Hedgehog Signaling Functions in Spermatogenesis and Keeping Hemolymph–Testis Barrier Stability in Eriocheir sinensis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
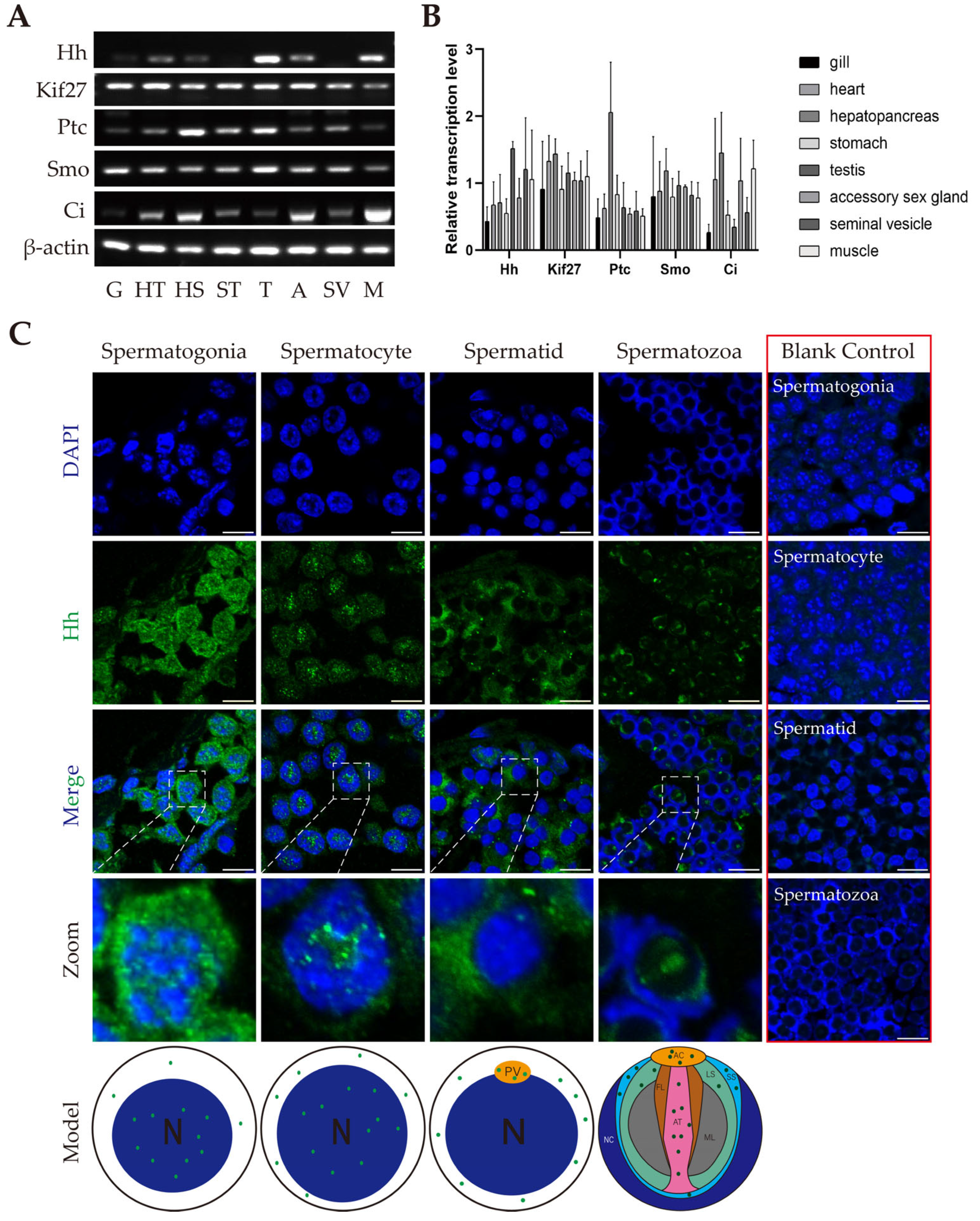
2.1. Identification and Characterization of Genes in HH Signaling in E. sinensis
2.2. Transcription and Distribution of Members of HH Signaling in E. sinensis Testes
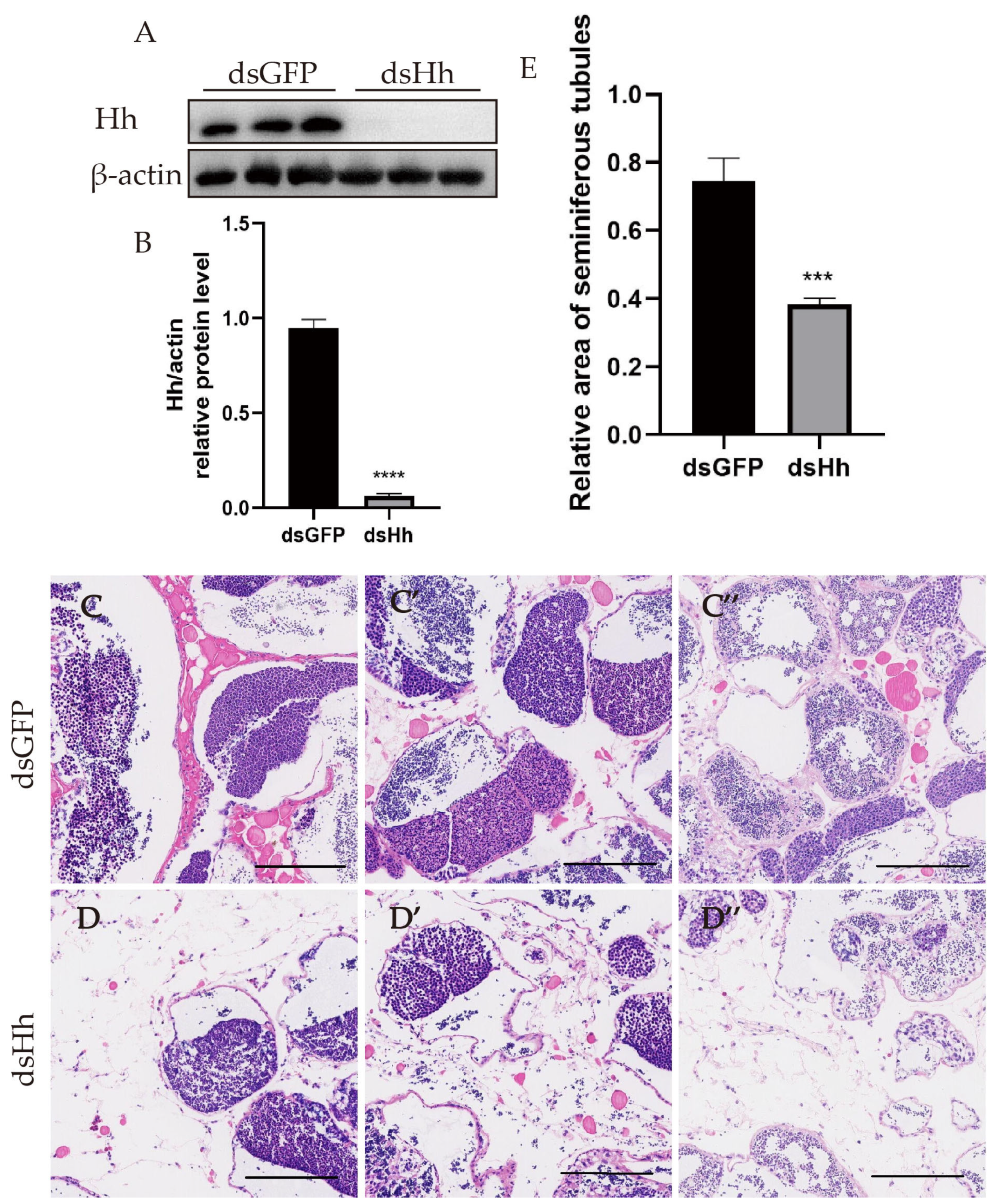
2.3. Knockdown of es-HH In Vivo Leads to the Contraction of the Seminiferous Tubule
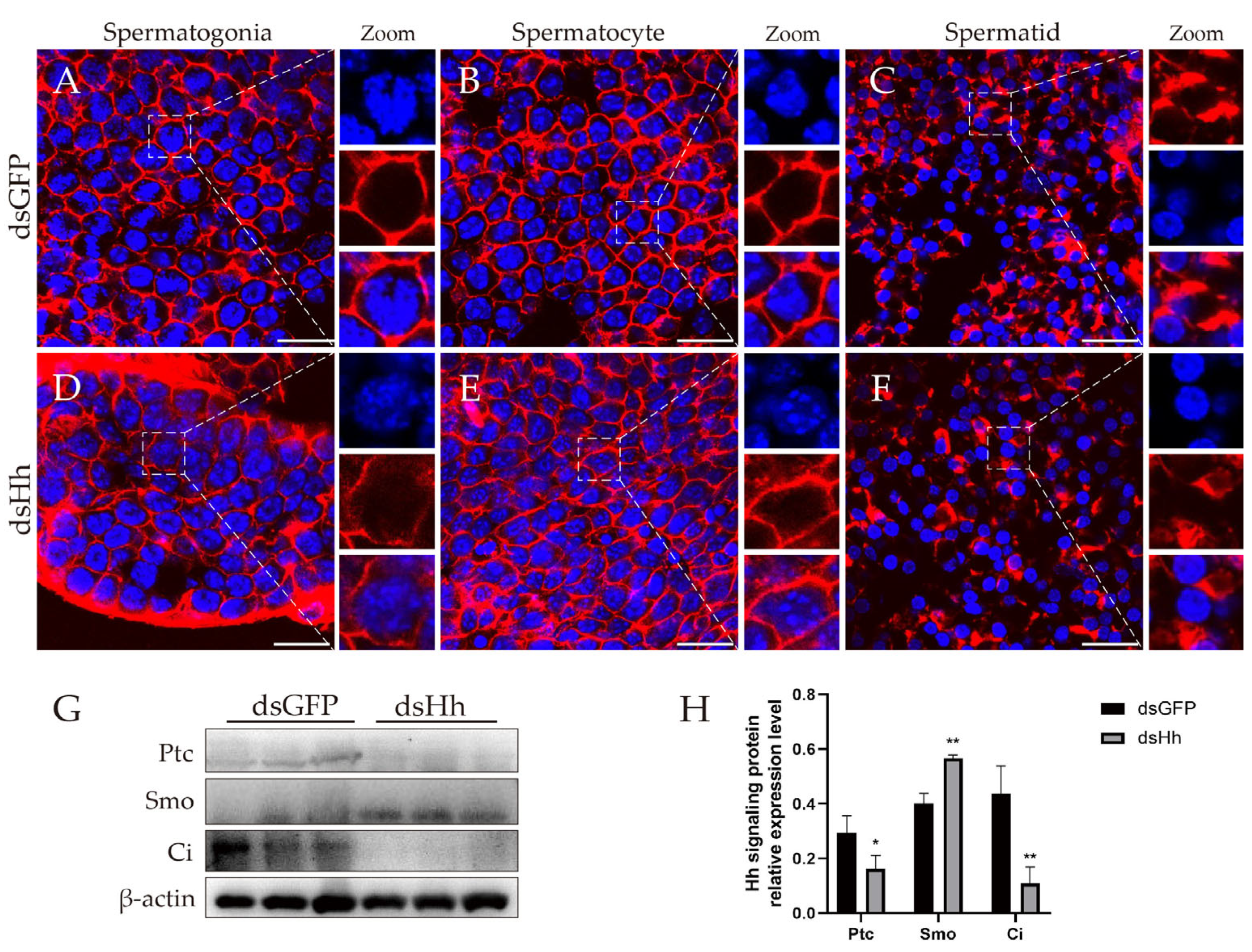
2.4. Knockdown of es-HH In Vivo Causes HTB Morphological Changes in E. sinensis Testes
2.5. Knockdown of es-HH In Vivo Disrupts F-Actin Aggregation and HH Signaling
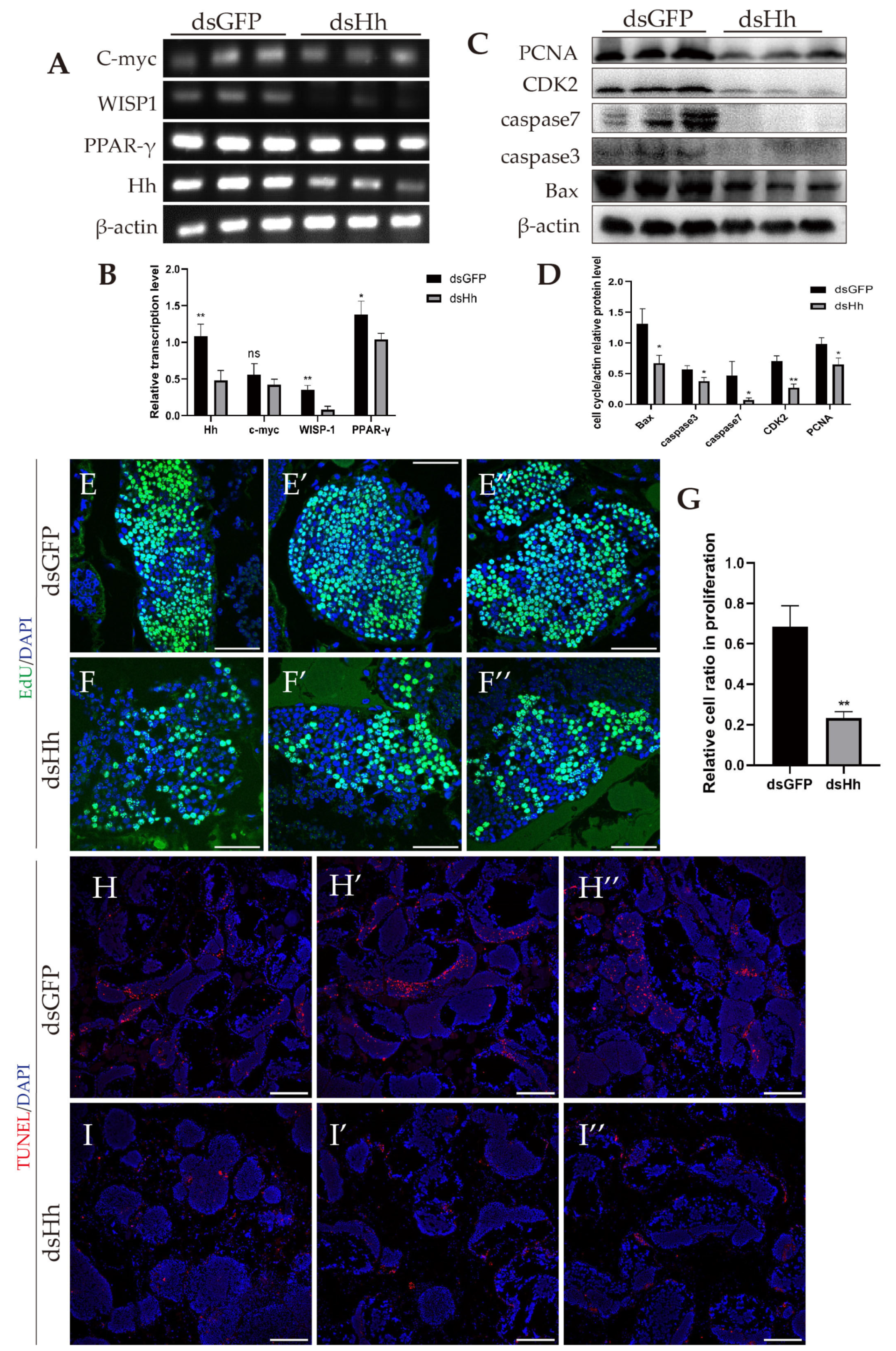
2.6. Abnormal HH Signaling Affects the Germ Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis in E. sinensis Testes
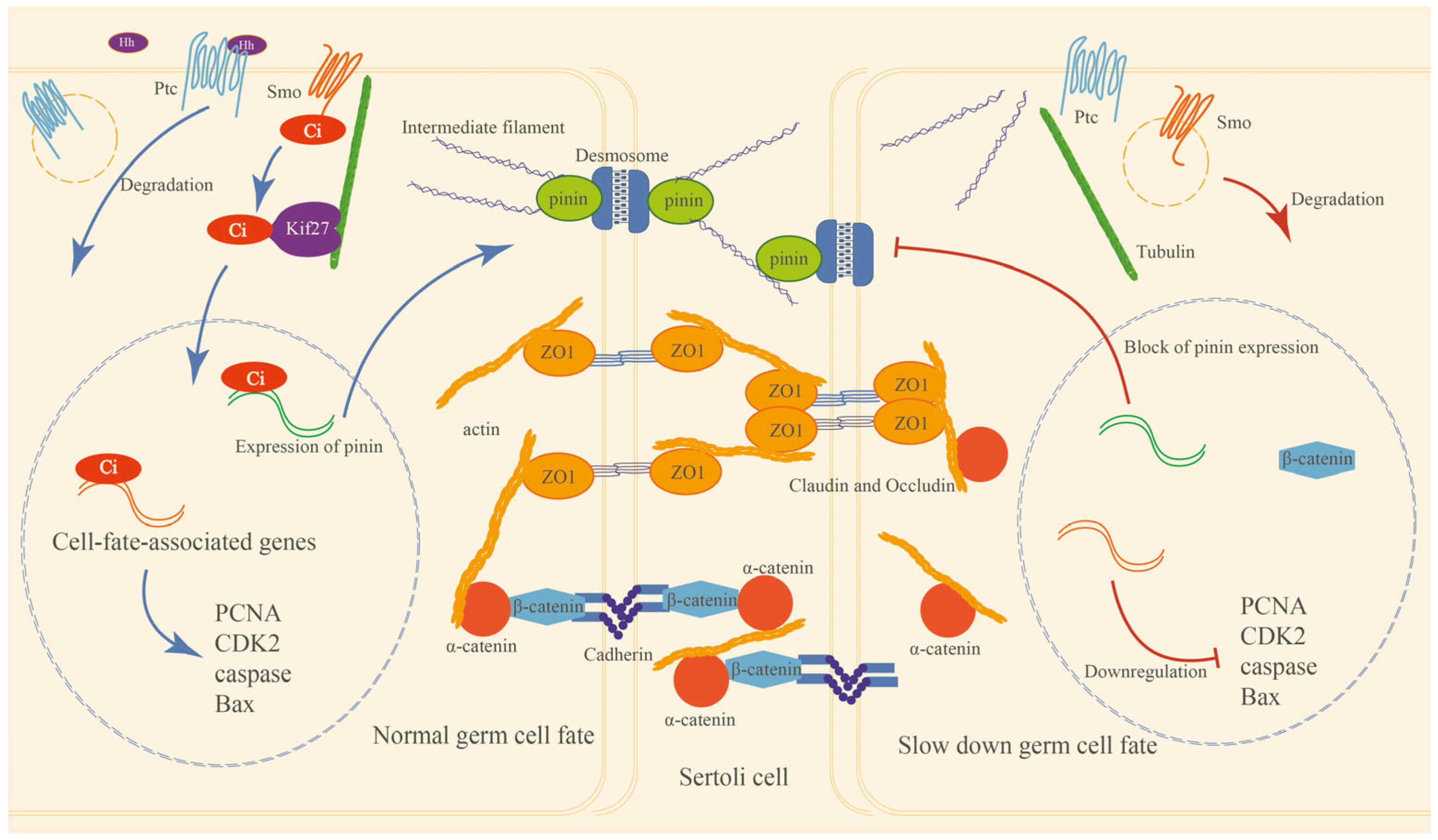
3. Discussion
3.1. HH Signaling Plays Important Roles in E. sinensis Testes
3.2. HH Signaling Regulates HTB Integrity of E. sinensis Testes
3.3. HH Signaling Regulates the Proliferation and Apoptosis of Germ Cells in E. sinensis Testes
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Animals
4.2. Cloning of Members in Hh Signaling in E. senensis
4.3. Sequence Analysis
4.4. Semiquantitative Reverse Transcriptional PCR (sq-PCR)
4.5. Preparation of Antibodies
4.6. Western Blotting (WB)
4.7. RNA Interference
4.8. Hematoxylin–Eosin (HE) Staining
4.9. TUNEL Assay
4.10. EdU Assay
4.11. Immunofluorescence (IF)
4.12. HTB Integrity Assay
4.13. Filamentous-Actin Staining
4.14. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hsia, E.Y.C.; Zhang, Y.; Tran, H.S.; Lim, A.; Chou, Y.; Lan, G.; Beachy, P.A.; Zheng, X. Hedgehog mediated degradation of Ihog adhesion proteins modulates cell segregation in Drosophila wing imaginal discs. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murone, M.; Rosenthal, A.; de Sauvage, F.J. Sonic hedgehog signaling by the patched-smoothened receptor complex. Curr. Biol. 1999, 9, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogden, S.K.; Ascano, M.; Stegman, M.A.; Suber, L.M.; Hooper, J.E.; Robbins, D.J. Identification of a Functional Interaction between the Transmembrane Protein Smoothened and the Kinesin-Related Protein Costal2. Curr. Biol. 2003, 13, 1998–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Tong, C.; Wang, G.; Wang, B.; Jia, J.; Jiang, J. Hedgehog-Regulated Costal2-Kinase Complexes Control Phosphorylation and Proteolytic Processing of Cubitus Interruptus. Dev. Cell 2005, 8, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.C.; Couzens, A.L.; Deshwar, A.R.; McBroom-Cerajewski, L.D.B.; Zhang, X.; Puviindran, V.; Scott, I.C.; Gingras, A.; Hui, C.; Angers, S. The PPFIA1-PP2A protein complex promotes trafficking of Kif7 to the ciliary tip and Hedgehog signaling. Sci. Signal. 2014, 7, a117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.M., Jr. Hedgehog signaling update. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2010, 152A, 1875–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Subramanian, R.; Bangs, F.; Omelchenko, T.; Liem, K.F., Jr.; Kapoor, T.M.; Anderson, K.V. The kinesin-4 protein Kif7 regulates mammalian Hedgehog signalling by organizing the cilium tip compartment. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 16, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, Y.; Katoh, M. KIF27 is one of orthologs for Drosophila Costal-2. Int. J. Oncol. 2004, 25, 1875–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachernegg, S.; Georges, E.; Ayers, K. The Desert Hedgehog Signalling Pathway in Human Gonadal Development and Differences of Sex Development. Sex. Dev. 2022, 16, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, S.; Tian, R.; Yang, Y.; Yang, G.; Xu, S.; Ren, W. Enhanced Negative Regulation of the DHH Signaling Pathway as a Potential Mechanism of Ascrotal Testes in Laurasiatherians. Evol. Biol. 2021, 48, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, Z.; Qu, X.; Bai, X.; Liu, X.; Tao, W.; Zhou, L.; Wang, D.; Wei, J. Desert hedgehog mediates the proliferation of medaka spermatogonia through Smoothened signaling. Reproduction 2022, 163, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.J.; Jung, K.M.; Park, K.J.; Lee, K.Y.; Woo, S.J.; Han, J.Y. Single-cell transcriptome analysis of male chicken germ cells reveals changes in signaling pathway-related gene expression profiles during mitotic arrest. FEBS Open Bio. 2023, 13, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Li, L.; Li, Z.; Gao, H.; Peng, G.; Zhu, C.; Chen, Y.; Yang, F.; Dong, W. Denovo RNA-Seq analysis of ovary and testis reveals potential differentially expressed transcripts associated with gonadal unsynchronization development in Onychostoma macrolepis. Gene Expr. Patterns 2023, 47, 119303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, H.; Qureshi, R.; Khodamoradi, K.; Seetharam, D.; Parmar, M.; Van Booven, D.J.; Issa, I.C.; Sackstein, R.; Lamb, D.; Hare, J.M.; et al. Leptin secreted from testicular microenvironment modulates hedgehog signaling to augment the endogenous function of Leydig cells. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Jorgensen, J.S. Fetal Leydig cells: What we know and what we don’t. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2024, 91, e23739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygaard, M.B.; Almstrup, K.; Lindbæk, L.; Christensen, S.T.; Svingen, T. Cell context-specific expression of primary cilia in the human testis and ciliary coordination of Hedgehog signalling in mouse Leydig cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.H.; Capel, B. Disruption of Testis Cords by Cyclopamine or Forskolin Reveals Independent Cellular Pathways in Testis Organogenesis. Dev. Biol. 2002, 246, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Cheng, S.; Zhang, W.; Wang, M.; Sun, C.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Jin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B. Hedgehog-Gli1 signaling regelates differentiation of chicken (Gallus gallus) embryonic stem cells to male germ cells. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2017, 182, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepny, A.; Hogarth, C.A.; Young, J.; Loveland, K.L. Identification of Hedgehog Signaling Outcomes in Mouse Testis Development Using a Hanging Drop-Culture System1. Biol. Reprod. 2009, 80, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Pan, C.; Zhang, Z.; Xia, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, S.; Guo, T.; Han, H.; Song, H.; Zhang, L.; et al. SUMO regulates somatic cyst stem cells maintenance and directly targets hedgehog pathway in adult Drosophila testis. Development 2016, 143, 1655–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkelä, J.; Saario, V.; Bourguiba-Hachemi, S.; Nurmio, M.; Jahnukainen, K.; Parvinen, M.; Toppari, J. Hedgehog signalling promotes germ cell survival in the rat testis. Reproduction 2011, 142, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kothandapani, A.; Lewis, S.R.; Noel, J.L.; Zacharski, A.; Krellwitz, K.; Baines, A.; Winske, S.; Vezina, C.M.; Kaftanovskaya, E.M.; Agoulnik, A.I.; et al. GLI3 resides at the intersection of hedgehog and androgen action to promote male sex differentiation. PLoS Genet. 2020, 16, e1008810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, H.K.L.; Svingen, T. Hedgehog signal disruption, gonadal dysgenesis and reproductive disorders: Is there a link to endocrine disrupting chemicals? Curr. Res. Toxicol. 2020, 1, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, A.M.; Garland, K.K.; Russell, L.D. Desert hedgehog (Dhh) gene is required in the mouse testis for formation of adult-type Leydig cells and normal development of peritubular cells and seminiferous tubules. Biol. Reprod. 2000, 63, 1825–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, Y.; Noguchi, J.; Akiyama, K.; Takeno, Y.; Fujiwara, Y.; Kajita, S.; Tsuji, T.; Kikuchi, K.; Kaneko, H.; Kunieda, T. A missense mutation of the Dhh gene is associated with male pseudohermaphroditic rats showing impaired Leydig cell development. Reproduction 2011, 141, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Wu, J.; Ru, W.; Chen, G.; Gao, L.; Tang, D. Novel compound heterozygous mutations in the desert hedgehog (DHH) gene in cases of siblings with 46,XY disorders of sexual development. BMC Med. Genom. 2022, 15, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baz-Redón, N.; Soler-Colomer, L.; Fernández-Cancio, M.; Benito-Sanz, S.; Garrido, M.; Moliné, T.; Clemente, M.; Camats-Tarruella, N.; Yeste, D. Novel variant in HHAT as a cause of different sex development with partial gonadal dysgenesis associated with microcephaly, eye defects, and distal phalangeal hypoplasia of both thumbs: Case report. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 957969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.; Singh, P.; Gupta, N.J.; Sankhwar, S.N.; Chakravarty, B.; Thangaraj, K.; Rajender, S. Mutations in the desert hedgehog (DHH) gene in the disorders of sexual differentiation and male infertility. J. Assist. Reprod. Gen. 2021, 38, 1871–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Tong, M.; Jameson, J.L. Distinct Roles for Steroidogenic factor 1 and Desert hedgehog Pathways in Fetal and Adult Leydig Cell Development. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 3704–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsoum, I.B.; Kaur, J.; Ge, R.S.; Cooke, P.S.; Yao, H.H.C. Dynamic changes in fetal Leydig cell populations influence adult Leydig cell populations in mice. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 2657–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroft, T.L.; Patterson, J.; Won Yoon, J.; Doglio, L.; Walterhouse, D.O.; Iannaccone, P.M.; Goldberg, E. GLI1 Localization in the Germinal Epithelial Cells Alternates Between Cytoplasm and Nucleus: Upregulation in Transgenic Mice Blocks Spermatogenesis in Pachytene1. Biol. Reprod. 2001, 65, 1663–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, X.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Tao, W.; Wang, D.; Wei, J. Smoothened mediates medaka spermatogonia proliferation via Gli1–Rgcc–Cdk1 axis. Biol. Reprod. 2023, 109, 772–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zuo, J.; Lv, X.; Ma, J.; Li, X.; Fu, S.; Sun, J. Hedgehog signaling is essential in the regulation of limb regeneration in the Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis. Fish Shellfish Immun. 2023, 140, 108981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Xu, Z.; Lu, J.; Cao, C.; Shen, H.; Li, X.; You, W.; Chen, G. Oestrogen ameliorates blood-brain barrier damage after experimental subarachnoid haemorrhage via the SHH pathway in male rats. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2023, 8, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, H.; Josten, F.; Fuss, B.; Bauer, R.; Hoch, M. Cross regulation of intercellular gap junction communication and paracrine signaling pathways during organogenesis in Drosophila. Dev. Biol. 2007, 310, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; He, J.; Tian, X.; Zhong, J.; Li, H.; Sun, X. Activation of the Hedgehog Pathway Promotes Recovery of Neurological Function After Traumatic Brain Injury by Protecting the Neurovascular Unit. Transl. Stroke Res. 2020, 11, 720–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, G.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Cui, P.; Li, M.; Li, D.; Zhang, N.; Jiang, W. Astrocytic Sonic Hedgehog Alleviates Intracerebral Hemorrhagic Brain Injury via Modulation of Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 575690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Yu, J.; Ning, K.; Qu, Y.; He, H.; Chen, Y.; Reinach, P.S.; et al. Ectodysplasin A regulates epithelial barrier function through sonic hedgehog signalling pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, M.; Mercola, M. Gap junction-mediated transfer of left-right patterning signals in the early chick blastoderm is upstream of Shh asymmetry in the node. Development 1999, 126, 4703–4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, T.; Sun, J.; Liu, W.; Prinz, R.A.; Peng, D.; Liu, X.; Xu, X. H1N1 Influenza Virus Cross-Activates Gli1 to Disrupt the Intercellular Junctions of Alveolar Epithelial Cells. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashizume, A.; Hieda, Y. Hedgehog peptide promotes cell polarization and lumen formation in developing mouse submandibular gland. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Co. 2006, 339, 996–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalasani, K.; Brewster, R.M. N-cadherin-mediated cell adhesion restricts cell proliferation in the dorsal neural tube. Mol. Biol. Cell 2011, 22, 1505–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Ruan, T.; Ji, X.; Ran, D.; Sun, J.; Shi, H.; Prinz, R.A.; Sun, J.; Pan, Z.; Jiao, X.; et al. The Gli1-Snail axis contributes to Salmonella Typhimurium-induced disruption of intercellular junctions of intestinal epithelial cells. Cell. Microbiol. 2020, 22, e13211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.B.; Singh, M.V.; Gorantla, S.; Poluektova, L.Y.; Maggirwar, S.B. Smoothened Agonist Reduces Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Breakdown in Humanized Mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, J.I.; Dodelet-Devillers, A.; Kebir, H.; Ifergan, I.; Fabre, P.J.; Terouz, S.; Sabbagh, M.; Wosik, K.; Bourbonnière, L.; Bernard, M.; et al. The Hedgehog pathway promotes blood-brain barrier integrity and CNS immune quiescence. Science 2011, 334, 1723–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, W.H.; Klezovitch, O.; Fernandez, T.E.; Delrow, J.; Vasioukhin, V. alpha E-catenin controls cerebral cortical size by regulating the hedgehog signaling pathway. Science 2006, 311, 1609–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joost, S.; Almada, L.L.; Rohnalter, V.; Holz, P.S.; Vrabel, A.M.; Fernandez-Barrena, M.G.; McWilliams, R.R.; Krause, M.; Fernandez-Zapico, M.E.; Lauth, M. GLI1 Inhibition Promotes Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Deng, W.; Lobo-Ruppert, S.M.; Ruppert, J.M. Gli1 acts through Snail and E-cadherin to promote nuclear signaling by b-catenin. Oncogene 2007, 26, 4489–4498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaguma, S.; Kasai, K.; Ikeda, H. GLI1 facilitates the migration and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells through MUC5AC-mediated attenuation of E-cadherin. Oncogene 2011, 30, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.Y.; Suh, H.N.; Choi, G.E.; Lee, H.J.; Jung, Y.H.; Ko, S.H.; Kim, J.S.; Chae, C.W.; Lee, C.K.; Han, H.J. Modulation of sonic hedgehog-induced mouse embryonic stem cell behaviours through E-cadherin expression and integrin β1-dependent F-actin formation. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 3548–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Ogle, S.A.; Schumacher, M.A.; Schilling, N.; Tokhunts, R.A.; Orr-Asman, M.A.; Miller, M.L.; Robbins, D.J.; Hollande, F.; Zavros, Y. Hedgehog signaling regulates E-cadherin expression for the maintenance of the actin cytoskeleton and tight junctions. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastr. L. 2010, 299, G1252–G1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, M.; Song, T.; Sun, M.; Wang, T.; Tan, J.; Zhang, J. Dhh signaling pathway regulates reconstruction of seminiferous tubule-like structure. Reprod. Biol. 2022, 22, 100684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El, O.H.; Leheup, B.P.; Gelly, J.L.; Grignon, G. Laminin ultrastructural immunolocalization in rat testis during ontogenesis. Histochemistry 1991, 95, 241–246. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, C.Y.; Mruk, D.D. The Blood-Testis Barrier and Its Implications for Male Contraception. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 64, 16–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Hao, S.; Wang, L.; Qi, H.; Wang, J.; Tan, F.; Yang, W. mTORC1/C2 regulate spermatogenesis in Eriocheir sinensis via alterations in the actin filament network and cell junctions. Cell Tissue Res. 2022, 390, 293–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Qi, H.; Zhao, Z.; Tan, F.; Yang, W. Es-β-CATENIN affects the hemolymph-testes barrier in Eriocheir sinensis by disrupting cell junctions and cytoskeleton. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 124867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, J.; Tan, F.; Yang, W. Myosin VI stabilizes intercellular junctions in the testis through the LHR and MAPK signalling pathway during spermatogenesis in Eriocheir sinensis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 248, 125842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Qi, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Tan, F.; Yang, W. Vangl2 regulates intercellular junctions by remodeling actin-based cytoskeleton through the Rock signaling pathway during spermatogenesis in Eriocheir sinensis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 135264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, W.; He, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, Q. Morphological alterations of all stages of spermatogenesis and acrosome reaction in Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis. Cell Tissue Res. 2015, 360, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jia, K.; Li, Z.; Qi, H.; Liu, D.; Liang, Y.; Hao, S.; Tan, F.; Yang, W. TiO2 nanoparticles affect spermatogenesis and adhesion junctions via the ROS-mediated mTOR signalling pathway in Eriocheir sinensis testes. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 331, 121952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adil, M.S.; Narayanan, S.P.; Somanath, P.R. Cell-cell junctions: Structure and regulation in physiology and pathology. Tissue Barriers 2021, 9, 1848212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leu, S. The role and regulation of Pnn in proliferative and non-dividing cells: Form embryogenesis to pathogenesis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 192, 114672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, Z.; Szczepny, A.; McLaughlin, E.A.; Meistrich, M.L.; Zhou, W.; Ustunel, I.; Loveland, K.L. Dynamic Hedgehog signalling pathway activity in germline stem cells. Andrology 2014, 2, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, J.-J.; Qi, H.-Y.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Tan, F.-Q.; Yang, W.-X. Hedgehog Signaling Functions in Spermatogenesis and Keeping Hemolymph–Testis Barrier Stability in Eriocheir sinensis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115378
Yu J-J, Qi H-Y, Zhao Z, Yang Y, Zhang S-Y, Tan F-Q, Yang W-X. Hedgehog Signaling Functions in Spermatogenesis and Keeping Hemolymph–Testis Barrier Stability in Eriocheir sinensis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115378
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Jun-Jie, Hong-Yu Qi, Zhan Zhao, Yu Yang, Shuang-Yi Zhang, Fu-Qing Tan, and Wan-Xi Yang. 2025. "Hedgehog Signaling Functions in Spermatogenesis and Keeping Hemolymph–Testis Barrier Stability in Eriocheir sinensis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115378
APA StyleYu, J.-J., Qi, H.-Y., Zhao, Z., Yang, Y., Zhang, S.-Y., Tan, F.-Q., & Yang, W.-X. (2025). Hedgehog Signaling Functions in Spermatogenesis and Keeping Hemolymph–Testis Barrier Stability in Eriocheir sinensis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115378







