Casein Kinase 2 Regulates the Intrinsic Activity of L-Type Calcium Currents in Cardiomyocytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
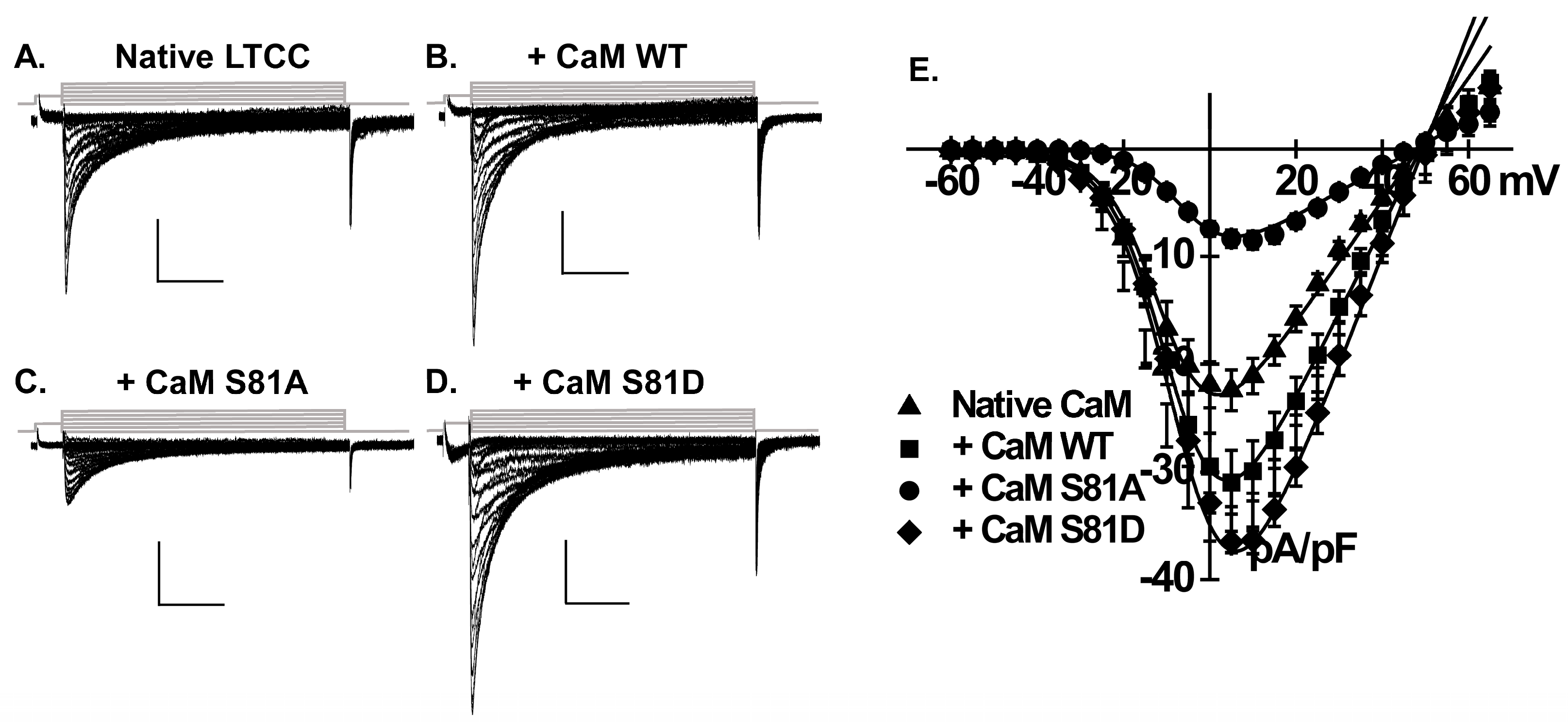
2.1. CaM Increases L-Type Ca2+ Current Density in Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes
2.2. Phosphorylation of CaM Stimulates LTCCs
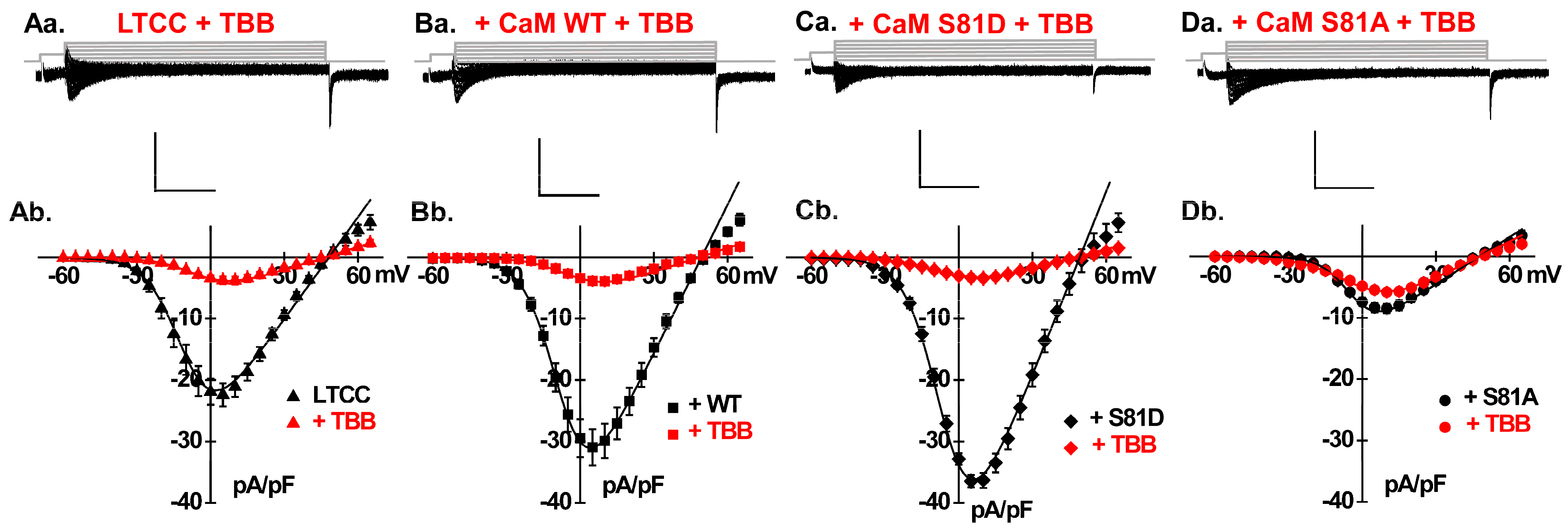
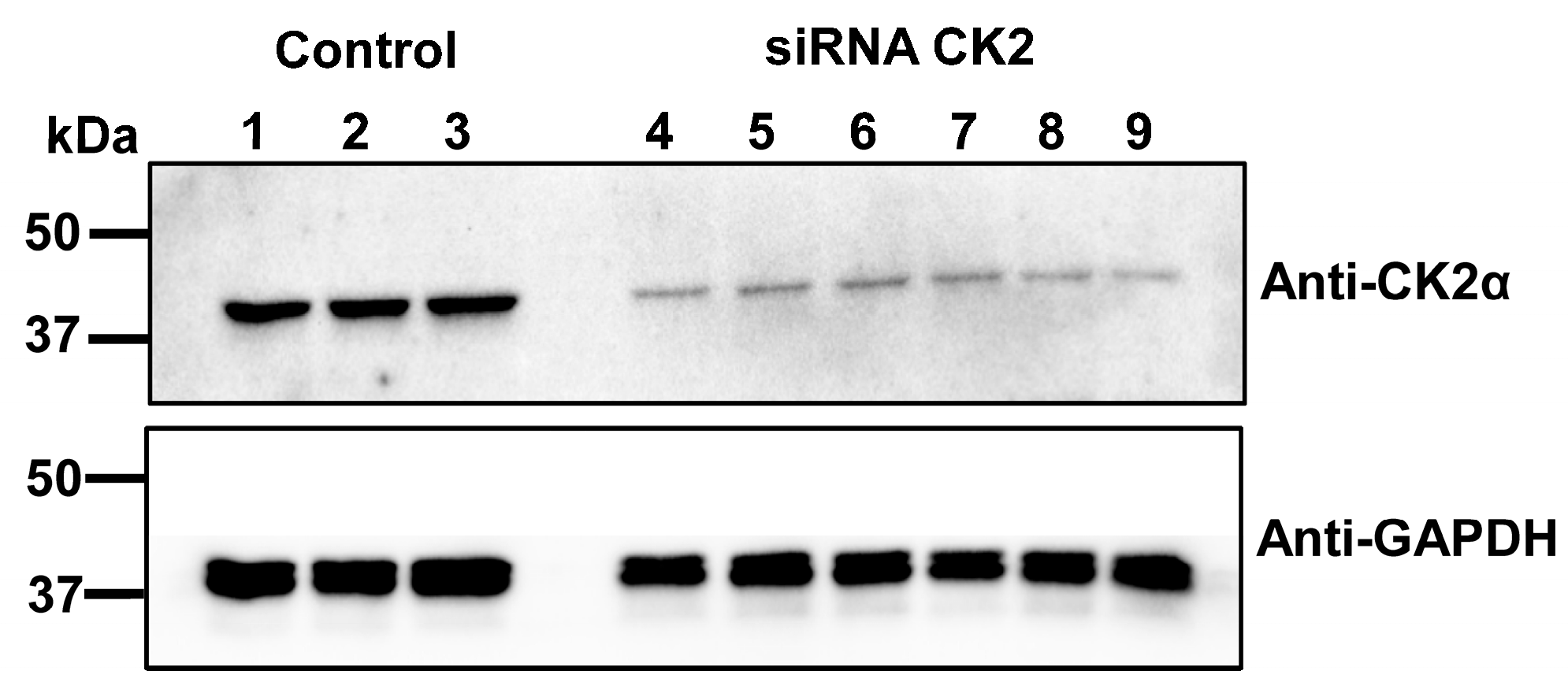
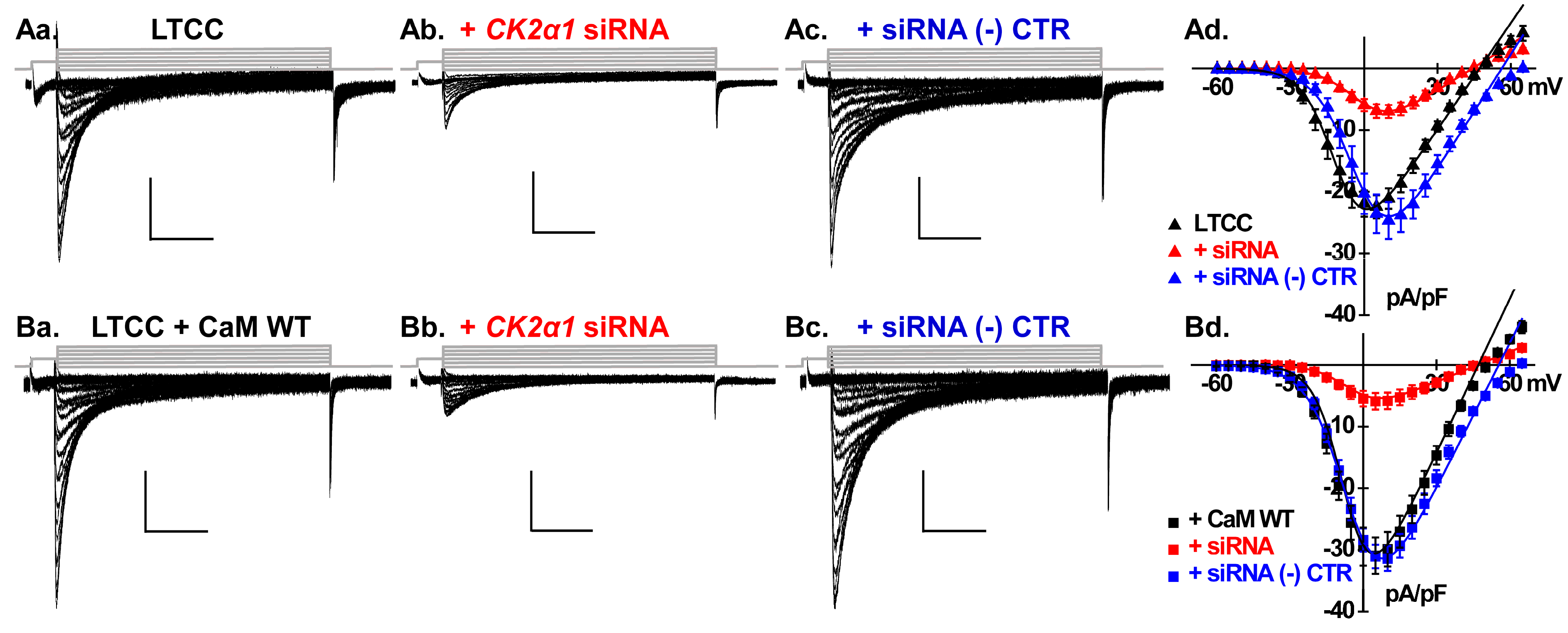
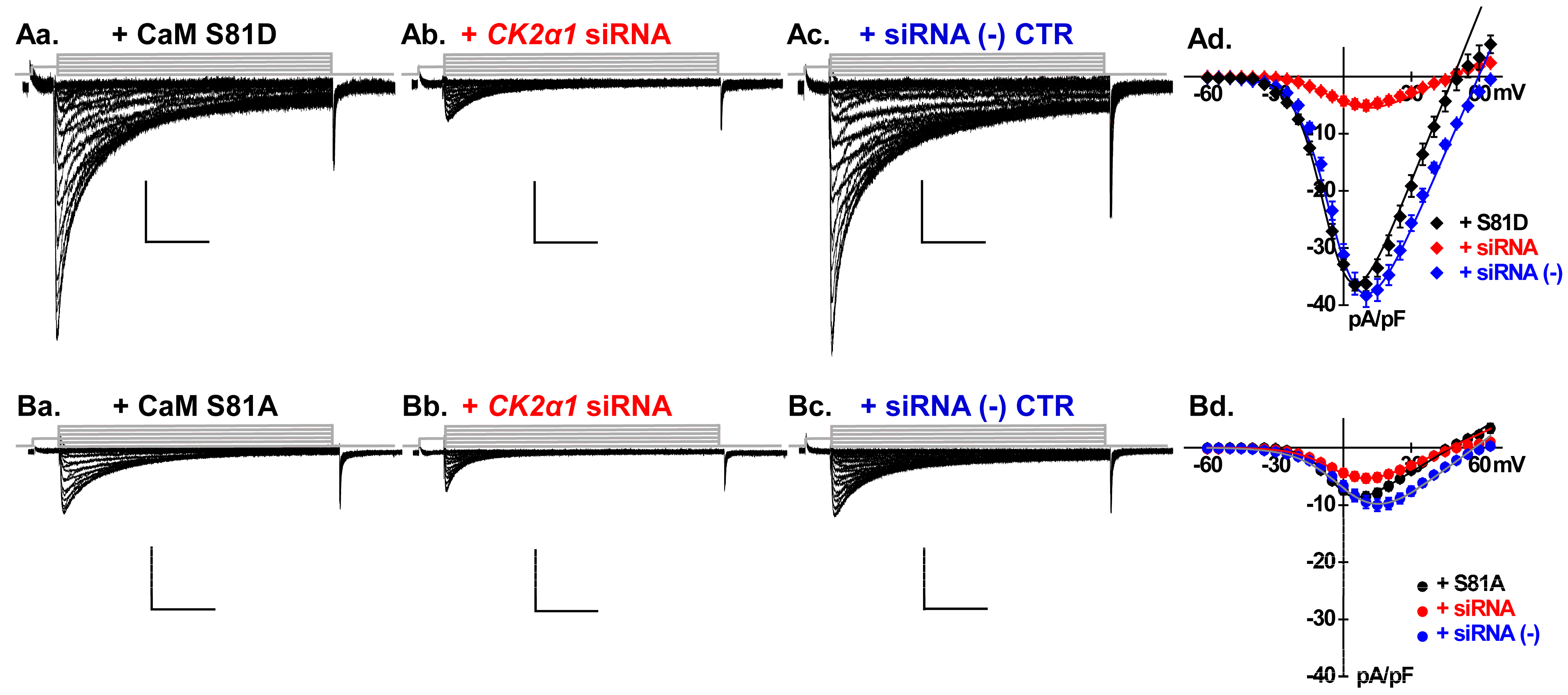
2.3. Silencing CK2 Expression Prevents CaM-Induced Functional Modulation of LTCCs
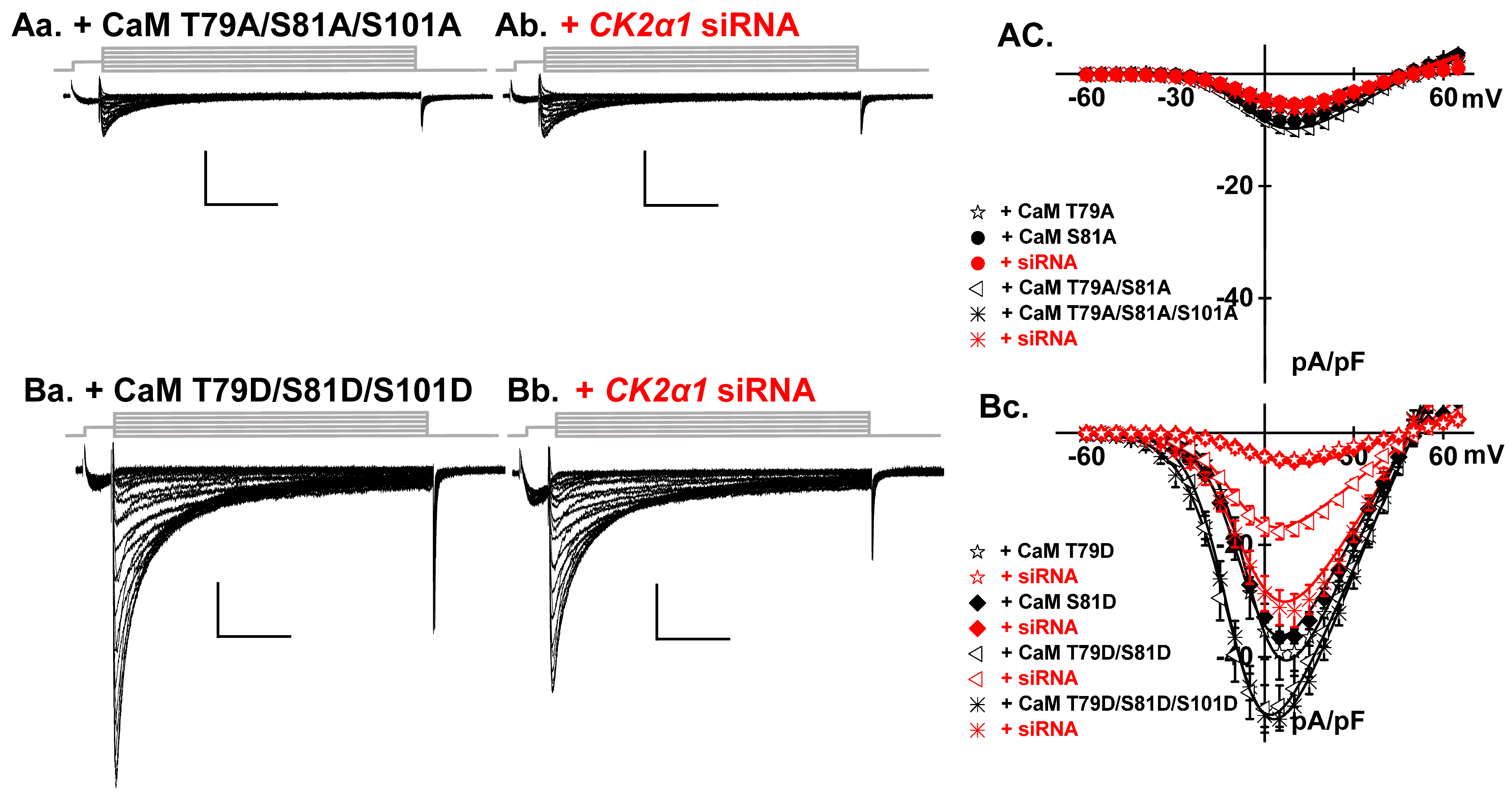
2.4. LTCCs Are Regulated by the CK2-Mediated Simultaneous Phosphorylation of CaM Thr79 and Ser81
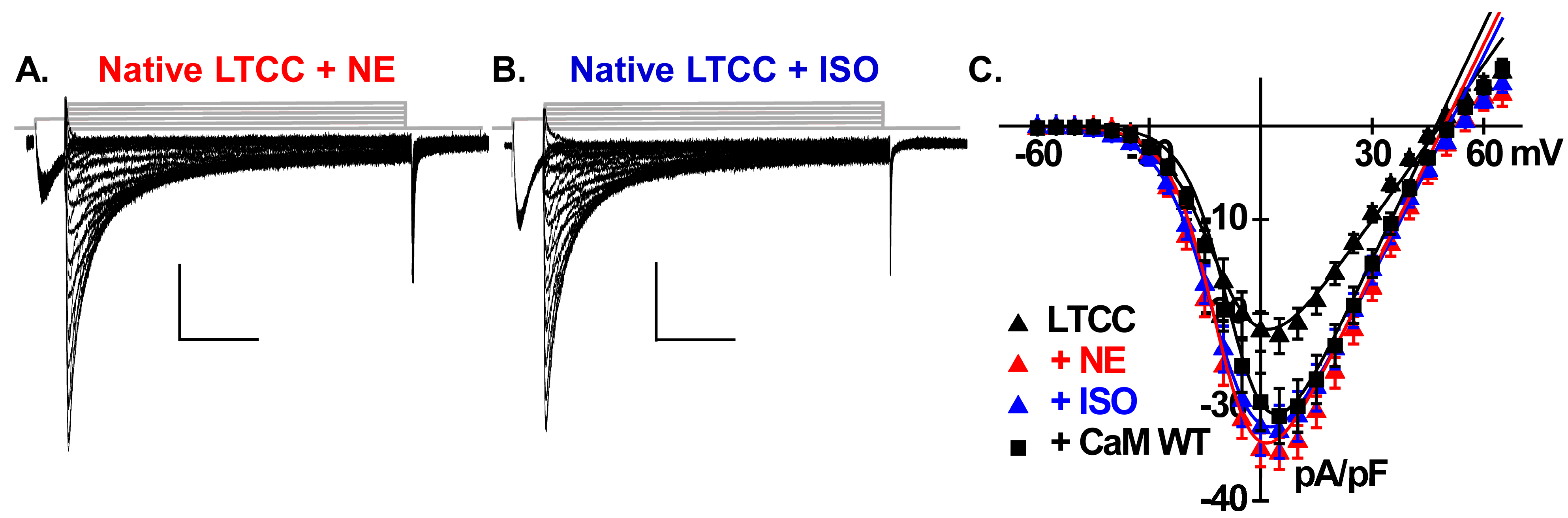
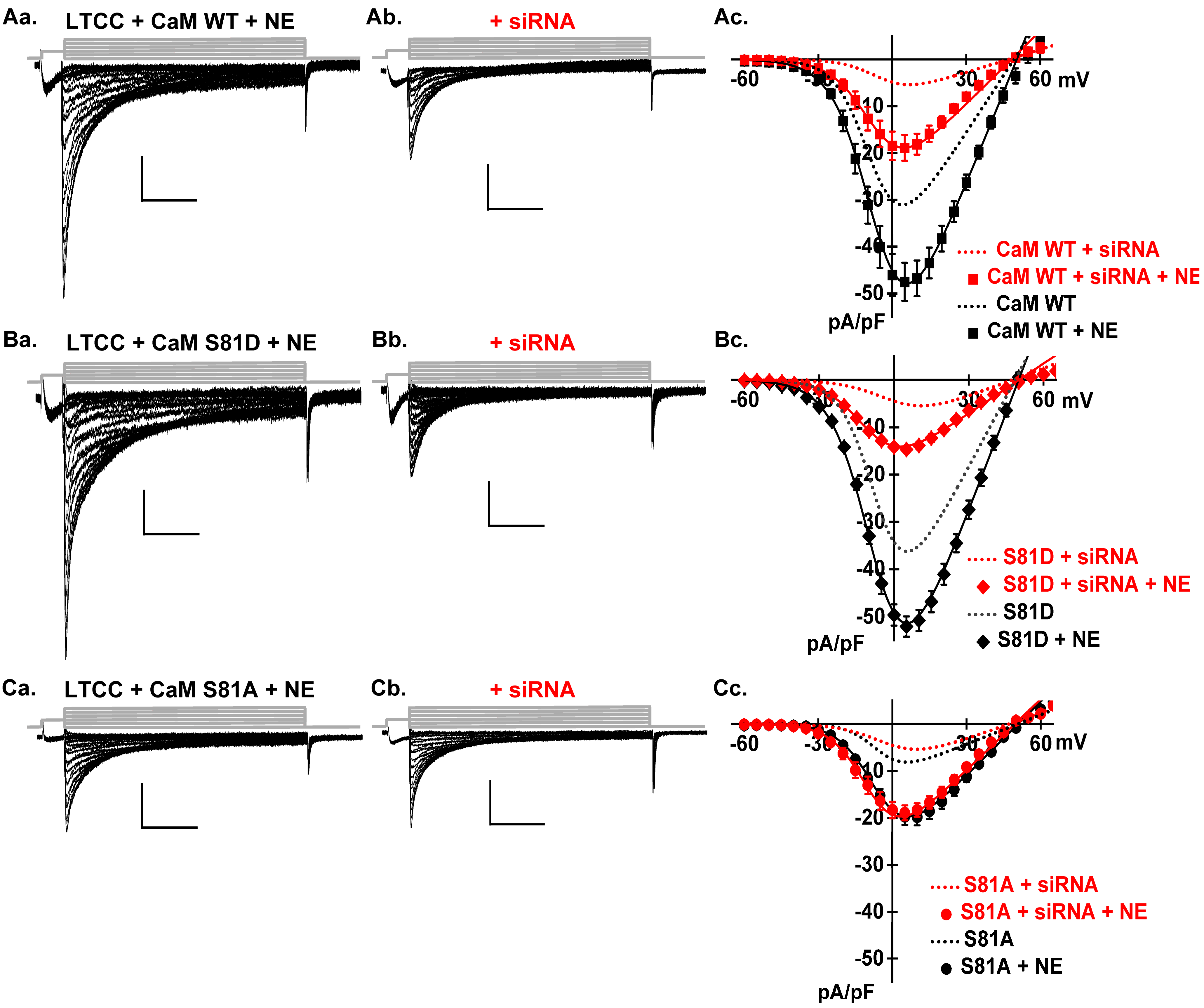
2.5. Catecholamines Partially Rescue CK2 Attenuation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lal, S.; Campbell, K.; Li, A. Editorial: Molecular and cellular mechanisms of heart failure: Pathophysiology, pathogenesis and therapeutics. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1260483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, B.; Ahmad, T.; Alexander, K.M.; Baker, W.L.; Bosak, K.; Breathett, K.; Fonarow, G.C.; Heidenreich, P.; Ho, J.E.; Hsich, E.; et al. Heart Failure Epidemiology and Outcomes Statistics: A Report of the Heart Failure Society of America. J. Card. Fail. 2023, 29, 1412–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseka, O.; Gare, S.R.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Alatawi, N.H.; Ross, C.; Liu, W. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Heart Failure and Their Therapeutic Potential. Cells 2025, 14, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, A.O. Cardiac ion channels. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2009, 2, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Q.; Song, L.S.; Lakatta, E.G.; Cheng, H. Ca2+ signalling between single L-type Ca2+ channels and ryanodine receptors in heart cells. Nature 2001, 410, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yan, Z.; Li, Z.; Qian, X.; Lu, S.; Dong, M.; Zhou, Q.; Yan, N. Structure of the voltage-gated calcium channel Cav1.1 at 3.6 Å resolution. Nature 2016, 537, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segura, E.; Bourdin, B.; Tétreault, M.P.; Briot, J.; Allen, B.G.; Mayer, G.; Parent, L. Proteolytic cleavage of the hydrophobic domain in the Ca(V)α2δ1 subunit improves assembly and activity of cardiac Ca(V)1.2 channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 11109–11124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Yao, X.; Chen, J.; Huang, G.; Fan, X.; Xue, L.; Li, Z.; Wu, T.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, J.; et al. Structural basis for human Cav1.2 inhibition by multiple drugs and the neurotoxin calciseptine. Cell 2023, 186, 5363–5374.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colecraft, H.M.; Alseikhan, B.; Takahashi, S.X.; Chaudhuri, D.; Mittman, S.; Yegnasubramanian, V.; Alvania, R.S.; Johns, D.C.; Marbán, E.; Yue, D.T. Novel functional properties of Ca(2+) channel beta subunits revealed by their expression in adult rat heart cells. J. Physiol. 2002, 541 Pt 2, 435–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Petegem, F.; Duderstadt, K.E.; Clark, K.A.; Wang, M.; Minor, D.L., Jr. Alanine-scanning mutagenesis defines a conserved energetic hotspot in the CaValpha1 AID-CaVbeta interaction site that is critical for channel modulation. Structure 2008, 16, 280–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafi, O.; Dodier, Y.; Berrou, L.; Raybaud, A.; Sauve, R.; Parent, L. Negatively charged residues in the N-terminal of the AID helix confer slow voltage dependent inactivation gating in Cav1.2. Biophys. J. 2004, 87, 3181–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hu, Z.; Li, G.; Wang, J.-W.; Chong, S.Y.; Yu, D.; Wang, X.; Soon, J.L.; Liang, M.C.; Wong, Y.P.; Huang, N.; et al. Regulation of Blood Pressure by Targeting CaV1.2-Galectin-1 Protein Interaction. Circulation 2018, 138, 1431–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlin, B.S.; Crump, S.M.; Satin, J.; Andres, D.A. Regulation of voltage-gated calcium channel activity by the Rem and Rad GTPases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 14469–14474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Papa, A.; Katchman, A.N.; Zakharov, S.I.; Roybal, D.; Hennessey, J.A.; Kushner, J.; Yang, L.; Chen, B.-X.; Kushnir, A.; et al. Mechanism of adrenergic CaV1.2 stimulation revealed by proximity proteomics. Nature 2020, 577, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papa, A.; Kushner, J.; Hennessey, J.A.; Katchman, A.N.; Zakharov, S.I.; Chen, B.X.; Yang, L.; Lu, R.; Leong, S.; Diaz, J.; et al. Adrenergic Ca(V)1.2 Activation via Rad Phosphorylation Converges at α(1C) I-II Loop. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servili, E.; Trus, M.; Maayan, D.; Atlas, D. Beta-Subunit of the voltage-gated Calcium channel Cav1.2 drives signaling to the nucleus via H-Ras. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E8624–E8633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, P.J.; Ben-Johny, M.; Dick, I.E.; Inoue, T.; Yue, D.T. Apocalmodulin itself promotes ion channel opening and Ca(2+) regulation. Cell 2014, 159, 608–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zühlke, R.D.; Pitt, G.S.; Tsien, R.W.; Reuter, H. Ca2+-sensitive inactivation and facilitation of L-type Ca2+ channels both depend on specific amino acid residues in a consensus calmodulin-binding motif in the (alpha)1C subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 21121–21129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pate, P.; Mochca-Morales, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.Z.; Rodney, G.G.; Serysheva, I.I.; Williams, B.Y.; Anderson, M.E.; Hamilton, S.L. Determinants for calmodulin binding on voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 39786–39792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanin, C.; Gamsjaeger, R.; Kahr, H.; Schaufler, D.; Carlson, O.; Abernethy, D.R.; Soldatov, N.M. Ca(2+) sensors of L-type Ca(2+) channel. FEBS Lett. 2000, 487, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, G.S.; Zühlke, R.D.; Hudmon, A.; Schulman, H.; Reuter, H.; Tsien, R.W. Molecular basis of calmodulin tethering and Ca2+-dependent inactivation of L-type Ca2+ channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 30794–30802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouton, J.; Feltz, A.; Maulet, Y. Interactions of calmodulin with two peptides derived from the c-terminal cytoplasmic domain of the Ca(v)1.2 Ca2+ channel provide evidence for a molecular switch involved in Ca2+-induced inactivation. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 22359–22367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, S.; Shimoni, Y. The calcium and frequency dependence of the slow inward current ‘staircase’ in frog atrium. J. Physiol. 1981, 310, 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marban, E.; Tsien, R.W. Enhancement of calcium current during digitalis inotrophy in mammalian heart: Positive feed-back regulation by intracellular calcium? J. Physiol. 1982, 329, 589–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuhlke, R.D.; Pitt, G.S.; Deisseroth, K.; Tsien, R.W.; Reuter, H. Calmodulin supports both inactivation and facilitation of L-type calcium channels. Nature 1999, 399, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satin, J.; Schroder EA FAU—Crump, S.; Crump, S.M. L-type calcium channel auto-regulation of transcription. Cell Calcium 2011, 49, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdin, B.; Shakeri, B.; Tetreault, M.P.; Sauve, R.; Lesage, S.; Parent, L. Functional Characterization of Cava2d Mutations Associated with Sudden Cardiac Death. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 2854–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Alonso, J.L.; Loucks, A.; Schobesberger, S.; van Cromvoirt, A.M.; Poulet, C.; Chowdhury, R.A.; Trayanova, N.; Gorelik, J. Nanoscale regulation of L-type calcium channels differentiates between ischemic and dilated cardiomyopathies. eBioMedicine 2020, 57, 102845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, A.; Zakharov, S.I.; Katchman, A.N.; Kushner, J.S.; Chen, B.X.; Yang, L.; Liu, G.; Jimenez, A.S.; Eisert, R.J.; Bradshaw, G.A.; et al. Rad regulation of Ca(V)1.2 channels controls cardiac fight-or-flight response. Nat. Cardiovasc. Res. 2022, 1, 1022–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, A.; Kushner, J.; Marx, S.O. Adrenergic Regulation of Calcium Channels in the Heart. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2022, 84, 285–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, A.; del Rivero Morfin, P.J.; Chen, B.-X.; Yang, L.; Katchman, A.N.; Zakharov, S.I.; Liu, G.; Bohnen, M.S.; Zheng, V.; Katz, M.; et al. A membrane-associated phosphoswitch in Rad controls adrenergic regulation of cardiac calcium channels. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e176943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.E. Totally Rad? The Long and Winding Road to Understanding Ca(V)1.2 Regulation. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 89–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bers, D.M. Calcium cycling and signaling in cardiac myocytes. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2008, 70, 23–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Fontes, S.K.; Bautista, E.N.; Cheng, Z. Physiological and pathological roles of protein kinase A in the heart. Cardiovasc. Res. 2022, 118, 386–398. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Qi, Z.; Szeto, C.; Tang, M.; Peng, Y.; Molkentin, J.D.; et al. Increasing T-type calcium channel activity by beta-adrenergic stimulation contributes to beta-adrenergic regulation of heart rates. J. Physiol. 2017, 596, 1137–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, L.S.; Bers, D.M. Calcium, calmodulin, and calcium-calmodulin kinase II: Heartbeat to heartbeat and beyond. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2002, 34, 919–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koval, O.M.; Guan, X.; Wu, Y.; Joiner, M.L.; Gao, Z.; Chen, B.; Grumbach, I.M.; Luczak, E.D.; Colbran, R.J.; Song, L.S.; et al. CaV1.2 beta-subunit coordinates CaMKII-triggered cardiomyocyte death and afterdepolarizations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4996–5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Segura, E.; Marsolais, M.; Parent, L. A CACNA1C variant associated with cardiac arrhythmias provides mechanistic insights in the calmodulation of L-type Ca2+ channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Johny, M.; Yue, D.T. Calmodulin regulation (calmodulation) of voltage-gated calcium channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 2014, 143, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameyama, M.; Minobe, E.; Shao, D.; Xu, J.; Gao, Q.; Hao, L. Regulation of Cardiac Cav1.2 Channels by Calmodulin. International J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6409. [Google Scholar]
- Sacks, D.B.; Mazus, B.; Joyal, J.L. The activity of calmodulin is altered by phosphorylation: Modulation of calmodulin function by the site of phosphate incorporation. Biochem. J. 1995, 312 Pt 1, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benaim, G.; Villalobo, A. Phosphorylation of calmodulin. Functional implications. Eur. J. Biochem. 2002, 269, 3619–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrigoni, G.; Marin, O.; Pagano, M.A.; Settimo, L.; Paolin, B.; Meggio, F.; Pinna, L.A. Phosphorylation of Calmodulin Fragments by Protein Kinase CK2. Mechanistic Aspects and Structural Consequences. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 12788–12798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarroel, A.; Taglialatela, M.; Bernardo-Seisdedos, G.; Alaimo, A.; Agirre, J.; Alberdi, A.; Gomis-Perez, C.; Soldovieri, M.V.; Ambrosino, P.; Malo, C.; et al. The Ever Changing Moods of Calmodulin: How Structural Plasticity Entails Transductional Adaptability. J. Mol. Biol. 2014, 426, 2717–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmara, H.; Minobe, E.; Saud, Z.A.; Kameyama, M. Interactions of calmodulin with the multiple binding sites of Cav1.2 Ca2+ channels. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 112, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simms, B.A.; Souza, I.A.; Zamponi, G.W. Effect of the Brugada syndrome mutation A39V on calmodulin regulation of Cav1.2 channels. Mol. Brain 2014, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMaria, C.D.; Soong, T.W.; Alseikhan, B.A.; Alvania, R.S.; Yue, D.T. Calmodulin bifurcates the local Ca2+ signal that modulates P/Q-type Ca2+ channels. Nature 2001, 411, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limpitikul, W.B.; Dick, I.E.; Joshi-Mukherjee, R.; Overgaard, M.T.; George, A.L., Jr.; Yue, D.T. Calmodulin mutations associated with long QT syndrome prevent inactivation of cardiac L-type Ca(2+) currents and promote proarrhythmic behavior in ventricular myocytes. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2014, 74, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, D.; Hermosilla, T.; Varela, D. Calcium-dependent inactivation controls cardiac L-type Ca2+ currents under β-adrenergic stimulation. J. General. Physiol. 2019, 151, 786–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaughan, J.P.; Hefner, C.A.; Houser, S.R. Electrophysiological properties of neonatal rat ventricular myocytes with alpha1-adrenergic-induced hypertrophy. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 1998, 275, H577–H592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehler, E.; Moore-Morris, T.F.; Lange, S. Isolation and culture of neonatal mouse cardiomyocytes. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 79, e50154. [Google Scholar]
- Villalobo, A. The multifunctional role of phospho-calmodulin in pathophysiological processes. Biochem. J. 2018, 475, 4011–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roffey, S.E.; Litchfield, D.W. CK2 Regulation: Perspectives in 2021. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quadroni, M.; James, P.; Carafoli, E. Isolation of phosphorylated calmodulin from rat liver and identification of the in vivo phosphorylation sites. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 16116–16122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadroni, M.; L’Hostis, E.L.; Corti, C.; Myagkikh, I.; Durussel, I.; Cox, J.; James, P.; Carafoli, E. Phosphorylation of calmodulin alters its potency as an activator of target enzymes. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 6523–6532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarno, S.; Reddy, H.; Meggio, F.; Ruzzene, M.; Davies, S.P.; Donella-Deana, A.; Shugar, D.; Pinna, L.A. Selectivity of 4,5,6,7-tetrabromobenzotriazole, an ATP site-directed inhibitor of protein kinase CK2 (‘casein kinase-2′). FEBS Lett. 2001, 496, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, D.T.; Herzig, S.; Marban, E. Beta-adrenergic stimulation of calcium channels occurs by potentiation of high-activity gating modes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Heyden, M.A.G.; Wijnhoven, T.J.M.; Opthof, T. Molecular aspects of adrenergic modulation of cardiac L-type Ca2+ channels. Cardiovasc. Res. 2005, 65, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebar, F.; Chavero, A.; Agell, N.; Lu, A.; Rentero, C.; Enrich, C.; Grewal, T. Pleiotropic Roles of Calmodulin in the Regulation of KRas and Rac1 GTPases: Functional Diversity in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3680. [Google Scholar]
- Bers, D.M. Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II regulation of cardiac excitation-transcription coupling. Heart Rhythm. 2011, 8, 1101–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulman, H.; Anderson, M.E. Ca/Calmodulin-dependent Protein Kinase II in Heart Failure. Drug Discov. Today Dis. Mech. 2010, 7, e117–e122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.E. Multiple downstream proarrhythmic targets for calmodulin kinase II: Moving beyond an ion channel-centric focus. Cardiovasc. Res. 2007, 73, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, Y.-W.; Kong, D.; Wang, D.; Orfali, R.; Sherpa, R.T.; Totonchy, J.; Nauli, S.M.; Zhang, M. Differential modulation of SK channel subtypes by phosphorylation. Cell Calcium 2021, 94, 102346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; MacKinnon, R. Activation mechanism of a human SK-calmodulin channel complex elucidated by cryo-EM structures. Science 2018, 360, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Petegem, F.; Chatelain, F.C.; Minor, D.L., Jr. Insights into voltage-gated calcium channel regulation from the structure of the Cav1.2 IQ domain-Ca/calmodulin complex. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2005, 12, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallon, J.L.; Halling, D.B.; Hamilton, S.L.; Quiocho, F.A. Structure of calmodulin bound to the hydrophobic IQ domain of the cardiac Ca(1.2 calcium channel. Structure 2005, 13, 1881–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.J.; Hao, L.Y.; Kameyama, A.; Kameyama, M. Calmodulin reverses rundown of L-type Ca(2+) channels in guinea pig ventricular myocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2004, 287, C1717–C1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Bers, D.M. Free and bound intracellular calmodulin measurements in cardiac myocytes. Cell Calcium 2007, 41, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issinger, O.G. Casein kinases: Pleiotropic mediators of cellular regulation. Pharmacol. Ther. 1993, 59, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgo, C.; D’Amore, C.; Sarno, S.; Salvi, M.; Ruzzene, M. Protein kinase CK2: A potential therapeutic target for diverse human diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 183. [Google Scholar]
- Hauck, L.; Harms, C.; An, J.; Rohne, J.; Gertz, K.; Dietz, R.; Endres, M.; von Harsdorf, R. Protein kinase CK2 links extracellular growth factor signaling with the control of p27(Kip1) stability in the heart. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.O.; Baines, C.P.; Critz, S.D.; Pelech, S.L.; Katz, S.; Downey, J.M.; Cohen, M.V. Ischemia induced activation of heat shock protein 27 kinases and casein kinase 2 in the preconditioned rabbit heart. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1999, 77, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| DNA Transfection | Treatment | Electrophysiological Properties | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaM | CSNK2α1 siRNA | n/N | Peak Current Density (pA/pF) | E0.5,act (mV) | |
| Native CaM | - | - | 21/5 | −22 ± 6 | −10 ± 3 |
| - | TBB | 10/3 | −4 ± 2 * | −5 ± 2 * | |
| - | NE | 12/3 | −35 ± 5 * | −11 ± 2 ** | |
| - | NE + TBB | 15/2 | −13 ± 3 * | −6 ± 3 * | |
| - | ISO | 10/2 | −33 ± 8 * | −11 ± 1 ** | |
| - | ISO + TBB | 5/1 | −12 ± 2 * | −8 ± 2 | |
| siRNA | - | 10/1 | −7 ± 3 * | −4 ± 2 * | |
| siRNA | NE | 7/1 | −15 ± 5 * | −7 ± 2 | |
| siRNA | ISO | 9/2 | −17 ± 3 * | −5 ± 3 * | |
| siRNA (−) | - | 8/1 | −25 ± 4 | −4 ± 2 * | |
| WT | - | - | 16/3 | −31 ± 6 * | −8 ± 3 |
| - | TBB | 8/2 | −4 ± 1 ** | −3 ± 2 ** | |
| - | NE | 7/1 | −48 ± 8 ** | −8 ± 1 | |
| - | NE + TBB | 5/1 | −14 ± 3 ** | −9 ± 2 | |
| siRNA | - | 6/1 | −6 ± 2 ** | −6 ± 2 ** | |
| siRNA | NE | 5/1 | −19 ± 4 ** | −8 ± 2 | |
| siRNA | ISO | 10/2 | −16 ± 3 ** | −6 ± 2 | |
| siRNA (−) | - | 9/1 | −31 ± 5 | −7 ± 2 | |
| S81A | - | - | 12/2 | −9 ± 3 *,** | −4 ± 2 *,** |
| - | TBB | 6/1 | −6 ± 0.8 # | −3 ± 2 | |
| - | NE | 10/2 | −20 ± 5 # | −7 ± 2 # | |
| siRNA | - | 11/2 | −5 ± 2 # | −2 ± 3 | |
| siRNA | NE | 10/3 | −19 ± 5 # | −9 ± 3 # | |
| siRNA | ISO | 7/1 | −12 ± 3 | −9 ± 2 # | |
| siRNA (-) | - | 13/2 | −10 ± 3 | 2 ± 3 # | |
| S81D | - | - | 11/3 | −37 ± 3 *,** | −6 ± 2 *,** |
| - | TBB | 6/1 | −3 ± 1 # | −6 ± 1 | |
| siRNA | - | 6/1 | −5 ± 2 # | −4 ± 2 | |
| - | NE | 8/1 | −52 ± 6 # | −8 ± 1 | |
| siRNA | NE | 10/2 | −15 ± 2 # | −11 ± 2 # | |
| siRNA (−) | - | 10/2 | −38 ± 5 | −3 ± 2 # | |
| T79A | - | - | 11/2 | −9 ± 4 *,** | −2 ± 3 *,** |
| - | NE | 7/1 | −20 ± 7 # | −9 ± 2 # | |
| T79D | - | - | 9/1 | −39 ± 12 *,** | −5 ± 2 *,** |
| siRNA | - | 6/1 | −5 ± 0.9 # | −4 ± 2 | |
| T79A/S81A | - | - | 11/1 | −9 ± 1 *,** | −4 ± 2 *,** |
| T79D/S81D | - | - | 7/1 | −49 ± 13 *,** | −12 ± 2 ** |
| sRNA | - | 10/2 | −18 ± 4 # | −8 ± 2 # | |
| T79A/S81A/S101A | - | - | 8/1 | −6 ± 2 *,** | −4 ± 2 *,** |
| siRNA | - | 11/2 | −6 ± 2 *,** | −3 ± 2 *,** | |
| T79D/S81D/S101D | - | - | 10/2 | −51 ± 5 *,** | −11 ± 2 ** |
| - | TBB | 12/2 | −23 ± 5 # | −6 ± 2 # | |
| siRNA | - | 14/3 | −32 ± 8 # | −6 ± 2 # | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, J.; Broszczak, M.; Parent, L. Casein Kinase 2 Regulates the Intrinsic Activity of L-Type Calcium Currents in Cardiomyocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6010. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136010
Zhao J, Broszczak M, Parent L. Casein Kinase 2 Regulates the Intrinsic Activity of L-Type Calcium Currents in Cardiomyocytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6010. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136010
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Juan, Marlena Broszczak, and Lucie Parent. 2025. "Casein Kinase 2 Regulates the Intrinsic Activity of L-Type Calcium Currents in Cardiomyocytes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6010. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136010
APA StyleZhao, J., Broszczak, M., & Parent, L. (2025). Casein Kinase 2 Regulates the Intrinsic Activity of L-Type Calcium Currents in Cardiomyocytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6010. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136010







