Transforming Prostate Cancer Care: Innovations in Diagnosis, Treatment, and Future Directions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overview of Prostate Cancer Epidemiology and Current Challenges
3. Importance of Advancements in Diagnosis and Treatment
3.1. Metastatic Castration-Sensitive Prostate Cancer (mCSPC)
3.2. Doublet Therapies
3.3. Triplet Therapies
3.4. Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer (mCRPC)
3.5. Radionuclide Therapy Combinations
- Optimizing therapy sequences to balance disease control and treatment burdens.
- Identifying clinical and biological subgroups that could benefit from personalized treatment strategies.
- Narrowing the gap between evidence-based guidelines and real-world practice, as many patients still do not receive recommended combination therapies [25].
3.6. Long-Term Impacts of PCa Advanced Therapies
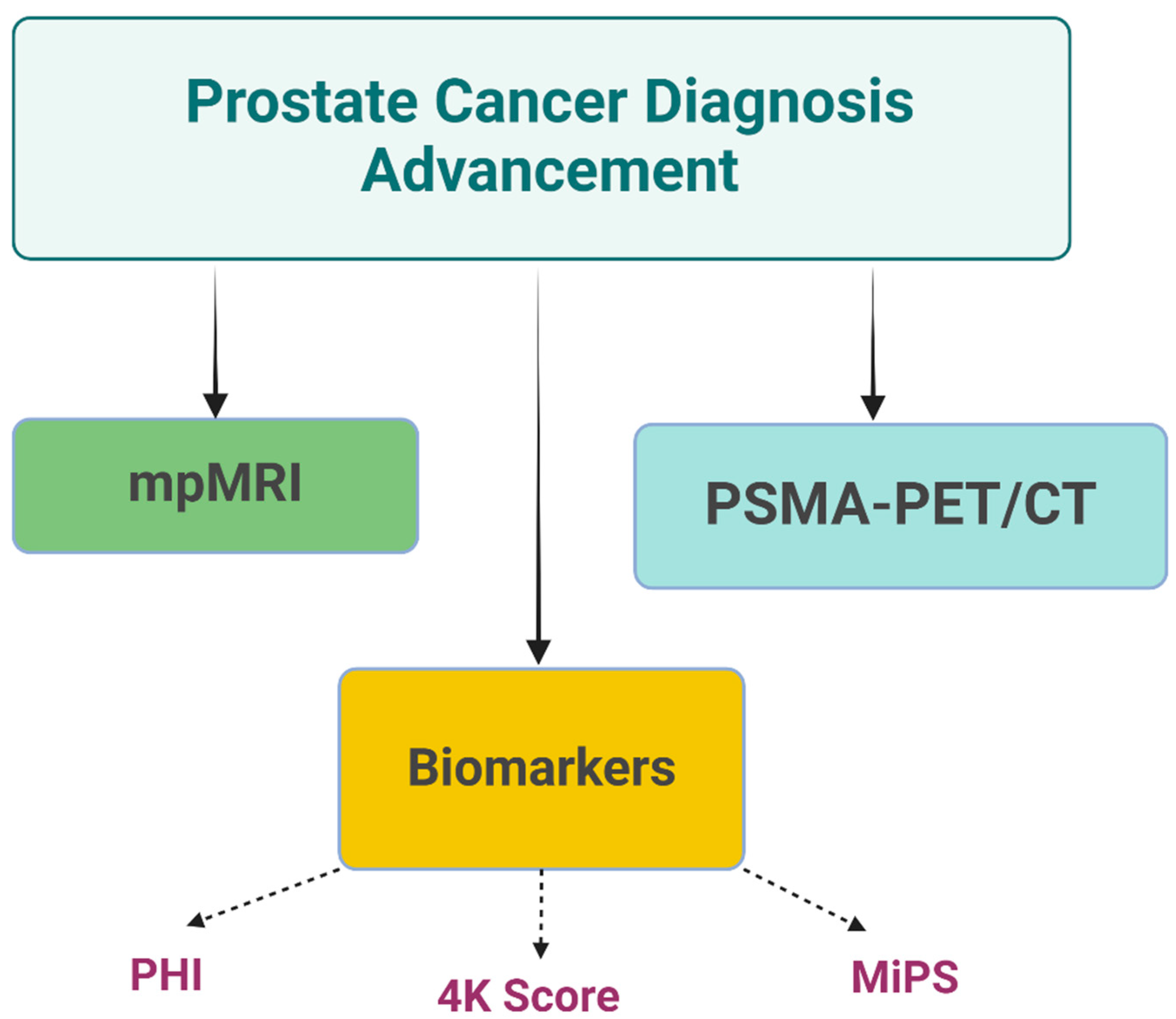
4. Advances in Prostate Cancer Diagnostics
4.1. A Biomarker-Based Approach
4.1.1. Prostate Health Index (PHI)
4.1.2. The 4K Score
4.1.3. Michigan Prostate Score (MiPS)
4.2. B Imaging
4.2.1. Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging (mpMRI)
4.2.2. Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen (PSMA) PET Imaging
4.2.3. MRI–Ultrasound Fusion-Guided Biopsies
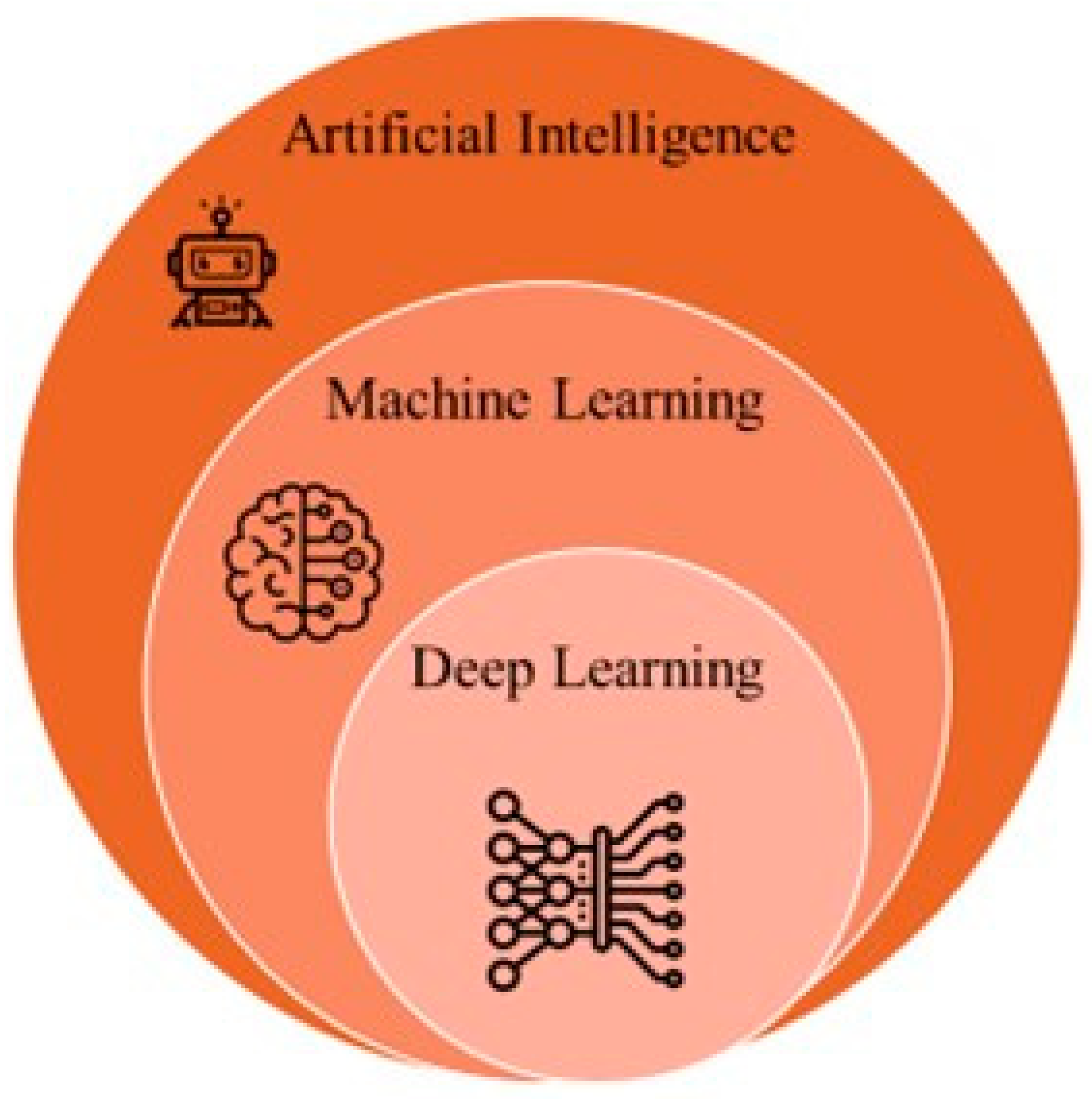
5. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in PCa
5.1. Predictive Models and Risk Stratification
5.2. AI in Pathology and Histopathology
5.3. Precision Medicine Applications
5.4. Predictive Analytics and Outcome Prediction
5.5. Natural Language Processing (NLP) for Clinical Data Extraction
6. Challenges and Future Opportunities in AI for Prostate Cancer
6.1. Challenges in AI Implementation
6.1.1. Data Quality and Bias
6.1.2. Validation and Generalization
6.1.3. Regulatory and Standardization Issues
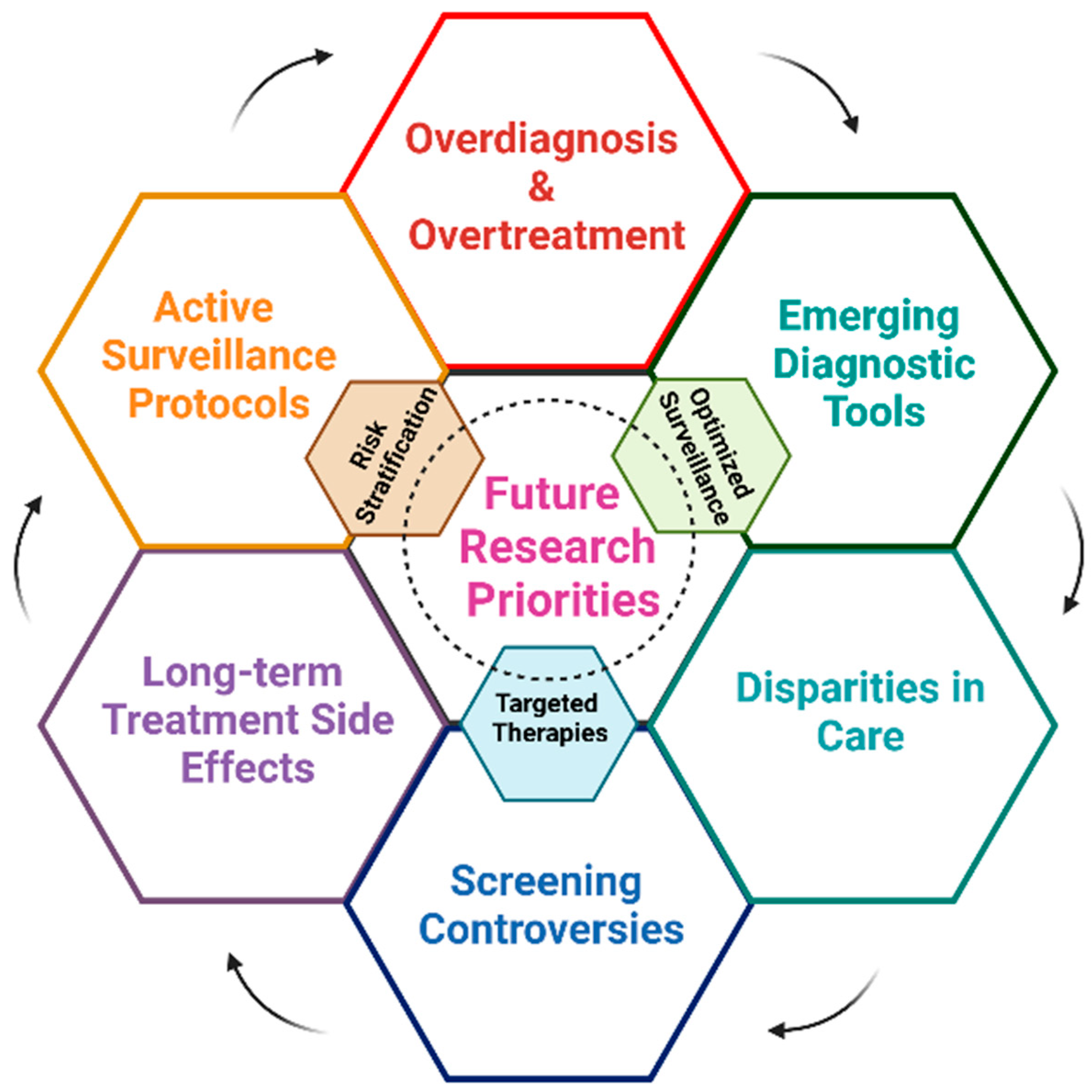
7. Future Opportunities
8. Predictive Models for Risk Stratification in Prostate Cancer
- Comprehensive Risk Models: for example, a study by Seibert et al. developed a model combining clinical factors, polygenic risk scores, and MRI findings, achieving an Area under the curve (AUC) of 0.84 for predicting csPCa [84].
- AI-Enhanced Nomograms: Researchers have created AI-augmented nomograms that outperform traditional risk calculators in predicting PCa outcomes. One model achieved an AUC of 0.89 for predicting biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy [85].
- Deep Learning for Genomic Risk Prediction: a deep learning model analyzing genomic data demonstrated superior performance in predicting PCa risk compared to traditional polygenic risk scores, with an AUC of 0.79 [86].
8.1. Clinical Validation Gaps: ProFound AI vs. Radiologists
8.2. MRI-Based Prediction Models
8.3. Novel Biomarkers and Risk Calculators
8.4. Precision Medicine Applications
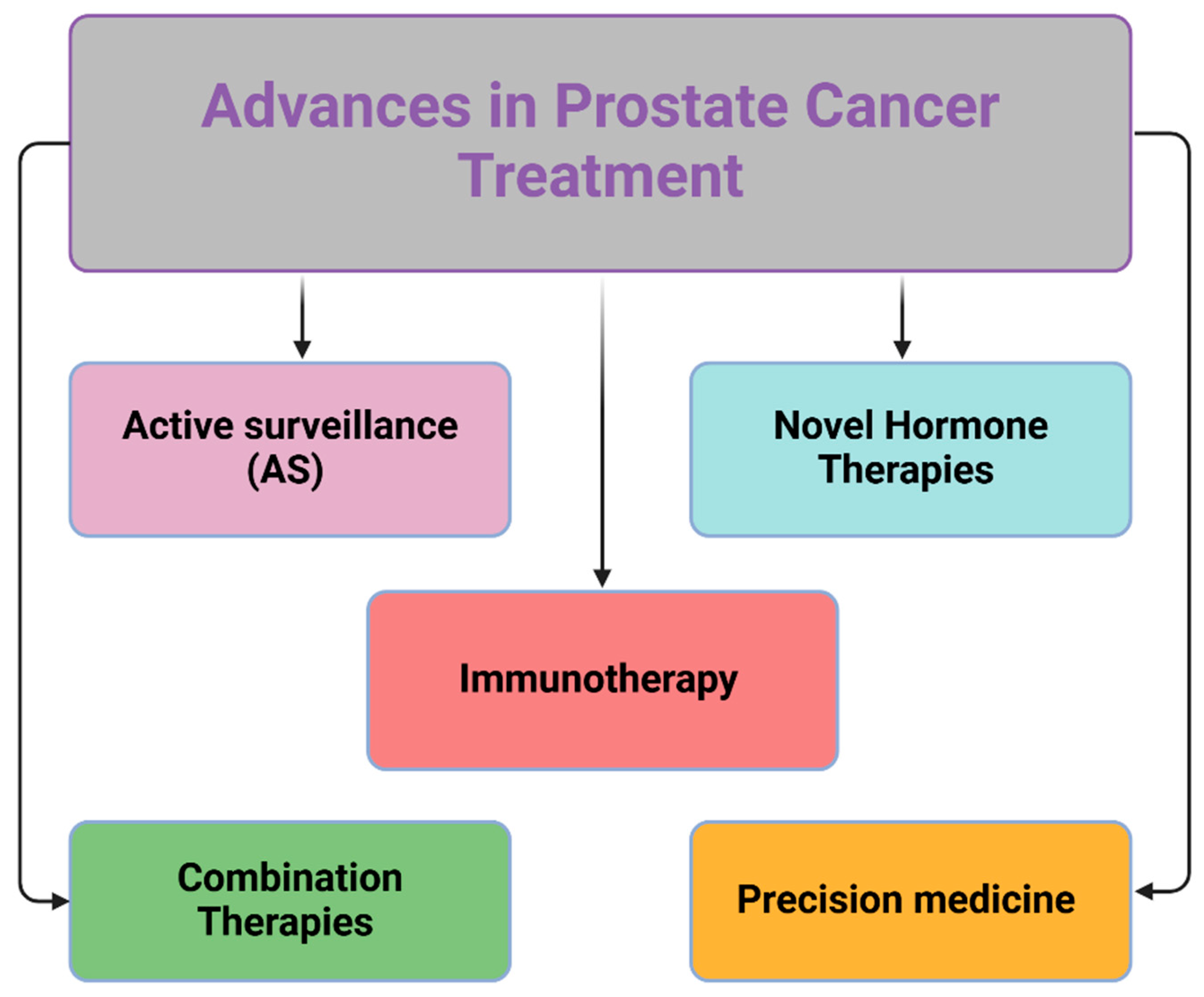
8.5. Advances in Prostate Cancer Treatment
8.6. Passive vs. Active Targeting in Nanomedicine: Mechanisms, Efficiency, and Clinical Implications
8.7. Advances in Radiation Therapy
8.8. Combination Therapies in PCa: Androgen Deprivation Therapy (ADT)
8.9. Emerging Frontiers: Radionuclide Therapy and Oligometastatic Disease
8.10. FDA-Approved Liquid Biopsy Assays: Guardant360 CDx Utility in CRPC
8.11. CRISPR-Mediated AR-V7
| Category | Treatment | Outcomes | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surgical Techniques | Robotic-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy (RALP) | -Improved precision and control -Less blood loss -Shorter hospital stays -Faster recovery -Similar cancer control rates to open surgery | [25,96] |
| Radiation Therapy | -Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) | -High dose delivery in fewer sessions -95.8% five-year survival rate for intermediate-risk localized PC | [9] |
| -Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) -Proton Beam Therapy -MRI-guided radiotherapy (MRIgRT) | -Improved dose conformity -Reduced toxicity -Better quality of life -Precise dose delivery -Minimized exposure to surrounding organs | [9,25,96,120] | |
| Systemic Treatments | -Abiraterone + ADT -Enzalutamide + ADT -Apalutamide + ADT | -Improved overall survival (HR: 0.63; 95% CI: 0.52-0.76) -Better progression-free survival -Improved overall survival -Reduced risk of radiologic progression or death by 61% -Improved overall survival (HR: 0.67; 95% CI: 0.51-0.89) -Improved radiographic progression-free survival | [96] |
| Docetaxel + ADT | -Improved overall survival (57.6 months vs. 47.2 months) -More effective in high-volume disease | [25,96] | |
| Lutetium-177-PSMA-617 | -Improved imaging-based progression-free survival (8.7 vs. 3.4 months) -Improved overall survival (15.3 vs. 11.3 months) in mCRPC | [9] | |
| Combination Therapies | ADT + Radiotherapy | -Improved outcomes for high-risk disease patients | [120] |
| ADT + Docetaxel + Abiraterone | -Enhanced metastasis-free survival | [120] | |
| Radium-223 + Enzalutamide | -33% reduction in radiologic disease progression or death | [99] |
8.12. Recent Advancements in PCa Clinical Trial Research
9. Conclusions and Future Direction
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Williams, I.S.; McVey, A.; Perera, S.; O’Brien, J.S.; Kostos, L.; Chen, K.; Siva, S.; Azad, A.A.; Murphy, D.G.; Kasivisvanathan, V.; et al. Modern paradigms for prostate cancer detection and management. Med. J. Aust. 2022, 217, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergengren, O.; Pekala, K.R.; Matsoukas, K.; Fainberg, J.; Mungovan, S.F.; Bratt, O.; Bray, F.; Brawley, O.; Luckenbaugh, A.N.; Mucci, L.; et al. 2022 Update on Prostate Cancer Epidemiology and Risk Factors-A Systematic Review. Eur. Urol. 2023, 84, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barqawi, A.B.; Krughoff, K.J.; Eid, K. Current Challenges in Prostate Cancer Management and the Rationale behind Targeted Focal Therapy. Adv. Urol. 2012, 2012, 862639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varaprasad, G.L.; Gupta, V.K.; Prasad, K.; Kim, E.; Tej, M.B.; Mohanty, P.; Verma, H.K.; Raju, G.S.R.; Bhaskar, L.; Huh, Y.S. Recent advances and future perspectives in the therapeutics of prostate cancer. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 12, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumanasuriya, S.; De Bono, J. Treatment of Advanced Prostate Cancer—A Review of Current Therapies and Future Promise. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a030635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lu, B.; He, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Du, L. Prostate Cancer Incidence and Mortality: Global Status and Temporal Trends in 89 Countries From 2000 to 2019. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 811044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawla, P. Epidemiology of Prostate Cancer. World J. Oncol. 2019, 10, 63–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silberstein, J.L.; Pal, S.K.; Lewis, B.; Sartor, O. Current clinical challenges in prostate cancer. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2013, 2, 122–136. [Google Scholar]
- Ibraheem, N.; Abdelglil, M.; Wanees, A.; Aosmali, A.M.; Shahid, M.H.; Mithany, R.H. Innovations and Emerging Trends in Prostate Cancer Management: A Literature Review. Cureus 2024, 16, e73128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.U.; El-Shater Bosaily, A.; Brown, L.C.; Gabe, R.; Kaplan, R.; Parmar, M.K.; Collaco-Moraes, Y.; Ward, K.; Hindley, R.G.; Freeman, A.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of multi-parametric MRI and TRUS biopsy in prostate cancer (PROMIS): A paired validating confirmatory study. Lancet 2017, 389, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, P.J.; Francis, R.; Emmett, L.; Hsiao, E.; Kneebone, A.; Hruby, G.; Eade, T.; Nguyen, Q.A.; Thompson, B.D.; Cusick, T.; et al. The Impact of 68Ga-PSMA PET/CT on Management Intent in Prostate Cancer: Results of an Australian Prospective Multicenter Study. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragan, J.; Kania, J.; Salagierski, M. Active surveillance in prostate cancer management: Where do we stand now? Arch. Med. Sci. 2021, 17, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jácome-Pita, F.; Sánchez-Salas, R.; Barret, E.; Amaruch, N.; Gonzalez-Enguita, C.; Cathelineau, X. Focal therapy in prostate cancer: The current situation. Ecancermedicalscience 2014, 8, 435. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nomura, T.; Mimata, H. Focal therapy in the management of prostate cancer: An emerging approach for localized prostate cancer. Adv. Urol. 2012, 2012, 391437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.H.; Barbulescu, D.V.; Marian, L.; Tung, M.C.; Ou, Y.C.; Wu, C.H. High-Intensity Focus Ultrasound Ablation in Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoreifi, A.; Gomella, L.; Hu, J.C.; Konety, B.; Lunelli, L.; Rastinehad, A.R.; Salomon, G.; Taneja, S.; Tourinho-Barbosa, R.; Lebastchi, A.H. Identifying the best candidate for focal therapy: A comprehensive review. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, R.; Sahu, A.; Klevansky, M.; Torres, J. Real-World Data on Outcomes in Metastatic Castrate-Resistant Prostate Cancer Patients Treated with Abiraterone or Enzalutamide: A Regional Experience. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 656146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafron, J.M.; Wilfehrt, H.M.; Ferro, C.; Harmon, M.; Flanders, S.C.; McKay, R.R. Real-World Effectiveness of Sipuleucel-T on Overall Survival in Men with Advanced Prostate Cancer Treated with Androgen Receptor-Targeting Agents. Adv. Ther. 2022, 39, 2515–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Guo, Z.; Hu, Z. The Role of PARP Inhibitors in the Treatment of Prostate Cancer: Recent Advances in Clinical Trials. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannantuono, G.M.; Chandran, E.; Floudas, C.S.; Choo-Wosoba, H.; Butera, G.; Roselli, M.; Gulley, J.L.; Karzai, F. Efficacy and safety of PARP inhibitors in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2023, 120, 102623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teyssonneau, D.; Margot, H.; Cabart, M.; Anonnay, M.; Sargos, P.; Vuong, N.-S.; Soubeyran, I.; Sevenet, N.; Roubaud, G. Prostate cancer and PARP inhibitors: Progress and challenges. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ditonno, F.; Bianchi, A.; Malandra, S.; Porcaro, A.B.; Fantinel, E.; Negrelli, R.; Ferro, M.; Milella, M.; Brunelli, M.; Autorino, R.; et al. PARP Inhibitors in Metastatic Prostate Cancer: A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Existing Evidence. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2024, 22, 402–412.e417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, A.K.; Kosoff, D.; Emamekhoo, H.; Lang, J.M.; Kyriakopoulos, C.E. PARP inhibitors in metastatic prostate cancer. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1159557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corn, P.G.; Agarwal, N.; Araujo, J.C.; Sonpavde, G. Taxane-based Combination Therapies for Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. Focus 2019, 5, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, W.A.; Song, Y.S.; Lee, M.K. Strategic Advances in Combination Therapy for Metastatic Castration-Sensitive Prostate Cancer: Current Insights and Future Perspectives. Cancers 2024, 16, 3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galsky, M.D.; Vogelzang, N.J. Docetaxel-based combination therapy for castration-resistant prostate cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2010, 21, 2135–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fizazi, K.; Tran, N.; Fein, L.; Matsubara, N.; Rodriguez-Antolin, A.; Alekseev, B.Y.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Ye, D.; Feyerabend, S.; Protheroe, A.; et al. Abiraterone plus Prednisone in Metastatic, Castration-Sensitive Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, K.N.; Chowdhury, S.; Bjartell, A.; Chung, B.H.; Pereira de Santana Gomes, A.J.; Given, R.; Juárez, A.; Merseburger, A.S.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Uemura, H.; et al. Apalutamide in Patients with Metastatic Castration-Sensitive Prostate Cancer: Final Survival Analysis of the Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase III TITAN Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 2294–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.J.; Iguchi, T.; Azad, A.A.; Villers, A.; Alekseev, B.; Petrylak, D.P.; Szmulewitz, R.Z.; Alcaraz, A.; Shore, N.D.; Holzbeierlein, J.; et al. The Efficacy of Enzalutamide plus Androgen Deprivation Therapy in Oligometastatic Hormone-sensitive Prostate Cancer: A Post Hoc Analysis of ARCHES. Eur. Urol. 2023, 84, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandel, P.; Hoeh, B.; Wenzel, M.; Preisser, F.; Tian, Z.; Tilki, D.; Steuber, T.; Karakiewicz, P.I.; Chun, F.K.H. Triplet or Doublet Therapy in Metastatic Hormone-sensitive Prostate Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. Eur. Urol. Focus 2023, 9, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Fizazi, K.; Shore, N.D.; Heidegger, I.; Smith, M.R.; Tombal, B.; Saad, F. Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive Prostate Cancer and Combination Treatment Outcomes: A Review. JAMA Oncol. 2024, 10, 807–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, I.D. Combination therapy in metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer: Is three a crowd? Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2022, 14, 17588359221086827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakita, N.; Hara, T.; Suzuki, K.; Terakawa, T.; Teishima, J.; Nakano, Y.; Miyake, H. Efficacy of Combination Therapy with Radium-223 and Enzalutamide in Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer with Bone Metastases. Anticancer Res. 2024, 44, 2627–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damiana, T.S.T.; Dalm, S.U. Combination Therapy, a Promising Approach to Enhance the Efficacy of Radionuclide and Targeted Radionuclide Therapy of Prostate and Breast Cancer. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, L. Prostate cancer overdiagnosis and overtreatment. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2013, 20, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, J.J.; Weyrich, M.S.; Durbin, S.; Liu, Y.; Bang, H.; Melnikow, J.U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Evidence Syntheses, formerly Systematic Evidence Reviews. In Prostate-Specific Antigen-Based Screening for Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Evidence Review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US): Rockville, MD, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Barbier, M.C.; Tomonaga, Y.; Menges, D.; Yebyo, H.G.; Haile, S.R.; Puhan, M.A.; Schwenkglenks, M. Survival modelling and cost-effectiveness analysis of treatments for newly diagnosed metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0277282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.M.; Chen, V.E.; Miller, R.C.; Greenberger, B.A. The Impact of Prostate Cancer Treatment on Quality of Life: A Narrative Review with a Focus on Randomized Data. Res. Rep. Urol. 2020, 12, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, T.; Ledesma, D.; Yoshihara, N. The Economic Burden of Metastatic Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer and Skeletal Related Events in Japanese University Hospitals. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2018, 19, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Groot, M.T.; Boeken Kruger, C.G.; Pelger, R.C.; Uyl-de Groot, C.A. Costs of prostate cancer, metastatic to the bone, in the Netherlands. Eur. Urol. 2003, 43, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handorf, E.A.; Beck, J.R.; Correa, A.; Ramamurthy, C.; Geynisman, D.M. Cost-Effectiveness Analysis for Therapy Sequence in Advanced Cancer: A Microsimulation Approach with Application to Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Med. Decis. Mak. 2023, 43, 949–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, N.D.; Tannock, I.; N’Dow, J.; Feng, F.; Gillessen, S.; Ali, S.A.; Trujillo, B.; Al-Lazikani, B.; Attard, G.; Bray, F.; et al. The Lancet Commission on prostate cancer: Planning for the surge in cases. Lancet 2024, 403, 1683–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Hatano, K.; Nonomura, N. Liquid Biomarkers in Prostate Cancer Diagnosis: Current Status and Emerging Prospects. World J. Mens Health 2024, 42, 8–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeb, S.; Sanda, M.G.; Broyles, D.L.; Shin, S.S.; Bangma, C.H.; Wei, J.T.; Partin, A.W.; Klee, G.G.; Slawin, K.M.; Marks, L.S.; et al. The prostate health index selectively identifies clinically significant prostate cancer. J. Urol. 2015, 193, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyrich, N.W.; Morgan, T.M.; Tosoian, J.J. Biomarkers for detection of clinically significant prostate cancer: Contemporary clinical data and future directions. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2021, 10, 3091–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattu, A.S.; Zappala, S.M.; Parekh, D.J.; Punnen, S. A 4Kscore Cut-off of 7.5% for Prostate Biopsy Decisions Provides High Sensitivity and Negative Predictive Value for Significant Prostate Cancer. Urology 2021, 148, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zappala, S.M.; Scardino, P.T.; Okrongly, D.; Linder, V.; Dong, Y. Clinical performance of the 4Kscore Test to predict high-grade prostate cancer at biopsy: A meta-analysis of us and European clinical validation study results. Rev. Urol. 2017, 19, 149–155. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.; Zargar-Shoshtari, K.; Pow-Sang, J.M. Biomarkers for prostate cancer: Present challenges and future opportunities. Future Sci. OA 2016, 2, Fso72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, A.K.; Hu, K.; Liu, C.J.; Siddiqui, J.; Zheng, Y.; Han, S.; Nallandhighal, S.; Hovelson, D.H.; Xiao, L.; Pham, T.; et al. Development of a Whole-urine, Multiplexed, Next-generation RNA-sequencing Assay for Early Detection of Aggressive Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2022, 5, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, I.M.; Ankerst, D.P.; Chi, C.; Goodman, P.J.; Tangen, C.M.; Lucia, M.S.; Feng, Z.; Parnes, H.L.; Coltman, C.A., Jr. Assessing prostate cancer risk: Results from the Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2006, 98, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.E.; van Leeuwen, P.J.; Moses, D.; Shnier, R.; Brenner, P.; Delprado, W.; Pulbrook, M.; Böhm, M.; Haynes, A.M.; Hayen, A.; et al. The Diagnostic Performance of Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Detect Significant Prostate Cancer. J. Urol. 2016, 195, 1428–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fütterer, J.J.; Briganti, A.; De Visschere, P.; Emberton, M.; Giannarini, G.; Kirkham, A.; Taneja, S.S.; Thoeny, H.; Villeirs, G.; Villers, A. Can Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer Be Detected with Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging? A Systematic Review of the Literature. Eur. Urol. 2015, 68, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-Y.; Wang, P.-Y.; Liu, M.-Z.; Lyu, F.; Ma, M.-W.; Ren, X.-Y.; Gao, X.-S. Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer: From Diagnosis to Treatment. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houshmand, S.; Lawhn-Heath, C.; Behr, S. PSMA PET imaging in the diagnosis and management of prostate cancer. Abdom. Radiol. 2023, 48, 3610–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgakopoulos, A.; Bamias, A.; Chatziioannou, S. Current role of PSMA-PET imaging in the clinical management of prostate cancer. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2023, 15, 17588359231208960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, M.; Papa, N.; Roberts, M.; Williams, M.; Udovicich, C.; Vela, I.; Christidis, D.; Bolton, D.; Hofman, M.S.; Lawrentschuk, N.; et al. Gallium-68 Prostate-specific Membrane Antigen Positron Emission Tomography in Advanced Prostate Cancer—Updated Diagnostic Utility, Sensitivity, Specificity, and Distribution of Prostate-specific Membrane Antigen-avid Lesions: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Eur. Urol. 2020, 77, 403–417. [Google Scholar]
- Alshamrani, A.F.A. Diagnostic Accuracy of Molecular Imaging Techniques for Detecting Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.M.; Rais-Bahrami, S.; Turkbey, B.; George, A.K.; Rothwax, J.; Shakir, N.; Okoro, C.; Raskolnikov, D.; Parnes, H.L.; Linehan, W.M.; et al. Comparison of MR/ultrasound fusion-guided biopsy with ultrasound-guided biopsy for the diagnosis of prostate cancer. JAMA 2015, 313, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, M.; Mirchandani, R.; Papa, N.; Breemer, G.; Effeindzourou, A.; Smith, L.; Swindle, P.; Smith, E. PSA-based machine learning model improves prostate cancer risk stratification in a screening population. World J. Urol. 2021, 39, 1897–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spratt, D.E.; Tang, S.; Sun, Y.; Huang, H.C.; Chen, E.; Mohamad, O.; Armstrong, A.J.; Tward, J.D.; Nguyen, P.L.; Lang, J.M.; et al. Artificial Intelligence Predictive Model for Hormone Therapy Use in Prostate Cancer. NEJM Evid. 2023, 2, EVIDoa2300023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arigbede, O.; Amusa, T.; Buxbaum, S.G. Exploring the Use of Artificial Intelligence and Robotics in Prostate Cancer Management. Cureus 2023, 15, e46021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzo, G.; Mangili, P.; Deantoni, C.; Fodor, A.; Broggi, S.; Castriconi, R.; Ubeira Gabellini, M.G.; Del Vecchio, A.; Di Muzio, N.G.; Fiorino, C. Real-world validation of Artificial Intelligence-based Computed Tomography auto-contouring for prostate cancer radiotherapy planning. Phys. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 28, 100501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayan, M.; Salari, K.; Bozzo, A.; Ganglberger, W.; Lu, G.; Carvalho, F.; Gusev, A.; Schneider, A.; Westover, B.M.; Feldman, A.S. A machine learning approach to predict progression on active surveillance for prostate cancer. Urol. Oncol. 2022, 40, 161.e1–161.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, W.; Chen, G.; Li, Y.; Li, R.; Jia, Z.; Zhong, C.; Wang, S.; Mao, X.; Cai, Z.; Deng, J.; et al. Identification of a 9-gene signature to enhance biochemical recurrence prediction in primary prostate cancer: A benchmarking study using ten machine learning methods and twelve patient cohorts. Cancer Lett. 2024, 588, 216739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.C.; Eclov, N.C.W.; Stephens, S.J.; Mowery, Y.M.; Palta, M. Implementation of machine learning in the clinic: Challenges and lessons in prospective deployment from the System for High Intensity EvaLuation During Radiation Therapy (SHIELD-RT) randomized controlled study. BMC Bioinform. 2022, 23 (Suppl. 12), 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Jian, T.; Chi, C.; Liang, Y.; Liang, X.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, F.; Lu, J. Machine Learning-Based Models Enhance the Prediction of Prostate Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 941349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satturwar, S.; Parwani, A.V. Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Prostate Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis: Current State and Future Implications. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2024, 31, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachbar, M.; Lo Russo, M.; Gani, C.; Boeke, S.; Wegener, D.; Paulsen, F.; Zips, D.; Roque, T.; Paragios, N.; Thorwarth, D. Automatic AI-based contouring of prostate MRI for online adaptive radiotherapy. Z. Med. Phys. 2024, 34, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkbey, B.; Haider, M.A. Artificial Intelligence for Automated Cancer Detection on Prostate MRI: Opportunities and Ongoing Challenges, From the AJR Special Series on AI Applications. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2022, 219, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulten, W.; Kartasalo, K.; Chen, P.C.; Strom, P.; Pinckaers, H.; Nagpal, K.; Cai, Y.; Steiner, D.F.; van Boven, H.; Vink, R.; et al. Artificial intelligence for diagnosis and Gleason grading of prostate cancer: The PANDA challenge. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, P. Re: Artificial Intelligence for Diagnosis and Gleason Grading of Prostate Cancer: The PANDA Challenge. Eur. Urol. 2022, 82, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartasalo, K.; Bulten, W.; Delahunt, B.; Chen, P.C.; Pinckaers, H.; Olsson, H.; Ji, X.; Mulliqi, N.; Samaratunga, H.; Tsuzuki, T.; et al. Artificial Intelligence for Diagnosis and Gleason Grading of Prostate Cancer in Biopsies-Current Status and Next Steps. Eur. Urol. Focus 2021, 7, 687–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodie, A.; Dai, N.; Teoh, J.Y.; Decaestecker, K.; Dasgupta, P.; Vasdev, N. Artificial intelligence in urological oncology: An update and future applications. Urol. Oncol. 2021, 39, 379–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soyer, P.; Dohan, A.; Barat, M. Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Urological Oncology Imaging: More Data Are Needed. Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. 2023, 74, 485–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Pan, J.; Mou, W.; Deng, L.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Pareek, G.; Hyams, E.; Carneiro, B.A.; Hadfield, M.J.; et al. Harnessing artificial intelligence for prostate cancer management. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaddad, A.; Tan, G.; Liang, X.; Hassan, L.; Rathore, S.; Desrosiers, C.; Katib, Y.; Niazi, T. Advancements in MRI-Based Radiomics and Artificial Intelligence for Prostate Cancer: A Comprehensive Review and Future Prospects. Cancers 2023, 15, 3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, G.; Warde, P.; Pickles, T.; Crook, J.; Brundage, M.; Souhami, L.; Lukka, H.; Genitourinary Radiation Oncologists of Canada. Pre-treatment risk stratification of prostate cancer patients: A critical review. Can. Urol. Assoc. J. 2012, 6, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dite, G.S.; Spaeth, E.; Murphy, N.M.; Allman, R. Development and validation of a simple prostate cancer risk prediction model based on age, family history, and polygenic risk. Prostate 2023, 83, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Vagha, S. A Comprehensive Review of Artificial Intelligence in Prostate Cancer Care: State-of-the-Art Diagnostic Tools and Future Outlook. Cureus 2024, 16, e66225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapper, W.; Carneiro, G.; Mikropoulos, C.; Thomas, S.A.; Evans, P.M.; Boussios, S. The Application of Radiomics and AI to Molecular Imaging for Prostate Cancer. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren Belal, S.; Frantz, S.; Minarik, D.; Enqvist, O.; Wikström, E.; Edenbrandt, L.; Trägårdh, E. Applications of Artificial Intelligence in PSMA PET/CT for Prostate Cancer Imaging. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2024, 54, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, I.; Khandwala, Y.S.; Vesal, S.; Shao, W.; Yang, Q.; Soerensen, S.J.C.; Fan, R.E.; Ghanouni, P.; Kunder, C.A.; Brooks, J.D.; et al. A review of artificial intelligence in prostate cancer detection on imaging. Ther. Adv. Urol. 2022, 14, 17562872221128791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiser, K.J.; Fuller, C.D.; Reed, V.K. Artificial intelligence in radiation oncology treatment planning: A brief overview. J. Med. Artif. Intell. 2019, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, E.Y.; Chu, T.N.; Ladi-Seyedian, S.S. Genomics and Artificial Intelligence: Prostate Cancer. Urol. Clin. N. Am. 2024, 51, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eloy, C.; Marques, A.; Pinto, J.; Pinheiro, J.; Campelos, S.; Curado, M.; Vale, J.; Polónia, A. Artificial intelligence-assisted cancer diagnosis improves the efficiency of pathologists in prostatic biopsies. Virchows Arch. 2023, 482, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabaan, A.A.; Bakhrebah, M.A.; AlSaihati, H.; Alhumaid, S.; Alsubki, R.A.; Turkistani, S.A.; Al-Abdulhadi, S.; Aldawood, Y.; Alsaleh, A.A.; Alhashem, Y.N.; et al. Artificial Intelligence for Clinical Diagnosis and Treatment of Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 5595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resch, D.; Lo Gullo, R.; Teuwen, J.; Semturs, F.; Hummel, J.; Resch, A.; Pinker, K. AI-enhanced Mammography with Digital Breast Tomosynthesis for Breast Cancer Detection: Clinical Value and Comparison with Human Performance. Radiol. Imaging Cancer 2024, 6, e230149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehralivand, S.; Shih, J.H.; Rais-Bahrami, S.; Oto, A.; Bednarova, S.; Nix, J.W.; Thomas, J.V.; Gordetsky, J.B.; Gaur, S.; Harmon, S.A.; et al. A Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Based Prediction Model for Prostate Biopsy Risk Stratification. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osses, D.F.; Roobol, M.J.; Schoots, I.G. Prediction Medicine: Biomarkers, Risk Calculators and Magnetic Resonance Imaging as Risk Stratification Tools in Prostate Cancer Diagnosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluckert, J.; Hötker, A.M.; Da Mutten, R.; Konukoglu, E.; Donati, O.F. AI-based automated evaluation of image quality and protocol tailoring in patients undergoing MRI for suspected prostate cancer. Eur. J. Radiol. 2024, 177, 111581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z. Ethics and discrimination in artificial intelligence-enabled recruitment practices. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2023, 10, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyberg, T.; Brook, M.N.; Ficorella, L.; Lee, A.; Dennis, J.; Yang, X.; Wilcox, N.; Dadaev, T.; Govindasami, K.; Lush, M.; et al. CanRisk-Prostate: A Comprehensive, Externally Validated Risk Model for the Prediction of Future Prostate Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 1092–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Cancer Society. What’s New in Prostate Cancer Research? Overview of Bladder Cancer. 2024. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/prostate-cancer/about/new-research.html (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- UC Urology & Oncology. New Advances in Prostate Cancer Treatment Options. 2024. Available online: https://www.kcuc.com/new-advances-in-prostate-cancer-treatment-options/ (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Nevedomskaya, E.; Baumgart, S.J.; Haendler, B. Recent Advances in Prostate Cancer Treatment and Drug Discovery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayegh, N.; Swami, U.; Agarwal, N. Recent Advances in the Management of Metastatic Prostate Cancer. JCO Oncol. Pract. 2022, 18, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handy, C.E.; Antonarakis, E.S. Sipuleucel-T for the treatment of prostate cancer: Novel insights and future directions. Future Oncol. 2018, 14, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swami, U.; McFarland, T.R.; Nussenzveig, R.; Agarwal, N. Advanced Prostate Cancer: Treatment Advances and Future Directions. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 702–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebrael, G.; Fortuna, G.G.; Sayegh, N.; Swami, U.; Agarwal, N. Advances in the treatment of metastatic prostate cancer. Trends Cancer 2023, 9, 840–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Lunawat, A.K.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, T.; Islam, M.M.; Kahlon, M.S.; Mukherjee, D.; Narang, R.K.; Raikwar, S. Recent Trends in Nanocarrier-Based Drug Delivery System for Prostate Cancer. AAPS PharmSciTech 2024, 25, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekiya, T.A.; Owoseni, O. Emerging frontiers in nanomedicine targeted therapy for prostate cancer. Cancer Treat. Res. Commun. 2023, 37, 100778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiburcius, S.; Krishnan, K.; Yang, J.H.; Hashemi, F.; Singh, G.; Radhakrishnan, D.; Trinh, H.T.; Verrills, N.M.; Karakoti, A.; Vinu, A. Silica-Based Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Vehicles for Prostate Cancer Treatment. Chem. Rec. 2021, 21, 1535–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Cao, Y.; Chi, C.; Zhao, J.; Chong, E.; Chin, K.X.C.; Tan, N.Z.V.; Dmitry, K.; Yang, G.; Yang, X.; et al. Unleashing novel horizons in advanced prostate cancer treatment: Investigating the potential of prostate specific membrane antigen-targeted nanomedicine-based combination therapy. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1265751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazak, R.; Houri, M.; El Achy, S.; Hussein, W.; Refaat, T. Passive targeting of nanoparticles to cancer: A comprehensive review of the literature. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 2, 904–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attia, M.F.; Anton, N.; Wallyn, J.; Omran, Z.; Vandamme, T.F. An overview of active and passive targeting strategies to improve the nanocarriers efficiency to tumour sites. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2019, 71, 1185–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar Khanna, V. Targeted delivery of nanomedicines. ISRN Pharmacol. 2012, 2012, 571394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dulaney, C.R.; Osula, D.O.; Yang, E.S.; Rais-Bahrami, S. Prostate Radiotherapy in the Era of Advanced Imaging and Precision Medicine. Prostate Cancer 2016, 2016, 4897515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.V.; Showalter, T.N. Pushing the limits of radiation therapy for prostate cancer: Where do we go next? Semin. Oncol. 2013, 40, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Millán, J.; Lara, M.F.; Correa Generoso, R.; Perez-Rozos, A.; Lupiáñez-Pérez, Y.; Medina Carmona, J.A. Advances in the treatment of prostate cancer with radiotherapy. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2015, 95, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Image Guided Radiotherapy (IGRT). Together We Will Beat Cancer. 2023. Available online: https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/treatment/radiotherapy/external/types/image-guided-radiotherapy-igrt#:~:text=IGRT%20is%20short%20for%20image,the%20surrounding%20tissues%20and%20bones (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Podder, T.K.; Fredman, E.T.; Ellis, R.J. Advances in Radiotherapy for Prostate Cancer Treatment. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1096, 31–47. [Google Scholar]
- What is Proton Beam Therapy for Prostate Cancer? Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer. 2024. Available online: https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/prostate-cancer/proton-therapy-for-prostate-cancer (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Murgić, J.; Gregov, M.; Mrčela, I.; Budanec, M.; Krengli, M.; Fröbe, A.; Franco, P. MRI-Guided Radiotherapy for Prostate Cancer: A New Paradigm. Acta Clin. Croat. 2022, 61, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sritharan, K.; Tree, A. MR-guided radiotherapy for prostate cancer: State of the art and future perspectives. Br. J. Radiol. 2022, 95, 20210800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, S.C.; D’Amico, A.V. Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 34, 45–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Jang, A.; Garcia, J.; Avril, N.; Li, Q.; Wojtylak, P.; Shore, N.; Tagawa, S.; Barata, P. Advances in prostate cancer treatment: Radionuclide therapy for prostate cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2024, 164, 311–358. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leighl, N.B.; Page, R.D.; Raymond, V.M.; Daniel, D.B.; Divers, S.G.; Reckamp, K.L.; Papadimitrakopoulou, V.A. Clinical Utility of Comprehensive Cell-free DNA Analysis to Identify Genomic Biomarkers in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Metastatic Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 4691–4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, L.; Duncan, R.; Adamson, B.; Kendall, H.; Brittain, N.; Luzzi, S.; Gaughan, L. Defining Splicing Factor Requirements for Androgen Receptor Variant Synthesis in Advanced Prostate Cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2024, 22, 1128–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Sethunath, V.; Metaferia, N.Y.; Nogueira, M.F.; Gallant, D.S.; Garner, E.R.; Viswanathan, S.R. A genome-scale CRISPR screen reveals PRMT1 as a critical regulator of androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer. Cell Rep. 2022, 38, 110417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murgić, J.; Fröbe, A.; Chua, M.L.K. Recent advances in radiotherapy modalities for prostate cancer. Acta Clin. Croat. 2022, 61 (Suppl. S3), 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Aniello, C.; Cavaliere, C.; Foglia, C.; Facchini, S.; Uricchio, F.; Balsamo, R.; Franzese, E.; De Falco, S.; Izzo, M.; Laterza, M.; et al. Management of systemic prostate cancer: Current algorithm from castration sensitive to castration resistant setting. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 26, 8481–8501. [Google Scholar]
- Stephen Freedland, R.S. Prostate-Specific Antigen Dynamics from the Phase 3 EMBARK Trial: A Post Hoc Analysis. UroToday 2024, 69, 107–108. [Google Scholar]
- Institite, N.C. Enzalutamide Gets Added Approval for Prostate Cancer That Hasn’t Spread. 2023. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/news-events/cancer-currents-blog/2024/fda-xtandi-prostate-cancer-psa-recurrence (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Nakazawa, M.; Paller, C.; Kyprianou, N. Mechanisms of Therapeutic Resistance in Prostate Cancer. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 19, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shore, N.D.; Antonarakis, E.S.; Cookson, M.S.; Crawford, E.D.; Morgans, A.K.; Albala, D.M.; Hafron, J.; Harris, R.G.; Saltzstein, D.; Brown, G.A.; et al. Optimizing the role of androgen deprivation therapy in advanced prostate cancer: Challenges beyond the guidelines. Prostate 2020, 80, 527–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, R.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, L. Tumor microenvironment heterogeneity an important mediator of prostate cancer progression and therapeutic resistance. npj Precis. Oncol. 2022, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyll, K.; Ersvær, E.; Vlatkovic, L.; Pradhan, M.; Kildal, W.; Avranden Kjær, M.; Kleppe, A.; Hveem, T.S.; Carlsen, B.; Gill, S.; et al. Tumour heterogeneity poses a significant challenge to cancer biomarker research. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haffner, M.C.; Zwart, W.; Roudier, M.P.; True, L.D.; Nelson, W.G.; Epstein, J.I.; De Marzo, A.M.; Nelson, P.S.; Yegnasubramanian, S. Genomic and phenotypic heterogeneity in prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2021, 18, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schutz, F.A.B.; Sirachainan, E.; Kuppusamy, S.; Hoa, N.T.T.; Dejthevaporn, T.; Bahadzor, B.; Toan, V.Q.; Chansriwong, P.; Alip, A.; Hue, N.T.M.; et al. Optimizing outcomes for patients with metastatic prostate cancer: Insights from South East Asia Expert Panel. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2021, 13, 1758835920985464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zu, C.; Rong, X.; Yu, Q.; Jiang, J. Synergistic Potential of Nanomedicine in Prostate Cancer Immunotherapy: Breakthroughs and Prospects. Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 19, 9459–9486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Cao, Y.; Cao, M.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Gong, T. Nanomedicine in cancer therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuchardt, C.; Weineisen, M.; Wiessalla, S.; Schottelius, M.; Kulkarni, H.; Mueller, D.; Klette, I.; Wester, H.; Baum, R. Biodistribution and dosimetry of Lu-177 PSMA in metastasized castrate resistant prostate cancer patients. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 641. [Google Scholar]
- Liss, M.A.; Leach, R.J.; Sanda, M.G.; Semmes, O.J. Prostate Cancer Biomarker Development: National Cancer Institute’s Early Detection Research Network Prostate Cancer Collaborative Group Review. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2020, 29, 2454–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higano, C.S.; Beer, T.M.; Taplin, M.E.; Efstathiou, E.; Hirmand, M.; Forer, D.; Scher, H.I. Long-term Safety and Antitumor Activity in the Phase 1-2 Study of Enzalutamide in Pre- and Post-docetaxel Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2015, 68, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellinger, J.; Alajati, A.; Kubatka, P.; Giordano, F.A.; Ritter, M.; Costigliola, V.; Golubnitschaja, O. Prostate cancer treatment costs increase more rapidly than for any other cancer-how to reverse the trend? EPMA J. 2022, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.-P.; Qin, B.-D.; Jiao, X.-D.; Liu, K.; Wang, Z.; Zang, Y.-S. New clinical trial design in precision medicine: Discovery, development and direction. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.R.; Ingersoll, M.A.; Teply, B.A.; Lin, M.F. Combination Treatment Options for Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. In Prostate Cancer; Bott, S.R.J., Ng, K.L., Eds.; Exon Publications: Bribane, Australia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
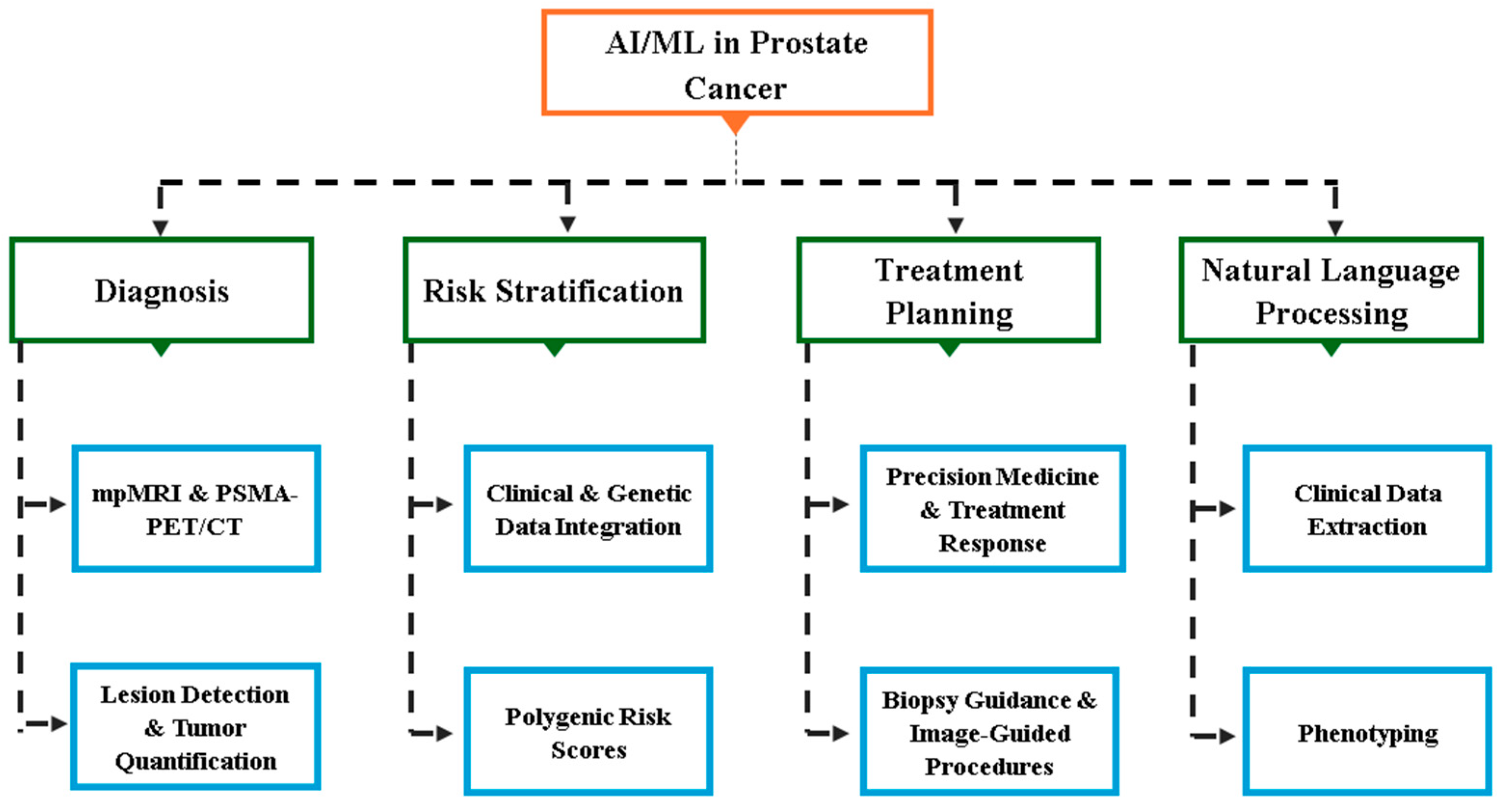

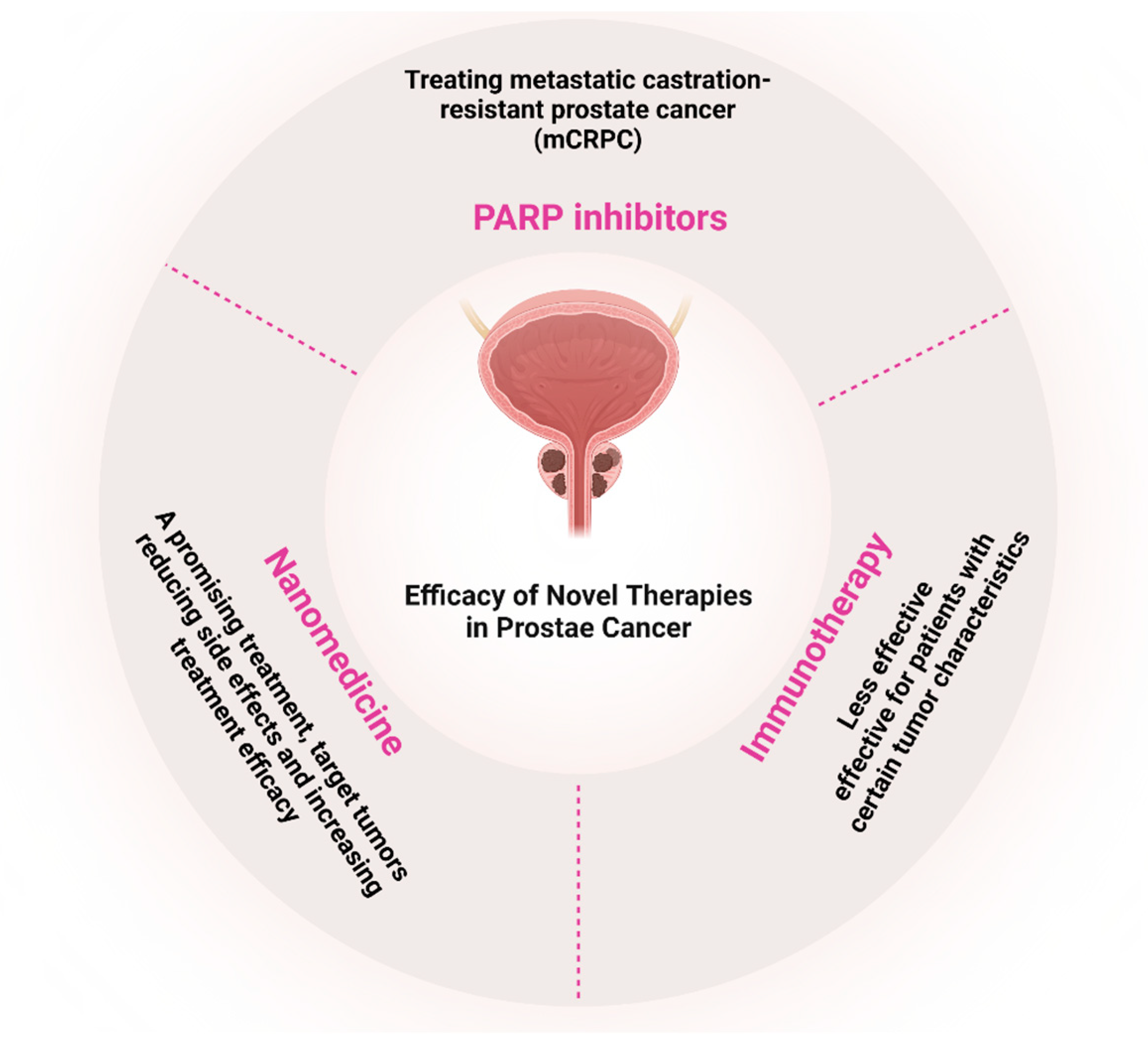
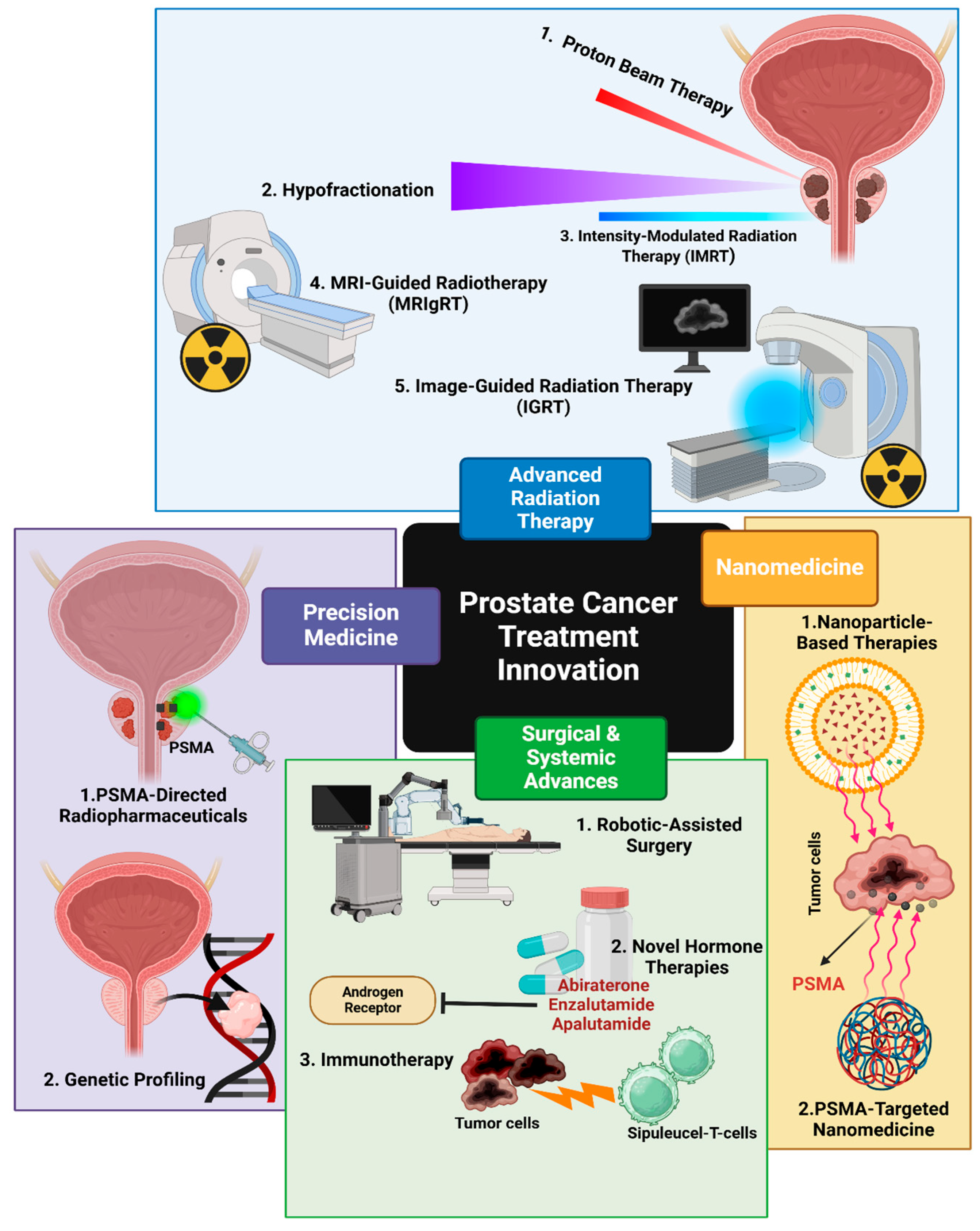

| Application Area | Use Cases | Key Benefits | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Imaging | -Lesion detection and classification on mpMR -Tumor segmentation and volume estimation -PSMA PET/CT image analysis -MRI–ultrasound fusion for targeted biopsies | -Improved accuracy and consistency in lesion detection -Reduced inter-reader variability -Automated quantification of tumor burden -Enhanced guidance for biopsy procedures | [79,80] |
| Predictive Modeling | -Risk stratification using clinical, genetic, and imaging data -Prediction of biochemical recurrence after treatment -Prediction of metastasis and treatment response | -More accurate prediction of clinically significant cancer -Personalized risk assessment -Improved patient counseling and treatment selection | [80,81,82] |
| Treatment Planning | -Automated organ-at-risk and target volume contouring -Dose optimization for radiation therapy -Prediction of optimal treatment modalities -Assessment of ADT benefits in combination with radiotherapy | -Increased efficiency in radiotherapy planning -More consistent treatment plans -Personalized treatment recommendations -Reduction of overtreatment | [79,83] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vakili, S.; Beheshti, I.; Barzegar Behrooz, A.; Łos, M.J.; Vitorino, R.; Ghavami, S. Transforming Prostate Cancer Care: Innovations in Diagnosis, Treatment, and Future Directions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5386. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115386
Vakili S, Beheshti I, Barzegar Behrooz A, Łos MJ, Vitorino R, Ghavami S. Transforming Prostate Cancer Care: Innovations in Diagnosis, Treatment, and Future Directions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5386. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115386
Chicago/Turabian StyleVakili, Sanaz, Iman Beheshti, Amir Barzegar Behrooz, Marek J. Łos, Rui Vitorino, and Saeid Ghavami. 2025. "Transforming Prostate Cancer Care: Innovations in Diagnosis, Treatment, and Future Directions" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5386. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115386
APA StyleVakili, S., Beheshti, I., Barzegar Behrooz, A., Łos, M. J., Vitorino, R., & Ghavami, S. (2025). Transforming Prostate Cancer Care: Innovations in Diagnosis, Treatment, and Future Directions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5386. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115386









