Disease-Specific Novel Role of Growth Differentiation Factor 15 in Organ Fibrosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Tissue Fibrosis
3. Chronic Inflammation: Primary Causative Factor, but Not the Sole Driver of the Fibrotic Process
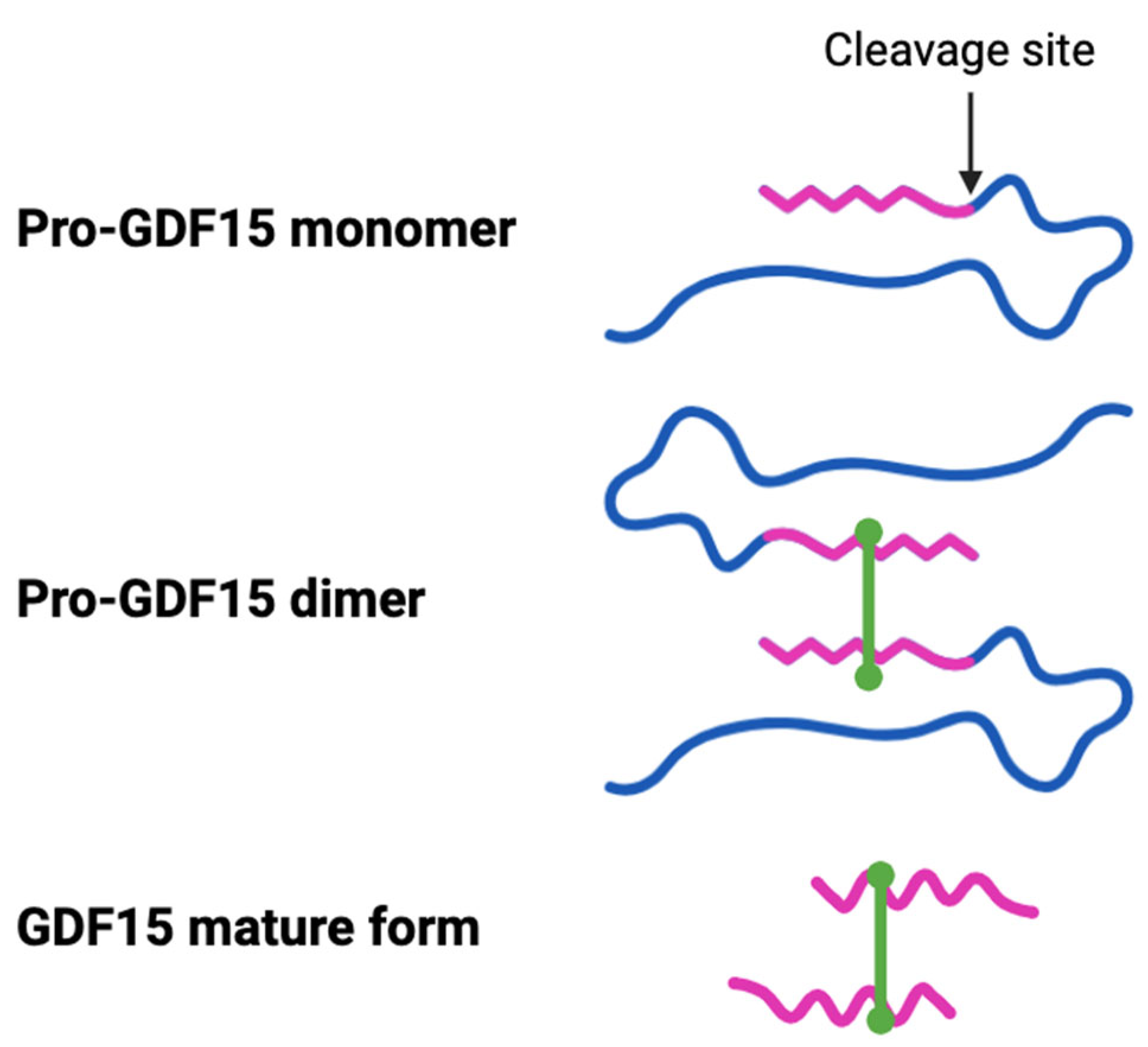
4. GDF15: An Inflammation and Stress-Associated Cytokine with Poorly Defined Biology
5. Emerging Role of GDF15 in Modulating Fibrosis in Different Organs
5.1. Pro- and Anti-Fibrotic Role of GDF15 in Liver Diseases
5.2. Role of GDF15 in Pulmonary Fibrosis
5.3. GDF15 Has Been Strongly Linked to Kidney Fibrosis
5.4. GDF15 Association with Cardiac Fibrosis
5.5. Is GDF15 Linked to Intestinal Fibrosis?
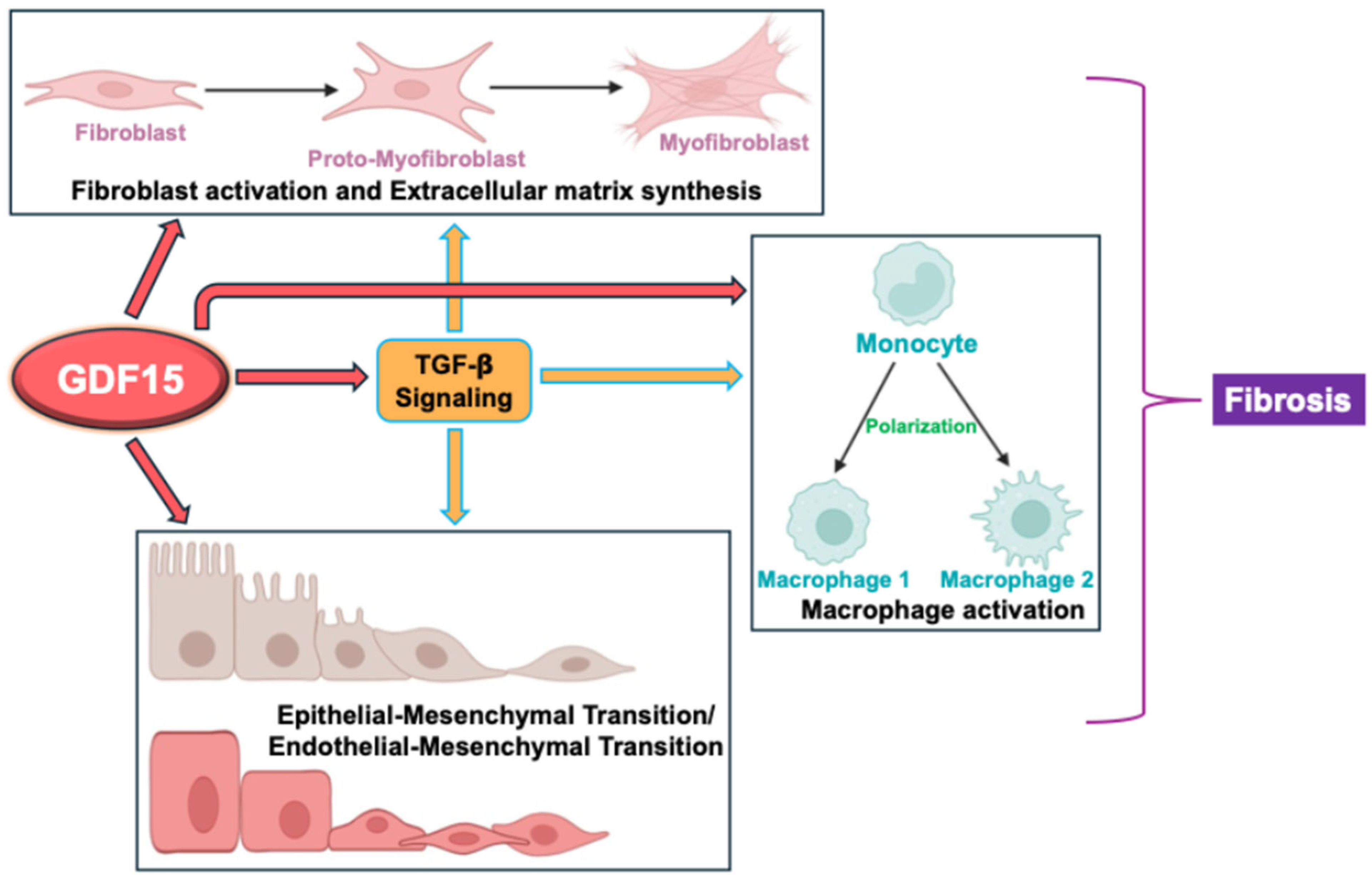
6. Knowledge Gap: Potential Mechanisms of GDF15 in Modulating Fibrosis
6.1. Myofibroblast Differentiation and Extracellular Matrix Formation
6.2. Macrophage Polarization
6.3. Epithelial-to or Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition
6.4. Regulation of TGF-β Activity
6.5. Characterizing GDF15-Interacting Receptors in Peripheral Tissues
6.6. Exploring GDF15 as a Target for Anti-Fibrotic Drugs
7. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wischhusen, J.; Melero, I.; Fridman, W.H. Growth/Differentiation Factor-15 (GDF-15): From Biomarker to Novel Targetable Immune Checkpoint. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bootcov, M.R.; Bauskin, A.R.; Valenzuela, S.M.; Moore, A.G.; Bansal, M.; He, X.Y.; Zhang, H.P.; Donnellan, M.; Mahler, S.; Pryor, K.; et al. MIC-1, a novel macrophage inhibitory cytokine, is a divergent member of the TGF-beta superfamily. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 11514–11519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, J.A.; Pothuraju, R.; Khan, P.; Sharma, G.; Muniyan, S.; Seshacharyulu, P.; Jain, M.; Nasser, M.W.; Batra, S.K. Pathophysiological role of growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF15) in obesity, cancer, and cachexia. Cytokine Growth Factor. Rev. 2022, 64, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Baek, S.J.; Eling, T.E. The diverse roles of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug activated gene (NAG-1/GDF15) in cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 85, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, A.B.; Codi, J.A.K.; Suchitha, G.P.; Hemavathi, K.N.; Dagamajalu, S.; Abhinand, C.S.; Raju, R.; Prasad, T.S.K. Mapping growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF15)-mediated signaling pathways in cancer: Insights into its role across different cancer types. Discov. Oncol. 2025, 16, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, A.; Kinscherf, R.; Bonaterra, G.A. Role of the Stress- and Inflammation-Induced Cytokine GDF-15 in Cardiovascular Diseases: From Basic Research to Clinical Relevance. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 24, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeisberg, M.; Kalluri, R. Cellular mechanisms of tissue fibrosis. 1. Common and organ-specific mechanisms associated with tissue fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2013, 304, C216–C225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speca, S.; Giusti, I.; Rieder, F.; Latella, G. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of intestinal fibrosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 3635–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andoh, A.; Nishida, A. Molecular Basis of Intestinal Fibrosis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Intest. Dis. 2023, 7, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, L.; Stalfort, J.; Barker, T.H.; Abebayehu, D. The interplay of fibroblasts, the extracellular matrix, and inflammation in scar formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 101530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, D.S.; Isnard, S.; Berini, C.; Lin, J.; Routy, J.P.; Royston, L. Coping With Stress: The Mitokine GDF-15 as a Biomarker of COVID-19 Severity. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 820350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwanska, A.; Cottage, C.T.; Piras, A.; Overed-Sayer, C.; Sihlbom, C.; Budida, R.; Wrench, C.; Connor, J.; Monkley, S.; Hazon, P.; et al. Increased expression and accumulation of GDF15 in IPF extracellular matrix contribute to fibrosis. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e153058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, B.K.; Um, S.H.; Seo, D.S.; Joo, S.K.; Bae, J.M.; Park, J.H.; Chang, M.S.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.; Jeong, W.I.; et al. Growth differentiation factor 15 predicts advanced fibrosis in biopsy-proven non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2018, 38, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.S.; Ahn, J.H.; Kim, M.Y.; Park, K.S. Elevated serum growth differentiation factor 15 and decorin predict the fibrotic progression of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huai, Q.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, X.; Xu, W.; Dai, H.; Wang, H. GDF15 Ameliorates Liver Fibrosis by Metabolic Reprogramming of Macrophages to Acquire Anti-Inflammatory Properties. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 16, 711–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Fu, P.; Ma, L. Kidney fibrosis: From mechanisms to therapeutic medicines. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, V.; Robinson-Cohen, C.; Smith, M.R.; Bellovich, K.A.; Bhat, Z.Y.; Bobadilla, M.; Brosius, F.; de Boer, I.H.; Essioux, L.; Formentini, I.; et al. Growth Differentiation Factor-15 and Risk of CKD Progression. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 2233–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.C.; Kuro-o, M.; Moe, O.W. Klotho and kidney disease. J. Nephrol. 2010, 23 (Suppl. S16), S136–S144. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.M.; Li, M.J.; Zhou, Y.L.; Ma, L.L.; Yi, X. Growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15), novel biomarker for assessing atrial fibrosis in patients with atrial fibrillation and rheumatic heart disease. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 21201–21207. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.; Li, Y.; Meng, L.; Yang, C.; Xia, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, F. Growth Differentiation Factor 15 Inhibits Cardiac Fibrosis, Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis in a Rat Model of Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction. Front. Biosci. 2025, 30, 26857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, T.A. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of fibrosis. J. Pathol. 2008, 214, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueha, S.; Shand, F.H.; Matsushima, K. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of chronic inflammation-associated organ fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junior, C.; Ulldemolins, A.; Narciso, M.; Almendros, I.; Farre, R.; Navajas, D.; Lopez, J.; Eroles, M.; Rico, F.; Gavara, N. Multi-Step Extracellular Matrix Remodelling and Stiffening in the Development of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiskirchen, R.; Weiskirchen, S.; Tacke, F. Organ and tissue fibrosis: Molecular signals, cellular mechanisms and translational implications. Mol. Aspects Med. 2019, 65, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, T.A.; Ramalingam, T.R. Mechanisms of fibrosis: Therapeutic translation for fibrotic disease. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1028–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johann, K.; Kleinert, M.; Klaus, S. The Role of GDF15 as a Myomitokine. Cells 2021, 10, 2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assadi, A.; Zahabi, A.; Hart, R.A. GDF15, an update of the physiological and pathological roles it plays: A review. Pflugers Arch. 2020, 472, 1535–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Su, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yu, D.; Jo, Y.; Joo, J.; Lee, H.J.; Ryu, D.; Wei, S. The implicated role of GDF15 in gastrointestinal cancer. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 54, e14290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Bermudez, L.S.; Kluter, H.; Kzhyshkowska, J.G. Macrophages as a Source and Target of GDF-15. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohensinner, P.J.; Niessner, A.; Huber, K.; Weyand, C.M.; Wojta, J. Inflammation and cardiac outcome. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 24, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Gu, L.; Guo, L.; Liu, M.; Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Elevated Expression of Growth Differentiation Factor-15 Is Associated With Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 891448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, M.; Nouraie, M.; Roth, M.G.; Tabib, T.; Winters, S.; Chen, X.; Sembrat, J.; Chu, Y.; Cardenes, N.; et al. GDF15 is an epithelial-derived biomarker of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2019, 317, L510–L521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takenouchi, Y.; Kitakaze, K.; Tsuboi, K.; Okamoto, Y. Growth differentiation factor 15 facilitates lung fibrosis by activating macrophages and fibroblasts. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 391, 112010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.F.; Chen, Y.C.; Li, Y.Z.; Wu, C.T.; Chang, P.C.; Yeh, W.L. Imperatorin ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis via GDF15 expression. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1292137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, W.; Cheng, D.; Sun, W.; Wang, T.; Jia, X.; Jia, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ni, C. Senescent alveolar type II epithelial cells-secreted GDF15 promotes silicosis progression via interfering intercellular communication. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 292, 117917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilson, J.; Scorletti, E.; Bindels, L.B.; Afolabi, P.R.; Targher, G.; Calder, P.C.; Sethi, J.K.; Byrne, C.D. Growth differentiation factor-15 and the association between type 2 diabetes and liver fibrosis in NAFLD. Nutr. Diabetes 2021, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, P.; Ma, M.Z.; Kuai, J.H. Identification of growth differentiation factor 15 as a pro-fibrotic factor in mouse liver fibrosis progression. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2021, 102, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.I.; Shin, H.W.; Chun, Y.S.; Park, J.W. CST3 and GDF15 ameliorate renal fibrosis by inhibiting fibroblast growth and activation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 500, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valino-Rivas, L.; Cuarental, L.; Ceballos, M.I.; Pintor-Chocano, A.; Perez-Gomez, M.V.; Sanz, A.B.; Ortiz, A.; Sanchez-Nino, M.D. Growth differentiation factor-15 preserves Klotho expression in acute kidney injury and kidney fibrosis. Kidney Int. 2022, 101, 1200–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucerka, O.; Blahutova, M.; Kosek, V.; Minarikova, P.; Horacek, J.M.; Urbanek, P.; Maly, M. Exploring the Role of GDF-15 in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Case-Controlled Study Comparing Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis with Non-Inflammatory Controls. Metabolites 2024, 14, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonkic, A.; Kumric, M.; Akrapovic Olic, I.; Rusic, D.; Zivkovic, P.M.; Supe Domic, D.; Sundov, Z.; Males, I.; Bozic, J. Growth differentiation factor-15 serum concentrations reflect disease severity and anemia in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 30, 1899–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreuter, M.; Ladner, U.M.; Costabel, U.; Jonigk, D.; Heussel, C.P. The Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Fibrosis. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2021, 118, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarcon-Dionet, A.; Ruiz, A.; Chavez-Galan, L.; Buendia-Roldan, I.; Selman, M. GDF15 as a potential biomarker to distinguish fibrotic from non-fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Collard, H.R.; Egan, J.J.; Martinez, F.J.; Behr, J.; Brown, K.K.; Colby, T.V.; Cordier, J.F.; Flaherty, K.R.; Lasky, J.A.; et al. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT statement: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 788–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collard, H.R.; Ryerson, C.J.; Corte, T.J.; Jenkins, G.; Kondoh, Y.; Lederer, D.J.; Lee, J.S.; Maher, T.M.; Wells, A.U.; Antoniou, K.M.; et al. Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. An International Working Group Report. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 194, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komaba, H. Renoprotection by GDF15 and Klotho: Birds of a feather flock together. Kidney Int. 2022, 101, 1112–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochette, L.; Dogon, G.; Zeller, M.; Cottin, Y.; Vergely, C. GDF15 and Cardiac Cells: Current Concepts and New Insights. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazagova, M.; Buikema, H.; Landheer, S.W.; Vavrinec, P.; Buiten, A.; Henning, R.H.; Deelman, L.E. Growth differentiation factor 15 impairs aortic contractile and relaxing function through altered caveolar signaling of the endothelium. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2013, 304, H709–H718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.M.; Kim, J.; Lee, Y.J.; Bae, S.U.; Lee, H.W. Inflammatory bowel disease-associated intestinal fibrosis. J. Pathol. Transl. Med. 2023, 57, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, S.; Liu, X.; He, C.; Gao, H.; Wang, B.; Hua, R.; Gao, L.; Shang, H.; Sun, F.; Xu, J. Inflammation accelerating intestinal fibrosis: From mechanism to clinic. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, B.; Jin, T.; Ocansey, D.K.W.; Jiang, J.; Mao, F. Intestinal Fibrosis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease and the Prospects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 835005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, J.H.; Holubar, S.; Rieder, F. Fibrostenotic strictures in Crohn’s disease. Intest. Res. 2020, 18, 379–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfredsson, J.; Wick, M.J. Mechanism of fibrosis and stricture formation in Crohn’s disease. Scand. J. Immunol. 2020, 92, e12990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamali Dolatabadi, R.; Feizi, A.; Halaji, M.; Fazeli, H.; Adibi, P. The Prevalence of Adherent-Invasive Escherichia coli and Its Association With Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 730243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigvardsen, C.M.; Richter, M.M.; Engelbeen, S.; Kleinert, M.; Richter, E.A. GDF15 is still a mystery hormone. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 36, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.T.; Tian, Q.Y.; Xie, B.; Hu, Y.B.; Deng, Z.H. GDF15 activates human fibroblast MRC5 cells via miR-338/STAT1 in silicosis. Clin. Exp. Med. 2025, 25, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.I.; Shin, H.W.; Chun, Y.S.; Cho, C.H.; Koh, J.; Chung, D.H.; Park, J.W. Epithelial cell-derived cytokines CST3 and GDF15 as potential therapeutics for pulmonary fibrosis. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Wang, J.; Cai, X.; Liou, Y.C.; Shen, H.M.; Hao, J.; Huang, C.; Luo, G.; He, W. Macrophage plasticity: Signaling pathways, tissue repair, and regeneration. MedComm (2020) 2024, 5, e658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locati, M.; Curtale, G.; Mantovani, A. Diversity, Mechanisms, and Significance of Macrophage Plasticity. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2020, 15, 123–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lis-Lopez, L.; Bauset, C.; Seco-Cervera, M.; Cosin-Roger, J. Is the Macrophage Phenotype Determinant for Fibrosis Development? Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Tang, G. Macrophages in intestinal fibrosis and regression. Cell Immunol. 2022, 381, 104614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrot, C.Y.; Karampitsakos, T.; Herazo-Maya, J.D. Monocytes and macrophages: Emerging mechanisms and novel therapeutic targets in pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2023, 325, C1046–C1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chang, C.C.; Sun, Z.; Madsen, D.; Zhu, H.; Padkjaer, S.B.; Wu, X.; Huang, T.; Hultman, K.; Paulsen, S.J.; et al. GFRAL is the receptor for GDF15 and is required for the anti-obesity effects of the ligand. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1158–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, H.; Lichtnekert, J.; Andrassy, J.; Schraml, B.U.; Romagnani, P.; Anders, H.J. Macrophages and fibrosis: How resident and infiltrating mononuclear phagocytes account for organ injury, regeneration or atrophy. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1194988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, J.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, D. New insights into fibrosis from the ECM degradation perspective: The macrophage-MMP-ECM interaction. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Xu, Z.; Yan, X. The role of the macrophage-to-myofibroblast transition in renal fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 934377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovisa, S.; Genovese, G.; Danese, S. Role of Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Crohns Colitis 2019, 13, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Shen, J.; Ran, Z. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in Crohn’s disease. Mucosal Immunol. 2018, 11, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Chen, C.Y.; Liu, C.C.; Stavropoulos, D.; Rao, M.; Petrash, J.M.; Chang, K.C. GDF-15 Attenuates the Epithelium-Mesenchymal Transition and Alleviates TGFbeta2-Induced Lens Opacity. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2024, 13, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Mulya, A.; Nieuwoudt, S.; Vandanmagsar, B.; McDowell, R.; Heintz, E.C.; Zunica, E.R.M.; Collier, J.J.; Bozadjieva-Kramer, N.; Seeley, R.J.; et al. GDF15 Mediates the Effect of Skeletal Muscle Contraction on Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion. Diabetes 2023, 72, 1070–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Qian, L.; Song, T.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, B. Growth differentiation factor-15 promotes immune escape of ovarian cancer via targeting CD44 in dendritic cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2021, 402, 112522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Ma, Y.M.; Zheng, P.S.; Zhang, P. GDF15 promotes the proliferation of cervical cancer cells by phosphorylating AKT1 and Erk1/2 through the receptor ErbB2. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; He, L.; Li, W.; Xu, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D.; Dou, K.; Zhuang, R.; Jin, B.; Zhang, W.; et al. GDF15 induces immunosuppression via CD48 on regulatory T cells in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, R.K.; Gogikar, A.; Nanda, A.; Janga, L.S.N.; Sambe, H.G.; Yasir, M.; Ramphall, S. A Comparison of the Effectiveness of Nintedanib and Pirfenidone in Treating Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2024, 16, e54268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Fu, J. GDF15 as a key disease target and biomarker: Linking chronic lung diseases and ageing. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2024, 479, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Organ/Tissues | Type of Study | Disease | Role of GDF15 | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lung | Clinical/Animal | Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis | Pro-fibrotic | [12,31,32] |
| Animal | Bleomycin-induced experimental fibrosis | Pro-fibrotic | [33] | |
| Animal/In vitro | Bleomycin-induced experimental fibrosis | Anti-fibrotic | [34] | |
| Animal/In vitro | Silicosis of alveolar epithelial cells | Pro-fibrotic | [35] | |
| Liver | Clinical | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease | Pro-fibrotic | [13,36] |
| Clinical | MASLD | Pro-fibrotic | [14] | |
| Animal | CCl4-induced experimental fibrosis in mice | Pro-fibrotic | [37] | |
| Animal | CCl4/DDC-induced fibrosis in mice | Anti-fibrotic | [15] | |
| Kidney | Clinical | Chronic kidney disease | Pro-fibrotic | [17] |
| Animal | Ureteral obstruction-induced fibrosis in mice | Anti-fibrotic | [38] | |
| Animal | Acute kidney injury-associated fibrosis | Anti-fibrotic | [39] | |
| Heart | Clinical | Atrial fibrillation and RHD | Pro-fibrotic | [19] |
| Animal | Rat model of heart failure | Anti-fibrotic | [20] | |
| Intestine | Clinical | Inflammatory bowel diseases | Increased GDF15 | [40,41] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sawant, H.; Borthakur, A. Disease-Specific Novel Role of Growth Differentiation Factor 15 in Organ Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125713
Sawant H, Borthakur A. Disease-Specific Novel Role of Growth Differentiation Factor 15 in Organ Fibrosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125713
Chicago/Turabian StyleSawant, Harshal, and Alip Borthakur. 2025. "Disease-Specific Novel Role of Growth Differentiation Factor 15 in Organ Fibrosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125713
APA StyleSawant, H., & Borthakur, A. (2025). Disease-Specific Novel Role of Growth Differentiation Factor 15 in Organ Fibrosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125713






