Identification and Screening of Novel Antioxidant Peptides from Yak Skin and Their Protective Effect on H2O2-Induced HepG2 Cells Oxidation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
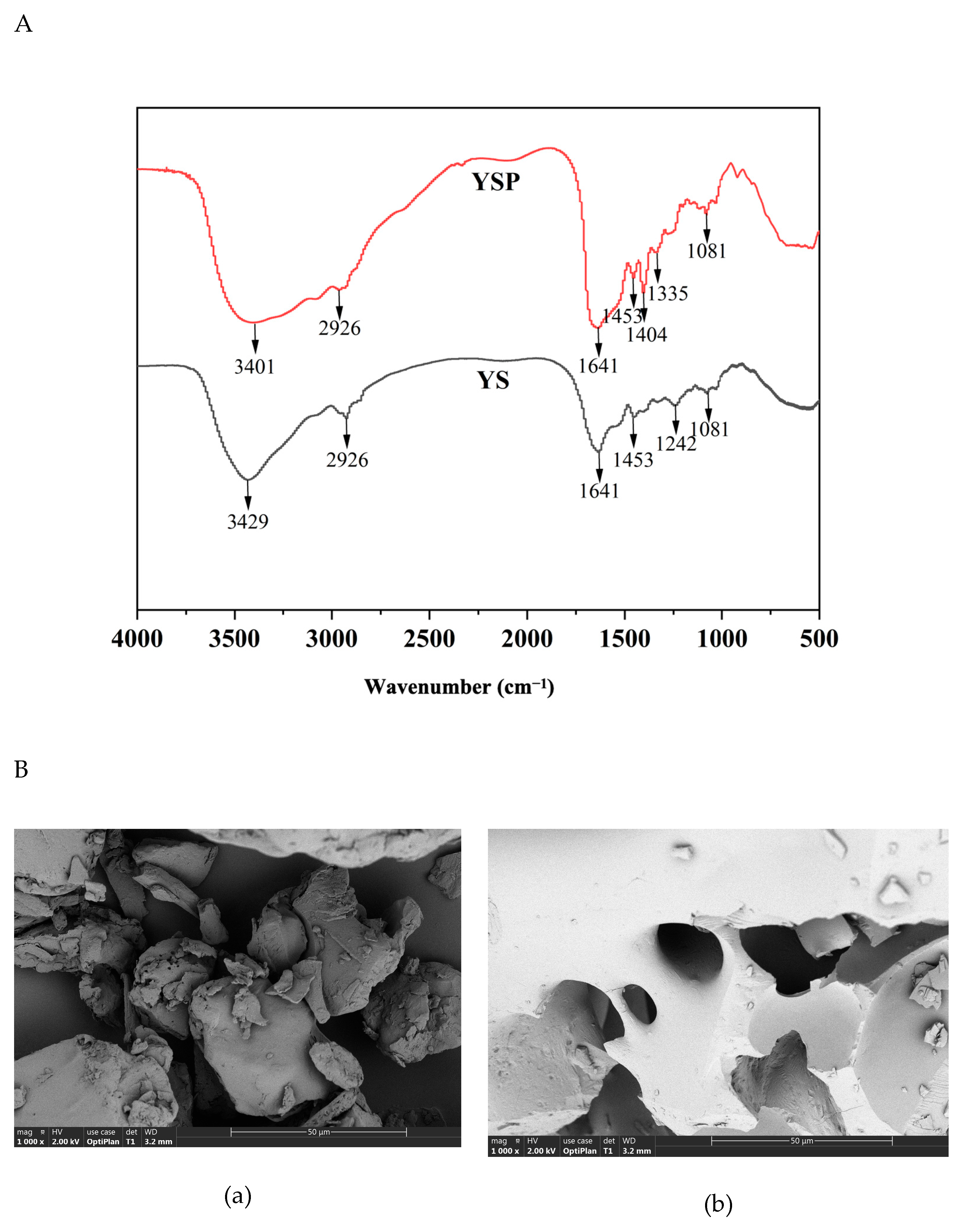
2.1. Structural Characterization of YSP
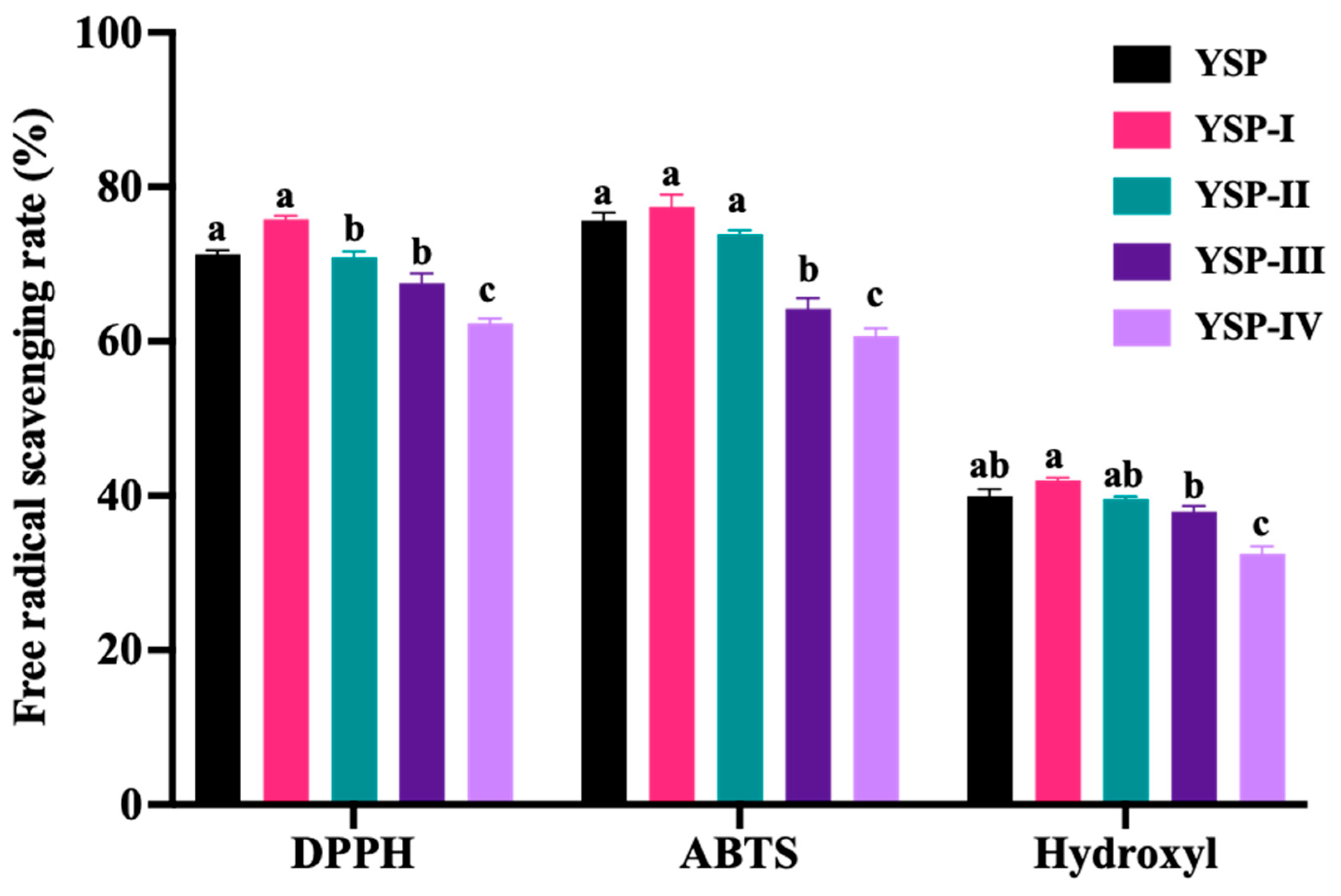
2.2. Free Radical Scavenging Activities of Ultrafiltrate Fractions
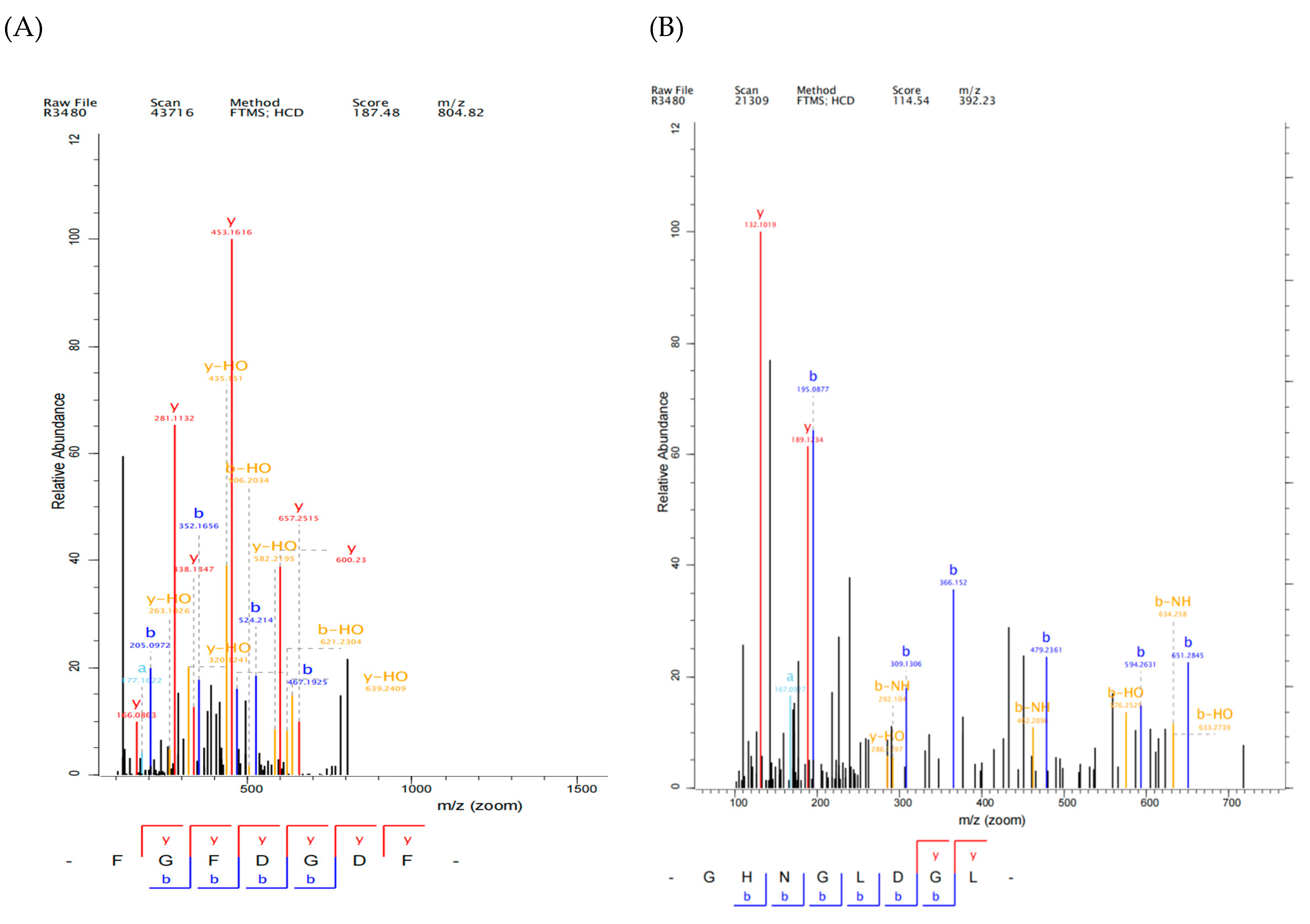
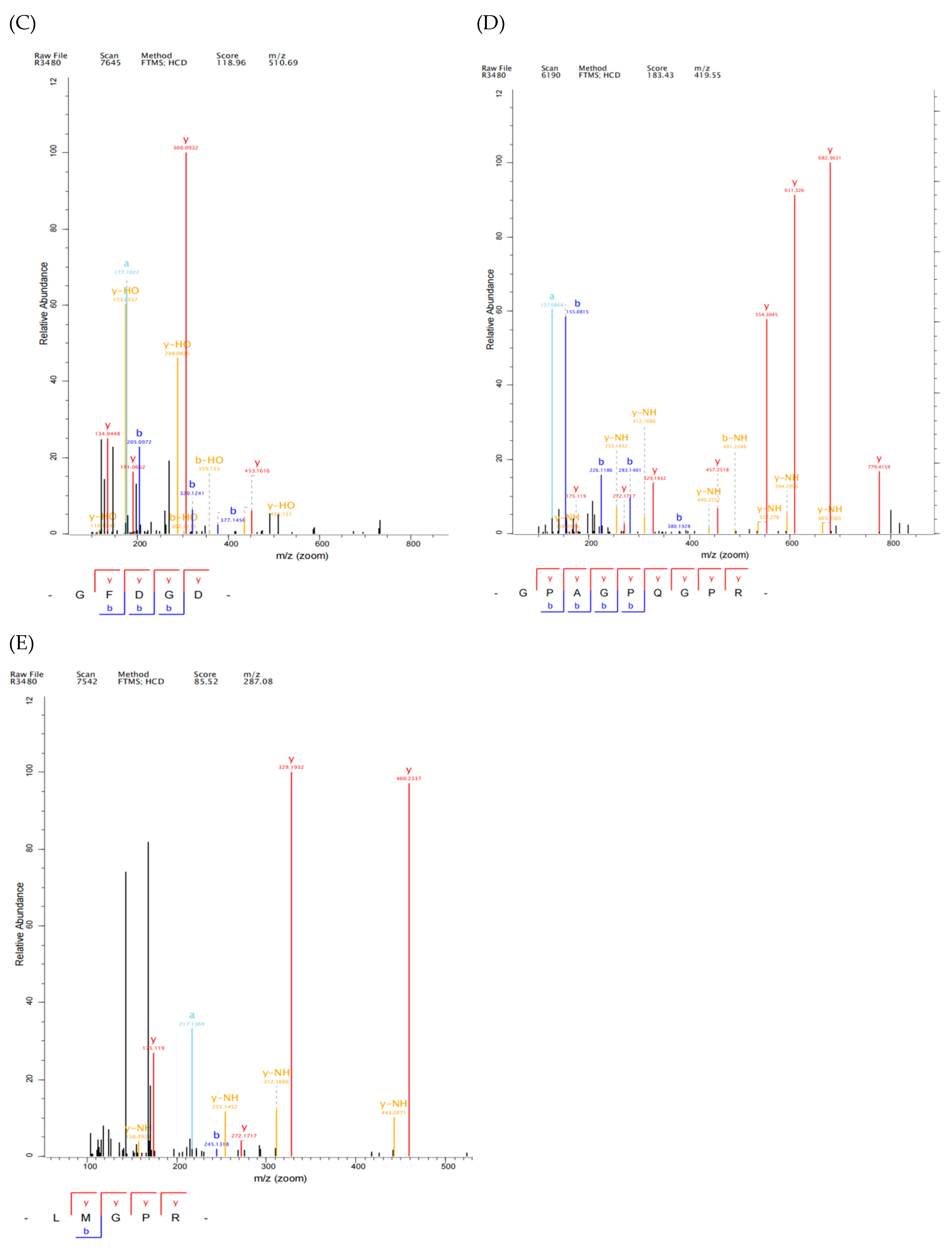
2.3. Identification and Screening of Antioxidant Peptide from YSP by LC-MS/MS
2.4. Molecular Docking Simulation of Antioxidant Peptides Interacting with Keap1
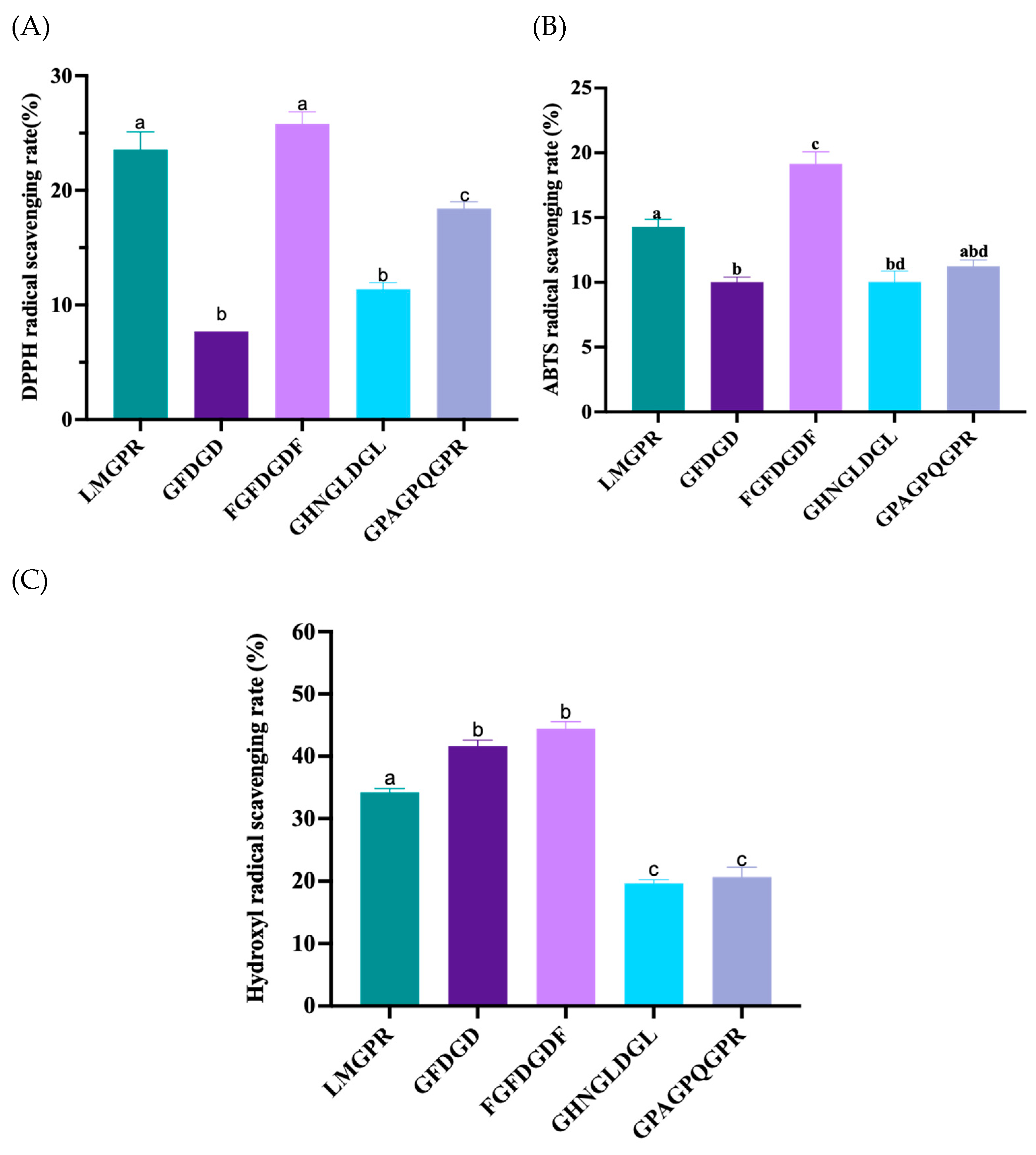
2.5. Free Radical Scavenging Activities of Peptides
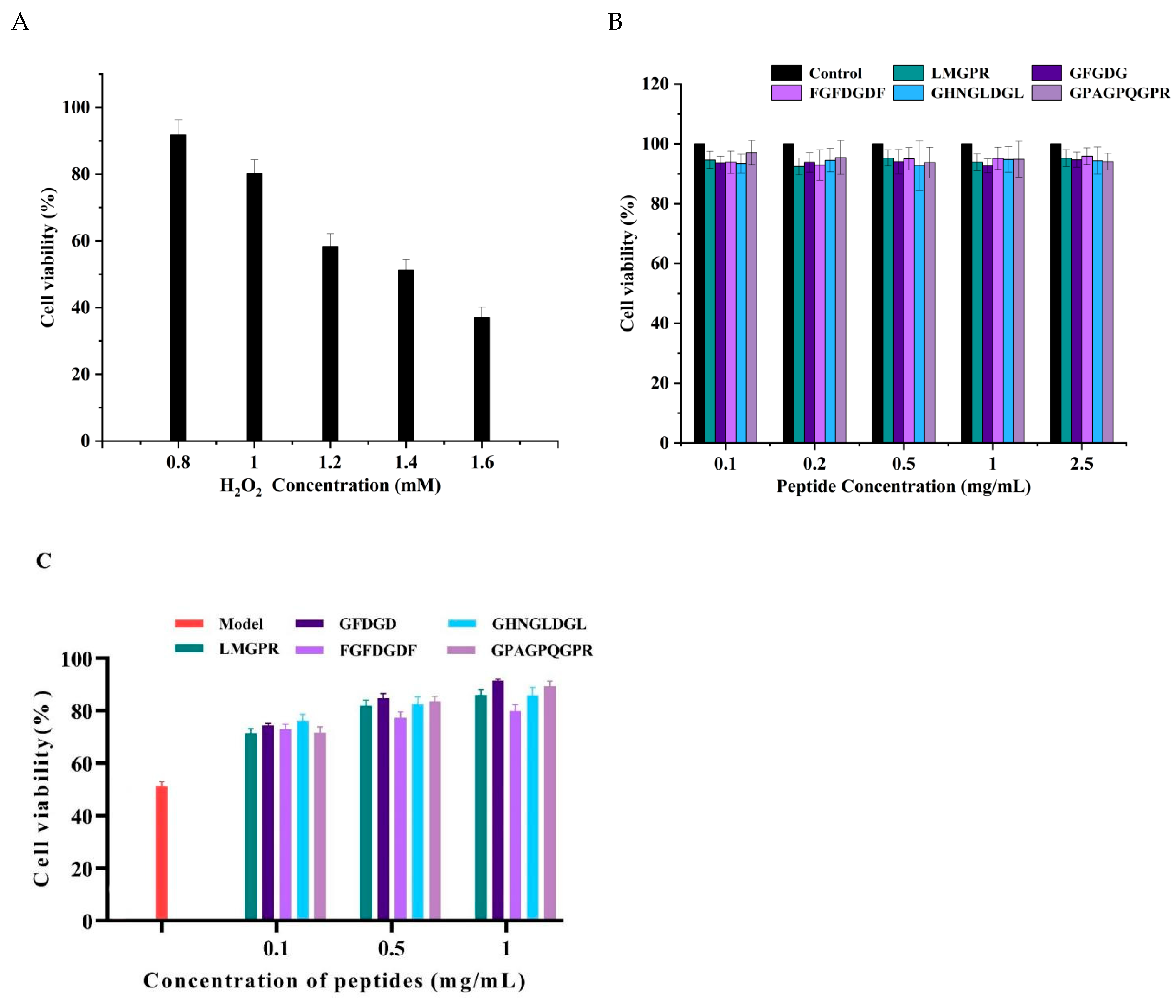
2.6. Protective Effect of Peptides on the Oxidative Damage of HepG2 Cells Induced by H2O2
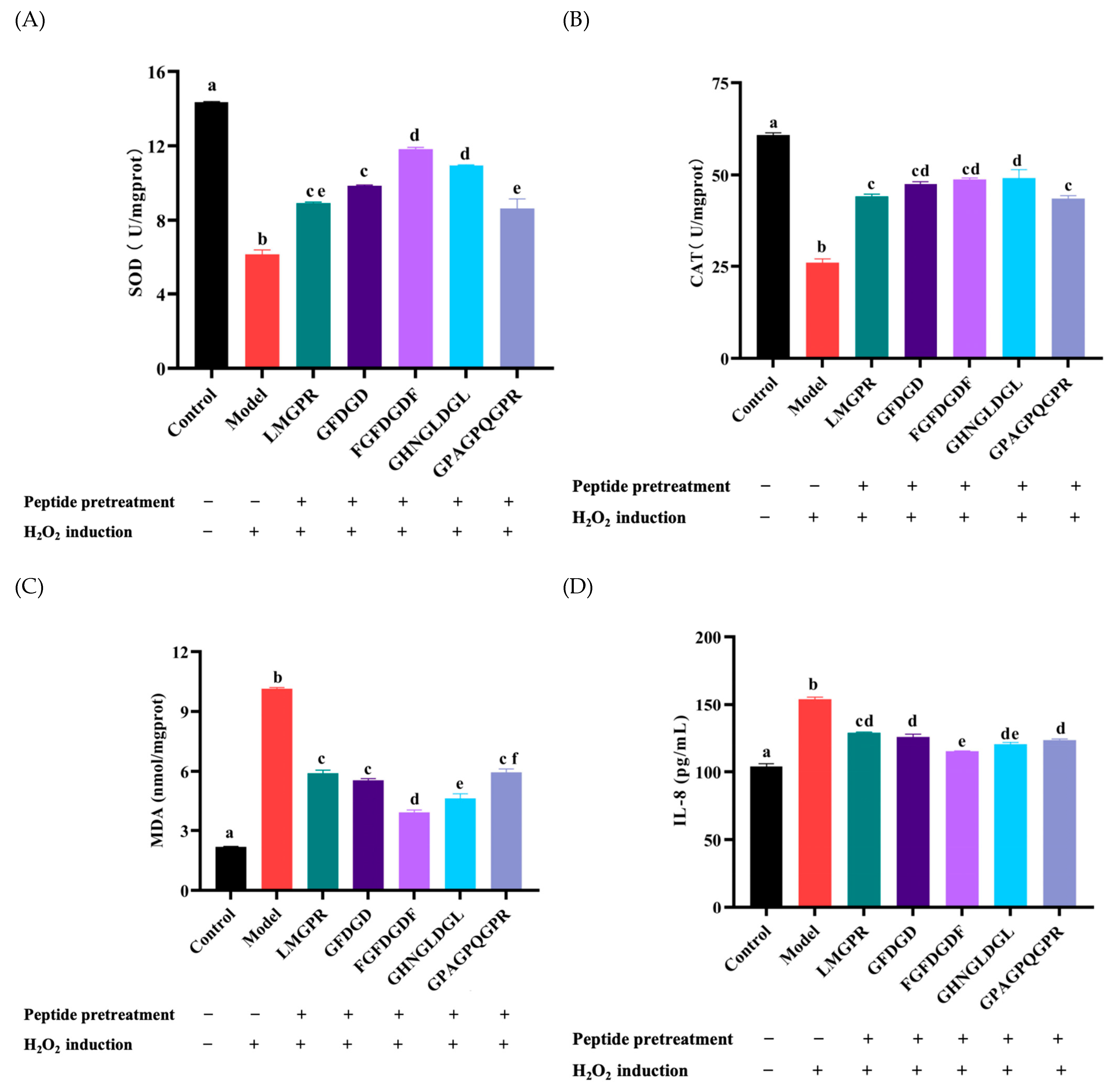
2.7. Effects of Antioxidant Peptides on Antioxidant Enzymes, Malondialdehyde (MDA), and IL-8 Contents in H2O2-Induced HepG2 Cells
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Preparation of YSP by Enzymatic Hydrolysis
3.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Analysis
3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy Analysis
3.5. Ultrafiltration Separation
3.6. Evaluation on the Free Radical Scavenging Activity
3.6.1. DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
3.6.2. ABTS Radical Scavenging Activity
3.6.3. Hydroxyl Radical Scavenging Activity
3.7. Sequence Identification of YSP
3.8. Online Informatics Screening of Potential Antioxidant Peptides
3.9. Molecular Docking of YSP with Keap1 Protein
3.10. Synthesis of Antioxidant Peptides
3.11. Evaluation on the Cellular Antioxidant Activity of YSP
3.11.1. Cell Culture
3.11.2. Determination of Cell Viability
3.11.3. Establishment of Oxidative Stress Model in HepG2 Cells
3.11.4. Treatment of Peptides on H2O2-Induced HepG2 Cells
3.12. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, J.N.; Yi, Z.W.; Chen, X.T.; Pan, N.; Su, X.; Shi, H.F.; Liu, Z.Y. Screening and mechanistic study of antioxidant peptides from Bangia fusco-purpurea targeting the Keap1–Nrf2 pathway. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 104122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.; Xu, L.; Fan, C.; Cao, L.L.; Guo, X.F. Structural Characteristics and Antioxidant Mechanism of Donkey-Hide Gelatin Peptides by Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Molecules 2023, 28, 7975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, A.A.A.; Hou, Y.; Hassan, F.A.; Al-Sheraji, S.H.; Aleryani, H.; Alanazi, A.; Sang, Y. Antioxidant potential and protective effect of modified sea cucumber peptides against H2O2-induced oxidative damage in vitro HepG2 cells and in vivo zebrafish model. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 266, 131090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Z.Y.; Fan, X.; Zhang, T.; Wang, H.; Ye, K.P. Novel antioxidant peptides from bovine blood: Purification, identification and mechanism of action. Lwt Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 205, 116499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.H.; Zhao, Y.; Xue, W.J.; Xia, Y.T.; Liang, G.Z. Novel antioxidant peptides from soybean protein by employ computational and experimental methods and their mechanisms of oxidative stress resistance. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1318, 139284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.M.; Zhang, Z.; Sheng, Y.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. A systematic review on marine umami peptides: Biological sources, preparation methods, structure-umami relationship, mechanism of action and biological activities. Food Biosci. 2024, 57, 103637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.J.; Dai, F.J.; Chen, C.Y.; Fan, S.L.; Zheng, J.H.; Chau, C.F.; Lin, Y.S.; Chen, C.S. Effects of molecular weight fraction on antioxidation capacity of rice protein hydrolysates. Sci. Rep Uk 2023, 13, 3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Shang, Y.T.; Li, S.T.; Chen, Z.; Xia, J.X.; Tian, Y.L.; Jia, Y.M.; Ma, A.J. Molecular Docking Revealed the Potential Anti-Oxidative Stress Mechanism of the Walnut Polypeptide on HT22 Cells. Foods 2023, 12, 1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.F.; Zou, X.X.; Wang, K.; Liu, H.G.; Hong, H.; Luo, Y.K.; Tan, Y.Q. Antifatigue and microbiome reshaping effects of yak bone collagen peptides on Balb/c mice. Food Biosci. 2023, 52, 102447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.; Shrestha, L.; Bisht, N.; Wu, N.; Ismail, M.; Dorji, T.; Dangol, G.; Long, R. Ethnic and Cultural Diversity amongst Yak Herding Communities in the Asian Highlands. Sustainability 2020, 12, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xue, Y.; Liu, J.; Song, S.; Zhang, L.; Song, Q.; Tian, L.; He, X.; He, S.; Zhu, H. Hydrolysis Process Optimization and Functional Characterization of Yak Skin Gelatin Hydrolysates. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 9105605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.Q.; Wei, L.X.; Xiao, Y.C.; Bi, H.T.; Yang, H.X.; Du, Y.Z. Molecular structural properties of extracted gelatin from Yak skin as analysed based on molecular weight. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, S543–S555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, W.; Shi, H.; Kong, X.; Zhang, L. Identification of novel antifreeze peptides from yak skin gelatin ultrasound-assisted enzymatic hydrolysate. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2024, 111, 107102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.N.; Meng, A.G.; Shi, X.Y.; Fu, Z.P.; Wang, Y.L.; Zhou, J.J.; Zhang, X.W.; Liu, C.Y. Preparation of antioxidant peptides from yak skin gelatin and their protective effect on myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 7961–7973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Liu, J.H.; Ma, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.P.; Yan, E.F.; Zhu, H.J. Isolation and Purification of Antioxidant and ACE-Inhibitory Peptides from Yak Skin. J. Food Process Pres. 2017, 41, e13123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ci, X.M.; Liu, R.; Sun, Y.T.; Rifky, M.; Liu, R.; Jin, Y.; Zhu, Q.M.; Zhang, M.; Wu, T. A novel antioxidant iron-chelating peptide from yak skin: Analysis of the chelating mechanism and digestion stability. J. Sci. Food Agr. 2024, 104, 7907–7916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Xing, L.J.; Fu, Q.Q.; Zhou, G.H.; Zhang, W.G. A Review of Antioxidant Peptides Derived from Meat Muscle and By-Products. Antioxidants 2016, 5, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.J.; Liu, J.X.; Wang, C.; Wen, Z.S.; Zheng, B. The Antioxidant Mechanism of Peptides Extracted from Tuna Protein Revealed Using a Molecular Docking Simulation. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouertani, A.; Chaabouni, I.; Mosbah, A.; Long, J.; Barakat, M.; Mansuelle, P.; Mghirbi, O.; Najjari, A.; Ouzari, H.I.; Masmoudi, A.S.; et al. Two new secreted proteases generate a casein-derived antimicrobial peptide in Bacillus cereus food born isolate leading to bacterial competition in milk. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, P.; Chattopadhyay, A. Nrf2–ARE signaling in cellular protection: Mechanism of action and the regulatory mechanisms. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 3119–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, H.S.; Wang, C.Y.; Diao, J.J. Restoration and preservation effects of mung bean antioxidant peptides on H2O2-induced WRL-68 cells via Keap1-Nrf2 pathway. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 7130–7144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonolo, F.; Folda, A.; Cesaro, L.; Scalcon, V.; Marin, O.; Ferro, S.; Bindoli, A.; Rigobello, M.P. Milk-derived bioactive peptides exhibit antioxidant activity through the Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 64, 103696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.Z.; Shan, Y.W.; Tang, X.; Han, D.; Wu, X.Y.; Wu, H.; Hosseininezhad, M. Effects of enzymatic hydrolysis on physicochemical property and antioxidant activity of mulberry (Morus atropurpurea Roxb.) leaf protein. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 5379–5390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouda, M.; Zu, L.L.; Ma, S.M.; Sheng, L.; Ma, M.H. Influence of bio-active terpenes on the characteristics and functional properties of egg yolk. Food Hydrocolloid 2018, 80, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimipanah, M.; Mahoonak, A.S.; Ghorbani, M.; Tabarestani, H.S.; Meybodi, M.N. Expeller-pressed pomegranate seed (Punica granatum L.) as a protein source for the production of antioxidant peptides. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2022, 28, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serajul, I.; Hongxin, W.; Habtamu, A.; Anwar, N.; Chaoyang, M.; Fu An, W. Degree of hydrolysis, functional and antioxidant properties of protein hydrolysates from Grass Turtle (Chinemys reevesii) as influenced by enzymatic hydrolysis conditions. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 4031–4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, M.; Hosseini, F.S.; Ramezani, R.; Rashidi, L. Optimized Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Olive Pomace Proteins Using Response Surface Methodology. Appl. Food Biotechnol. 2022, 9, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.W.; Feng, M.Q.; Sun, J. Novel antioxidant peptides in fermented pork sausage: Purification, characterization, and cytoprotective functions on Caco-2 cells. Food Chem. 2023, 426, 136566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Han, L.; Wang, Y.R.; Yu, Q.L. Appropriate ultrasonic treatment improves the production of antioxidant peptides by modifying gelatin extracted from yak skin. Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 2022, 57, 5897–5908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, C.; Haslam, N.J.; Pollastri, G.; Shields, D.C. Towards the Improved Discovery and Design of Functional Peptides: Common Features of Diverse Classes Permit Generalized Prediction of Bioactivity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.Z.; Su, L.J.; Huo, S.T.; Yu, Z.P.; Li, J.R.; Liu, J.B. Virtual screening, molecular docking and identification of umami peptides derived from Oncorhynchus mykiss. Food Sci. Hum. Well 2023, 12, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.Z.; Xu, G.; Yu, Z.P.; Li, J.R.; Liu, J.B. Identification of nut protein-derived peptides against SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and main protease. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 138, 104937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Kapoor, P.; Chaudhary, K.; Gautam, A.; Kumar, R.; Raghava, G.P.S.; Discovery, O.S.D. In silico approach for predicting toxicity of peptides and proteins. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.H.; Dou, L.; Zhang, J.; Su, R.A.; Corazzin, M.; Sun, L.A.; Zhao, L.H.; Jin, Y.; Su, L. Exploring the antioxidant stability of sheep bone protein hydrolysate-identification and molecular docking. Lwt Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 192, 115682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.T.; Huang, R.L.; Sedykh, A.; Wang, W.Y.; Xia, M.H.; Zhu, H. Mechanism Profiling of Hepatotoxicity Caused by Oxidative Stress Using Antioxidant Response Element Reporter Gene Assay Models and Big Data. Environ. Health Persp 2016, 124, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, J.; Kulkarni, D.; Kadu, P.; Pandya, A.; Kale, P. Use of in silico tools for screening buffers to overcome physical instability of abatacept. Transpl. Immunol. 2022, 71, 101551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Li, L.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Four antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolysate of red stingray (Dasyatis akajei) cartilages: Isolation, identification, and in vitro activity evaluation. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiva-Portilla, D.; Martínez, R.; Bernal, C. Valorization of shrimp (Heterocarpus reedi) processing waste via enzymatic hydrolysis: Protein extractions, hydrolysates and antioxidant peptide fractions. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2023, 48, 102625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeynayake, R.; Zhang, S.T.; Yang, W.Z.; Chen, L.Y. Development of antioxidant peptides from brewers’ spent grain proteins. Lwt Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 158, 113162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, Z.Y.; Zhou, Y.J.; Xiao, Q.; Wang, H.Y.; Peng, Y. Emerging substrate proteins of kelch-like ECH associated protein 1 (Keap1) and potential challenges for the development of small-molecule inhibitors of the Keap1-nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) protein–protein interaction. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 7986–8002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Yu, D.; Lin, J.; Hu, Y.; Peng, N.; Zhao, S. Structural characterization, HepG2 cell cytoprotective ability, and antioxidant mechanism of novel antioxidant peptides identified from black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens L.). Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, K.I.; Padmanabhan, B.; Kobayashi, A.; Shang, C.; Hirotsu, Y.; Yokoyama, S.; Yamamoto, M. Different electrostatic Potentials define ETGE and DLG motifs as hinge and latch in oxidative stress response. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 27, 7511–7521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzaei, M.; Mirdamadi, S.; Ehsani, M.R.; Aminlari, M. Production of antioxidant and ACE-inhibitory peptides from protein hydrolysates: Purification and molecular docking. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 26, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, M.; Lamont, D.J.; Beattie, K.A.; Hayes, J.D. Keap1 perceives stress via three sensors for the endogenous signaling molecules nitric oxide, zinc, and alkenals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2010, 107, 18838–18843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.D.; He, Y.N.; Wu, Q.L.; Zhang, Y.M.; Li, F.; Jiao, D.Q.; Liu, X.L.; Wang, C.H. Novel Antioxidant Peptides Derived from Feather Keratin Alleviate H2O2-Induced Oxidative Damage in HepG2 Cells via Keap1/Nrf2 Pathway. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 20062–20072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liang, J.; Xiao, G.; Vargas-De-La-Cruz, C.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Xiao, J.; Wang, Q. Active sites of peptides Asp-Asp-Asp-Tyr and Asp-Tyr-Asp-Asp protect against cellular oxidative stress. Food Chem. 2022, 366, 130626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Gu, F.; Liu, Y.; Yang, M.; Wu, X.Z.; Sheng, J.; Tian, Y. Preparation of antioxidant peptides from Moringa oleifera leaves and their protection against oxidative damage in HepG2 cells. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1062671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.T.; Zhang, J.X.; Zhang, H.H.; Duan, Y.Q.; Ma, H.L. Plant protein-derived antioxidant peptides: Isolation, identification, mechanism of action and application in food systems: A review. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2020, 105, 308–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollati, C.; Cruz-Chamorro, I.; Aiello, G.; Li, J.Q.; Bartolomei, M.; Santos-Sánchez, G.; Ranaldi, G.; Ferruzza, S.; Sambuy, Y.; Arnoldi, A.; et al. Investigation of the intestinal trans-epithelial transport and antioxidant activity of two hempseed peptides WVSPLAGRT (H2) and IGFLIIWV (H3). Food Res. Int. 2022, 152, 110720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, A.; Sekido, N.; Akahoshi, T.; Wada, T.; Mukaida, N.; Matsushima, K. Essential involvement of interleukin-8 (IL-8) in acute inflammation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1994, 56, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.E.; Liang, Z.Q.; Tian, S.F.; Liu, L.; Wang, S. Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) modification of structural and functional properties of whey protein isolate. Food Res. Int. 2022, 158, 111534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.Y.; Fan, W.L.; Xu, Y. Identification of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory and antioxidant peptides derived from Pixian broad bean paste. Lwt Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 151, 112221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, Z.; Peighambardoust, S.H.; Hesari, J.; Akbari-Adergani, B.; Andreu, D. Antioxidant, anticancer and ACE-inhibitory activities of bioactive peptides from wheat germ protein hydrolysates. Food Biosci. 2019, 32, 100450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Pradhan, R.; Manickavasagan, A.; Thimmanagari, M.; Saha, D.; Singh, S.S.; Dutta, A. Production of antioxidative protein hydrolysates from corn distillers solubles: Process optimization, antioxidant activity evaluation, and peptide analysis. Ind. Crop Prod. 2022, 184, 115107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Hua, Y.; Zhou, C.Y.; Xiong, Y.Z.; Pan, D.D.; Liu, Z.; Dang, Y.L. Umami peptides screened based on peptidomics and virtual screening from. Food Chem. 2022, 394, 133504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Guo, S.; Wang, K.; Kang, J. The interaction of peptide inhibitors and Aβ protein: Binding mode analysis, inhibition of the formation of Aβ aggregates, and then exert neuroprotective effects. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1139418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


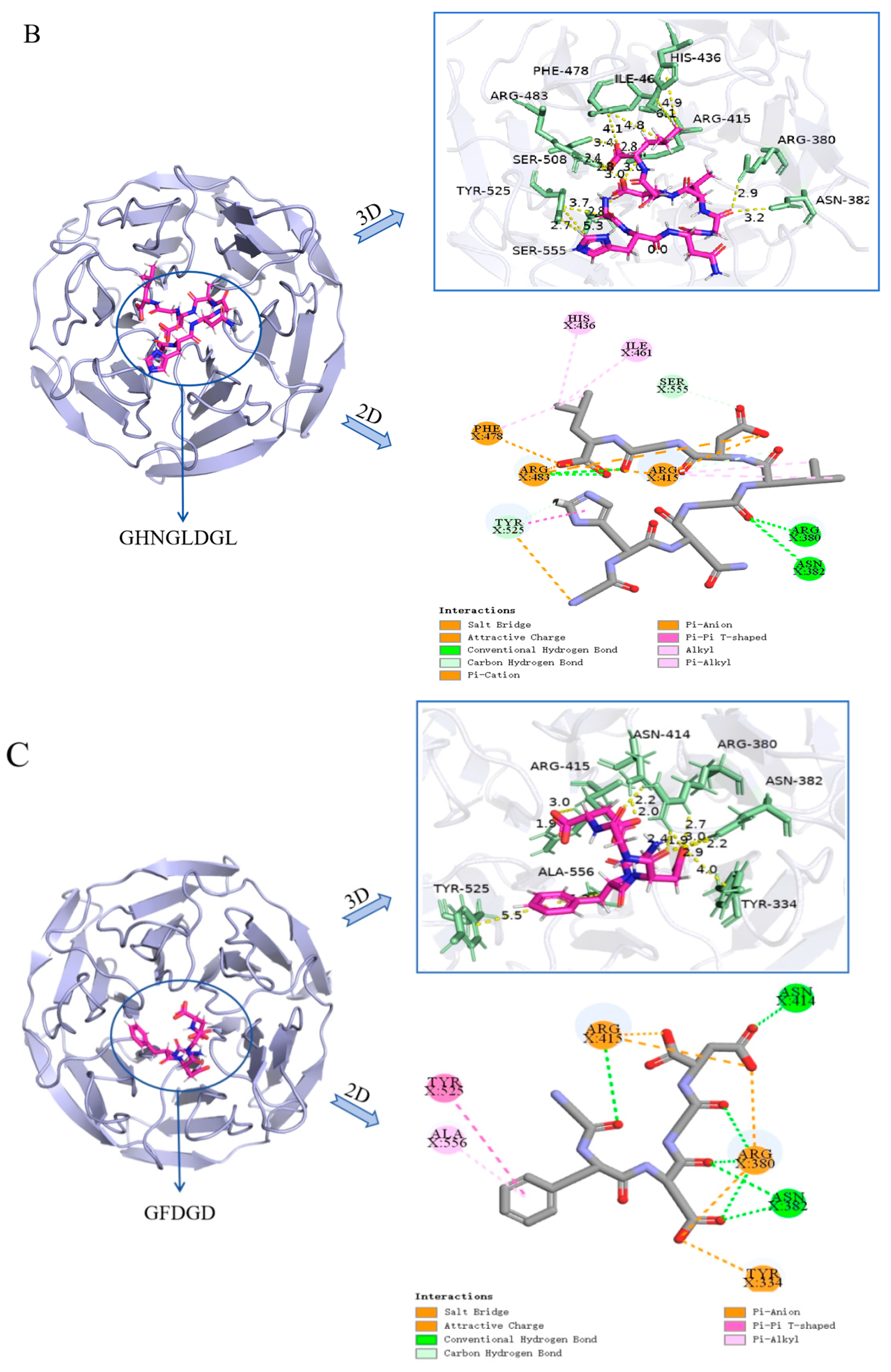

| NO. | Sequence | Length | Mass | Score | Peptide Ranker | CDockerenergy (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | FGFDGDF | 7 | 803.31262 | 187.48 | 0.93535 | −141.445 |
| 2 | GHNGLDGL | 8 | 781.37187 | 114.54 | 0.534861 | −136.723 |
| 3 | GFDGDF | 6 | 656.24421 | 148.12 | 0.913215 | −119.541 |
| 4 | FDGDF | 5 | 599.22274 | 78.156 | 0.94884 | −116.697 |
| 5 | GFDGD | 5 | 509.17579 | 118.96 | 0.637708 | −115.582 |
| 6 | GPSGPPGPDGN | 11 | 950.40937 | 206.38 | 0.839787 | −90.731 |
| 7 | FEL | 3 | 407.20564 | 18.31 | 0.566207 | −84.218 |
| 8 | GPAGPQGPR | 9 | 835.43005 | 183.43 | 0.846699 | −83.766 |
| 9 | GFE | 3 | 351.14304 | 12.647 | 0.720069 | −83.496 |
| 10 | GPAGPAGRPG | 10 | 835.43005 | 131.04 | 0.873123 | −82.544 |
| 11 | FGE | 3 | 351.14304 | 65.815 | 0.675338 | −82.025 |
| 12 | GEGGPQGPR | 9 | 853.40423 | 142.64 | 0.536924 | −81.513 |
| 13 | WDT | 3 | 420.1645 | 25.115 | 0.593031 | −81.295 |
| 14 | DML | 3 | 377.16206 | 25.115 | 0.667515 | −80.952 |
| 15 | MDL | 3 | 377.16206 | 47.364 | 0.679551 | −78.408 |
| 16 | WAD | 3 | 390.15393 | 20.412 | 0.721933 | −77.465 |
| 17 | GPAGPAGRP | 9 | 778.40859 | 155.73 | 0.846699 | −71.902 |
| 18 | PGPAGPAGRP | 10 | 875.46135 | 107.32 | 0.871669 | −71.298 |
| 19 | DWP | 3 | 416.16958 | 20.675 | 0.948036 | −69.084 |
| 20 | LMGPR | 5 | 572.31045 | 85.518 | 0.767987 | −68.852 |
| 21 | PAGPAGPR | 8 | 721.38712 | 109.7 | 0.813961 | −68.468 |
| 22 | DPC | 3 | 333.09946 | 5.9869 | 0.819965 | −68.046 |
| 23 | FSGLD | 5 | 537.24348 | 41.717 | 0.692962 | −67.018 |
| 24 | FCK | 3 | 396.18313 | 11.715 | 0.907916 | −62.174 |
| 25 | GPK | 3 | 300.17976 | 40.566 | 0.567438 | −45.198 |
| 26 | PQPPQ | 5 | 565.28601 | 104.03 | 0.631168 | −42.868 |
| 27 | PAGRP | 5 | 496.27578 | 91.004 | 0.74837 | −42.160 |
| 28 | PGS | 3 | 259.11682 | 11.355 | 0.526816 | −38.120 |
| 29 | PGR | 3 | 328.1859 | 32.689 | 0.839926 | −34.945 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, Y.; Zhang, N.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, E.; Kong, Y.; Sui, W.; Wu, T.; Zhang, M. Identification and Screening of Novel Antioxidant Peptides from Yak Skin and Their Protective Effect on H2O2-Induced HepG2 Cells Oxidation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5976. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26135976
Jin Y, Zhang N, Huang Y, Zhang Z, Jin E, Kong Y, Sui W, Wu T, Zhang M. Identification and Screening of Novel Antioxidant Peptides from Yak Skin and Their Protective Effect on H2O2-Induced HepG2 Cells Oxidation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):5976. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26135976
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Yan, Nan Zhang, Yurong Huang, Ziyao Zhang, Enhui Jin, Yu Kong, Wenjie Sui, Tao Wu, and Min Zhang. 2025. "Identification and Screening of Novel Antioxidant Peptides from Yak Skin and Their Protective Effect on H2O2-Induced HepG2 Cells Oxidation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 5976. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26135976
APA StyleJin, Y., Zhang, N., Huang, Y., Zhang, Z., Jin, E., Kong, Y., Sui, W., Wu, T., & Zhang, M. (2025). Identification and Screening of Novel Antioxidant Peptides from Yak Skin and Their Protective Effect on H2O2-Induced HepG2 Cells Oxidation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 5976. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26135976








