Prediction of Extraintestinal Manifestations in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Using Clinical and Genetic Variables with Machine Learning in a Latin IBD Group †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
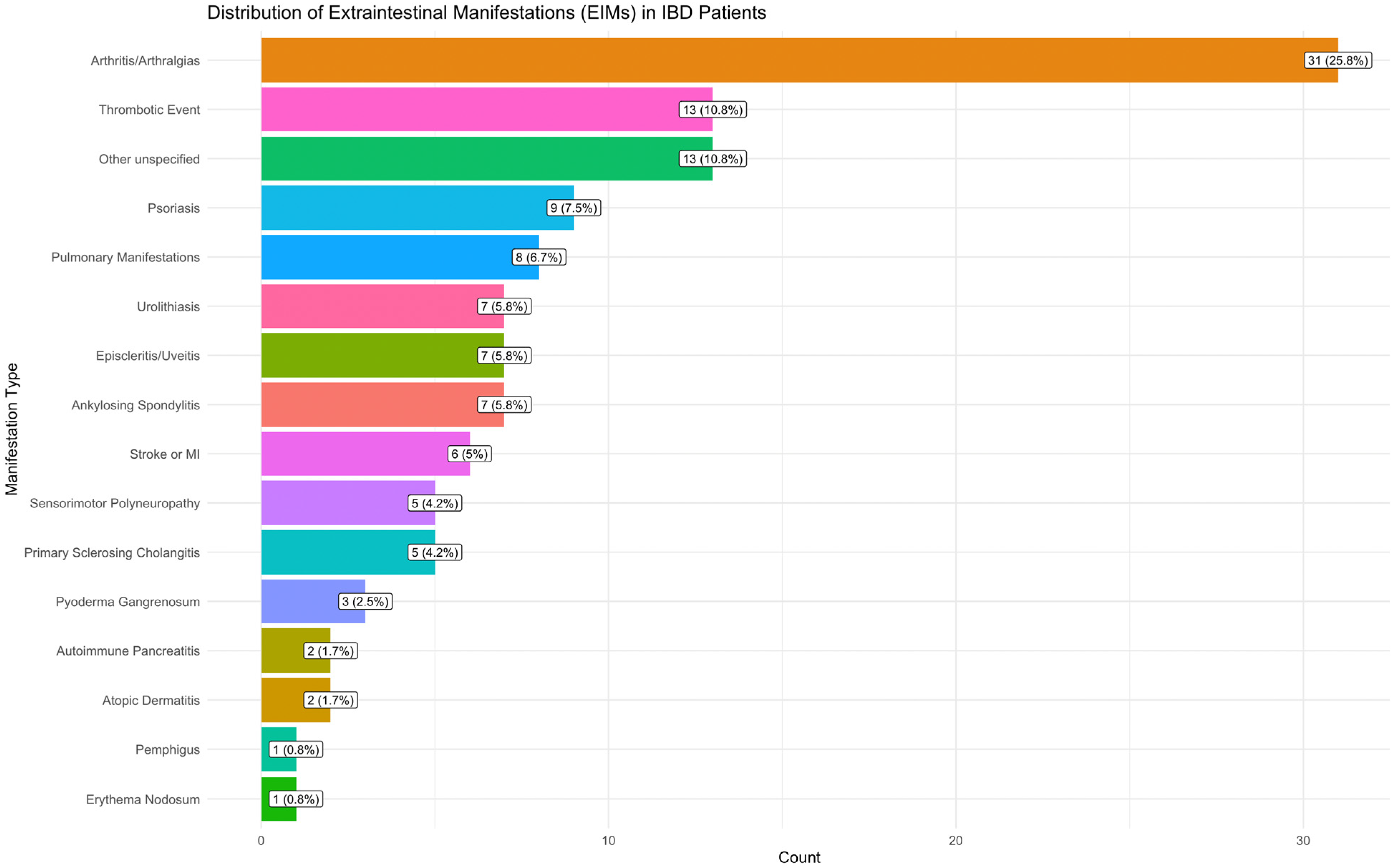
2.1. Clinical Results
2.2. Genotyping and Genetics Variants
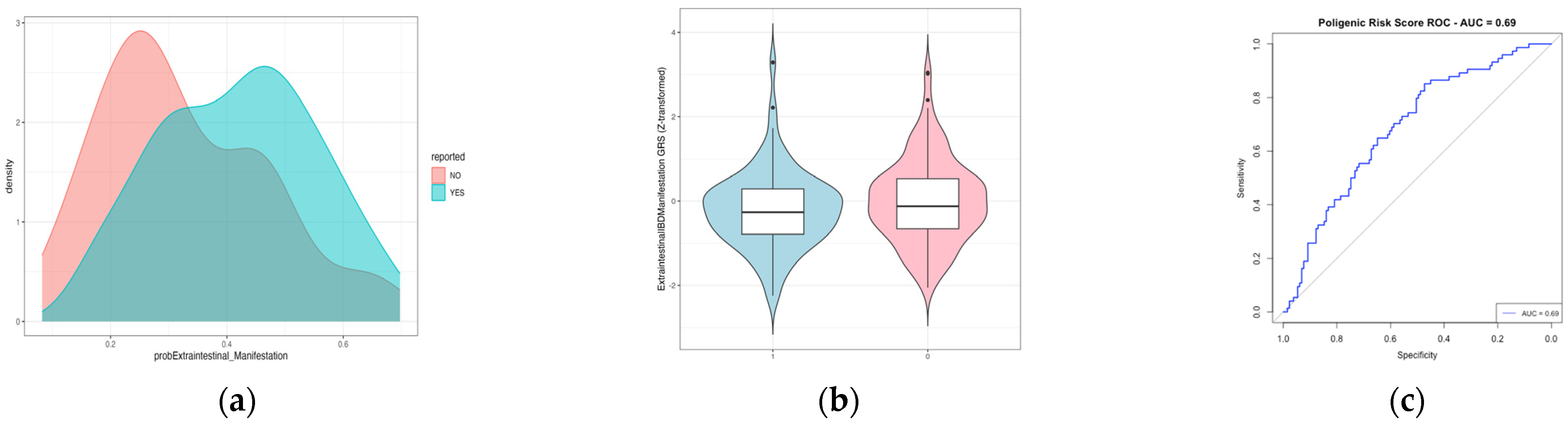
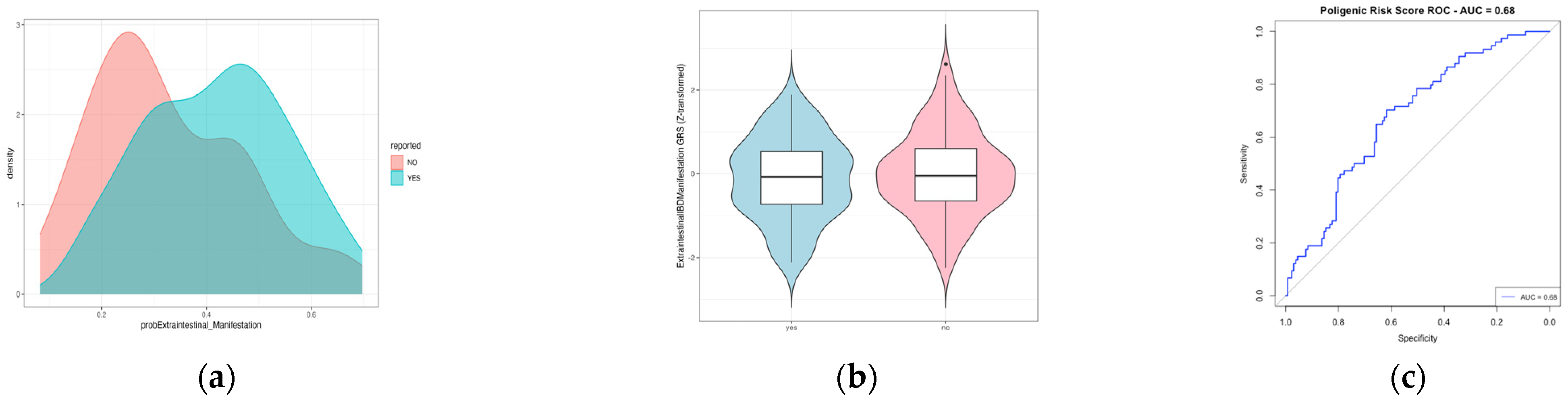
2.3. Polygenic Risk Score to Predict Extraintestinal Manifestation
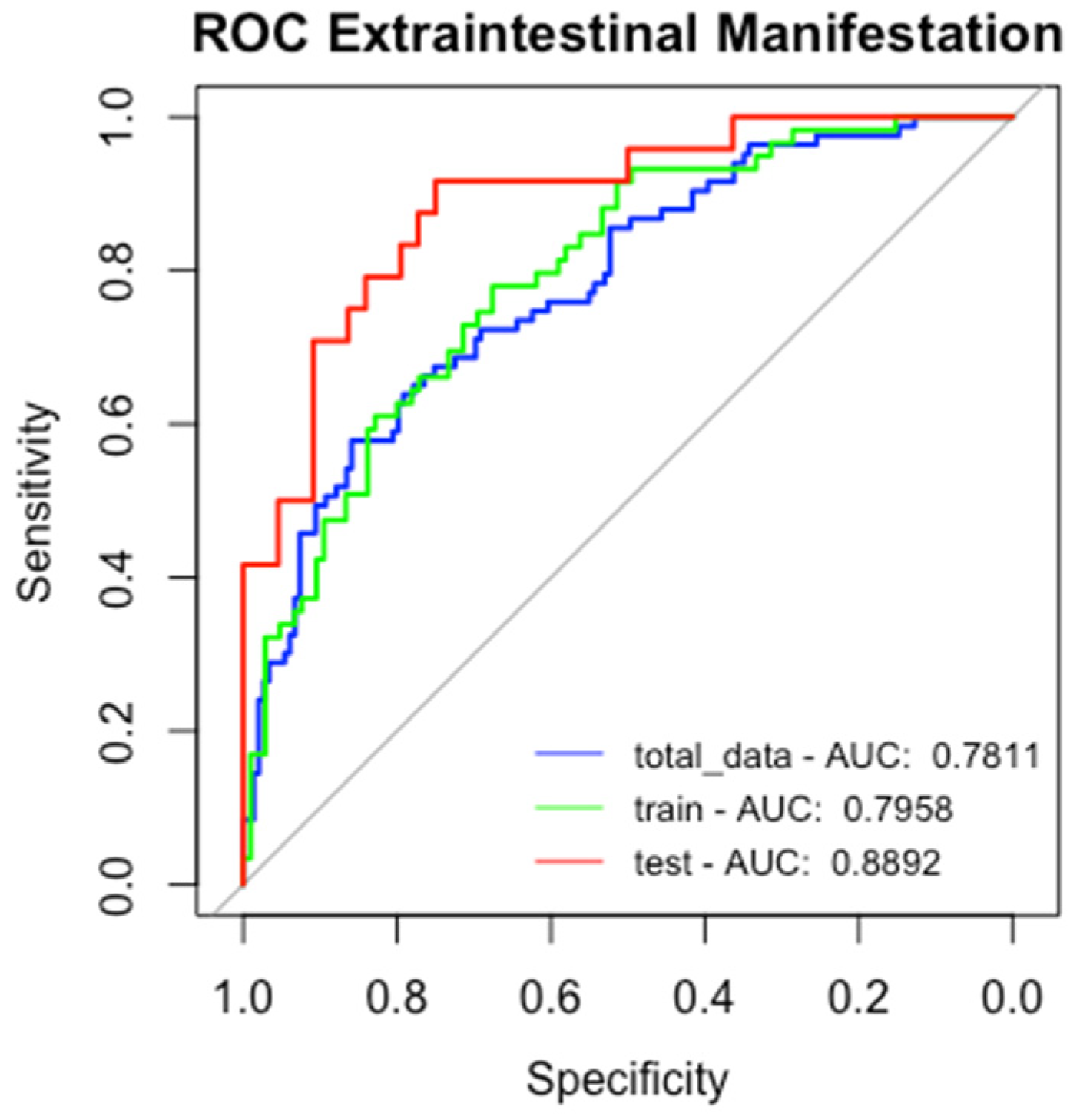
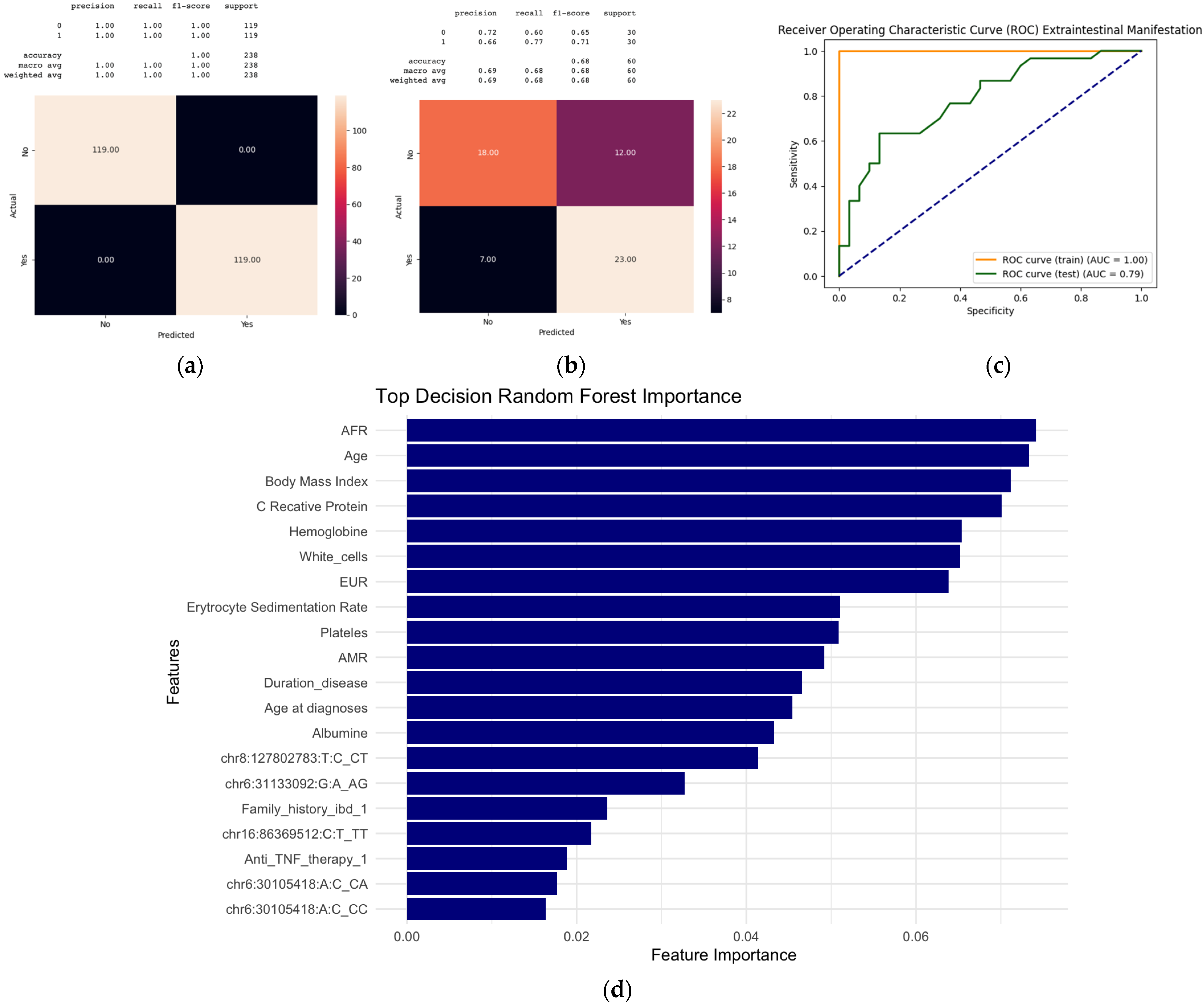
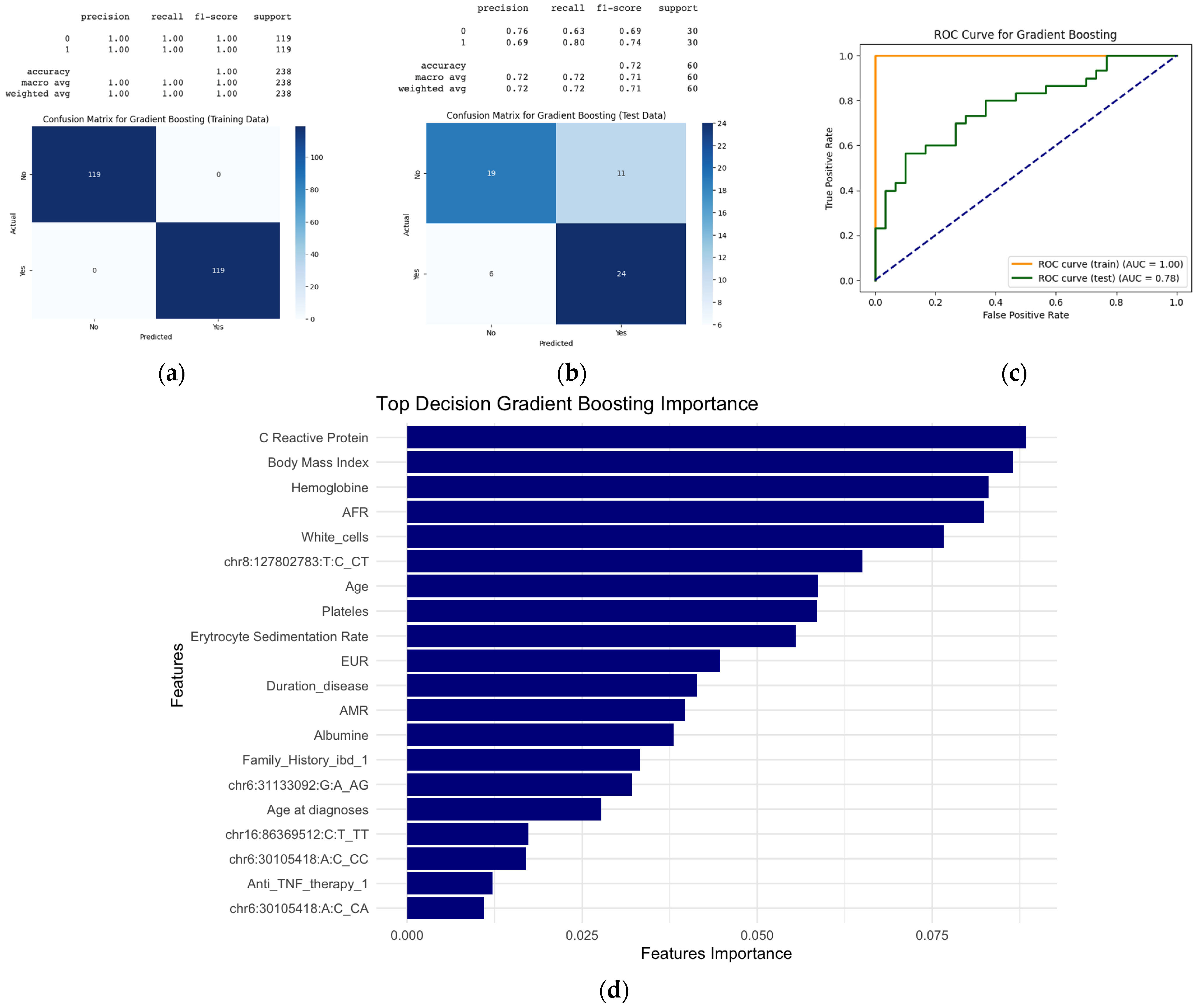
2.4. Machine Learning Models to Predict Extraintestinal Manifestation
2.4.1. Logistic Regression for EIMs
2.4.2. Random Forest and Gradient Boosting
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Genotyping and Genetic Risk Score Calculation
4.3. Data Analysis
4.3.1. Clinical Predictors
4.3.2. Genetic Predictors
4.3.3. Machine Learning Models
Regression Model
Random Forest and Gradient Boosting
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khor, B.; Gardet, A.; Xavier, R.J. Genetics and pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 2011, 474, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swaminathan, A.; Day, A.S.; Sparrow, M.P.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Siegel, C.A.; Gearry, R.B. Review article: Measuring disease severity in inflammatory bowel disease—Beyond treat to target. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 60, 1176–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, H.; Burisch, J.; Ellul, P.; Karmiris, K.; Katsanos, K.; Allocca, M.; Bamias, G.; Barreiro-de Acosta, M.; Braithwaite, T.; Greuter, T.; et al. ECCO Guidelines on Extraintestinal Manifestations in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2024, 18, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hadad, J.; Schreiner, P.; Vavricka, S.R.; Greuter, T. The Genetics of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2024, 28, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rankin, G.B.; Watts, H.D.; Melnyk, C.S.; Kelley, M.L. National Cooperative Crohn’s Disease Study: Extraintestinal manifestations and perianal complications. Gastroenterology 1979, 77, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, C.N.; Wajda, A.; Blanchard, J.F. The Clustering of Other Chronic Inflammatory Diseases in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Population-Based Study. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, C.N.; Blanchard, J.F.; Rawsthorne, P.; Yu, N. The Prevalence of Extraintestinal Diseases in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Population-Based Study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2001, 96, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eksteen, D.H.A.B. Aberrant homing of mucosal T cells and extra-intestinal manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breban, M.; Tap, J.; Leboime, A.; Said-Nahal, R.; Langella, P.; Chiocchia, G.; Furet, J.P.; Sokol, H. Faecal microbiota study reveals specific dysbiosis in spondyloarthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1614–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marineata, A.; Rezus, E.; Mihai, C.; Prelipcean, C.C. Extra intestinal manifestations and complications in inflammatory bowel disease. Med.-Surg. J. 2014, 118, 279–288. [Google Scholar]
- van Sommeren, S.; Janse, M.; Karjalainen, J.; Fehrmann, R.; Franke, L.; Fu, J.; Weersma, R.K. Extraintestinal Manifestations and Complications in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2014, 20, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravina, A.G.; Panarese, I.; Trotta, M.C.; D’Amico, M.; Pellegrino, R.; Ferraraccio, F.; Galdiero, M.; Alfano, R.; Grieco, P.; Federico, A. Melanocortin 3,5 receptors immunohistochemical expression in colonic mucosa of inflammatory bowel disease patients: A matter of disease activity? World J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 30, 1132–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinne, P.; Taylor, A.W.; Montero-Melendez, T. Editorial: Melanocortins and melanocortin receptors in the regulation of inflammation: Mechanisms and novel therapeutic strategies. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1226886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellinghaus, D.; Jostins, L.; Spain, S.L.; Cortes, A.; Bethune, J.; Han, B.; Park, Y.R.; Raychaudhuri, S.; Pouget, J.G.; Hübenthal, M.; et al. Analysis of five chronic inflammatory diseases identifies 27 new associations and highlights disease-specific patterns at shared loci. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satsangi, J.; Grootscholten, C.; Holt, H.; Jewell, D.P. Clinical patterns of familial inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 1996, 385, 738–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavricka, S.R.; Brun, L.; Ballabeni, P.; Pittet, V.; Vavricka, B.M.; Zeitz, J.; Rogler, G.; Schoepfer, A.M.; Swiss IBD Cohort Study Group. Frequency and Risk Factors for Extraintestinal Manifestations in the Swiss Inflammatory Bowel Disease Cohort. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khrom, M.; Long, M.; Dube, S.; Robbins, L.; Botwin, G.J.; Yang, S.; Mengesha, E.; Li, D.; Naito, T.; Bonthala, N.N.; et al. Comprehensive Association Analyses of Extraintestinal Manifestations in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterology 2024, 167, 315–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, R.; Gao, H.; Jung, S.; Gao, X.; Sun, R.; Liu, X.; Kim, Y.; Lee, H.S.; Kawai, Y.; et al. Genetic architecture of the inflammatory bowel diseases across East Asian and European ancestries. Nat. Genet. 2023, 55, 796–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Jeldres, T.; Magne, F.; Ascui, G.; Alvares, D.; Orellana, M.; Alvarez-Lobos, M.; Hernandez-Rocha, C.; Azocar, L.; Aguilar, N.; Espino, A.; et al. Amerindian ancestry proportion as a risk factor for inflammatory bowel diseases: Results from a Latin American Andean cohort. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1258395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdugo, R.A.; Di Genova, A.; Herrera, L.; Moraga, M.; Acuña, M.; Berríos, S.; Llop, E.; Valenzuela, C.Y.; Bustamante, M.L.; Digman, D.; et al. Development of a small panel of SNPs to infer ancestry in Chileans that distinguishes Aymara and Mapuche components. Biol. Res. 2020, 53, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez -Jeldres, T.; Pizarro, B.; Ascui, G.; Orellana, M.; Cerda-Villablanca, M.; Alvares, D.; de la Vega, A.; Cannistra, M.; Cornejo, B.; Baéz, P.; et al. Ethnicity influences phenotype and clinical outcomes: Comparing a South American with a North American inflammatory bowel disease cohort. Medicine 2022, 101, e30216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Jeldres, T.; Bustamante, M.L.; Alvares, D.; Alvarez-Lobos, M.; Kalmer, L.; Azocar, L.; Melero, R.S.; Ascui, G.; Aguilar, N.; Estela, R.; et al. Impact of Amerindian ancestry on clinical outcomes in Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis in a Latino population. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 15331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogler, G.; Singh, A.; Kavanaugh, A.; Rubin, D.T. Extraintestinal Manifestations of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Current Concepts, Treatment, and Implications for Disease Management. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 1118–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, S.; Malham, M.; Paerregaard, A.; Jakobsen, C.; Wewer, V. Extraintestinal Manifestations Are Associated With Disease Severity in Pediatric Onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2020, 71, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stidham, R.W.; Yu, D.; Zhao, X.; Bishu, S.; Rice, M.; Bourque, C.; Vydiswaran, V.V.G. Identifying the Presence, Activity, and Status of Extraintestinal Manifestations of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Using Natural Language Processing of Clinical Notes. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2023, 29, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.H.; Picetti, D.; Dulai, P.S.; Jairath, V.; Sandborn, W.J.; Ohno-Machado, L.; Chen, P.L.; Singh, S. Machine Learning-based Prediction Models for Diagnosis and Prognosis in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Systematic Review. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2022, 16, 398–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottigliengo, D.; Berchialla, P.; Lanera, C.; Azzolina, D.; Lorenzoni, G.; Martinato, M.; Giachino, D.; Baldi, I.; Gregori, D. The Role of Genetic Factors in Characterizing Extra-Intestinal Manifestations in Crohn’s Disease Patients: Are Bayesian Machine Learning Methods Improving Outcome Predictions? J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menti, E.; Lanera, C.; Lorenzoni, G.; Giachino, D.F.; Marchi, M.; Gregori, D.; Berchialla, P.; Piedmont Study Group on the Genetics of IBD. Bayesian Machine Learning Techniques for revealing complex interactions among genetic and clinical factors in association with extra-intestinal Manifestations in IBD patients. AMIA Annu. Symp. Proc. 2016, 2016, 884–893. [Google Scholar]
- Homo Sapiens Genome Browser (GRCh38) [Database]. Ensembl Genome Browser. Available online: https://www.ensembl.org/Homo_sapiens/Info/Index?db=core (accessed on 9 June 2025).
- Pérez, T.; Bustamante, M.L.; Pérez, P.R.; Rivera, A.M.; Avendano, C.; Azocar, L.; Estela, R.; Aguilar, N.; Melero, R.S.; Silva, V.; et al. Prediction of extraintestinal manifestations in inflammatory bowel disease using clinical and genetic variables with machine learning. In Proceedings of the European Crohn’s and Colitis Organization Congress, Berlin, Germany, 21–24 February 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto-Furusho, J.K.; Parra-Holguín, N.N.; Juliao-Baños, F.; Puentes, F.; López, R.; Bosques-Padilla, F.; Torres, E.A.; Nieves-Jimenéz, H.; Veitia-Velásquez, G.R.; Jara-Alba, M.L.; et al. Clinical differentiation of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in Latin America and the Caribbean. Medicine 2022, 101, e28624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thia, K.T.; Loftus, J.E.V.; Sandborn, W.J.; Yang, S.-K. An Update on the Epidemiology of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Asia. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 3167–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prideaux, L.; Kamm, M.A.; De Cruz, P.P.; Chan, F.K.L.; Ng, S.C. Inflammatory bowel disease in Asia: A systematic review. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 27, 1266–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.K.; El-Serag, H.; Thirumurthi, S. Distribution and Manifestations of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Asians, Hispanics and African Americans: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 104, 2100–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, D.G.; Williams, H.R.; Kane, S.P.; Mawdsley, J.E.; Arnold, J.; McNeil, I.; Thomas, H.J.; Teare, J.P.; Hart, A.L.; Pitcher, M.C.; et al. Differences in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Phenotype between South Asians and Northern Europeans Living in North West London, UK. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vavricka, S.R.; Gubler, M.; Gantenbein, C.; Spoerri, M.; Froehlich, F.; Seibold, F.; Protic, M.; Michetti, P.; Straumann, A.; Fournier, N.; et al. Anti-TNF Treatment for Extraintestinal Manifestations of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in the Swiss IBD Cohort Study. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2017, 23, 1174–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedin, C.R.H.; Vavricka, S.R.; Stagg, A.J.; Schoepfer, A.; Raine, T.; Puig, L.; Pleyer, U.; Navarini, A.; van der Meulen-de Jong, A.E.; Maul, J.; et al. The Pathogenesis of Extraintestinal Manifestations: Implications for IBD Research, Diagnosis, and Therapy. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2019, 13, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Y.; Qi, X.; Gao, Y.; Chen, K. LINC01977 promotes colorectal cancer growth and metastasis by enhancing aerobic glycolysis via the ERK/c-Myc axis. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2024, 15, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares-Pineda, T.; Peña-Montero, N.; Fragoso-Bargas, N.; Gutiérrez-Repiso, C.; Lima-Rubio, F.; Suarez-Arana, M.; Sánchez-Pozo, A.; Tinahones, F.J.; Molina-Vega, M.; Picón-César, M.J.; et al. Epigenetic marks associated with gestational diabetes mellitus across two time points during pregnancy. Clin. Epigenet. 2023, 15, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, D.; Aslibekyan, S.; Irvin, M.R.; Claas, S.A.; Borecki, I.B.; Ordovas, J.M.; Absher, D.M.; Arnett, D.K. SNPs located at CpG sites modulate genome-epigenome interaction. Epigenetics 2013, 8, 802–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, M.C.; Huang, C.; Liang, Y.; Sathiaseelan, R.; Zeng, X.; Liu, L. Long non-coding RNA FENDRR regulates IFNγ-induced M1 phenotype in macrophages. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Tie, Y.; Lu, J.; Li, L.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, M.; Zhang, S. Tripartite motif family proteins in inflammatory bowel disease: Mechanisms and potential for interventions. Cell Prolif. 2022, 55, e13222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, N.Z.; Abdallah, H.Y.; Hassan, R.; Hosny, A.; Ghanem, D.E.; Adel, A.; Atwa, M.A. PSORS1 Locus Genotyping Profile in Psoriasis: A Pilot Case-Control Study. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayoub, S.E.; Ahmed, T.I.; Amin, A. Expression Profile of Long Non Coding RNA PVT1 in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis. Egypt. J. Med. Microbiol. 2021, 30, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, P.S.; Makarious, M.B.; Elsayed, I.; Sanyaolu, A.; Crea, P.W.; Schuh, A.F.S.; Levine, K.S.; Vitale, D.; Korestky, M.J.; Global Parkinsons Genetics Program (GP2). Insights into Ancestral Diversity in Parkinson’s Disease Risk: A Comparative Assessment of Polygenic Risk Scores. Preprint. [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Rathi, B.; Sharda, S. Machine Learning Based Risk Assessment and Early Diagnostic Model of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Associated Arthropathy. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1099, 012017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgart, D.C.; Cheng, C.H.; Du, T.X.; Parkes, M.D.; Sadowski, D.C.; Wine, E.; Hoentjen, F.; Halloran, B.P.; Montano-Loza, A.; Zepeda-Gomez, S.; et al. Network analysis of extraintestinal manifestations and associated autoimmune disorders in Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. NPJ Digit. Med. 2025, 8, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenstein, G.R.; Loftus, E.V.; Isaacs, K.L.; Regueiro, M.D.; Gerson, L.B.; Sands, B.E. ACG Clinical Guideline: Management of Crohn’s Disease in Adults. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 481–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, D.T.; Ananthakrishnan, A.N.; Siegel, C.A.; Sauer, B.G.; Long, M.D. ACG Clinical Guideline: Ulcerative Colitis in Adults. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, 384–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaser, C.; Sturm, A.; Vavricka, S.R.; Kucharzik, T.; Fiorino, G.; Annese, V.; Calabrese, E.; Baumgart, D.C.; Bettenworth, D.; Borralho Nunes, P.; et al. ECCO-ESGAR Guideline for Diagnostic Assessment in IBD Part 1: Initial diagnosis, monitoring of known IBD, detection of complications. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2019, 13, 144–164K. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rom, H.; Snir, Y.; Schwartz, N.; Hodak, E.; Leshem, Y.A. The association between atopic dermatitis and inflammatory bowel disease in adults: A cross-sectional study in a specialized atopic dermatitis clinic. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2024, 38, 1357–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-J.; Juan, C.-K.; Chang, Y.-T.; Wu, C.-Y.; Ho, H.J.; Tseng, H.-C. Association between inflammatory bowel disease and bullous pemphigoid: A population-based case–control study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gala, D.; Newsome, T.; Roberson, N.; Lee, S.M.; Thekkanal, M.; Shah, M.; Kumar, V.; Bandaru, P.; Gayam, V. Thromboembolic Events in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Comprehensive Overview. Diseases 2022, 10, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Hu, T.; Hao, H.; Hill, M.A.; Xu, C.; Liu, Z. Inflammatory bowel disease and cardiovascular diseases: A concise review. Eur. Heart J. Open 2022, 2, oeab029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, W.; Zhu, B.; Chen, J.; Jin, X. Risk relationship between inflammatory bowel disease and urolithiasis: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0301545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eder, P.; Verstock, B.; Culver, E.; Dragoni, G.; Kredel, L.I.; Wypych, J.; de Paredes, A.G.G.; Kaniewska, M.; Leibovitzh, H.; Lobaton, T.; et al. Autoimmune Pancreatitis in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Real-World Multicentre Collaborative ECCO CONFER Study. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2023, 17, 1791–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herling, A.; Perluk, T.M.; Freund, O.; Maharshak, N.; Cohen, N.A. Pulmonary Manifestations of IBD: Case Report and Review of the Literature. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondim, F.A.A. Peripheral neuropathy in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Brain 2005, 128, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asociación de Investigadores de Mercado y Opinión Pública. Grupos Socioeconómicos de Chile (2025). Socioeconomic Groups of Chile. Available online: https://aimchile.cl/gse-chile/ (accessed on 9 June 2025).
- Das, S.; Forer, L.; Schönherr, S.; Sidore, C.; Locke, A.E.; Kwong, A.; Vrieze, S.I.; Chew, E.Y.; Levy, S.; McGue, M.; et al. Next-generation genotype imputation service and methods. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1284–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchsberger, C.; Abecasis, G.R.; Hinds, D.A. minimac2: Faster genotype imputation. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 782–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, D.H.; Novembre, J.; Lange, K. Fast model-based estimation of ancestry in unrelated individuals. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1655–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| N = 414 (100%) | EIMs− (N = 294) | EIMs+ (N = 120) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ulcerative Colitis/Crohn’s | 231 (78.6%)/63 (21.4%) | 83 (69%)/37 (30%) | 0.06 |
| Age (years) (median, max–min) | 45 (80–14) | 52 (81–20) | 0.001 |
| Family history IBD (no/yes/NA) | 256 (87%)/36 (12%)/2 (1%) | 89 (74%)/31 (26%) | 0.02 |
| Sex (female/male) | 168 (57%)/126 (43%) | 80 (67%)/40 (37%) | 0.09 |
| Resective Surgery (no/yes) | 266 (90%)/28 (10%) | 103 (86%)/17 (14%) | 0.22 |
| Smoking (no/yes) | 250 (85%)/44 (15%) | 98 (82%)/22 (18%) | 0.48 |
| Body Mass Index (BMI, kg/m2) | 26 (43–16) | 27 (45–18) | 0.006 |
| Age Diagnoses (years) (median, min–max) | 35 (77–4) | 37 (67–7) | 0.21 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) (median, min–max) | 14 (17–6) | 14 (16.5–4) | 0.31 |
| White Cells (×109/L) (median, min–max) | 6.800 (2.550–19.200) | 7.260 (3.500–14.900) | 0.04 |
| Platelets (μ/L) (median, min–max) | 296.000 (17.600–743.000) | 294,000 (67.000–616.000) | 0.98 |
| C Reactive Protein (mg/dL) (median, min–max) | 0.6 (0.02–19.5) | 0.6 (0.04–11.7) | 0.01 |
| Erythrocyte Sedimental Rate (mm/h) (median, min–max) | 9 (0.5–125) | 10 (0.2–72) | 0.01 |
| Albumine (median, max–min) | 4.4 (5.23–2.0) | 4.4 (5.2–3.4) | 0.7 |
| Steroids (no/yes) | 252 (86%)/42 (14%) | 99 (82.5%)/21 (17.5%) | 0.49 |
| Anti-TNF (no/yes) | 267 (91%)/27 (9%) | 98 (82%)/22 (18%) | 0.01 |
| Immunomodulator (no/yes/NA) | 227 (77.2%)/66 (22.4%)/1 (0.4%) | 86 (72%)/34 (28%) | 0.52 |
| Aminosalycilates (no/yes) | 64 (22%)/230 (88%) | 30 (33.3%)/90 (66.7%) | 0.56 |
| JAK inhibitors (no/yes) | 292 (99.3%)/2 (0.7%) | 120 (100%)/0 | 0.9 |
| Anti-IL12/IL23 (no/yes) | 291 (98.9%)/3 (1.1%) | 119 (99%)/1 (1%) | 1 |
| Montreal Classification | |||
| E1/E2/E3/NA | 49 (21%)/60 (26%)/113 (50%)/9 (3%) | 9 (11%)//23 (28%)/48 (58%)/3 (3%) | 0.20 |
| Montreal Classification CD | |||
| Age | |||
| A1/A2/A3/No registered | 6 (9%)/37 (59%)/20 (32%) | 2 (5%)/18 (49%)/17 (46%) | 0.33 |
| Localization | |||
| Ileal (L1) | 8 (13%) | 7 (19%) | 0.70 |
| Colonic (L2) | 35 (55%) | 19 (51%) | |
| Ileocolonic (L3) | 20 (32%) | 11 (30%) | |
| Upper compromise (L4) (no/yes) | 58 (92%)/5 (8%) | 34 (92%)/3 (8%) | 1 |
| Behavior | |||
| B1 (inflammatory) | 39 (62%) | 20 (54%) | 0.74 |
| B2 (structuring) | 11 (17%) | 8 (22%) | |
| B3 (penetrating) | 13 (20%) | 9 (24%) | |
| Perianal Disease (no/yes) | 45 (71%)/18 (29%) | 20 (54%)/17 (46%) | 0.12 |
| Clinical Variable | Extraintestinal Manifestation Group | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Family History IBD | EIM − (n = 292) | EIM + (n = 120) | OR | CI | p-value * |
| No | 256 (87%) | 89 (74%) | Reference | Reference | 0.001 |
| Yes | 36 (12%) | 31 (28%) | 2.47 | 1.44–4.23 | |
| Anti-TNF | No (n = 294) | Yes (n = 120) | OR | CI | p-value |
| No | 267 (91%) | 98 (82%) | Reference | Reference | 0.01 |
| Yes | 27 (9%) | 22 (18%) | 2.21 | 1.20–4.08 | |
| rs9936833 | Univariate | Adjusted by Ancestry, Sex, and Age | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recesive | No = 149 | Yes = 83 | OR | CI | p -value | OR | Recesive | No = 149 | p-value |
| TT_TC | 128 | 61 | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | TT_TC | 128 | Ref. | |
| CC | 21 | 22 | 2.20 | 1.12–4.32 | 0.02 | 2.21 | CC | 21 | 0.02 |
| Dominant | No = 149 | Yes = 83 | OR | CI | p -value | OR | Dominant | No = 149 | p-value |
| TT | 53 | 19 | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | TT | 53 | Ref. | |
| CC_TC | 96 | 64 | 1.85 | 1.02–3.49 | 0.05 | 2.00 | CC_TC | 96 | 0.03 |
| Three Genotypes | No = 149 | Yes = 83 | OR | CI | p -value | OR | Three Genotypes | No = 149 | p-value |
| CC | 21 | 22 | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | CC | 21 | Ref. |
| CT | 75 | 42 | 0.53 | 0.26–1.08 | 0.08 | 0.55 | CT | 75 | 0.10 |
| TT | 53 | 19 | 0.34 | 0.15–0.75 | 0.008 | 0.32 | TT | 53 | 0.01 |
| Additive | No = 149 | Yes = 83 | OR | CI | p -value | OR | Aditivo | No = 149 | p-value |
| TT_0 | 53 | 19 | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | Ref. | TT_0 | 53 | Ref. |
| TC_1 | 75 | 42 | 1.56 | 0.82–3.02 | 0.18 | 1.69 | TC_1 | 75 | 0.12 |
| CC_2 | 21 | 22 | 2.92 | 1.32–6.55 | 0.008 | 3.09 | CC_2 | 21 | 0.01 |
| CHR | SNP # | Position-hg19 (Mb) | Candidate Gene (s) | Effect Allele | p-Value | Beta | EIM * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | rs3132680 | 30,073,195 | TRIM31, TRIM31-AS1 | A | 1,67 × 10 −5 | 0.602 | PS |
| 6 | rs3823417 | 31,100,869 | PSORS1C1 | A | 5,79 × 10 −5 | 0.351 | PS |
| 8 | rs4410871 | 128,815,029 | PVT1 | A | 7,51 × 10 −5 | −0.318 | PSC |
| 16 | rs9936833 | 86,403,118 | LINC917, FENDRR | G | 7,68 × 10 −5 | −0.163 | EIM7 |
| SNP | Alleles | IBD | IBD EIM+ | IBD MEI- | Latin Population * | European Population * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3132680 | A/C | 0.295/ 0.705 | 0.295/ 0.705 | 0.295/ 0.705 | 0.242/ 0.758 | 0.320/ 0.680 |
| rs3823417 | A/G | 0.261/ 0.739 | 0.240/ 0.760 | 0.272/ 0.728 | 0.195/ 0.805 | 0.242/ 0.758 |
| rs4410871 | T/C | 0.338/ 0.662 | 0.361/ 0.639 | 0.326/ 0.674 | 0.401/ 0.599 | 0.307/ 0.693 |
| rs9936833 | C/T | 0.416/ 0.583 | 0.518/ 0.481 | 0.392/ 0.607 | 0.427 /0.573 | 0.356/ 0.644 |
| Dataset | Threshold | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full | 0.20 | 0.60 | 0.88 | 0.44 | 0.61 |
| Data | 0.50 | 0.75 | 0.54 | 0.86 | 0.62 |
| 0.70 | 0.71 | 0.24 | 0.97 | 0.36 | |
| Training | 0.20 | 0.64 | 0.93 | 0.48 | 0.65 |
| 0.50 | 0.75 | 0.59 | 0.84 | 0.63 | |
| 0.70 | 0.74 | 0.32 | 0.97 | 0.46 | |
| Testing | 0.20 | 0.72 | 0.92 | 0.61 | 0.70 |
| 0.50 | 0.84 | 0.66 | 0.91 | 0.72 | |
| 0.70 | 0.78 | 0.58 | 0.95 | 0.70 |
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | OR | CI | p-Value | OR | CI | p-Value |
| Family History of IBD | 3.16 | 1.43–6.95 | 0.004 | 2.84 | 1.13–7.14 | 0.03 |
| Age | 1.02 | 1.00–1.04 | 0.02 | 1.04 | 1.01–1.06 | 0.007 |
| Use Anti-TNF | 2.94 | 1.32–6.51 | 0.007 | 5.10 | 1.82–14.27 | 0.002 |
| rs9936833TT | 0.34 | 0.15–0.75 | 0.008 | 0.21 | 0.08–0.57 | 0.002 |
| rs3132680CA | 0.29 | 0.12–0.72 | 0.007 | 0.24 | 0.08–0.72 | 0.01 |
| rs3823417AG | 0.30 | 0.15–0.75 | 0.008 | 0.25 | 0.07–0.85 | 0.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pérez-Jeldres, T.; Reyes-Pérez, P.; Gonzalez-Hormazabal, P.; Avendano, C.; Segovia Melero, R.; Azocar, L.; Silva, V.; De La Vega, A.; Arriagada, E.; Hernandez, E.; et al. Prediction of Extraintestinal Manifestations in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Using Clinical and Genetic Variables with Machine Learning in a Latin IBD Group. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5741. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125741
Pérez-Jeldres T, Reyes-Pérez P, Gonzalez-Hormazabal P, Avendano C, Segovia Melero R, Azocar L, Silva V, De La Vega A, Arriagada E, Hernandez E, et al. Prediction of Extraintestinal Manifestations in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Using Clinical and Genetic Variables with Machine Learning in a Latin IBD Group. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5741. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125741
Chicago/Turabian StylePérez-Jeldres, Tamara, Paula Reyes-Pérez, Patricio Gonzalez-Hormazabal, Cristóbal Avendano, Roberto Segovia Melero, Lorena Azocar, Veronica Silva, Andres De La Vega, Elizabeth Arriagada, Elisa Hernandez, and et al. 2025. "Prediction of Extraintestinal Manifestations in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Using Clinical and Genetic Variables with Machine Learning in a Latin IBD Group" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5741. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125741
APA StylePérez-Jeldres, T., Reyes-Pérez, P., Gonzalez-Hormazabal, P., Avendano, C., Segovia Melero, R., Azocar, L., Silva, V., De La Vega, A., Arriagada, E., Hernandez, E., Aguilar, N., Pavez-Ovalle, C., Hernández-Rocha, C., Candia, R., Miquel, J. F., Alvarez-Lobos, M., Valdes, I., Medina-Rivera, A., & Bustamante, M. L. (2025). Prediction of Extraintestinal Manifestations in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Using Clinical and Genetic Variables with Machine Learning in a Latin IBD Group. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5741. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125741






