Chromosome-Contiguous Ancylostoma duodenale Reference Genome from a Single Archived Specimen Elucidates Human Hookworm Biology and Host–Parasite Interactions †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
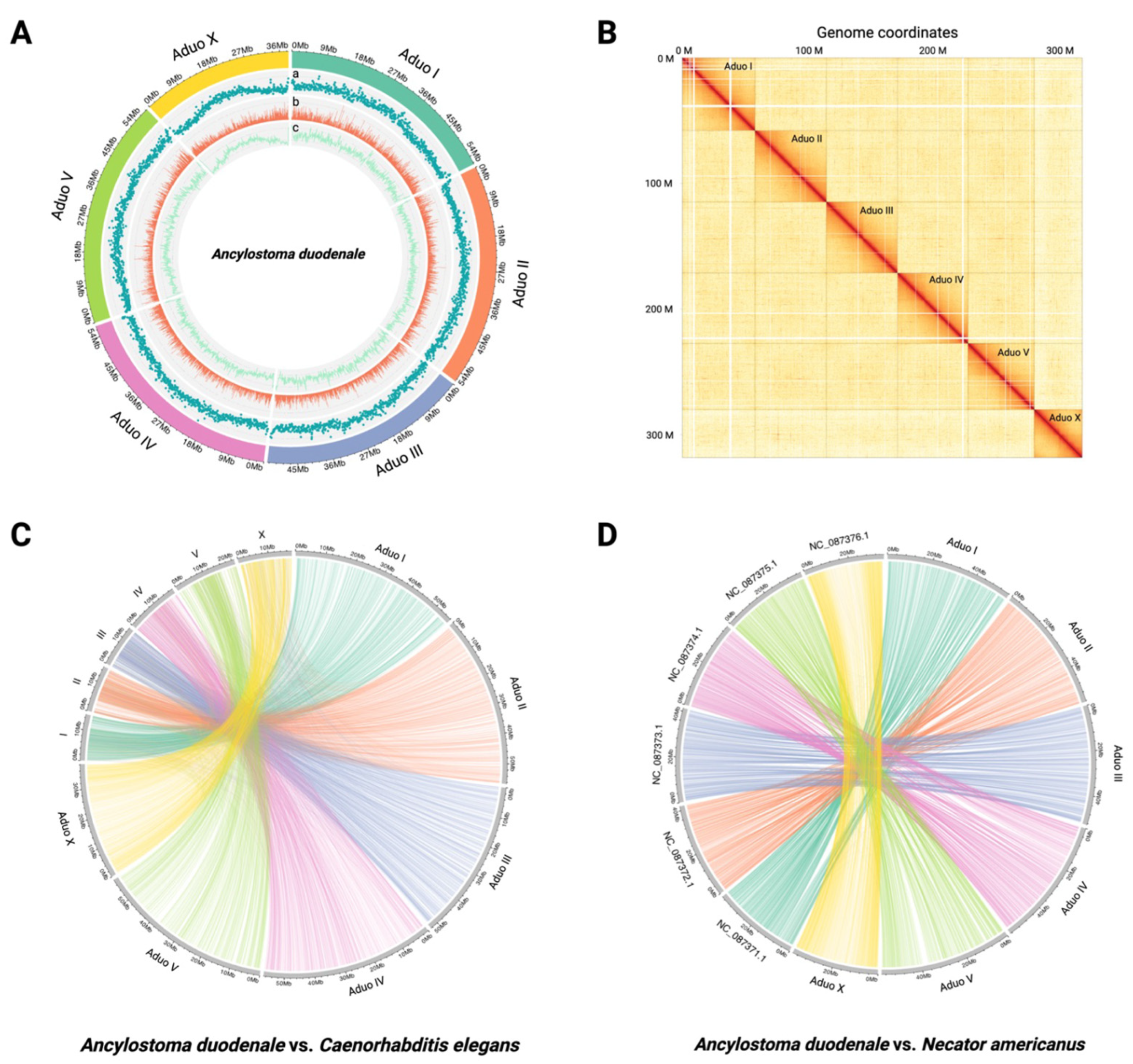
2.1. Chromosome-Contiguous Genome for A. duodenale
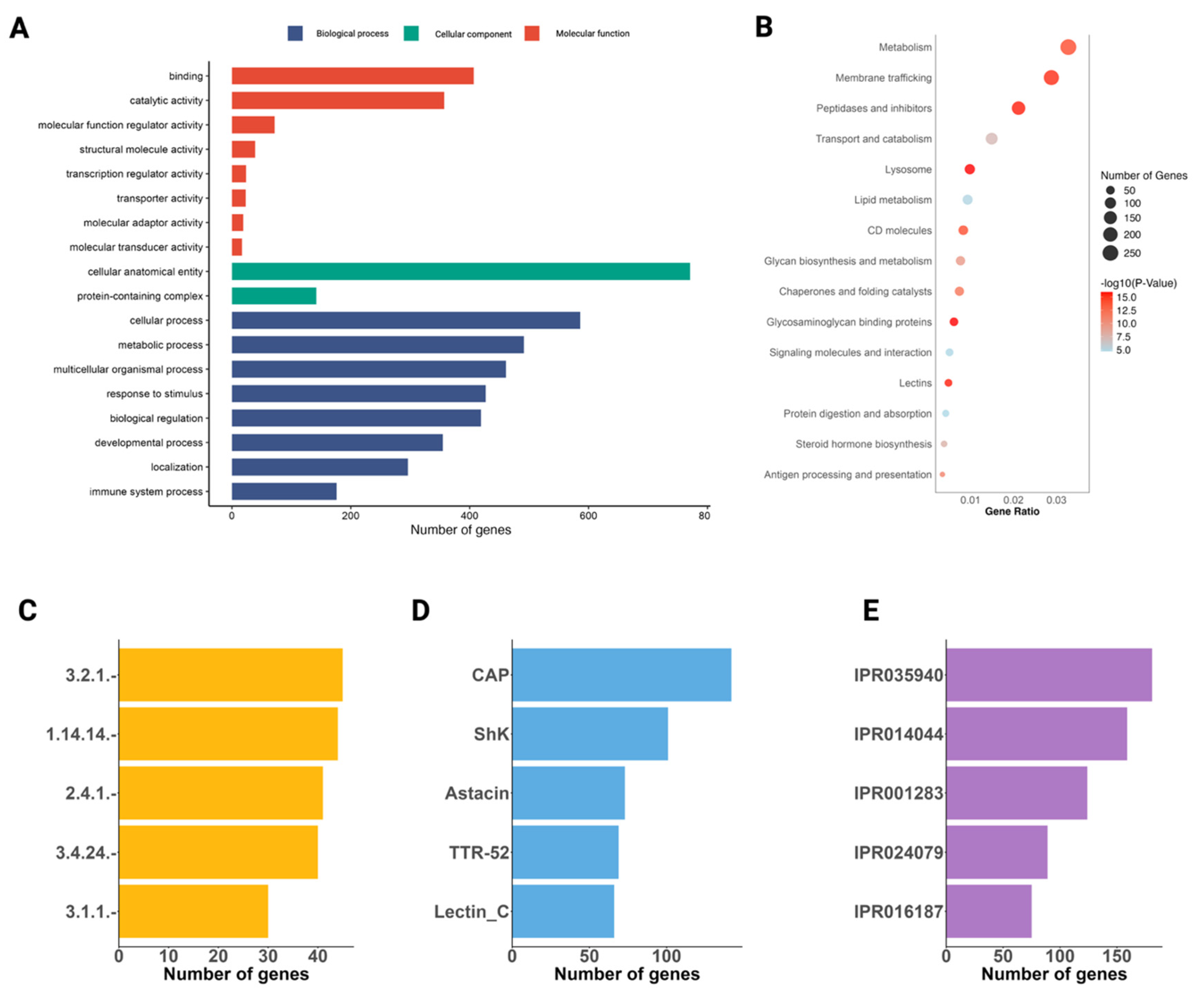
2.2. The Annotated Genome
2.3. Genome Comparisons Between A. duodenale and N. americanus
2.4. The Secretome of A. duodenale
2.5. Conserved Single-Copy Genes Associate with Critical Functions in Nerves, Gap Junction Channel or Pore Activities, Oxidative Phosphorylation, or Thermogenesis
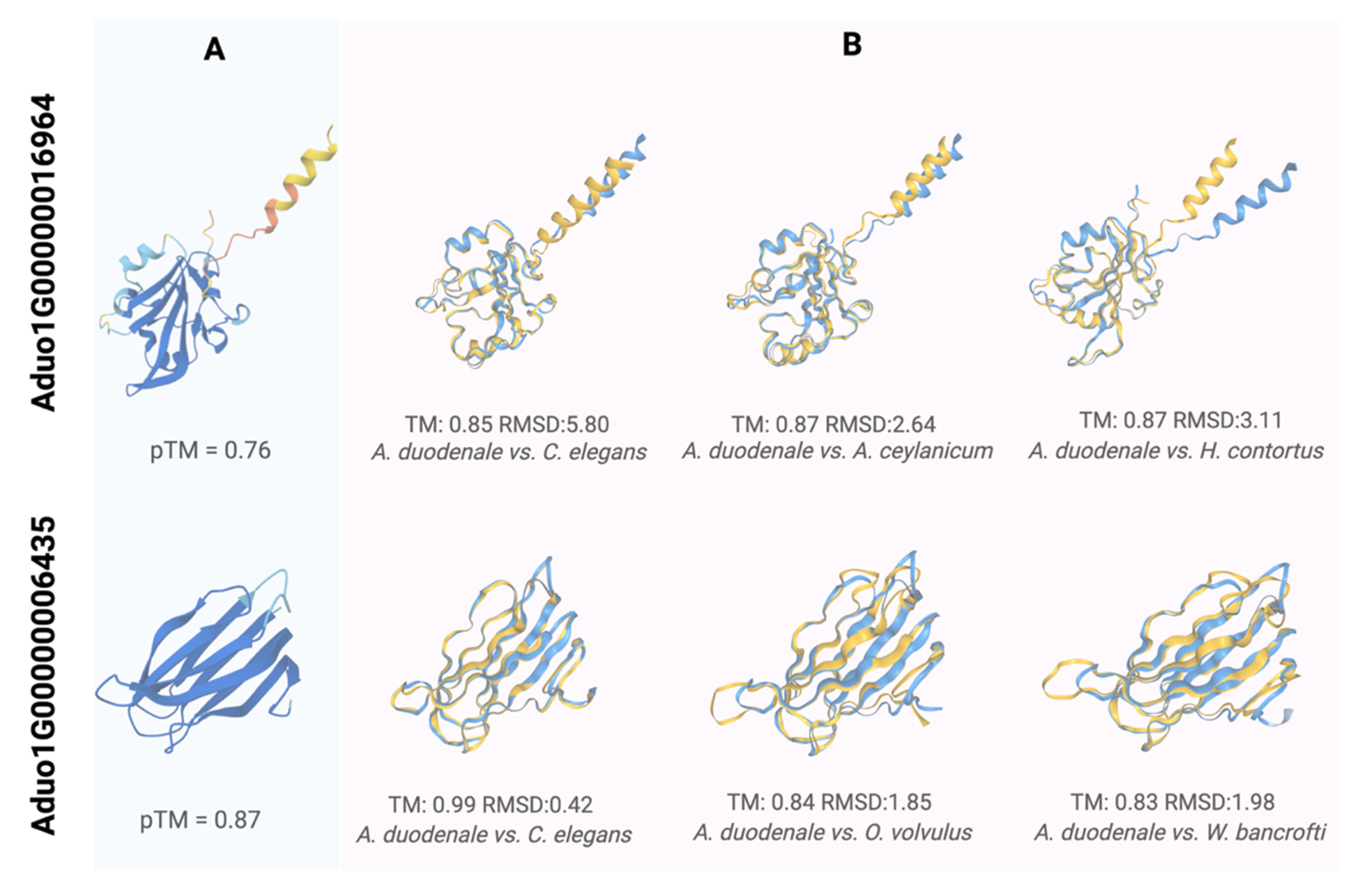
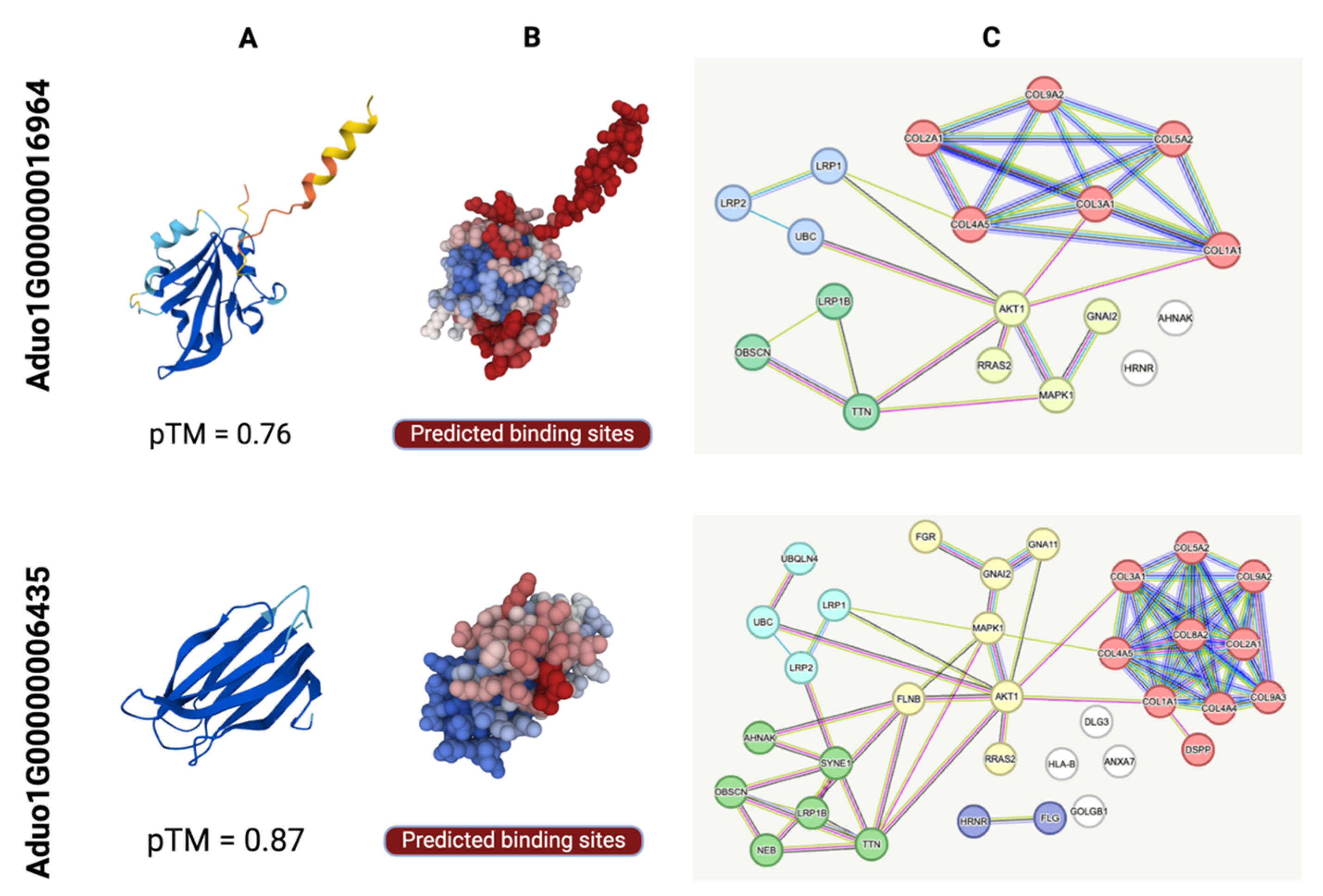
2.6. Structural Characterisation of ES Proteins Encoded by Aduo1G00000016964 and Aduo1G00000006435 and Their Association with Host Proteins
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. DNA Isolation
4.2. DNA Sequencing
4.3. RNA Sequencing
4.4. Genome Survey and Assembly
4.5. Prediction and Functional Annotation of Protein-Coding Genes
4.6. Synteny and Genome Comparisons
4.7. Identification of Invariable Gene Sets, Inference of Essentiality, and Biological Pathway/Process Associations
4.8. Identification and Annotation of Excretory/Secretory (ES) Proteins
4.9. Structural Characterisation of ES Proteins Inferred for eSCOs, and In Silico Interactions with the Human Proteome Employing Machine Learning and Omic Data
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Soil-Transmitted Helminth Infections. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/soil-transmitted-helminth-infections (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Schlosser-Brandenburg, J.; Midha, A.; Mugo, R.M.; Ndombi, E.M.; Gachara, G.; Njomo, D.; Rausch, S.; Hartmann, S. Infection with soil-transmitted helminths and their impact on coinfections. Front. Parasitol. 2023, 2, 1197956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loukas, A.; Hotez, P.J.; Diemert, D.; Yazdanbakhsh, M.; McCarthy, J.S.; Correa-Oliveira, R.; Croese, J.; Bethony, J.M. Hookworm infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihumuro, R.B.; Atimango, L.; Kintu, T.M.; Makai, C.; Kanyike, A.M.; Bazira, J. Exploring healthcare professionals’ perspectives on neglected tropical diseases in Eastern Uganda: A qualitative study with a focus on schistosomiasis and soil-transmitted helminths. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2024, 118, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, A.C.A.; Addis Alene, K. Global distribution of human hookworm species and differences in their morbidity effects: A systematic review. Lancet Microbe 2022, 3, e72–e79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotez, P.J.; Bethony, J.; Bottazzi, M.E.; Brooker, S.; Diemert, D.; Loukas, A. New technologies for the control of human hookworm infection. Trends Parasitol. 2006, 22, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotez, P.J.; Bottazzi, M.E.; Kaye, P.M.; Lee, B.Y.; Puchner, K.P. Neglected tropical disease vaccines: Hookworm, leishmaniasis, and schistosomiasis. Vaccine 2023, 41 (Suppl. 2), S176–S179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldrer, S.; Ursini, T.; Santucci, B.; Motta, L.; Angheben, A. Soil-transmitted helminths and anaemia: A neglected association outside the tropics. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Helminth Genomes Consortium. Comparative genomics of the major parasitic worms. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Genomics of the parasitic nematode Ascaris and its relatives. Genes 2021, 12, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, S.R. Improving helminth genome resources in the post-genomic era. Trends Parasitol. 2022, 38, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilík, V.; Schwarz, E.M.; Nosková, E.; Pafčo, B. Hookworm genomics: Dusk or dawn? Trends Parasitol. 2024, 40, 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Young, N.D.; Wang, T.; Chang, B.C.H.; Song, J.; Gasser, R.B. Systems biology of Haemonchus contortus–Advancing biotechnology for parasitic nematode control. Biotechnol. Adv. 2025, 81, 108567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.T.; Gao, X.; Rosa, B.A.; Abubucker, S.; Hallsworth-Pepin, K.; Martin, J.; Tyagi, R.; Heizer, E.; Zhang, X.; Bhonagiri-Palsikar, V.; et al. Genome of the human hookworm Necator americanus. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, E.M.; Hu, Y.; Antoshechkin, I.; Miller, M.M.; Sternberg, P.W.; Aroian, R.V. The genome and transcriptome of the zoonotic hookworm Ancylostoma ceylanicum identify infection-specific gene families. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoads, A.; Au, K.F. PacBio sequencing and its applications. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2015, 13, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Giordano, F.; Ning, Z. Oxford Nanopore MinION sequencing and genome assembly. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2016, 14, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.R.; Cowley, M.J.; Davis, R.L. Next-generation sequencing and emerging technologies. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2019, 45, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Chitnis, N.; Monos, D.; Dinh, A. Next-generation sequencing technologies: An overview. Hum. Immunol. 2021, 82, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafontaine, D.L.; Yang, L.; Dekker, J.; Gibcus, J.H. Hi-C 3.0: Improved protocol for genome-wide chromosome conformation capture. Curr. Protoc. 2021, 1, e198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimková, H.; Câmara, A.S.; Mascher, M. Hi-C techniques: From genome assemblies to transcription regulation. J. Exp. Bot. 2024, 75, 5357–5365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogvadze, E.; Buzdin, A. Retroelements and their impact on genome evolution and functioning. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 3727–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feschotte, C.; Pritham, E.J. DNA transposons and the evolution of eukaryotic genomes. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2007, 41, 331–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, Y.; Rosa, B.A.; Becker, L.; Camberis, M.; LeGros, G.; Zhan, B.; Bottazzi, M.E.; Fujiwara, R.T.; Ritmejeryte, E.; Laha, T.; et al. Proteomic characterization and comparison of the infective and adult life stage secretomes from Necator americanus and Ancylostoma ceylanicum. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2025, 19, e0012780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, J.H.; Bargmann, C.I.; Sengupta, P. The Caenorhabditis elegans odr-2 gene encodes a novel Ly-6-related protein required for olfaction. Genetics 2001, 157, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanasekar, M.; Padmavathi, B.; Ramaswamy, K. Cloning and characterization of a novel immunogenic protein 3 (NIP3) from Brugia malayi by immuno screening of a phage-display cDNA expression library. Parasitol. Res. 2005, 97, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaye, D.D.; Greenwald, I. OrthoList: A compendium of C. elegans genes with human orthologs. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Underwood, R.S.; Greenwald, I.; Shaye, D.D. OrthoList 2: A new comparative genomic analysis of human and Caenorhabditis elegans genes. Genetics 2018, 210, 445–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Yu, Y.; Fox, B.W.; Liu, Y.; Thirumalaikumar, V.P.; Skirycz, A.; Lin, H.; Schroeder, F.C. Amino acid and protein specificity of protein fatty acylation in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2307515121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, R.; Arnaboldi, V.; Chen, W.J.; Sternberg, P.W. Expanding automated gene summaries for Caenorhabditis and parasitic nematode species in WormBase. Micropubl. Biol. 2024, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coakley, G.; Buck, A.H.; Maizels, R.M. Host parasite communications-Messages from helminths for the immune system: Parasite communication and cell-cell interactions. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2016, 208, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Young, N.D.; Song, J.; Gasser, R.B. Genome-wide analysis of haemonchus contortus proteases and protease inhibitors using advanced informatics provides insights into parasite biology and host-parasite interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, O.; Edgley, M.; Strasbourger, P.; Flibotte, S.; Ewing, B.; Adair, R.; Au, V.; Chaudhry, I.; Fernando, L.; Hutter, H.; et al. The Million Mutation Project: A new approach to genetics in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genome Res. 2013, 23, 1749–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canzler, S.; Fischer, M.; Ulbricht, D.; Ristic, N.; Hildebrand, P.W.; Staritzbichler, R. ProteinPrompt: A webserver for predicting protein-protein interactions. Bioinform. Adv. 2022, 2, vbac059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Franceschini, A.; Wyder, S.; Forslund, K.; Heller, D.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Roth, A.; Santos, A.; Tsafou, K.P.; et al. STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D447–D452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drabikowski, K.; Ferralli, J.; Kistowski, M.; Oledzki, J.; Dadlez, M.; Chiquet-Ehrismann, R. Comprehensive list of SUMO targets in Caenorhabditis elegans and its implication for evolutionary conservation of SUMO signaling. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lizotte-Waniewski, M.; Tawe, W.; Guiliano, D.B.; Lu, W.; Liu, J.; Williams, S.A.; Lustigman, S. Identification of potential vaccine and drug target candidates by expressed sequence tag analysis and immunoscreening of Onchocerca volvulus larval cDNA libraries. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 3491–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzeid, A.M.I.; Zhou, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, G. Twenty-five-year research progress in hookworm excretory/secretory products. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, J.; Pearson, M.S.; Manda, S.S.; Choi, Y.J.; Field, M.; Eichenberger, R.M.; Mulvenna, J.; Nagaraj, S.H.; Fujiwara, R.T.; Gazzinelli-Guimaraes, P.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of the secreted proteome of adult Necator americanus hookworms. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethony, J.M.; Simon, G.; Diemert, D.J.; Parenti, D.; Desrosiers, A.; Schuck, S.; Fujiwara, R.; Santiago, H.; Hotez, P.J. Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial of the Na-ASP-2 hookworm vaccine in unexposed adults. Vaccine 2008, 26, 2408–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, Y.; Geary, T.G.; Tritten, L. When secretomes meet anthelmintics: Lessons for therapeutic interventions. Trends Parasitol. 2021, 37, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, E.M.; Noon, J.B.; Chicca, J.D.; Garceau, C.; Li, H.; Antoshechkin, I.; Ilík, V.; Pafčo, B.; Weeks, A.M.; Homan, E.J.; et al. Hookworm genes encoding intestinal excreted-secreted proteins are transcriptionally upregulated in response to the host’s immune system. bioRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schad, G.A. Ancylostoma duodenale: Maintenance through six generations in helminth-native pups. Exp. Parasitol. 1979, 47, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, P.R.; Webster, R.; Giacomin, P.; Llewellyn, S.; Becker, L.; Pearson, M.S.; De Labastida Rivera, F.; O’Rourke, P.; Engwerda, C.R.; Loukas, A.; et al. Vaccination of human participants with attenuated Necator americanus hookworm larvae and human challenge in Australia: A dose-finding study and randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 1 trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 1725–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diemert, D.J.; Zumer, M.; Campbell, D.; Grahek, S.; Li, G.; Peng, J.; Elena Bottazzi, M.; Hotez, P.; Bethony, J. Safety and immunogenicity of the Na-APR-1 hookworm vaccine in infection-naïve adults. Vaccine 2022, 40, 6084–6092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoogerwerf, M.A.; Janse, J.J.; Kuiper, V.P.; van Schuijlenburg, R.; Kruize, Y.C.; Sijtsma, J.C.; Nosoh, B.A.; Koopman, J.R.; Verbeek-Menken, P.H.; Westra, I.M.; et al. Protective efficacy of short-term infection with Necator americanus hookworm larvae in healthy volunteers in the Netherlands: A single-centre, placebo-controlled, randomised, controlled, phase 1 trial. Lancet Microbe 2023, 4, e1024–e1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinsou, J.F.; Diemert, D.J.; Dejon-Agobé, J.C.; Adégbité, B.R.; Honkpehedji, Y.J.; Vodonou, K.G.; Bikangui, R.; Edoa, J.R.; Massinga Loembe, M.; Li, G.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of the co-administered Na-APR-1 and Na-GST-1 hookworm vaccines in school-aged children in Gabon: A randomised, controlled, observer-blind, phase 1, dose-escalation trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 760–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasser, R.B.; Monti, J.R.; Bao-Zhen, Q.; Polderman, A.M.; Nansen, P.; Chilton, N.B. A mutation scanning approach for the identification of hookworm species and analysis of population variation. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1998, 92, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Cheng, H.; Concepcion, G.T.; Feng, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, H. Haplotype-resolved de novo assembly using phased assembly graphs with hifiasm. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, M.J.; Schmidt, S.A.; Borneman, A.R. Purge Haplotigs: Allelic contig reassignment for third-gen diploid genome assemblies. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Song, L.; Wang, X.; Cheng, H.; Wang, C.; Meyer, C.A.; Liu, T.; Tang, M.; Aluru, S.; Yue, F.; et al. Fast alignment and preprocessing of chromatin profiles with Chromap. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; McCarthy, S.A.; Durbin, R. YaHS: Yet another Hi-C scaffolding tool. Bioinformatics 2023, 39, btac808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serizay, J.; Matthey-Doret, C.; Bignaud, A.; Baudry, L.; Koszul, R. Orchestrating chromosome conformation capture analysis with Bioconductor. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durand, N.C.; Robinson, J.T.; Shamim, M.S.; Machol, I.; Mesirov, J.P.; Lander, E.S.; Aiden, E.L. Juicebox provides a visualization system for Hi-C contact maps with unlimited zoom. Cell Syst. 2016, 3, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, A.; Pippel, M.; Myers, G.; Hiller, M. DENTIST-using long reads for closing assembly gaps at high accuracy. GigaScience 2022, 11, giab100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikheenko, A.; Prjibelski, A.; Saveliev, V.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A. Versatile genome assembly evaluation with QUAST-LG. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i142–i150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seppey, M.; Manni, M.; Zdobnov, E.M. BUSCO: Assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1962, 227–245. [Google Scholar]
- Flynn, J.M.; Hubley, R.; Goubert, C.; Rosen, J.; Clark, A.G.; Feschotte, C.; Smit, A.F. RepeatModeler2 for automated genomic discovery of transposable element families. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 9451–9457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarailo-Graovac, M.; Chen, N. Using Repeat Masker to identify repetitive elements in genomic sequences. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2009, 25, 4.10.1–4.10.14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoff, K.J.; Lomsadze, A.; Borodovsky, M.; Stanke, M. Whole-genome annotation with BRAKER. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1962, 65–95. [Google Scholar]
- Brůna, T.; Hoff, K.J.; Lomsadze, A.; Stanke, M.; Borodovsky, M. BRAKER2: Automatic eukaryotic genome annotation with GeneMark-EP+ and AUGUSTUS supported by a protein database. NAR Genom. Bioinform. 2021, 3, lqaa108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.M.; Stajich, J. Funannotate v1. 8.1: Eukaryotic Genome Annotation. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/4054262 (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Haas, B.J.; Salzberg, S.L.; Zhu, W.; Pertea, M.; Allen, J.E.; Orvis, J.; White, O.; Buell, C.R.; Wortman, J.R. Automated eukaryotic gene structure annotation using EVidenceModeler and the Program to Assemble Spliced Alignments. Genome Biol. 2008, 9, R7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovell, J.T.; Sreedasyam, A.; Schranz, M.E.; Wilson, M.; Carlson, J.W.; Harkess, A.; Emms, D.; Goodstein, D.M.; Schmutz, J. GENESPACE tracks regions of interest and gene copy number variation across multiple genomes. eLife 2022, 11, e78526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevers, Y.; Warwick Vesztrocy, A.; Rossier, V.; Train, C.M.; Altenhoff, A.; Dessimoz, C.; Glover, N.M. Quality assessment of gene repertoire annotations with OMArk. Nat. Biotechnol. 2025, 43, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Young, N.D.; Song, J.; Chang, B.C.H.; Gasser, R.B. An informatic workflow for the enhanced annotation of excretory/secretory proteins of Haemonchus contortus. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2023, 21, 2696–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, P.; Binns, D.; Chang, H.Y.; Fraser, M.; Li, W.; McAnulla, C.; McWilliam, H.; Maslen, J.; Mitchell, A.; Nuka, G.; et al. InterProScan 5: Genome-scale protein function classification. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1236–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantalapiedra, C.P.; Hernández-Plaza, A.; Letunic, I.; Bork, P.; Huerta-Cepas, J. eggNOG-mapper v2: Functional annotation, orthology assignments, and domain prediction at the metagenomic scale. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 5825–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dainat, J.; Hereñú, D.; Pucholt, P. AGAT: Another Gff Analysis Toolkit to Handle Annotations in Any GTF/GFF Format. Available online: https://github.com/NBISweden/AGAT (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Pertea, G.; Pertea, M. GFF utilities: GffRead and GffCompare. F1000Research 2020, 9, ISCB Comm J-304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emms, D.M.; Kelly, S. OrthoFinder: Solving fundamental biases in whole genome comparisons dramatically improves orthogroup inference accuracy. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jia, L.; Tian, G.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Luo, X.; Li, Y.; Yao, W. shinyCircos-V2.0: Leveraging the creation of Circos plot with enhanced usability and advanced features. iMeta 2023, 2, e109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ley, P.; Blaxter, M. Systematic Position and Phylogeny. In The Biology of Nematodes; Lee, D.L., Ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2002; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, M.; Zaretskaya, I.; Raytselis, Y.; Merezhuk, Y.; McGinnis, S.; Madden, T.L. NCBI BLAST: A better web interface. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, W5–W9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, P.; Longden, I.; Bleasby, A. EMBOSS: The European molecular biology open software suite. Trends Genet. 2000, 16, 276–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurk, S.; Koren, S.; Rhie, A.; Rautiainen, M.; Bzikadze, A.V.; Mikheenko, A.; Vollger, M.R.; Altemose, N.; Uralsky, L.; Gershman, A.; et al. The complete sequence of a human genome. Science 2022, 376, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, T.L.; Korhonen, P.K.; Hofmann, A.; Gasser, R.B.; Young, N.D. Harnessing model organism genomics to underpin the machine learning-based prediction of essential genes in eukaryotes–Biotechnological implications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2022, 54, 107822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, T.L.; Korhonen, P.K.; Young, N.D.; Wang, T.; Song, J.; Marhoefer, R.; Chang, B.C.H.; Selzer, P.M.; Gasser, R.B. Inference of essential genes of the parasite Haemonchus contortus via machine learning. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Hu, E.; Xu, S.; Chen, M.; Guo, P.; Dai, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhou, L.; Tang, W.; Zhan, L.; et al. clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation 2021, 2, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, J.; Adler, J.; Dunger, J.; Evans, R.; Green, T.; Pritzel, A.; Ronneberger, O.; Willmore, L.; Ballard, A.J.; Bambrick, J.; et al. Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature 2024, 630, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Käll, L.; Krogh, A.; Sonnhammer, E.L. A combined transmembrane topology and signal peptide prediction method. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 338, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Käll, L.; Krogh, A.; Sonnhammer, E.L. Advantages of combined transmembrane topology and signal peptide prediction--the Phobius web server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W429–W432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teufel, F.; Almagro Armenteros, J.J.; Johansen, A.R.; Gíslason, M.H.; Pihl, S.I.; Tsirigos, K.D.; Winther, O.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 6.0 predicts all five types of signal peptides using protein language models. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1023–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kempen, M.; Kim, S.S.; Tumescheit, C.; Mirdita, M.; Lee, J.; Gilchrist, C.L.M.; Söding, J.; Steinegger, M. Fast and accurate protein structure search with Foldseek. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, R.S.; Levy Karin, E.; Mirdita, M.; Chikhi, R.; Steinegger, M. BFVD—A large repository of predicted viral protein structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D340–D347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varadi, M.; Anyango, S.; Deshpande, M.; Nair, S.; Natassia, C.; Yordanova, G.; Yuan, D.; Stroe, O.; Wood, G.; Laydon, A.; et al. AlphaFold protein structure database: Massively expanding the structural coverage of protein-sequence space with high-accuracy models. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D439–D444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearl, F.M.; Bennett, C.F.; Bray, J.E.; Harrison, A.P.; Martin, N.; Shepherd, A.; Sillitoe, I.; Thornton, J.; Orengo, C.A. The CATH database: An extended protein family resource for structural and functional genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 452–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, L.; Allen, B.; Baldi, G.; Beracochea, M.; Bileschi, M.L.; Burdett, T.; Burgin, J.; Caballero-Pérez, J.; Cochrane, G.; Colwell, L.J.; et al. MGnify: The microbiome sequence data analysis resource in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D753–D759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burley, S.K.; Bhikadiya, C.; Bi, C.; Bittrich, S.; Chen, L.; Crichlow, G.V.; Christie, C.H.; Dalenberg, K.; Di Costanzo, L.; Duarte, J.M.; et al. RCSB Protein Data Bank: Powerful new tools for exploring 3D structures of biological macromolecules for basic and applied research and education in fundamental biology, biomedicine, biotechnology, bioengineering and energy sciences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D437–D451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubiana, J.; Schneidman-Duhovny, D.; Wolfson, H.J. ScanNet: A web server for structure-based prediction of protein binding sites with geometric deep learning. J. Mol. Biol. 2022, 434, 167758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Genome Features | Ancylostoma duodenale (This Study) | Necator americanus (GCF_031761385.1) d |
|---|---|---|
| Genome size (bp) | 319,205,898 | 234,457,255 |
| Number of chromosomes | 6 | 6 |
| Number of scaffolds | 14 | 38 |
| Largest chromosome (bp) | 54,937,347 | 42,005,516 |
| N50 | 56,497,455 | 38,919,484 |
| GC content | 42.95% | 40.09% |
| Ns (gaps) a | 59,000 | 209,725 |
| Number of gene models | 20,015 | 26,579 |
| BUSCO—genome (c; s; d; f; m) b | 96.1; 93.9; 2.2; 2.4; 1.5 | 96.7; 95.9; 0.8; 2.1; 1.1 |
| BUSCO—proteome (c; s; d; f; m) b | 94.1; 91.1; 3.0; 2.7; 3.3 | 94.2; 93.1; 1.1; 1.2; 4.6 |
| OMark—proteome (cs; ics; ct; uk) c | 69.6; 6.5; 0; 24.0 | 65.7; 4.7; 0; 29.6 |
| A. duodenale Gene | C. elegans Orthologue | N. americanus Homologue (NCBI) | ES Protein | Transcriptomic Evidence in A. duodenale | ES Proteomic Evidence in A. duodenale | Functional Annotation (EggNOG; Pfam; KEGG) | Predicted Structure | Biological Context |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aduo1G00000008440 | F21F3.6 | XM_064179072 | No | L3; adult (mixed sexes) | NI | NI |  | PL: Lysosomal membrane. |
| Aduo1G00000016964 | hot-3 | XM_013451594 | Yes | L3; adult (mixed sexes) | NI | Ly-6-related |  | PF: Involved in olfactory behaviour and odorant response. PL: Axon and neuronal cell body. |
| Aduo1G00000003031 | ssna-1 | XM_064198606 | No | L3; adult (mixed sexes) | NI | NI | 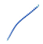 | AC: Rotenone, rifampin, psoralens. AG: atfs-1, etr-1, hsf-1. EI: ABaraapapp, ABaraapppp, anterior hypodermis, germ line, neurons. PD: Phosphorylation site. |
| Aduo1G00000003651 | T27E4.7 | XM_013440797 | No | L3; adult (mixed sexes) | NI | NI | 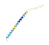 | AC: Tunicamycin, psoralens, allantoin. AG: nuo-6, cua-1, atfs-1. EI: AVF, I2L, XXXL, anchor cell, sensory neurons. |
| Aduo1G00000006435 | ZK856.7 | XM_013445741 | Yes | L3; adult (mixed sexes) | L3; adult (mixed sexes) | NI |  | AC: Rotenone, stavudine, zidovudine. AG: cyc-1, nuo-6, qui-1. EI: M cell, accessory cell, intestine, muscle cell. |
| Aduo1G00000011445 | R12H7.1 | XM_013444081 | No | L3; adult (mixed sexes) | NI | Gap junctions (component); innexin; K22037 |  | EI: Anchor cell, muscle cell, neurons, phasmid sheath cell, somatic nervous system. PF: Actin filament binding, gap junction channel activity; involved in monoatomic ion transmembrane transport, positive regulation of locomotion. PL: Gap junction. |
| Aduo1G00000012651 | pfn-2 | XM_013442503 | No | L3; adult (mixed sexes) | NI | Profilin; K05759 |  | EI: Pharynx, spermatheca. PF: Actin monomer binding, muscle thin filament assembly. PL: Cell cortex. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Young, N.D.; Zheng, Y.; Sumanam, S.B.; Wang, T.; Song, J.; Chang, B.C.H.; Gasser, R.B. Chromosome-Contiguous Ancylostoma duodenale Reference Genome from a Single Archived Specimen Elucidates Human Hookworm Biology and Host–Parasite Interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5576. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125576
Young ND, Zheng Y, Sumanam SB, Wang T, Song J, Chang BCH, Gasser RB. Chromosome-Contiguous Ancylostoma duodenale Reference Genome from a Single Archived Specimen Elucidates Human Hookworm Biology and Host–Parasite Interactions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5576. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125576
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoung, Neil D., Yuanting Zheng, Sunita B. Sumanam, Tao Wang, Jiangning Song, Bill C. H. Chang, and Robin B. Gasser. 2025. "Chromosome-Contiguous Ancylostoma duodenale Reference Genome from a Single Archived Specimen Elucidates Human Hookworm Biology and Host–Parasite Interactions" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5576. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125576
APA StyleYoung, N. D., Zheng, Y., Sumanam, S. B., Wang, T., Song, J., Chang, B. C. H., & Gasser, R. B. (2025). Chromosome-Contiguous Ancylostoma duodenale Reference Genome from a Single Archived Specimen Elucidates Human Hookworm Biology and Host–Parasite Interactions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5576. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125576








