The Recurring Loss of ORF8 Secretion in Dominant SARS-CoV-2 Variants
Abstract
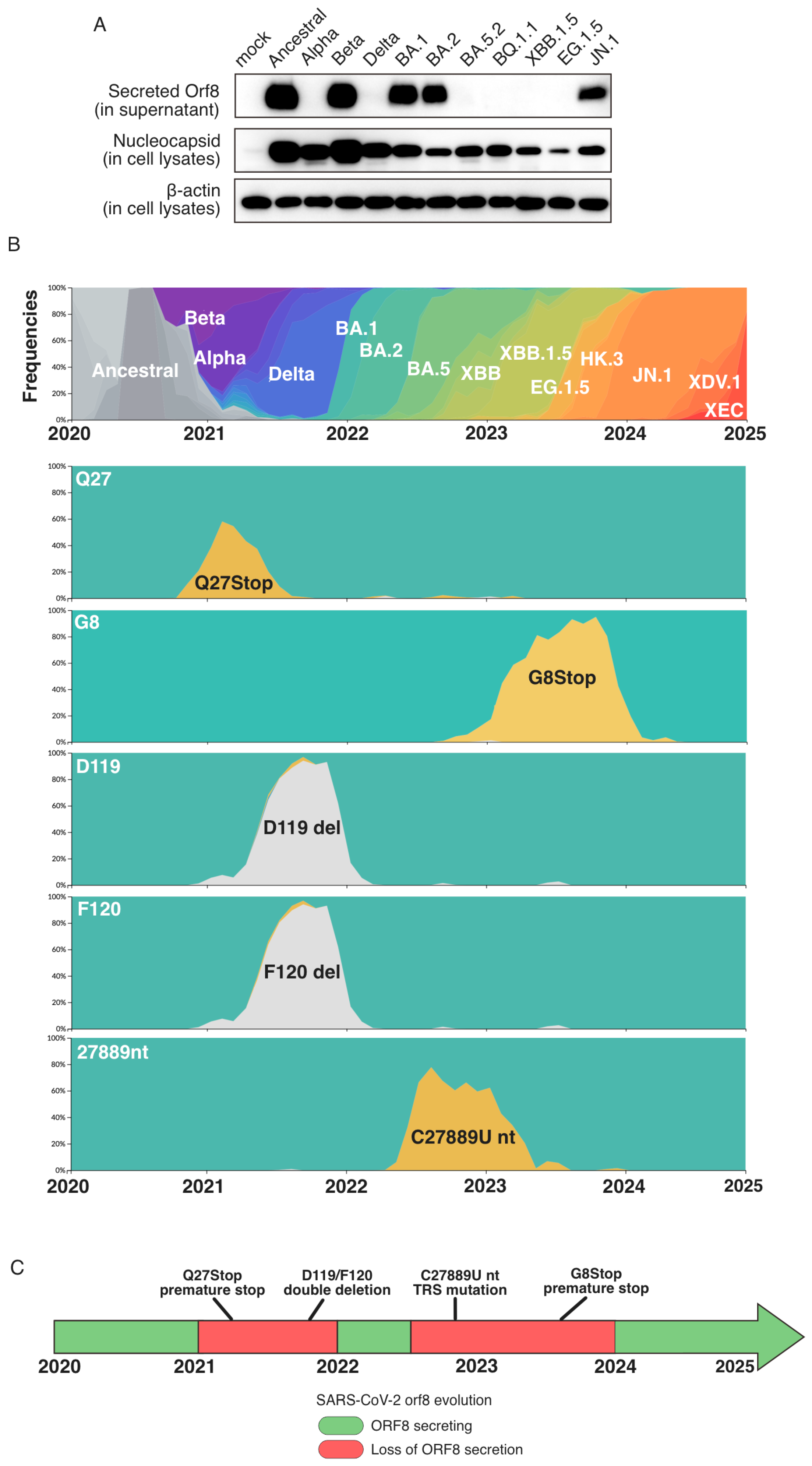
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sequence Analysis
4.2. Protein Analysis in Infected Cells
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chan, J.F.; Kok, K.H.; Zhu, Z.; Chu, H.; To, K.K.; Yuan, S.; Yuen, K.Y. Genomic characterization of the 2019 novel human-pathogenic coronavirus isolated from a patient with atypical pneumonia after visiting Wuhan. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriyama, M.; Lucas, C.; Monteiro, V.S.; Yale SARS-CoV-2 Genomic Surveillance Initiative; Iwasaki, A. Enhanced inhibition of MHC-I expression by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2221652120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, F.; Luo, B.; Yuan, Y.; Xia, B.; Ma, X.; Yang, T.; Yu, F.; et al. The ORF8 protein of SARS-CoV-2 mediates immune evasion through down-regulating MHC-Iota. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2024202118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Fu, B.; Xiong, Y.; Xing, N.; Xue, W.; Guo, D.; Zaky, M.; Pavani, K.; Kunec, D.; Trimpert, J.; et al. Unconventional secretion of unglycosylated ORF8 is critical for the cytokine storm during SARS-CoV-2 infection. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Fu, B.; Yin, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Xing, N.; Wang, Y.; Xue, W.; Xiong, Y.; et al. ORF8 contributes to cytokine storm during SARS-CoV-2 infection by activating IL-17 pathway. iScience 2021, 24, 102293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kee, J.; Thudium, S.; Renner, D.M.; Glastad, K.; Palozola, K.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Lan, Y.; Cesare, J.; Poleshko, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 disrupts host epigenetic regulation via histone mimicry. Nature 2022, 610, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Xia, T.; Shin, W.J.; Yu, K.M.; Jung, W.; Herrmann, A.; Foo, S.S.; Chen, W.; Zhang, P.; Lee, J.S.; et al. Viral Mimicry of Interleukin-17A by SARS-CoV-2 ORF8. mBio 2022, 13, e0040222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdorf, M.; Imhof, T.; Bailey-Elkin, B.; Betz, J.; Theobald, S.J.; Simonis, A.; Di Cristanziano, V.; Gieselmann, L.; Dewald, F.; Lehmann, C.; et al. The unique ORF8 protein from SARS-CoV-2 binds to human dendritic cells and induces a hyper-inflammatory cytokine storm. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2024, 15, mjad062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Manske, M.K.; Ruan, G.J.; Witter, T.L.; Nowakowski, K.E.; Abeykoon, J.P.; Tang, X.; Yu, Y.; Gwin, K.A.; Wu, A.; et al. Secreted ORF8 induces monocytic pro-inflammatory cytokines through NLRP3 pathways in patients with severe COVID-19. iScience 2023, 26, 106929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lam, J.Y.; Wong, W.M.; Yuen, C.K.; Cai, J.P.; Au, S.W.; Chan, J.F.; To, K.K.W.; Kok, K.H.; Yuen, K.Y. Accurate Diagnosis of COVID-19 by a Novel Immunogenic Secreted SARS-CoV-2 orf8 Protein. mBio 2020, 11, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, C.; Kistler, K.E.; Perchetti, G.A.; Baker, N.; Frisbie, L.A.; Torres, L.M.; Aragona, F.; Yun, C.; Figgins, M.; Greninger, A.L.; et al. Positive selection underlies repeated knockout of ORF8 in SARS-CoV-2 evolution. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flower, T.G.; Buffalo, C.Z.; Hooy, R.M.; Allaire, M.; Ren, X.; Hurley, J.H. Structure of SARS-CoV-2 ORF8, a rapidly evolving immune evasion protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2021785118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, T.; Irie, T.; Deguchi, S.; Yajima, H.; Tsuda, M.; Nasser, H.; Mizuma, K.; Plianchaisuk, A.; Suzuki, S.; Uriu, K.; et al. Virological characteristics of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron XBB.1.5 variant. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsuwairi, F.A.; Alsaleh, A.N.; Obeid, D.A.; Al-Qahtani, A.A.; Almaghrabi, R.S.; Alahideb, B.M.; AlAbdulkareem, M.A.; Alsanea, M.S.; Alharbi, L.A.; Althawadi, S.I.; et al. Genomic Surveillance and Mutation Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Variants among Patients in Saudi Arabia. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imbiakha, B.; Ezzatpour, S.; Buchholz, D.W.; Sahler, J.; Ye, C.; Olarte-Castillo, X.A.; Zou, A.; Kwas, C.; O’Hare, K.; Choi, A.; et al. Age-dependent acquisition of pathogenicity by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.5. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadj1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuen, C.K.; Wong, W.M.; Mak, L.F.; Lam, J.Y.; Cheung, L.Y.; Cheung, D.T.; Ng, Y.Y.; Lee, A.C.; Zhong, N.; Yuen, K.Y.; et al. An interferon-integrated mucosal vaccine provides pan-sarbecovirus protection in small animal models. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schon, J.; Barut, G.T.; Trueb, B.S.; Halwe, N.J.; Berenguer Veiga, I.; Kratzel, A.; Ulrich, L.; Kelly, J.N.; Brugger, M.; Wylezich, C.; et al. A safe, effective and adaptable live-attenuated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine to reduce disease and transmission using one-to-stop genome modifications. Nat. Microbiol. 2024, 9, 2099–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuoka, K.; Imahashi, N.; Ohno, M.; Ode, H.; Nakata, Y.; Kubota, M.; Sugimoto, A.; Imahashi, M.; Yokomaku, Y.; Iwatani, Y. SARS-CoV-2 accessory protein ORF8 is secreted extracellularly as a glycoprotein homodimer. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 101724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadfield, J.; Megill, C.; Bell, S.M.; Huddleston, J.; Potter, B.; Callender, C.; Sagulenko, P.; Bedford, T.; Neher, R.A. Nextstrain: Real-time tracking of pathogen evolution. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 4121–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagulenko, P.; Puller, V.; Neher, R.A. TreeTime: Maximum-likelihood phylodynamic analysis. Virus Evol. 2018, 4, vex042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lam, J.-Y.; Kok, K.-H. The Recurring Loss of ORF8 Secretion in Dominant SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5778. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125778
Lam J-Y, Kok K-H. The Recurring Loss of ORF8 Secretion in Dominant SARS-CoV-2 Variants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5778. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125778
Chicago/Turabian StyleLam, Joy-Yan, and Kin-Hang Kok. 2025. "The Recurring Loss of ORF8 Secretion in Dominant SARS-CoV-2 Variants" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5778. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125778
APA StyleLam, J.-Y., & Kok, K.-H. (2025). The Recurring Loss of ORF8 Secretion in Dominant SARS-CoV-2 Variants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5778. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125778




