Male Sex, B Symptoms, Bone Marrow Involvement, and Genetic Alterations as Predictive Factors in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
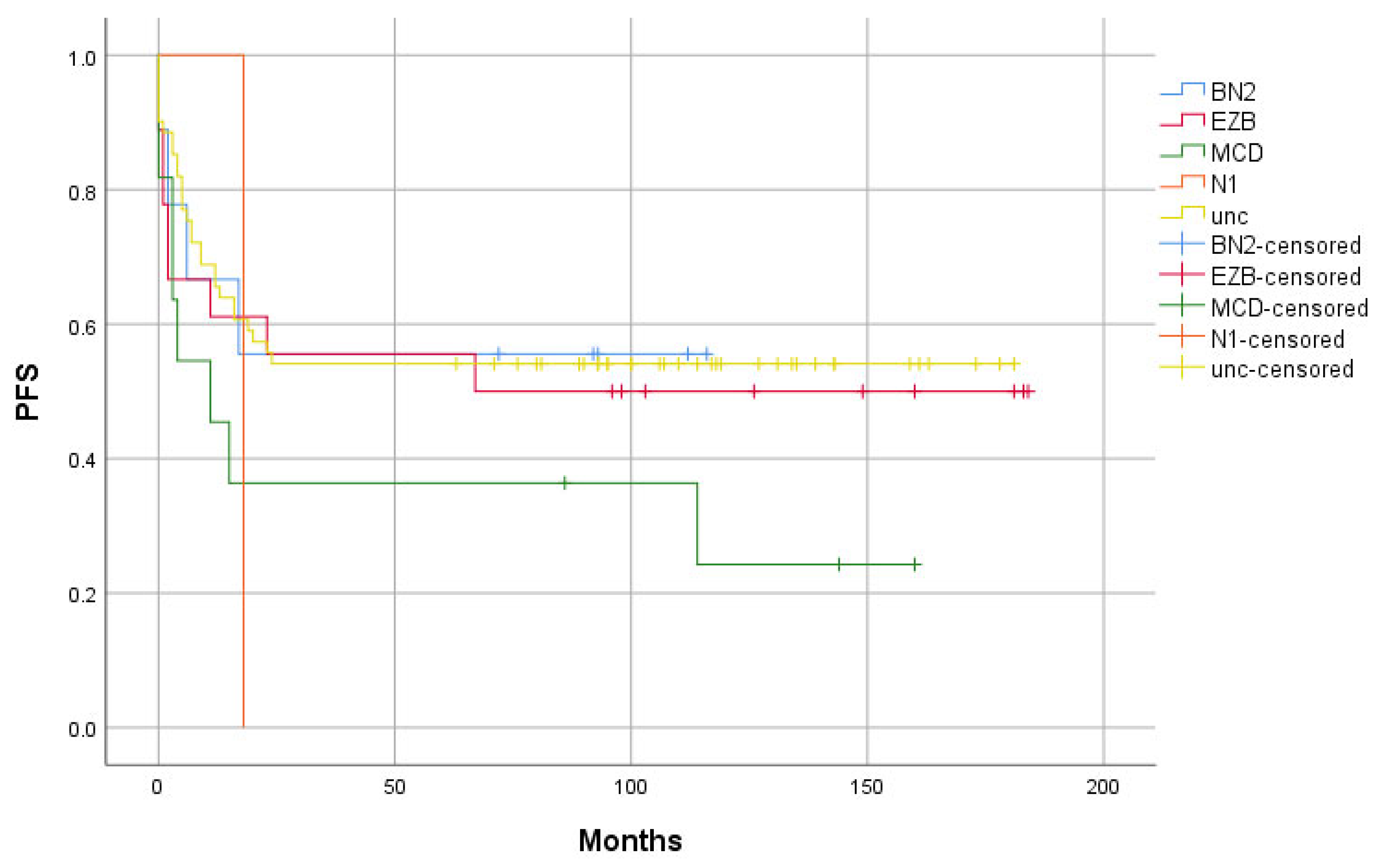
- The “Relapse” group has a higher proportion of the MCD and N1 subtype, as well as a lower proportion of the BN2 and EZB genetic groups, compared to the “Remission” group.
- The “Relapse” group shows a higher proliferation index and a greater proportion of ABC subtype cases than the “Remission” group.
- Patients in the “Relapse” group have higher IPI scores, as well as a greater frequency of B symptoms and bone marrow involvement, compared to the “Remission” group.
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. Immunohistochemistry and FISH
4.3. Molecular Analysis
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alaggio, R.; Amador, C.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Attygalle, A.D.; de Araujo, I.B.O.; Berti, E.; Bhagat, G.; Borges, A.M.; Boyer, D.; Calaminici, M.; et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Lymphoid Neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1720–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SEER. Cancer Stat Facts: NHL—Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/dlbcl.html (accessed on 5 August 2024).
- Sarkozy, C.; Sehn, L.H. New drugs for the management of relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Ann. Lymphoma 2019, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crump, M.; Neelapu, S.S.; Farooq, U.; Van Den Neste, E.; Kuruvilla, J.; Westin, J.; Link, B.K.; Hay, A.; Cerhan, J.R.; Zhu, L.; et al. Outcomes in refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Results from the international SCHOLAR-1 study. Blood 2017, 130, 1800–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilton, L.K.; Ngu, H.S.; Collinge, B.; Dreval, K.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Rushton, C.K.; Wong, J.C.; Cruz, M.; Roth, A.; Boyle, M.; et al. Relapse Timing Is Associated With Distinct Evolutionary Dynamics in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 4164–4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisselbrecht, C.; Glass, B.; Mounier, N.; Gill, D.S.; Linch, D.C.; Trneny, M.; Bosly, A.; Ketterer, N.; Shpilberg, O.; Hagberg, H.; et al. Salvage regimens with autologous transplantation for relapsed large B-cell lymphoma in the rituximab era. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 4184–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.-C.; Tian, S.; Fu, D.; Wang, L.; Cheng, S.; Yi, H.-M.; Jiang, X.-F.; Song, Q.; Zhao, Y.; He, Y.; et al. Genetic subtype-guided immunochemotherapy in diffuse large B cell lymphoma: The randomized GUIDANCE-01 trial. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 1705–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziepert, M.; Hasenclever, D.; Kuhnt, E.; Glass, B.; Schmitz, N.; Pfreundschuh, M.; Loeffler, M. Standard International prognostic index remains a valid predictor of outcome for patients with aggressive CD20+ B-cell lymphoma in the rituximab era. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2373–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Prognostic Factors Project. A predictive model for aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 987–994. [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, A.; Younes, A. High grade B-cell lymphoma with rearrangements of MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6: Double hit and triple hit lymphomas and double expressing lymphoma. Blood Rev. 2017, 31, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehn, L.H.; Scott, D.W.; Chhanabhai, M.; Berry, B.; Ruskova, A.; Berkahn, L.; Connors, J.M.; Gascoyne, R.D. Impact of concordant and discordant bone marrow involvement on outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 1452–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, A.A.; Eisen, M.B.; Davis, R.E.; Ma, C.; Lossos, I.S.; Rosenwald, A.; Boldrick, J.C.; Sabet, H.; Tran, T.; Yu, X.; et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature 2000, 403, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hans, C.P.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Greiner, T.C.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Delabie, J.; Ott, G.; Müller-Hermelink, H.K.; Campo, E.; Braziel, R.M.; Jaffe, E.S.; et al. Confirmation of the molecular classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood 2004, 103, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, R.; Wright, G.W.; Huang, D.W.; Johnson, C.A.; Phelan, J.D.; Wang, J.Q.; Roulland, S.; Kasbekar, M.; Young, R.M.; Shaffer, A.L.; et al. Genetics and Pathogenesis of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1396–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapuy, B.; Stewart, C.; Dunford, A.J.; Kim, J.; Kamburov, A.; Redd, R.A.; Lawrence, M.S.; Roemer, M.G.M.; Li, A.J.; Ziepert, M.; et al. Molecular subtypes of diffuse large B cell lymphoma are associated with distinct pathogenic mechanisms and outcomes. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacy, S.E.; Barrans, S.L.; Beer, P.A.; Painter, D.; Smith, A.G.; Roman, E.; Cooke, S.L.; Ruiz, C.; Glover, P.; Van Hoppe, S.J.L.; et al. Targeted sequencing in DLBCL, molecular subtypes, and outcomes: A Haematological Malignancy Research Network report. Blood 2020, 135, 1759–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, G.W.; Huang, D.W.; Phelan, J.D.; Coulibaly, Z.A.; Roulland, S.; Young, R.M.; Wang, J.Q.; Schmitz, R.; Morin, R.D.; Tang, J.; et al. A Probabilistic Classification Tool for Genetic Subtypes of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma with Therapeutic Implications. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 551–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.; Zhang, J.; Davis, N.S.; Moffitt, A.; Love, C.L.; Waldrop, A.; Leppä, S.; Pasanen, A.; Meriranta, L.; Karjalainen-Lindsberg, M.-L.; et al. Genetic and Functional Drivers of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. Cell 2017, 171, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissinger, S.E.; Moeller, P.; Marienfeld, R.; Bloehdorn, J.; Viardot, A. Primary Extranodal Diffuse Large B-Cell Are Enriched for Mutations in MYD88 and CD79B. Blood 2018, 132, 1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovira, J.; Karube, K.; Valera, A.; Colomer, D.; Enjuanes, A.; Colomo, L.; Martínez-Trillos, A.; Giné, E.; Dlouhy, I.; Magnano, L.; et al. MYD88 L265P Mutations, But No Other Variants, Identify a Subpopulation of DLBCL Patients of Activated B-cell Origin, Extranodal Involvement, and Poor Outcome. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2755–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Jeong, H.; Choi, J.-W.; Oh, H.; Kim, Y.-S. Clinicopathologic significance of MYD88 L265P mutation in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visco, C.; Tanasi, I.; Quaglia, F.M.; Ferrarini, I.; Fraenza, C.; Krampera, M. Oncogenic Mutations of MYD88 and CD79B in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma and Implications for Clinical Practice. Cancers 2020, 12, 2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flossbach, L.; Antoneag, E.; Buck, M.; Siebert, R.; Mattfeldt, T.; Möller, P.; Barth, T.F. BCL6 gene rearrangement and protein expression are associated with large cell presentation of extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, D.; Trifonov, V.; Fangazio, M.; Bruscaggin, A.; Rasi, S.; Spina, V.; Monti, S.; Vaisitti, T.; Arruga, F.; Famà, R.; et al. The coding genome of splenic marginal zone lymphoma: Activation of NOTCH2 and other pathways regulating marginal zone development. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 1537–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Yu, F.; Ye, W.; Mao, L.; Huang, J.; Shao, Y.; Yan, J.; Yu, W.; Jin, J.; Wang, J. Clinical Features and Prognostic Significance of NOTCH1 Mutations in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 746577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, E.M.; Roulland, S.; Okosun, J. DLBCL arising from indolent lymphomas: How are they different? Semin. Hematol. 2023, 60, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, R.D.; Johnson, N.A.; Severson, T.M.; Mungall, A.J.; An, J.; Goya, R.; Paul, J.E.; Boyle, M.; Woolcock, B.W.; Kuchenbauer, F.; et al. Somatic mutations altering EZH2 (Tyr641) in follicular and diffuse large B-cell lymphomas of germinal-center origin. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, W.H.; Young, R.M.; Schmitz, R.; Yang, Y.; Pittaluga, S.; Wright, G.; Lih, C.-J.; Williams, P.M.; Shaffer, A.L.; Gerecitano, J.; et al. Targeting B cell receptor signaling with ibrutinib in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 922–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.W.; Mottok, A.; Ennishi, D.; Wright, G.W.; Farinha, P.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Kridel, R.; Barry, G.S.; Hother, C.; Abrisqueta, P.; et al. Prognostic Significance of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Cell of Origin Determined by Digital Gene Expression in Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissue Biopsies. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2848–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, J.A.; Koff, J.L.; Nastoupil, L.J.; Williams, J.N.; Cohen, J.B.; Flowers, C.R. Evaluating cell-of-origin subtype methods for predicting diffuse large B-cell lymphoma survival: A meta-analysis of gene expression profiling and immunohistochemistry algorithms. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2014, 14, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, G.; Ziepert, M.; Klapper, W.; Horn, H.; Szczepanowski, M.; Bernd, H.-W.; Thorns, C.; Feller, A.C.; Lenze, D.; Hummel, M.; et al. Immunoblastic morphology but not the immunohistochemical GCB/nonGCB classifier predicts outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the RICOVER-60 trial of the DSHNHL. Blood 2010, 116, 4916–4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, R.; Lai, R.; Wei, P.; Lee, J.; Hanson, J.; Belch, A.R.; Turner, A.R.; Reiman, T. Concordant but not discordant bone marrow involvement in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma predicts a poor clinical outcome independent of the International Prognostic Index. Blood 2007, 110, 1278–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Álvarez, S.; Alcoceba, M.; García-Álvarez, M.; Blanco, O.; Rodríguez, M.; Baile, M.; Caballero, J.C.; Dávila, J.; Vidriales, M.B.; Esteban, C.; et al. Biological Features and Prognostic Impact of Bone Marrow Infiltration in Patients with Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preti, H.A.; Cabanillas, F.; Talpaz, M.; Tucker, S.L.; Seymour, J.F.; Kurzrock, R. Prognostic value of serum interleukin-6 in diffuse large-cell lymphoma. Ann. Intern. Med. 1997, 127, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legouffe, E.; Rodriguez, C.; Picgt, M.C.; Richard, B.; Klein, B.; Rossi, J.F.; Commes, T. C-reactive protein serum level is a valuable and simple prognostic marker in non Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 1998, 31, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yıldırım, M.; Kaya, V.; Demirpençe, Ö.; Paydaş, S. The role of gender in patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma treated with rituximab-containing regimens: A meta-analysis. Arch. Med. Sci. 2015, 11, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozman, S.; Grabnar, I.; Novaković, S.; Mrhar, A.; Novaković, B.J. Population pharmacokinetics of rituximab in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and association with clinical outcome. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 83, 1782–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.; Murawski, N.; Wiesen, M.H.J.; Held, G.; Poeschel, V.; Zeynalova, S.; Wenger, M.; Nickenig, C.; Peter, N.; Lengfelder, E.; et al. The role of sex and weight on rituximab clearance and serum elimination half-life in elderly patients with DLBCL. Blood 2012, 119, 3276–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughn, J.L.; Ramdhanny, A.; Munir, M.; Rimmalapudi, S.; Epperla, N. A comparative analysis of transformed indolent lymphomas and de novo diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A population-based cohort study. Blood Cancer J. 2024, 14, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmuganathan, N.; Wadham, C.; Thomson, D.; Shahrin, N.H.; Vignaud, C.; Obourn, V.; Chaturvedi, S.; Yang, F.; Feng, J.; Saunders, V.; et al. RNA-Based Targeted Gene Sequencing Improves the Diagnostic Yield of Mutant Detection in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. J. Mol. Diagn. 2022, 24, 803–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.M.; Datto, M.; Duncavage, E.J.; Kulkarni, S.; Lindeman, N.I.; Roy, S.; Tsimberidou, A.M.; Vnencak-Jones, C.L.; Wolff, D.J.; Younes, A.; et al. Standards and Guidelines for the Interpretation and Reporting of Sequence Variants in Cancer: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the Association for Molecular Pathology, American Society of Clinical Oncology, and College of American Pathologists. J. Mol. Diagn. 2017, 19, 4–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Diagnosis | B Symptoms | Stage | IPI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DLBCL NOS | 102 (97%) | 45 (43%) | 1 | 16 (15%) | 0–1 | 32 (30%) |
| 2 | 22 (21%) | |||||
| DLBCL/HGBCL | 3 (3%) | 3 | 22 (21%) | 2 | 27 (26%) | |
| 4 | 45 (43%) | |||||
| Male sex | Age (years, median) | GEP COO (N = 100) | 3 | 26 (25%) | ||
| ABC | 29 (29%) | |||||
| 49 (47%) | 65 (range 27–89) | GCB | 57 (57%) | 4–5 | 20 (19%) | |
| Unc. | 14 (14%) | |||||
| Genetic Group | EZB | MCD | BN2 | N1 | Unc | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| “Remission” group | 10 (56%) | 4 (36%) | 5 (56%) | 0 (0%) | 33 (54%) | 52 |
| “Relapse” group | 8 (44%) | 7 (64%) | 4 (44%) | 1 (100%) | 28 (46%) | 48 |
| Total | 18 | 11 | 9 | 1 | 61 |
| Genetic Group | EZB (N = 18) | MCD (N = 11) | BN2 (N = 9) | N1 (N = 1) | Unc (N = 61) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 63.5 | 71 | 74 | 59 | 65 |
| Male sex | 33% (6) | 36% (4) | 56% (5) | 0% (0) | 52% (32) |
| IPI | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Bone marrow involvement * | 13% (2) | 56% (5) | 33% (3) | 100% (1) | 32% (19) |
| Stage | 3.5 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 3 |
| Elevated LDH | 83% (15) | 55% (6) | 44% (4) | 0% (0) | 48% (29) |
| B symptoms | 50% (9) | 45% (5) | 33% (3) | 0% (0) | 44% (27) |
| Indolent lymphoma transformation ** | 3 (2/0/0) | 3 (0/1/0) | 2 (0/1/0) | 1 (0/0/1) | 20 (7/4/2) |
| Clinical Characteristic | >1 Extranodal Site Involved | Elevated LDH | PS WHO > 1 | Bone Marrow Involvement * | B Symptoms | Male Sex | ABC/GCB Cases (GEP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| “Remission” group (N = 52) | 16 (31%) | 20 (38%) | 4 (8%) | 7 (13%) | 15 (29%) | 19 (37%) | 12/34 |
| “Relapse” group (N = 53) | 23 (43%) | 37 (70%) | 7 (13%) | 25 (47%) | 30 (57%) | 30 (57%) | 17/23 |
| p-value | 0.181 | 0.001 | 0.356 | <0.001 | 0.004 | 0.039 | / |
| IPI | Age | Stage | MIB-1 (%) * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| “Remission” group | 2 | 62 | 2 | 80 |
| “Relapse” group | 3 | 68 | 4 | 80 |
| p-value | 0.001 | 0.356 | <0.001 | 0.206 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Panjan, M.; Šetrajčič Dragoš, V.; Gašljević, G.; Novaković, S.; Jezeršek Novaković, B. Male Sex, B Symptoms, Bone Marrow Involvement, and Genetic Alterations as Predictive Factors in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5087. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115087
Panjan M, Šetrajčič Dragoš V, Gašljević G, Novaković S, Jezeršek Novaković B. Male Sex, B Symptoms, Bone Marrow Involvement, and Genetic Alterations as Predictive Factors in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5087. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115087
Chicago/Turabian StylePanjan, Matej, Vita Šetrajčič Dragoš, Gorana Gašljević, Srdjan Novaković, and Barbara Jezeršek Novaković. 2025. "Male Sex, B Symptoms, Bone Marrow Involvement, and Genetic Alterations as Predictive Factors in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5087. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115087
APA StylePanjan, M., Šetrajčič Dragoš, V., Gašljević, G., Novaković, S., & Jezeršek Novaković, B. (2025). Male Sex, B Symptoms, Bone Marrow Involvement, and Genetic Alterations as Predictive Factors in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5087. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115087






