Thyroid Cancer: Epidemiology, Classification, Risk Factors, Diagnostic and Prognostic Markers, and Current Treatment Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology of Thyroid Cancer
3. Classification of Thyroid Cancer
3.1. Papillary Thyroid Cancer
3.2. Follicular Thyroid Cancer
3.3. Medullary Thyroid Cancer
3.4. Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer
4. Risk Factors and Causes of Thyroid Cancer
4.1. Modifiable Factors
4.1.1. Obesity
4.1.2. Smoking and Secondhand Smoking
4.1.3. Alcohol Consumption
4.1.4. Lack of Exercise
4.1.5. Exposure to High Levels of Radiation
4.2. Unmodifiable Factors
4.2.1. Sex
4.2.2. Genetic Factors
4.3. Genes
4.3.1. Papillary Thyroid Cancer
4.3.2. Medullary Thyroid Cancer
4.3.3. Follicular Thyroid Cancer
4.3.4. Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer
4.3.5. Preexisting Benign Thyroid Disease
5. Symptoms and Diagnosis of Thyroid Cancer
6. Diagnostic Markers of Thyroid Cancer
6.1. Thyroglobulin
6.2. Calcitonin
6.3. Carcinoembryonic Antigen
6.4. Procalcitonin
6.5. Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone
6.6. microRNA
6.7. BRAF
6.8. RAS
6.9. RET
6.10. Summary
7. Current Treatment Strategies
7.1. Surgical Treatment of Thyroid Cancer
7.1.1. Papillary Thyroid Cancer
7.1.2. Follicular Thyroid Cancer
7.1.3. Medullary Thyroid Cancer
7.1.4. Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer
7.2. Radioiodine Therapy
7.3. Chemotherapy
7.4. Immunotherapy
7.5. Comparison of First-Line and Second-Line Therapies
7.6. Molecularly Targeted Therapies in Thyroid Cancer: Recent Advances
7.7. Considerations in Resource-Limited Settings
8. Future Perspectives
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 131I | iodine-131 |
| AHR | aryl hydrocarbon receptor |
| AI | artificial intelligence |
| AP1 | activator protein 1 |
| ATA | American Thyroid Association |
| ATC | anaplastic thyroid cancer |
| BMI | body mass index |
| CEA | carcinoembryonic antigen |
| CGRP | calcitonin gene-related peptide |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| CT | computed tomography |
| Ctn | calcitonin |
| DC | dendritic cell |
| DSS | disease-specific survival |
| DSV | diffuse sclerosing variant |
| DTC | differentiated thyroid cancer |
| EDCs | endocrine-disrupting chemicals |
| ERα | estrogen receptor alpha |
| ERβ | estrogen receptor beta |
| FMTC | familial medullary thyroid cancer |
| FNA | fine-needle aspiration |
| FNAB | fine-needle aspiration biopsy |
| FNAC | fine-needle aspiration cytology |
| FT3 | free triiodothyronine |
| FT4 | free thyroxine |
| FTC | follicular thyroid carcinoma |
| FTC | follicular thyroid cancer |
| FVPTC | follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma |
| FVPTC | PTC with a dominant follicular variant |
| HDI | Human Development Index |
| HT | Hashimoto thyroiditis |
| HV | hobnail |
| IGF-1 | insulin-like growth factor 1 |
| LND | lymph node dissection |
| LNM | lymph node metastasis |
| MAPK | MAP kinase |
| MEN2 | multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 |
| MEN4 | multiple endocrine neoplasia type 4 |
| MRI | magnetic resonance |
| MTC | medullary thyroid cancer |
| NF-kB | nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B |
| NIFTP | non-invasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features |
| NIS | sodium–iodide symporter |
| ORR | treatment response rate |
| OS | overall survival |
| PCR | reverse-transcriptase polymerase reaction |
| Pct | procalcitonin |
| PTC | papillary thyroid cancer |
| RAI | radioactive iodine |
| RF | radiofrequency |
| SHS | secondhand smoking |
| SPECT | single-proton emission computed tomography |
| SV | solid variant |
| T3 | triiodothyronine |
| T4 | thyroxine |
| TAMs | tumor-associated macrophages |
| TBG | thyroxine-binding globulin |
| TBSRTC | The Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology |
| TC | thyroid cancer |
| TCV | tall cell variant |
| TG | thyroglobulin |
| TKIs | tyrosine kinase inhibitors |
| TME | tumor microenvironment |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
| TSH | thyroid-stimulating hormone |
| TSHRs | TSH receptors |
| TT | total thyroidectomy |
| TgAb | anti-TG antibody |
| US | ultrasonography |
| VIP | vasoactive intestinal peptide |
| lncRNAs | long non-coding RNAs |
| mRNA | messenger RNA |
| miRNA | microRNA |
References
- Wells, S.A., Jr. Progress in Endocrine Neoplasia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 4981–4988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, L.G.; Sikora, A.G.; Tosteson, T.D.; Davies, L. The increasing incidence of thyroid cancer: The influence of access to care. Thyroid 2013, 23, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, S.; Cai, Z.; Jiang, G. Thyroid Cancer "Epidemic": A Socio-Environmental Health Problem Needs Collaborative Efforts. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3725–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruger, E.; Toraih, E.A.; Hussein, M.H.; Shehata, S.A.; Waheed, A.; Fawzy, M.S.; Kandil, E. Thyroid Carcinoma: A Review for 25 Years of Environmental Risk Factors Studies. Cancers 2022, 14, 6172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, S.M.; Fallahi, P.; Antonelli, A.; Benvenga, S. Environmental Issues in Thyroid Diseases. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogović Crnčić, T.; Ilić Tomaš, M.; Girotto, N.; Grbac Ivanković, S. Risk Factors for Thyroid Cancer: What Do We Know So Far? Acta Clin. Croat. 2020, 59, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, M.; Conti, G.O.; Caltabiano, R.; Buffone, A.; Zuccarello, P.; Cormaci, L.; Cannizzaro, M.A.; Ferrante, M. Role of Emerging Environmental Risk Factors in Thyroid Cancer: A Brief Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shank, J.B.; Are, C.; Wenos, C.D. Thyroid Cancer: Global Burden and Trends. Indian J. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 13, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Ervik, M.; Lam, F.; Laversanne, M.; Colombet, M.; Mery, L.; Pineros, M.; Znaor, A.; Soerjomataram, I.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2024; Available online: https://gco.iarc.who.int/today (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- Rahbari, R.; Zhang, L.; Kebebew, E. Thyroid cancer gender disparity. Future Oncol. 2010, 6, 1771–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/thyroid-cancer/about/key-statistics.html (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Girardi, F.M. Thyroid Carcinoma Pattern Presentation According to Age. Int. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 21, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Magreni, A.; Bann, D.V.; Schubart, J.R.; Goldenberg, D. The Effects of Race and Ethnicity on Thyroid Cancer Incidence. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2015, 141, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alagoz, O.; Zhang, Y.; Arroyo, N.; Fernandes-Taylor, S.; Yang, D.-Y.; Krebsbach, C.; Venkatesh, M.; Hsiao, V.; Davies, L.; Francis, D.O. Modeling Thyroid Cancer Epidemiology in the United States Using Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Microsimulation Model. Value Health 2024, 27, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Ngai, C.H.; Deng, Y.; Pun, C.N.; Lok, V.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Q.; Lucero-Prisno, D.E.; Xu, W.; Zheng, Z.J.; et al. Incidence and mortality of thyroid cancer in 50 countries: A joinpoint regression analysis of global trends. Endocrine 2023, 80, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzato, M.; Li, M.; Vignat, J.; Laversanne, M.; Singh, D.; La Vecchia, C.; Vaccarella, S. The epidemiological landscape of thyroid cancer worldwide: GLOBOCAN estimates for incidence and mortality rates in 2020. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, S. High aggressiveness of papillary thyroid cancer: From clinical evidence to regulatory cellular networks. Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.thyroidcancer.com/thyroid-cancer/papillary (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Verburg, F.A.; Van Santen, H.M.; Luster, M. Pediatric papillary thyroid cancer: Current management challenges. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 10, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, D.T.; Haymart, M.R.; Miller, B.S.; Gauger, P.G.; Doherty, G.M. The most commonly occurring papillary thyroid cancer in the United States is now a microcarcinoma in a patient older than 45 years. Thyroid 2011, 21, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coca-Pelaz, A.; Shah, J.P.; Hernandez-Prera, J.C.; Ghossein, R.A.; Rodrigo, J.P.; Hartl, D.M.; Olsen, K.D.; Shaha, A.R.; Zafereo, M.; Suarez, C.; et al. Papillary Thyroid Cancer-Aggressive Variants and Impact on Management: A Narrative Review. Adv. Ther. 2020, 37, 3112–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Lee, J.S.; Yun, H.J.; Kim, S.M.; Chang, H.; Lee, Y.S.; Chang, H.-S.; Park, C.S. Aggressive Subtypes of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Smaller Than 1 cm. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 108, 1370–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksimovic, S.; Jakovljevic, B.; Gojkovic, Z. Lymph Node Metastases Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma and their Importance in Recurrence of Disease. Med. Arch. 2018, 72, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.D.; Oyekunle, T.O.; Thomas, S.M.; Puscas, L.; Rocke, D.J. Association of Lymph Node Ratio with Overall Survival in Patients with Metastatic Papillary Thyroid Cancer. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2020, 146, 962–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, K.; Li, D.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, R.; Wang, X.; He, X. Lymph node metastasis in young and middle-aged papillary thyroid carcinoma patients: A SEER-based cohort study. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limaiem, F.; Rehman, A.; Mazzoni, T. Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK536943/ (accessed on 6 April 2025).
- Toraih, E.A.; Hussein, M.H.; Zerfaoui, M.; Attia, A.S.; Marzouk Ellythy, A.; Mostafa, A.; Ruiz, E.M.L.; Shama, M.A.; Russell, J.O.; Randolph, G.W.; et al. Site-Specific Metastasis and Survival in Papillary Thyroid Cancer: The Importance of Brain and Multi-Organ Disease. Cancers 2021, 13, 1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LiVolsi, V.A. Papillary thyroid carcinoma: An update. Mod. Pathol. 2011, 24, S1–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Miyauchi, A. Prognostic factors of papillary and follicular carcinomas in Japan based on data of kuma hospital. J. Thyroid Res. 2012, 2012, 973497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Miyauchi, A.; Kihara, M.; Fukushima, M.; Higashiyama, T.; Miya, A. Overall Survival of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Patients: A Single-Institution Long-Term Follow-Up of 5897 Patients. World J. Surg. 2018, 42, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luvhengo, T.E.; Bombil, I.; Mokhtari, A.; Moeng, M.S.; Demetriou, D.; Sanders, C.; Dlamini, Z. Multi-Omics and Management of Follicular Carcinoma of the Thyroid. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosai, J.; Carcangiu, M.L.; DeLellis, R.A. Tumors of the thyroid gland. In Atlas of Tumor Pathology, 3rd Series, Fas 5; Armed Forces Institute of Pathology: Washington, DC, USA, 1992; pp. 21–48. [Google Scholar]
- Correa, P.; Chen, V.W. Endocrine gland cancer. Cancer 1995, 75, 338–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashorobi, D.; Anastasopoulou, C.; Lopez, P.P. Follicular Thyroid Cancer. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539775/ (accessed on 6 April 2025).
- Seib, C.D.; Sosa, J.A. Evolving Understanding of the Epidemiology of Thyroid Cancer. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 48, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/follicular-thyroid-cancer-including-oncocytic-carcinoma-of-the-thyroid (accessed on 6 April 2025).
- Available online: https://www.thyroidcancer.com/thyroid-cancer/follicular/diagnosis (accessed on 6 April 2025).
- Basolo, F.; Macerola, E.; Poma, A.M.; Torregrossa, L. The 5th edition of WHO classification of tumors of endocrine organs: Changes in the diagnosis of follicular-derived thyroid carcinoma. Endocrine 2023, 80, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Goffredo, P.; Cheung, K.; Roman, S.A.; Sosa, J.A. Can minimally invasive follicular thyroid cancer be approached as a benign lesion? A population-level analysis of survival among 1,200 patients. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 20, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, H.; Sugino, K.; Katoh, R.; Matsuzu, K.; Kitagawa, W.; Nagahama, M.; Rino, Y.; Ito, K. New Insights on the Importance of the Extent of Vascular Invasion in Widely Invasive Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma. World J. Surg. 2023, 47, 2767–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, D.; Gill, A.J.; Turchini, J.; Waller, M.; Clifton-Bligh, R.; Glover, A.; Sywak, M.; Sidhu, S. The Prognostic Impact of Extent of Vascular Invasion in Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma. World J. Surg. 2023, 47, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.-D.; Chao, T.-C. Follicular thyroid carcinoma: From diagnosis to treatment. Endocr. J. 2006, 53, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, N.; Hamidi, S.; Ouni, R.; Rico, R.; Henderson, Y.C.; Puche, M.; Alekseev, S.; Colunga-Minutti, J.G.; Zafereo, M.E.; Lai, S.Y.; et al. Emerging therapeutic options for follicular-derived thyroid cancer in the era of immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1369780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rajan, N.; Khanal, T.; Ringel, M.D. Progression and dormancy in metastatic thyroid cancer: Concepts and clinical implications. Endocrine 2020, 70, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Parameswaran, R.; Brooks, S.; Sadler, G.P. Molecular pathogenesis of follicular cell derived thyroid cancers. Int. J. Surg. 2010, 8, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, T.; Ezzat, S.; Asa, S.L. Pathogenetic mechanisms in thyroid follicular-cell neoplasia. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 292–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHenry, C.R.; Phitayakorn, R. Follicular adenoma and carcinoma of the thyroid gland. Oncologist 2011, 16, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Panda, S.K.; Patro, B.; Samantaroy, M.R.; Mishra, J.; Mohapatra, K.C.; Meher, R.K. Unusual presentation of follicular carcinoma thyroid with special emphasis on their management. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2014, 5, 408–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Omar, B.; Yassir, H.; Youssef, O.; Sami, R.; Larbi, A.R.; Mohamed, R.; Mohamed, M. A rare case of follicular thyroid carcinoma metastasis to the sacral region: A case report with literature review. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2022, 94, 107001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Aboelnaga, E.M.; Ahmed, R.A. Difference between papillary and follicular thyroid carcinoma outcomes: An experience from Egyptian institution. Cancer Biol. Med. 2015, 12, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Parameswaran, R.; Hu, J.S.; En, N.M.; Tan, W.; Yuan, N. Patterns of metastasis in follicular thyroid carcinoma and the difference between early and delayed presentation. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2017, 99, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shen, J.; Yan, M.; Chen, L.; Ou, D.; Yao, J.; Feng, N.; Zhou, X.; Lei, Z.; Xu, D. Prognosis and influencing factors of follicular thyroid cancer. Cancer Med. 2024, 13, e6727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hirokawa, M.; Ito, Y.; Kuma, S.; Takamura, Y.; Miya, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Miyauchi, A. Nodal metastasis in well-differentiated follicular carcinoma of the thyroid: Its incidence and clinical significance. Oncol. Lett. 2010, 1, 873–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central][Green Version]
- Phitayakorn, R.; McHenry, C.R. Follicular and Hurthle cell carcinoma of the thyroid gland. Surg. Oncol. Clin. 2006, 15, 603–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Avanzo, A.; Treseler, P.; Ituarte, P.H.G.; Wong, M.; Streja, L.; Greenspan, F.S.; Siperstein, A.E.; Duh, Q.; Clark, O.H. Follicular thyroid carcinoma: Histology and prognosis. Cancer 2004, 100, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliszewski, K.; Ludwig, M.; Ludwig, B.; Mikuła, A.; Greniuk, M.; Rudnicki, J. Update on the Diagnosis and Management of Medullary Thyroid Cancer: What Has Changed in Recent Years? Cancers 2022, 14, 3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Santillan, V.R.; Master, S.R.; Menon, G.; Burns, B. Medullary Thyroid Cancer. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459354/ (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Matrone, A.; Gambale, C.; Prete, A.; Elisei, R. Sporadic Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma: Towards a Precision Medicine. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 864253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Available online: https://www.thyroidcancer.com/thyroid-cancer/medullary#:~:text=Sporadic%20(not%20inherited)%20medullary%20thyroid,effect%20women%20equally%20to%20men (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Gild, M.L.; Clifton-Bligh, R.J.; Wirth, L.J.; Robinson, B.G. Medullary Thyroid Cancer: Updates and Challenges. Endocr. Rev. 2023, 44, 934–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosé, V. Familial thyroid cancer: A review. Mod. Pathol. 2011, 24, S19–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, M.; Rowland, D.; Lekarev, O.; Ergun-Longmire, B. Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia in Childhood: An Update on Diagnosis, Screening, Management and Treatment. Endocrines 2022, 3, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, M.; Mulji, N.J.; Kasi, A. Multiple Endocrine Neoplasias Type 2. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK519054/ (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Hyer, S.L.; Newbold, K.; Harmer, C. Familial medullary thyroid cancer: Clinical aspects and prognosis. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2005, 31, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halling, K.C.; Bufill, J.A.; Cotter, M.; Artz, S.A.; Carpenter, A.B.; Schaid, D.; Hartman-Adams, H.; Chang, H.H.; Boustany, M.M.; Fithian, L.; et al. Age-Related Disease Penetrance in a Large Medullary Thyroid Cancer Family with a Codon 609 RET Gene Mutation. Mol. Diagn. 1997, 2, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinner, M.A.; DeBenedetti, M.K.; Moley, J.F.; Norton, J.A.; Wells, S.A., Jr. Medullary thyroid carcinoma in children with multiple endocrine neoplasia types 2A and 2B. J. Pediatr. Surg. 1996, 31, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rich, T.A.; Feng, L.; Busaidy, N.; Cote, G.J.; Gagel, R.F.; Hu, M.; Jimenez, C.; Lee, J.E.; Perrier, N.; Sherman, S.I.; et al. Prevalence by age and predictors of medullary thyroid cancer in patients with lower risk germline RET proto-oncogene mutations. Thyroid 2014, 24, 1096–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Skinner, M.A.; Moley, J.A.; Dilley, W.G.; Owzar, K.; Debenedetti, M.K.; Wells, S.A., Jr. Prophylactic thyroidectomy in multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1105–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, X.; Wei, T.; Li, Z.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Y.W. Well-defined survival outcome disparity across age cutoffs at 45 and 60 for medullary thyroid carcinoma: A long-term retrospective cohort study of 3601 patients. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1393904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kazakou, P.; Simeakis, G.; Alevizaki, M.; Saltiki, K. Medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC): Unusual metastatic sites. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. Case Rep. 2021, 21, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Limaiem, F.; Kashyap, S.; Naing, P.T.; Mathias, P.M.; Giwa, A.O. Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lowe, N.M.; Loughran, S.; Slevin, N.J.; Yap, B.K. Anaplastic thyroid cancer: The addition of systemic chemotherapy to radiotherapy led to an observed improvement in survival—A single centre experience and review of the literature. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 674583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, J.P.; Shaha, A.R. Anaplastic thyroid cancer. Oral Oncol. 2013, 49, 702–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smallridge, R.C.; Copland, J.A. Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma: Pathogenesis and emerging therapies. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 22, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.N.; Smallridge, R.C. Anaplastic thyroid cancer: An update. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 37, 101678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filetti, S.; Durante, C.; Hartl, D.; Leboulleux, S.; Locati, L.D.; Newbold, K.; Papotti, M.G.; Berruti, A.; ESMO Guidelines Committee. Thyroid cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1856–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Janjua, T.K.; Afridi, H.K.; Zahid, N.A. Anaplastic carcinoma of thyroid gland with widespread soft tissue metastasis: An unusual presentation. BMJ Case Rep. 2017, 2017, bcr2017220793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, D.; Yamamoto, Y.; Matsui, A.; Yasukawa, M.; Okamoto, S.; Toda, S.; Iwasaki, H. Lung cavitation in patients with anaplastic thyroid cancer treated with lenvatinib. Gland Surg. 2022, 11, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Lee, J.S.; Yun, H.J.; Chang, H.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, Y.S.; Chang, H.S.; Park, C.S. Prognosis of Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer with Distant Metastasis. Cancers 2022, 14, 5784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/23539-anaplastic-thyroid-cancer-atc#:~:text=The%20average%20survival%20rate%20of,alive%20one%20year%20after%20diagnosis (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Moreno, F.; Reyes, C.; Pineda, C.A.; Castellanos, G.; Cálix, F.; Calderón, J.; Vasquez-Bonilla, W.O. Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma with unusual long-term survival: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2022, 16, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, S.M.; Mandish, S.F.; Gill, B.S.; Balasubramani, G.K.; Clump, D.A.; Beriwal, S. Anaplastic thyroid cancer: Prognostic factors, patterns of care, and overall survival. Head Neck 2016, 38, E2083–E2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleki, Z.; Hassanzadeh, J.; Ghaem, H. Relationship of modifiable risk factors with the incidence of thyroid cancer: A worldwide study. BMC Res. Notes 2025, 18, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; He, H.; Shan, G.; Lin, Y. Research progress in epidemiology and risk factors of thyroid cancer. China Oncol. 2025, 35, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Hisan, U.K.; Myung, S.K.; Nguyen, G.V. Associations Between Obesity and Risk of Thyroid Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. Nutr. Cancer 2025, 77, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrone, A.; Ferrari, F.; Santini, F.; Elisei, R. Obesity as a risk factor for thyroid cancer. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2020, 27, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.; Han, K.D.; Park, C.Y. Weight change is significantly associated with risk of thyroid cancer: A nationwide population-based cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.G.; Cheng, S.Y. Mechanisms Linking Obesity and Thyroid Cancer Development and Progression in Mouse Models. Horm. Cancer 2018, 9, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Moli, R.; Vella, V.; Tumino, D.; Piticchio, T.; Naselli, A.; Belfiore, A.; Frasca, F. Inflammasome activation as a link between obesity and thyroid disorders: Implications for an integrated clinical management. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 959276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flor, L.S.; Anderson, J.A.; Ahmad, N.; Aravkin, A.; Carr, S.; Dai, X.; Gil, G.F.; Hay, S.I.; Malloy, M.J.; McLaughlin, S.A.; et al. Health effects associated with exposure to secondhand smoke: A Burden of Proof study. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 149–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Gong, W.W.; Lu, F.; He, Q.F.; Hu, R.Y.; Zhong, J.M.; Yu, M. Associations of intensity, duration, cumulative dose, and age at start of smoking, with thyroid cancer in Chinese males: A hospital-based case-control study in Zhejiang Province. Tob. Induc. Dis. 2020, 18, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Xiong, D.; Wu, C.; Cen, L.; Xie, L.; Li, X. Modifiable risk factors for thyroid cancer: Lifestyle and residence environment. Endokrynol. Pol. 2024, 75, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leko, M.B.; Gunjača, I.; Pleić, N.; Zemunik, T. Environmental Factors Affecting Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone and Thyroid Hormone Levels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.-Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Oh, D.J.; Min, C.; Sim, S.; Choi, H.G. Obesity is positively related and tobacco smoking and alcohol consumption are negatively related to an increased risk of thyroid cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, Y.; Shin, D.W.; Han, K.; Kim, D.; Kim, T.H.; Chun, S.; Jeong, S.M.; Song, Y.M. Smoking, Alcohol Consumption, and the Risk of Thyroid Cancer: A Population-Based Korean Cohort Study of 10 Million People. Thyroid 2022, 32, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedenreich, C.M.; Ryder-Burbidge, C.; McNeil, J. Physical activity, obesity and sedentary behavior in cancer etiology: Epidemiologic evidence and biologic mechanisms. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Feng, X.; Yang, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, K.; Feng, S.; Wang, F.; Yang, X. Appraising the Effect of Potential Risk Factors on Thyroid Cancer: A Mendelian Randomization Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, e2783–e2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Wang, F.; Yang, W.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, C.; Huang, L.; Li, L.; Cheng, H.; Cai, H.; Li, X.; et al. Association Between Genetic Risk, Adherence to Healthy Lifestyle Behavior, and Thyroid Cancer Risk. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2246311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, Y.; Han, K.; Shin, D.W.; Kim, D.; Jeong, S.M.; Chun, S.; Choi, I.Y.; Jeon, K.H.; Kim, T.H. Changes in Smoking, Alcohol Consumption, and the Risk of Thyroid Cancer: A Population-Based Korean Cohort Study. Cancers 2021, 13, 2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q. Role of exercise on the reduction of cancer development: A mechanistic review from the lncRNA point of view. Clin. Exp. Med. 2025, 25, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, M.; Cristaldi, A.; Okatyeva, V.; Bianco, S.L.; Conti, G.O.; Zuccarello, P.; Copat, C.; Caltabiano, R.; Cannizzaro, M.; Ferrante, M. Physical Activity and Thyroid Cancer Risk: A Case-Control Study in Catania (South Italy). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.S.; Lee, K.P. A systematic review of the biological mechanisms linking physical activity and breast cancer. Phys. Act. Nutr. 2020, 24, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Han, K.; Jung, J.-H.; Ha, J.; Jeong, C.; Heu, J.-Y.; Lee, S.-W.; Lee, J.; Lim, Y.; Kim, M.K.; et al. Physical activity and reduced risk of fracture in thyroid cancer patients after thyroidectomy—Anationwide cohort study. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1173781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrante, M.; Distefano, G.; Distefano, C.; Copat, C.; Grasso, A.; Conti, G.O.; Cristaldi, A.; Fiore, M. Benefits of Physical Activity during and after Thyroid Cancer Treatment on Fatigue and Quality of Life: A Systematic Review. Cancers 2022, 14, 3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Li, H.; Deziel, N.C.; Huang, H.; Zhao, N.; Ma, S.; Ni, X.; Udelsman, R.; Zhang, Y. Genetic susceptibility may modify the association between cell phone use and thyroid cancer: A population-based case-control study in Connecticut. Environ. Res. 2020, 182, 109013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlberg, M.; Koppel, T.; Hedendahl, L.K.; Hardell, L. Is the Increasing Incidence of Thyroid Cancer in the Nordic Countries Caused by Use of Mobile Phones? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parad, M.T.; Fararouei, M.; Mirahmadizadeh, A.R.; Afrashteh, S. Thyroid cancer and its associated factors: A population-based case-control study. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saenko, V.; Mitsutake, N. Radiation-Related Thyroid Cancer. Endocr. Rev. 2024, 45, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, L.M.; Karyadi, D.M.; Stewart, C.; Bogdanova, T.I.; Dawson, E.T.; Steinberg, M.K.; Dai, J.; Hartley, S.W.; Schonfeld, S.J.; Sampson, J.N.; et al. Radiation-related genomic profile of papillary thyroid carcinoma after the Chernobyl accident. Science 2021, 372, eabg2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suteau, V.; Munier, M.; Briet, C.; Rodien, P. Sex Bias in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahedi, A.; Bondaz, L.; Rajaraman, M.; Leslie, W.D.; Jefford, C.; Young, J.E.; Pathak, K.A.; Bureau, Y.; Rachinsky, I.; Badreddine, M.; et al. Risk for Thyroid Cancer Recurrence Is Higher in Men Than in Women Independent of Disease Stage at Presentation. Thyroid 2020, 30, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda-Filho, A.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Bray, F.; Cao, B.; Franceschi, S.; Vaccarella, S.; Dal Maso, L. Thyroid cancer incidence trends by histology in 25 countries: A population-based study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, A.K. Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: Current Position in Epidemiology, Genomics, and Classification. In Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma; Lam, A.K., Ed.; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagin, J.A. Genetics of papillary thyroid cancer initiation: Implications for therapy. Trans. Am. Clin. Climatol. Assoc. 2005, 116, 259–269. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, D.; Yu, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, M.; Chen, J. BRAF V600E mutation and the Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology of fine-needle aspiration biopsy for distinguishing benign from malignant thyroid nodules. Medicine 2021, 100, e27167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capezzone, M.; Robenshtok, E.; Cantara, S.; Castagna, M.G. Familial non-medullary thyroid cancer: A critical review. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2021, 44, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, M.I.; Junit, S.M.; Ng, K.L.; Jayapalan, J.J.; Karikalan, B.; Hashim, O.H. Papillary Thyroid Cancer: Genetic Alterations and Molecular Biomarker Investigations. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 16, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uno, D.; Endo, K.; Yoshikawa, T.; Hirai, N.; Kobayashi, E.; Nakanishi, Y.; Kondo, S.; Yoshizaki, T. Correlation between gene mutations and clinical characteristics in papillary thyroid cancer: A retrospective analysis of BRAF mutations and RET rearrangements. Thyroid Res. 2024, 17, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlidis, E.; Sapalidis, K.; Chatzinikolaou, F.; Kesisoglou, I. Medullary thyroid cancer: Molecular factors, management and treatment. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2020, 61, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Gong, H.; Jiang, T.; Su, A.; Yi, L. Diagnostic value of preoperative systemic inflammatory markers and carcinoembryonic antigen in medullary thyroid carcinoma and the risk factors affecting its prognosis. Gland Surg. 2025, 14, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barletta, J.A.; Nosé, V.; Sadow, P.M. Genomics and Epigenomics of Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma: From Sporadic Disease to Familial Manifestations. Endocr. Pathol. 2021, 32, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercè, F.; Asla, Q.; Illana, F.J.; Victòria, F.; Javier, H.-L.; Marta, S.; Iglesias, C.; Webb, S.M.; Aulinas, A. A novel likely pathogenic germline variant in CDKN1B in a patient with MEN4 and medullary thyroid cancer. Fam. Cancer 2025, 24, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macerola, E.; Poma, A.M.; Vignali, P.; Basolo, A.; Ugolini, C.; Torregrossa, L.; Santini, F.; Basolo, F. Molecular Genetics of Follicular-Derived Thyroid Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, P.; Póvoa, A.A.; Melo, M.; Vinagre, J.; Máximo, V.; Eloy, C.; Cameselle-Teijeiro, J.M.; Sobrinho-Simões, M. Molecular Pathology of Non-familial Follicular Epithelial–Derived Thyroid Cancer in Adults: From RAS/BRAF-like Tumor Designations to Molecular Risk Stratification. Endocr. Pathol. 2021, 32, 44–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.; Landa, I. The prognostic power of gene mutations in thyroid cancer. Endocr. Connect. 2025, 13, e230297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Ghossein, R.A. Advances in Thyroid Pathology: High Grade Follicular Cell-derived Thyroid Carcinoma and Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2023, 30, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landa, I.; Ibrahimpasic, T.; Boucai, L.; Sinha, R.; Knauf, J.A.; Shah, R.H.; Dogan, S.; Ricarte-Filho, J.C.; Krishnamoorthy, G.P.; Xu, B.; et al. Genomic and transcriptomic hallmarks of poorly differentiated and anaplastic thyroid cancers. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 1052–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.K.; Ryoo, J.H.; Kim, M.H.; Jung, J.Y.; Jung, Y.S.; Kim, K.N.; Shin, S.; Oh, C.M. Association Between Eight Autoimmune Diseases and Thyroid Cancer: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Thyroid 2024, 34, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, D.S.; Bedno, S.A.; Cooper, D.S.; Hutfless, S.M.; Ippolito, S.; Jordan, S.J.; Matos, P.G.; Neale, R.E.; Sabini, E.; Whiteman, D.C.; et al. Pre-existing Thyroid Autoimmunity and Risk of Papillary Thyroid Cancer: A Nested Case-Control Study of US Active-Duty Personnel. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 2578–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasgholizadeh, P.; Naseri, A.; Nasiri, E.; Sadra, V. Is Hashimoto thyroiditis associated with increasing risk of thyroid malignancies? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Thyroid Res. 2021, 14, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, M.; Gou, J. Symptoms and negative emotions in patients with advanced thyroid cancer: A prospective cross-sectional study. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lincango-Naranjo, E.; Solis-Pazmino, P.; El Kawkgi, O.; Salazar-Vega, J.; Garcia, C.; Ledesma, T.; Rojas, T.; Alvarado-Mafla, B.; Young, G.; Dy, B.; et al. Triggers of thyroid cancer diagnosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Endocrine 2021, 72, 644–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabhan, F.; Dedhia, P.H.; Ringel, M.D. Thyroid cancer, recent advances in diagnosis and therapy. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 984–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, L.; Gomes, K.; dos Santos Silva, I. Thyroid Cancer and Quality of Life: A Literature Review. Clin. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2024, 7, 007–013. [Google Scholar]
- Nelim, R. Thyroid Cancer: Current Understanding and Emerging Trends in Diagnosis and Treatment. Rep. Thyroid Res. 2023, 7, 36. [Google Scholar]
- Ulisse, S.; Baldini, E.; Lauro, A.; Pironi, D.; Tripodi, D.; Lori, E.; Ferent, I.C.; Amabile, M.I.; Catania, A.; Di Matteo, F.M.; et al. Papillary Thyroid Cancer Prognosis: An Evolving Field. Cancers 2021, 13, 5567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraz, C. Molecular testing for thyroid nodules: Where are we now? Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2024, 25, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajab, M.; Payne, R.J.; Forest, V.-I.; Pusztaszeri, M. Molecular Testing for Thyroid Nodules: The Experience at McGill University Teaching Hospitals in Canada. Cancers 2022, 14, 4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukyanov, S.A.; Titov, S.E.; Kozorezova, E.S.; Demenkov, P.S.; Veryaskina, Y.A.; Korotovskii, D.V.; Ilyina, T.E.; Vorobyev, S.L.; Zhivotov, V.A.; Bondarev, N.S.; et al. Prediction of the Aggressive Clinical Course of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Based on Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy Molecular Testing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belaiche, A.; Morand, G.B.; Turkdogan, S.; Kang, E.S.; Forest, V.-I.; Pusztaszeri, M.P.; Hier, M.P.; Mlynarek, A.M.; Richardson, K.; Sadeghi, N.; et al. Molecular Markers in Follicular and Oncocytic Thyroid Carcinomas: Clinical Application of Molecular Genetic Testing. Curr. Oncol. 2024, 31, 5919–5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livhits, M.J.; Zhu, C.Y.; Kuo, E.J.; Nguyen, D.T.; Kim, J.; Tseng, C.-H.; Leung, A.M.; Rao, J.; Levin, M.; Douek, M.L.; et al. Effectiveness of Molecular Testing Techniques for Diagnosis of Indeterminate Thyroid Nodules: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarty, N.; Mahajan, A.; Basu, S.; D’Cruz, A.K. Comprehensive Review of the Imaging Recommendations for Diagnosis, Staging, and Management of Thyroid Carcinoma. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, E.; Grazhdani, H.; Tattaresu, G.; Pittari, A.; Foti, P.V.; Palmucci, S.; Spatola, C.; Lo Greco, M.C.; Inì, C.; Tiralongo, F.; et al. Thyroid Nodule Characterization: Overview and State of the Art of Diagnosis with Recent Developments, from Imaging to Molecular Diagnosis and Artificial Intelligence. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Al Harbawi, L.; Abed, Z.; Jawhar, N. Neck Masses as The First Presentation of Occult Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: Case Series. Egypt. J. Hosp. Med. 2023, 90, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyroglou, A.; Kostopoulos, G.; Tseleni, S.; Toulis, K.; Bramis, K.; Mastorakos, G.; Konstadoulakis, M.; Vamvakidis, K.; Alexandraki, K.I. Hobnail Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma, A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2022, 14, 2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanani, R.; Faisal, M.; Akram, M.; Shakeel, O.; Zahid, M.T.; Hassan, A.; Hussain, R. Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma: Distant Metastasis as an Unusual Sole Initial Manifestation. Turk. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 59, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Li, J.; Zhou, J.; Xiao, Q.; Gao, H. Metastatic papillary thyroid carcinoma with no primary tumor in the thyroid gland: A case report and review of literature. Transl. Cancer Res. 2022, 11, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakir, M.K.M.; Spiro, A.J.; Mai, V.Q.; Hoang, T.D. Diarrhea as an Initial Presentation in Patients with Medullary Thyroid Cancer: Delaying the Diagnosis. Case Rep. Gastroenterol. 2020, 14, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelizzo, M.R.; Mazza, E.I.; Mian, C.; Boschin, I.M. Medullary thyroid carcinoma. Expert Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2023, 23, 943–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawęska, W.; Dominik, H.; Dominik, B. Anaplastic thyroid cancer with life-threatening symptoms in an older female—A case report. J. Educ. Health Sport. 2023, 41, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, Y.J.; Koo, J.S. Next-generation sequencing in thyroid cancer. J Transl Med. 2016, 14, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newfield, R.S.; Jiang, W.; Sugganth, D.X.; Hantash, F.M.; Lee, E. Newbury RO. Mutational analysis using next generation se-quencing in pediatric thyroid cancer reveals BRAF and fusion oncogenes are common. Int J PediatrOtorhinolaryngol. 2022, 157, 111121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellevicine, C.; Migliatico, I.; Sgariglia, R.; Nacchio, M.; Vigliar, E.; Pisapia, P.; Iaccarino, A.; Bruzzese, D.; Fonderico, F.; Salvatore, D.; et al. Evaluation of BRAF, RAS, RET/PTC, and PAX8/PPARg alterations in different Bethesda diagnostic cate-gories: A multicentric prospective study on the validity of the 7-gene panel test in 1172 thyroid FNAs deriving from different hospitals in South Italy. Cancer Cytopathol. 2020, 128, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Zhang, W.; Xia, Q.; Liu, F.; Li, L.; Zhao, S.; Gao, X.; Zang, C.; Ge, R.; Sun, Y. RNA sequencing identifies crucial genes in papil-lary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) progression. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2016, 100, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.G.; Carty, S.E.; Lee, A.J. Molecular Testing for Thyroid Nodules Including Its Interpretation and Use in Clinical Practice. Ann Surg Oncol. 2021, 28, 8884–8891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, A.; Bar, Y.; Maurice-Dror, C.; Finkel, I.; Goldvaser, H.; Dudnik, E.; Goldstein, D.A.; Gordon, N.; Billan, S.; Gutfeld, O.; et al. Next-generation sequencing in thyroid cancers: Do targetable alterations lead to a therapeutic advantage?: A multicenter experience. Medicine 2021, 100, e26388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacini, F.; Castagna, M.G. Approach to and treatment of differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 96, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovanella, L.; D’Aurizio, F.; Petranović Ovčariček, P.; Görges, R. Diagnostic, Theranostic and Prognostic Value of Thyroglobulin in Thyroid Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-D. Thyroglobulin and human thyroid cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2008, 388, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlińska, A.; Świątkowska-Stodulska, R. Clinical use of thyroglobulin: Not only thyroid cancer. Endocrine 2024, 84, 786–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Liu, C.; Kuang, Z.; Li, X. The role of preoperative serum thyroglobulin in the diagnosis and treatment of differentiated thyroid cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1426785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prpić, M.; Franceschi, M.; Romić, M.; Jukić, T.; Kusić, Z. Thyroglobulin as a tumor marker in differentiated thyroid cancer—Clinical considerations. Acta Clin. Croat. 2018, 57, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ren, C.; Gong, Y.; Ye, F.; Tang, Y.; Xu, J.; Guo, C.; Huang, J. The Role of Thyroglobulin in Preoperative and Postoperative Evaluation of Patients with Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 872527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrienti, A.; Pecce, V.; Grani, G.; Del Gatto, V.; Barp, S.; Maranghi, M.; Giacomelli, L.; Di Gioia, C.; Biffoni, M.; Filetti, S.; et al. Serum microRNA-146a-5p and microRNA-221-3p as potential clinical biomarkers for papillary thyroid carcinoma. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2025, 48, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, F.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Cai, H.; Wang, Y.; Peng, X.; Lu, L.; He, R.; Hou, Y.; Li, Z.; et al. Development and validation of an interpretable machine learning model for predicting the risk of distant metastasis in papillary thyroid cancer: A multicenter study. eClinicalMedicine 2024, 77, 102913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hataya, Y.; Fujishima, Y.; Fujimoto, K.; Iwakura, T.; Matsuoka, N. Association between serum thyroglobulin levels and glycemic control in patients with thyroid cancer after radioiodine therapy. Endocr. J. 2025, 72, 637–643, epub ahead of printing. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Lin, B.; Xu, T.; Jiang, J.; Luo, S.; Chen, W.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Liao, G.; Wang, J.; et al. The neurotransmitter calcitonin gene-related peptide shapes an immunosuppressive microenvironment in medullary thyroid cancer. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, S.A.; Asa, S.L.; Dralle, H.; Elisei, R.; Evans, D.B.; Gagel, R.F.; Lee, N.; Machens, A.; Moley, J.F.; Pacini, F.; et al. American Thyroid Association Guidelines Task Force on Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma. Revised American Thyroid Association guidelines for the management of medullary thyroid carcinoma. Thyroid 2015, 25, 567–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, I.Y.; Yun, H.J.; Kim, S.M.; Park, Y. Diagnostic Performance of Preoperative Calcitonin and Procalcitonin Tests for Differential Diagnosis of Medullary Thyroid Cancer. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baylin, S.B.; Bailey, A.L.; Hsu, T.H.; Foster, G.V. Degradation of human calcitonin in human plasmas. Metabolism 1977, 26, 1345–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faggiano, A.; Milone, F.; Ramundo, V.; Chiofalo, M.G.; Ventre, I.; Giannattasio, R.; Severino, R.; Lombardi, G.; Colao, A.; Pezzullo, L. A decrease of calcitonin serum concentrations less than 50 percent 30 minutes after thyroid surgery suggests incomplete C-cell tumor tissue removal. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, E32–E36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Modigliani, E.; Cohen, R.; Campos, J.M.; Conte-Devolx, B.; Maes, B.; Boneu, A.; Schlumberger, M.; Bigorgne, J.C.; Dumontier, P.; Leclerc, L.; et al. Prognostic factors for survival and for biochemical cure in medullary thyroid carcinoma: Results in 899 patients. The GETC Study Group. Groupe d’étude des tumeurs à calcitonine. Clin. Endocrinol. 1998, 48, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réti, Z.; Tabák, Á.G.; Garami, M.; Kalina, I.; Kiss, G.; Sápi, Z.; Tóth, M.; Tőke, J. Spontaneous and Treatment-Related Changes of Serum Calcitonin in Medullary Thyroid Cancer: Long-Term Experience in a Patient with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 2B. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2024, 8, e2300675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Wu, T.; Jiang, M.; Jiang, S.; Jiang, K.; Peng, J.; Luo, G.; Yu, Y.; Chen, W.; Yang, A. Early postoperative calcitonin-to-preoperative calcitonin ratio as a predictive marker for structural recurrence in sporadic medullary thyroid cancer: A retrospective study. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1094242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeek, H.H.; de Groot, J.W.B.; Sluiter, W.J.; Muller Kobold, A.C.; van den Heuvel, E.R.; Plukker, J.T.; Links, T.P. Calcitonin testing for detection of medullary thyroid cancer in people with thyroid nodules. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 3, CD010159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepet, K.; Alhefdhi, A.; Lai, N.; Mazeh, H.; Sippel, R.; Chen, H. Hereditary medullary thyroid cancer: Age-appropriate thyroidectomy improves disease-free survival. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 20, 1451–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, S.; Guddati, A.K. Carcinoembryonic Antigen, Carbohydrate Antigen 19-9, Cancer Antigen 125, Prostate-Specific Antigen and Other Cancer Markers: A Primer on Commonly Used Cancer Markers. World J. Oncol. 2023, 14, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Chen, L. Management of medullary thyroid cancer based on variation of carcinoembryonic antigen and calcitonin. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1418657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhao, K.; Li, F.; He, X. Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma with Elevated Serum CEA and Normal Serum Calcitonin After Surgery: A Case Report and Literature Review. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 526716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos, I.; Stefanidou, E.; Meditskou-Eythymiadou, S.; Mironidou-Tzouveleki, M.; Manaki, V.; Magra, V.; Laskou, S.; Mantalovas, S.; Pantea, S.; Kesisoglou, I.; et al. A Review of the Significance in Measuring Preoperative and Postoperative Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA) Values in Patients with Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma (MTC). Medicina 2021, 57, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Liang, N.; Sun, H.; Frattini, F.; Sui, C.; Yang, M.; Wang, H.; Dionigi, G. Critically evaluated key points on hereditary medullary thyroid carcinoma. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1412942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendelsohn, G.; Wells, S.A., Jr.; Baylin, S.B. Relationship of tissue carcinoembryonic antigen and calcitonin to tumor virulence in medullary thyroid carcinoma. An immunohistochemical study in early, localized, and virulent disseminated stages of disease. Cancer 1984, 54, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaghaghi, A.; Salari, A.; Jalaeefar, A.; Shirkhoda, M. Management of lymph nodes in medullary thyroid carcinoma: A review. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 81, 104538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi-Yang, Y.; Kaixun, Z.; Dongling, L.; Zhou, Y.; Chengbin, Z.; Jimei, C.; Caojin, Z. Carcinoembryonic antigen levels are increased with pulmonary output in pulmonary hypertension due to congenital heart disease. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 300060520964378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilek, O.N.; Arslan Kahraman, D.İ.; Kahraman, G. Carcinoembryonic antigen in the diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of focal liver lesions. World J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2024, 16, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turkdogan, S.; Forest, V.I.; Hier, M.P.; Tamilia, M.; Florea, A.; Payne, R.J. Carcinoembryonic antigen levels correlated with advanced disease in medullary thyroid cancer. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 47, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotwal, A.; Erickson, D.; Geske, J.R.; Hay, I.D.; Castro, M.R. Predicting Outcomes in Sporadic and Hereditary Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma over Two Decades. Thyroid 2021, 31, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kankanala, V.L.; Zubair, M.; Mukkamalla, S.K.R. Carcinoembryonic Antigen. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Pishdad, R.; Vahidi Rad, M.; Cespedes, L. A Benign Medullary Thyroid Cancer. Cureus 2022, 14, e21038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, F.; Alsafdi, T. Elevated Procalcitonin Levels can Occur in Bacterial Infections and also in Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma. Eur. J. Case Rep. Intern. Med. 2024, 11, 004679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cui, W. Progress in Procalcitonin Detection Based on Immunoassay. Research 2024, 7, 0345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisieska-Żołnierczyk, S.; Gajęcka, M.; Zielonka, Ł.; Dąbrowski, M.; Gajęcki, M.T. Blood levels of zearalenone, thyroid-stimulating hormone, and thyroid hormones in patients with colorectal cancer. Toxicon 2024, 251, 108125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adıgüzel Akman, Ö.; Esnafoglu, E. Evaluation of procalcitonin and C-reactive protein levels in children with autism spectrum disorder and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Int. J. Dev. Disabil. 2023, 71, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiriakopoulos, A.; Giannakis, P.; Menenakos, E. Calcitonin: Current concepts and differential diagnosis. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 13, 20420188221099344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandric, M.; Zlojutro, B.; Momcicevic, D.; Dragic, S.; Topolovac, S.; Kovacevic, T.; Kovacevic, P. Incidental diagnosis of medullary thyroid microcarcinoma in COVID-19 patient with elevated procalcitonin levels. Arch. Clin. Cases 2024, 11, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Censi, S.; Manso, J.; Benvenuti, T.; Piva, I.; Iacobone, M.; Mondin, A.; Torresan, F.; Basso, D.; Crivellari, G.; Zovato, S.; et al. The role of procalcitonin in the follow-up of medullary thyroid cancer. Eur. Thyroid J. 2023, 12, e220161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucci, I.; Di Dalmazi, G.; Giuliani, C.; Russo, P.; Ciappini, B.; Amatetti, C.; Guarino, P.; Napolitano, G. Advanced medullary thyroid carcinoma uncovered by persistently elevated procalcitonin in a patient with COVID-19. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. Case Rep. 2024, 2024, 24–0052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Mukhopadhyay, M.; Paul, S.; Bera, A.; Bandyopadhyay, T. Incidental diagnosis of medullary thyroid carcinoma due to persistently elevated procalcitonin in a patient with COVID-19 pneumonia: A case report. World J. Clin. Cases 2022, 10, 7171–7177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, H.; Khokhar, A.J.; Ibrahim, S.; Farooq, M.U.; Rashid, R.; Raheem, H.U.; Singh, G. High Procalcitonin Does Not Always Indicate a Bacterial Infection. Cureus 2024, 16, e72274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruna, P.; Nedelníková, K.; Gürlich, R. Physiology and genetics of procalcitonin. Physiol. Res. 2000, 49, S57–S61. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wu, C.; Jiang, J.; Hashimoto, K.; Zhou, X. The role of thyroid-stimulating hormone in regulating lipid metabolism: Implications for body-brain communication. Neurobiol. Dis. 2024, 201, 106658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirahanchi, Y.; Toro, F.; Jialal, I. Physiology, Thyroid Stimulating Hormone. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Won, H.R.; Jeon, E.; Chang, J.W.; Kang, Y.E.; Song, K.; Kim, S.W.; Lim, D.M.; Ha, T.K.; Chung, K.W.; Kim, H.J.; et al. Is Maintaining Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Effective in Patients Undergoing Thyroid Lobectomy for Low-Risk Differentiated Thyroid Cancer? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2022, 14, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Bhandari, A.; Sindan, N.; Hirachan, S.; Yang, Q.; Guo, G.; Shen, Y. Serum TSH levels are associated with postoperative recurrence and lymph node metastasis of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 6108–6116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.; Sun, J.; He, X.; Jia, L. An age-and sex-matched postoperative therapy should be required in thyroid papillary carcinoma. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1339191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugitani, I.; Fujimoto, Y. Effect of postoperative thyrotropin suppressive therapy on bone mineral density in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma: A prospective controlled study. Surgery 2011, 150, 1250–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haymart, M.R.; Esfandiari, N.H.; Stang, M.T.; Sosa, J.A. Controversies in the Management of Low-Risk Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Endocr. Rev. 2017, 38, 351–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzaferri, E.L.; Young, R.L.; Oertel, J.E.; Kemmerer, W.T.; Page, C.P. Papillary thyroid carcinoma: The impact of therapy in 576 patients. Medicine 1977, 56, 171–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Brumpton, B.; Kabil, O.; Gudmundsson, J.; Thorleifsson, G.; Weinstock, J.; Zawistowski, M.; Nielsen, J.B.; Chaker, L.; Medici, M.; et al. G.W.A.S of thyroid stimulating hormone highlights pleiotropic effects and inverse association with thyroid cancer. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Niu, S.; Zhou, L. Gender, FT4 levels, T stage, and BMI as predictors of TSH levels in thyroid cancer patients. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 16, 1422464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, K.; Yuan, Y.; Bai, H.; Meng, L. Exosomal miRNA as biomarker in cancer diagnosis and prognosis: A review. Medicine 2024, 103, e40082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazlauskiene, M.; Klimaite, R.; Kondrotiene, A.; Dauksa, A.; Dauksiene, D.; Verkauskiene, R.; Zilaitiene, B. Plasma miRNA-146b-3p, -222-3p, -221-5p, -21a-3p Expression Levels and TSHR Methylation: Diagnostic Potential and Association with Clinical and Pathological Features in Papillary Thyroid Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabané, P.; Correa, C.; Bode, I.; Aguilar, R.; Elorza, A.A. Biomarkers in Thyroid Cancer: Emerging Opportunities from Non-Coding RNAs and Mitochondrial Space. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armos, R.; Bojtor, B.; Papp, M.; Illyes, I.; Lengyel, B.; Kiss, A.; Szili, B.; Tobias, B.; Balla, B.; Piko, H.; et al. MicroRNA Profiling in Papillary Thyroid Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayosso-Gómez, L.V.; Ortiz-Quintero, B. Circulating MicroRNAs in Blood and Other Body Fluids as Biomarkers for Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Therapy Response in Lung Cancer. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calin, G.A.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Guan, L.; Sun, W.; Zhang, Y.; Du, Y.; Yuan, S.; Cao, X.; Yu, Z.; Jia, Q.; Zheng, X.; et al. Targeting miR-31 represses tumourigenesis and dedifferentiation of BRAFV600E-associated thyroid carcinoma. Clin. Transl. Med. 2024, 14, e1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Xie, R.; Chen, Y.; Han, X.; Li, X.E. Diagnostic value of microRNA-129-5p and TSH combination for papillary thyroid cancer with cervical lymph node metastasis. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2025, 40, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Matos, M.L.G.; Pinto, M.; Gonçalves, A.; Canberk, S.; Bugalho, M.J.M.; Soares, P. Insights in biomarkers complexity and routine clinical practice for the diagnosis of thyroid nodules and cancer. PeerJ 2025, 13, e18801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silaghi, C.A.; Lozovanu, V.; Silaghi, H.; Georgescu, R.D.; Pop, C.; Dobrean, A.; Georgescu, C.E. The Prognostic Value of MicroRNAs in Thyroid Cancers-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2020, 12, 2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Li, X.; Tong, D.; Han, C.; Zhao, R.; He, Y.; Jin, X. miR-136 suppresses tumor invasion and metastasis by targeting RASAL2 in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Huang, Z.; Chen, R. Microrna-136 promotes proliferation and invasion ingastric cancer cells through Pten/Akt/P-Akt signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 4683–4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, L.; Kelly, L.; Shuai, Y.; Armstrong, M.J.; Nikiforov, Y.E.; Carty, S.E.; Nikiforova, M.N. MicroRNA signature distinguishes the degree of aggressiveness of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 18, 2035–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galuppini, F.; Censi, S.; Moro, M.; Carraro, S.; Sbaraglia, M.; Iacobone, M.; Fassan, M.; Mian, C.; Pennelli, G. MicroRNAs in Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma: A State of the Art Review of the Regulatory Mechanisms and Future Perspectives. Cells 2021, 10, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisell, L.E.; Oden, A.; Muth, A.; Altiparmak, G.; Mõlne, J.; Ahlman, H.; Nilsson, O. The Ki67 index a prognostic marker in medullary thyroid carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 89, 2093–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante, C.; Puxeddu, E.; Ferretti, E.; Morisi, R.; Moretti, S.; Bruno, R.; Barbi, F.; Avenia, N.; Scipioni, A.; Verrienti, A.; et al. BRAF mutations in papillary thyroid carcinomas inhibit genes involved in iodine metabolism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 2840–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Abdel-Mageed, A.B.; Kandil, E. BRAF mutation in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2012, 5, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Song, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, S. Mannose enhances anti-tumor effect of PLX4032 in anaplastic thyroid cancer. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2025, 32, e240209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, H.; Matsumoto, H.; Ando, Y.; Nakajo, M.; Yamashita, M. Mutations in Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma: An Analysis of the Japanese National Genomic Database. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2025, 10, e70110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.T.; Thompson, E.K.; Bhimani, N.; Duong, M.C.; Nguyen, H.G.; Bullock, M.; Gild, M.L.; Glover, A. Prognostic Significance of Key Molecular Markers in Thyroid Cancer: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2025, 17, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Guo, D.; Yang, B.; Huang, S.H. Location based BRAF V600E mutation status and dimension patterns of sporadic thyroid nodules: A population-based study. BMC Cancer 2025, 25, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instrum, R.; Swartzwelder, C.E.; Ghossein, R.A.; Xu, B.; Givi, B.; Wong, R.J.; Untch, B.R.; Morris, L.G.T. Clinical and Pathologic Characteristics of Cytologically Indeterminate Thyroid Nodules with Non-V600E BRAF Alterations. Cancers 2025, 17, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannino, D.; Basilotta, R.; De Luca, F.; Casili, G.; Esposito, E.; Paterniti, I. KRAS-SOS-1 Inhibition as New Pharmacological Target to Counteract Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma (ATC). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikas, A.; Ahmadi, S.; Pappa, T.; Marqusee, E.; Wong, K.; Nehs, M.A.; Cho, N.L.; Haase, J.; Doherty, G.M.; Sehgal, K.; et al. Additional Oncogenic Alterations in RAS-Driven Differentiated Thyroid Cancers Associate with Worse Clinicopathologic Outcomes. Clin. Cancer. Res. 2023, 29, 2678–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Liu, S.; Zhang, W.; Zeng, C.; Liao, D.; Tang, T.; Wang, S.; Guo, Y. Annotation-free genetic mutation estimation of thyroid cancer using cytological slides from multi-centers. Diagn. Pathol. 2025, 20, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGoron, A.J.; Garcia, J.M.; Uluvar, B.; Gulec, S.A. Thyroid differentiation profile for differentiated thyroid cancer. Endocr. Oncol. 2025, 5, e240072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabi, E.M. The role of genetic and epigenetic modifications as potential biomarkers in the diagnosis and prognosis of thyroid cancer. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1474267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikiforov, Y.E. Genetic alterations involved in the transition from well-differentiated to poorly differentiated and anaplastic thyroid carcinomas. Endocr. Pathol. 2004, 15, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkhardt, A.; Smith, C.L.; Singh, R.R. Validation of a Compact and Self-Contained Pyrosequencing Platform for Clinical Screening of RAS Mutations in Thyroid Cancers. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccio, I.; Laforteza, A.; Landau, M.B.; Hussein, M.H.; Linhuber, J.; Staav, J.; Issa, P.P.; Toraih, E.A.; Kandil, E. Decoding RAS mutations in thyroid cancer: A meta-analysis unveils specific links to distant metastasis and increased mortality. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2025, 46, 104570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsou, P.; Wu, C.J. Classifying driver mutations of papillary thyroid carcinoma on whole slide image: An automated workflow applying deep convolutional neural network. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1395979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, M.; Carlomagno, F. Central role of RET in thyroid cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a009233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforov, Y.E. RET/PTC rearrangement in thyroid tumors. Endocr. Pathol. 2002, 13, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khonrak, T.; Watcharadetwittaya, S.; Chamgramol, Y.; Intarawichian, P.; Deenonpoe, R. RET rearrangements are relevant to histopathologic subtypes and clinicopathological features in Thai papillary thyroid carcinoma patients. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2023, 29, 1611138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, S.; Hou, Y.; Yan, Z.; Ao, X.; Wang, P.; Zhou, L.; Chen, H.; Liang, X.; et al. Low-dose ionizing radiation-induced RET/PTC1 rearrangement via the non-homologous end joining pathway to drive thyroid cancer. MedComm 2024, 5, e690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.H.; Lu, Q. Pro-oncogenic and anti-oncogenic pathways: Opportunities and challenges of cancer therapy. Future Oncol. 2010, 6, 587–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lin, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Xing, M. Coexisting RET/PTC and TERT Promoter Mutation Predict Poor Prognosis but Effective RET and MEK Targeting in Thyroid Cancer. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 109, 3166–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luciano, N.; Orlandella, F.M.; Braile, M.; Cavaliere, C.; Aiello, M.; Franzese, M.; Salvatore, G. Association of radiomic features with genomic signatures in thyroid cancer: A systematic review. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikita, M.E.; Jiang, W.; Cheng, S.M.; Hantash, F.M.; McPhaul, M.J.; Newbury, R.O.; Phillips, S.A.; Reitz, R.E.; Waldman, F.M.; Newfield, R.S. Mutational Analysis in Pediatric Thyroid Cancer and Correlations with Age, Ethnicity, and Clinical Presentation. Thyroid 2016, 26, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cendra, A.S.; Pekarek, L.; Pedrejón, B.I.; Bernier, L.; Cervantes, E.D.R.; Cendra, C.S.; Cassinello, J.; López-Gonzalez, L.; Mañez, F.; Carrero, C.B.; et al. New Horizons of Biomarkers in Metastatic Thyroid Cancer. J. Cancer 2025, 16, 241–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapio, M.R.; Guerra, A.; Marotta, V.; Campanile, E.; Formisano, R.; Deandrea, M.; Motta, M.; Limone, P.P.; Fenzi, G.; Rossi, G.; et al. High growth rate of benign thyroid nodules bearing RET/PTC rearrangements. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E916–E919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwini, B.R.; Nirmala, C.; Natarajan, M.; Biligi, D.S. A study to evaluate association of nuclear grooving in benign thyroid lesions with RET/PTC1 and RET/PTC3 gene translocation. Thyroid Res. 2023, 16, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank-Raue, K.; Rondot, S.; Raue, F. Molecular genetics and phenomics of RET mutations: Impact on prognosis of MTC. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010, 322, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachdev, C.; Gattani, R.G.; Agrawal, J. Carney Complex and Its Association with Thyroid Cancer, Molecular Pathway, and Treatment. Cureus 2023, 15, e48503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagin, J.A.; Mitsiades, N. Molecular pathology of thyroid cancer: Diagnostic and clinical implications. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 22, 955–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugaresi, M.; Moneta, C.; Saruggia, G.; Dionigi, G.; Gazzano, G.; Fugazzola, L. Changing the paradigm: Lobectomy for sporadic medullary thyroid cancer. Eur. Thyroid J. 2025, 14, e250040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuahmed, M.Y.; Rashid, R.; Aboelwafa, W.A.; Hamza, Y.M. The Oncologic Outcomes of Bilateral Central Lymph Node Dissection in Unilobar Papillary Thyroid Cancer and Its Risks: A Prospective Cohort Study. Cureus 2024, 16, e65443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hay, I.D.; Gonzalez-Losada, T.; Reinalda, M.S.; Honetschlager, J.A.; Richards, M.L.; Thompson, G.B. Long-term outcome in 215 children and adolescents with papillary thyroid cancer treated during 1940 through 2008. World J. Surg. 2010, 34, 1192–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozel, T.M.; Soytas, Y.; Akbulut, S.; Celik, A.; Yildiz, G.; Karatay, H.; Sari, S. The necessity of prophylactic central lymph node dissection in clinically n0 papillary thyroid carcinoma: Perspective from the endemic region. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2025, 410, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moo, T.A.; McGill, J.; Allendorf, J.; Lee, J.; Fahey, T., 3rd; Zarnegar, R. Impact of prophylactic central neck lymph node dissection on early recurrence in papillary thyroid carcinoma. World J. Surg. 2010, 34, 1187–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, D.S.; Yang, L.; Huang, Y.H.; He, Y.; Chen, M.S.; Wang, Z.Y.; Fan, L.; Yang, H.W. A nomogram based on the 3-gene signature and clinical characteristics for predicting lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid cancer. Cancer Biomark. 2025, 42, 18758592241311195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomeli, S.R.; LeBeau, S.O.; Ferris, R.L. Evaluation of a thyroid nodule. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 43, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasim, S.; Dean, D.S.; Gharib, H. Fine-Needle Aspiration of the Thyroid Gland. In Endotext; Feingold, K.R., Ahmed, S.F., Anawalt, B., Blackman, M.R., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., Corpas, E., de Herder, W.W., Dhatariya, K., Dungan, K., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Gopalan, V.; Deshpande, S.G.; Zade, A.A.; Tote, D.; Rajendran, R.; Durge, S.; Bhargava, A. Advances in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Review. Cureus 2024, 16, e66186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekel, M.; Nucera, C.; Hodin, R.A.; Parangi, S. Surgical implications of B-RafV600E mutation in fine-needle aspiration of thyroid nodules. Am. J. Surg. 2010, 200, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yamazaki, H.; Sugino, K.; Katoh, R.; Matsuzu, K.; Kitagawa, W.; Nagahama, M.; Saito, A.; Ito, K. Management of follicular thyroid carcinoma. Eur. Thyroid J. 2024, 13, e240146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante, C.; Hegedüs, L.; Czarniecka, A.; Paschke, R.; Russ, G.; Schmitt, F.; Soares, P.; Solymosi, T.; Papini, E. 2023 European Thyroid Association Clinical Practice Guidelines for thyroid nodule management. Eur. Thyroid J. 2023, 12, e230067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, E.; Angelos, P.; Applewhite, M.; Mercier, F.; Grogan, R.H. Chapter 21 SURGERY OF THE THYROID. In Endotext; Feingold, K.R., Ahmed, S.F., Anawalt, B., Blackman, M.R., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., Corpas, E., de Herder, W.W., Dhatariya, K., Dungan, K., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Kong, D.; Bu, L.; Wu, G. Surgical management for follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 79507–79516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantinidis, A.; Stang, M.; Roman, S.A.; Sosa, J.A. Surgical management of medullary thyroid carcinoma. Updates Surg. 2017, 69, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniuchi, M.; Kawata, R.; Terada, T.; Higashino, M.; Aihara, T.; Jinnin, T. Central node dissection from the perspective of lateral neck node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Auris Nasus Larynx 2024, 51, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machens, A.; Dralle, H. Surgical Treatment of Medullary Thyroid Cancer. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2025, 223, 247–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.V.; Hughes, E.G.; Steinmetz, D.; Troob, S.; Kim, J.; Tseng, C.H.; Fishbein, G.A.; Sajed, D.P.; Livhits, M.J.; Yeh, M.W.; et al. Extent of Surgery for Medullary Thyroid Cancer and Prevalence of Occult Contralateral Foci. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2024, 150, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleere, E.F.; Crotty, T.J.; Hintze, J.M.; Fitzgerald, C.W.R.; Kinsella, J.; Lennon, P.; Timon, C.V.I.; Woods, R.S.R.; Shine, N.P.; O’Neill, J.P. The role of surgery for anaplastic thyroid carcinoma in the era of targeted therapeutics: A scoping review. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2023, 8, 1673–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliinyk, D.; Augustin, T.; Rauch, J.; Koehler, V.F.; Belka, C.; Spitzweg, C.; Käsmann, L. Role of surgery to the primary tumor in metastatic anaplastic thyroid carcinoma: Pooled analysis and SEER-based study. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol.. 2023, 149, 3527–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koda, K.; Katoh, M.; Yasuhara, K. Management of anaplastic thyroid cancer and proposed treatment guidelines-A 5-year case series study. Cancer Rep. 2022, 5, e1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIver, B.; Hay, I.D.; Giuffrida, D.F.; Dvorak, C.E.; Grant, C.S.; Thompson, G.B.; van Heerden, J.A.; Goellner, J.R. Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma: A 50-year experience at a single institution. Surgery 2001, 130, 1028–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Helman, S.N.; Hanly, E.; Likhterov, I. The role of surgery in anaplastic thyroid cancer: A systematic review. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2017, 38, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luster, M.; Clarke, S.E.; Dietlein, M.; Lassmann, M.; Lind, P.; Oyen, W.J.; Tennvall, J.; Bombardieri, E.; European Association of Nuclear Medicine (EANM). Guidelines for radioiodine therapy of differentiated thyroid cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2008, 35, 1941–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erten, A.; Abidin Sayiner, Z.; Erkılıç, S.; Oğuzkan Balcı, S.; Akarsu, E. The effect of SLC5A5 gene expression in tumor tissues on refractoriness to radioactive iodine treatment of differentiated thyroid carcinomas. Qatar Med. J. 2025, 2025, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weis, H.; Weindler, J.; Schmidt, K.; Hellmich, M.; Drzezga, A.; Schmidt, M. Impact of Radioactive Iodine Treatment on Long-Term Relative Survival in Patients with Papillary and Follicular Thyroid Cancer: A SEER-Based Study Covering Histologic Subtypes and Recurrence Risk Categories. J. Nucl. Med. 2025, 66, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhu, C.; Huang, S.; Xu, M.; Li, C.; Fu, H.; Yin, Y.; Liang, S.; Wang, H.; Cui, Z.; et al. Efficient delivery of anlotinib and radioiodine by long circulating nano-capsules for active enhanced suppression of anaplastic thyroid carcinoma. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2025, 23, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padda, I.S.; Nguyen, M. Radioactive Iodine Therapy. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Van Nostrand, D.; Wartofsky, L. Radioiodine in the treatment of thyroid cancer. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2007, 36, 807–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparano, C.; Moog, S.; Hadoux, J.; Dupuy, C.; Al Ghuzlan, A.; Breuskin, I.; Guerlain, J.; Hartl, D.; Baudin, E.; Lamartina, L. Strategies for Radioiodine Treatment: What’s New. Cancers 2022, 14, 3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orosco, R.K.; Hussain, T.; Noel, J.E.; Chang, D.C.; Dosiou, C.; Mittra, E.; Divi, V.; Orloff, L.A. Radioactive iodine in differentiated thyroid cancer: A national database perspective. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2019, 26, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Hu, X.; Pan, Z.; Xu, T.; Xu, J.; Jiang, L.; Huang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, M. Radioiodine therapy in advanced differentiated thyroid cancer: Resistance and overcoming strategy. Drug Resist. Updat. 2023, 68, 100939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayson, S.E.; Chan, C.M.; Haugen, B.R. Tailoring the approach to radioactive iodine treatment in thyroid cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer. 2021, 28, T125–T140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berta, D.M.; Teketelew, B.B.; Cherie, N.; Tamir, M.; Abriham, Z.Y.; Ayele Angelo, A.; Tarekegne, A.M.; Chane, E.; Mulatie, Z.; Walle, M. Effect of radioactive iodine therapy on hematological parameters in patients with thyroid cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 16, 1562851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, A.S.; McKenzie, G.A.G.; Green, V.; Schettino, G.; England, R.J.A.; Greenman, J. The effect of radioiodine treatment on the diseased thyroid gland. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2019, 95, 1718–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albero, A.; Lopéz, J.E.; Torres, A.; de la Cruz, L.; Martín, T. Effectiveness of chemotherapy in advanced differentiated thyroid cancer: A systematic review. Endocr. Relat. Cancer. 2016, 23, R71–R84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veiga, L.H.; Bhatti, P.; Ronckers, C.M.; Sigurdson, A.J.; Stovall, M.; Smith, S.A.; Weathers, R.; Leisenring, W.; Mertens, A.C.; Hammond, S.; et al. Chemotherapy and thyroid cancer risk: A report from the childhood cancer survivor study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2012, 21, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.C.; Lin, G.H.; Kuang, B.H.; Cao, R.B. Emerging chemotherapy-based treatments in anaplastic thyroid cancer: An updated analysis of prospective studies. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1385747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, S.; Tchounwou, P.B. Cisplatin in cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 364–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, O.; Karen, D.; Zidan, J. Cisplatin based chemotherapy in patients with advanced differentiated thyroid carcinoma refractory to I131 treatment. Indian J. Med. Paediatr. Oncol. 2013, 34, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Matuszczyk, A.; Petersenn, S.; Bockisch, A.; Gorges, R.; Sheu, S.Y.; Veit, P.; Mann, K. Chemotherapy with doxorubicin in progressive medullary and thyroid carcinoma of the follicular epithelium. Horm. Metab. Res. 2008, 40, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullmer, T.; Cabanillas, M.E.; Zafereo, M. Novel Therapeutics in Radioactive Iodine-Resistant Thyroid Cancer. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 720723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelousi, A.; Tzoulis, P.; Tsoli, M.; Chatzellis, E.; Koumarianou, A.; Kaltsas, G. Immunotherapy for endocrine tumours: A clinician’s perspective. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2024, 31, e230296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.Z.; Ye, W.D.; Yu, P.C.; Tan, L.C.; Shi, X.; Chen, X.F.; He, C.; Hu, J.Q.; Wei, W.J.; Lu, Z.W.; et al. A distinct tumor microenvironment makes anaplastic thyroid cancer more lethal but immunotherapy sensitive than papillary thyroid cancer. JCI Insight 2024, 9, e173712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valerio, L.; Pieruzzi, L.; Giani, C.; Agate, L.; Bottici, V.; Lorusso, L.; Cappagli, V.; Puleo, L.; Matrone, A.; Viola, D.; et al. Targeted Therapy in Thyroid Cancer: State of the Art. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 29, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puliafito, I.; Esposito, F.; Prestifilippo, A.; Marchisotta, S.; Sciacca, D.; Vitale, M.P.; Giuffrida, D. Target Therapy in Thyroid Cancer: Current Challenge in Clinical Use of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and Management of Side Effects. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 860671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, Y.; Park, S.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, S.W.; Ahn, M.J.; Jung, H.A.; Chung, J.H. Combination of Dabrafenib and Trametinib in Patients with Metastatic BRAFV600E-Mutated Thyroid Cancer. Cancer Res. Treat. 2024, 56, 1270–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viola, D.; Valerio, L.; Molinaro, E.; Agate, L.; Bottici, V.; Biagini, A.; Lorusso, L.; Cappagli, V.; Pieruzzi, L.; Giani, C.; et al. Treatment of advanced thyroid cancer with targeted therapies: Ten years of experience. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2016, 23, R185–R205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Feng, Q.; Wang, J.; Tan, Z.; Li, Q.; Ge, M. Molecular basis and targeted therapy in thyroid cancer: Progress and opportunities. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2023, 1878, 188928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Omri, M.; Gabsi, O.; Bellakhdher, M.; Ghammem, M.; Kermani, W.; Abdelkefi, M. Management of Thyroid Nodules in Children: A single-center experience. Iran J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2025, 37, 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Duval, M.A.D.S.; Zanella, A.B.; Cristo, A.P.; Faccin, C.S.; Graudenz, M.S.; Maia, A.L. Impact of Serum TSH and Anti-Thyroglobulin Antibody Levels on Lymph Node Fine-Needle Aspiration Thyroglobulin Measurements in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Patients. Eur. Thyroid J. 2017, 6, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbiah, V.; Hu, M.I.; Mansfield, A.S.; Taylor, M.H.; Schuler, M.; Zhu, V.W.; Hadoux, J.; Curigliano, G.; Wirth, L.; Gainor, J.F.; et al. Pralsetinib in Patients with Advanced/Metastatic Rearranged During Transfection (RET)-Altered Thyroid Cancer: Updated Efficacy and Safety Data from the ARROW Study. Thyroid. 2024, 34, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratajczak, M.; Gaweł, D.; Godlewska, M. Novel Inhibitor-Based Therapies for Thyroid Cancer—An Update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.F.; Repetto, M.; Wilhelm, C.; Drilon, A. RET Inhibitors in RET Fusion-Positive Lung Cancers: Past, Present, and Future. Drugs. 2024, 84, 1035–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capdevila, J.; Wirth, L.J.; Ernst, T.; Aix, S.P.; Lin, C.-C.; Ramlau, R.; Butler, M.O.; Delord, J.-P.; Gelderblom, H.; Ascierto, P.A.; et al. PD-1 Blockade in Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 2620–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. U.S. National Library of Medicine: Bethesda, MD, USA. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 8 April 2025).
- Pulumati, A.; Pulumati, A.; Dwarakanath, B.S.; Verma, A.; Papineni, R.V.L. Technological advancements in cancer diagnostics: Improvements and limitations. Cancer Rep. 2023, 6, e1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, J.K.; Branstetter, B.F., 4th; Gafton, A.R.; Lee, W.K.; Glastonbury, C.M. Imaging of thyroid carcinoma with CT and MRI: Approaches to common scenarios. Cancer Imaging 2013, 13, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, R.B.; Wang, Q.G.; Liu, C.; Liu, F.; Zhao, Q.; Han, J.G.; Ren, D.L.; Liu, B.; Li, C.L. Low versus high radioiodine activity for ablation of the thyroid remnant after thyroidectomy in Han Chinese with low-risk differentiated thyroid cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2017, 10, 4051–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Yang, L.; Sun, Z.; Zhan, X. Personalized Drug Therapy: Innovative Concept Guided with Proteoformics. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2024, 23, 100737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conroy, P.C.; Wilhelm, A.; Calthorpe, L.; Ullmann, T.M.; Davis, S.; Huang, C.Y.; Shen, W.T.; Gosnell, J.; Duh, Q.Y.; Roman, S.; et al. Endocrine surgeons are performing more thyroid lobectomies for low-risk differentiated thyroid cancer since the 2015 ATA guidelines. Surgery 2022, 172, 1392–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Jeon, M.J.; Song, E.; Oh, H.S.; Kim, M.; Kwon, H.; Kim, T.Y.; Hong, S.J.; Shong, Y.K.; Kim, W.B.; et al. Clinical Features of Early and Late Postoperative Hypothyroidism After Lobectomy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, M.S.R.; Pozas, J.; Molina-Cerrillo, J.; Gómez, J.; Pian, H.; Pozas, M.; Carrato, A.; Grande, E.; Alonso-Gordoa, T. Current and Future Role of Tyrosine Kinases Inhibition in Thyroid Cancer: From Biology to Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-R.; Du, B.; Liu, H.-Q.; Chen, C. Artificial Intelligence for Personalized Medicine in Thyroid Cancer: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Front. Oncol. 2021, 10, 604051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modica, R.; Benevento, E.; Colao, A. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) and cancer: New perspectives on an old relationship. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2022, 46, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panagiotidis, E.; Zhang-Yin, J.T. The Role of Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography in the Management of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Current Applications and Future Perspectives. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
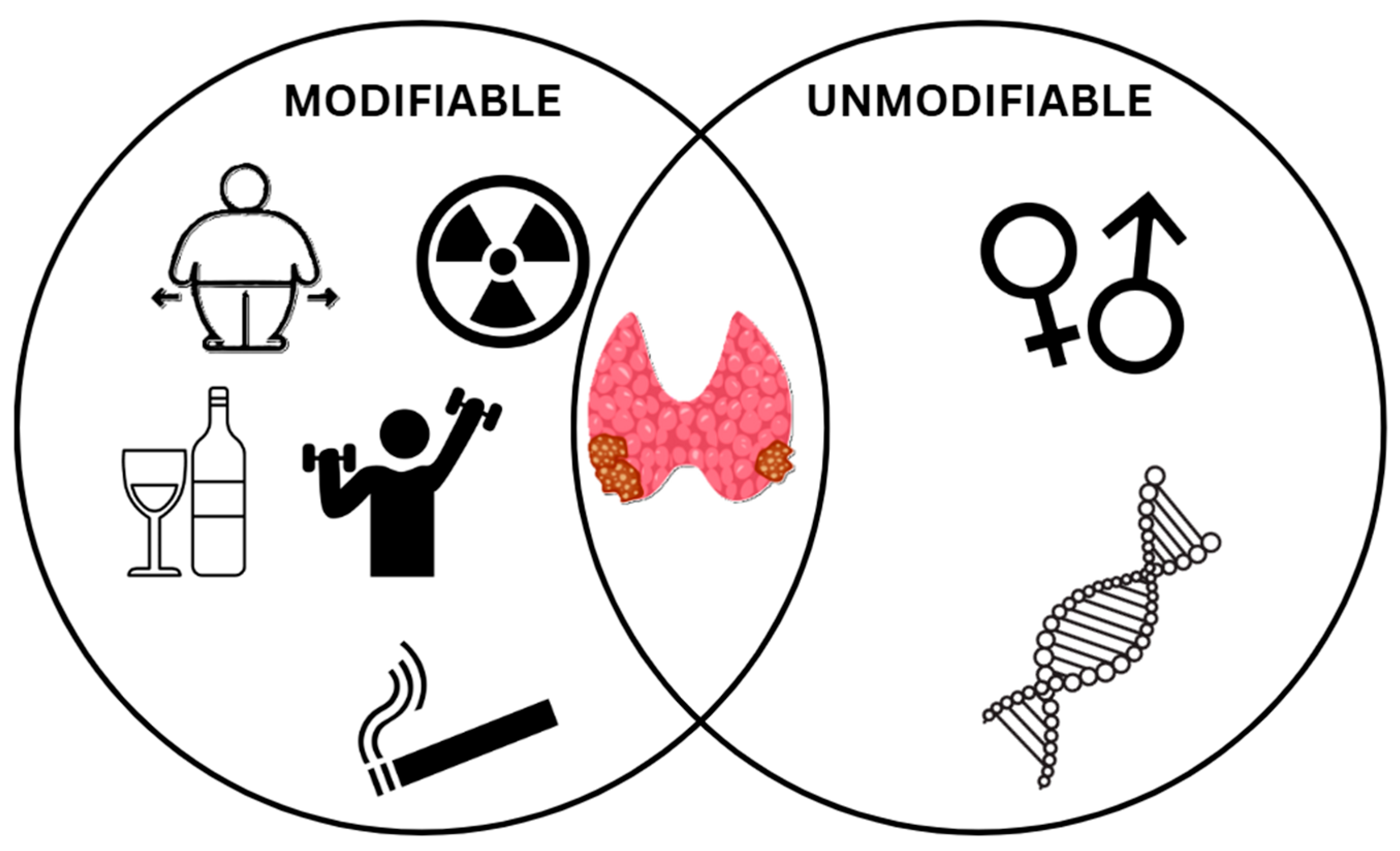
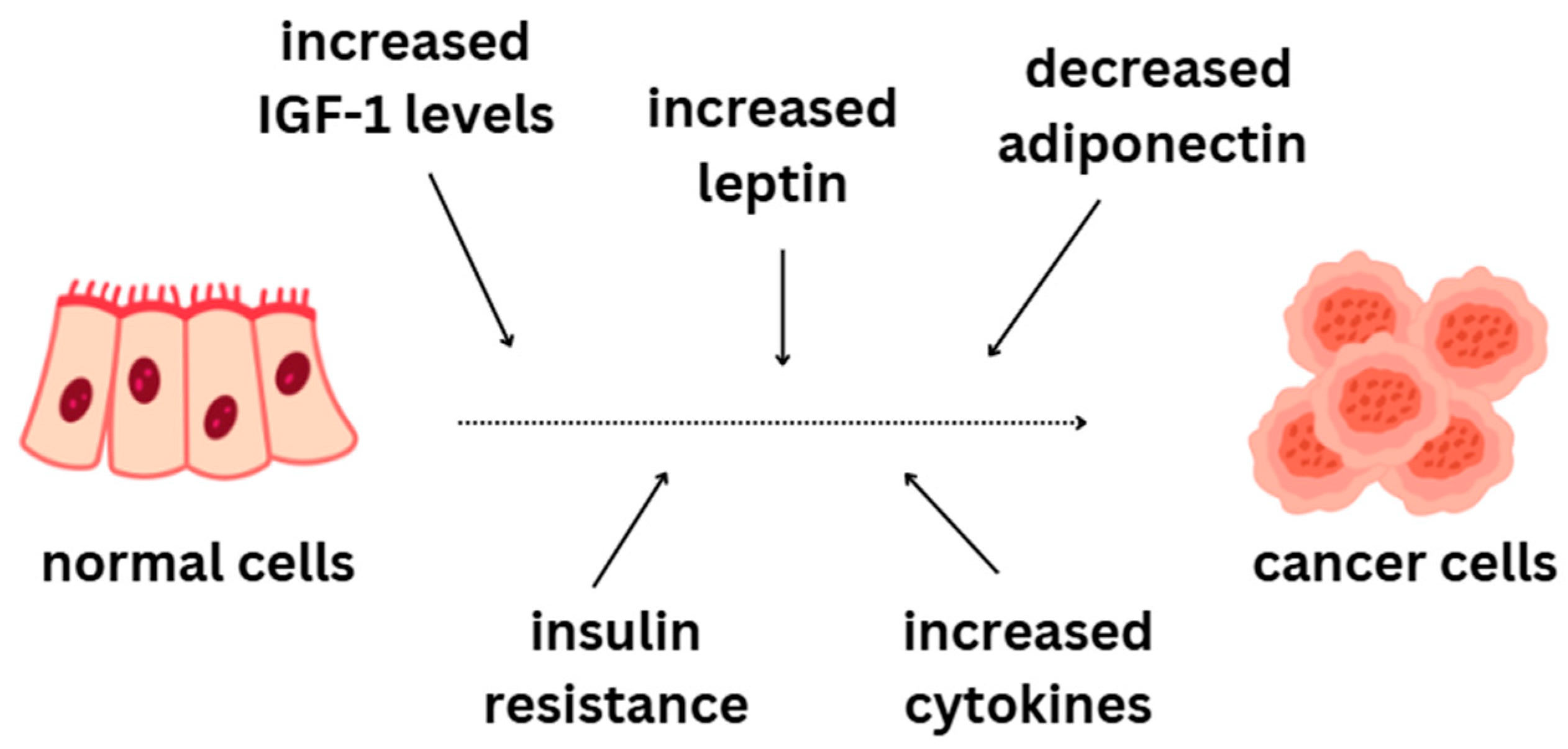
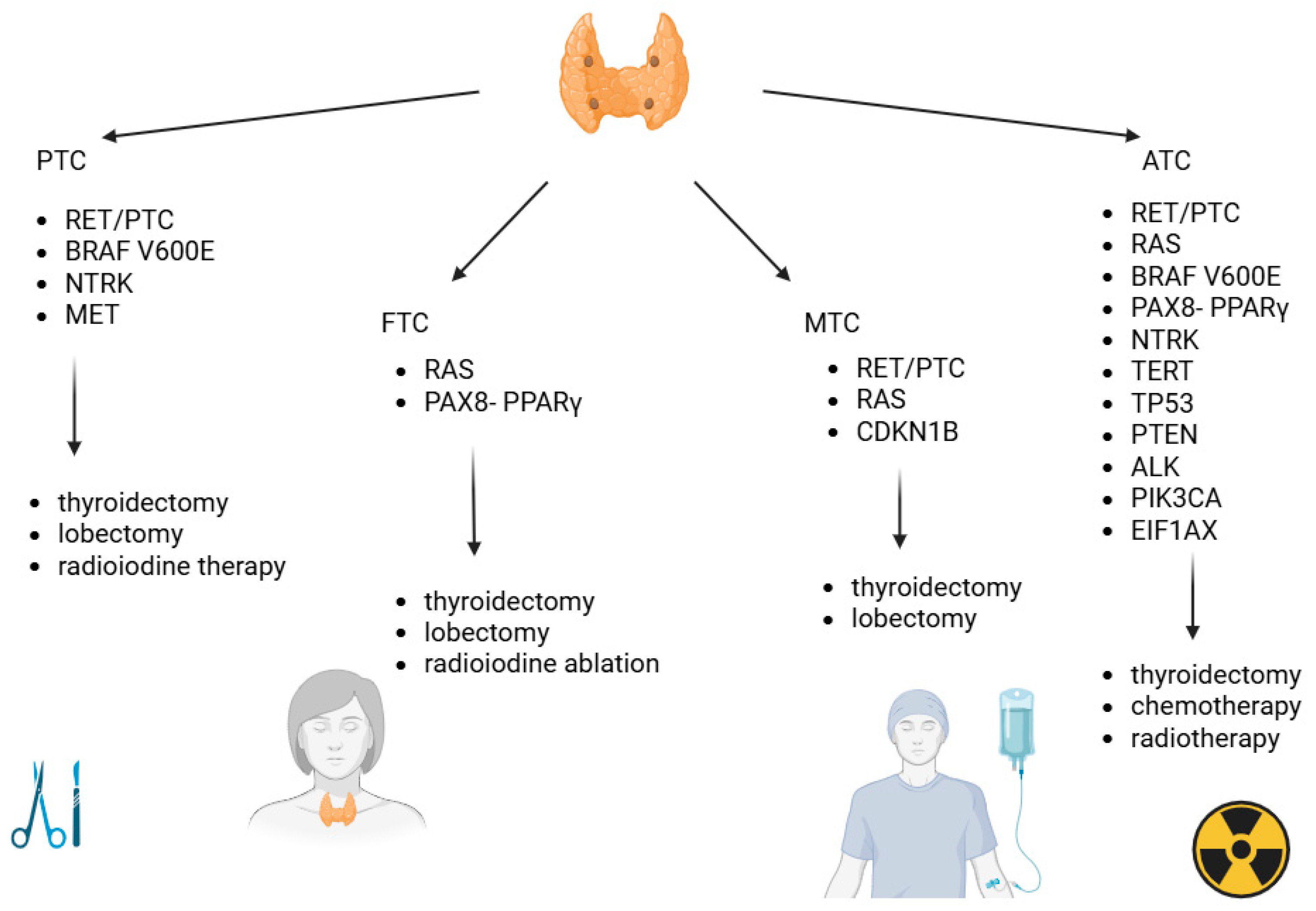
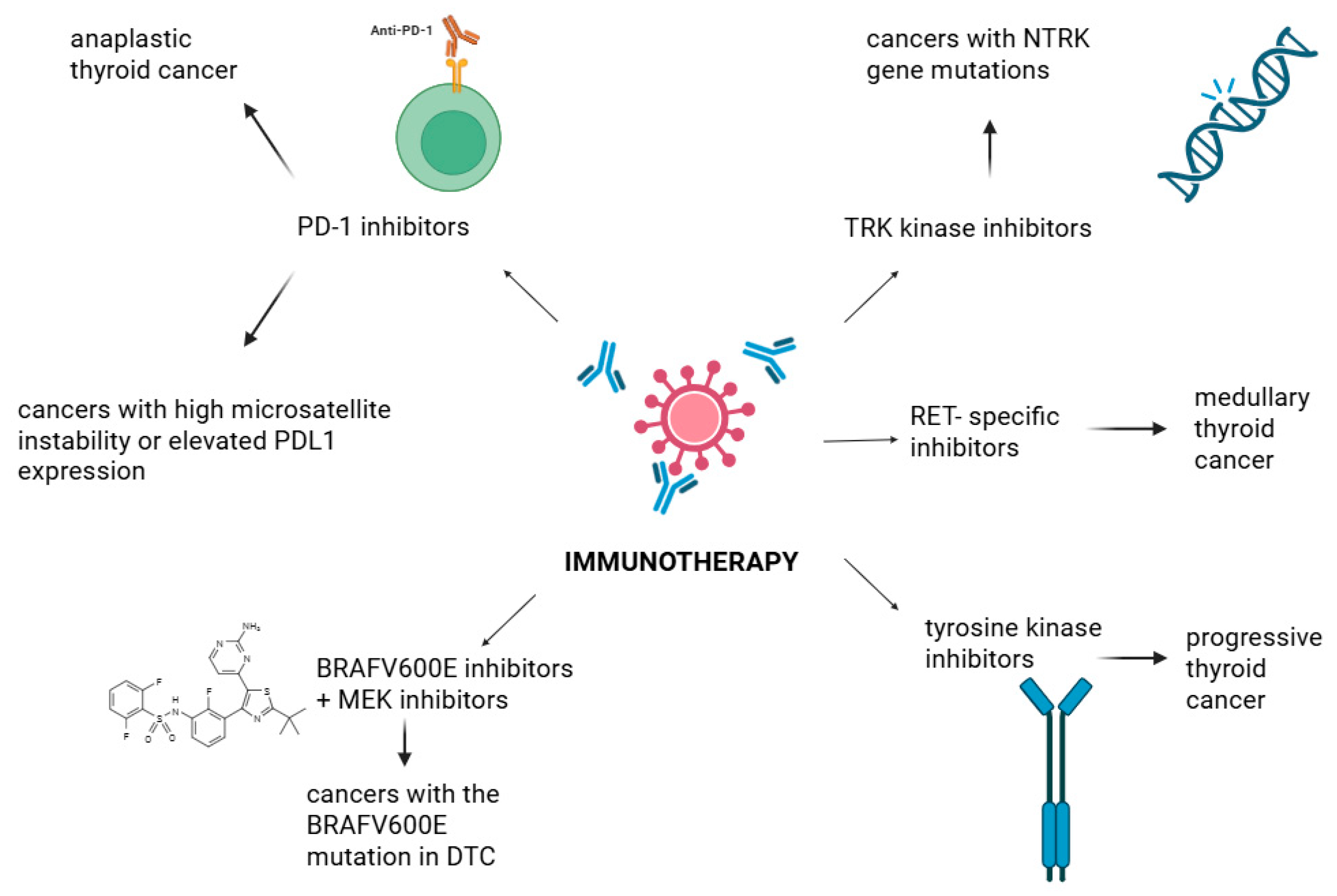
| Type of Cancer/Mutation | Papillary (PTC) | Medullary (MTC) | Follicular (FTC) | Anaplastic (ATC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RET/PTC | + | + | − | + |
| RAS | − | + | + | + |
| BRAF V600E | + | − | − | + |
| PAX8-PPARγ | − | − | + | + |
| NTRK | + | − | − | + |
| MET | + | − | − | − |
| CDKN1B | − | + | − | |
| TERT | − | − | − | + |
| TP53 | − | − | − | + |
| PTEN | − | − | − | + |
| ALK | − | − | − | + |
| PIK3CA | − | − | − | + |
| EIF1AX | − | − | − | + |
| Cancer Type | PTC | FTC | MTC | ATC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incidence (% of all TC cases) | 90% | 20% | 1–5% | 2% |
| Age | 30–50 years old | 40–50 years old | 40–60 years old | Over 65 years old |
| Prognosis | Relatively mild cancer | 80% mild; 20% aggressive | Poor prognosis | Very poor prognosis |
| Metastatic potential | 70% of patients present metastases to the lymph nodes of the neck | Metastases present more often than in PTC cases | High probability of metastasis | 20–50% of ATC cases present metastases |
| Diagnostic Technique | Diagnostic Value | Limitations | Recommendations (ATA, NCCN) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ultrasound (US) | Primary method for evaluating thyroid nodules, detects features suspicious for malignancy (e.g., microcalcifications) [131] | May not be sufficient for definitive diagnosis, especially in indeterminate nodules [136] | Recommended as the first step in diagnosis (ATA, NCCN) [133] |
| Fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) | Cytological evaluation helps assess malignancy risk, particularly in indeterminate nodules [133] | Results can be indeterminate for Bethesda III/IV nodules [137] | Essential for indeterminate nodules (ATA, NCCN) [135] |
| Molecular genetic testing | Increases diagnostic accuracy, particularly for Bethesda III/IV nodules, aiding in treatment planning [137] | High cost, availability may be limited, not always accessible in every center [137] | Recommended for indeterminate nodules (ATA, NCCN) [137] |
| Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) | Helps assess malignant changes and potential metastasis [135] | Requires specialized equipment, less useful for evaluating small nodules [136] | Recommended in advanced disease, particularly for metastasis assessment (ATA) [71] |
| Computed tomography (CT) | Useful for assessing metastasis, especially in advanced cases [71] | Limited value for diagnosing early thyroid tumors [135] | Recommended for metastasis assessment (NCCN) [71] |
| Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) | Helps differentiate between benign and malignant nodules, especially in advanced disease [134] | Expensive, time-consuming, requires specialized equipment [134] | Recommended for assessing local invasion and metastasis (NCCN) [134] |
| PET/CT, PET/MRI | Advanced techniques useful for assessing poorly differentiated or dedifferentiated TC [142,143] | Expensive, limited availability in some centers [142,143] | Recommended in advanced TC, particularly for staging and follow-up (ATA, NCCN) [142,143] |
| High-throughput sequencing (NGS, WES, RNA-Seq) | Allows for the complete profiling of genetic changes (mutations, fusions, expression), which enhances diagnosis and tailored therapy selection in intermediate or aggressive situations [151,152,154] | Expensive, requires bioinformatics support, limited access in some contexts [156] | Suggested in cases of ambiguous cytology or probable advanced illness (ATA, NCCN) [153,155] |
| Marker | Subtype(s) | Clinical Application | Limitations/Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thyroglobulin (Tg) | PTC, FTC (DTC) [157,158,159,160] | Recurrence detection, residual disease monitoring, preoperative risk assessment [158,161,165] | Affected by TgAb; also secreted by benign thyroid remnants [163,164] |
| Calcitonin (Ctn) | MTC [167,168] | Early diagnosis, postoperative monitoring, biochemical cure assessment [169,171,172,173,175] | Elevated in non-malignant conditions; rapidly degraded in plasma [168,170] |
| Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) | MTC [177,179,181] | Disease progression monitoring, aggressiveness estimation [179,183,186,187,189] | Non-specific; influenced by liver function; high levels correlate with poor prognosis [180,181,185,186] |
| Procalcitonin (Pct) | MTC [190,198] | Tumor size correlation, progression monitoring; adjunct to Ctn and CEA [190,198,199] | Elevated in infections, trauma, surgery; not exclusive to C cells [191,192,193,195] |
| TSH | PTC, FTC (DTC) [202,204] | Postoperative management, recurrence risk stratification [205,206,208,209] | Oversuppression risks (e.g., osteoporosis); complex relationship with recurrence [207,210,211] |
| miRNAs | PTC, FTC, ATC [212,217] | Diagnostic and prognostic value, patient stratification [216,220,221,224,225] | Experimental; conflicting evidence; requires clinical validation [218,219,222,223] |
| BRAF V600E | PTC, ATC [218,229,232] | Risk of lymph node metastasis, iodine-refractory tumor indication [227,228,232] | Not reliable as a sole prognostic marker in low-risk disease [230,231,233] |
| RAS mutations | FTC, PTC (follicular variant), ATC [234,236,237] | Diagnostic aid, metastatic risk, mortality prediction [239,240,241] | Common in follicular-pattern tumors; also present in benign lesions [238,242] |
| RET/PTC rearrangements | PTC (esp. radiation-induced), pediatric MTC [244,246,250] | Diagnostic relevance, aggressive behavior predictor, pediatric cases [249,250,251] | Present in both benign and malignant lesions; strongly linked to radiation exposure [252,253] |
| Type of Thyroid Cancer | First-Line Therapy | Second-Line Therapy |
|---|---|---|
| PCT |
| |
| FTC |
| |
| MTC |
|
|
| ATC |
| |
| RAI-refractory DTC |
|
|
| RET/NTRK mutated cancers |
|
|
| Study ID (NCT) | Drug Combination | Molecular Target | Thyroid Cancer Type | Phase | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT04760288 | Pralsetinib vs. standard care | RET | RET-mutant MTC | 3 | Recruiting |
| NCT04006676 | Pralsetinib | RET | MTC | 1/2 | Active, not recruiting |
| NCT03954791 | Entrectinib | NTRK | NTRK fusion-positive thyroid cancers | 2 | Completed |
| NCT04222972 | Spartalizumab + lenvatinib | PD-1 + VEGF | ATC | 1/2 | Recruiting |
| NTC03157128 | Selpercatinib | RET inhibitor | MTC, DTC | 1/2 | Completed |
| NTC03037385 | Pralsetinib | RET inhibitor | MTC, DTC | 1/2 | Completed |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Forma, A.; Kłodnicka, K.; Pająk, W.; Flieger, J.; Teresińska, B.; Januszewski, J.; Baj, J. Thyroid Cancer: Epidemiology, Classification, Risk Factors, Diagnostic and Prognostic Markers, and Current Treatment Strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115173
Forma A, Kłodnicka K, Pająk W, Flieger J, Teresińska B, Januszewski J, Baj J. Thyroid Cancer: Epidemiology, Classification, Risk Factors, Diagnostic and Prognostic Markers, and Current Treatment Strategies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115173
Chicago/Turabian StyleForma, Alicja, Karolina Kłodnicka, Weronika Pająk, Jolanta Flieger, Barbara Teresińska, Jacek Januszewski, and Jacek Baj. 2025. "Thyroid Cancer: Epidemiology, Classification, Risk Factors, Diagnostic and Prognostic Markers, and Current Treatment Strategies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115173
APA StyleForma, A., Kłodnicka, K., Pająk, W., Flieger, J., Teresińska, B., Januszewski, J., & Baj, J. (2025). Thyroid Cancer: Epidemiology, Classification, Risk Factors, Diagnostic and Prognostic Markers, and Current Treatment Strategies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115173








