Multi-Targeted Anti-Cancer Effects of Triptophenolide in Hormone-Responsive and Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Models
Abstract
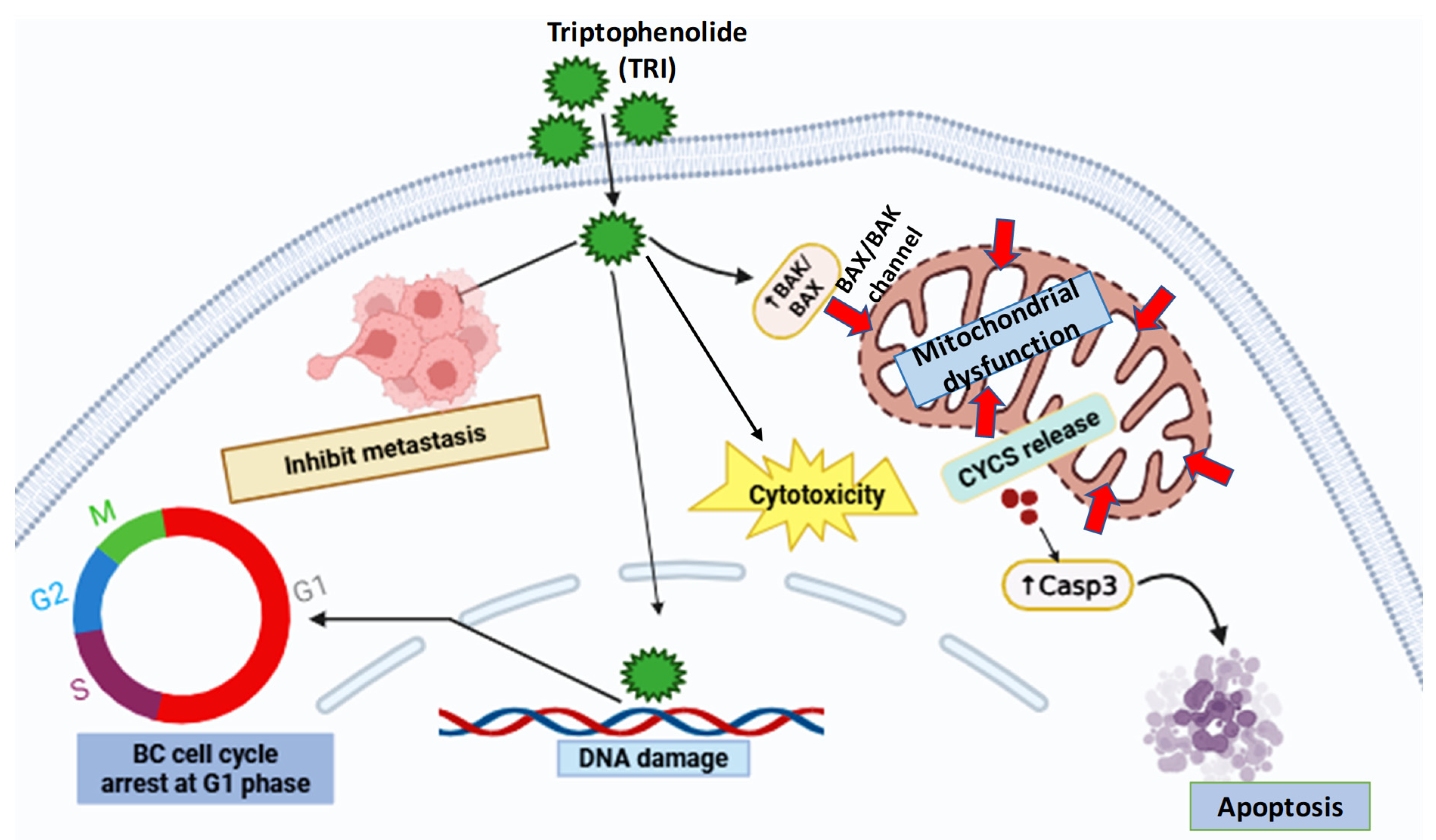
1. Introduction
2. Results
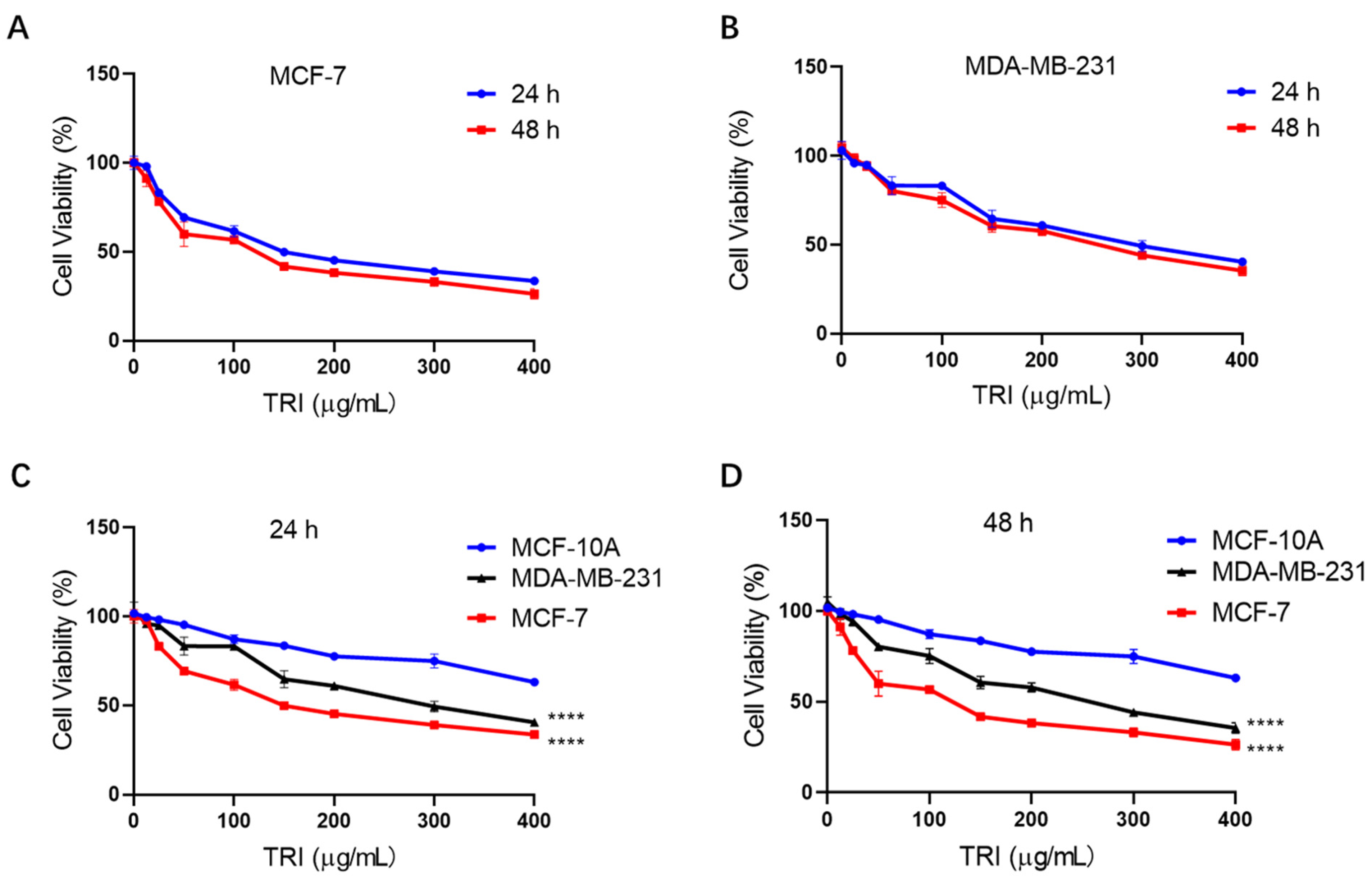
2.1. TRI Inhibits BC Cell Proliferation in a ConcentrationDependent Manner
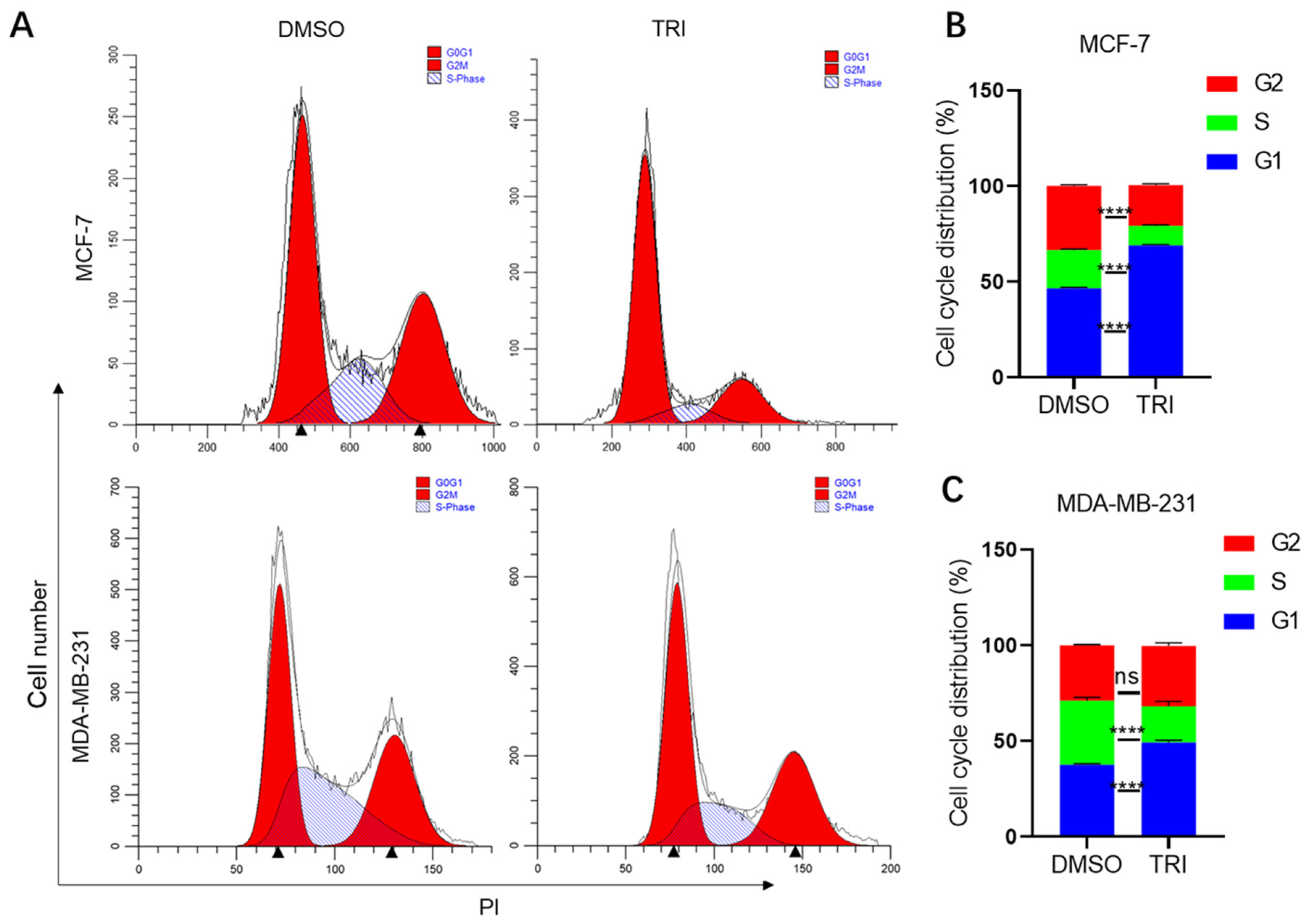
2.2. TRI Induces Cell Cycle Arrest in BC Cells
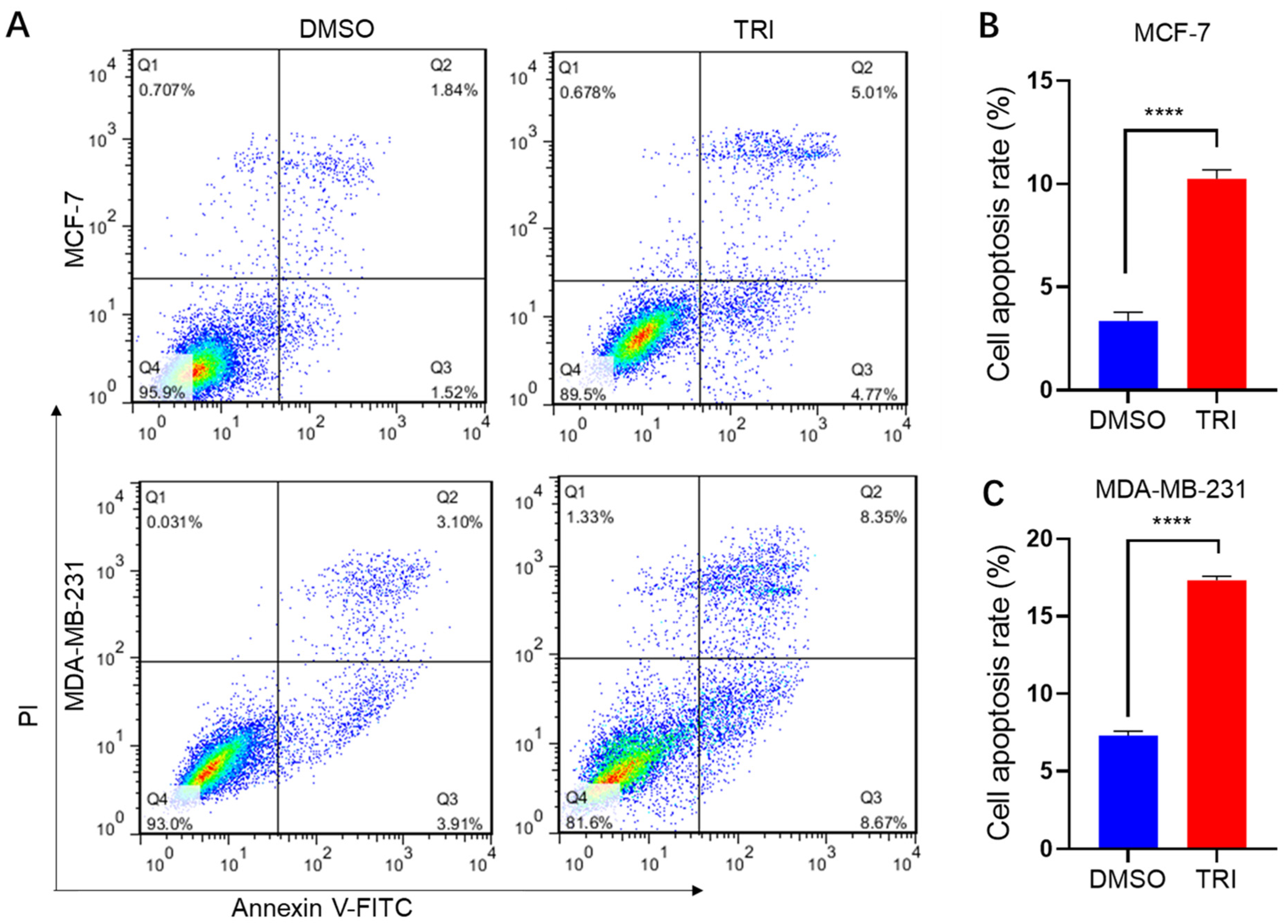
2.3. TRI Induces Apoptosis in BC Cells
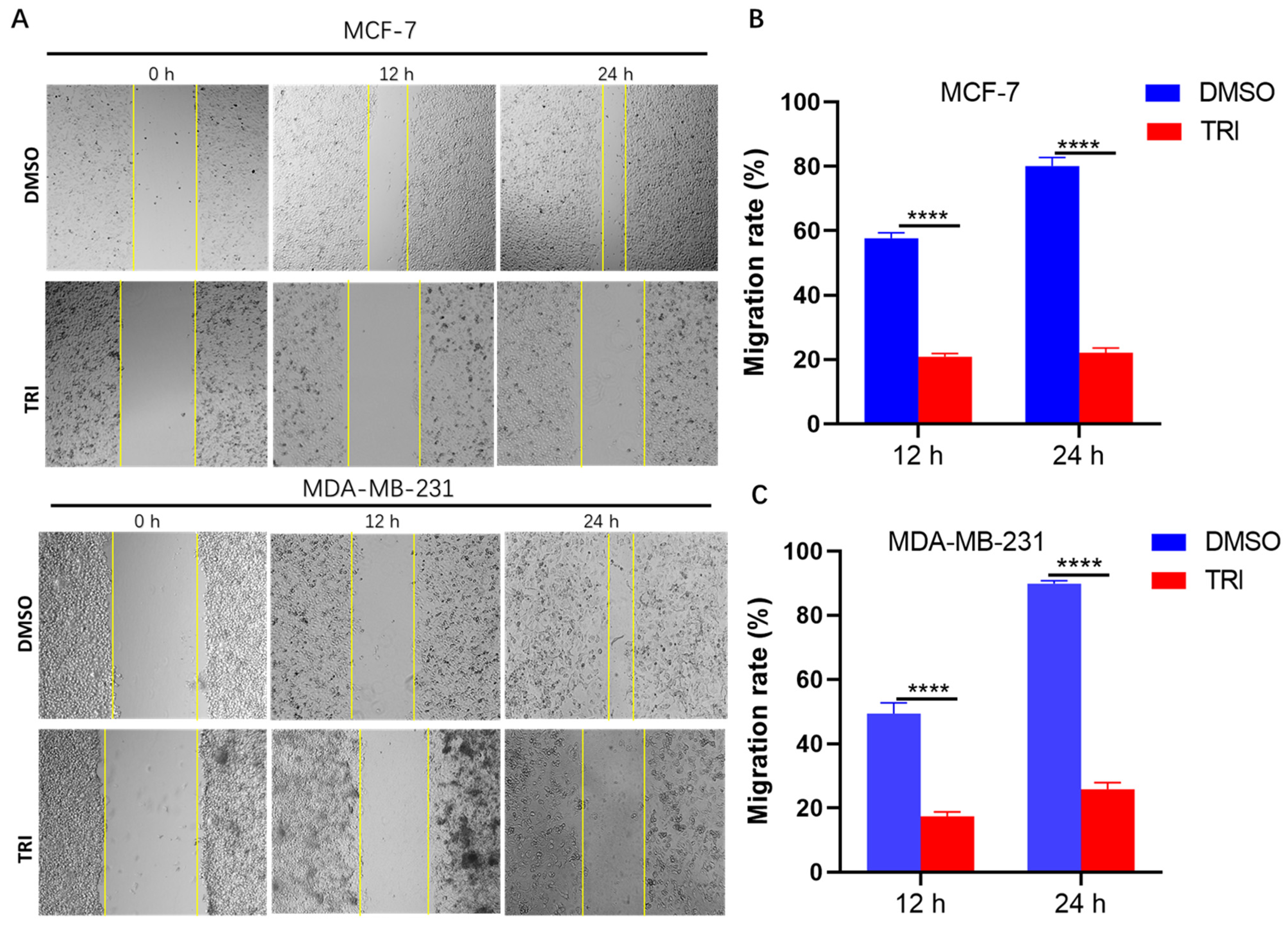
2.4. TRI Suppresses BC Cell Migration
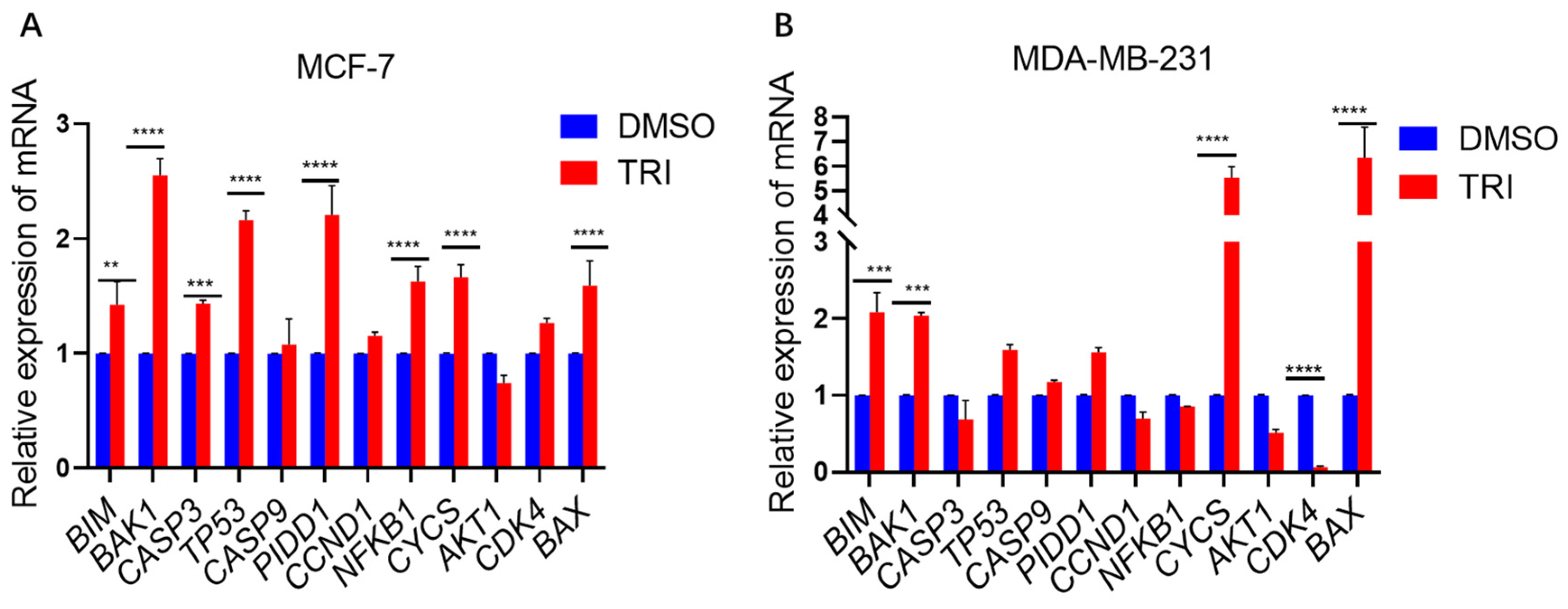
2.5. TRI Induces Apoptosis in BC Cells by Modulating the Expression of Key Apoptotic Genes
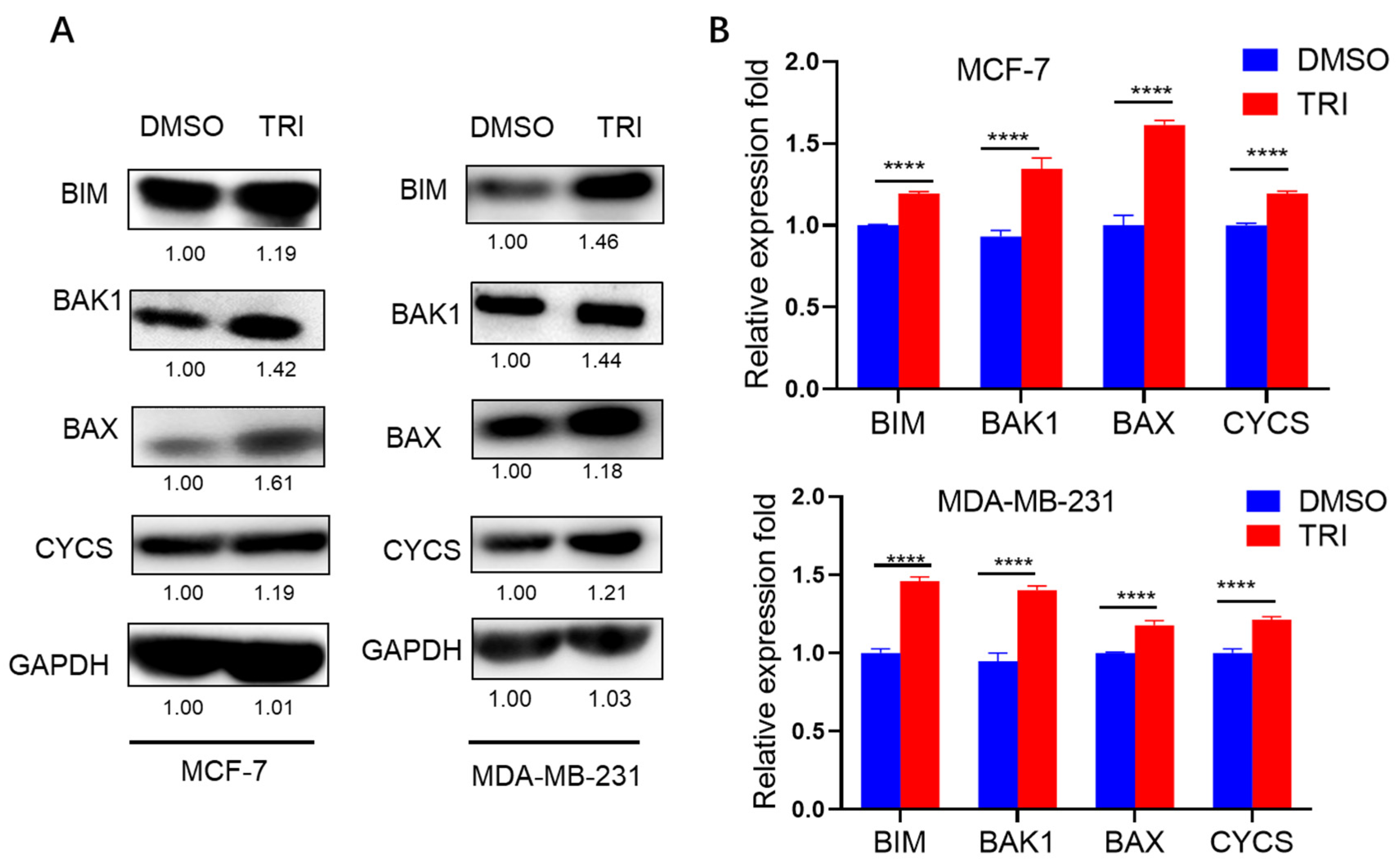
2.6. WB Analysis of Apoptosis-Related Protein Expression in Response to TRI Treatment
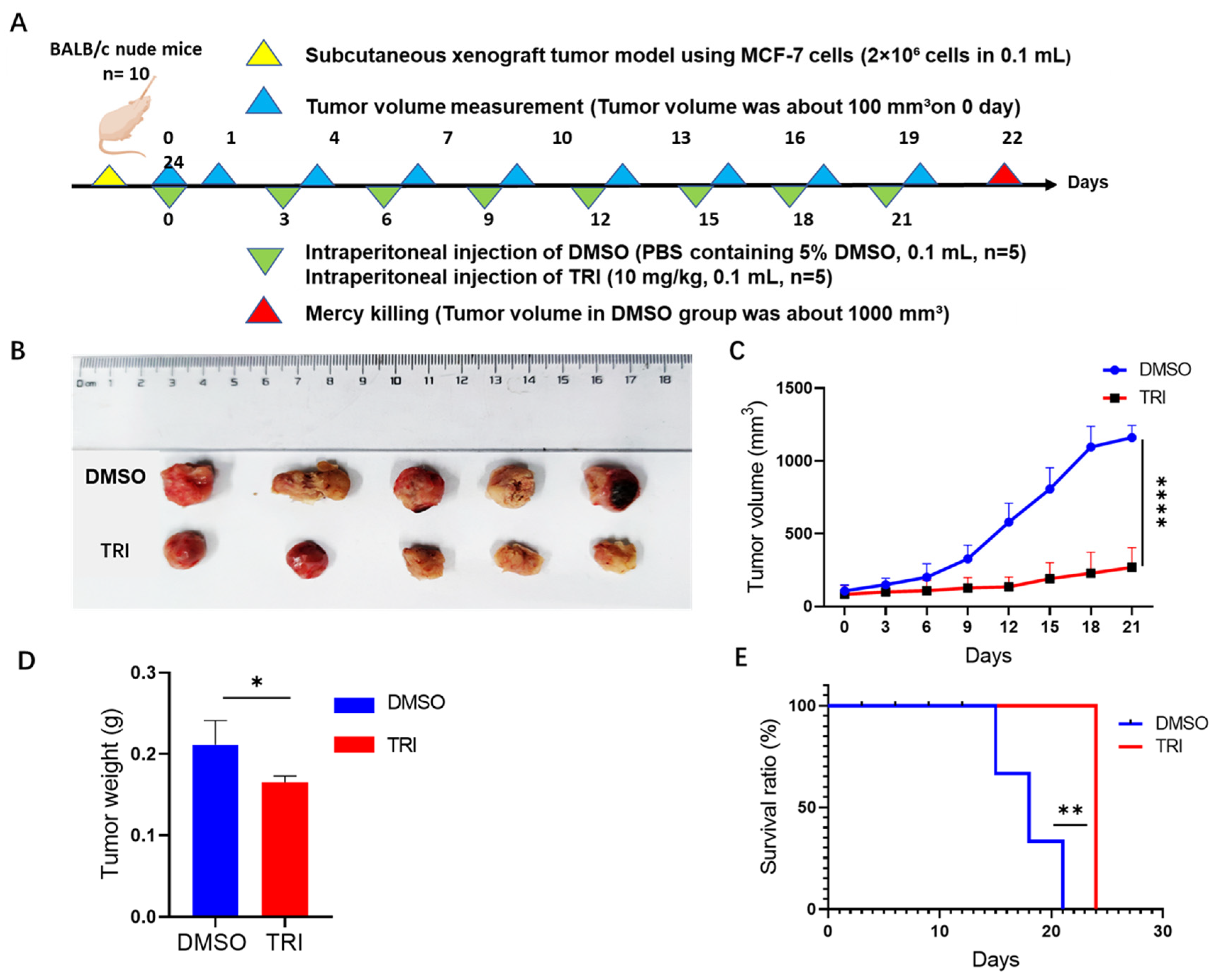
2.7. TRI-Induced Suppression of Tumor Progression in a Nude Mouse Model
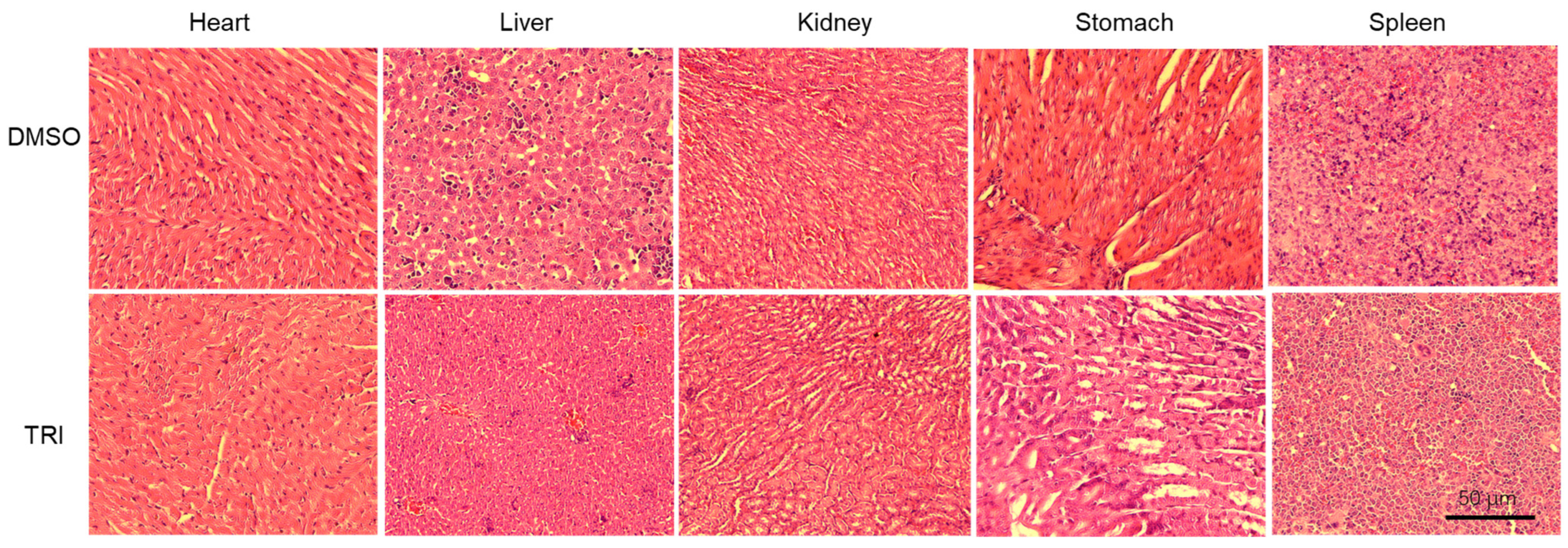
2.8. Histopathological Evaluation of Major Organs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Cell Culture
4.2. Cell Proliferation Assay (CCK-8)
4.3. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.4. Apoptosis Analysis by Annexin V-FITC/PI Dual Staining
4.5. Cell Migration Assessment by Wound Healing Assay
4.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) Analysis
4.7. Western Blot Analysis
4.8. Xenograft Tumor Model
4.9. Histopathological Analysis
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wan, M.; Pan, S.; Shan, B.; Diao, H.; Jin, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, W.; Han, S.; Liu, W.; He, J.; et al. Lipid metabolic reprograming: The unsung hero in breast cancer progression and tumor microenvironment. Mol. Cancer 2025, 24, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Harper, A.; McCormack, V.; Sung, H.; Houssami, N.; Morgan, E.; Mutebi, M.; Garvey, G.; Soerjomataram, I.; Fidler-Benaoudia, M.M.; et al. Global patterns and trends in breast cancer incidence and mortality across 185 countries. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Li, M.; Wang, L.; Hu, Y.; Liu, W.; Long, Z.; Zhou, Z.Z.; Yin, P.Y.; Zhou, M.Z. National and subnational trends in cancer burden in China, 2005–2020: An analysis of national mortality surveillance data. Lancet Public Health 2023, 8, e943–e955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łukasiewicz, S.; Czeczelewski, M.; Forma, A.; Baj, J.; Sitarz, R.; Stanisławek, A. Breast cancer—Epidemiology, risk factors, classification, prognostic markers, and current treatment strategies—An updated review. Cancers 2021, 13, 4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Shu, X.; Yin, C.; Hu, S.; Liu, P. The role of the mTOR pathway in breast cancer stem cells (BCSCs): Mechanisms and therapeutic potentials. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2025, 16, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Chen, H.; Hong, M.; Xia, J.; Zhang, W.; Luan, X.; Zheng, G.; Lu, D. Identifying traditional Chinese medicine combinations for breast cancer treatment based on transcriptional regulation and chemical structure. Chin. Med. 2025, 20, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salerno, C.; Vento, A.R.; Giacchino, M.; Lissidini, G.; Galimberti, V.; Corso, G. Intra-operative radiotherapy management for breast cancer treatment in patients with pseudoxanthoma elasticum: A case report. Breast J. 2018, 24, 385–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, H.; Gonda, K.; Kitamura, N.; Ishida, T. Clinical significance of ABCG2/BCRP quantified by fluorescent nanoparticles in breast cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Cancers 2023, 15, 2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Liang, Y.; Yang, M.; Bao, S.-N.; Bai, J.-L.; Yin, Y.-M.; Yu, H. Effect of breast-conserving surgery plus radiotherapy versus mastectomy on breast cancer-specific survival for early-stage contralateral breast cancer. Gland. Surg. 2021, 10, 2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwalt, I.; Zaza, N.; Das, S.; Li, B.D. Precision Medicine and Targeted Therapies in Breast Cancer. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 29, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.Y.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.-C.; Lee, S.K.; Kil, W.H.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, J.E.; Nam, S.J. Poor prognosis of single hormone receptor-positive breast cancer: Similar outcome as triple-negative breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Xu, C.; Song, J.; Jin, Y.; Gao, X. Mechanisms of Traditional Chinese medicine/natural medicine in HR-positive Breast Cancer: A comprehensive Literature Review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 319, 117322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, Y.; Yun, L.; Zhangm, T.; Zhang, C.; Ding, X.; Zhu, C.; Shi, J.; Jing, Y. Traditional Chinese medicine for breast cancer treatment: A bibliometric and visualization analysis. Pharm. Biol. 2024, 62, 499–512. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, J.K.S.; Leung, W.C.; Ho, W.K.; Chiu, P. Herbal diterpenoids induce growth arrest and apoptosis in colon cancer cells with increased expression of the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-activated gene. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 559, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wei, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zuo, H.; Dong, J.; Zhao, Z.; Hao, M.; et al. Carnosic acid: An effective phenolic diterpenoid for prevention and management of cancers via targeting multiple signaling pathways. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 206, 107288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J.H.; Ren, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, H. Targeting regulated cell death with plant natural compounds for cancer therapy: A revisited review of apoptosis, autophagy-dependent cell death, and necroptosis. Phytother. Res. 2023, 37, 1488–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Ying, L.; Guo, R.; Hao, M.; Liang, Y.; Bi, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yu, C.; Yang, Z. Ligustilide induces apoptosis and reduces proliferation in human bladder cancer cells by NFκB1 and mitochondria pathway. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2023, 101, 1252–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, M.; Zhang, K.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Cheng, R.; Zhai, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z. Paeonol Inhibits Glioma Growth In Vivo and In Vitro by Inducing Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2023, 33, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, L.; Hao, M.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, R.; Liang, Y.; Yu, C.; Yang, Z. Medicarpin suppresses proliferation and triggeres apoptosis by upregulation of BID, BAX, CASP3, CASP8, and CYCS in glioblastoma. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2023, 102, 1097–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Islam, F.; Nafady, M.H.; Akter, M.; Mitra, S.; Das, R.; Urmee, H.; Shohang, S.; Akter, A.; Chidambaram, K.; et al. Natural Small Molecules in Breast Cancer Treatment: Understandings from a Therapeutic Viewpoint. Molecules 2022, 27, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Yang, X.; Xia, G.; Wang, G. Natural products and derivatives for breast cancer treatment: From drug discovery to molecular mechanism. Phytomedicine 2024, 129, 155600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, X.; Ye, Q. Triptophenolide Improves Rheumatoid Arthritis and Progression by Inducing Macrophage Toxicity. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2025, 39, e70096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Hou, Q.; Wu, S.; He, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, R. Metabolic profiling of triptophenolide in rat plasma, urine, bile and faeces after intragastric administration. Nat. Prod. Res. 2024, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zou, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Guo, F. Tripterygium glycoside tablets and triptolide alleviate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice involving the PACAP/cAMP signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2025, 347, 119748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.-Q.; Li, S.-Q.; Liao, C.-C.; Dai, W.-F.; Rao, K.-R.; Ma, X.-R.; Li, R.-T.; Chen, X.-Q. Structurally diversified ent-kaurane and abietane diterpenoids from the stems of Tripterygium wilfordii and their anti-inflammatory activity. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 115, 105178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Chen, Z.; Wu, S.-S.; Xu, J.; Kong, L.-C.; Wei, P. Celastrol enhances the anti-liver cancer activity of sorafenib. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2019, 25, 4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Zhan, J.C.; Wang, G.Z.; Zhao, X.C.; Huang, W.D.; Zhou, G.B. The red wine component ellagic acid induces autophagy and exhibits anti-lung cancer activity in vitro and in vivo. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.F.; Chen, Y.Y.; Lin, J.J.; Liao, C.L.; Ko, Y.C.; Tang, N.Y.; Kou, C.-L.; Liu, K.-C.; Chung, J.-G. Triptolide induced cell death through apoptosis and autophagy in murine leukemia WEHI-3 cells in vitro and promoting immune responses in WEHI-3 generated leukemia mice in vivo. Environ. Toxicol. 2017, 32, 550–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; He, L.; He, F.; Wang, N.; Peng, J.; Yu, C.; Wang, S. Synergetic HepG2 cells suppression efficacy of Tripterygium wilfordii and Scutellaria barbata through EGFR/PI3K/Akt pathway. Pharmacol. Res.-Mod. Chin. Med. 2022, 4, 100130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.-F.; Yuan, Y.; Luk, J.M. Tripterygium wilfordii bioactive compounds as anticancer and anti-inflammatory agents. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2012, 39, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.-D.; Li, L.-Q.; Li, M.-M.; Geng, H.-C.; Qin, H.-B. Catalytic asymmetric formal total synthesis of (−)-Triptophenolide and (+)-Triptolide. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2016, 6, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Liu, X.; Lu, Y.; Ma, X.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, M.; Su, P.; Tong, Y.; Guan, H.; et al. A specific UDP-glucosyltransferase catalyzes the formation of triptophenolide glucoside from Tripterygium wilfordii Hook. f. Phytochemistry 2019, 166, 112062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noel, P.; Von Hoff, D.D.; Saluja, A.K.; Velagapudi, M.; Borazanci, E.; Han, H. Triptolide and Its Derivatives as Cancer Therapies. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 40, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Tripterine and miR-184 show synergy to suppress breast cancer progression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 561, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, C.; Peng, S.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, J. Toxicity of triptolide and the molecular mechanisms involved. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 90, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Luo, Q.; Chen, X.; Qiu, F.; Tao, Y.; Sun, X.; Liu, C. Screening of major hepatotoxic components of Tripterygium wilfordii based on hepatotoxic injury patterns. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2023, 23, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Shen, F.; Su, S.; Bai, Y.; Guo, S.; Yan, H.; Ji, T.; Wang, Y.; Qian, D.; Duan, J. Comparative analysis of four terpenoids in root and cortex of Tripterygium wilfordii Radix by different drying methods. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tang, S.-M.; Deng, X.-T.; Zhou, J.; Li, Q.-P.; Ge, X.-X.; Miao, L. Pharmacological basis and new insights of quercetin action in respect to its anti-cancer effects. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 121, 109604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, E.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, B.; Gao, Y.; Wu, X.; Wei, W.; Li, S. Anti-collagenase, anti-hyaluronidase, anti-elastase, and anti breast cancer potentials of hirsutenone as natural compound: In vitro study, molecular docking and dynamics simulation studies. Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2025, 72, 187–199. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M.; Liu, Y.; Wen, Z.; Tan, H.; Li, S.; Yu, X.; Luo, H.; Li, D.; Wang, J.; Qin, F. Exploration of Traditional Chinese Medicine Comprehensive Treatment of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Based on Molecular Pathological Mechanism. Breast Cancer: Targets Ther. 2025, 17, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, Y.-J.; Kim, Y.-E.; Kim, H.-N.; Lee, E.-H.; Cho, E.-B.; Sultanov, A.; Kwon, S.; Cho, Y. Inhibition effect against elastase, collagenase, hyaluronidase and anti-oxidant activity of thinning Green ball apple. J. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2020, 63, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utpal, B.K.; Bouenni, H.; Zehravi, M.; Sweilam, S.H.; Mortuza, M.R.; Arjun, U.V.N.V.; Shanmugarajan, T.S.; Mahesh, P.G.; Roja, P.; Dodda, R.K.; et al. Exploring natural products as apoptosis modulators in cancers: Insights into natural product-based therapeutic strategies. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2025, 15, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.-Q.; De-Hui, L.; Xu-Kuo, L.; Xiao-Hui, Z.; Qian-Er, W.; Yang, Y. Traditional Chinese Medicine for Breast Cancer: A Review. Breast Cancer Targets Ther. 2023, 15, 747–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Li, X.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, D.; Tian, L. Mechanisms of cancer cell death induction by triptolide: A comprehensive overview. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Hu, M.; He, Z.; Zeng, J.; Ding, Y.; Song, P.; He, X.; et al. Revealing the molecular mechanism of baohuoside I for the treatment of breast cancer based on network pharmacology and molecular docking. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2025, 337, 118918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Xie, J.; Wang, F.; Jiao, S.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, D.; Wang, C.; Wei, X.; Tan, P.; et al. Commiphora myrrha n-hexane extract suppressed breast cancer progression through induction of G0/G1 phase arrest and apoptotic cell death by inhibiting the Cyclin D1/CDK4-Rb signaling pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1425157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seksaria, K.; Patial, D.; Aneja, A.; Arora, P.; Kumar, S. Recent Advances in the Chemistry of Herbal Drugs for the Management of Breast Cancer: An Update. Nat. Prod. J. 2025, 2210–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezginer, E.K.; Yildirim, A.K.; Cosar, A.; Kirlangic, O.F. Remifentanil induces apoptosis and G1-phase cell cycle arrest in human MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Int. J. Med. Biochem. 2025, 8, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, S.; Halagowder, D.; Sivasithambaram, N.D. Quercetin suppresses twist to induce apoptosis in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, P.; Yuan, G.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, L.; He, N. Kuwanon C inhibits proliferation and induction of apoptosis via the intrinsic pathway in MDA-MB231 and T47D breast cancer cells. Steroids 2024, 208, 109450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Sabeel, Z.; Ying, L.; Liang, Y.; Guo, R.; Hao, M.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Dong, J.; Liu, Y.; et al. Rhoifolin Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells In Vitro and In Vivo. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effat, H.; Abosharaf, H.A.; Radwan, A.M. Combined effects of naringin and doxorubicin on the JAK/STAT signaling pathway reduce the development and spread of breast cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, F.G.; Sampaio, B.B.; do Couto, G.O.; da Silva, A.D.; da Silva, W.J.; Peronni, K.C.; Evangelista, A.F.; Hossain, M.; Dimmock, J.R.; Bandy, B.; et al. The Transcriptome of BT-20 Breast Cancer Cells Exposed to Curcumin Analog NC2603 Reveals a Relationship between EGR3 Gene Modulation and Cell Migration Inhibition. Molecules 2024, 29, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momtaz, S.; Niaz, K.; Maqbool, F.; Abdollahi, M.; Rastrelli, L.; Nabavi, S.M. STAT3 targeting by polyphenols: Novel therapeutic strategy for melanoma. BioFactors 2017, 43, 347–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene | Forward Primer Sequence (5′–3′) | Reverse Primer Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | AAGGTGAAGGTCGGAGTCAA | GGAAGATGGTGATGGGATT |
| BIM | CTGAGTGTGACCGAGAAG | GATTACCTTGTGGCTCTGT |
| BAK1 | TCTGGCCCTACACGTCTACC | ACAAACTGGCCCAACAGAA |
| CASP3 | AAGCGAATCAATGGACTCT | TGTACCAGACCGAGATGT |
| CASP9 | CGAACTAACAGGCAAGCA | AATCCTCCAGAACCAATGTC |
| BAX | CCTTTTGCTTCAGGGTTTCA | CAGTTGAAGTTGCCGTCAGA |
| TP53 | GTTCCGAGAGCTGAATGAGG | TCTGAGTCAGGCCCTTCTGT |
| CYCS | GGTGATGTTGAGAAAGGCAAG | GTTCTTATTGGCGGCTGTGT |
| PIDD1 | TCAGAGGATTCGGACGCAG | GTGAGTGCTCAGACGCAAGAA |
| NFKB1 | AACAGAGAGGATTCGTTTCCG | TTTGACCTGAGGGTAAGACTTCT |
| AKT1 | TCCTCCTCAAGAATGATGGCA | GTGCGTTCGATGACAGTGG |
| CDK4 | CCAGGACCTAAGGACATATC | TGACTGTTCCACCACTTG |
| CCND1 | CAATGACCCCGCACGATTTC | CATGGAGGGCGGATTGGAA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sabeel, Z.; Chai, G.; Chen, R.; Ying, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Pan, S.; Chen, X.; Yu, C.; Yang, Z. Multi-Targeted Anti-Cancer Effects of Triptophenolide in Hormone-Responsive and Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5469. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125469
Sabeel Z, Chai G, Chen R, Ying L, Liu Y, Zhang W, Pan S, Chen X, Yu C, Yang Z. Multi-Targeted Anti-Cancer Effects of Triptophenolide in Hormone-Responsive and Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Models. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5469. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125469
Chicago/Turabian StyleSabeel, Zufa, Guangshuai Chai, Ruolan Chen, Lu Ying, Yan Liu, Wenjing Zhang, Shangyang Pan, Xiaoyang Chen, Changyuan Yu, and Zhao Yang. 2025. "Multi-Targeted Anti-Cancer Effects of Triptophenolide in Hormone-Responsive and Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Models" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5469. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125469
APA StyleSabeel, Z., Chai, G., Chen, R., Ying, L., Liu, Y., Zhang, W., Pan, S., Chen, X., Yu, C., & Yang, Z. (2025). Multi-Targeted Anti-Cancer Effects of Triptophenolide in Hormone-Responsive and Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Models. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5469. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125469







