Copeptin as a New Blood-Based Marker for Differential Diagnosis in Stroke Patients
Abstract
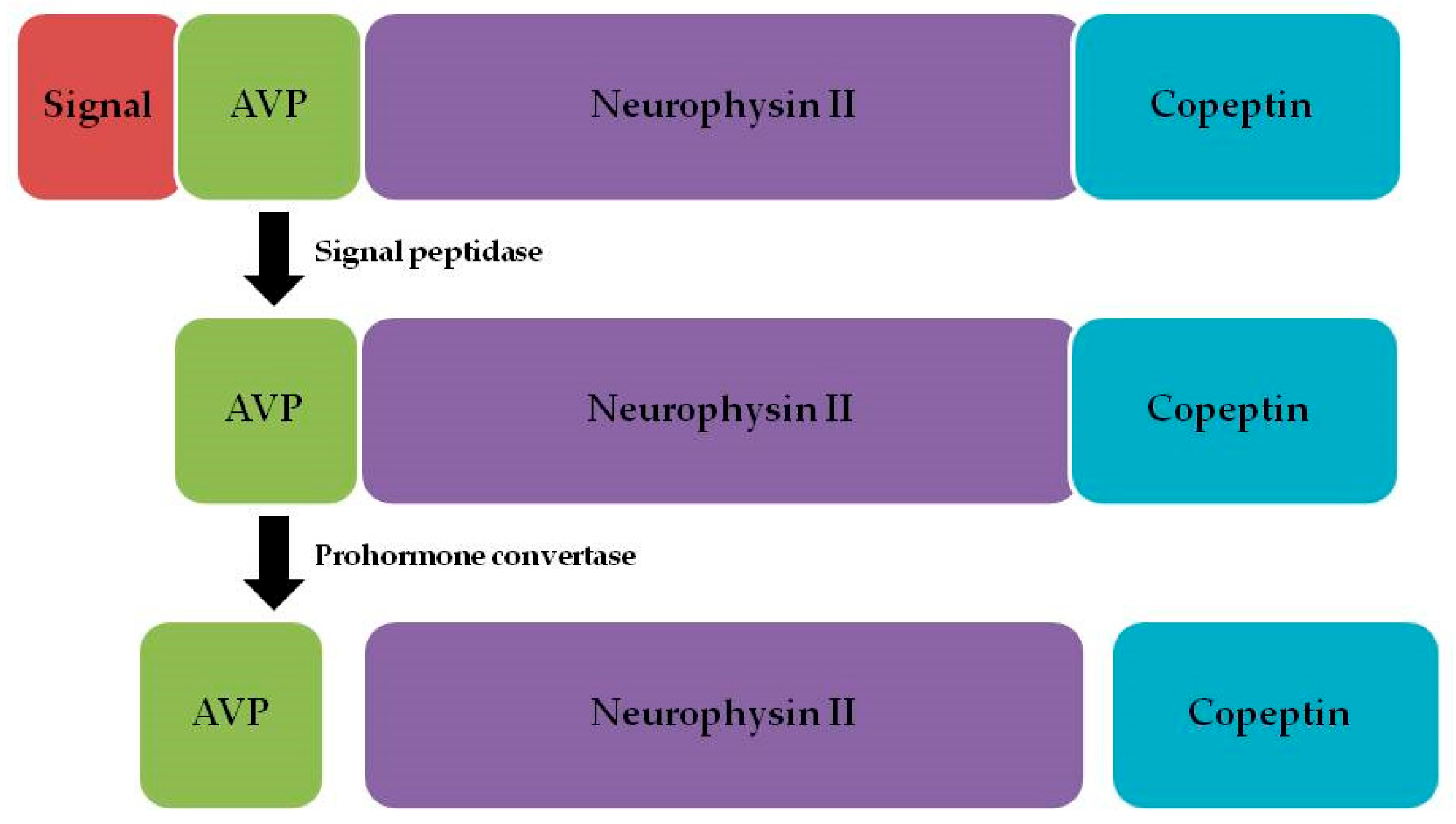
1. Introduction
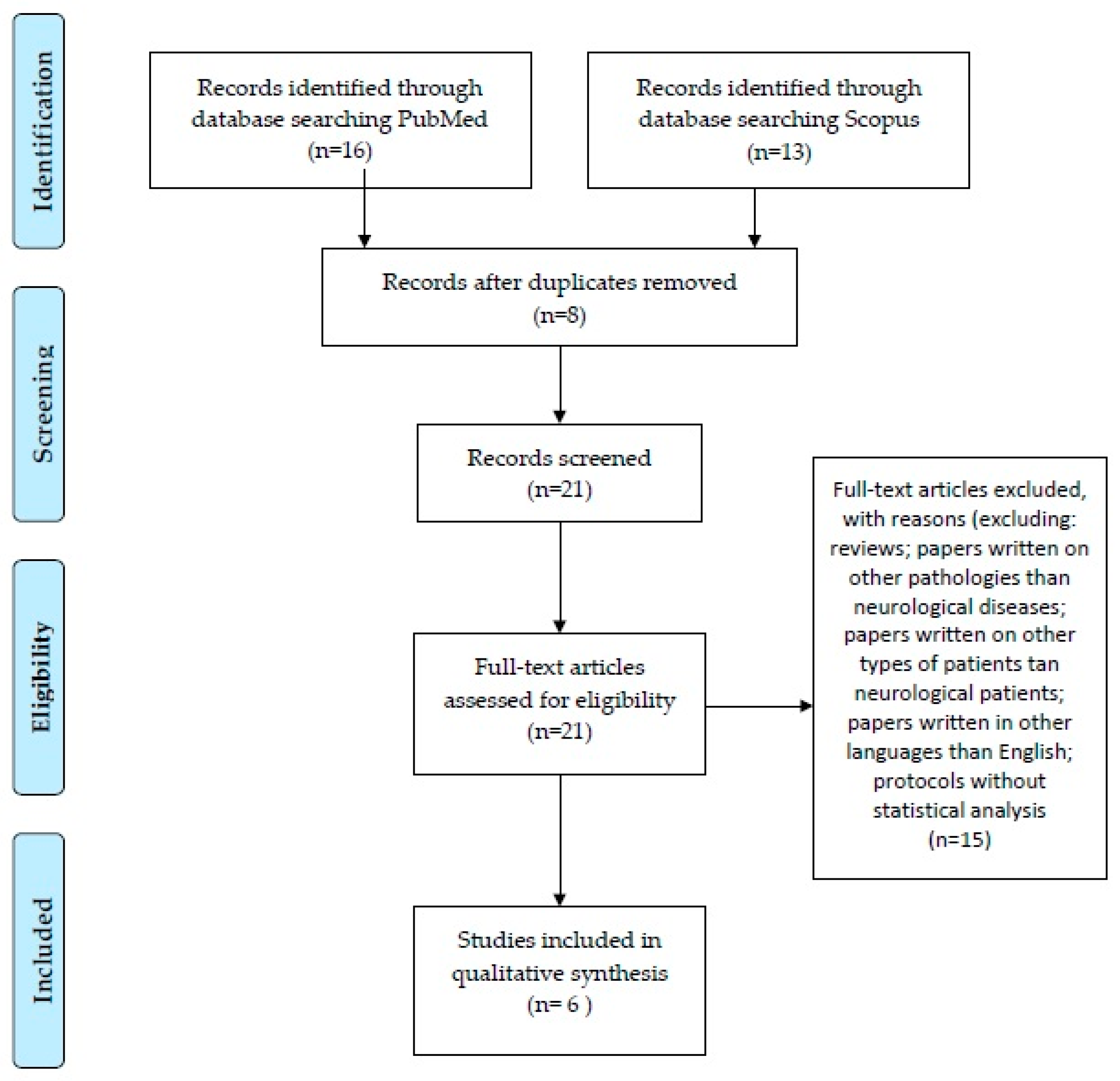
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
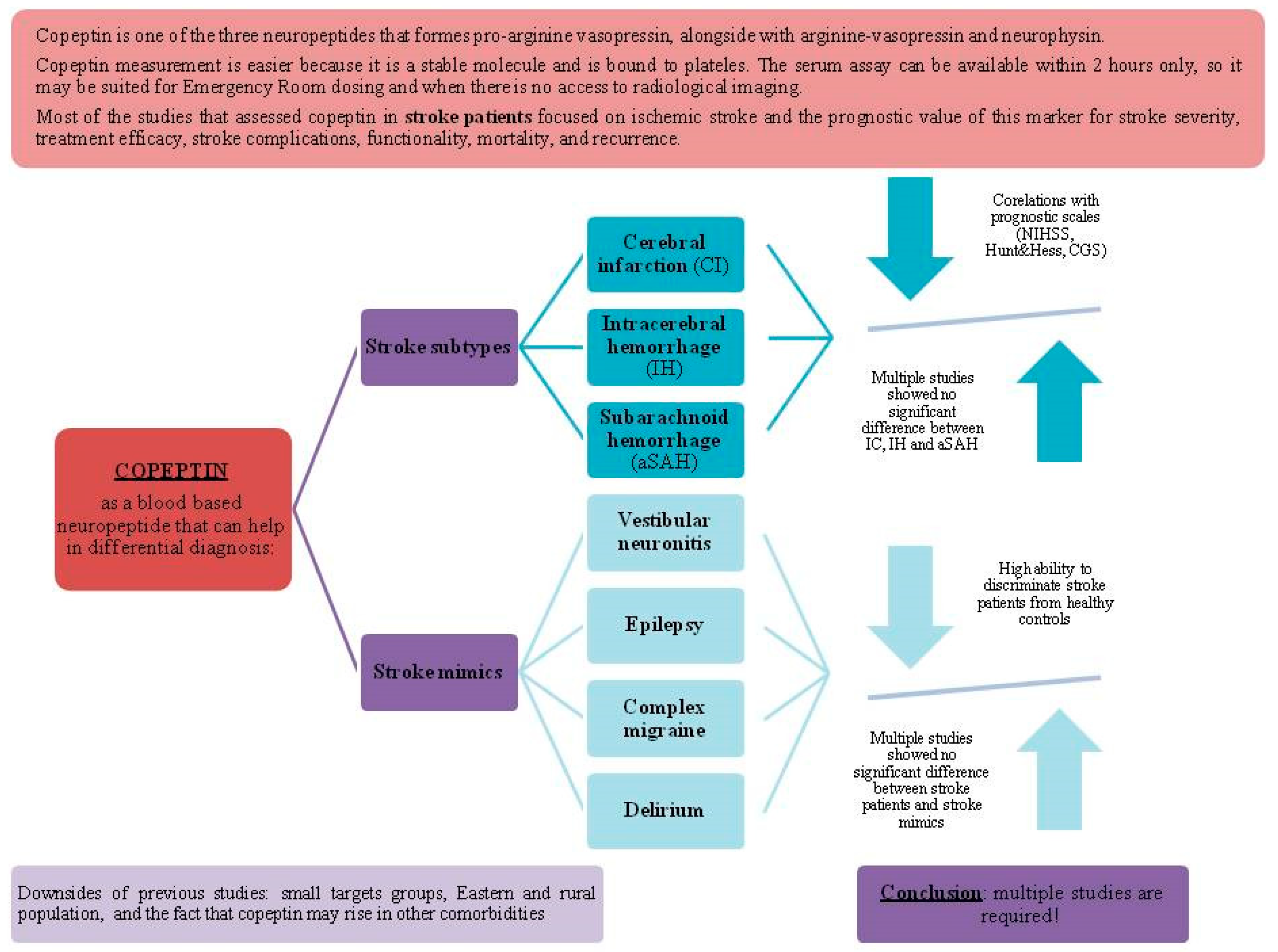
3.1. Copeptin May Differentiate Between Stroke Subtypes
3.2. Copeptin May Differentiate Between Stroke Mimics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Von Recum, J.; Searle, J.; Slagman, A.; Vollert, J.O.; Endres, M.; Möckel, M.; Ebinger, M. Copeptin: Limited Usefulness in Early Stroke Differentiation? Stroke Res. Treat. 2015, 2015, 768401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chai, S.B.; Hui, Y.M.; Li, X.M.; Xiao, Y.; Tang, C.S. Plasma Levels of Copeptin in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease. Heart Vessel. 2009, 24, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.Q.; Dhillon, O.S.; O’Brien, R.J.; Struck, J.; Quinn, P.A.; Morgenthaler, N.G.; Squire, I.B.; Davies, J.E.; Bergmann, A.; Ng, L.L. C-Terminal Provasopressin (Copeptin) as a Novel and Prognostic Marker in Acute Myocardial Infarction: Leicester Acute Myocardial Infarction Peptide (LAMP) Study. Circulation 2007, 115, 2103–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voors, A.A.; von Haehling, S.; Anker, S.D.; Hillege, H.L.; Struck, J.; Hartmann, O.; Bergmann, A.; Squire, I.; van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Dickstein, K.; et al. C-Terminal Provasopressin (Copeptin) Is a Strong Prognostic Marker in Patients with Heart Failure after an Acute Myocardial Infarction: Results from the OPTIMAAL Study. Eur. Heart J. 2009, 30, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westermann, I.; Dünser, M.W.; Haas, T.; Jochberger, S.; Luckner, G.; Mayr, V.D.; Wenzel, V.; Stadlbauer, K.-H.; Innerhofer, P.; Morgenthaler, N.; et al. Endogenous Vasopressin and Copeptin Response in Multiple Trauma Patients. Shock 2007, 28, 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.-F.; Huang, Q.; Dai, W.-M.; Jie, Y.-Q.; Fan, X.-F.; Wu, A.; Lv, Y.; Li, Y.-P.; Yan, X.-J. Prognostic Value of Copeptin: One-Year Outcome in Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury. Peptides 2012, 33, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu, F.; Gurger, M.; Yilmaz, M.; Atescelik, M.; Yildiz, M.; Ilhan, N.; Ilhan, S.; Goktekin, M.C. Copeptin Levels in Cerebral Infarction, Intracranial Hemorrhage and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Clin. Lab. 2016, 62, 2387–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blek, N.; Szwed, P.; Putowska, P.; Nowicka, A.; Drela, W.L.; Gasecka, A.; Ladny, J.R.; Merza, Y.; Jaguszewski, M.J.; Szarpak, L. The Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Copeptin in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke and Transient Ischemic Attack: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cardiol. J. 2022, 29, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.-S.; Kim, H.J.; Chun, H.-J.; Kim, J.M.; Yi, H.-J.; Cheong, J.-H.; Kim, C.-H.; Oh, S.-J.; Ko, Y.; Kim, Y.-S.; et al. Prognostic Role of Copeptin after Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christ-Crain, M. Vasopressin and Copeptin in Health and Disease. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2019, 20, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montellano, F.A.; Ungethüm, K.; Ramiro, L.; Nacu, A.; Hellwig, S.; Fluri, F.; Whiteley, W.N.; Bustamante, A.; Montaner, J.; Heuschmann, P.U. Role of Blood-Based Biomarkers in Ischemic Stroke Prognosis. Stroke 2021, 52, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranowska, B.; Kochanowski, J. Copeptin-a New Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker in Neurological and Cardiovascular Diseases. Neuroendocrinol. Lett. 2019, 40, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Morgenthaler, N.G. Copeptin: A Biomarker of Cardiovascular and Renal Function. Congest. Heart Fail. 2010, 16, S37–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enhörning, S.; Hedblad, B.; Nilsson, P.M.; Engström, G.; Melander, O. Copeptin Is an Independent Predictor of Diabetic Heart Disease and Death. Am. Heart J. 2015, 169, 549–556.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreca, T.; Gandolfo, C.; Corsini, G.; Del Sette, M.; Cataldi, A.; Rolandi, E.; Franceschini, R. Evaluation of the Secretory Pattern of Plasma Arginine Vasopressin in Stroke Patients. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2001, 11, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greisenegger, S.; Segal, H.C.; Burgess, A.I.; Poole, D.L.; Mehta, Z.; Rothwell, P.M. Copeptin and Long-Term Risk of Recurrent Vascular Events after Transient Ischemic Attack and Ischemic Stroke: Population-Based Study. Stroke 2015, 46, 3117–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgenthaler, N.G.; Struck, J.; Alonso, C.; Bergmann, A. Assay for the Measurement of Copeptin, a Stable Peptide Derived from the Precursor of Vasopressin. Clin. Chem. 2006, 52, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigro, N.; Müller, B.; Morgenthaler, N.G.; Fluri, F.; Schuetz, P.; Neiderta, S.; Stolz, D.; Bingisser, R.; Tamm, M.; Christ-Crain, M.; et al. The Use of Copeptin, the Stable Peptide of the Vasopressin Precursor, in the Differential Diagnosis of Sodium Imbalance in Patients with Acute Diseases. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2011, 141, w13270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, S.S.; Loke, I.; Davies, J.E.; Squire, I.B.; Struck, J.; Ng, L.L. Gender and Renal Function Influence Plasma Levels of Copeptin in Healthy Individuals. Clin. Sci. 2009, 116, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobsa, L.; Cullen Edozien, K. Copeptin and Its Potential Role in Diagnosis and Prognosis of Various Diseases. Biochem. Med. 2013, 23, 172–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potocki, M.; Breidthardt, T.; Mueller, A.; Reichlin, T.; Socrates, T.; Arenja, N.; Reiter, M.; Morgenthaler, N.G.; Bergmann, A.; Noveanu, M. Copeptin and Risk Stratification in Patients with Acute Dyspnea. Crit. Care 2010, 14, R213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-L.; Yin, C.-H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L.-B.; Fu, H.-J.; Feng, J.-C. Plasma Copeptin and Long-Term Outcomes in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2013, 128, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Săcărescu, A.; Turliuc, M.-D.; Brănișteanu, D.D. Role of Copeptin in the Diagnosis of Traumatic Neuroendocrine Dysfunction. Neuropeptides 2021, 89, 102167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marchis, G.M.; Katan, M.; Weck, A.; Fluri, F.; Foerch, C.; Findling, O.; Schuetz, P.; Buhl, D.; El-Koussy, M.; Gensicke, H.; et al. Copeptin Adds Prognostic Information after Ischemic Stroke: Results from the CoRisk Study. Neurology 2013, 80, 1278–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasile, A.I.; Tiu, C.; Badiu, C. Copeptin as Biomarker for Acute Ischemic Stroke Prognosis and Revascularization Treatment Efficacy. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1447355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhari, H.F. Advancing Stroke Diagnosis and Management through Nuclear Medicine: A Systematic Review of Clinical Trials. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1425965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katan, M.; Fluri, F.; Morgenthaler, N.G.; Schuetz, P.; Zweifel, C.; Bingisser, R.; Müller, K.; Meckel, S.; Gass, A.; Kappos, L.; et al. Copeptin: A Novel, Independent Prognostic Marker in Patients with Ischemic Stroke. Ann. Neurol. 2009, 66, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; The PRISMA Group. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, E.; Kim, H.; Cho, B.; Lee, J.-J.; Shin, S.; Oh, E.-J.; Chae, H. Plasma Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein and N-Terminal Pro B-Type Natriuretic Peptide: Potential Biomarkers to Differentiate Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, L.F.; Ghirnikar, R.S.; Lee, Y.L. Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein: GFAP-Thirty-One Years (1969–2000). Neurochem. Res. 2000, 25, 1439–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunkhorst, R.; Pfeilschifter, W.; Foerch, C. Astroglial Proteins as Diagnostic Markers of Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage—Pathophysiological Background and Clinical Findings. Transl. Stroke Res. 2010, 1, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Huang, D.; Wang, H.; Zhou, B.; Wu, X.; Ma, B.; Shi, J. Association between Serum Copeptin and Stroke in Rural Areas of Northern China: A Matched Case-Control Study. Dis. Markers 2018, 2018, 9316162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfo, F.S.; Owusu, D.; Adamu, S.; Awuah, D.; Appiah, L.; Amamoo, M.; Loglo, A.; Owolabi, M.; Ovbiagele, B. Plasma Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein, Copeptin, and Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Concentrations among West African Stroke Subjects Compared with Stroke-Free Controls. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2018, 27, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lu, X.-M.; Huang, L.-F.; Ye, H. Copeptin Is Associated with One-Year Mortality and Functional Outcome in Patients with Acute Spontaneous Basal Ganglia Hemorrhage. Peptides 2012, 33, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweifel, C.; Katan, M.; Schuetz, P.; Siegemund, M.; Morgenthaler, N.G.; Merlo, A.; Mueller, B.; Christ-Crain, M. Copeptin Is Associated with Mortality and Outcome in Patients with Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage. BMC Neurol. 2010, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galea, J.; Ogungbenro, K.; Hulme, S.; Patel, H.; Scarth, S.; Hoadley, M.; Illingworth, K.; McMahon, C.J.; Tzerakis, N.; King, A.T. Reduction of Inflammation after Administration of Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist Following Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Results of the Subcutaneous Interleukin-1Ra in SAH (SCIL-SAH) Study. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 128, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergouwen, M.D.; Vermeulen, M.; van Gijn, J.; Rinkel, G.J.; Wijdicks, E.F.; Muizelaar, J.P.; Mendelow, A.D.; Juvela, S.; Yonas, H.; Terbrugge, K.G. Definition of Delayed Cerebral Ischemia after Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage as an Outcome Event in Clinical Trials and Observational Studies: Proposal of a Multidisciplinary Research Group. Stroke 2010, 41, 2391–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Z.; Ji, X. Prognostic Value of Copeptin in Patients with Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. J. Neuroimmunol. 2019, 330, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fung, C.; de Marchis, G.M.; Katan, M.; Seiler, M.; Arnold, M.; Gralla, J.; Raabe, A.; Beck, J. Copeptin as a Marker for Severity and Prognosis of Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.-D.; Chen, J.-S.; Zhou, F.; Liu, Q.-C.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J.-M. Detection of Copeptin in Peripheral Blood of Patients with Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Crit. Care 2011, 15, R288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deboevere, N.; Marjanovic, N.; Sierecki, M.; Marchetti, M.; Dubocage, M.; Magimel, E.; Mimoz, O.; Guenezan, J. Value of Copeptin and the S-100b Protein Assay in Ruling out the Diagnosis of Stroke-Induced Dizziness Pattern in Emergency Departments. Scand. J. Trauma Resusc. Emerg. Med. 2019, 27, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaudeux, J.L.; Soler, C.; Foglietti, M.J. Physiopathologie de La Protéine S-100 β: Intérêt de Son Dosage En Biologie Clinique. Immuno-Anal. Biol. Spéc. 2002, 17, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Undén, L.; Calcagnile, O.; Undén, J.; Reinstrup, P.; Bazarian, J. Validation of the Scandinavian Guidelines for Initial Management of Minimal, Mild and Moderate Traumatic Brain Injury in Adults. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, D.L.; Bellolio, M.F.; Stead, L.G. S100 as a Marker of Acute Brain Ischemia: A Systematic Review. Neurocrit. Care 2008, 8, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szmydynger-Chodobska, J.; Fox, L.M.; Lynch, K.M.; Zink, B.J.; Chodobski, A. Vasopressin Amplifies the Production of Proinflammatory Mediators in Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2010, 27, 1449–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purrucker, J.C.; Herrmann, O.; Lutsch, J.K.; Zorn, M.; Schwaninger, M.; Bruckner, T.; Auffarth, G.U.; Veltkamp, R. Serum Protein S100β Is a Diagnostic Biomarker for Distinguishing Posterior Circulation Stroke from Vertigo of Nonvascular Causes. Eur. Neurol. 2014, 72, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendt, M.; Ebinger, M.; Kunz, A.; Rozanski, M.; Waldschmidt, C.; Weber, J.E.; Winter, B.; Koch, P.M.; Nolte, C.H.; Hertel, S. Copeptin Levels in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke and Stroke Mimics. Stroke 2015, 46, 2426–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hand, P.J.; Kwan, J.; Lindley, R.I.; Dennis, M.S.; Wardlaw, J.M. Distinguishing between Stroke and Mimic at the Bedside: The Brain Attack Study. Stroke 2006, 37, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liamis, G.; Barkas, F.; Megapanou, E.; Christopoulou, E.; Makri, A.; Makaritsis, K.; Ntaios, G.; Elisaf, M.; Milionis, H. Hyponatremia in Acute Stroke Patients: Pathophysiology, Clinical Significance, and Management Options. Eur. Neurol. 2019, 82, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbalis, J.G.; Goldsmith, S.R.; Greenberg, A.; Korzelius, C.; Schrier, R.W.; Sterns, R.H.; Thompson, C.J. Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Treatment of Hyponatremia: Expert Panel Recommendations. Am. J. Med. 2013, 126, S1–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spasovski, G.; Vanholder, R.; Allolio, B.; Annane, D.; Ball, S.; Bichet, D.; Decaux, G.; Fenske, W.; Hoorn, E.J.; Ichai, C.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline on Diagnosis and Treatment of Hyponatraemia. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 170, G1–G47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterns, R.H.; Silver, S.M. Cerebral Salt Wasting Versus SIADH: What Difference? J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 194–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrier, R.W.; Gross, P.; Gheorghiade, M.; Berl, T.; Verbalis, J.G.; Czerwiec, F.S.; Orlandi, C. Tolvaptan, a Selective Oral Vasopressin V2-Receptor Antagonist, for Hyponatremia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 2099–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeynalov, E.; Jones, S. Recent Advances and Future Directions in Preclinical Research of Arginine-Vasopressin (AVP) Receptor Blocker Conivaptan in the Context of Stroke. Neural Regen. Res. 2016, 11, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Jia, Y.; Zhu, B. BNP and NT-proBNP as Diagnostic Biomarkers for Cardiac Dysfunction in Both Clinical and Forensic Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mućka, S.; Jakubiak, G.K.; Pawlas, N. Procalcitonin: Infection or Maybe Something More? Noninfectious Causes of Increased Serum Procalcitonin Concentration: Updated Knowledge. Life 2025, 15, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marchis, G.M.; Dankowski, T.; König, I.R.; Fladt, J.; Fluri, F.; Gensicke, H.; Foerch, C.; Findling, O.; Kurmann, R.; Fischer, U.; et al. A Novel Biomarker-Based Prognostic Score in Acute Ischemic Stroke: The CoRisk Score. Neurology 2019, 92, E1517–E1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mindt, S.; Andrade-Barazarte, H.; Tokhi, U.; Ludtka, C.; Neumaier, M.; Hänggi, D. Immunoluminometric assay for copeptin measurement in cerebrospinal fluid: Technical aspects and pilot study. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 490, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ion, A.; Stafie, C.; Mitu, O.; Ciobanu, C.E.; Halitchi, D.I.; Costache, A.D.; Bobric, C.; Troase, R.; Mitu, I.; Huzum, B.; et al. Biomarkers Utility: At the Borderline between Cardiology and Neurology. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2021, 8, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möckel, M.; Searle, J. Copeptin—Marker of Acute Myocardial Infarction. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2014, 16, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study | Participants | Assessed Markers | Differential Diagnosis | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aksu et al. (2016) [7] | 176 patients before imaging diagnosis | Copeptin | Cerebral infarction, intracerebral hemorrhage, and subarachnoid hemorrhage |
|
| Han et al. (2023) [29] | 73 patients (51 with cerebral infarction and 22 with intracerebral hemorrhage) | Copeptin GFAP NT-proBNP | Cerebral infarction and intracerebral hemorrhage |
|
| Sun et al. (2018) [32] | 119 patients (87 with cerebral infarction and 32 with intracerebral hemorrhage) and 119 healthy controls | Copeptin | Cerebral infarction and intracerebral hemorrhage |
|
| Sarfo et al. (2018) [33] | 156 patients (99 with cerebral infarction and 57 with intracerebral hemorrhage) and 74 healthy controls | Copeptin GFAP MMP-9 | Cerebral infarction and intracerebral hemorrhage |
|
| Deboevere et al. (2019) [41] | 135 patients who presented at the emergency room for vertigo | Copeptin PS100 | Central vestibular disorder and peripheral vestibular disorder |
|
| Von Recum et al. (2015) [1] | 36 patients who presented at the emergency room for stroke-like symptoms | Copeptin | Cerebral infarction, transient ischemic attack, and stroke mimics (such as complex migraine, delirium, epilepsy, or vestibular neuronitis) |
|
| Study | Main Findings |
|---|---|
| Aksu et al. (2016) [7] |
|
| Han et al. (2023) [29] |
|
| Sun et al. (2018) [32] |
|
| Sarfo et al. (2018) [33] |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vasile, A.I.; Tuță, S.; Tiu, C.; Badiu, C. Copeptin as a New Blood-Based Marker for Differential Diagnosis in Stroke Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5328. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115328
Vasile AI, Tuță S, Tiu C, Badiu C. Copeptin as a New Blood-Based Marker for Differential Diagnosis in Stroke Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5328. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115328
Chicago/Turabian StyleVasile, Antonia Ioana, Sorin Tuță, Cristina Tiu, and Corin Badiu. 2025. "Copeptin as a New Blood-Based Marker for Differential Diagnosis in Stroke Patients" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5328. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115328
APA StyleVasile, A. I., Tuță, S., Tiu, C., & Badiu, C. (2025). Copeptin as a New Blood-Based Marker for Differential Diagnosis in Stroke Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5328. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115328






