Fucoxanthin-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Exert Potent Therapeutic Efficacy in Combating High-Fat Diet Induced Obesity in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of SLN Formulation
2.1.1. Particle Size, PDI, and Zeta Potential
2.1.2. Encapsulation Efficiency (EE%)
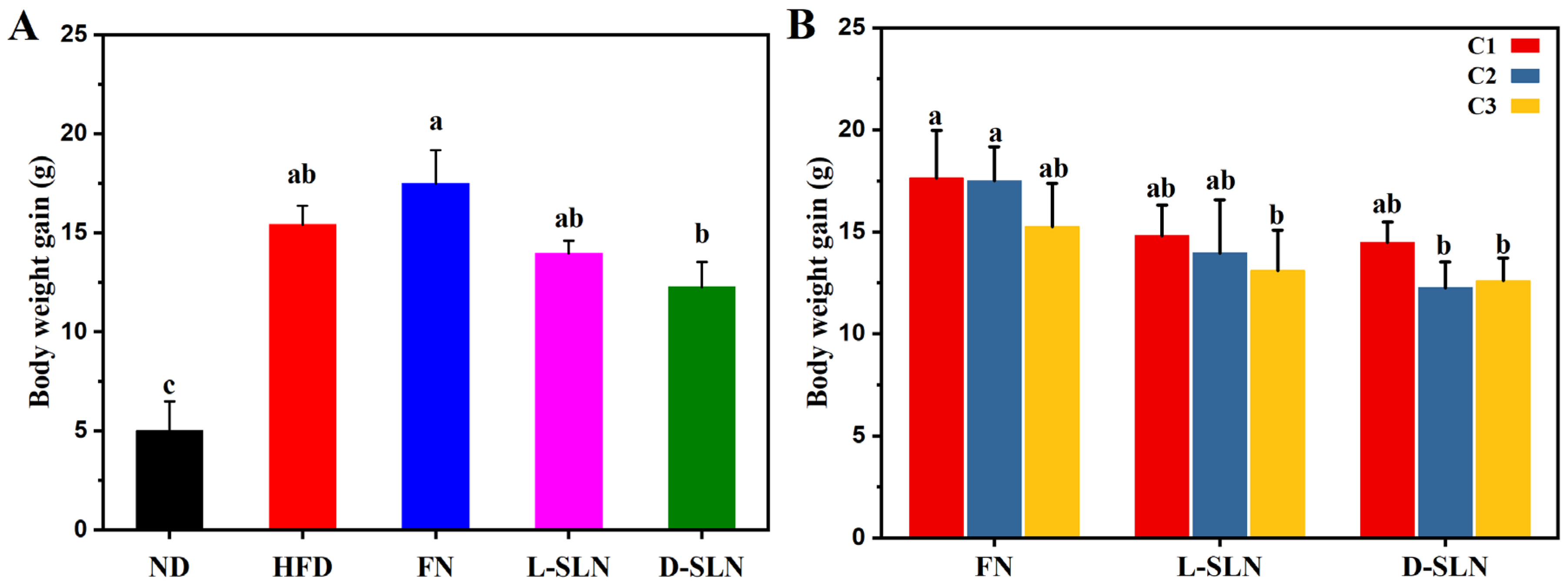
2.2. Body Weight Modulation
2.2.1. Dose Form-Dependent Efficacy
2.2.2. Concentration-Dependent Effects
2.3. Fat Deposition Analysis
2.3.1. Adipose Tissue Visualization
2.3.2. Formulation and Dose-Dependent Suppression of Adiposity
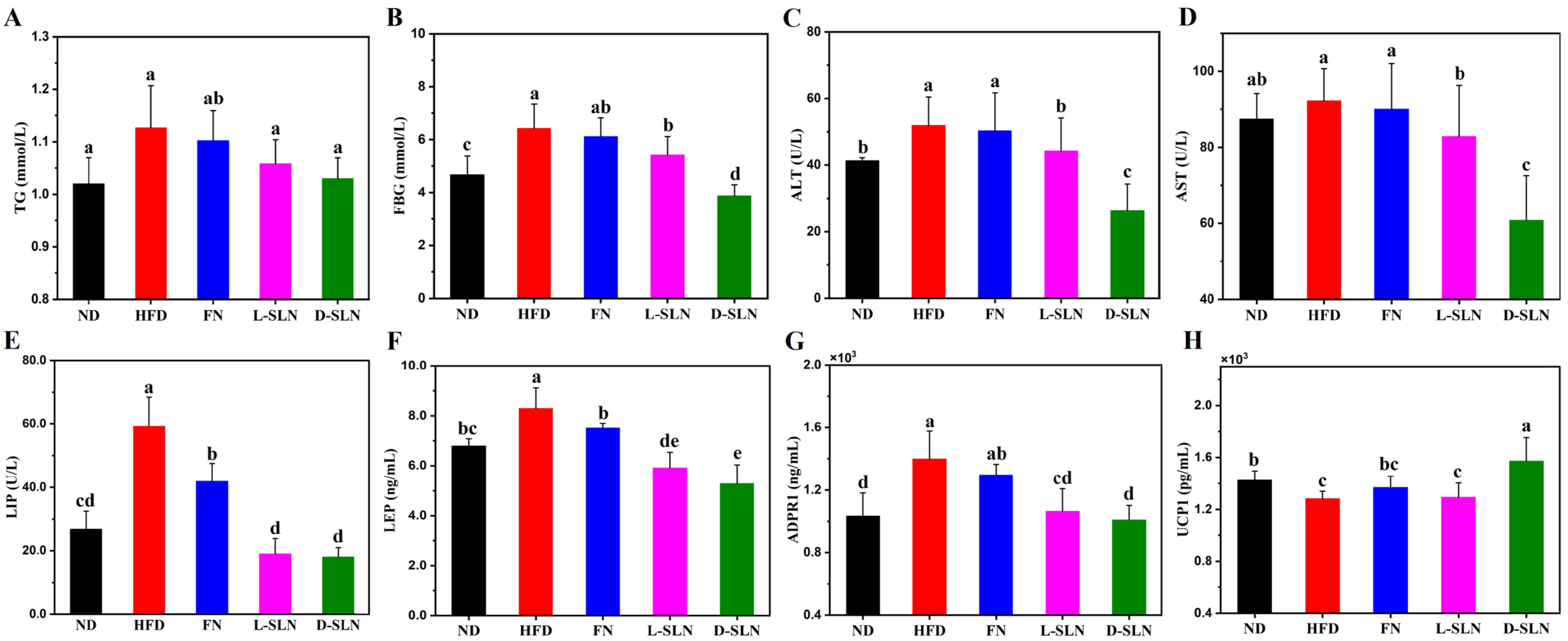
2.4. Metabolic and Hepatic Improvements via Serum Analysis
2.5. MCP1 Protein Expression in Liver
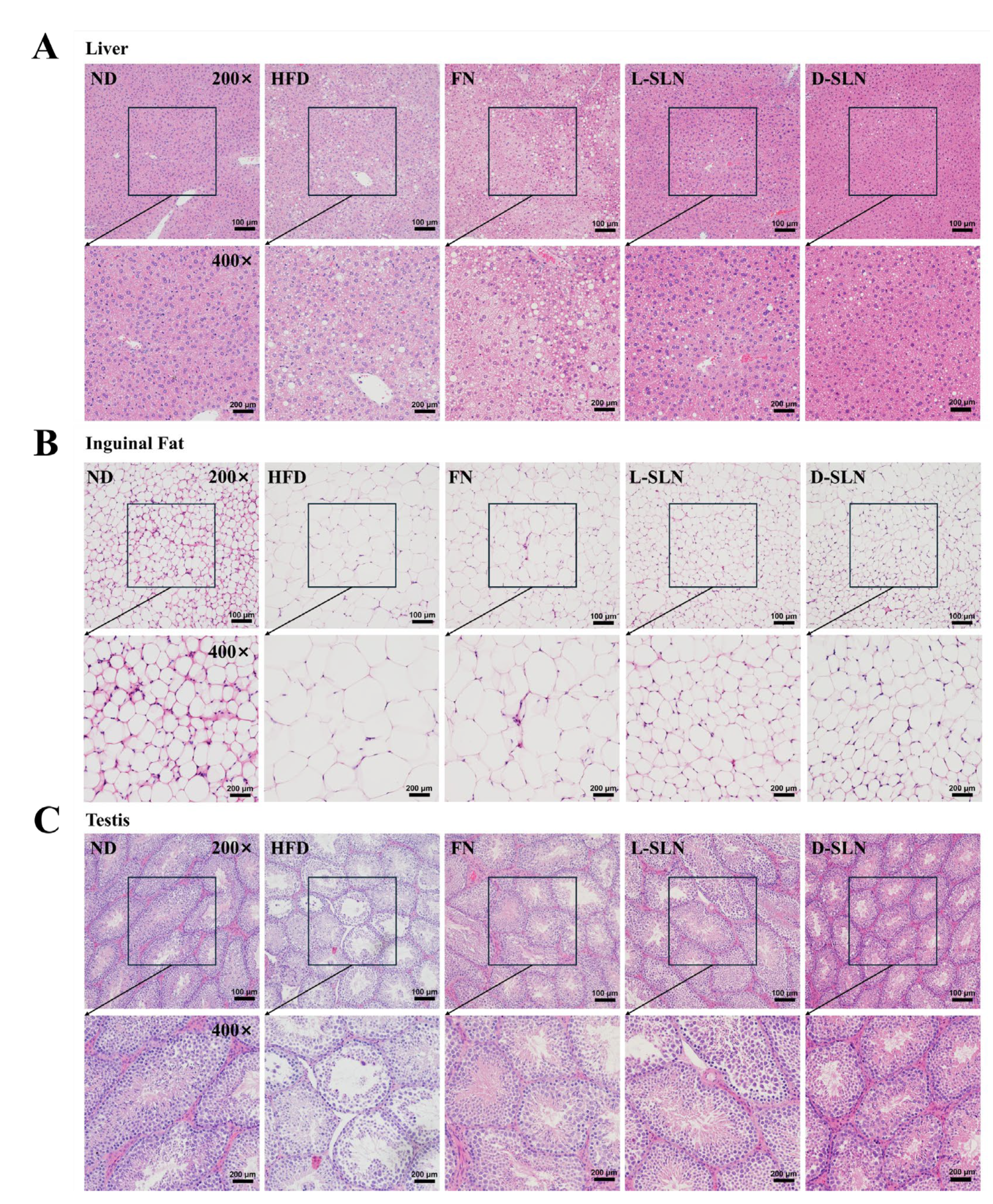
2.6. Histopathological Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Fabrication of FN-SLNs
4.2.2. Characterization
4.2.3. Animal Diets and Experimental Designs
- Group 1 (Normal diet, ND): Fed standard chow.
- Group 2 (HFD + saline): Fed high-fat diet (HFD, D12492, Research Diets, containing 60% kcal from fat [20% saturated, 40% monounsaturated], 20% kcal from protein, and 20% kcal from carbohydrates, supplemented with 0.2% cholesterol) and gavaged with saline (0.2 mL/day).
- Group 3–5 (free FN powder): Fed HFD and gavaged with fucoxanthin powder at low (33.33 mg/kg), medium (66.67 mg/kg), and high (100 mg/kg) doses.
- Group 6–8 (lyophilized fucoxanthin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: L-SLNs): Fed HFD and gavaged with L-SLNs at low (33.33 mg/kg), medium (66.67 mg/kg), and high (100 mg/kg) doses.
- Group 9–11 (freshly dispersed fucoxanthin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: D-SLNs): Fed HFD and gavaged with D-SLNs at low (33.33 mg/kg), medium (66.67 mg/kg), and high (100 mg/kg) doses.
4.2.4. Physiological Analysis
4.2.5. Micro-CT Analysis of Adipose Tissue Depots
4.2.6. Serum Biochemical Parameters Determination
4.2.7. ELISA for Cytokine Quantification
4.2.8. Western Blot for Protein Expression Analysis
4.2.9. Histopathological Evaluation
4.2.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SLN | Solid Lipid Nanoparticle |
| HFD | High-Fat Diet |
| ND | Normal Diet |
| L-SLN | lyophilized SLN |
| D-SLN | dispersed SLN |
| MCP-1 | Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein 1 |
| UCP-1 | uncoupling protein-1 |
| PPARγ | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma |
| C/EBPs | CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins |
| SREBP-1c | sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c |
| EE% | Encapsulation Efficiency |
| AMPK | Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase |
| TG | Triglyceride |
| FBG | fasting blood glucose |
| ALT | alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | aspartate aminotransferase |
| LEP | leptin |
| LIP | Lipase |
| ADPR 1 | Adiponectin receptor 1 |
| H&E | Hematoxylin–eosin |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor-κB |
| GMS | glyceryl monostearate |
| HPLC | High-Performance Liquid Chromatography |
References
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight Fact Sheet. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- World Obesity Federation. Obesity Atlas 2024. Available online: https://data.worldobesity.org/publications/?cat=22 (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- Blüher, M.; Aronne, L.J.; Batterham, R.L.; Giorgino, F.; Ji, L.; Pietiläinen, K.H.; Schnell, O.; Tonchevska, E.; Wilding, J.P.H. New insights into the treatment of obesity. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023, 25, 2058–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagi, M.A.; Ahmed, H.; Rezq, M.A.A.; Sangroongruangsri, S.; Chaikledkaew, U.; Almalki, Z.; Thavorncharoensap, M. Economic costs of obesity: A systematic review. Int. J. Obes. 2024, 48, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gammone, M.A.; D’Orazio, N. Anti-obesity activity of the marine carotenoid fucoxanthin. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2196–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pangestuti, R.; Kim, S.-K. Biological Activities and Potential Health Benefits of Fucoxanthin Derived from Marine Brown Algae. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2011, 64, 111–128. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.; Wong, Y.C.; Chen, X.; Tan, H.; Wen, W. In-vitro blood purification using tiny pinch holographic optical tweezers based on deep learning. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2025, 267, 116781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Wu, C.; Zhang, J.; Xu, J.; Tan, H.; Zhang, B.; Xie, J.; Tao, C.; Huang, K.; Cheng, X.; et al. Direct dielectrophoretic characterization of particles in the high-density microwell array using optical tweezers. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2024, 174, 107976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-I.; Kim, K.H.-C.; Shim, H.-S.; Kim, H.-M.; Han, Y.-S.; Lee, N.-H.; Kim, S.-J. Fucoxanthin exerts differing effects on 3T3-L1 cells according to differentiation stage and inhibits glucose uptake in mature adipocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 409, 769–774. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J.J.; Tian, X.X.; Xu, B.G.; Yuan, F.L.; Wang, B.; Yang, Z.S.; Huang, F.F. Fucoxanthin Attenuates Free Fatty Acid-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Regulating Lipid Metabolism/Oxidative Stress/Inflammation via the AMPK/Nrf2/TLR4 Signaling Pathway. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Hosokawa, M.; Sashima, T.; Funayama, K.; Miyashita, K. Fucoxanthin from edible seaweed, Undaria pinnatifida, shows antiobesity effect through UCP1 expression in white adipose tissues. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 332, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.P.; Wang, W.X.; Huang, X.Q.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Ren, Q.Q.; Hong, Z.; Huang, M.Q.; Xing, X. Fucoxanthin ameliorates hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia and insulin resistance in diabetic mice partially through IRS-1/PI3K/Akt and AMPK pathways. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 48, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Z.; Sun, X.; Zhang, D.; Wang, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, D. Modulation of Gut Microbiota by Fucoxanthin During Alleviation of Obesity in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 5118–5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, V.; Mamatha, B.S. Fucoxanthin, a Functional Food Ingredient: Challenges in Bioavailability. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2023, 12, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takatani, N.; Sato, K.; Nagata, K.; Beppu, F.; Yamano, Y.; Maoka, T.; Hosokawa, M. Identification and tissue distribution of fucoxanthinol and amarouciaxanthin A fatty acid esters in fucoxanthin-fed mice. Food Chem. 2023, 410, 135318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.B.; Lee, Y.; Kang, H.; Hu, S.; Pham, T.X.; Park, Y.K.; Lee, J.Y. Consumption of Low Dose Fucoxanthin Does Not Prevent Hepatic and Adipose Inflammation and Fibrosis in Mouse Models of Diet-Induced Obesity. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Lee, M.K.; Park, Y.B.; Shin, Y.C.; Choi, M.S. Beneficial effects of Undaria pinnatifida ethanol extract on diet-induced-insulin resistance in C57BL/6J mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Hosokawa, M.; Sashima, T.; Funayama, K.; Miyashita, K. Effect of medium-chain triacylglycerols on anti-obesity effect of fucoxanthin. J. Oleo Sci. 2007, 56, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, S.; Tan, M.; Wang, H. Development of intestine-targeted microcapsules for enhanced delivery of fucoxanthin: A strategy to mitigate lipid accumulation in vitro and in vivo. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 104167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iio, K.; Okada, Y.; Ishikura, M. Single and 13-week oral toxicity study of fucoxanthin oil from microalgae in rats. Shokuhin Eiseigaku Zasshi 2011, 52, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaragozá, M.C.; López, D.; Martínez-Puig, S.; Poquet, M.; Pérez, J.; Puig-Parellada, P.; Màrmol, F.; Simonetti, P.; Gardana, C.; Lerat, Y.; et al. Toxicity and antioxidant activity in vitro and in vivo of two Fucus vesiculosus extracts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 7773–7780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.J.; Luo, X.; Xian, Q.Y.; Zhu, S.S.; Wen, W.J. Innovative Approaches to Fucoxanthin Delivery: Characterization and Bioavailability of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles with Eco-Friendly Ingredients and Enteric Coating. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajpoot, K. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles: A Promising Nanomaterial in Drug Delivery. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 3943–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigani, B.; Valentino, C.; Sandri, G.; Listro, R.; Fagiani, F.; Collina, S.; Lanni, C.; Bonferoni, M.C.; Caramella, C.M.; Rossi, S.; et al. A Composite Nanosystem as a Potential Tool for the Local Treatment of Glioblastoma: Chitosan-Coated Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Embedded in Electrospun Nanofibers. Polymers 2021, 13, 1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzol, C.D.; Filippin-Monteiro, F.B.; Restrepo, J.A.; Pittella, F.; Silva, A.H.; Alves de Souza, P.; Machado de Campos, A.; Creczynski-Pasa, T.B. Influence of surfactant and lipid type on the physicochemical properties and biocompatibility of solid lipid nanoparticles. Int. J. Env. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 8581–8596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, J.A.; Andrade, S.; Duarte, A.; Neves, A.R.; Queiroz, J.F.; Nunes, C.; Sevin, E.; Fenart, L.; Gosselet, F.; Coelho, M.A.; et al. Resveratrol and Grape Extract-loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecules 2017, 22, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Hosokawa, M.; Sashima, T.; Takahashi, N.; Kawada, T.; Miyashita, K. Fucoxanthin and its metabolite, fucoxanthinol, suppress adipocyte differentiation in 3T3-L1 cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2006, 18, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qiu, Y.; Gu, H.; Gan, M.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, K.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Niu, L.; Zhang, S.; et al. Regulation of Adipose Thermogenesis and its Critical Role in Glucose and Lipid Metabolism. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 4950–4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwaib, H.S.; Michel, M.C. Is the β(3)-Adrenoceptor a Valid Target for the Treatment of Obesity and/or Type 2 Diabetes? Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, J.; Yan, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, B.; Tong, H.; Lin, X. Molecular Mechanisms of Fucoxanthin in Alleviating Lipid Deposition in Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 10391–10405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grases-Pintó, B.; Abril-Gil, M.; Rodríguez-Lagunas, M.J.; Castell, M.; Pérez-Cano, F.J.; Franch, À. Leptin and adiponectin supplementation modifies mesenteric lymph node lymphocyte composition and functionality in suckling rats. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 119, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grases-Pintó, B.; Abril-Gil, M.; Rodríguez-Lagunas, M.J.; Castell, M.; Pérez-Cano, F.J.; Franch, À. Leptin and adiponectin regulate the activity of nuclei involved in sleep-wake cycle in male rats. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 907508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, B.; Chen, K.; Tong, Z.; Chen, L.; Chen, Q.; Su, J. Advances in Fucoxanthin Research for the Prevention and Treatment of Inflammation-Related Diseases. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajasekaran, M.; Sul, O.J.; Choi, E.K.; Kim, J.E.; Suh, J.H.; Choi, H.S. MCP-1 deficiency enhances browning of adipose tissue via increased M2 polarization. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 242, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Luo, Z.; Zhou, H.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, X.; Huang, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, S.; et al. A nanoemulsion targeting adipose hypertrophy and hyperplasia shows anti-obesity efficiency in female mice. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, R.Z.; Diab, A.E.A. Testicular protective and antioxidant effects of selenium nanoparticles on Monosodium glutamate-induced testicular structure alterations in male mice. Toxicol. Rep. 2020, 7, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koury, J.P.; Burke, C.T. Endovascular management of acute upper extremity deep venous thrombosis and the use of superior vena cava filters. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 2011, 28, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Y.; Guo, J.G. Nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems for cancer therapy. Smart Mater. Med. 2020, 1, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatto, M.S.; Najahi-Missaoui, W. Lyophilization of Nanoparticles, Does It Really Work? Overview of the Current Status and Challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.Y.; He, G.P.H.; Tang, H.Y.; Cheng, B.; Saung, M.T.; Santos, J.L.; Mao, H.Q. Physical and chemical profiles of nanoparticles for lymphatic targeting. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 151–152, 72–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amekyeh, H.; Billa, N. Lyophilized Drug-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Formulated with Beeswax and Theobroma Oil. Molecules 2021, 26, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| SLN | Size (nm) | Zeta Potential (mV) | PDI | (EE%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| lyophilized SLN powder | 261.30 ± 3.14 | −30.60 ± 0.51 | 0.24 ± 0.01 | 96.91 ± 2.06 |
| fresh SLN dispersion | 237.21 ± 1.75 | −32.71 ± 0.22 | 0.17 ± 0.04 | 98.17 ± 1.21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, L.; Luo, X.; Wen, W. Fucoxanthin-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Exert Potent Therapeutic Efficacy in Combating High-Fat Diet Induced Obesity in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115249
Ding L, Luo X, Wen W. Fucoxanthin-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Exert Potent Therapeutic Efficacy in Combating High-Fat Diet Induced Obesity in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115249
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Lijun, Xiao Luo, and Weijia Wen. 2025. "Fucoxanthin-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Exert Potent Therapeutic Efficacy in Combating High-Fat Diet Induced Obesity in Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115249
APA StyleDing, L., Luo, X., & Wen, W. (2025). Fucoxanthin-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Exert Potent Therapeutic Efficacy in Combating High-Fat Diet Induced Obesity in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115249






