Nanoplastics and Immune Disruption: A Systematic Review of Exposure Routes, Mechanisms, and Health Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Rationale
1.2. Objectives
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Focused Question
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Selection of Studies
2.4. Risk of Bias in Individual Studies
2.5. Data Extraction
3. Results
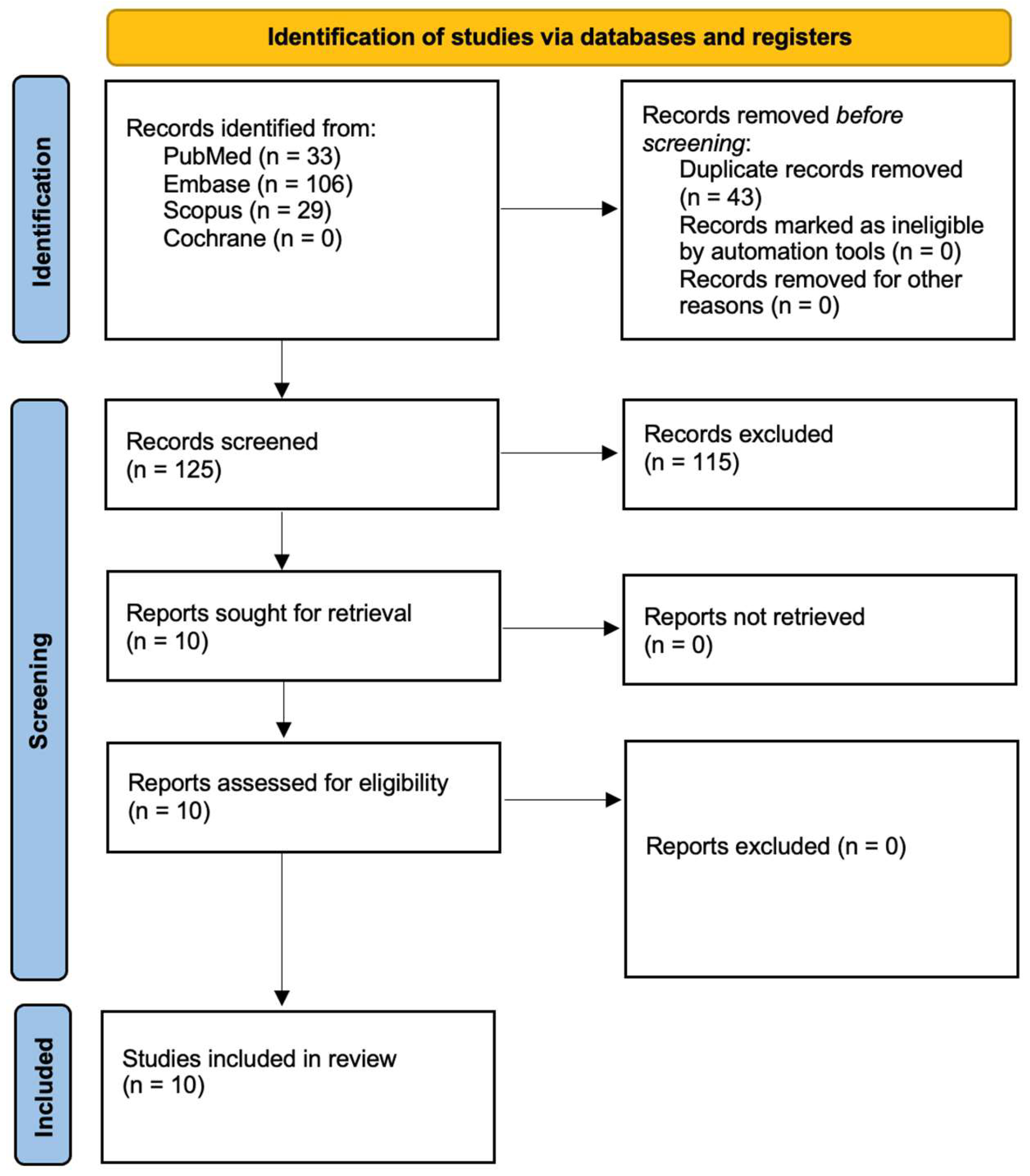
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Data Presentation
3.3. General Characteristics of the Included Studies
3.4. Main Study Outcomes
4. Discussion
4.1. Results in the Context of Other Evidence
4.2. Limitations of the Evidence
4.3. Limitations of the Review Process
4.4. Implications for Practice, Policy, and Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiao, H.; Ali, S.S.; Alsharbaty, M.H.M.; Elsamahy, T.; Abdelkarim, E.; Schagerl, M.; Al-Tohamy, R.; Sun, J. A critical review on plastic waste life cycle assessment and management: Challenges, research gaps, and future perspectives. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 271, 115942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Verma, A.; Shome, A.; Sinha, R.; Sinha, S.; Jha, P.K.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, P.; Shubham; Das, S.; et al. Impacts of Plastic Pollution on Ecosystem Services, Sustainable Development Goals, and Need to Focus on Circular Economy and Policy Interventions. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutkar, P.R.; Gadewar, R.D.; Dhulap, V.P. Recent trends in degradation of microplastics in the environment: A state-of-the-art review. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2023, 11, 100343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibria, M.G.; Masuk, N.I.; Safayet, R.; Nguyen, H.Q.; Mourshed, M. Plastic waste: Challenges and opportunities to mitigate pollution and effective management. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2023, 17, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament. Directorate-General for Internal Policies. In The Environmental Impacts of Microplastics and Possible Regulatory Strategies; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2020; Report No.: IPOL_STU(2020)658279. [Google Scholar]
- Government of Canada. Science Assessment of Plastic Pollution. Environment and Climate Change Canada. 2020. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/environment-climate-change/services/evaluating-existing-substances/science-assessment-plastic-pollution.html (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Paul, M.B.; Stock, V.; Cara-Carmona, J.; Lisicki, E.; Shopova, S.; Fessard, V.; Braeuning, A.; Sieg, H.; Böhmert, L. Micro- and nanoplastics—Current state of knowledge with the focus on oral uptake and toxicity. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 4350–4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hardy, A.; Benford, D.; Halldorsson, T.; Jeger, M.J.; Knutsen, H.K.; More, S.; Naeheli, H.; Noteborn, H.; Ockleford, C.; Ricci, A.; et al. Guidance on risk assessment of the application of nanoscience and nanotechnologies in the food and feed chain: Part 1, human and animal health. EFSA J. 2018, 16, e05327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Presence of microplastics and nanoplastics in food, with particular focus on seafood. EFSA J. 2016, 14, e04501. [Google Scholar]
- Horton, A.A.; Walton, A.; Spurgeon, D.J.; Lahive, E.; Svendsen, C. Microplastics in freshwater and terrestrial environments: Evaluating the current understanding to identify the knowledge gaps and future research priorities. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auta, H.S.; Emenike, C.U.; Fauziah, S.H. Distribution and importance of microplastics in the marine environment: A review of the sources, fate, effects, and potential solutions. Environ. Int. 2017, 102, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, K.D.; Covernton, G.A.; Davies, H.L.; Dower, J.F.; Juanes, F.; Dudas, S.E. Human consumption of microplastics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 7068–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwaferts, C.; Niessner, R.; Elsner, M.; Ivleva, N.P. Methods for the analysis of submicrometer-and nanoplastic particles in the environment. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 112, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, J.N.; Löder, M.G.; Laforsch, C. Finding microplastics in soils: A review of analytical methods. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 2078–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Shi, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, L.; Wei, W.; Ni, B.-J. Nanoplastics are significantly different from microplastics in urban waters. Water Res. X 2023, 19, 100169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhuang, Z.; Zhuang, Q.; Dong, S.; Zhao, X.; Mao, L. Nanoplastics in soil plastisphere: Occurrence, bio-interactions and environmental risks. Nano Today 2024, 58, 102409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.B.; Bastos, A.S.; Justino, C.I.; da Costa, J.P.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T.A. Microplastics in the environment: Challenges in analytical chemistry—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1017, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehaut, A.; Hermabessiere, L.; Duflos, G. Current frontiers and recommendations for the study of microplastics in seafood. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 116, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, G.; Déniel, M.; Nicolai, T.; Chassenieux, C.; Lagarde, F. Towards more realistic reference microplastics and nanoplastics: Preparation of polyethylene micro/nanoparticles with a biosurfactant. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokiwa, Y.; Calabia, B.P.; Ugwu, C.U.; Aiba, S. Biodegradability of plastics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 3722–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, M.S.; Hii, L.W.; Looi, C.K.; Lim, W.M.; Wong, S.F.; Kok, Y.Y.; Tan, B.K.; Wong, C.Y.; Leong, C.O. Impact of Microplastics and Nanoplastics on Human Health. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hernandez, L.M.; Yousefi, N.; Tufenkji, N. Are There Nanoplastics in Your Personal Care Products? Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigault, J.; Halle, A.; Baudrimont, M.; Pascal, P.-Y.; Gauffre, F.; Phi, T.-L.; El Hadri, H.; Grassl, B.; Reynaud, S. Current opinion: What is a nanoplastic? Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 1030–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendran, D.; Chandrasekaran, N. Journey of micronanoplastics with blood components. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 31435–31459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Okoye, C.O.; Addey, C.I.; Oderinde, O.; Okoro, J.O.; Uwamungu, J.Y.; Ikechukwu, C.K.; Okeke, E.S.; Ejeromedoghene, O.; Odii, E.C. Toxic chemicals and persistent organic pollutants associated with micro-and nanoplastics pollution. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2022, 11, 100310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junaid, M.; Abbas, Z.; Siddiqui, J.A.; Liu, S.; Tabraiz, S.; Yue, Q.; Wang, J. Ecotoxicological impacts associated with the interplay between micro(nano)plastics and pesticides in aquatic and terrestrial environments. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 165, 117133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgeman, L.; Cimbalo, A.; López-Rodríguez, D.; Pamies, D.; Frangiamone, M. Exploring toxicological pathways of microplastics and nanoplastics: Insights from animal and cellular models. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 490, 137795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, F.; Sarker, D.B.; Jocelyn, J.A.; Sang, Q.A. Molecular and Cellular Effects of Microplastics and Nanoplastics: Focus on Inflammation and Senescence. Cells 2024, 13, 1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bonanomi, M.; Salmistraro, N.; Porro, D.; Pinsino, A.; Colangelo, A.M.; Gaglio, D. Polystyrene micro and nano-particles induce metabolic rewiring in normal human colon cells: A risk factor for human health. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 134947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, L.; Gazzi, A.; Giro, L.; Schefer, R.B.; D’Almeida, S.M.; Cagliani, R.; Zoccheddu, M.; Uyar, R.; Besbinar, Ö.; Çelik, D.; et al. Nanoplastics: Immune impact, detection, and internalization after human blood exposure by single-cell mass cytometry. Adv. Mater. 2024, 37, 2413413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzelec, M.; Detka, J.; Mieszczak, P.; Sobocińska, M.K.; Majka, M. Immunomodulation—A general review of the current state-of-the-art and new therapeutic strategies for targeting the immune system. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1127704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hu, M.; Palić, D. Micro- and nano-plastics activation of oxidative and inflammatory adverse outcome pathways. Redox Biol. 2020, 37, 101620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Krause, S.; Ouellet, V.; Allen, D.; Allen, S.; Moss, K.; Nel, H.A.; Manaseki-Holland, S.; Lynch, I. The potential of micro- and nanoplastics to exacerbate the health impacts and global burden of non-communicable diseases. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gopinath, P.M.; Saranya, V.; Vijayakumar, S.; Mythili Meera, M.; Ruprekha, S.; Kunal, R.; Pranay, A.; Thomas, J.; Mukherjee, A.; Chandrasekaran, N. Assessment on interactive prospectives of nanoplastics with plasma proteins and the toxicological impacts of virgin, coronated and environmentally released-nanoplastics. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Lan, J.; Li, Z.; Zong, W.; Zhao, Z. Co-existing nanoplastics further exacerbate the effects of triclosan on the physiological functions of human serum albumin. Life 2025, 15, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Yang, Q.; Jiang, J.; Dalu, T.; Kadushkin, A.; Singh, J.; Fakhrullin, R.; Wang, F.; Cai, X.; Li, R. Coronas of micro/nanoplastics: A key determinant in their risk assessments. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2022, 19, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihara, S.; Ghosh, S.; McDougall, D.R.; Whitten, A.E.; Mata, J.P.; Koper, I.; McGillivray, D.J. Structure of soft and hard protein corona around polystyrene nanoplastics-Particle size and protein types. Biointerphases 2020, 15, 051002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; Khanna, S.; Khanna, K. Unveiling the toxicity of micro-nanoplastics: A systematic exploration of understanding environmental and health implications. Toxicol. Rep. 2025, 14, 101844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prattichizzo, F.; Ceriello, A.; Pellegrini, V.; La Grotta, R.; Graciotti, L.; Olivieri, F.; Paolisso, P.; D’Agostino, B.; Iovino, P.; Balestrieri, M.L.; et al. Micro-nanoplastics and cardiovascular diseases: Evidence and perspectives. Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 4099–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Silva, M.G.; Oliveira, M.M.; Peixoto, F. The impact of micro-nanoplastics on mitochondria in the context of diet and diet-related diseases. Stresses 2025, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preda, O.T.; Vlasceanu, A.M.; Andreescu, C.V.; Tsatsakis, A.; Mezhuev, Y.; Negrei, C.; Baconi, D.L. Health implications of widespread micro- and nanoplastic exposure: Environmental prevalence, mechanisms, and biological impact on humans. Toxics 2024, 12, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Shi, H.; Li, X.; Gao, C.; Liu, R. Combined toxicity of micro/nanoplastics loaded with environmental pollutants to organisms and cells: Role, effects, and mechanism. Environ. Int. 2023, 171, 107711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, B.E.; Sharpe, E.E.; Brander, S.M.; Landis, W.G.; Harper, S.L. Critical gaps in nanoplastics research and their connection to risk assessment. Front. Toxicol. 2023, 5, 1154538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Christopher, E.A.; Christopher-de Vries, Y.; Devadoss, A.; Mandemaker, L.D.B.; van Boxel, J.; Copsey, H.M.; Dusza, H.M.; Legler, J.; Meirer, F.; Muncke, J.; et al. Impacts of micro- and nanoplastics on early-life health: A roadmap towards risk assessment. Microplast. Nanoplast. 2024, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Tu, C.; Li, R.; Wu, D.; Yang, J.; Xia, Y.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Luo, Y. A systematic review of the impacts of exposure to micro- and nano-plastics on human tissue accumulation and health. Eco-Environ. Health 2023, 2, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Schardt, C.; Adams, M.B.; Owens, T.; Keitz, S.; Fontelo, P. Utilization of the PICO framework to improve searching PubMed for clinical questions. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2007, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, P.F.; Petrie, A. Method agreement analysis: A review of correct methodology. Theriogenology 2010, 73, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thomas, J.; Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Welch, V.A. (Eds.) Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; Cochrane: London, UK, 2024; Version 6.5 (Updated August 2024); Available online: https://www.training.cochrane.org/handbook (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Busch, M.; Bredeck, G.; Kämpfer, A.A.M.; Schins, R.P.F. Investigations of acute effects of polystyrene and polyvinyl chloride micro- and nanoplastics in an advanced in vitro triple culture model of the healthy and inflamed intestine. Environ. Res. 2021, 193, 110536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, S.; Zu, D.; Liu, H.; He, H.; Bao, Q.; He, Y.; Liang, C.; Shi, Y.; et al. Polyvinyl chloride nanoplastics suppress homology-directed repair and promote oxidative stress to induce esophageal epithelial cellular senescence and cGAS-STING-mediated inflammation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2025, 226, 288–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Wei, S. Nanoplastics trigger the aging and inflammation of porcine kidney cells. Toxicology 2024, 506, 153870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poinsignon, L.; Lefrère, B.; Ben Azzouz, A.; Chissey, A.; Colombel, J.; Djelidi, R.; Ferecatu, I.; Fournier, T.; Beaudeux, J.-L.; Lespes, G.; et al. Exposure of the human placental primary cells to nanoplastics induces cytotoxic effects, an inflammatory response and endocrine disruption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 490, 137713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, A.; Schwiebs, A.; Solhaug, H.; Stenvik, J.; Nilsen, A.M.; Wagner, M.; Relja, B.; Radeke, H.H. Nanoplastics affect the inflammatory cytokine release by primary human monocytes and dendritic cells. Environ. Int. 2022, 163, 107173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Deng, S.; Wang, B.; Zhang, F.; Luo, T.; Kuang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhang, D. Exposure to polystyrene nanoplastics induces hepatotoxicity involving NRF2-NLRP3 signaling pathway in mice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 278, 116439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, T.; Gong, S.; Wan, X.; Zhu, Y.; Fang, Y.; Hu, C.; Yang, F.; Yin, L.; et al. Ferroptosis participated in inhaled polystyrene nanoplastics-induced liver injury and fibrosis. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 916, 170342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, F.; Guo, M.; Gao, D.; Song, Y. Nasal instillation of polystyrene nanoplastics induce lung injury via mitochondrial DNA release and activation of the cyclic GMP-AMP synthase-stimulator of interferon genes-signaling cascade. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 948, 174674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Feng, C.; Wu, Y.; Guo, X. Impacts of nanoplastics on bivalve: Fluorescence tracing of organ accumulation, oxidative stress and damage. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 392, 122418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cid-Samamed, A.; Nunes, C.S.E.; Lomas Martínez, C.; Diniz, M.S. Development of a New Aggregation Method to Remove Nanoplastics from the Ocean: Proof of Concept Using Mussel Exposure Tests. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, K.B.; Yoo, J.Y.; Min, H. The Emerging Threat of Micro- and Nanoplastics on the Maturation and Activity of Immune Cells. Biomol. Ther. 2025, 33, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ali, N.; Katsouli, J.; Marczylo, E.L.; Gant, T.W.; Wright, S.; Bernardino de la Serna, J. The potential impacts of micro-and-nano plastics on various organ systems in humans. EBioMedicine 2024, 99, 104901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yang, W.; Jannatun, N.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhang, G.; Chen, C.; Li, Y. Impacts of microplastics on immunity. Front. Toxicol. 2022, 4, 956885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, L.; Xu, R.; Jiang, L.; Xu, E.G.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Li, B.; Hu, M.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y. Effects of microplastics on immune responses of the yellow catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco under hypoxia. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 753999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Xiong, X.; He, M.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Gupta, J.; Khan, E.; Harrad, S.; Hou, D.; Ok, Y.S.; Bolan, N.S. Microplastics as pollutants in agricultural soils. J. Hazard. Mater. Lett. 2023, 4, 100067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Chen, N.; Yang, X.; Xia, Y.; Wu, D. Effects induced by polyethylene microplastics oral exposure on colon mucin release, inflammation, gut microflora composition and metabolism in mice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 220, 112340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.F.; Chen, C.Y.; Lu, T.H.; Liao, C.M. Toxicity-based toxicokinetic/toxicodynamic assessment for bioaccumulation of polystyrene microplastics in mice. J. Hazard. Mat. 2019, 366, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, R.; Yang, K.; Cheng, X.; Guo, C.; Xing, X.; Sun, H.; Liu, D.; Liu, X.; Wang, D. Accumulation of polystyrene microplastics induces liver fibrosis by activating cGAS/STING pathway. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 300, 118986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, H.; Hou, L.; Guo, T.; Zhao, H.; Xing, M. Polystyrene microplastics promote liver inflammation by inducing the formation of macrophages extracellular traps. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 452, 131236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Du, J.; Liu, D.; Zhuo, J.; Chu, L.; Li, Y.; Gao, L.; Xu, M.; Chen, W.; Huang, W.; et al. Polystyrene microplastics induce pulmonary fibrosis by promoting alveolar epithelial cell ferroptosis through cGAS/STING signaling. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 277, 116357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mckechnie, J.L.; Blish, C.A. The innate immune system: Fighting on the front lines or fanning the flames of COVID-19? Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asharani, P.V.; Low Kah Mun, G.; Hande, M.P.; Valiyaveettil, S. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human cells. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Yoon, J.; Kim, K.J. Microplastic contamination in soil environment—A review. Soil Science Annual. 2020, 71, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Xie, J.; Han, Q.; Chen, M. Comparing the effects of polystyrene microplastics exposure on reproduction and fertility in male and female mice. Toxicology 2022, 465, 153059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Man, Y.B.; Wong, M.H.; Owen, R.B.; Chow, K.L. Environmental health impacts of microplastics exposure on structural organization levels in the human body. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 825, 154025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Zhao, H.; Wang, M.; Chow, A.; Fang, M. Metabolomics and in silico docking-directed discovery of small-molecule enzyme targets. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 3072–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawczyk-Krupka, A.; Bartusik-Aebisher, D.; Latos, W.; Cieślar, G.; Sieroń, K.; Kwiatek, S.; Oleś, P.; Kwiatek, B.; Aebisher, D.; Krupka, M.; et al. Clinical Trials and Basic Research in Photodynamic Diagnostics and Therapies from the Center for Laser Diagnostics and Therapy in Poland. Photochem. Photobiol. 2020, 96, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilowski, Ł.; Wiench, R.; Polakiewicz-Gilowska, A.; Dwornicka, K. Necrotizing sialometaplasia of the palatal mucosa in patient with history of anorexia: Review and case report. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2014, 35, 400–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakosz, K.; Zakliczyński, M.; Król, W.; Pyka, L.; Zakliczyńska, H.; Trybunia, D.; Wiench, R.; Ilewicz, L.; Skrzep-Poloczek, B.; Przybylski, R.; et al. Association of transforming growth factor β1 (TGF- β1) with gingival hyperplasia in heart transplant patients undergoing cyclosporine—A treatment. Ann. Transplant. 2012, 17, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayavel, S.; Govindaraju, B.; Michael, J.R.; Viswanathan, B. Impacts of micro and nanoplastics on human health. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2024, 48, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega-Herrera, A.; Llorca, M.; Borrell-Diaz, X.; Redondo-Hasselerharm, P.E.; Abad, E.; Villanueva, C.M.; Farre, M. Polymers of micro (nano) plastic in household tap water of the Barcelona Metropolitan Area. Water Res. 2022, 220, 118645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN. UNEP Report. Plastic in Cosmetics: Are We Polluting the Environment through our Personal Care? Plastic Ingredients that Contribute to Marine Microplastic Litter; UN: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, H.; Yue, T.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xing, B. Microplastics reduce lipid digestion in simulated human gastrointestinal system. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 12285–12294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, I.; Huy, D.T.; Alsaikhan, F.; Opulencia, M.J.; Van Tuan, P.; Nurmatova, K.C.; Majdi, A.; Shoukat, S.; Yasin, G.; Margiana, R.; et al. Toxic effects on enzymatic activity, gene expression and histopathological biomarkers in organisms exposed to microplastics and nanoplastics: A review. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2022, 34, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | Total | Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Busch et al. 2021 [50] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | Low |
| Huang et al. 2025 [51] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | Low |
| Lu et al. 2024 [52] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | Low |
| Poinsignon et al. 2025 [53] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | Low |
| Weber et al. 2022 [54] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | Low |
| Wen et al. 2024 [55] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | Low |
| Ge et al. 2024 [56] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | Low |
| Liu et al. 2024 [57] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | Low |
| Li et al. 2020 [58] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 7 | Low |
| Cid-Samamed et al. 2024 [59] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | Low |
| Author and Year | Country | Study Design |
|---|---|---|
| Busch et al. 2021 [50] | Germany | In vitro study |
| Huang et al. 2025 [51] | China and USA | In vitro study |
| Lu et al. 2024 [52] | China | In vitro study |
| Poinsignon et al. 2025 [53] | France | In vitro study |
| Weber et al. 2022 [54] | Germany and Norway | In vitro study |
| Wen et al. 2024 [55] | China | In vivo (mice) and in vitro (hepatocytes) study |
| Ge et al. 2024 [56] | China | In vivo (mice) study |
| Liu et al. 2024 [57] | China | In vivo (mice) study |
| Li et al. 2020 [58] | China | In vivo study |
| Cid-Samamed et al. 2024 [59] | Spain and Portugal | Proof-of-concept experimental study |
| Author and Year | Target Organ/System | Mechanisms of Damage | Main Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Busch et al. 2021 [50] | Intestine | Loss of epithelial cells, increased IL-1β release, DNA damage, impaired barrier integrity (especially under inflammatory conditions) |
|
| Huang et al. 2025 [51] | Esophagus | Oxidative stress, inhibition of DNA repair (homology-directed repair suppression), cGAS-STING activation, inflammation, and cellular senescence |
|
| Lu et al. 2024 [52] | Kidneys | Oxidative stress, mitochondrial damage, ROS accumulation, inflammation, and cellular senescence |
|
| Poinsignon et al. 2025 [53] | Placenta | Cytotoxicity, inflammatory response (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α), endocrine disruption (reduced β-hCG hormone levels) |
|
| Weber et al. 2022 [54] | Immune system (monocytes, dendritic cells) | Inflammatory cytokine release from immune cells (IL-6, TNF-α, IL-12p70, IL-23), immune system activation, polymer and shape-dependent toxicity |
|
| Wen et al. 2024 [55] | Liver | Polystyrene nanoplastics caused liver damage via ROS generation, NRF2 suppression, and NF-κB/NLRP3-mediated inflammation |
|
| Ge et al. 2024 [56] | Liver | Polystyrene nanoplastics caused liver injury and fibrosis by inducing oxidative stress and iron overload, which trigger ferroptosis, a form of regulated cell death |
|
| Liu et al. 2024 [57] | Lungs | Polystyrene nanoplastics caused lung injury by inducing mitochondrial DNA release and activating the cGAS-STING signaling pathway, which promotes inflammation, apoptosis, and pulmonary fibrosis |
|
| Li et al. 2020 [58] | Gill, intestine, stomach, liver, mantle, and visceral mass | Polystyrene nanoplastics induced oxidative stress by generating excess ROS, disrupting antioxidant enzymes, and causing lipid peroxidation, liver damage, intestinal inflammation, and neurotoxicity |
|
| Cid-Samamed et al. 2024 [59] | Gills and digestive glands | Polystyrene nanoplastics induced oxidative stress and antioxidant disruption in mussels by increasing reactive oxygen species (ROS), altering enzyme activities (SOD, CAT, GST, GPx), and enhancing lipid peroxidation |
|
| Author and Year | Particle Type | Species | Model/Cells |
|---|---|---|---|
| Busch et al. 2021 [50] | PS, PVC | Human-derived cell lines (Homo sapiens) | In vitro triple culture model of the human intestine composed of Caco-2, HT29-MTX-E12, and PMA-differentiated THP-1 cells to simulate healthy and inflamed gut conditions for assessing nanoplastic toxicity. |
| Huang et al. 2025 [51] | PVC | Humans (Homo sapiens) | Human esophageal epithelial cells (HEEC and HET-1A) and human embryonic kidney 293T cells. |
| Lu et al. 2024 [52] | unspecified | Pig (Sus scrofa domesticus) | Two porcine kidney cell lines—IB-RS-2 and PK15. |
| Poinsignon et al. 2025 [53] | PS | Humans (Homo sapiens) | Primary human villous cytotrophoblasts (VCTs) isolated from term placentas. |
| Weber et al. 2022 [54] | PS, PVC, PMMA | Humans (Homo sapiens) | Primary human monocytes and monocyte-derived dendritic cells (moDCs) isolated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). |
| Wen et al. 2024 [55] | PS | Mouse (Mus musculus) | In vitro triple culture model of the human intestine, consisting of Caco-2 (enterocytes), HT29-MTX-E12 (mucus-producing goblet cells), and PMA-differentiated THP-1 (macrophages). |
| Ge et al. 2024 [56] | PS | Mouse (Mus musculus) | HepG2 human liver cells for in vitro experiments to study polystyrene nanoplastics (PS-NPs)-induced hepatotoxicity and C57BL/6 mice. |
| Liu et al. 2024 [57] | PS | Mouse (Mus musculus) | Mouse-derived RAW264.7 macrophage cells for in vitro experiments and C57BL/6 mice. |
| Li et al. 2020 [58] | PS-NPs | Asian clam (Corbicula fluminea) | Live freshwater bivalves, Corbicula fluminea, as an in vivo whole-organism model. |
| Cid-Samamed et al. 2024 [59] | PS-NH₂ NPs, PS MPs | Mediterranean mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) | Live Mediterranean mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) as the in vivo biological model. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skaba, D.; Fiegler-Rudol, J.; Dembicka-Mączka, D.; Wiench, R. Nanoplastics and Immune Disruption: A Systematic Review of Exposure Routes, Mechanisms, and Health Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5228. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115228
Skaba D, Fiegler-Rudol J, Dembicka-Mączka D, Wiench R. Nanoplastics and Immune Disruption: A Systematic Review of Exposure Routes, Mechanisms, and Health Implications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5228. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115228
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkaba, Dariusz, Jakub Fiegler-Rudol, Diana Dembicka-Mączka, and Rafał Wiench. 2025. "Nanoplastics and Immune Disruption: A Systematic Review of Exposure Routes, Mechanisms, and Health Implications" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5228. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115228
APA StyleSkaba, D., Fiegler-Rudol, J., Dembicka-Mączka, D., & Wiench, R. (2025). Nanoplastics and Immune Disruption: A Systematic Review of Exposure Routes, Mechanisms, and Health Implications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5228. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115228






