Salvinorin A and Salvia divinorum: Toxicology, Pharmacological Profile, and Therapeutic Potential
Abstract
1. Introduction
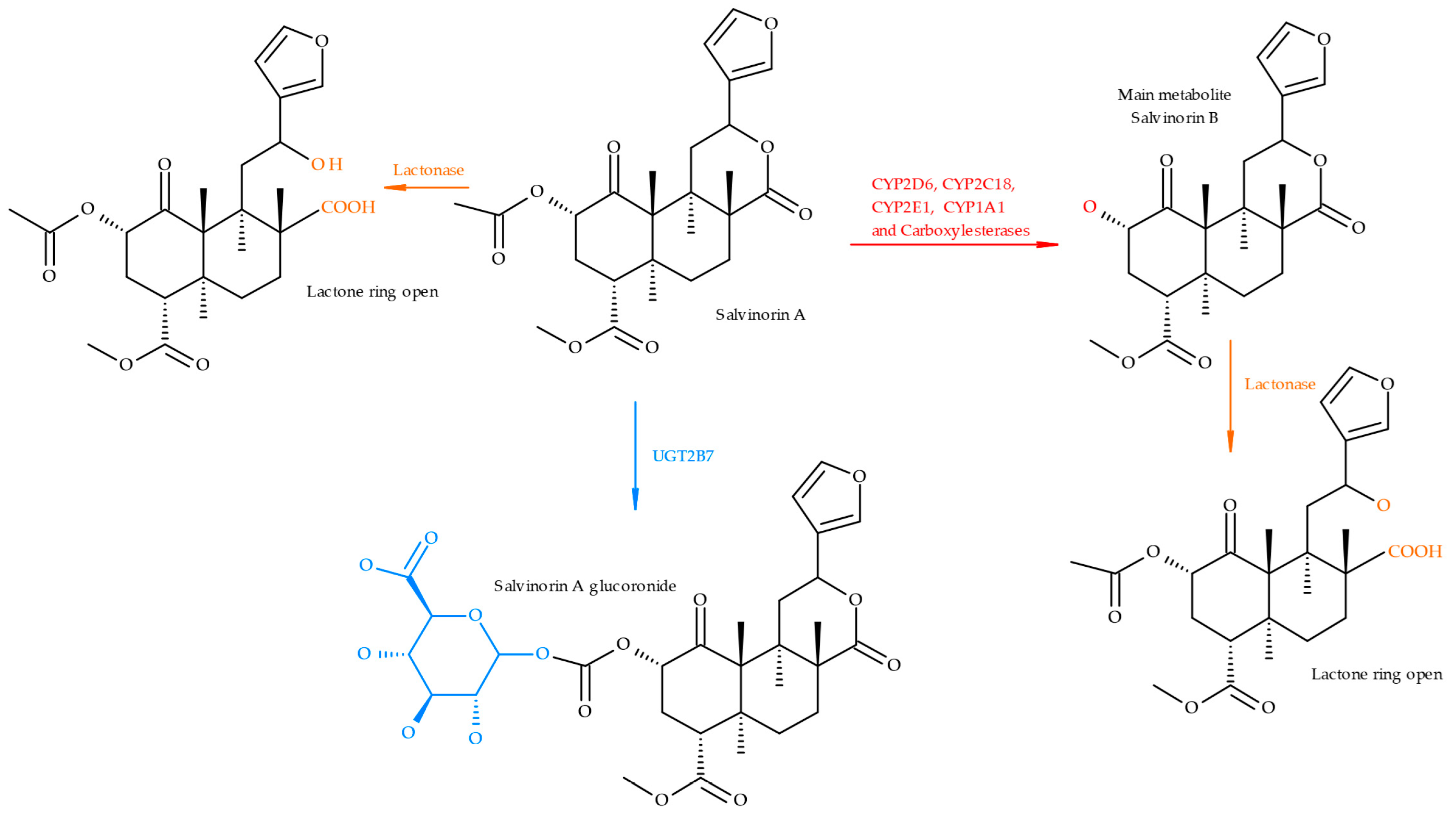
2. Toxicology and Pharmacokinetics
3. Recreational Use and Legislation
4. Potential Therapeutic Uses
4.1. Pain Management
4.2. Mental Health Applications
Depression and Anxiety
4.3. Substance Use Disorders
4.4. Neuroprotection
4.5. Anti-Inflammatory and Antinociceptive Effects
4.6. Microdosing
5. Analysis of Salvinorin A in Biological Specimens
6. General Discussion and Future Directions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maqueda, A.E. The Use of Salvia divinorum from a Mazatec Perspective. In Plant Medicines, Healing and Psychedelic Science: Cultural Perspectives; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 55–70. ISBN 9783319767208. [Google Scholar]
- Vohra, R.; Seefeld, A.; Cantrell, F.L.; Clark, R.F. Salvia divinorum: Exposures Reported to a Statewide Poison Control System over 10 Years. J. Emerg. Med. 2011, 40, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahendran, R.; Lim, H.A.; Tan, J.Y.S.; Chua, S.M.; Winslow, M. Salvia divinorum: An Overview of the Usage, Misuse, and Addiction Processes. Asia-Pac. Psychiatry 2016, 8, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faudree, P. “Making Medicine” with Salvia divinorum: Competing Approaches and Their Implications. Med. Anthropol. Cross Cult. Stud. Health Illn. 2020, 39, 582–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczuk, A.P.; Raman, V.; Galal, A.M.; Khan, I.A.; Siebert, D.J.; Zjawiony, J.K. Vegetative Anatomy and Micromorphology of Salvia divinorum (Lamiaceae) from Mexico, Combined with Chromatographic Analysis of Salvinorin A. J. Nat. Med. 2014, 68, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinho, A.; Silva, S.M.; Gallardo, E. Cytotoxic Effects of Salvinorin A, A Major Constituent of Salvia divinorum. Med. Chem. 2016, 12, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Listos, J.; Merska, A.; Fidecka, S. Pharmacological Activity of Salvinorin A, the Major Component of Salvia divinorum. Pharmacol. Rep. 2011, 63, 1305–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Bello, R.; García-Rodríguez, R.V.; García-Sosa, K.; Peña-Rodríguez, L.M.; Vázquez-Hernández, M.; Ramos-Morales, F.R.; Corcoran, O.; Sánchez-Medina, A. Salvinorin A Content in Legal High Products of Salvia divinorum Sold in Mexico. Forensic Sci. Int. 2015, 249, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutrzeba, L.M.; Ferreira, D.; Zjawiony, J.K. Salvinorins J from Salvia divinorum: Mutarotation in the Neoclerodane System. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1361–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Metz, P. Total Synthesis of the Neoclerodane Diterpene Salvinorin A via an Intramolecular Diels-Alder Strategy. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 3418–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, S.J.; Brion, A.U.C.M.; Shenvi, R.A. Chemical Syntheses of the Salvinorin Chemotype of KOR Agonist. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2020, 37, 1478–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, S.A.; Ness, R.W.; Kwon, M.; Ro, D.K.; Phillips, M.A. A Chromosome Level Reference Genome of Diviner’s Sage (Salvia divinorum) Provides Insight into Salvinorin A Biosynthesis. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tlacomulco-Flores, L.L.; Déciga-Campos, M.; González-Trujano, M.E.; Carballo-Villalobos, A.I.; Pellicer, F. Antinociceptive Effects of Salvia divinorum and Bioactive Salvinorins in Experimental Pain Models in Mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 248, 112276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, A.; Blount, J.F.; Manchand, P.S. Salvinorin, a New Trans-Neoclerodane Diterpene from Salvia divinorum (Labiatae). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin 1 1982, 17, 2505–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdes III, L.; Butler, W.; Hatfield, G.; Paul, A.; Koreeda, M. Divinorin A, a Psychotropic Terpenoid, and Divinorin B from the Hallucinogenic Mexican Mint Salvia divinorum. J. Org. Chem. 1984, 49, 4716–4720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prisinzano, T.E. Neoclerodanes as Atypical Opioid Receptor Ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 3435–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Alvarado, R.B.; Madariaga-Mazón, A.; Ortega, A.; Martinez-Mayorga, K. DARK Classics in Chemical Neuroscience: Salvinorin A. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 3979–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, J.J.; Shenvi, R.A. A Review of Salvinorin Analogs and Their Kappa-Opioid Receptor Activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 1436–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundmann, O.; Phipps, S.M.; Zadezensky, I.; Butterweck, V. Salvia divinorum and Salvinorin A: An Update on Pharmacology and Analytical Methodology. Planta Med. 2007, 73, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, C.W.; Rothman, R.B.; Prisinzano, T.E. Neuropharmacology of the Naturally Occurring κ-Opioid Hallucinogen Salvinorin A. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 316–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiñonez-Bastidas, G.N.; Grijalva-Contreras, L.E.; Patiño-Camacho, S.I.; Navarrete, A. Emerging Psychotropic Drug for the Treatment of Trigeminal Pain: Salvinorin A. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibouti, S.; Barriault, L. An Overview of Syntheses of Salvinorin A and Its Analogues. ChemCatChem 2024, 16, e202400182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawilska, J.B.; Wojcieszak, J. Salvia divinorum: From Mazatec Medicinal and Hallucinogenic Plant to Emerging Recreational Drug. Hum. Psychopharmacol. 2013, 28, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, S.; Majumdar, S. Natural Products for the Treatment of Pain: Chemistry and Pharmacology of Salvinorin A, Mitragynine, and Collybolide. Biochemistry 2021, 60, 1381–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teksin, Z.S.; Lee, I.J.; Nemieboka, N.N.; Othman, A.A.; Upreti, V.V.; Hassan, H.E.; Syed, S.S.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Eddington, N.D. Evaluation of the Transport, In Vitro Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics of Salvinorin A, a Potent Hallucinogen NIH Public Access. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 72, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.D.; Schmidt, M.S.; Butelman, E.R.; Harding, W.W.; Tidgewell, K.; Murry, D.J.; Kreek, M.J.; Prisinzano, T.E. Pharmacokinetics of the Plant-Derived κ-Opioid Hallucinogen Salvinorin A in Nonhuman Primates. Synapse 2005, 58, 208–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, A.E.; Qualls, C.; Hasler, G.; Elmiger, D.; Strassman, R. The Hallucinogen Rating Scale: Updated Factor Structure in a Large, Multistudy Sample. Biol. Psychiatry Glob. Open Sci. 2025, 5, 100436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, I.; Kumar, R.; Li, L.; Kim, S.W.; Kwon, M.; Ro, D.K. Identification of Clerodane Diterpene Modifying Cytochrome P450 (CYP728D26) in Salvia divinorum—En Route to Psychotropic Salvinorin A Biosynthesis. Physiol. Plant 2024, 176, e14569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.-T.; Woody, G.; Yang, C.; Li, J.-H. Blazer Recent National Trends in Salvia divinorum Use and Substance-Use Disorders among Recent and Former Salvia divinorum Users Compared with Nonusers. Subst. Abuse Rehabil. 2011, 2, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Prisinzano, T.E. Psychopharmacology of the Hallucinogenic Sage Salvia divinorum. Life Sci. 2005, 78, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butelman, E.R.; Kreek, M.J. Salvinorin A, a Kappa-Opioid Receptor Agonist Hallucinogen: Pharmacology and Potential Template for Novel Pharmacotherapeutic Agents in Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; Simão, A.Y.; Gonçalves, J.; Caramelo, D.; Soares, S.; Luís, Â.; Rosado, T.; Barroso, M.; Duarte, A.P.; Gallardo, E. Salvia divinorum: Beyond Its Therapeutic Uses. In Salvia: Chemistry and Effects; Rendón Villalobos, J.R., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2020; Chapter 5; pp. 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Bagdasarian, F.A.; Hansen, H.D.; Chen, J.; Yoo, C.H.; Placzek, M.S.; Hooker, J.M.; Wey, H.Y. Acute Effects of Hallucinogens on Functional Connectivity: Psilocybin and Salvinorin-A. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2024, 15, 2654–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction Salvia divinorum Drug Profile. Available online: https://www.euda.europa.eu/publications/drug-profiles/salvia_en#control (accessed on 16 February 2025).
- Fotovvat, M.; Radjabian, T.; Saboora, A. HPLC Fingerprint of Important Phenolic Compounds in Some Salvia L. Species from Iran. Rec. Natl. Prod. 2019, 13, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodnar Willard, M.A.; McGuffin, V.L.; Waddell Smith, R. Forensic Analysis of Salvia divinorum Using Multivariate Statistical Procedures. Part I: Discrimination from Related Salvia Species. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- José Petit-Rodríguez, M. Salvia Legality by State: In What States Is Salvia Legal? Available online: https://addictionresource.com/drugs/salvia/legality/ (accessed on 16 March 2025).
- Coffeen, U.; Pellicer, F. Salvia divinorum: From Recreational Hallucinogenic Use to Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Action. J. Pain. Res. 2019, 12, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviello, G.; Borrelli, F.; Guida, F.; Romano, B.; Lewellyn, K.; De Chiaro, M.; Luongo, L.; Zjawiony, J.K.; Maione, S.; Izzo, A.A.; et al. Ultrapotent Effects of Salvinorin A, a Hallucinogenic Compound from Salvia divinorum, on LPS-Stimulated Murine Macrophages and Its Anti-Inflammatory Action in vivo. J. Mol. Med. 2011, 89, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capasso, R.; Borrelli, F.; Cascio, M.G.; Aviello, G.; Huben, K.; Zjawiony, J.K.; Marini, P.; Romano, B.; Di Marzo, V.; Capasso, F.; et al. Inhibitory Effect of Salvinorin A, from Salvia divinorum, on Ileitis-Induced Hypermotility: Cross-Talk between κ-Opioid and Cannabinoid CB 1 Receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 155, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanes, K.R.P. Antidepressant Effects of the Herb Salvia divinorum: A Case Report. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2001, 21, 634–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appel, J.; Kim-Appel, D. The Rise of a New Psychoactive Agent: Salvia divinorum. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2007, 5, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Reiff, C.M.; Richman, E.E.; Nemeroff, C.B.; Carpenter, L.L.; Widge, A.S.; Rodriguez, C.I.; Kalin, N.H.; McDonald, W.M. Psychedelics and Psychedelic-Assisted Psychotherapy. Am. J. Psychiatry 2020, 177, 391–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, A.N.; Meshkat, S.; Benitah, K.; Lipsitz, O.; Gill, H.; Lui, L.M.W.; Teopiz, K.M.; McIntyre, R.S.; Rosenblat, J.D. Registered Clinical Studies Investigating Psychedelic Drugs for Psychiatric Disorders. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2021, 139, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glick, S.D.; Maisonneuve, I.M.; Raucci, J.; Sydney, A. Kappa Opioid Inhibition of Morphine and Cocaine Self-Administration in Rats. Brain Res. 1995, 681, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothman, R.B.; Gorelick, D.A.; Heishman, S.J.; Eichmiller, P.R.; Hill, B.H.; Norbeck, J.; Liberto, J.G. An Open-Label Study of a Functional Opioid κ Antagonist in the Treatment of Opioid Dependence. J. Subst. Abuse Treat. 2000, 18, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Cai, J.H.; Wu, T.X.; Gao, Z.Q.; Zhou, C.; Wu, Q.; Ji, M.J. Salvinorin A Ameliorates Pilocarpine-Induced Seizures by Regulating Hippocampal Microglia Polarization. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 335, 118697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, D.; Riley, J.; Kiessling, W.J.; Armstead, W.M.; Liu, R. Salvinorin A Produces Cerebrovasodilation through Activation of Nitric Oxide Synthase, κ Receptor, and Adenosine Triphosphate–Sensitive Potassium Channel. Anesthesiology 2011, 114, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.; Zhang, Y.; He, Z.; Wang, Z. Highly Selective Non-Opioid Kappa Opioid Receptor (KOR) Agonist Salvinorin A Protects against Forebrain Ischemia-Induced Brain Injury in Rats. Brain Res. 2016, 1637, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.; Caiazzo, E.; Bilancia, R.; Riemma, M.A.; Pagano, E.; Cicala, C.; Ialenti, A.; Zjawiony, J.K.; Izzo, A.A.; Capasso, R.; et al. Salvinorin A Inhibits Airway Hyperreactivity Induced by Ovalbumin Sensitization. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 7, 233757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Polito, V.; Liknaitzky, P. The Emerging Science of Microdosing: A Systematic Review of Research on Low Dose Psychedelics (1955–2021) and Recommendations for the Field. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 139, 104706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutten, N.R.P.W.; Mason, N.L.; Dolder, P.C.; Kuypers, K.P.C. Motives and Side-Effects of Microdosing With Psychedelics Among Users. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019, 22, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichna, J.; Dicay, M.; Lewellyn, K.; Janecka, A.; Zjawiony, J.K.; MacNaughton, W.K.; Storr, M.A. Salvinorin A Has Antiinflammatory and Antinociceptive Effects in Experimental Models of Colitis in Mice Mediated by KOR and CB1 Receptors. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2012, 18, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaertner, L.S.; Steinborn, M.B.; Kettner, H.; Spriggs, M.J.; Roseman, L.; Buchborn, T.; Balaet, M.; Timmermann, C.; Erritzoe, D.; Carhart-Harris, R.L. Positive Expectations Predict Improved Mental-Health Outcomes Linked to Psychedelic Microdosing. Sci Rep. 2021, 11, 1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margalho, C.; Corte-Real, F.; López-Rivadulla, M.; Gallardo, E. Salvia divinorum: Toxicological Aspects and Analysis in Human Biological Specimens. Bioanalysis 2016, 8, 1415–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, B.B.; Snow, N.H. Analysis of Salvinorin A in Plants, Water, and Urine Using Solid-Phase Microextraction-Comprehensive Two-Dimensional Gas Chromatography–Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1226, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, I.; Da Fonseca, B.; Oppolzer, D.; Martinho, A.; Barroso, M.; Cruz, A.; Queiroz, J.A.; Gallardo, E. Analysis of Salvinorin A in Urine Using Microextraction in Packed Syringe and GC–MS/MS. Bioanalysis 2013, 5, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.S.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Tidgewell, K.; Harding, W.; Butelman, E.R.; Kreek, M.J.; Murry, D.J. Determination of Salvinorin A in Body Fluids by High Performance Liquid Chromatography–Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization. J. Chromatogr. B 2005, 818, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidgewell, K.; Harding, W.W.; Schmidt, M.; Holden, K.G.; Murry, D.J.; Prisinzano, T.E. A Facile Method for the Preparation of Deuterium Labeled Salvinorin A: Synthesis of [2,2,2-2H3]-Salvinorin A. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 5099–5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caspers, M.J.; Williams, T.D.; Lovell, K.M.; Lozama, A.; Butelman, E.R.; Kreek, M.J.; Johnson, M.; Griffiths, R.; MacLean, K.; Prisinzano, T.E. LC-MS/MS Quantification of Salvinorin A from Biological Fluids. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 7042–7048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pichini, S.; Abanades, S.; Farré, M.; Pellegrini, M.; Marchei, E.; Pacifici, R.; De La Torre, R.; Zuccaro, P. Quantification of the Plant-Derived Hallucinogen Salvinorin A in Conventional and Non-Conventional Biological Fluids by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry after Salvia divinorum Smoking. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 1649–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichini, S.; Marchei, E.; García-Algar, O.; Gomez, A.; Di Giovannandrea, R.; Pacifici, R. Ultra-High-Pressure Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry Determination of Hallucinogenic Drugs in Hair of Psychedelic Plants and Mushrooms Consumers. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 100, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margalho, C.; Gallardo, E.; Castanheira, A.; Vieira, D.N.; López-Rivadulla, M.; Real, F.C. A Validated Procedure for Detection and Quantitation of Salvinorin a in Pericardial Fluid, Vitreous Humor, Whole Blood and Plasma Using Solid Phase Extraction and Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1304, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelson, J.E.; Coyle, J.R.; Lopez, J.C.; Baggott, M.J.; Flower, K.; Everhart, E.T.; Munro, T.A.; Galloway, G.P.; Cohen, B.M. Lack of Effect of Sublingual Salvinorin A, a Naturally Occurring Kappa Opioid, in Humans: A Placebo-Controlled Trial. Psychopharmacology 2011, 214, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonough, P.C.; Holler, J.M.; Vorec, S.P.; Bosy, T.Z.; Magluilo, J.; Past, M.R. The Detection and Quantitative Analysis of the Psychoactive Component of Salvia divinorum, Salvinorin A, in Human Biological Fluids Using Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2008, 32, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compounds | Sample/ Volume | Extraction Procedure | Analytical | LOD (ng/mL) | LOQ (ng/mL) | Recoveries (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salvinorin A | Urine (20 mL) | LLE (chloroform). SPME (85 μm polyacrylate fibre) | GC × GC-ToFMS | 200 for LLE; 4 for SPME | 300 for LLE; 8 for SPME | n.s. | [56] |
| Salvinorin A | Urine (0.2 mL) | MEPS (C18) | GC-MS/MS (EI) | 5 | 20 | 71.91–80.15 | [57] |
| Salvinorin A Salvinorin B | Plasma and Urine (0.5 mL) | SPE (Oasis HLB (30 mg, 1 mL)) | LC-MS (APCI) | 2 (Salvinorin A in Plasma) | 2 (Salvinorin A in Plasma) 50 (Salvinorin B in Plasma) | 104.00–106.00 (Urine) | [58] |
| Salvinorin A | Plasma (0.25 mL) | SPE (Waters Oasis SPE cartridges) | LC-MS (APCI) | n.s. | 1 | n.s. | [59] |
| Salvinorin A | Plasma (0.4 mL) | SPE (Strata C18-E 55 micron, 70 Å) | LC-MS/MS (ESI) | n.s. | 0.05 | 93.00–114.00 | [60] |
| Salvinorin A | Plasma, Urine, Saliva, and Sweat (1 mL) | LLE (chloroform/isopropanol (9:1)) | GC-MS (EI) | 5 (Plasma, Urine and Saliva); 0.003 µg/patch (Sweat) | 15 (Plasma, Urine and Saliva); 0.01 µg/patch (Sweat) | 84.60 (Plasma); 93.70 (Urine); 84.20 (Saliva); 77.10 (Sweat) | [61] |
| Salvinorin A | Hair (25 mg) | LLE (Diethyl ether) | UHPLC-MS/MS (ESI) | 0.02 ng/mg | 0.05 ng/mg | 79.60–97.40 | [62] |
| Salvinorin A | Vitreous humour, Pericardial fluid, Blood, and Plasma (0.1– 0.25 mL) | SPE (Oasis® HLB (3 mL, 60 mg)) | GC-MS (EI) | 5 | 5 | 79.60–100.60 (Vitreous humour); 93.40–100.20 (Pericardial fluid); 88.80–99.10 (Blood); 88.30–98.00 (Plasma) | [63] |
| Salvinorin A Salvinorin B | Urine and Plasma (1 mL) | LLE (DMSO/ PEG-400, (25:75, v/v) | LC-MS/MS (APCI) | n.s. | 0.5 | n.s. | [64] |
| Salvinorin A | Urine and Blood (1 mL) | SPE (Oasis® HLB (3 mL, 60 mg)) | LC-MS (ESI) | 2.5 | 5 | 71.70 | [65] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Calado, S.; Pires, B.; Rosendo, L.M.; Rosado, T.; Gallardo, E.; Duarte, A.P. Salvinorin A and Salvia divinorum: Toxicology, Pharmacological Profile, and Therapeutic Potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5588. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125588
Calado S, Pires B, Rosendo LM, Rosado T, Gallardo E, Duarte AP. Salvinorin A and Salvia divinorum: Toxicology, Pharmacological Profile, and Therapeutic Potential. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5588. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125588
Chicago/Turabian StyleCalado, Sara, Bruno Pires, Luana M. Rosendo, Tiago Rosado, Eugenia Gallardo, and Ana Paula Duarte. 2025. "Salvinorin A and Salvia divinorum: Toxicology, Pharmacological Profile, and Therapeutic Potential" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5588. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125588
APA StyleCalado, S., Pires, B., Rosendo, L. M., Rosado, T., Gallardo, E., & Duarte, A. P. (2025). Salvinorin A and Salvia divinorum: Toxicology, Pharmacological Profile, and Therapeutic Potential. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5588. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125588









