Functional Analysis of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway Inhibitor, Gedatolisib, Plus Fulvestrant with and Without Palbociclib in Breast Cancer Models
Abstract
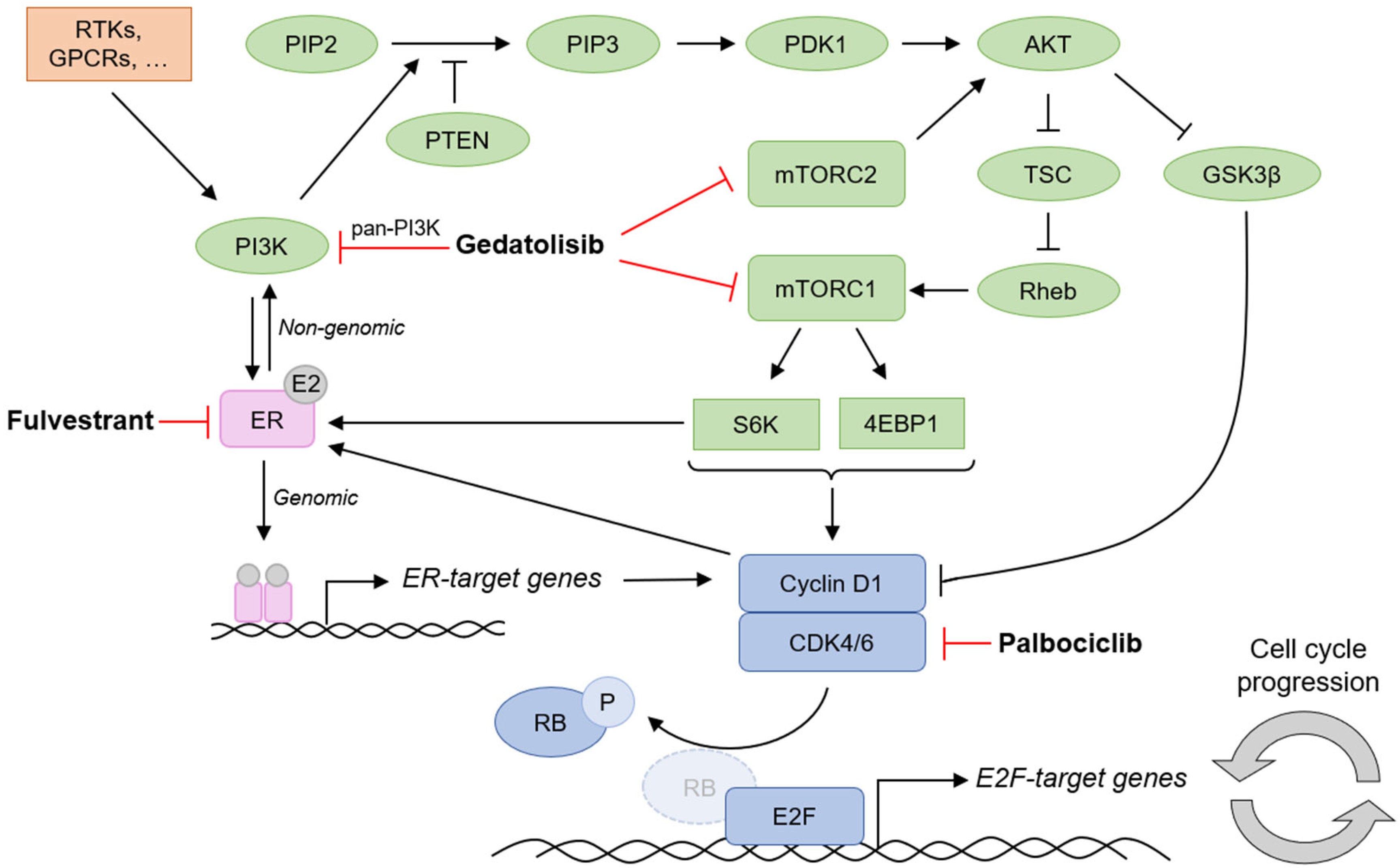
1. Introduction
2. Results
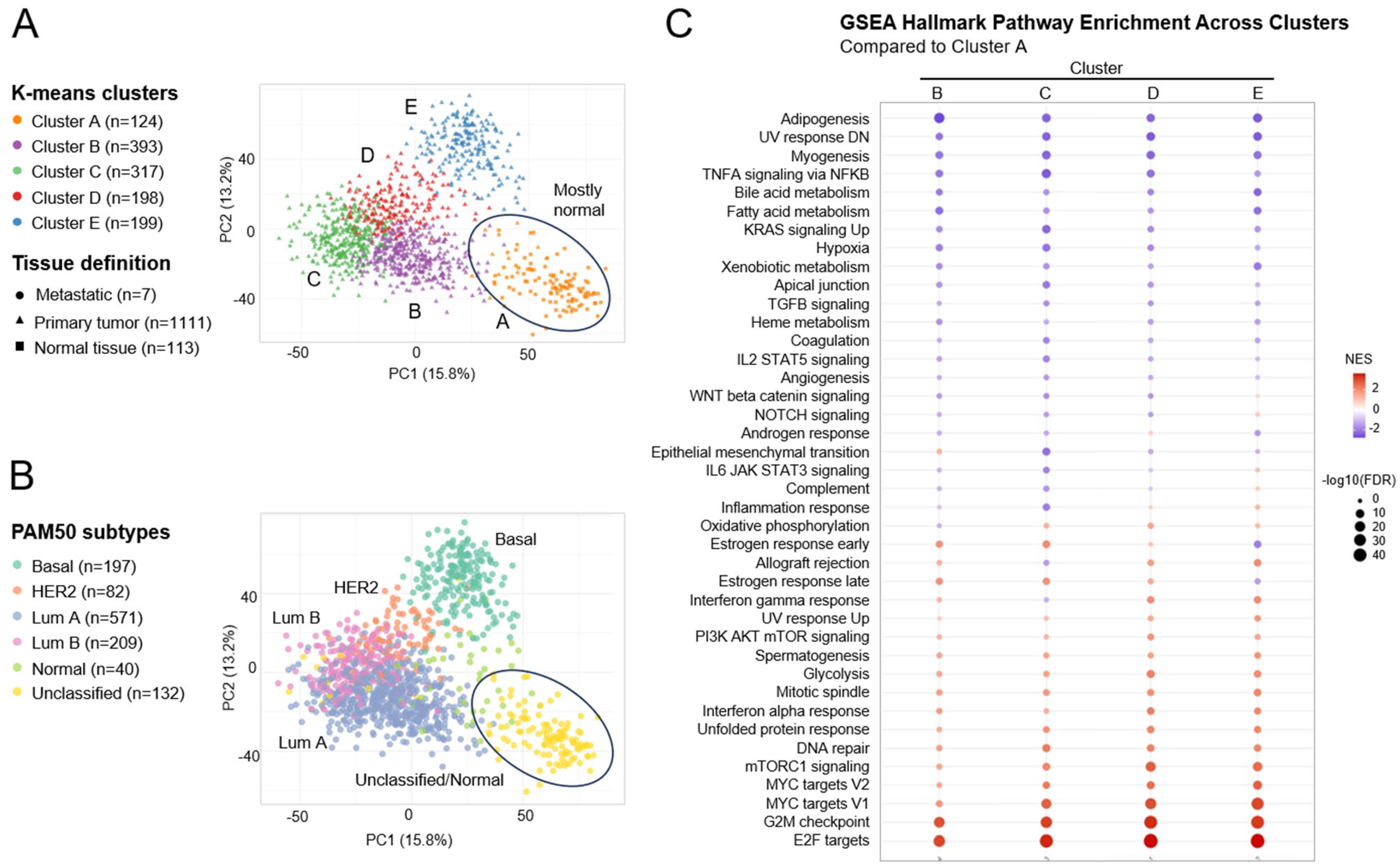
2.1. Concomitant Dysregulation of PAM, ER, and Cell Cycle-Related Pathways in Breast Cancer Patients
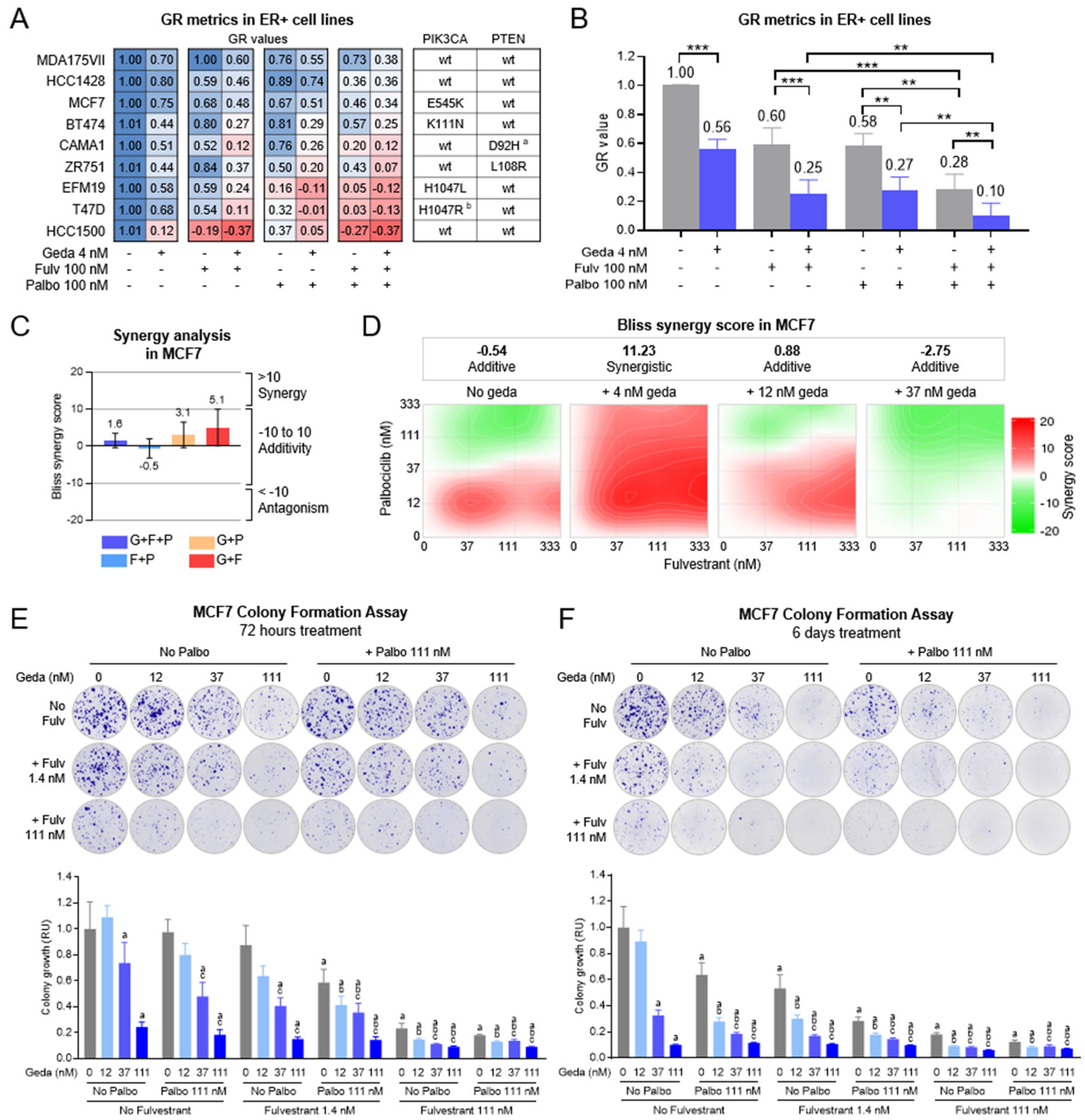
2.2. Growth Inhibitory Effects of Gedatolisib Combined with Fulvestrant and/or Palbociclib in BC Cell Lines
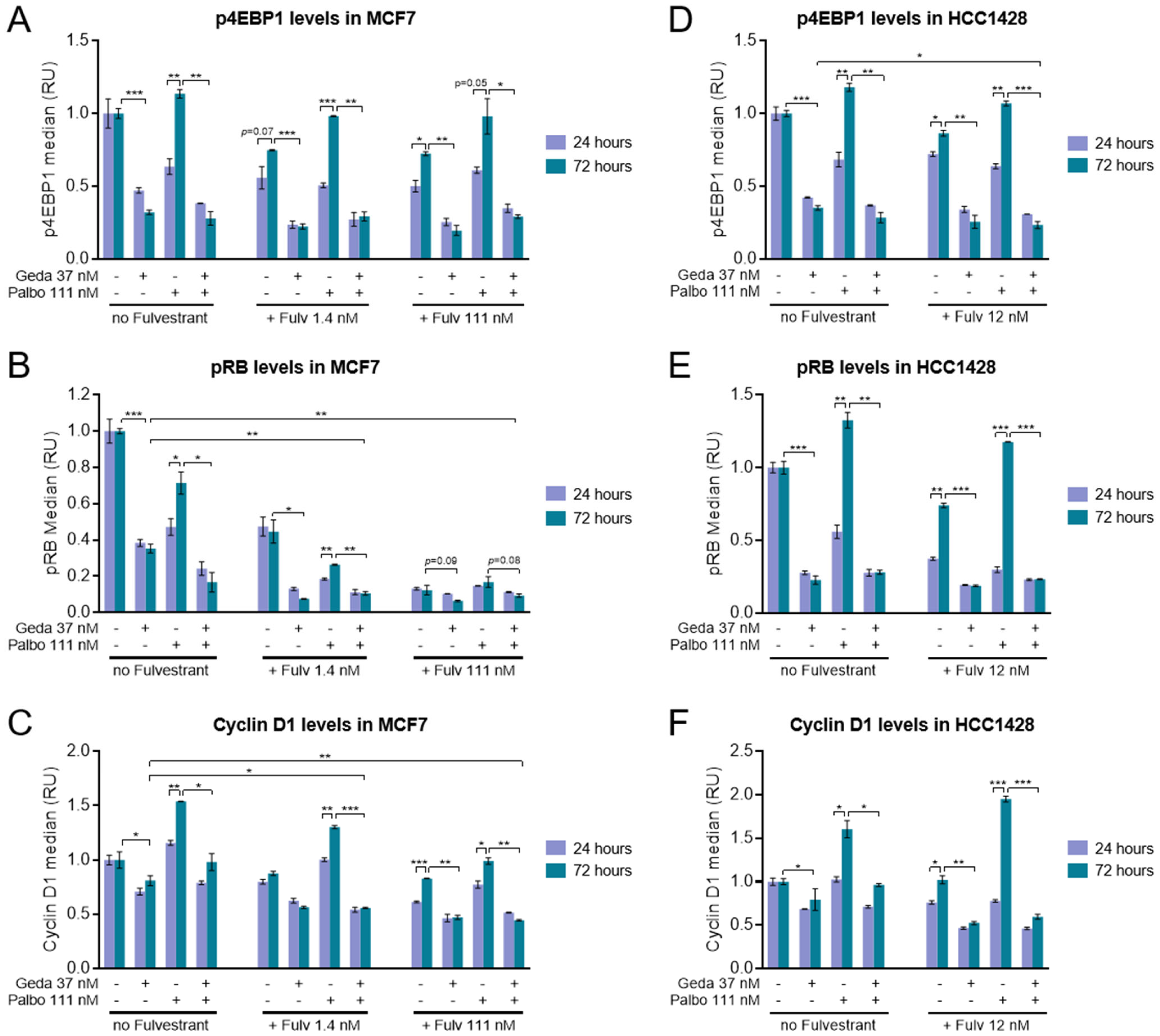
2.3. Effects of the Gedatolisib/Fulvestrant/Palbociclib Triplet on PAM and CDK Pathway Activity
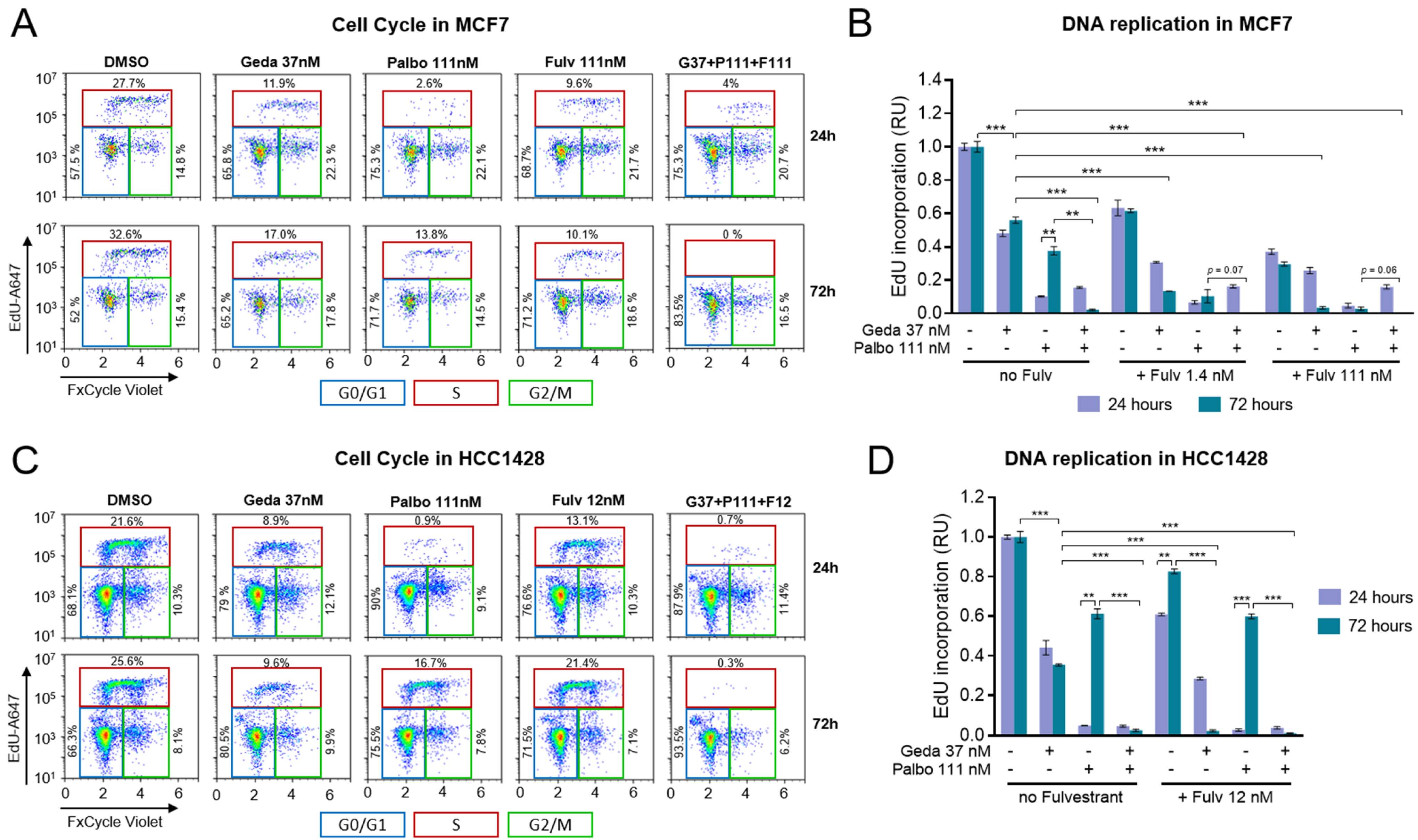
2.4. Effects of the Drug Triplet on Cell Cycling
2.5. Effects of the Drug Triplet on Cell Death and Apoptosis
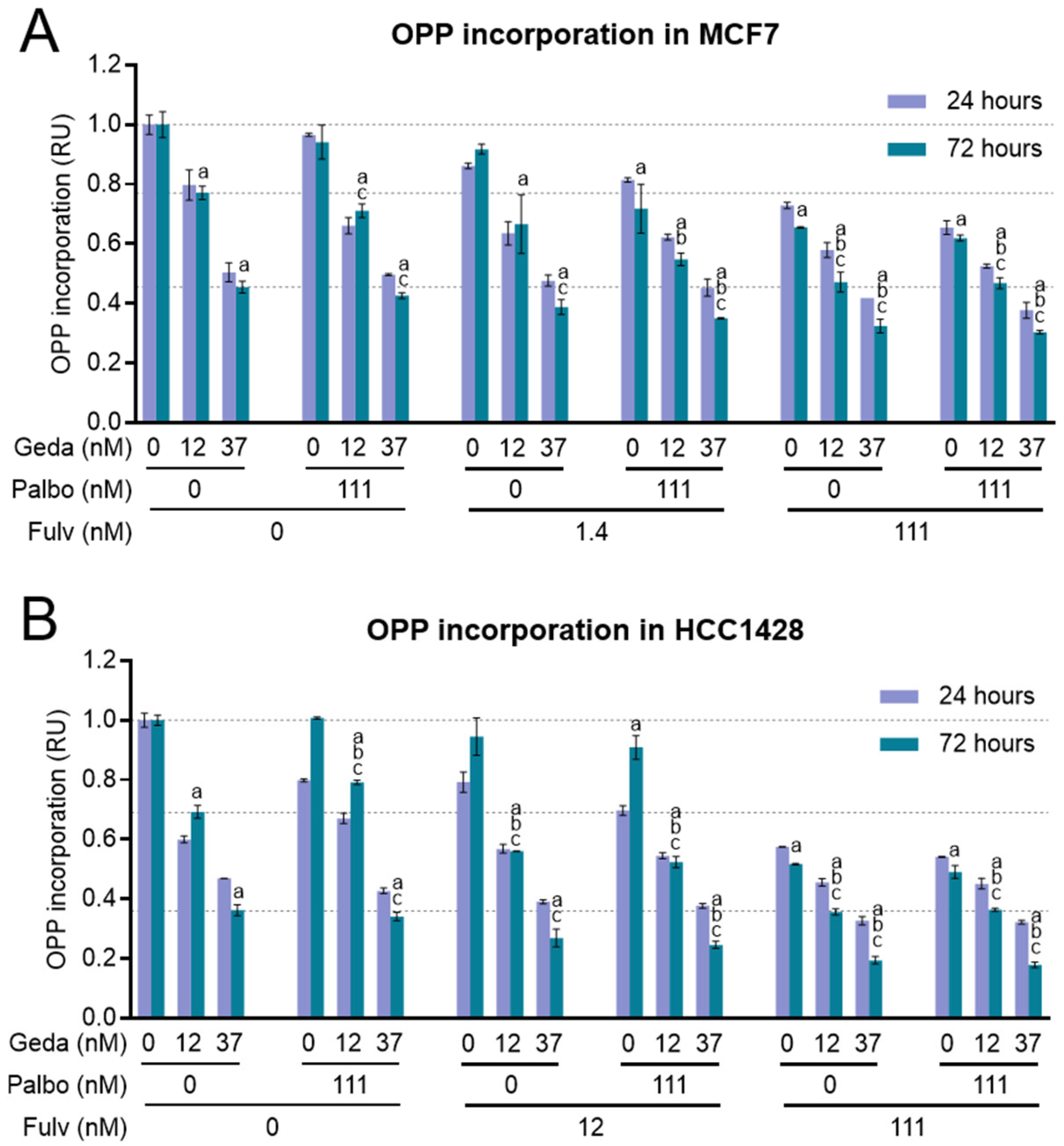
2.6. Effects of the Drug Triplet on Protein Synthesis
2.7. Effects of the Drug Triplet on Glucose Metabolism
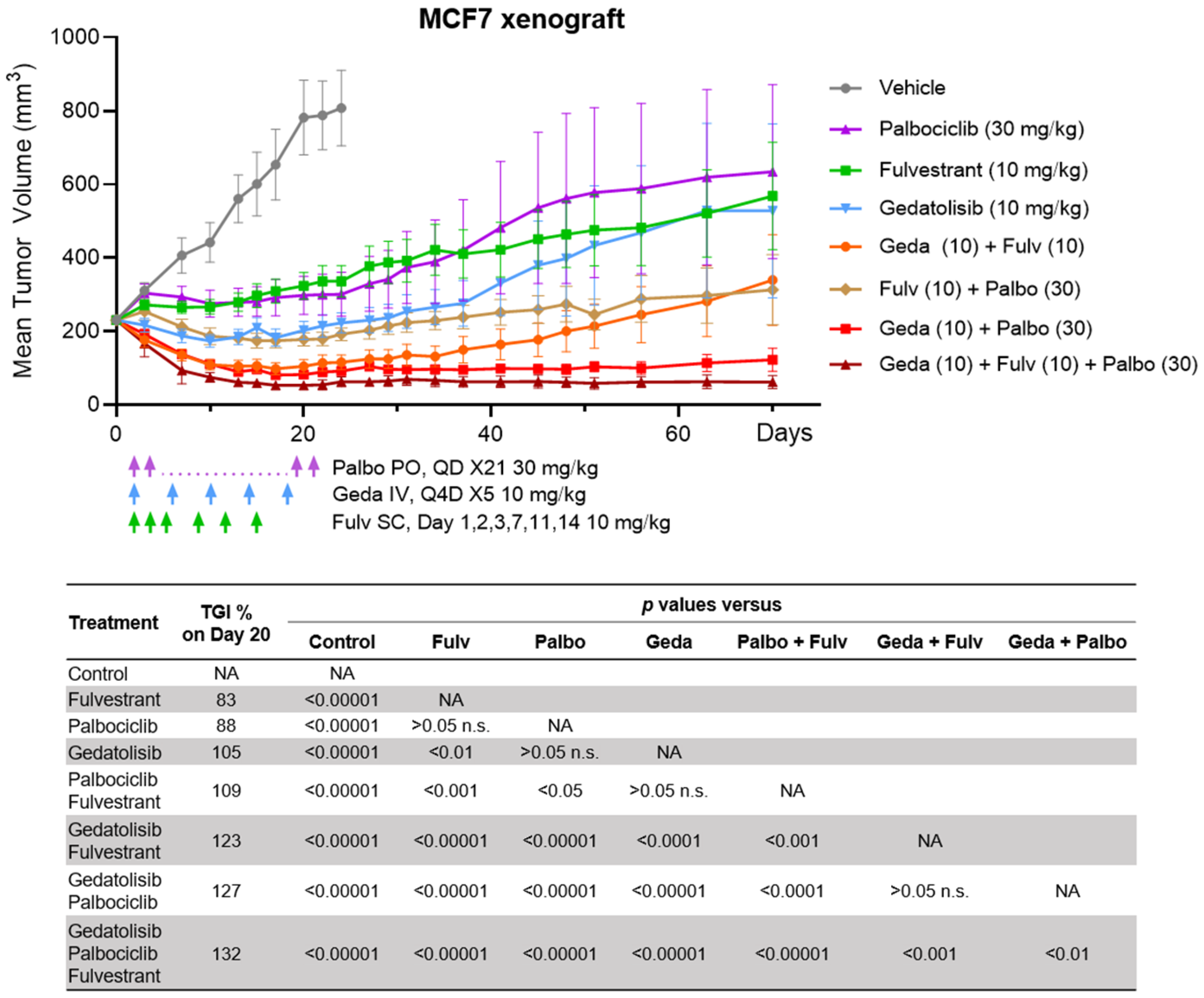
2.8. Efficacy of the Drug Triplet in a Mouse Model
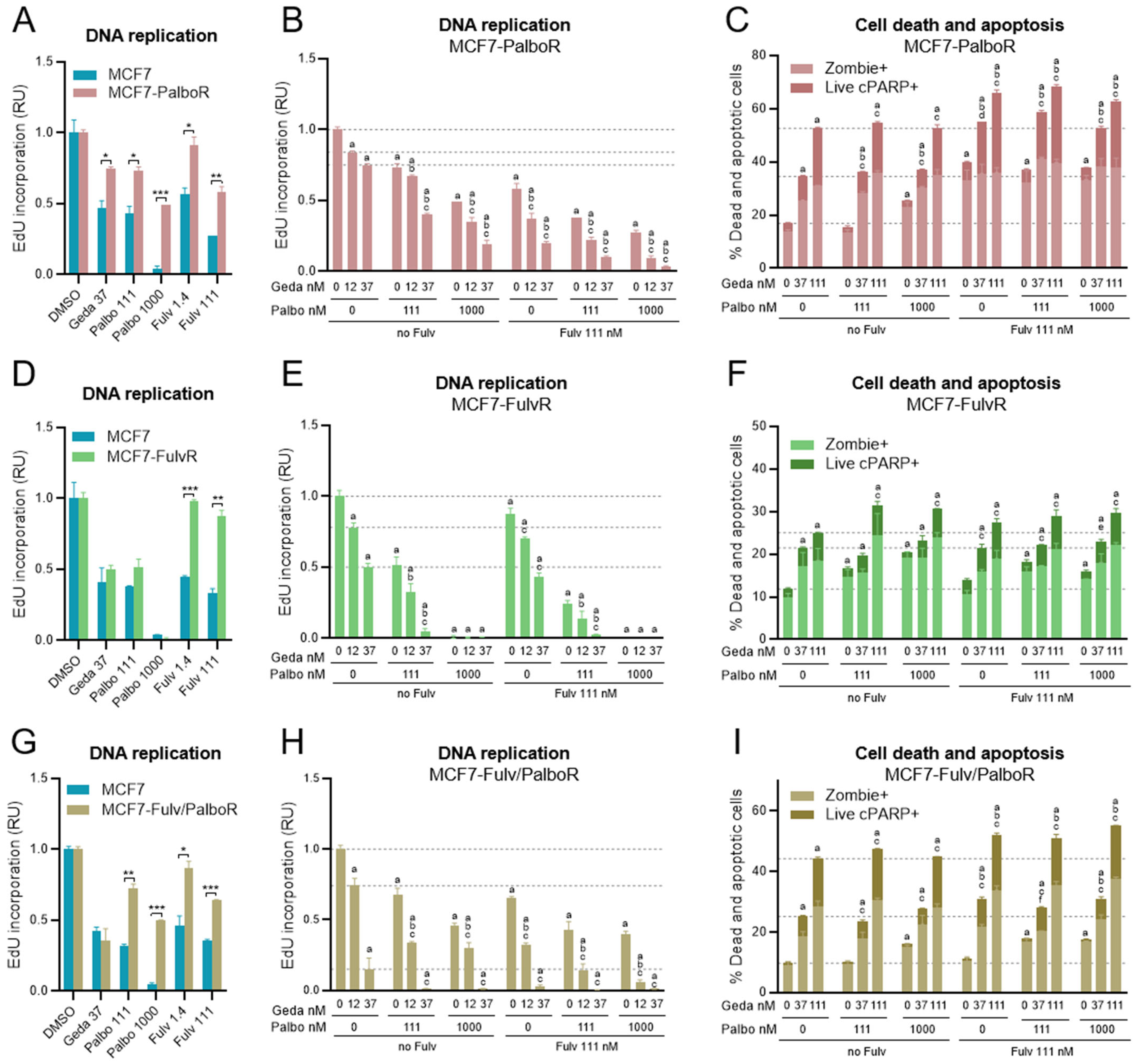
2.9. Effects of the Drug Triplet on BC Cells Adapted to Fulvestrant and/or Palbociclib
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bioinformatics Analyses
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. In Vitro Treatments with Inhibitors
4.4. Cell Viability Assay
4.5. Proliferation-Normalized Inhibition of Growth Rate (GR) Assays
4.6. Drug Synergy Analysis
4.7. Flow Cytometry
4.8. Glucose Uptake and Lactate
4.9. Colony Formation Assay
4.10. Quantitative PCR
4.11. Animal Studies
4.12. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 4EBP1 | eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1 |
| ABC | advanced breast cancer |
| BC | breast cancer |
| cCasp3 | cleaved caspase 3 |
| cPARP | cleaved PARP |
| CCLE | Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia |
| CDK | cyclin-dependent kinase |
| cPARP | cleaved PARP |
| EdU | 5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine |
| ER | estrogen receptor |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| Fulv | fulvestrant |
| FulvR | fulvestrant-adapted cells |
| Fulv/PalboR | fulvestrant/palbociclib-adapted cells |
| GDC | genomic data commons |
| Geda | gedatolisib |
| GPCRs | G protein-coupled receptors |
| GR | growth rate |
| GSEA | gene set enrichment analysis |
| HER2 | human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 |
| HR | hormone receptor |
| IC50 | half-maximal inhibitory concentration |
| IV | intravenous(ly) |
| Lum A | luminal A |
| Lum B | luminal B |
| mTOR | mechanistic target of rapamycin |
| mTORC1 | mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 |
| mTORC2 | mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 2 |
| Mut | driver mutation |
| NES | normalized enrichment scores |
| NIR | near-infrared |
| OPP | O-propargyl-puromycin |
| Palbo | palbociclib |
| PalboR | palbociclib-adapted cells |
| Palbo/FulvR | palbociclib/fulvestrant-adapted cells |
| PAM | PI3K-AKT-mTOR |
| PAM50 | prediction analysis of microarray 50-gene classifier |
| PARP | poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase |
| PC | principal component |
| PCA | principal component analysis |
| PI3K | phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
| PIP2 | phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate |
| PIP3 | phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate |
| PO | oral |
| PTEN | phosphatase and tensin homolog |
| Q4D | once every 4 days |
| QD | once a day |
| RP | retinoblastoma |
| RPS6 | ribosomal protein R6 |
| RTK | receptor tyrosine kinase |
| RU | relative units |
| SC | subcutaneous |
| SCID | severe-combined-immunodeficient |
| SD | standard deviation |
| SEM | standard error of mean |
| SERD | selective estrogen receptor degrader |
| SSC | side scatter |
| TGI | tumor growth inhibition |
| wt | wild type |
References
- Glaviano, A.; Foo, A.S.C.; Lam, H.Y.; Yap, K.C.H.; Jacot, W.; Jones, R.H.; Eng, H.; Nair, M.G.; Makvandi, P.; Geoerger, B.; et al. PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling transduction pathway and targeted therapies in cancer. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoxhaj, G.; Manning, B.D. The PI3K-AKT network at the interface of oncogenic signalling and cancer metabolism. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, B.D.; Toker, A. AKT/PKB Signaling: Navigating the Network. Cell 2017, 169, 381–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millis, S.Z.; Ikeda, S.; Reddy, S.; Gatalica, Z.; Kurzrock, R. Landscape of Phosphatidylinositol-3-Kinase Pathway Alterations Across 19 784 Diverse Solid Tumors. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 1565–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnaghi, R.; Antonarelli, G.; Battaiotto, E.; Castellano, G.; Guidi, L.; Izzo, D.; Zagami, P.; Trapani, D.; Curigliano, G. An update on promising and emerging protein kinase B/AKT inhibitors for breast cancer. Expert. Opin. Pharmacother. 2025, 26, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castel, P.; Toska, E.; Engelman, J.A.; Scaltriti, M. The present and future of PI3K inhibitors for cancer therapy. Nat. Cancer 2021, 2, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, P.; Ramisetty, S.; Nair, M.; Kulkarni, P.; Horne, D.; Salgia, R.; Singhal, S.S. Strategic advancements in targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway for Breast cancer therapy. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2025, 236, 116850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, C.; Wei, Y.; Meng, W.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X. PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibitors for hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2025, 132, 102861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasan, N.; Cantley, L.C. At a crossroads: How to translate the roles of PI3K in oncogenic and metabolic signalling into improvements in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 19, 471–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.L.; Ditzel, H.J. Drugging the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway in ER+ Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.S.; Makhlin, I.; DeMichele, A. Setting the Pick: Can PI3K Inhibitors Circumvent CDK4/6 Inhibitor Resistance? Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 371–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yu, W.; Kang, L. Mechanisms of endocrine resistance in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1448687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaviano, A.; Wander, S.A.; Baird, R.D.; Yap, K.C.; Lam, H.Y.; Toi, M.; Carbone, D.; Geoerger, B.; Serra, V.; Jones, R.H.; et al. Mechanisms of sensitivity and resistance to CDK4/CDK6 inhibitors in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer treatment. Drug Resist. Updates 2024, 76, 101103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, S.; Bergholz, J.S.; Zhao, J.J. Targeting CDK4 and CDK6 in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2022, 22, 356–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.C.E.; Vasilevski, N.; Serra, V.; Rodon, J.; Eichhorn, P.J.A. Mechanisms of Resistance to PI3K Inhibitors in Cancer: Adaptive Responses, Drug Tolerance and Cellular Plasticity. Cancers 2021, 13, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, T.W.; Balko, J.M.; Fox, E.M.; Ghazoui, Z.; Dunbier, A.; Anderson, H.; Dowsett, M.; Jiang, A.; Smith, R.A.; Maira, S.M.; et al. ERalpha-dependent E2F transcription can mediate resistance to estrogen deprivation in human breast cancer. Cancer Discov. 2011, 1, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pancholi, S.; Ribas, R.; Simigdala, N.; Schuster, E.; Nikitorowicz-Buniak, J.; Ressa, A.; Gao, Q.; Leal, M.F.; Bhamra, A.; Thornhill, A.; et al. Tumour kinome re-wiring governs resistance to palbociclib in oestrogen receptor positive breast cancers, highlighting new therapeutic modalities. Oncogene 2020, 39, 4781–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, V.M.; Bhola, N.E.; Bauer, J.A.; Formisano, L.; Lee, K.M.; Hutchinson, K.E.; Witkiewicz, A.K.; Moore, P.D.; Estrada, M.V.; Sanchez, V.; et al. Kinome-Wide RNA Interference Screen Reveals a Role for PDK1 in Acquired Resistance to CDK4/6 Inhibition in ER-Positive Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2488–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, T.W.; Hennessy, B.T.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Fox, E.M.; Mills, G.B.; Chen, H.; Higham, C.; Garcia-Echeverria, C.; Shyr, Y.; Arteaga, C.L. Hyperactivation of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase promotes escape from hormone dependence in estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 2406–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, A.; Li, Z.; Bergamaschi, A.; Ellis, H.; Toska, E.; Prat, A.; Tao, J.J.; Spratt, D.E.; Viola-Villegas, N.T.; Castel, P.; et al. PI3K inhibition results in enhanced estrogen receptor function and dependence in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 283ra251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vora, S.R.; Juric, D.; Kim, N.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Huynh, T.; Costa, C.; Lockerman, E.L.; Pollack, S.F.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; et al. CDK 4/6 inhibitors sensitize PIK3CA mutant breast cancer to PI3K inhibitors. Cancer Cell 2014, 26, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Abreu, M.T.; Palafox, M.; Asghar, U.; Rivas, M.A.; Cutts, R.J.; Garcia-Murillas, I.; Pearson, A.; Guzman, M.; Rodriguez, O.; Grueso, J.; et al. Early Adaptation and Acquired Resistance to CDK4/6 Inhibition in Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2301–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopcroft, L.; Wigmore, E.M.; Williamson, S.C.; Ros, S.; Eberlein, C.; Moss, J.I.; Urosevic, J.; Carnevalli, L.S.; Talbot, S.; Bradshaw, L.; et al. Combining the AKT inhibitor capivasertib and SERD fulvestrant is effective in palbociclib-resistant ER+ breast cancer preclinical models. NPJ Breast Cancer 2023, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, L.; Alves, C.L.; Terp, M.G.; Tuttolomondo, M.; Portman, N.; Ehmsen, S.; Johansen, L.E.; Bak, M.; Lim, E.; Ditzel, H.J. Triple combination targeting PI3K, ER, and CDK4/6 inhibits growth of ER-positive breast cancer resistant to fulvestrant and CDK4/6 or PI3K inhibitor. Cancer Commun. 2023, 43, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaloglou, C.; Crafter, C.; Siersbaek, R.; Delpuech, O.; Curwen, J.O.; Carnevalli, L.S.; Staniszewska, A.D.; Polanska, U.M.; Cheraghchi-Bashi, A.; Lawson, M.; et al. Combined Inhibition of mTOR and CDK4/6 Is Required for Optimal Blockade of E2F Function and Long-term Growth Inhibition in Estrogen Receptor-positive Breast Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 908–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, N.A.; McDermott, M.S.J.; Conklin, D.; Luo, T.; Ayala, R.; Salgar, S.; Chau, K.; DiTomaso, E.; Babbar, N.; Su, F.; et al. Targeting activated PI3K/mTOR signaling overcomes acquired resistance to CDK4/6-based therapies in preclinical models of hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2020, 22, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, M.J.; Perrone, M.C.; Riggio, M.; Palafox, M.; Salinas, V.; Elia, A.; Salgueiro, N.D.; Werbach, A.E.; Marks, M.P.; Kauffman, M.A.; et al. Targeting mTOR to overcome resistance to hormone and CDK4/6 inhibitors in ER-positive breast cancer models. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Shi, Q.; Jin, L.; Li, S.; Zhu, M.; Wang, Q.; Wong, L.L.; Yang, W.; et al. Overexpressed Cyclin D1 and CDK4 proteins are responsible for the resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitor in breast cancer that can be reversed by PI3K/mTOR inhibitors. Sci. China Life Sci. 2023, 66, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baselga, J.; Campone, M.; Piccart, M.; Burris, H.A., 3rd; Rugo, H.S.; Sahmoud, T.; Noguchi, S.; Gnant, M.; Pritchard, K.I.; Lebrun, F.; et al. Everolimus in postmenopausal hormone-receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, F.; Ciruelos, E.; Rubovszky, G.; Campone, M.; Loibl, S.; Rugo, H.S.; Iwata, H.; Conte, P.; Mayer, I.A.; Kaufman, B.; et al. Alpelisib for PIK3CA-Mutated, Hormone Receptor-Positive Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1929–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, N.C.; Oliveira, M.; Howell, S.J.; Dalenc, F.; Cortes, J.; Gomez Moreno, H.L.; Hu, X.; Jhaveri, K.; Krivorotko, P.; Loibl, S.; et al. Capivasertib in Hormone Receptor-Positive Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 2058–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardia, A.; Hurvitz, S.A.; DeMichele, A.; Clark, A.S.; Zelnak, A.; Yardley, D.A.; Karuturi, M.; Sanft, T.; Blau, S.; Hart, L.; et al. Phase I/II Trial of Exemestane, Ribociclib, and Everolimus in Women with HR(+)/HER2(-) Advanced Breast Cancer after Progression on CDK4/6 Inhibitors (TRINITI-1). Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 4177–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, J.; Lim, J.S.J.; Macpherson, I.R.; Armstrong, A.C.; Ring, A.; Okines, A.F.C.; Cutts, R.J.; Herrera-Abreu, M.T.; Garcia-Murillas, I.; Pearson, A.; et al. Triplet Therapy with Palbociclib, Taselisib, and Fulvestrant in PIK3CA-Mutant Breast Cancer and Doublet Palbociclib and Taselisib in Pathway-Mutant Solid Cancers. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 92–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolaney, S.M.; Im, Y.H.; Calvo, E.; Lu, Y.S.; Hamilton, E.; Forero-Torres, A.; Bachelot, T.; Maur, M.; Fasolo, A.; Tiedt, R.; et al. Phase Ib Study of Ribociclib plus Fulvestrant and Ribociclib plus Fulvestrant plus PI3K Inhibitor (Alpelisib or Buparlisib) for HR(+) Advanced Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, N.C.; Im, S.A.; Saura, C.; Juric, D.; Loibl, S.; Kalinsky, K.; Schmid, P.; Loi, S.; Sunpaweravong, P.; Musolino, A.; et al. Inavolisib-Based Therapy in PIK3CA-Mutated Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 1584–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallon, R.; Feldberg, L.R.; Lucas, J.; Chaudhary, I.; Dehnhardt, C.; Santos, E.D.; Chen, Z.; dos Santos, O.; Ayral-Kaloustian, S.; Venkatesan, A.; et al. Antitumor efficacy of PKI-587, a highly potent dual PI3K/mTOR kinase inhibitor. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 3193–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, A.M.; Dehnhardt, C.M.; Delos Santos, E.; Chen, Z.; Dos Santos, O.; Ayral-Kaloustian, S.; Khafizova, G.; Brooijmans, N.; Mallon, R.; Hollander, I.; et al. Bis(morpholino-1,3,5-triazine) derivatives: Potent adenosine 5′-triphosphate competitive phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors: Discovery of compound 26 (PKI-587), a highly efficacious dual inhibitor. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 2636–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broege, A.; Rossetti, S.; Sen, A.; Menon, A.S.; MacNeil, I.; Molden, J.; Laing, L. Functional Assessments of Gynecologic Cancer Models Highlight Differences Between Single-Node Inhibitors of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway and a Pan-PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor, Gedatolisib. Cancers 2024, 16, 3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossetti, S.; Broege, A.; Sen, A.; Khan, S.; MacNeil, I.; Molden, J.; Kopher, R.; Schulz, S.; Laing, L. Gedatolisib shows superior potency and efficacy versus single-node PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibitors in breast cancer models. NPJ Breast Cancer 2024, 10, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, A.; Khan, S.; Rossetti, S.; Broege, A.; MacNeil, I.; DeLaForest, A.; Molden, J.; Davis, L.; Iversrud, C.; Seibel, M.; et al. Assessments of prostate cancer cell functions highlight differences between a pan-PI3K/mTOR inhibitor, gedatolisib, and single-node inhibitors of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Mol. Oncol. 2025, 19, 225–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, I.; Genta, S.; Martorana, F.; Guidi, M.; Frattini, M.; Samartzis, E.P.; Brandt, S.; Gaggetta, S.; Moser, L.; Pascale, M.; et al. Phase I Dose-Escalation Study of the Dual PI3K-mTORC1/2 Inhibitor Gedatolisib in Combination with Paclitaxel and Carboplatin in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 5012–5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curigliano, G.; Shapiro, G.I.; Kristeleit, R.S.; Abdul Razak, A.R.; Leong, S.; Alsina, M.; Giordano, A.; Gelmon, K.A.; Stringer-Reasor, E.; Vaishampayan, U.N.; et al. A Phase 1B open-label study of gedatolisib (PF-05212384) in combination with other anti-tumour agents for patients with advanced solid tumours and triple-negative breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2023, 128, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Campo, J.M.; Birrer, M.; Davis, C.; Fujiwara, K.; Gollerkeri, A.; Gore, M.; Houk, B.; Lau, S.; Poveda, A.; Gonzalez-Martin, A.; et al. A randomized phase II non-comparative study of PF-04691502 and gedatolisib (PF-05212384) in patients with recurrent endometrial cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2016, 142, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Layman, R.M.; Han, H.S.; Rugo, H.S.; Stringer-Reasor, E.M.; Specht, J.M.; Dees, E.C.; Kabos, P.; Suzuki, S.; Mutka, S.C.; Sullivan, B.F.; et al. Gedatolisib in combination with palbociclib and endocrine therapy in women with hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer: Results from the dose expansion groups of an open-label, phase 1b study. Lancet Oncol. 2024, 25, 474–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, G.I.; Bell-McGuinn, K.M.; Molina, J.R.; Bendell, J.; Spicer, J.; Kwak, E.L.; Pandya, S.S.; Millham, R.; Borzillo, G.; Pierce, K.J.; et al. First-in-Human Study of PF-05212384 (PKI-587), a Small-Molecule, Intravenous, Dual Inhibitor of PI3K and mTOR in Patients with Advanced Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 1888–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, J.S.; Mullins, M.; Cheang, M.C.; Leung, S.; Voduc, D.; Vickery, T.; Davies, S.; Fauron, C.; He, X.; Hu, Z.; et al. Supervised risk predictor of breast cancer based on intrinsic subtypes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1160–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.P.; Chan, T.E.; Lombardo, Y.; Corleone, G.; Rotmensz, N.; Bravaccini, S.; Rocca, A.; Pruneri, G.; McEwen, K.R.; Coombes, R.C.; et al. Single-cell transcriptomics reveals multi-step adaptations to endocrine therapy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portman, N.; Alexandrou, S.; Carson, E.; Wang, S.; Lim, E.; Caldon, C.E. Overcoming CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance in ER-positive breast cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2019, 26, R15–R30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, A.; Stebbing, J.; Giamas, G.; Murphy, J. Endocrine Resistance in Hormone Receptor Positive Breast Cancer-From Mechanism to Therapy. Front Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.L.; Ehmsen, S.; Terp, M.G.; Portman, N.; Tuttolomondo, M.; Gammelgaard, O.L.; Hundebol, M.F.; Kaminska, K.; Johansen, L.E.; Bak, M.; et al. Co-targeting CDK4/6 and AKT with endocrine therapy prevents progression in CDK4/6 inhibitor and endocrine therapy-resistant breast cancer. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalski, J.R.; Kuzuoglu-Ozturk, D.; Ruggero, D. Protein synthesis control in cancer: Selectivity and therapeutic targeting. EMBO J. 2022, 41, e109823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux, P.P.; Topisirovic, I. Signaling Pathways Involved in the Regulation of mRNA Translation. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 38, e00070-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Kusnadi, E.P.; Furic, L.; Selth, L.A. Regulation of mRNA Translation by Hormone Receptors in Breast and Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, E.; Koo, J.S. Glucose Metabolism and Glucose Transporters in Breast Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 728759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Armand, J.; Safonov, A.; Zhang, M.; Soni, R.K.; Schwartz, G.; McGuinness, J.E.; Hibshoosh, H.; Razavi, P.; Kim, M.; et al. Sequential activation of E2F via Rb degradation and c-Myc drives resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 113198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, S.; El-Sibai, M. Signaling networks of Rho GTPases in cell motility. Cell Signal 2013, 25, 1955–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Juvekar, A.; Lyssiotis, C.A.; Lien, E.C.; Albeck, J.G.; Oh, D.; Varma, G.; Hung, Y.P.; Ullas, S.; Lauring, J.; et al. Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Regulates Glycolysis through Mobilization of Aldolase from the Actin Cytoskeleton. Cell 2016, 164, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, R.; Finney, G.L.; Carroll, J.S.; Lee, C.S.; Musgrove, E.A.; Sutherland, R.L. Constitutive overexpression of cyclin D1 but not cyclin E confers acute resistance to antiestrogens in T-47D breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 6916–6923. [Google Scholar]
- Kenny, F.S.; Hui, R.; Musgrove, E.A.; Gee, J.M.; Blamey, R.W.; Nicholson, R.I.; Sutherland, R.L.; Robertson, J.F. Overexpression of cyclin D1 messenger RNA predicts for poor prognosis in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 1999, 5, 2069–2076. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcken, N.R.; Prall, O.W.; Musgrove, E.A.; Sutherland, R.L. Inducible overexpression of cyclin D1 in breast cancer cells reverses the growth-inhibitory effects of antiestrogens. Clin. Cancer Res. 1997, 3, 849–854. [Google Scholar]
- Averous, J.; Fonseca, B.D.; Proud, C.G. Regulation of cyclin D1 expression by mTORC1 signaling requires eukaryotic initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1. Oncogene 2008, 27, 1106–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, N.N.; Zhu, J.; Thompson, C.B. The hallmarks of cancer metabolism: Still emerging. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 355–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stine, Z.E.; Schug, Z.T.; Salvino, J.M.; Dang, C.V. Targeting cancer metabolism in the era of precision oncology. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 141–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufail, M.; Hu, J.J.; Liang, J.; He, C.Y.; Wan, W.D.; Huang, Y.Q.; Jiang, C.H.; Wu, H.; Li, N. Hallmarks of cancer resistance. iScience 2024, 27, 109979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X. Drug resistance and combating drug resistance in cancer. Cancer Drug Resist. 2019, 2, 141–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Butler, E.B.; Tan, M. Targeting cellular metabolism to improve cancer therapeutics. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Dering, J.; Conklin, D.; Kalous, O.; Cohen, D.J.; Desai, A.J.; Ginther, C.; Atefi, M.; Chen, I.; Fowst, C.; et al. PD 0332991, a selective cyclin D kinase 4/6 inhibitor, preferentially inhibits proliferation of luminal estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer cell lines in vitro. Breast Cancer Res. 2009, 11, R77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Nie, J.; Ma, X.; Wei, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wei, X. Targeting PI3K in cancer: Mechanisms and advances in clinical trials. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kwok-Shing Ng, P.; Kucherlapati, M.; Chen, F.; Liu, Y.; Tsang, Y.H.; de Velasco, G.; Jeong, K.J.; Akbani, R.; Hadjipanayis, A.; et al. A Pan-Cancer Proteogenomic Atlas of PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway Alterations. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 820–832.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrakis, P.A.; Kampjut, D.; Steele, G.F.; Lindstrom, H.J.G.; Chirnomas, D.; Hopkins, B.D.; Goncalves, M.D.; Mukherjee, S.; Cantley, L.C.; Maddocks, O.D.K. Multi-node inhibition targeting mTORC1, mTORC2 and PI3Kalpha potently inhibits the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in endometrial and breast cancer models. Br. J. Cancer 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghandi, M.; Huang, F.W.; Jane-Valbuena, J.; Kryukov, G.V.; Lo, C.C.; McDonald, E.R., 3rd; Barretina, J.; Gelfand, E.T.; Bielski, C.M.; Li, H.; et al. Next-generation characterization of the Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia. Nature 2019, 569, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafner, M.; Niepel, M.; Chung, M.; Sorger, P.K. Growth rate inhibition metrics correct for confounders in measuring sensitivity to cancer drugs. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ianevski, A.; Giri, A.K.; Aittokallio, T. SynergyFinder 3.0: An interactive analysis and consensus interpretation of multi-drug synergies across multiple samples. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W739–W743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Broege, A.; Rossetti, S.; Sen, A.; De La Forest, A.; Davis, L.; Seibel, M.; Menon, A.S.; Stokke, S.; Macaulay, A.; Molden, J.; et al. Functional Analysis of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway Inhibitor, Gedatolisib, Plus Fulvestrant with and Without Palbociclib in Breast Cancer Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125844
Broege A, Rossetti S, Sen A, De La Forest A, Davis L, Seibel M, Menon AS, Stokke S, Macaulay A, Molden J, et al. Functional Analysis of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway Inhibitor, Gedatolisib, Plus Fulvestrant with and Without Palbociclib in Breast Cancer Models. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125844
Chicago/Turabian StyleBroege, Aaron, Stefano Rossetti, Adrish Sen, Ann De La Forest, Laura Davis, Megan Seibel, Arul S. Menon, Sydney Stokke, Allison Macaulay, Jhomary Molden, and et al. 2025. "Functional Analysis of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway Inhibitor, Gedatolisib, Plus Fulvestrant with and Without Palbociclib in Breast Cancer Models" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125844
APA StyleBroege, A., Rossetti, S., Sen, A., De La Forest, A., Davis, L., Seibel, M., Menon, A. S., Stokke, S., Macaulay, A., Molden, J., & Laing, L. (2025). Functional Analysis of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway Inhibitor, Gedatolisib, Plus Fulvestrant with and Without Palbociclib in Breast Cancer Models. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125844





