Proteomic Profiling Identifies MARCO in Extracellular Vesicles, as a Potential Biomarker for Leishmaniasis in HIV Co-Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) Results for Antigens SPLA, rK28 and SECA
2.2. Purification and Characterization of Plasma-Derived EVs
2.3. Leishmania Proteins Identification in Patient HIV+/VL+
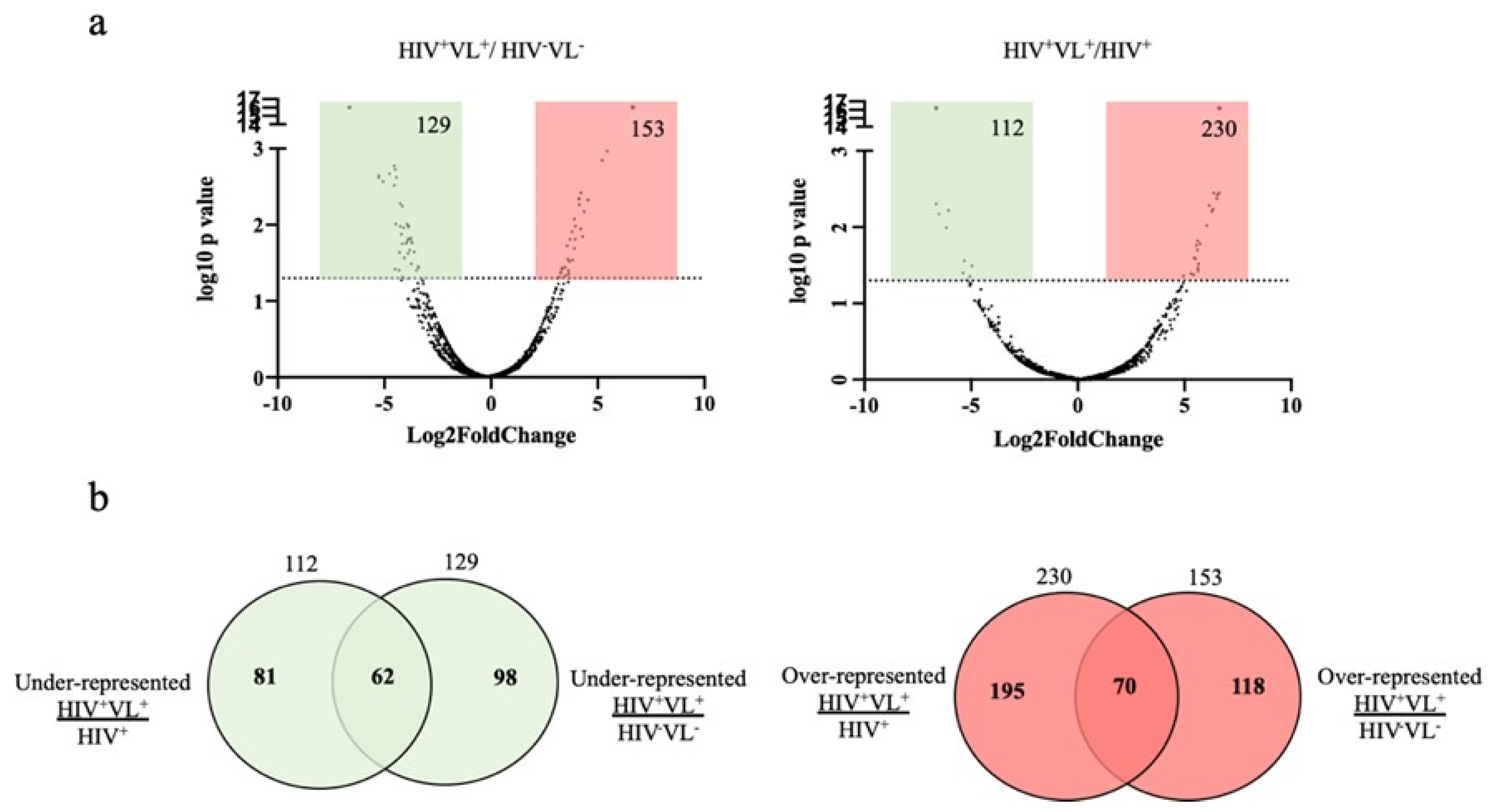
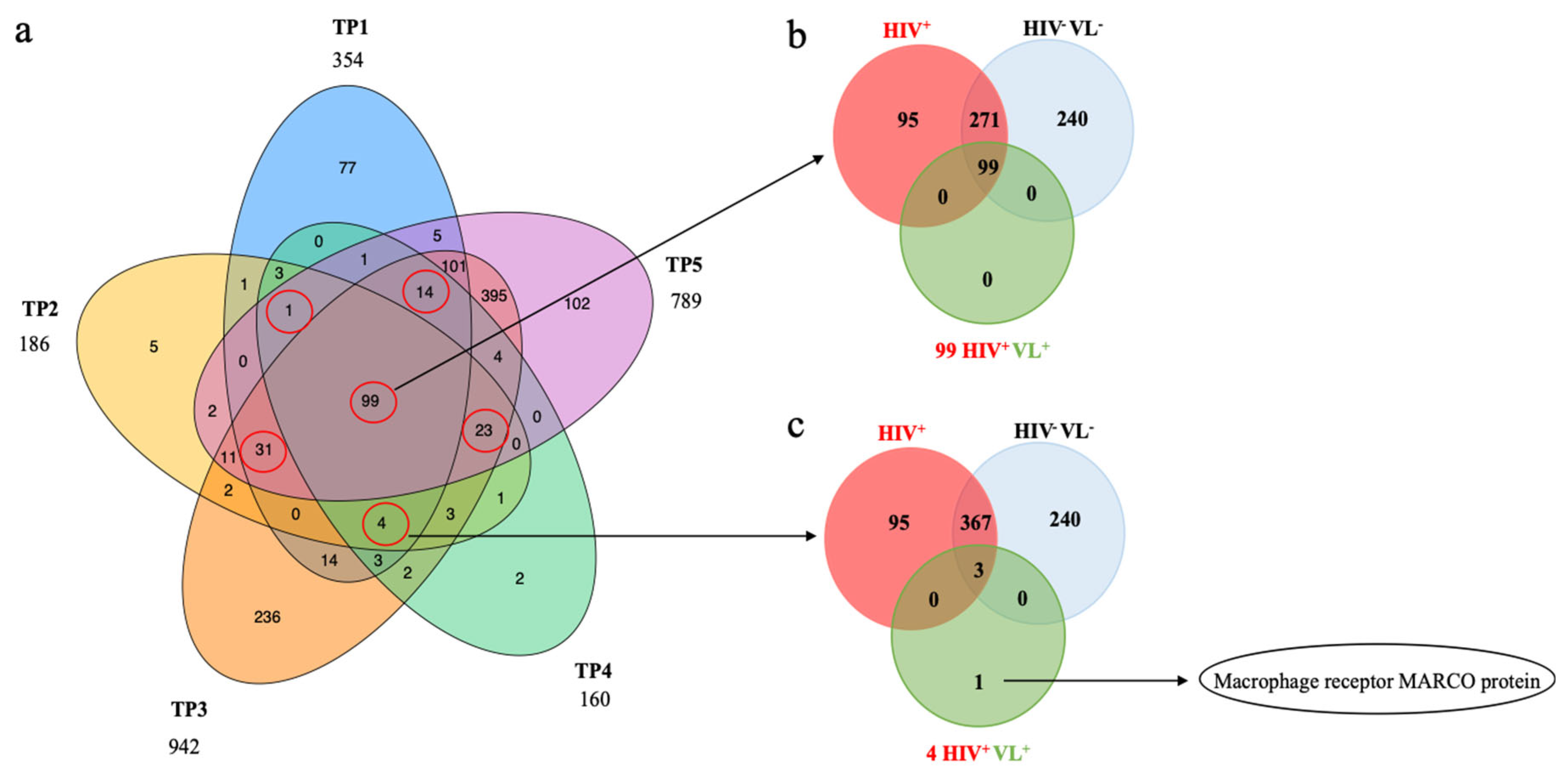
2.4. Human Proteins Identification in Patient HIV+VL+
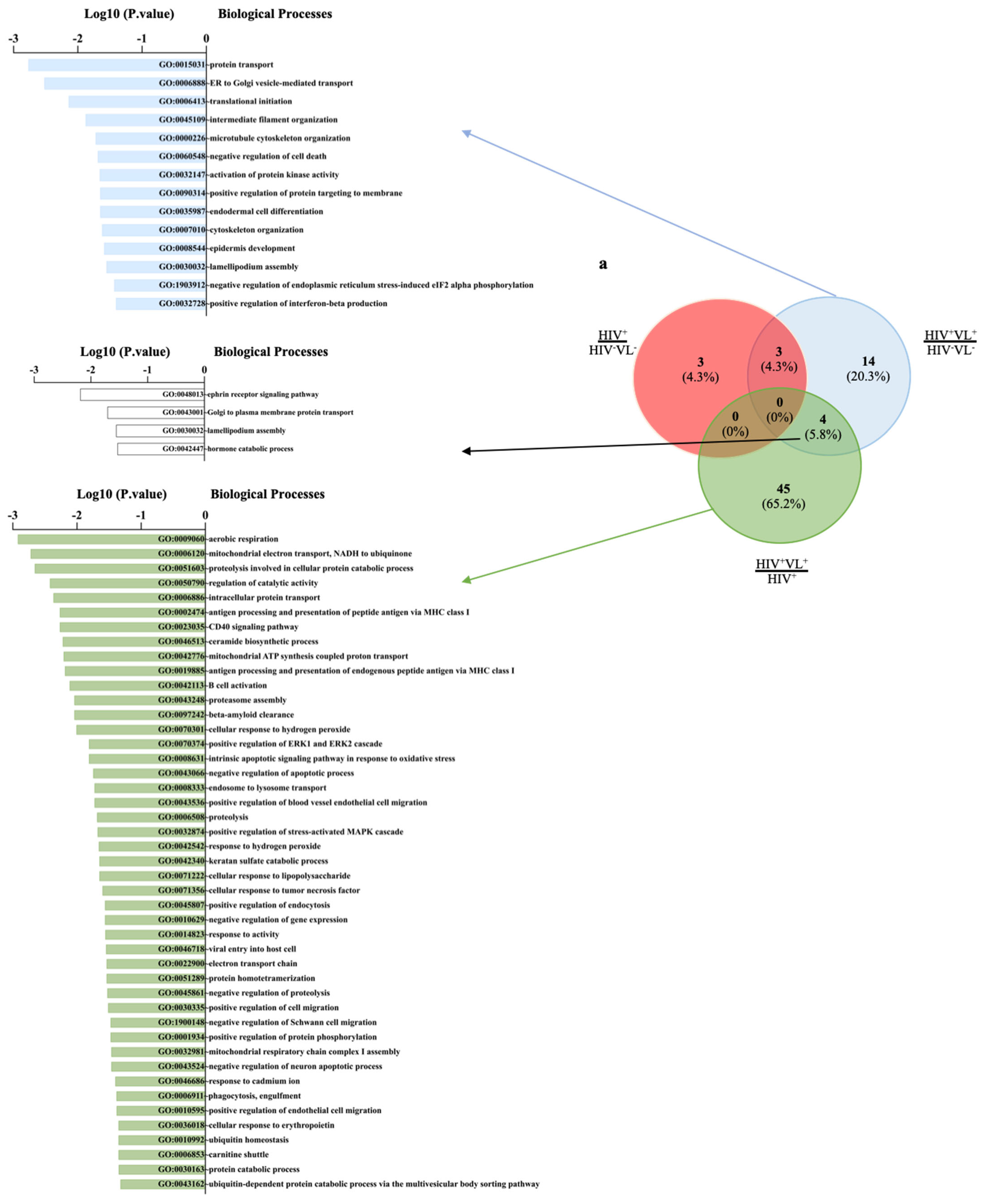
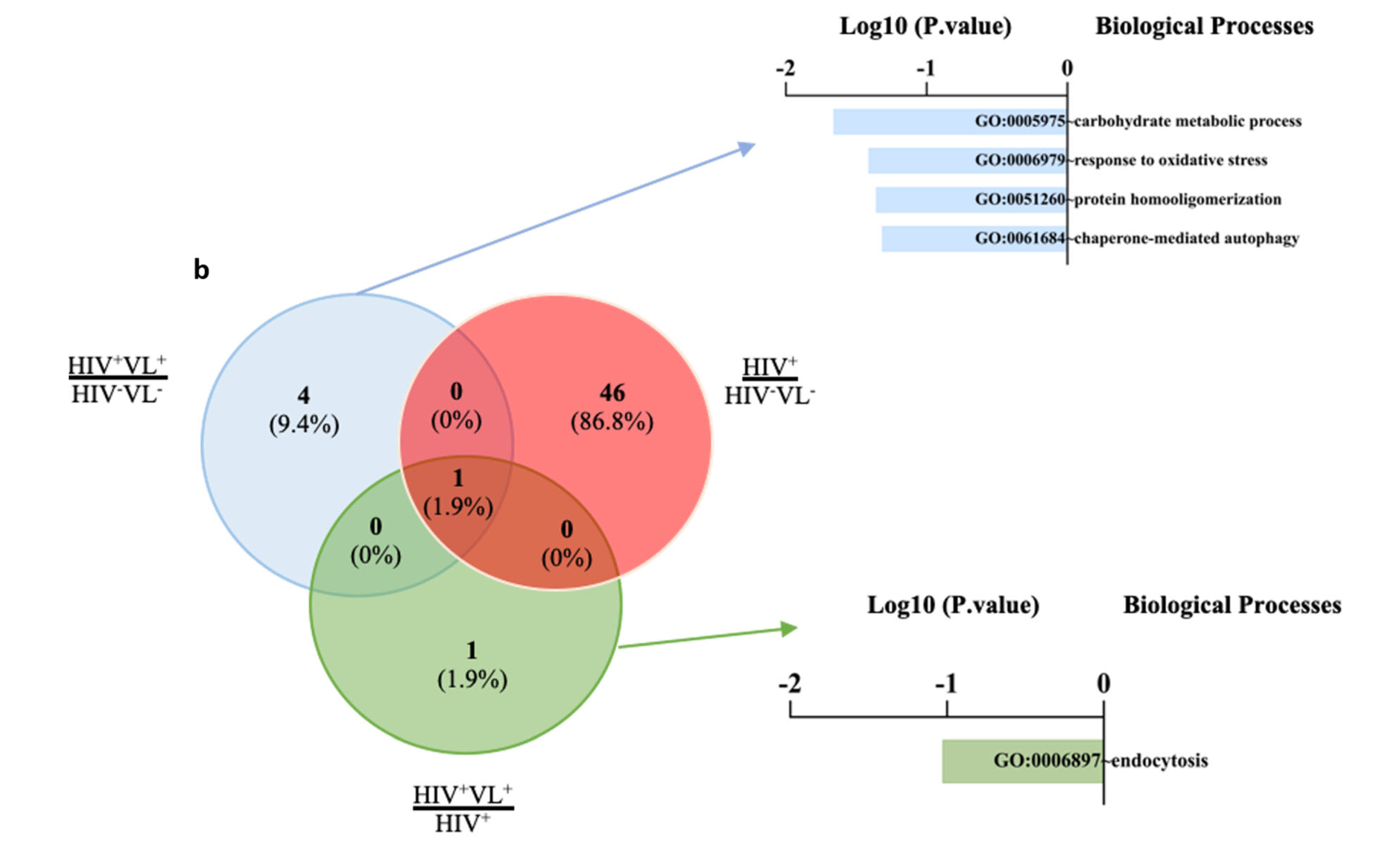
2.5. Quantitative Analysis of Human Proteins
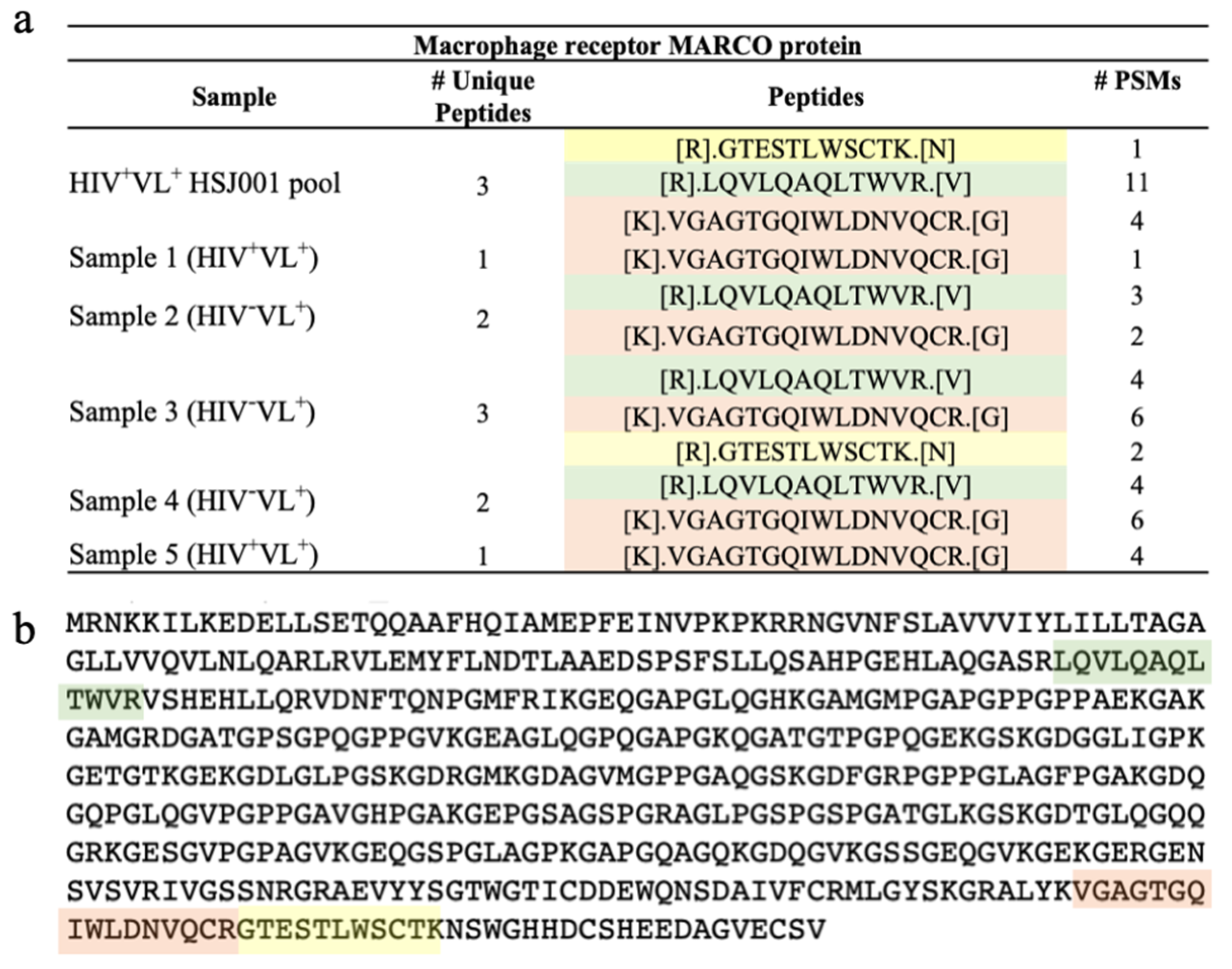
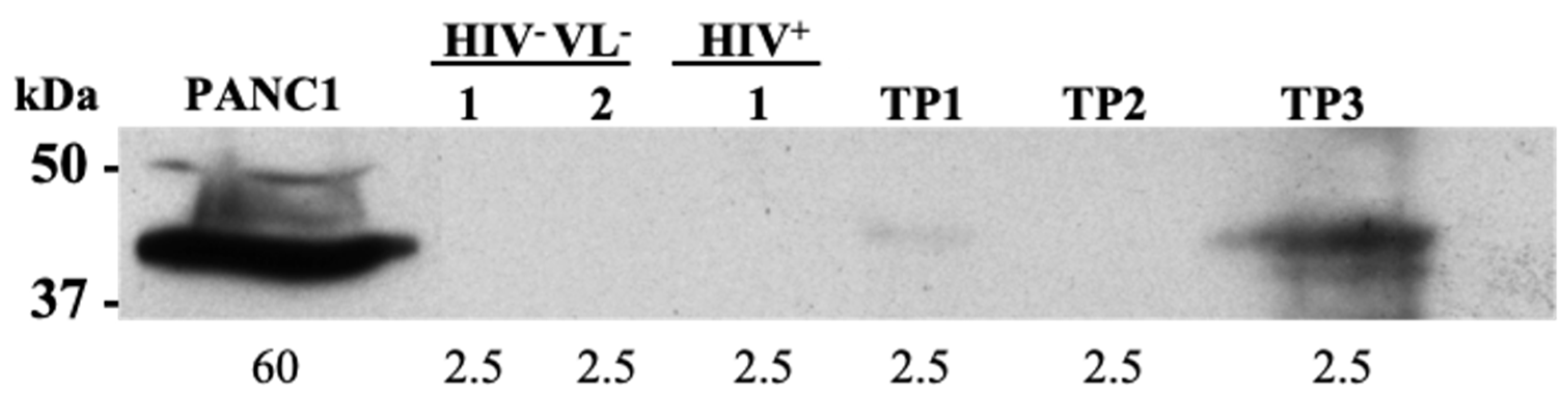
2.6. Human Derived Biomarkers of VL
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Clinical Description of the Study Patient
4.2. Cohort Design: Leishmania+HIV+ Patient, HIV+ Patients and HIV−VL− Controls
4.3. Blood Collection and Plasma Processing
4.4. Parasites and Cell Culture
4.5. Antigens
4.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.7. Roc Curve Determination
4.8. Purification of Plasma-Derived EVs by Size-Exclusion Chromatograph
4.9. Bead-Based Flow Cytometry Assay
4.10. Plasma EVs Protein Quantification
4.11. Nanoparticle Track Analysis
4.12. Electron Microscopy
4.13. Samples Preparation and Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)
4.14. Quantitative Evaluation of Human Proteins
4.15. Western Blot
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Leishmaniasis. Fact Sheet. 2023. Available online: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/leishmaniasis# (accessed on 12 January 2024).
- Roberts, M.T.M. Current understandings on the immunology of leishmaniasis and recent developments in prevention and treatment. Br. Med. Bull. 2005, 75–76, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakkas, H.; Gartzonika, C.; Levidiotou, S. Laboratory Diagnosis of Visceral Leishmaniasis. J. Vector Borne Dis. 2016, 53, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Nedawi, K.; Meehan, B.; Micallef, J.; Lhotak, V.; May, L.; Guha, A.; Rak, J. Intercellular transfer of the oncogenic receptor EGFRvIII by microvesicles derived from tumour cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 6, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzás, E.I.; György, B.; Nagy, G.; Falus, A.; Gay, S. Emerging role of extracellular vesicles in inflammatory diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2014, 6, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Conde, I.; Shrimpton, C.N.; Thiagarajan, P.; López, J.A. Tissue-factor-bearing microvesicles arise from lipid rafts and fuse with activated platelets to initiate coagulation. Blood 2005, 106, 1604–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camussi, G.; Deregibus, M.C.; Bruno, S.; Grange, C.; Fonsato, V.; Tetta, C. Exosome/microvesicle-mediated epigenetic reprogramming of cells. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2011, 1, 98–110. [Google Scholar]
- Yáñez-Mó, M.; Siljander, P.R.-M.; Andreu, Z.; Bedina Zavec, A.; Borràs, F.E.; Buzas, E.I.; Buzas, K.; Casal, E.; Cappello, F.; Carvalho, J.; et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerobin, J.; Abou-Samra, A.-B.; Mir, R.; Kumar, R.; Sadida, H.Q.; Akil, A.S.A.-S.; Macha, M.A.; Algehainy, N.; Bhat, A.A.; Kumar, M.A.; et al. Extracellular vesicles as tools and targets in therapy for diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Silverman, J.M.; Chan, S.K.; Robinson, D.P.; Dwyer, D.M.; Nandan, D.; Foster, L.J.; Reiner, N.E. Proteomic analysis of the secretome of Leishmania donovani. Genome Biol. 2008, 9, R35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves, S.; Costa, I.; Luelmo, S.; Santarém, N.; Cordeiro-da-Silva, A. Leishmania Vesicle-Depleted Exoproteome: What, Why, and How? Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, J.P.B.; Almeida, T.F.; Petersen, A.L.O.A.; Guedes, C.E.S.; Mota, M.S.V.; Lima, J.G.B.; Palma, L.C.; Buck, G.A.; Krieger, M.A.; Probst, C.M.; et al. Proteomic analysis reveals differentially expressed proteins in macrophages infected with Leishmania amazonensis or Leishmania major. Microbes Infect. 2013, 15, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasra Hassani, M.O. Immunomodulatory Impact of Leishmania-Induced Macrophage Exosomes: A Comparative Proteomic and Functional Analysis. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2185. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Gioseffi, A.; Hamerly, T.; Van, K.; Dinglasan, R.R.; A Yates, P.; E Kima, P. Leishmania-infected macrophages release extracellular vesicles that can promote lesion development. Life Sci. Alliance 2020, 3, e202000742. [Google Scholar]
- Esteves, S.; Lima, C.; Costa, I.; Osório, H.; Fernandez-Becerra, C.; Santarém, N.; Cordeiro-da-Silva, A. Characterization and proteomic analysis of plasma EVs recovered from healthy and diseased dogs with Canine Leishmaniosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aparici-Herraiz, I.; Gualdrón-López, M.; Castro-Cavadía, C.J.; Carmona-Fonseca, J.; Yasnot, M.F.; Fernandez-Becerra, C.; Del Portillo, H.A. Antigen Discovery in Circulating Extracellular Vesicles From Plasmodium vivax Patients. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 11, 811390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes-Serra, N.; Mendes, M.T.; Mazagatos, C.; Segui-Barber, J.; Ellis, C.C.; Ballart, C.; Garcia-Alvarez, A.; Gállego, M.; Gascon, J.; Ballart, C.; et al. Plasma-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Potential Biomarkers in Heart Transplant Patient with Chronic Chagas Disease. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1846–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Kong, Q.; Cho, W.C.; Ju, X.; Shen, Y.; et al. Proteomic profiling of serum extracellular vesicles identifies diagnostic markers for echinococcosis. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes-Serra, N.; Pinazo, M.-J.; Fernandez-Becerra, C.; Torrecilhas, A.C.; Gualdron-Lopez, M. Extracellular Vesicles in Trypanosoma cruzi Infection: Immunomodulatory Effects and Future Perspectives as Potential Control Tools against Chagas Disease. J. Immunol. Res. 2022, 2022, 5230603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualdrón-López, M.; Díaz-Varela, M.; Zanghi, G.; Aparici-Herraiz, I.; Steel, R.W.J.; Schäfer, C.; Cuscó, P.; Chuenchob, V.; Kangwangransan, N.; Billman, Z.P.; et al. Mass Spectrometry Identification of Biomarkers in Extracellular Vesicles From Plasmodium vivax Liver Hypnozoite Infections. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2022, 21, 100406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, A.I.; Caldas, C.; Santarem, N.; Luelmo, S.; Costa, I.; Martins, C.; Monteiro, R.; Conde, S.; Tavares, R.; da Silva, A.C. Leishmania and HIV co-infection: First naturally Leishmania strain presenting decreased susceptibility to miltefosine, recovered from a patient in Portugal. J. Infect. Public Health 2024, 17, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toda, H.; Diaz-Varela, M.; Segui-Barber, J.; Roobsoong, W.; Baro, B.; Garcia-Silva, S.; Galiano, A.; Gualdrón-López, M.; Almeida, A.G.G.; Brito, M.A.M.; et al. Plasma-derived extracellular vesicles from Plasmodium vivax patients signal spleen fibroblasts via NF-kB facilitating parasite cytoadherence. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chitti, S.V.; Gummadi, S.; Kang, T.; Shahi, S.; Marzan, A.L.; Nedeva, C.; Sanwlani, R.; Bramich, K.; Stewart, S.; Petrovska, M.; et al. Vesiclepedia 2024: An extracellular vesicles and extracellular particles repository. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D1694–D1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musante, L.; Duriez, E.; Byrne, B.; Ravidà, A.; Domon, B.; Holthofer, H.; Saraswat, M. Biochemical and physical characterisation of urinary nanovesicles following CHAPS treatment. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, J.M.; Reiner, N.E. Leishmania Exosomes Deliver Preemptive Strikes to Create an Environment Permissive for Early Infection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2011, 1, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambertz, U.; Silverman, J.M.; Nandan, D.; McMaster, W.R.; Clos, J.; Foster, L.J.; Reiner, N.E. Secreted virulence factors and immune evasion in visceral leishmaniasis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 91, 887–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, S.; Baker, K.; Padman, B.S.; Patwa, R.; Dunstan, R.A.; Weston, T.A.; Schlosser, K.; Bailey, B.; Lithgow, T.; Lazarou, M.; et al. Bacteriophage Transcytosis Provides a Mechanism To Cross Epithelial Cell Layers. Am. Soc. Microbiol. 2018, 8, e01874-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petris, C.K.; Golomb, M.; Phillips, T.E. Bacterial Transcytosis across Conjunctival M Cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 2172–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, F.M.; Carvalho, L.H.; Teixeira-Carvalho, A.; Franklin, B.S.; Filho, A.L.; de Paula, S.C.; Fontes, C.J.; Brito, C.F. Augmented plasma microparticles during acute Plasmodium vivax infection. Malar. J. 2010, 9, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Menezes-Neto, A.; Sáez, M.J.; Lozano-Ramos, I.; Segui-Barber, J.; Martin-Jaular, L.; Ullate, J.M.; Fernandez-Becerra, C.; Borrás, F.E.; Del Portillo, H.A. Size-exclusion chromatography as a stand-alone methodology identifies novel markers in mass spectrometry analyses of plasma-derived vesicles from healthy individuals. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, P.L.; Reed, S.G.; Santos, M.L.B.; Cunha, L.C.S.; Lino, M.T.B.; Bomfim, M.O.M.; Silva, A.M.; de Jesus, A.R.; de Moura, T.R.; de Almeida, R.P.; et al. The Severity of Visceral Leishmaniasis Correlates with Elevated Levels of Serum IL-6, IL-27 and sCD14. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krastinova, E.; Goujard, C.; Leroy, C.; Venet, A.; Meyer, L.; Seng, R.; Rami, A.; Lecuroux, C.; Cabié, A. High Soluble CD14 Levels at Primary HIV-1 Infection Predict More Rapid Disease Progression. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, 909–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, P.K.; Schorey, J.S. Exosomes derived from M. Bovis BCG infected macrophages activate antigen-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kropf, P.; Freudenberg, M.A.; Modolell, M.; Price, H.P.; Herath, S.; Antoniazi, S.; Galanos, C.; Smith, D.F.; Muller, I. Toll-Like Receptor 4 Contributes to Efficient Control of Infection with the Protozoan Parasite Leishmania major. Infect. Immun. 2004, 4, 1920–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pessenda, G.; da Silva, J.S. Arginase and its mechanisms in Leishmania persistence. Parasite Immunol. 2020, 42, e12722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, I.; Hailu, A.; Choi, B.S.; Abebe, T.; Fuentes, J.M.; Munder, M.; Modolell, M.; Kropf, P. Age-related alteration of arginase activity impacts on severity of leishmaniasis. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2008, 2, e235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iniesta, V.; Carcelén, J.; Molano, I.; Peixoto, P.M.; Redondo, E.; Parra, P.; Mangas, M.; Monroy, I.; Campo, M.L.; Nieto, C.G.; et al. Arginase I induction during Leishmania major infection mediates the development of disease. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 6085–6090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kropf, P.; Modolell, M.; Müller, I.; Arpa, L.; Fähnrich, E.; Herath, S.; Weber, V.; Fuentes, J.M.; Celada, A.; Soler, G. Arginase and polyamine synthesis are key factors in the regulation of experimental leishmaniasis in vivo. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1000–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solano-Gálvez, S.G.; Gutiérrez-Kobeh, L.; Álvarez-Hernández, D.-A.; Vázquez-López, R. Leishmania: Manipulation of signaling pathways to inhibit host cell apoptosis. Ther. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2021, 8, 20499361211014977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra-Meneses, A.V.; Sanchez, C.; Alvar, J.; Carrillo, E.; Moreno, J. Monocyte Chemotactic Protein 1 in Plasma from Soluble Leishmania Antigen-Stimulated Whole Blood as a Potential Biomarker of the Cellular Immune Response to Leishmania infantum. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plüddemann, A.; Neyen, C.; Gordon, S. Macrophage scavenger receptors and host-derived ligands. Methods 2007, 43, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, S.; Bowdish, D.M.E. Conserved domains of the class A scavenger receptors: Evolution and function. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 227, 19–31. [Google Scholar]
- Kanno, S.; Hirano, S.; Sakamoto, T.; Furuyama, A.; Takase, H.; Kato, H.; Fukuta, M.; Aoki, Y. Scavenger receptor MARCO contributes to cellular internalization of exosomes by dynamin-dependent endocytosis and macropinocytosis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Varin, A.; Chen, Y.; Liu, B.; Tryggvason, K.; Gordon, S. SR-A/MARCO-mediated ligand delivery enhances intracellular TLR and NLR function, but ligand scavenging from cell surface limits TLR4 response to pathogens. Blood 2011, 117, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novakowski, K.E.; Huynh, A.; Han, S.; Dorrington, M.G.; Yin, C.; Tu, Z.; Pelka, P.; Whyte, P.; Guarné, A.; Sakamoto, K.; et al. A naturally occurring transcript variant of MARCO reveals the SRCR domain is critical for function. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2016, 94, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beattie, L.; Sawtell, A.; Mann, J.; Frame, T.C.M.; Teal, B.; de Labastida Rivera, F.; Brown, N.; Walwyn-Brown, K.; Moore, J.W.J.; MacDonald, S.; et al. Bone marrow-derived and resident liver macrophages display unique transcriptomic signatures but similar biological functions. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 758–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillaume Hoeffel, F.G. Fetal monocytes and the origins of tissue-resident macrophages. Cell. Immunol. 2018, 330, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarov, T.; Cox, N.; Juarez-Carreño, S.; Geissmann, F. Physiology and diseases of tissue-resident macrophages. Nature 2023, 618, 698–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Józefowski, S. The role of the class A scavenger receptors, SR-A and MARCO, in the immune system. Part 2. Contribution to recognition and phagocytosis of pathogens as well as induction of immune response. Postepy Hig. Med. Dosw. (Online) 2012, 66, 120–131. [Google Scholar]
- Pessenda, G.; Ferreira, T.R.; Paun, A.; Kabat, J.; Amaral, E.P.; Kamenyeva, O.; Gazzinelli-Guimaraes, P.H.; Perera, S.R.; Ganesan, S.; Lee, S.H.; et al. Kupffer cell and recruited macrophage heterogeneity orchestrate granuloma maturation and hepatic immunity in visceral leishmaniasis. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, I.N.; Palma, L.C.; Campos, G.O.; Lima, J.G.; DE Almeida, T.F.; DE Menezes, J.P.; Ferreira, C.A.; Santos, R.R.; Buck, G.A.; Manque, P.A.; et al. The scavenger receptor MARCO is involved in Leishmania major infection by CBA/J macrophages. Parasite Immunol. 2009, 31, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Chen, Y.; Sankala, M.; Peiser, L.; Pikkarainen, T.; Kraal, G.; Tryggvason, K.; Gordon, S. MARCO, an innate activation marker of macrophages, is a class A scavenger receptor for Neisseria meningitidis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2006, 36, 940–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Song, J.; Weng, C.; Xu, J.; Huang, M.; Huang, Q.; Sun, R.; Xiao, W.; Sun, C. Association of decreased expression of the macrophage scavenger receptor MARCO with tumor progression and poor prognosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 32, 1107–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campino, L.; Maia, C. Epidemiology of leishmaniases in Portugal. Acta Med. Port. 2010, 23, 859–864. [Google Scholar]
- Santarém, N.; Cunha, J.; Silvestre, R.; Silva, C.; Moreira, D.; Ouellette, M.; Cordeiro-DA-Silva, A. The impact of distinct culture media in Leishmania infantum biology and infectivity. Parasitology 2014, 141, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, D.; Amorim, A.M.; Cordeiro-Da-Silva, A.; Tavares, J.; Silvestre, R.; Santarém, N.; Silva, A.M.; Loureiro, I. Impact of continuous axenic cultivation in Leishmania infantum virulence. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2012, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaish, M.; Bhatia, A.; Chakravarty, J.; Reed, S.; Sundar, S. Evaluation of rK28 antigen for serodiagnosis of visceral Leishmaniasis in India. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattabhi, S.; Whittle, J.; Mohamath, R.; El-Safi, S.; Moulton, G.G.; Guderian, J.A.; Colombara, D.; Abdoon, A.O.; Mukhtar, M.M.; Mondal, D.; et al. Design, development and evaluation of rK28-based point-of-care tests for improving rapid diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Varela, M.; de Menezes-Neto, A.; Perez-Zsolt, D.; Gámez-Valero, A.; Barber, J.S.; Izquierdo-Useros, N.; Martinez-Picado, J.; Fernández-Becerra, C.; Del Portillo, H.A. Proteomics study of human cord blood reticulocyte-derived exosomes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osório, H.; Silva, C.; Ferreira, M.; Gullo, I.; Máximo, V.; Barros, R.; Mendonça, F.; Oliveira, C.; Carneiro, F. Proteomics Analysis of Gastric Cancer Patients with Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Bioinformatics enrichment tools: Paths toward the comprehensive functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
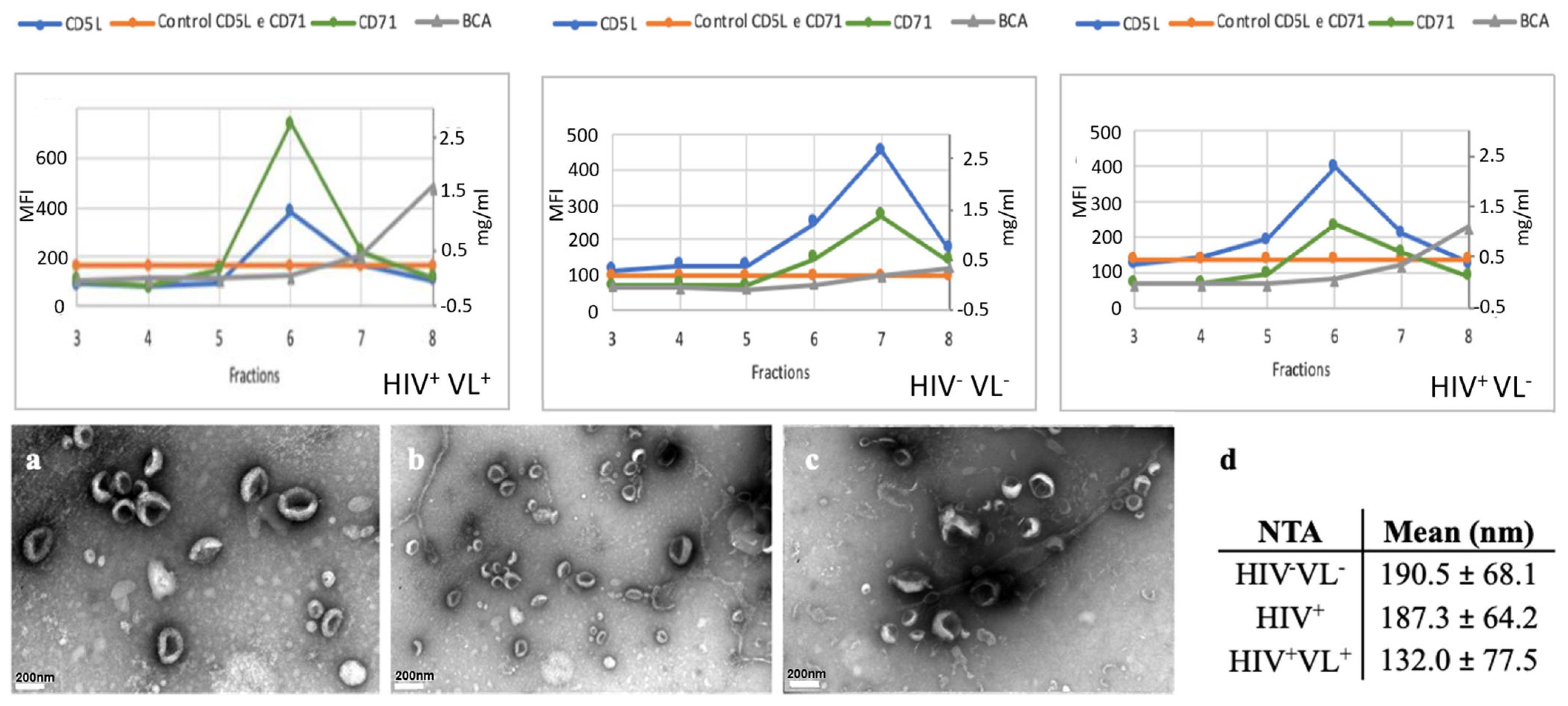

| Sample | Collection Date | Sex | Age | Hospital | Clinical Aspects (Date Diagnostic) | Treatment | Parasitemia PCR (Copies/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIV+/VL+ | 16/05/19 (TP1) | M | 45 | Centro Hospitalar Universitário de São João, Porto, Portugal | HIV (2000) and VL (2013) | Lipossomal Amphotericin B and Miltefosine | 5000 |
| 14/01/20 (TP2) | 6500 | ||||||
| 30/07/20 (TP3) | 7500 | ||||||
| 14/01/21 (TP4) | 3000 | ||||||
| 29/07/21 (TP5) | 7000 |
| Sample | FDR | Accession (UniProtKB) | Leishmania Locus Tag | Description | PSMs | UPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP1 | Medium | A4HSB7 | LINJ_04_1200 | Uncharacterized protein | 1 | 1 |
| Medium | A4HUI7 | LINJ_10_0800 | Uncharacterized protein | 1 | 1 | |
| TP2 | Low | A4HTG6 | LINJ_08_0160 | GPI-GlcNAc transferase complex PIG-H component conserved domain-containing protein | 1 | 1 |
| TP3 | Medium | A4I7M2 | LINJ_32_0630 | Uncharacterized protein | 1 | 1 |
| TP4 | Medium | A4HVH9 ** | LINJ_13_0390 | Putative RNA helicase | 1 | 1 |
| TP5 | Medium | A4HVL3 | LINJ_13_0740 | Uncharacterized protein | 1 | 1 |
| Low | E9AHM5 | LINJ_32_4140 | Putative GIPL galf transferase | 1 | 1 | |
| Pool HIV+VL+ | High | A4HSC2 ** | LINJ_04_1250 | Actin | 72 | 1 |
| High | A4I7Z7 * | LINJ_32_1910 | Superoxide dismutase | 3 | 1 | |
| High | A4IA22 * | LINJ_34_2280 | Uncharacterized protein | 3 | 1 | |
| High | A4I0Q2 | LINJ_24_0650 | Kinesin-like protein | 1 | 1 | |
| Medium | A4I2B2 | LINJ_26_1790 | HEAT repeat-containing protein 1 | 2 | 1 | |
| Medium | A4I7L3 | LINJ_32_0720 | Small ribosomal subunit protein uS4 N-terminal domain-containing protein | 4 | 1 | |
| Medium | A4HW49 | LINJ_14_1140 | Protein kinase domain-containing protein | 2 | 1 | |
| Medium | A4HT30 | LINJ_07_0090 | RAVE complex protein Rav1 C-terminal domain-containing protein | 4 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Costa, I.; Pinto, A.I.; Esteves, S.; Caldas, C.; Osório, H.; Santarém, N.; Fernandez-Becerra, C.; Cordeiro-da-Silva, A. Proteomic Profiling Identifies MARCO in Extracellular Vesicles, as a Potential Biomarker for Leishmaniasis in HIV Co-Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5691. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125691
Costa I, Pinto AI, Esteves S, Caldas C, Osório H, Santarém N, Fernandez-Becerra C, Cordeiro-da-Silva A. Proteomic Profiling Identifies MARCO in Extracellular Vesicles, as a Potential Biomarker for Leishmaniasis in HIV Co-Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5691. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125691
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosta, Inês, Ana Isabel Pinto, Sofia Esteves, Cátia Caldas, Hugo Osório, Nuno Santarém, Carmen Fernandez-Becerra, and Anabela Cordeiro-da-Silva. 2025. "Proteomic Profiling Identifies MARCO in Extracellular Vesicles, as a Potential Biomarker for Leishmaniasis in HIV Co-Infection" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5691. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125691
APA StyleCosta, I., Pinto, A. I., Esteves, S., Caldas, C., Osório, H., Santarém, N., Fernandez-Becerra, C., & Cordeiro-da-Silva, A. (2025). Proteomic Profiling Identifies MARCO in Extracellular Vesicles, as a Potential Biomarker for Leishmaniasis in HIV Co-Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5691. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125691







