Development of Molecular Markers for Bacterial Leaf Streak Resistance Gene bls2 and Breeding of New Resistance Lines in Rice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
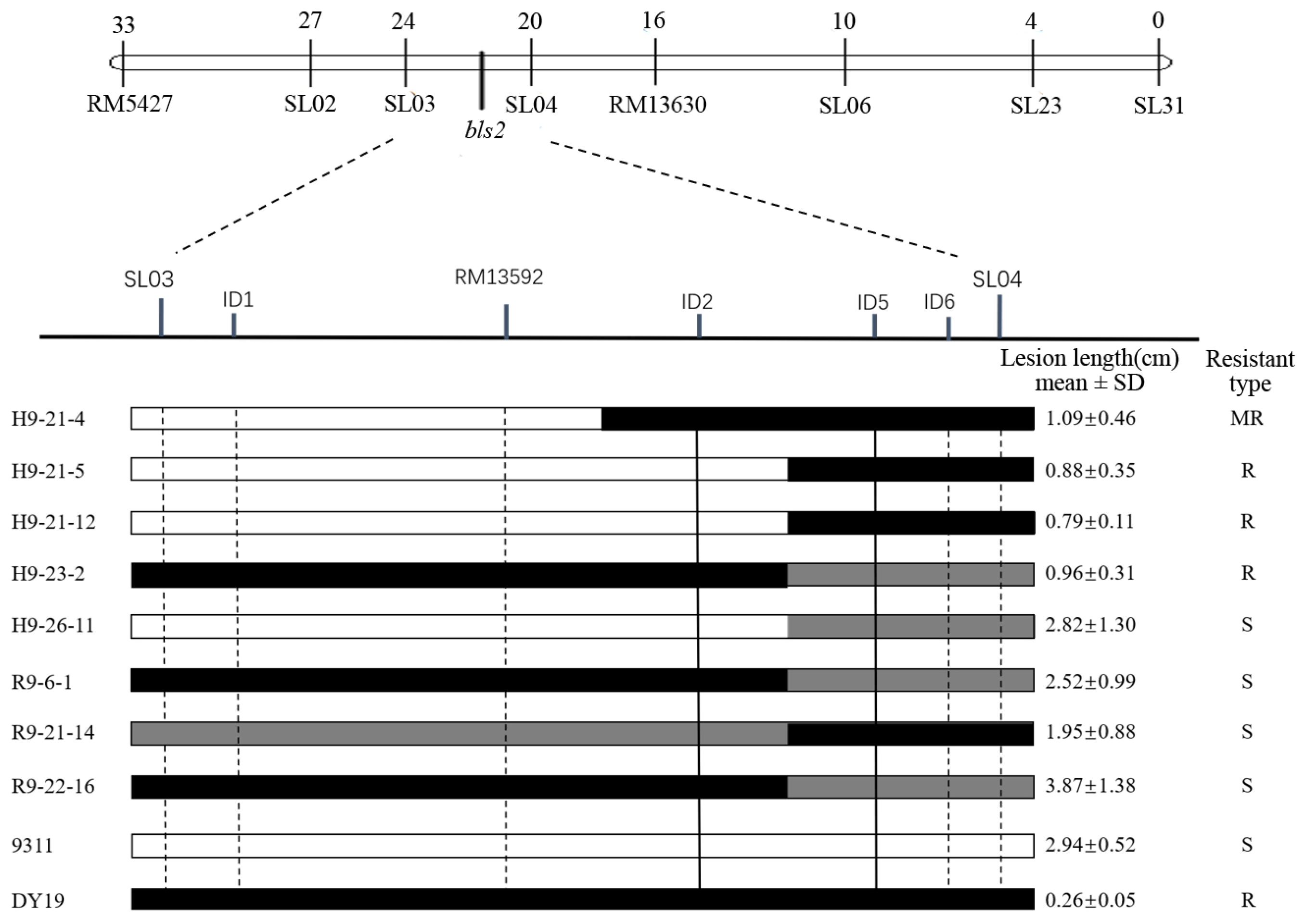
2.1. Fine Mapping of bls2
2.2. Accuracy of ID2 and ID5 Assisted Selection
2.3. Development of New BLS-Resistant Lines
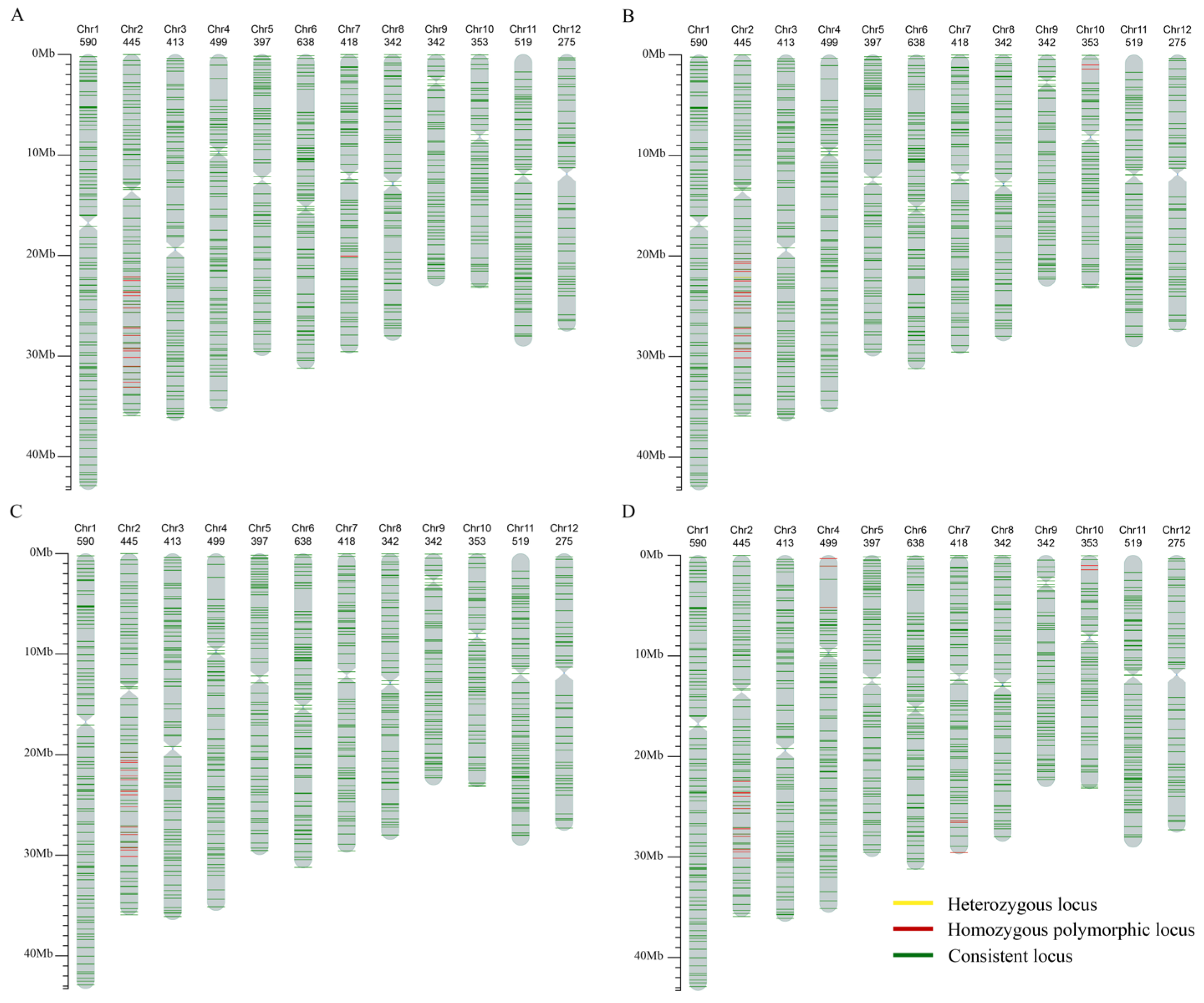
2.4. SNP Detection of the Resistant Lines
2.5. Resistance Responses of the Resistant Lines to Different Xoc Strains
2.6. Agronomic Traits of the Resistant Lines
3. Discussion
3.1. The Candidate Genes of bls2
3.2. Development of bls2 Molecular Marker
3.3. Application of MAS in the Development of New Resistant Lines
3.4. Identification of Selected Lines Using SNP Chip
3.5. Application Value of bls2
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Materials and Breeding Methods
4.2. Molecular Marker
4.3. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Electrophoresis Detection
4.4. SNP Chip Detection
4.5. Bacterial Leaf Streak Resistance Identification
4.5.1. Inoculation Strain
4.5.2. Culture Method for Xoc Strain
4.5.3. Inoculation Method
4.5.4. Inoculation Treatment and Resistance Identification
4.5.5. Rice Cultivation and Trait Investigation
4.5.6. Data Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Azizi, P.; Rafii, M.Y.; Abdullah, S.N.A.; Nejat, N.; Maziah, M.; Hanafi, M.M.; Latif, M.A.; Sahebi, M. Toward understanding of rice innate immunity against Magnaporthe oryzae. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2016, 36, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Tang, B.; Zhao, Y.C.; Liu, F.Q. Research advance on bacterial leaf streak of rice. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. 2025, 48, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, A.Q.; Chen, S.; Wang, C.Y.; Yang, J.Y.; Feng, J.Q.; Chen, K.L.; Chen, B.; Zhu, X.Y. Evaluation on the disease control efficacy of eight fungicides against rice bacterial leaf streak. J. South. Agric. 2021, 52, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.Y.; Ma, Z.F.; Huang, D.H.; Qin, Y.Y.; Liu, C.; Lu, Y.P.; Luo, T.P.; Li, Z.J.; Zhang, Y.X.; Qin, G. QTL-Seq analysis for identification of resistance locus to bacterial leaf streak in rice. Rice Sci. 2023, 37, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Yan, J.; Liang, Y.; Shi, Y.L.; He, Z.Z.; Wu, Y.T.; Zeng, Q.; Liu, X.L.; Peng, J.H. Resistance genes and their interactions with bacterial blight/leaf streak pathogens (Xanthomonas oryzae) in rice (Oryza sativa L.): An Updated Review. Rice 2020, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, A.Q.; Wang, C.Y.; Su, J.; Feng, J.Q.; Chen, K.L.; Lin, X.P.; Chen, B.; Liang, M.L.; Yang, J.Y.; Zhu, X.Y.; et al. Development and agronomic traits analysis of new rice resistance lines to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola. Rice Sci. 2023, 37, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Lin, X.; Poland, J.; Trick, H.; Leach, J.; Hulbert, S. A maize resistance gene functions against bacterial streak disease in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15383–15388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.L.; Xu, M.R.; Zhao, M.F.; Xie, X.W.; Zhu, L.H.; Fu, B.Y.; Li, Z.K. Genome-wide gene responses in a transgenic rice line carrying the maize resistance gene Rxo1 to the rice bacterial streak pathogen, Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triplett, L.R.; Cohen, S.P.; Heffelfinger, C.; Schmidt, C.L.; Huerta, A.; Tekete, C.; Verdier, V.; Bogdanove, A.J. A resistance locus in the American heirloom rice variety Carolina Gold Select is triggered by TAL effectors with diverse predicted targets and is effective against African strains of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola. Plant J. 2016, 87, 472–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, A.C.; Hutin, M.; Moscou, M.J.; Rinaldi, F.C.; Bogdanove, A.J. Cloning of the rice Xo1 resistance gene and interaction of the Xo1 protein with the defense-suppressing Xanthomonas effector Tal2h. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2020, 33, 1189–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Feng, A.Q.; Wang, C.Y.; Zhao, J.L.; Feng, J.Q.; Chen, B.; Yang, J.Y.; Wang, W.J.; Zhang, M.Y.; Chen, K.L.; et al. Identification and fine-mapping of Xo2, a novel rice bacterial leaf streak resistance gene. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2022, 135, 3195–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.F.; Chen, Z.W.; Cao, J.L.; Guan, H.Z.; Lin, D.G.; Li, C.L.; Lan, T.; Duan, Y.L.; Mao, D.M.; Wu, W.R. Toward the positional cloning of qBlsr5a, a QTL underlying resistance to bacterial leaf streak, using overlapping Sub-CSSLs in rice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.A.; Huang, D.H.; Li, R.B.; Qiu, Y.F.; Song, J.D.; Yang, H.N.; Zheng, J.X.; Huang, Y.Y.; Li, X.Q.; Liu, C.; et al. Identification of a resistance gene bls1 to bacterial leaf streak in wild rice Oryza rufipogon Griff. J. Integr. Agric. 2012, 11, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.F.; Qin, G.; Zhang, Y.X.; Liu, C.; Wei, M.Y.; Cen, Z.L.; Yan, Y.; Luo, T.P.; Li, Z.J.; Liang, H.F.; et al. Bacterial leaf streak 1 encoding a mitogen-activated protein kinase confers resistance to bacterial leaf streak in rice. Plant J. 2021, 107, 1084–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.J.; Luo, D.J.; Zhao, Y.; Cen, Z.L.; Liu, F.; Li, R.B. Genetic analysis and mapping of bacterial leaf streak resistance genes in Oryzae rufipogon Griff. J. South China Agric. Univ. 2019, 40, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.Q.; Sheng, P.K.; Tan, J.J.; Chen, X.L.; Lu, G.W.; Ma, W.W.; Heng, Y.Q.; Lin, Q.B.; Zhu, S.S.; Wang, J.L.; et al. Plasma membrane receptor-like kinase leaf panicle 2 acts downstream of the DROUGHT AND SALT TOLERANCE transcription factor to regulate drought sensitivity in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornero, P.; Mayda, E.; Gomez, M.D.; Canas, L.; Conejero, V.; Vera, P. Characterization of LRP, a leucine-rich repeat (LRR) protein from tomato plants that is processed during pathogenesis. Plant J. 1996, 10, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacques, A.; Ghannam, A.; Erhardt, M.; de Ruffray, P.; Baillieul, F.; Kauffmann, S. NtLRP1, a tobacco leucine-rich repeat gene with a possible role as a modulator of the hypersensitive response. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2006, 19, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Cheung, M.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lei, C.L.; Zhang, S.H.; Sun, S.S.M.; Lam, H.M. A novel simple extracellular leucine-rich repeat (eLRR) domain protein from rice (OsLRR1) enters the endosomal pathway and interacts with the hypersensitive-induced reaction protein 1 (OsHIR1). Plant Cell Environ. 2009, 32, 1804–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caddell, D.F.; Park, C.J.; Thomas, N.C.; Canlas, P.E.; Ronald, P.C. Silencing of the rice gene LRR1 compromises rice Xa21 transcript accumulation and XA21-mediated immunity. Rice 2017, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.Y.; Wang, G.L.; Chen, L.L.; Kim, H.S.; Pi, L.Y.; Holsten, T.; Gardner, J.; Wang, B.; Zhai, W.X.; Zhu, L.H.; et al. A receptor kinase-like protein encoded by the rice disease resistance gene, Xa21. Science 1995, 270, 1804–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruitt, R.N.; Schwessinger, B.; Joe, A.; Thomas, N.; Liu, F.; Albert, M.; Robinson, M.R.; Chan, L.J.G.; Luu, D.D.; Chen, H.; et al. The rice immune receptor XA21 recognizes a tyrosine-sulfated protein from a Gram-negative bacterium. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercoli, M.F.; Luu, D.D.; Rim, E.Y.; Shigenaga, A.; de Araujo, A.T.; Chern, M.; Jain, R.; Ruan, R.; Joe, A.; Stewart, V.; et al. Plant immunity: Rice XA21-mediated resistance to bacterial infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2121568119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Zhang, M.Y.; Liu, W.; Xia, K.F.; Zeng, X. Research progress of immune and resistance mechanisms of rice bacterial blight disease. Life Sci. Res. 2024, 28, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofori, D.A.; Zheng, T.D.; Titriku, J.K.; Appiah, C.; Xiang, X.; Kandhro, A.G.; Ahmed, M.I.; Zheng, A.P. The role of genetic resistance in rice disease management. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Qian, Q.; Gao, Z.Y. Research progress on rice bio-breeding. China Basic Sci. 2022, 24, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.Y.; Guo, R.; Du, W.H. Combining ability and heterosis analysis on main traits of hybrid offspring of triticale and wheat. Acta Agric. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2024, 33, 2223–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.Y.; Duan, S.H.; Xu, N.N.; Guo, Y.M.; Dou, J.L.; Yang, S.; Niu, H.H.; Liu, D.M.; Yang, L.M.; Hu, J.B.; et al. Molecular markers assisted construction of Cmerecta near isogenic line of melon dwarfing gene. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2024, 51, 2048–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanksley, S.D.; Mccouch, S.R. Seed banks and molecular maps: Unlocking genetic potential from the wild. Science 1997, 277, 1063–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellur, R.K.; Khanna, A.; Yadav, A.; Pathania, S.; Rajashekara, H.; Singh, V.K.; Krishnan, S.G.; Bhowmick, P.K.; Nagarajan, M.; Vinod, K.K.; et al. Improvement of basmati rice varieties for resistance to blast and bacterial blight diseases using marker assisted backcross breeding. Plant Sci. 2016, 242, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sager, V.; Krishnan, S.G.; Dwivedi, P.; Mondel, K.K.; Prakash, G.; Nagarajan, M.; Singh, A.K. Development of basmati rice genotypes with resistance to both bacterial blight and blast diseases using marker assisted restricted backcross breeding. Indian J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2018, 78, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Z.Y.; Wu, D.; Wang, M.; Zhang, T. Marker-assisted selection of near isogenic lines for clubroot resistant gene in Chinese cabbage. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2010, 37, 1264–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.R.; Chae, E. Variation patterns of NLR clusters in Arabidopsis thaliana genomes. Plant Commun. 2020, 1, 100089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.X.; Jia, Z.Q.; Li, J.S.; Kang, D.M.; Li, M.X.; Ma, S.J.; Cheng, Q.; Shen, H.L.; Sun, L. Development of a 45K pepper GBTS liquid-phase gene chip and its application in genome-wide association studies. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1405190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravel, C.; Faye, A.; Ben-Sadoun, S.; Ranoux, M.; Dardevet, M.; Dupuits, C.; Exbrayat, F.; Poncet, C.; Sourdille, P.; Branlard, G. SNP markers for early identification of high molecular weight glutenin subunits (HMW-GSs) in bread wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2020, 133, 751–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.L.; Yang, S.H.; Li, T.; Guan, Y.W.; Yang, W.H.; Pan, Z.D.; Zhou, L.Z.; Zhao, Q.Z. Genetic diversity analysis and core germplasm construction of Guizhou kam sweet rice based on SNP chip. Seed 2024, 43, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.W.; Zhong, X.; Fang, X.Q.; Liu, Y.H.; Zhao, Z.H.; Fan, G.Y.; Wang, X.M. Genome-wide association analysis of foxtail millet traits at heading stage based on 96K SNP chip. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2025, 53, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Ke, Y.G.; Huang, R.Y.; Ma, L.; Yang, Z.Y.; Chu, Z.H.; Xiao, J.H.; Li, X.H.; Wang, S.P. A host basal transcription factor is a key component for infection of rice by TALE-carrying bacteria. eLife 2016, 5, e19605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Bogdanove, A. Inoculation and virulence assay for bacterial blight and bacterial leaf streak of rice. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 956, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Luo, D.J.; He, S.X.; Liu, F. Comparative study on four inoculation methods of rice bacterial leaf streak. Subtrop. Agric. Res. 2018, 14, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Gene ID | Description |
|---|---|
| Os02g0614966 | Leucine-rich repeat domain containing protein |
| Os02g0615300 | LRR-receptor-like kinase (LRR-RLK) family protein |
| Os02g0615400 | Leucine-rich repeat domain containing protein |
| Os02g0615500 | LRR-receptor-like kinase (LRR-RLK) family protein |
| Os02g0615800 | Leucine-rich repeat-receptor kinase-like protein |
| Os02g0616100 | Similar to protein binding protein |
| Os02g0616199 | Conserved hypothetical protein |
| Molecular Marker | Field BLS-Resistance Identification | Marker Assisted Selection | Subgroup Accuracy | Difference of Subgroup Accuracy | Group Accuracy | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phenotype | Number of Plants | Number of Plants with Resistance Marker Genotypes | Number of Plants with Susceptible Marker Genotypes | ||||
| ID2 | resistant | 151 | 149 | 2 | 98.68 | 1.32 | 99.35 |
| Susceptible | 156 | 0 | 156 | 100.00 | |||
| ID5 | resistant | 151 | 147 | 4 | 97.35 | 2.65 | 98.70 |
| Susceptible | 156 | 0 | 156 | 100.00 | |||
| ID2/ID5 | resistant | 151 | 147 | 4 | 97.35 | 2.65 | 98.70 |
| Susceptible | 156 | 0 | 156 | 100.00 | |||
| Growth Stage | Material | Xoc Strain | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GX01 | BNN3-Xoc | YN-Xoc | 2019-Xoc | ||
| Seedling stage | Y9-1 | 0.73 ± 0.060 (R) b | 0.95 ± 0.143 (R) b | 1.02 ± 0.190 (MR) b | 1.03 ± 0.138 (MR) b |
| Y9-2 | 0.77 ± 0.065 (R) b | 0.81 ± 0.066 (R) b | 0.96 ± 0.220 (R) b | 0.99 ± 0.323 (R) b | |
| Y9-3 | 0.74 ± 0.084 (R) b | 0.77 ± 0.079 (R) b | 0.77 ± 0.094 (R) b | 0.83 ± 0.133 (R) b | |
| Y9-4 | 0.72 ± 0.075 (R) b | 0.91 ± 0.138 (R) b | 1.01 ± 0.188 (MR) b | 1.13 ± 0.134 (MR) b | |
| 9311 | 3.03 ± 0.228 (HS) a | 2.88 ± 0.213 (S) a | 2.94 ± 0.183 (S) a | 2.98 ± 0.428 (S) a | |
| Tillering stage | Y9-1 | 0.83 ± 0.048 (R) b | 1.00 ± 0.124 (MR) b | 1.10 ± 0.191 (MR) b | 1.20 ± 0.137 (MR) b |
| Y9-2 | 0.74 ± 0.064 (R) b | 0.80 ± 0.065 (R) b | 0.80 ± 0.078 (R)c | 0.84 ± 0.140 (R)c | |
| Y9-3 | 0.80 ± 0.057 (R) b | 0.84 ± 0.063 (R) b | 0.99± 0.219 (R) bc | 1.04 ± 0.321 (MR) bc | |
| Y9-4 | 0.74 ± 0.048 (R) b | 0.94 ± 0.132 (R) b | 1.03 ± 0.175 (MR) bc | 1.14 ± 0.133 (MR) bc | |
| 9311 | 3.11 ± 0.418 (HS) a | 3.01 ± 0.233 (HS) a | 2.97 ± 0.200 (S) a | 3.11 ± 0.131 (HS) a | |
| Booting stage | Y9-1 | 0.69 ± 0.069 (R)c | 0.91 ± 0.147 (R) b | 0.99 ± 0.196 (R) b | 1.09 ± 0.135 (MR) bc |
| Y9-2 | 0.71 ± 0.075 (R)c | 0.74 ± 0.079 (R) b | 0.74 ± 0.089 (R) b | 0.80 ± 0.139 (R)c | |
| Y9-3 | 0.74 ± 0.071 (R) bc | 0.78 ± 0.059 (R) b | 0.93 ± 0.224 (R) b | 0.96 ± 0.315 (R) bc | |
| Y9-4 | 0.89 ± 0.116 (R) b | 0.88 ± 0.139 (R) b | 0.98 ± 0.183 (R) b | 1.26 ± 0.132 (MR) b | |
| 9311 | 2.84 ± 0.228 (S) a | 2.68 ± 0.213 (S) a | 2.74 ± 0.210 (S) a | 2.78 ± 0.456 (S) a | |
| Material | Plant Height (cm) | No. of Effective Panicle | Spike Length (cm) | Setting Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y9-1 | 113.50 ± 2.83 ns | 8.33 ± 1.53 ns | 23.57 ± 2.99 ns | 89.12 ± 2.13 ns |
| Y9-2 | 109.90 ± 4.88 ns | 9.67 ± 1.53 ns | 25.30 ± 1.74 ns | 85.21 ± 3.71 ns |
| Y9-3 | 113.77 ± 5.41 ns | 8.00 ± 1.00 ns | 24.36 ± 0.41 ns | 78.25 ± 4.89 ns |
| Y9-4 | 110.67 ± 5.82 ns | 8.00 ± 2.65 ns | 24.59 ± 1.83 ns | 83.27 ± 2.39 ns |
| 9311 | 111.43 ± 2.67 | 6.67 ± 0.58 | 24.44 ± 0.63 | 79.85 ± 6.45 |
| Material | Grain Length (cm) | Grain Width (cm) | Length-Width Ratio | 1000-Grain Weight (g) |
| Y9-1 | 1.21 ± 0.115 ns | 0.28 ± 0.008 ns | 4.37 ± 0.30 ns | 28.33 ± 0.36 ns |
| Y9-2 | 1.47 ± 0.253 ns | 0.29 ± 0.016 ns | 5.09 ± 0.81 ns | 27.62 ± 1.57 ns |
| Y9-3 | 1.51 ± 0.235 ns | 0.29 ± 0.016 ns | 5.28 ± 0.68 ns | 26.29 ± 1.23 ns |
| Y9-4 | 1.29 ± 0.238 ns | 0.28 ± 0.009 ns | 4.64 ± 0.73 ns | 27.59 ± 0.64 ns |
| 9311 | 1.38 ± 0.140 | 0.29 ± 0.005 | 4.82 ± 0.43 | 27.79 ± 1.10 |
| Primers Name | Forward (5′–3′) | Reverse (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|
| SL03 | GCAAATTCCTCTGTTCTGTG | ACTTGCAAAGCAAATTCTGT |
| ID1 | CATGCTGATGCGATTAAGACTGC | CTAACCTGTGCCTTGTTTGATGG |
| RM13592 | GTGTCTGCATTTCTGTATGTGTGG | CGCTTAGCATTTACACACTCTCTCG |
| ID2 | AGTGTCATCTACTCATCTTG | TTGTAACTCAGAGTGAACTA |
| ID5 | GAGTCGGTATAGGCCCAGAG | TCCATTTATGCAGCTGTTCG |
| ID6 | GTTGCATTTGATTTTCTACG | GCTTATGCCATTAAACTATG |
| SL04 | TAAAAGTGGAGTCATCCGTC | GAGAATGGGTTGTGGATTAG |
| Lesion Length/cm | Disease Index | Resistant Type |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | Immunity |
| 0.1–0.5 | 1 | High resistance |
| 0.6–1.0 | 3 | Resistance |
| 1.0–1.5 | 5 | Moderate resistance |
| 1.6–3.0 | 7 | Susceptibility |
| >3.0 | 9 | High susceptibilty |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, J.; Wei, X.; Tang, M.; Deng, Z.; Lan, Y.; Liu, F. Development of Molecular Markers for Bacterial Leaf Streak Resistance Gene bls2 and Breeding of New Resistance Lines in Rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5264. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115264
Huang J, Wei X, Tang M, Deng Z, Lan Y, Liu F. Development of Molecular Markers for Bacterial Leaf Streak Resistance Gene bls2 and Breeding of New Resistance Lines in Rice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5264. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115264
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Jieyi, Xuan Wei, Min Tang, Ziqiu Deng, Yi Lan, and Fang Liu. 2025. "Development of Molecular Markers for Bacterial Leaf Streak Resistance Gene bls2 and Breeding of New Resistance Lines in Rice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5264. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115264
APA StyleHuang, J., Wei, X., Tang, M., Deng, Z., Lan, Y., & Liu, F. (2025). Development of Molecular Markers for Bacterial Leaf Streak Resistance Gene bls2 and Breeding of New Resistance Lines in Rice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5264. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115264





