, 179–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; He, S.; Li, Y.; Ding, R.; Li, X.; Guo, N.; Luo, L. Identification of Lipocalin 2 as a Potential Ferroptosis-related Gene in Ulcerative Colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2023, 29, 1446–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremer, M. Mechanism of the Fenton reaction. Evidence for a new intermediate. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 1999, 1, 3595–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerit, J.; Beaumont, C.; Trivin, F. Iron metabolism, free radicals, and oxidative injury. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2001, 55, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaschler, M.M.; Stockwell, B.R. Lipid peroxidation in cell death. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 482, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonarduzzi, G.; Arkan, M.C.; Başağa, H.; Chiarpotto, E.; Sevanian, A.; Poli, G. Lipid oxidation products in cell signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000, 28, 1370–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astudillo, A.M.; Balboa, M.A.; Balsinde, J. Selectivity of phospholipid hydrolysis by phospholipase A2 enzymes in activated enteroids leading to polyunsaturated fatty acid mobilization. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)–Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2019, 1864, 772–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braverman, N.E.; Moser, A.B. Functions of plasmalogen lipids in health and disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)–Mol. Basis Dis. 2012, 1822, 1442–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broniec, A.; Klosinski, R.; Pawlak, A.; Wrona-Krol, M.; Thompson, D.; Sarna, T. Interactions of plasmalogens and their diacyl analogs with singlet oxygen in selected model systems. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 50, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindelar, P.J.; Guan, Z.; Dallner, G.; Ernster, L. The protective role of plasmalogens in iron-induced lipid peroxidation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyström, N.; Prast-Nielsen, S.; Correia, M.; Globisch, D.; Engstrand, L.; Schuppe-Koistinen, I.; Halfvarson, J. Mucosal and Plasma Metabolomes in New-onset Paediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Correlations with Disease Characteristics and Plasma Inflammation Protein Markers. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2022, 17, 418–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosche, T.; Bertsch, T.; Sieber, C.C.; Hoffmann, U. Reduced plasmalogen concentration as a surrogate marker of oxidative stress in elderly septic patients. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2013, 57, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Zhou, J.; Yang, S.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; Fang, X.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Han, X.; Wen, C. Oxidative stress leads to reduction of plasmalogen serving as a novel biomarker for systemic lupus erythematosus. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 101, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraitou, M.; Dimitriou, E.; Dekker, N.; Monopolis, I.; Aerts, J.; Michelakakis, H. Gaucher disease: Plasmalogen levels in relation to primary lipid abnormalities and oxidative stress. Blood Enteroids Mol. Dis. 2014, 53, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagan, N.; Zoeller, R.A. Plasmalogens: Biosynthesis and functions. Prog. Lipid Res. 2001, 40, 199–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trumbo, P.; Schlicker, S.; Yates, A.A.; Poos, M. Dietary Reference Intakes for Energy, Carbohydrate, Fiber, Fat, Fatty Acids, Cholesterol, Protein and Amino Acids. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2002, 102, 1621–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, P.C. Polyunsaturated fatty acids and inflammation. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2006, 75, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roškarić, P.; Šperanda, M.; Mašek, T.; Verbanac, D.; Starčević, K. Low Dietary n6/n3 Ratio Attenuates Changes in the NRF 2 Gene Expression, Lipid Peroxidation, and Inflammatory Markers Induced by Fructose Overconsumption in the Rat Abdominal Adipose Tissue. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonpane, C.; Ares, G.; Yuan, C.; Schlegel, C.; Liebe, H.; Hunter, C.J. Experimental Modeling of Necrotizing Enterocolitis in Human Infant Intestinal Enteroids. J. Investig. Surg. 2022, 35, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebe, H.; Schlegel, C.; Cai, X.; Golubkova, A.; Loerke, C.; Leiva, T.; Hunter, C.J. Apical-Out Enteroids as an Innovative Model for Necrotizing Enterocolitis. J. Surg. Res. 2023, 283, 1106–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, T.L.; Neves, J.V.; Duarte, T.L. Measurement of Tissue Non-Heme Iron Content using a Bathophenanthroline-Based Colorimetric Assay. JoVE 2022, 179, e63469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Elechalawar, C.K.; Yang, W.; Frickenstein, A.N.; Asfa, S.; Fung, K.-M.; Murphy, B.N.; Dwivedi, S.K.; Rao, G.; Dey, A.; et al. Disabling partners in crime: Gold nanoparticles disrupt multicellular communications within the tumor microenvironment to inhibit ovarian tumor aggressiveness. Mater. Today 2022, 56, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubik, E.; Moynier, F.; Paquet, M.; Siebert, J. Iron Isotopic Composition of Biological Standards Relevant to Medical and Biological Applications. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 696367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breil, C.; Abert Vian, M.; Zemb, T.; Kunz, W.; Chemat, F. “Bligh and Dyer” and Folch Methods for Solid-Liquid-Liquid Extraction of Lipids from Microorganisms. Comprehension of Solvatation Mechanisms and towards Substitution with Alternative Solvents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbaga, M.P.; Merriman, D.K.; Brush, R.S.; Lydic, T.A.; Conley, S.M.; Naash, M.I.; Jackson, S.; Woods, A.S.; Reid, G.E.; Busik, J.V.; et al. Differential composition of DHA and very-long-chain PUFAs in rod and cone photoreceptors. J. Lipid Res. 2018, 59, 1586–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbaga, M.-P.; Brush, R.S.; Mandal, M.N.A.; Henry, K.; Elliott, M.H.; Anderson, R.E. Role of Stargardt-3 macular dystrophy protein (ELOVL4) in the biosynthesis of very long chain fatty acids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 12843–12848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | Forward Primer Sequence | Reverse Primer Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| Glutathione Peroxidase 1 | 5’-CAGTCGGTGTATGCCTTCTCG-3’ | 5’-GAGGGACGCCACATTCTCG-3’ |
| Glutathione Peroxidase 2 | 5’-GGTAGATTTCAATACGTTCCGGG-3’ | 5’-TGACAGTTCTCCTGATGTCCAAA-3’ |
| Glutathione Synthetase | 5’-GGGAGCCTCTTGCAGGATAAA-3’ | 5’-GAATGGGGCATAGCTCACCAC-3’ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gershner, G.H.; Calkins, C.; Golubkova, A.; Schlegel, C.; Massahi, A.; Lerner, M.; Frickenstein, A.N.; Bonvicino, S.; Agbaga, M.-P.; Hunter, C.J. The Role of GPX Enzymes, Lipid Profiles, and Iron Accumulation in Necrotizing Enterocolitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6077. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136077
Gershner GH, Calkins C, Golubkova A, Schlegel C, Massahi A, Lerner M, Frickenstein AN, Bonvicino S, Agbaga M-P, Hunter CJ. The Role of GPX Enzymes, Lipid Profiles, and Iron Accumulation in Necrotizing Enterocolitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6077. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136077
Chicago/Turabian StyleGershner, Grant H., Chase Calkins, Alena Golubkova, Camille Schlegel, Aslan Massahi, Megan Lerner, Alex N. Frickenstein, Sarah Bonvicino, Martin-Paul Agbaga, and Catherine J. Hunter. 2025. "The Role of GPX Enzymes, Lipid Profiles, and Iron Accumulation in Necrotizing Enterocolitis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6077. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136077
APA StyleGershner, G. H., Calkins, C., Golubkova, A., Schlegel, C., Massahi, A., Lerner, M., Frickenstein, A. N., Bonvicino, S., Agbaga, M.-P., & Hunter, C. J. (2025). The Role of GPX Enzymes, Lipid Profiles, and Iron Accumulation in Necrotizing Enterocolitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6077. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136077





