Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals Candidate Genes Regulating Plant Height and First-Branch Height in Brassica napus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Phenotypic Variations for PH and FBH
2.2. Genotype Analysis
2.3. Genome-Wide Association Mapping for PH and FBH
2.4. Haplotype Analysis of Peak SNPs
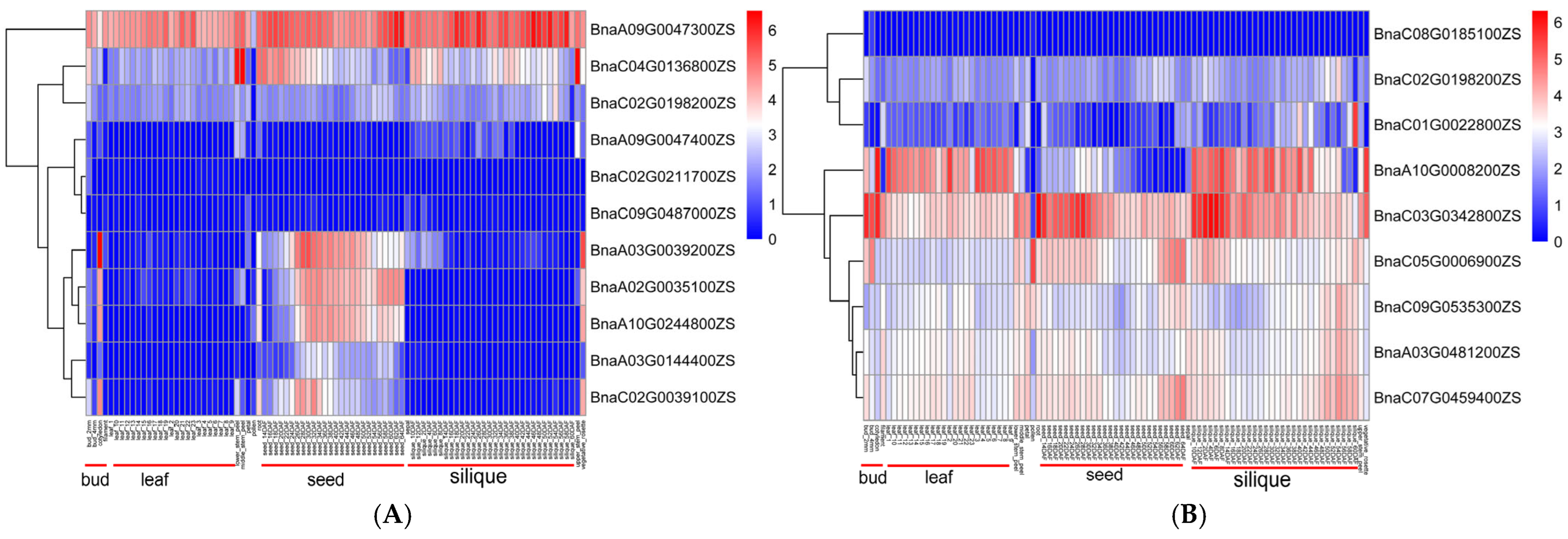
2.5. Gene Annotation and Candidate Gene Prediction
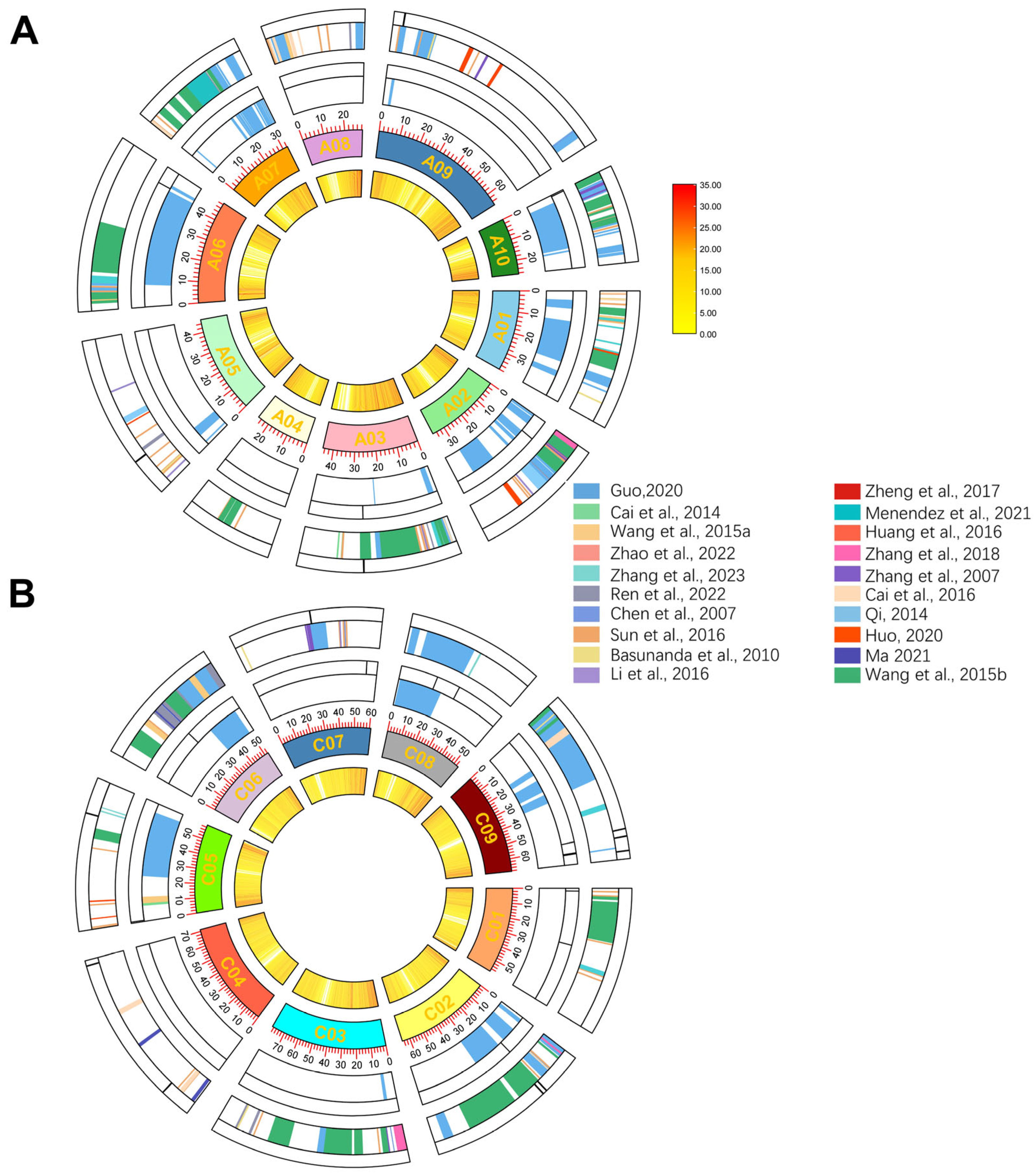
2.6. Meta-Analysis of QTLs Controlling PH and FBH in Rapessed
3. Discussion
3.1. Novel QTLs Associated with PH and FBH
3.2. Further Functional Analyses of Candidate Genes
3.3. Visualizing QTL Through Meta-Analysis
3.4. QTL Detection: Effects of Background and Sample Size
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Phenotyping and Data Analysis
4.3. Genotyping Data Processing
4.4. Genome-Wide Association Analyses
4.5. Gene Functional Annotation
4.6. Assessing Allelic Contributions to PH and FBH
4.7. Integration of Localization Insights for PH and FBH in Rapeseed
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, D.; Jing, J.; Snowdon, R.J.; Mason, A.S.; Shen, J.; Meng, J.; Zou, J. Exploring the Gene Pool of Brassica napus by Genomics-based Approaches. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 1693–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chmielewska, A.; Kozłowska, M.; Rachwał, D.; Wnukowski, P.; Amarowicz, R.; Nebesny, E.; Rosicka-Kaczmarek, J. Canola/Rapeseed Protein–Nutritional Value, Functionality and Food Application: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 3836–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Raman, H.; Xiang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y. De Novo Design of Future Rapeseed Crops: Challenges and Opportunities. Crop J. 2022, 10, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Yang, L.; Tang, M.; Liu, L.; Huang, J.; Tong, C.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, S.; Cheng, X.; Xie, M. Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals a GLYCOGEN SYNTHASE KINASE 3 Gene Regulating Plant Height in Brassica napus. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1061196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhardt, D.; Kuhlemeier, C. Plant Architecture. EMBO Rep. 2002, 3, 846–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Yang, Q.; Chen, H.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Fan, C.; Zhou, Y. Genetic Dissection of Plant Architecture and Yield-Related Traits in Brassica napus. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Tang, M.; Cui, X.; Zhao, C.; Tong, C.; Liu, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, J.; Cheng, X.; et al. Integrating GWAS, Linkage Mapping and Gene Expression Analyses Reveal the Genetic Control of First Branch Height in Brassica napus L. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1080999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Zhan, L.; Zhang, J.; Song, W.; Xu, X. Identification of Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) Plant Height-Associated QTL Using BSA-Seq and RNA-Seq. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikorska, A.; Gugała, M.; Zarzecka, K.; Mystkowska, I.; Ginter, A.; Findura, P.; Pristavka, M. Biometric Characteristics of Winter Rape Plants (Brassica napus L.) before Harvest in the Soil and Climatic Conditions of North-Eastern Poland. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0289947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Pei, W.; Ma, Q.; Geng, Y.; Liu, G.; Liu, J.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, M.; Li, X.; et al. QTL Analysis and Candidate Gene Identification for Plant Height in Cotton Based on an Interspecific Backcross Inbred Line Population of Gossypium Hirsutum × Gossypium Barbadense. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2019, 132, 2663–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xiang, F.; Zhang, W.; Yan, J.; Li, X.; Zhong, M.; Yang, P.; Chen, C.; Liu, X.; Mao, D.; et al. Characterization and Fine Mapping of a New Dwarf Mutant in Brassica napus. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, R.; Liu, W.; Yao, M.; Jia, Y.; Huang, L.; Li, W.; Guan, M.; Liu, Z.; Guan, C.; Hua, W.; et al. Regional Association and Transcriptome Analysis Revealed Candidate Genes Controlling Plant Height in Brassica napus. Mol. Breed. 2022, 42, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Gong, R.; Zhong, H.; Dai, C.; Zhang, R.; Dong, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Hu, J. Integrated Multi-Locus Genome-Wide Association Studies and Transcriptome Analysis for Seed Yield and Yield-Related Traits in Brassica napus. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1153000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuai, J.; Sun, Y.; Zuo, Q.; Huang, H.; Liao, Q.; Wu, C.; Lu, J.; Wu, J.; Zhou, G. The Yield of Mechanically Harvested Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) Can Be Increased by Optimum Plant Density and Row Spacing. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Cui, Z.; Lu, Y.; Lv, X.; Cao, Q.; Hou, Y.; Yang, X.; Gu, Y. Maize Grain Yield Enhancement in Modern Hybrids Associated with Greater Stalk Lodging Resistance at a High Planting Density: A Case Study in Northeast China. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.N.; Harper, A.L.; Trick, M.; Wellner, N.; Werner, P.; Waldron, K.W.; Bancroft, I. Dissecting the Complex Regulation of Lodging Resistance in Brassica napus. Mol. Breed. 2018, 38, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, L.; Ma, Z. Screen Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus) Suitable for Low-Loss Mechanized Harvesting. Agriculture 2021, 11, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, Y. Study on Pod Shatter Resistance, Plant Type Structure and Reel Mechanism for Low-Loss Mechanized Harvesting. Ph.D. Thesis, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Su, J.; Jia, F.; He, Y.; Liao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, J.; Guan, Z.; Fang, W.; Chen, F.; et al. Genetic Architecture and Genomic Prediction of Plant Height-Related Traits in Chrysanthemum. Hortic. Res. 2024, 11, uhad236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, B.; Tu, J.; Tingdong, F. Detection of QTL for Six Yield-Related Traits in Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus) Using DH and Immortalized F2 Populations. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2007, 115, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.U.; Saeed, S.; Khan, M.H.U.; Fan, C.; Ahmar, S.; Arriagada, O.; Shahzad, R.; Branca, F.; Mora-Poblete, F. Advances and Challenges for QTL Analysis and GWAS in the Plant-Breeding of High-Yielding: A Focus on Rapeseed. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B.; Yang, X.; Hammond, J.P.; Ding, G.; Wang, S.; Cai, H.; Wang, C.; Xu, F.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study Dissects the Genetic Control of Plant Height and Branch Number in Response to Low-Phosphorus Stress in Brassica napus. Ann. Bot. 2021, 128, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Zhang, L.; Tang, M.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Yang, H.; Fan, S.; Terzaghi, W.; Wang, H.; Hua, W. Knockout of Two Bna MAX 1 Homologs by CRISPR/Cas9-targeted Mutagenesis Improves Plant Architecture and Increases Yield in Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, D.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, W.; Ye, W.; Wang, B.; Younas, M.; Wu, J.; Liu, K. Association Mapping of Six Yield-Related Traits in Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2014, 127, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Alam, M.K.; Xie, M.; Yang, L.; Liu, J.; Helal, M.M.U.; Huang, J.; Cheng, X.; Liu, Y.; Tong, C.; et al. Mapping of a Major QTL Controlling Plant Height Using a High-Density Genetic Map and QTL-Seq Methods Based on Whole-Genome Resequencing in Brassica napus. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2021, 11, jkab118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y. Genetic Analysis of Stalk Bending Force and Cellulose Content in Rapeseed. Master’s Thesis, Oil Crops Research Institute, Graduate School, Wuhan, China, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C. Joint Linkage Analysis and Genome-Wide Association Analysis of Yield-Related Traits in Rapeseed. Master’s Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jing, L.-Y.; Jian, H.-J.; Qu, C.-M.; Chen, L.; Li, J.-N.; Liu, L.-Z. Quantitative Trait Loci Mapping for Plant Height, the First Branch Height, and Branch Number and Possible Candidate Genes Screening in Brassica napus L. Acta Agron. Sin. 2015, 41, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Long, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, J.; Zhao, W.; Li, B.; Chen, L.; Chao, H.; et al. Dynamic and Comparative QTL Analysis for Plant Height in Different Developmental Stages of Brassica napus L. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2015, 128, 1175–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wang, B.; Wang, X.; Hu, K.; Li, K.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; Yan, L.; Guan, C.; Zhang, J.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study Dissecting the Genetic Architecture Underlying the Branch Angle Trait in Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basunanda, P.; Radoev, M.; Ecke, W.; Friedt, W.; Becker, H.C.; Snowdon, R.J. Comparative Mapping of Quantitative Trait Loci Involved in Heterosis for Seedling and Yield Traits in Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2010, 120, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Peng, C.; Liu, H.; Tang, M.; Yang, H.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.; Xu, J.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals Candidate Genes for Control of Plant Height, Branch Initiation Height and Branch Number in Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menendez, Y.C.; Sanchez, D.H.; Snowdon, R.J.; Rondanini, D.P.; Botto, J.F. Unraveling the Impact on Agronomic Traits of the Genetic Architecture Underlying Plant-Density Responses in Canola. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 5426–5441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L. Molecular Mapping and Candidate Genes for Main Inflorescence Length and Stem Height in Brassica napus L. Master’s Thesis, Southwest University, Chongqing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.F.; Fu, T.D.; Zhu, J.C.; Wang, J.P.; Wen, Y.C.; Ma, C.Z.; Jiang, Y.Z. QTL Mapping and Epistasis Analysis for Plant Height and Height to the First Branch in Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). In Proceedings of the 12th International Rapeseed Congress, Preparatory Committee of the 12th International Rapeseed Congress. Wuhan, China, 26–30 March 2007; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Cheng, M.X.; Tang, M.Q.; Zhang, F.Q.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Tong, C.B.; Liu, Y.Y.; Cheng, X.H.; Dong, C.H.; Huang, J.Y.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study of Plant Height in Rapeseed RIL Population. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci. 2016, 38, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L. QTL Analysis for the Traits Associated with Plant Architecture and Silique in Brassica napus L. Ph.D. Dissertation, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, Q.; Yang, H.; Chen, Z.Y.; Jian, H.; Qu, C.; Lu, K.; Li, J. Candidate genes screening for plant height and the first branch height based on QTL map** and genome-wide association study in rapessed (Brassica napus L.). Acta Agron. Sin. 2020, 46, 214–227. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, N. Mapping of Plant Height Genes and Analysis of Candidate Genes in Brassica napus L. Master’s Thesis, College of Agronomy, Northwest A&F University, Yangling, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Chen, B.; Xu, K.; Gao, G.; Yan, G.; Qiao, J.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Li, L.; Xiao, X.; et al. A Genome-Wide Association Study of Plant Height and Primary Branch Number in Rapeseed (Brassica napus). Plant Sci. 2016, 242, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.; Li, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, P.; Jiao, Y.; Zhao, C.; Yang, G.; Hong, D. Linkage and Association Mapping of Ovule Number per Ovary (ON) in Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus L.). Mol. Breed. 2023, 43, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raboanatahiry, N.; Chao, H.; He, J.; Li, H.; Yin, Y.; Li, M. Construction of a Quantitative Genomic Map, Identification and Expression Analysis of Candidate Genes for Agronomic and Disease-Related Traits in Brassica napus. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 862363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raboanatahiry, N.; Chao, H.; Dalin, H.; Pu, S.; Yan, W.; Yu, L.; Wang, B.; Li, M. QTL Alignment for Seed Yield and Yield Related Traits in Brassica napus. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, M.A.; Guerra, R.F.; Berns, M.C.; Manzo, C.; Masiero, S.; Finzi, L.; Kater, M.M.; Colombo, L. MADS Domain Transcription Factors Mediate Short-Range DNA Looping that Is Essential for Target Gene Expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 2560–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, M.; Challa, K.R.; Sarvepalli, K.; Nath, U. CINCINNATA-Like TCP Transcription Factors in Cell Growth—An Expanding Portfolio. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 825341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimzadeh, J.; Nacry, P.; Christodoulidou, A.; Drevensek, S.; Camilleri, C.; Amiour, N.; Parcy, F.; Pastuglia, M.; Bouchez, D. Arabidopsis TONNEAU1 Proteins Are Essential for Preprophase Band Formation and Interact with Centrin. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 2146–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkenberg, B.; Witt, I.; Zanor, M.I.; Steinhauser, D.; Mueller-Roeber, B.; Hesse, H.; Hoefgen, R. Transcription Factors Relevant to Auxin Signalling Coordinate Broad-Spectrum Metabolic Shifts Including Sulphur Metabolism. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 2831–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, T.; Tanaka, A.; Inahashi, H.; Nishizawa, N.K.; Tsutsumi, N.; Inukai, Y.; Nakazono, M. Fine Control of Aerenchyma and Lateral Root Development through AUX/IAA- and ARF-Dependent Auxin Signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 20770–20775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karannagoda, N.; Spokevicius, A.; Hussey, S.; Cassan-Wang, H.; Grima-Pettenati, J.; Bossinger, G. Eucalyptus Grandis AUX/INDOLE-3-ACETIC ACID 13 (EgrIAA13) Is a Novel Transcriptional Regulator of Xylogenesis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2022, 109, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, R.; Jiang, X.; Yue, C.; Su, Y.; Ren, H.; Wang, M. A Gain-of-Function Mutant of IAA7 Inhibits Stem Elongation by Transcriptional Repression of EXPA5 Genes in Brassica napus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudolf, J.; Tomovičová, L.; Panzarová, K.; Fajkus, J.; Hejátko, J.; Skalák, J. Epigenetics and Plant Hormone Dynamics—A Functional and Methodological Perspective. J. Exp. Bot. 2024, erae054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Richards, D.E.; Fleck, B.; Xie, D.; Burton, N.; Harberd, N.P. The Arabidopsis Mutant Sleepy1gar2-1 Protein Promotes Plant Growth by Increasing the Affinity of the SCFSLY1 E3 Ubiquitin Ligase for DELLA Protein Substrates. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 1406–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, W.; Hu, Q.; Raman, H.; Liu, J. Genome-Wide Association and RNA-Seq Analyses Identify Loci for Pod Orientation in Rapeseed (Brassica napus). Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 13, 1097534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, M.J.; Spears, B.J.; Djajasaputra, A.; Van Der Gragt, M.; Vlachakis, G.; Beerens, B.; Gassmann, W.; Van Den Burg, H.A. Arabidopsis TCP Transcription Factors Interact with the SUMO Conjugating Machinery in Nuclear Foci. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ren, Z.; Li, L.; Du, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; Yi, F.; Duan, L. Meta-QTL Analysis Explores the Key Genes, Especially Hormone Related Genes, Involved in the Regulation of Grain Water Content and Grain Dehydration Rate in Maize. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selamat, N.; Nadarajah, K.K. Meta-Analysis of Quantitative Traits Loci (QTL) Identified in Drought Response in Rice (Oryza Sativa L.). Plants 2021, 10, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Yang, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, Z.; Zhu, C.; Hu, Q.; Liu, J. Decryption of Superior Allele and Candidate Genes for Total Lignin Contents of Rapeseed. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 214, 118483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hühn, M. Estimation of Broad Sense Heritability in Plant Populations: An Improved Method. Theoret. Appl. Genet. 1975, 46, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freed, D.; Aldana, R.; Weber, J.A.; Edwards, J.S. The Sentieon Genomics Tools—A Fast and Accurate Solution to Variant Calling from next-Generation Sequence Data. bioRxiv 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; De Bakker, P.I.W.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A Tool Set for Whole-Genome Association and Population-Based Linkage Analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, S.D. Qqman: An R Package for Visualizing GWAS Results Using QQ and Manhattan Plots. bioRxiv 2014, 005165. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2025; Available online: https://www.R-project.org (accessed on 15 May 2024).
- Bilgrami, S.; Liu, L.; Farokhzadeh, S.; Najafabadi, A.S.; Ramandi, H.D.; Nasiri, N.; Darwish, I. Meta-Analysis of QTLs Controlling Seed Quality Traits Based on QTL Alignment in Brassica napus. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 176, 114307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
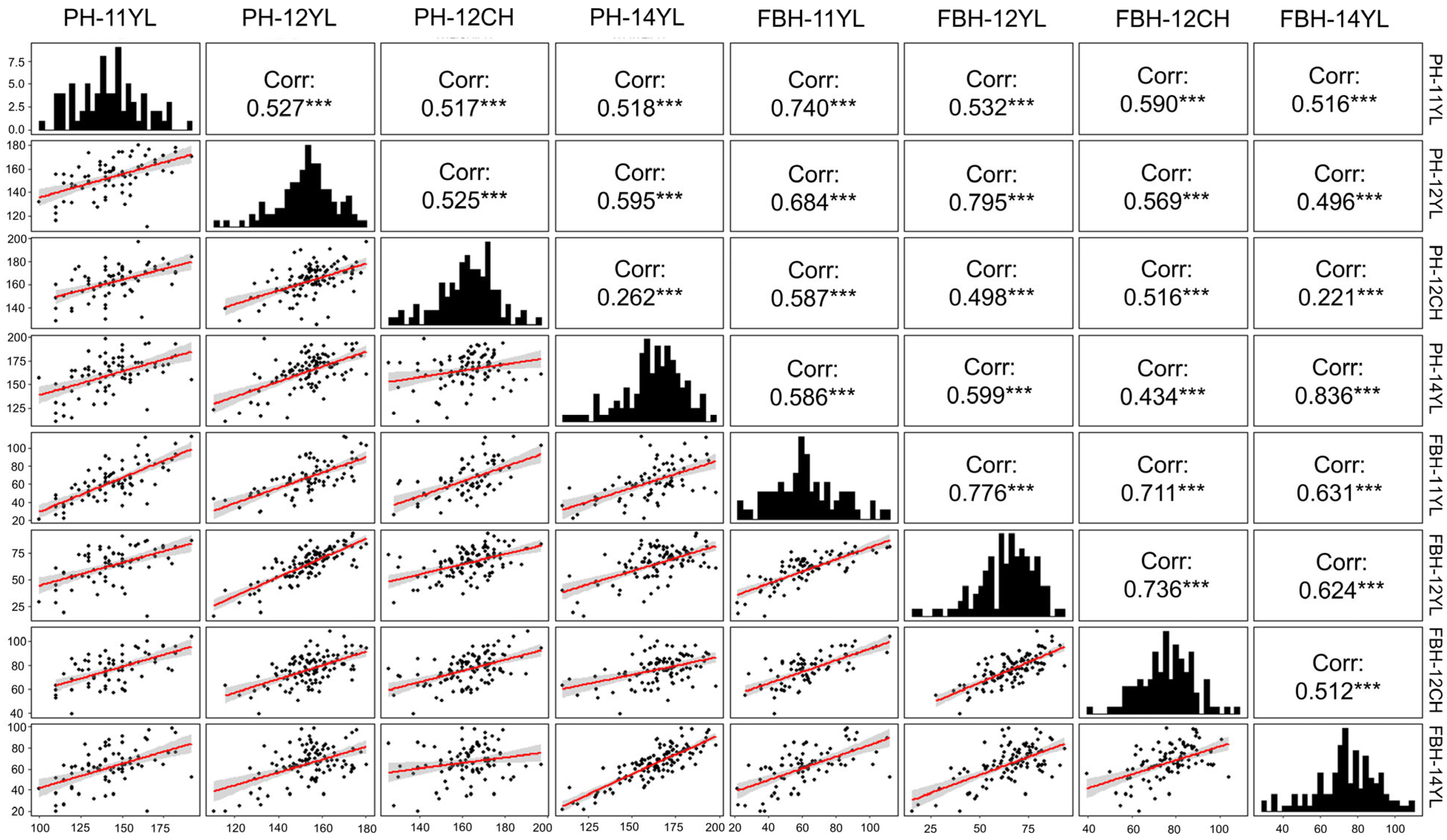



| Traits | Envirment | Min (cm) | Max (cm) | Mean b (cm) | SD | Var | CV (%) | G | E | G × E | H2% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PH | 2011 YL | 100.00 | 192.00 | 143.39 | 19.74 | 394.93 | 13.77 | 0.000 ** | 0.000 ** | 0.145 | 81.59% |
| 2012 YL | 110.53 | 180.23 | 153.11 | 13.05 | 170.23 | 8.52 | |||||
| 2012 CH | 125.30 | 197.00 | 163.09 | 13.47 | 181.47 | 8.26 | |||||
| 2014 YL | 110.70 | 198.00 | 163.17 | 17.49 | 308.36 | 10.72 | |||||
| FBH | 2011 YL | 21.60 | 112.40 | 62.27 | 20.16 | 406.55 | 32.38 | 0.000 ** | 0.000 ** | 0.835 | 77.69% |
| 2012 YL | 15.56 | 93.49 | 64.62 | 14.83 | 220.03 | 22.95 | |||||
| 2012 CH | 39.50 | 108.80 | 76.83 | 12.19 | 148.51 | 15.86 | |||||
| 2014 YL | 29.70 | 108.60 | 74.12 | 16.35 | 267.45 | 22.06 |
| Traits | QTL | Environment | SNP Information | Chr | −log10(p) Value | Physical Position (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PH | qBnPH.A05 | 11 YL | BnA05-10548415 | A05 | 6.06292651 | 10,548,428 |
| qBnPH.C04.1 | 11 YL | BnC04-12197885 | C04 | 5.35438533 | 12,197,885 | |
| qBnPH.C04.2 | 11 YL | BnC04-69054635 | C04 | 5.93871751 | 69,054,635 | |
| qBnPH.C07 | 11 YL | BnC07-32385832 | C07 | 6.18474012 | 32,385,849 | |
| qBnPH.A03 | 12 CH | BnA03-26668095 | A03 | 5.8933031 | 26,668,095 | |
| qBnPH.A09 | 12 CH | BnA09-2924514 | A09 | 5.32251692 | 2,924,514 | |
| qBnPH.C05 | 12 CH | BnC05-45487644 | C05 | 5.45243419 | 45,487,682 | |
| qBnPH.C09.2 | 12 CH | BnC09-59839160 | C09 | 5.24223678 | 59,839,160 | |
| qBnPH.C02.1 | 12 YL | BnC02-16589091 | C02 | 6.33308716 | 16,618,291 | |
| qBnPH.C09.3 | 12 YL | BnC09-65242550 | C09 | 7.0368198 | 65,242,550 | |
| qBnPH.C02.2 | 14 YL | BnC02-18325320 | C02 | 5.51436998 | 18,325,630 | |
| qBnPH.C02.3 | 14 YL | BnC02-18337801 | C02 | 7.19441013 | 18,337,869 | |
| qBnPH.C09.1 | 14 YL | BnC09-56950142 | C09 | 5.16269108 | 56,950,142 | |
| FBH | qBnFBH.C03 | 11 YL | BnA03-27045466 | A03 | 5.59538325 | 27,045,466 |
| qBnFBH.A06 | 12 CH | BnA06-42775073 | A06 | 5.56208905 | 42,775,086 | |
| qBnFBH.C06 | 12 CH | BnC06-25425361 | C06 | 5.36219091 | 25,425,373 | |
| qBnFBH.C08.1 | 12 CH | BnC08-17906537 | C08 | 5.56745805 | 17,906,542 | |
| qBnFBH.C09.1 | 12 CH | BnC09-57958042 | C09 | 5.20144207 | 57,958,080 | |
| qBnFBH.A03 | 12 YL | BnA03-26665934 | A03 | 6.30674196 | 26,665,934 | |
| qBnFBH.A10 | 12 YL | BnA10-417971 | A10 | 5.69221294 | 417,971 | |
| qBnFBH.C02 | 12 YL | BnC02-16617997 | C02 | 5.82304965 | 16,617,997 | |
| qBnFBH.C05 | 12 YL | BnC05-566653 | C05 | 5.48276675 | 566,653 | |
| qBnFBH.C07 | 12 YL | BnC07-55737453 | C07 | 7.40440208 | 55,737,453 | |
| qBnFBH.C09.3 | 12 YL | BnC09-63425475 | C09 | 5.88970586 | 63,425,475 | |
| qBnFBH.A02 | 14 YL | BnA02-7019008 | A02 | 5.34107964 | 7,019,015 | |
| qBnFBH.C01 | 14 YL | BnC01-1292356 | C01 | 5.12742125 | 1,292,356 | |
| qBnFBH.C08.2 | 14 YL | BnC08-29359074 | C08 | 5.78943439 | 29,359,078 | |
| qBnFBH.C09.2 | 14 YL | BnC09-63013243 | C09 | 5.33866552 | 63,013,469 |
| Traits | QTL | Candidate Gene ID | Gene Position (bp) | Ath Homolog | Gene Symbol | Gene Annotation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PH | qBnPH.A05 | BnaA05G0163200ZS | A05:10,547,350–10,548,463 | AT1G53180 | NA a | Unannotated |
| qBnPH.C02.3 | BnaC02G0211700ZS | C02:18,337,482–18,338,522 | AT1G67260 | TCP1 | Transcription factor TCP1 | |
| qBnPH.C04.1 | BnaC04G0136800ZS | C04:12,190,541–12,191,612 | AT2G33310 | IAA13 | Auxin-responsive protein IAA13 | |
| qBnPH.A09 | BnaA09G0047400ZS | A09:2,921,978–2,922,436 | AT5G48170 | SNE | Encodes an F-box protein whose protein sequence is similar to SLY1 | |
| BnaA09G0047300ZS | A09:2,917,591–2,920,949 | AT5G48160 | OBE2 | Encodes a nuclear PHD finger protein | ||
| qBnPH.C09.2 | BnaC09G0487000ZS | C09:59,837,097–59,837,300 | AT3G55005 | TON1B | Encodes protein TONNEAU 1b, which is involved in cortical microtubule organization | |
| qBnPH.C02.1 | BnaC02G0198200ZS | C02:16,615,930–16,619,295 | AT1G65080 | ALB3L2 | Membrane insertion protein ALBINO3-like protein 2 | |
| FBH | qBnFBH.C09.2 | BnaC09G0535300ZS | C09:63,011,337–63,013,676 | AT5G12230 | MED19A | Mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 19a |
| qBnFBH.C08.2 | BnaC08G0185100ZS | C08:29,352,671–29,355,012 | AT1G54560 | XI-E | MYO11C2, encodes a class XI myosin | |
| qBnFBH.C03 | BnaC03G0342800ZS | C03:23,336,848–23,337,775 | AT5G15320 | NA | Unannotated | |
| qBnFBH.A03 | BnaA03G0481200ZS | A03:26,664,082–26,671,174 | AT4G24680 | MOS1 | Encodes Protein MODIFIER OF SNC1 1 | |
| qBnFBH.A10 | BnaA10G0008200ZS | A10:412,537–413,602 | AT5G19550 | NA | RNA-binding (RRM/RBD/RNP motifs) family protein | |
| qBnFBH.C02 | BnaC02G0198200ZS | C02:16,615,930–16,619,295 | AT4G24680 | MOS1 | Homologous to ALB3L2 | |
| qBnFBH.C07 | BnaC07G0459400ZS | C07:55,733,820–55,740,425 | AT1G01080 | NA | Encodes Protein MODIFIER OF SNC1 1 | |
| qBnFBH.C01 | BnaC01G0022800ZS | C01:1,289,753–1,290,852 | AT1G65080 | ALB3L2 | Calcium uniporter protein 1 | |
| qBnFBH.C05 | BnaC05G0006900ZS | C05:566,307–570,741 | AT1G01510 | AN | Encodes a C-terminal binding protein AN |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, W.; Cheng, H.; Mei, D.; Hu, Q.; Wei, W.; Liu, J. Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals Candidate Genes Regulating Plant Height and First-Branch Height in Brassica napus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5090. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115090
Cui T, Wang X, Wang W, Cheng H, Mei D, Hu Q, Wei W, Liu J. Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals Candidate Genes Regulating Plant Height and First-Branch Height in Brassica napus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5090. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115090
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Tianyu, Xinao Wang, Wenxiang Wang, Hongtao Cheng, Desheng Mei, Qiong Hu, Wenliang Wei, and Jia Liu. 2025. "Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals Candidate Genes Regulating Plant Height and First-Branch Height in Brassica napus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5090. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115090
APA StyleCui, T., Wang, X., Wang, W., Cheng, H., Mei, D., Hu, Q., Wei, W., & Liu, J. (2025). Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals Candidate Genes Regulating Plant Height and First-Branch Height in Brassica napus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5090. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115090






