Serums miR-24-3p and miR-1301-3p as Potential Biomarkers in MEN1 Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patient Characteristics
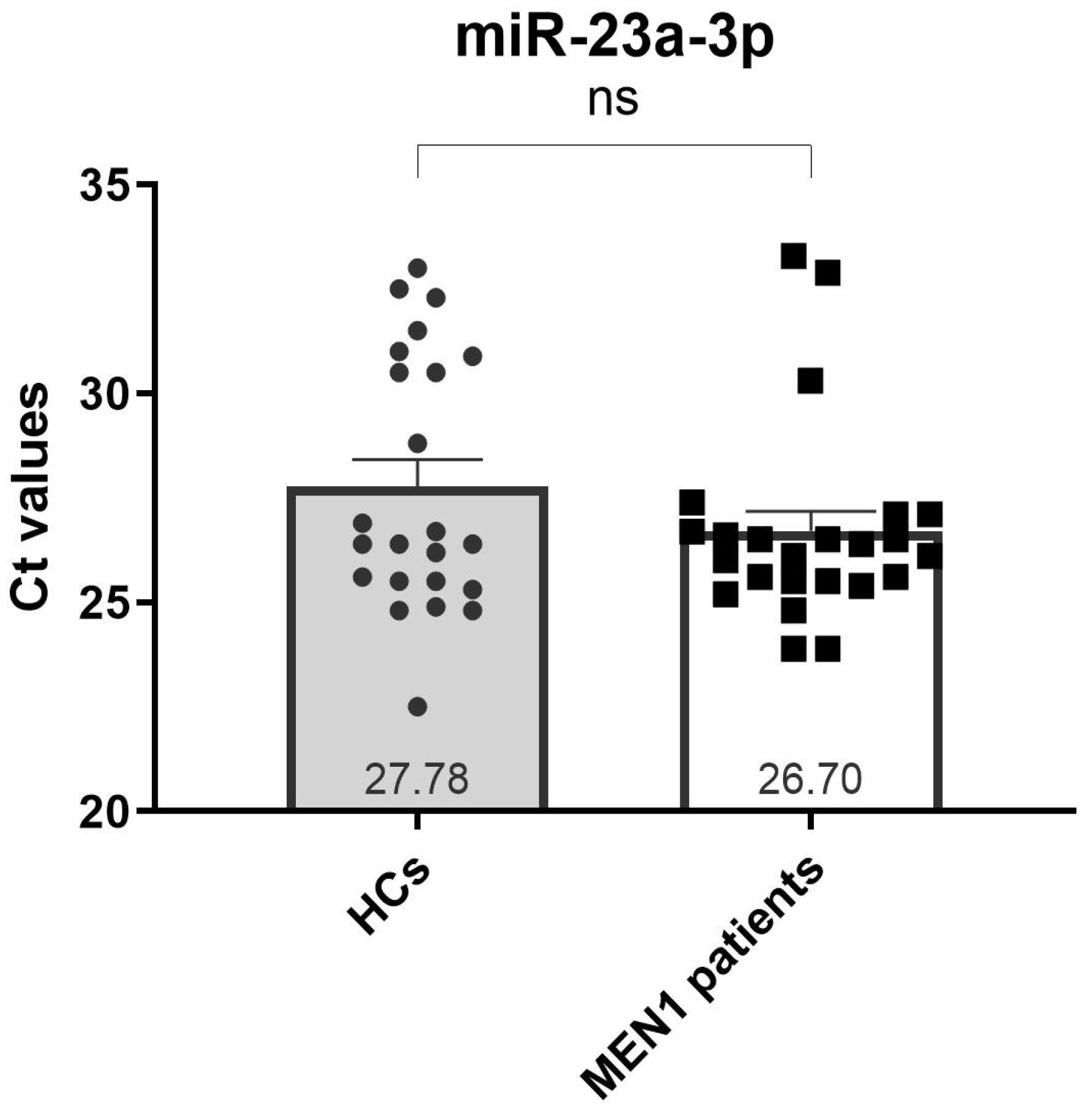
2.2. Selection of a Suitable Endogenous Reference miRNA
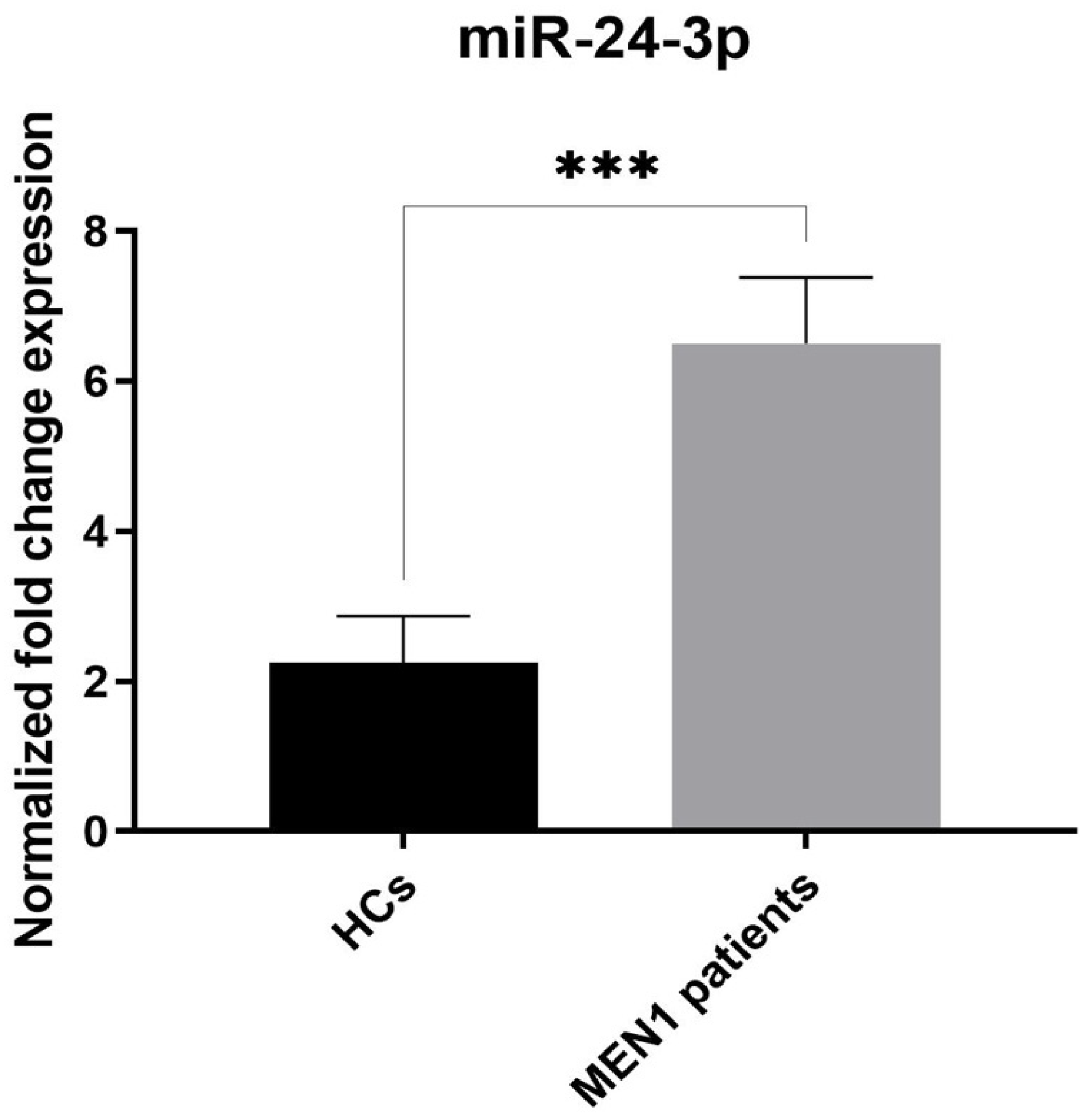
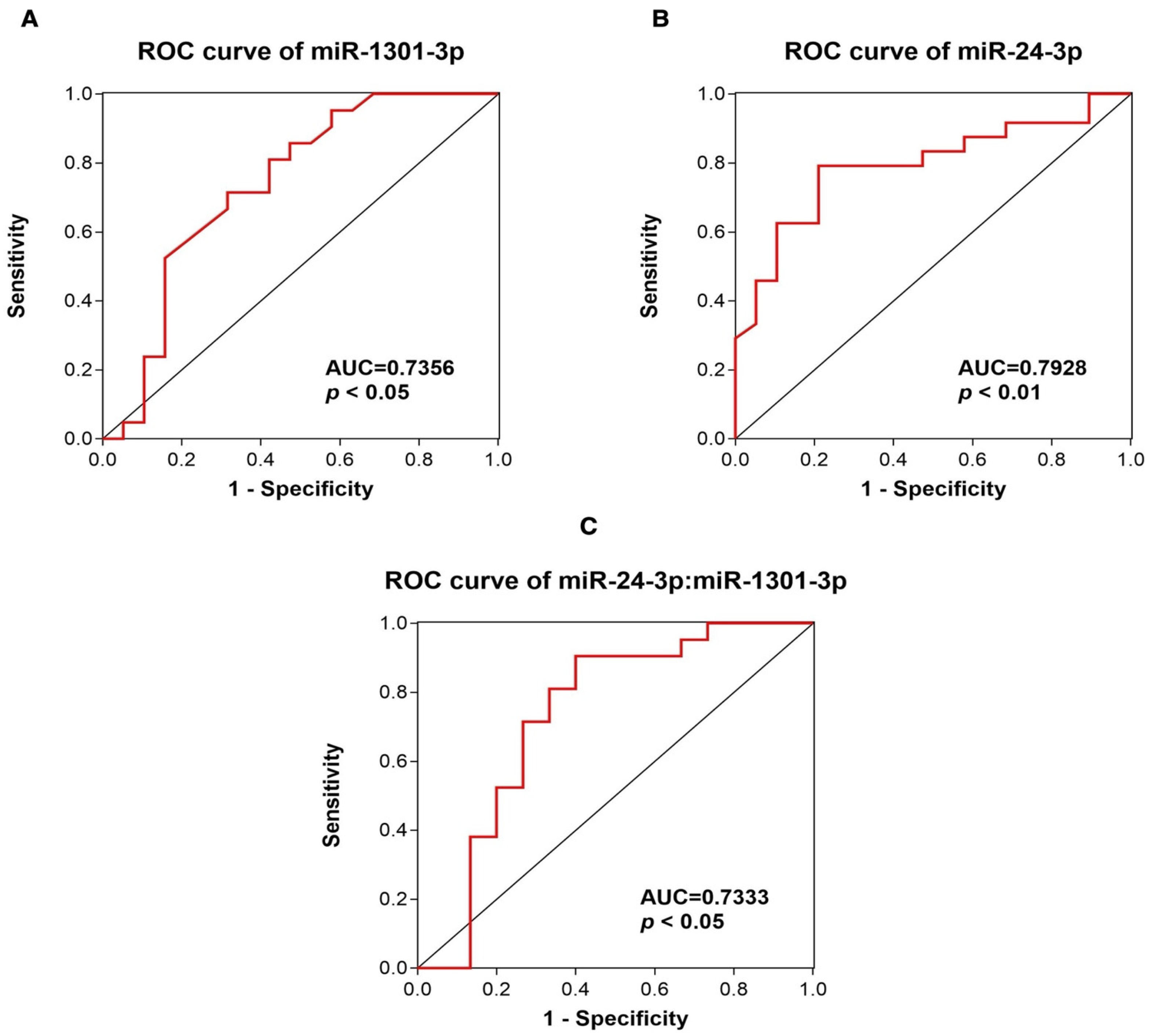
2.3. Analysis of c-miRNA Expression Levels and Assessment of the Diagnostic Value of miR-1301-3p and miR-24-3p
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Information and Serum Collection
4.2. Hemolysis Assessment
4.3. RNA Extraction
4.4. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) Analyses
4.5. Selection of Reference miRNA and qPCR Data Normalization
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Falchetti, A. Genetics of Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 1 Syndrome: What’s New and What’s Old. F1000Research 2017, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandi, M.L.; Agarwal, S.K.; Perrier, N.D.; Lines, K.E.; Valk, G.D.; Thakker, R.V. Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 1: Latest Insights. Endocr. Rev. 2021, 42, 133–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekharappa, S.C.; Guru, S.C.; Manickam, P.; Olufemi, S.E.; Collins, F.S.; Emmert-Buck, M.R.; Debelenko, L.V.; Zhuang, Z.; Lubensky, I.A.; Liotta, L.A.; et al. Positional Cloning of the Gene for Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia-Type 1. Science 1997, 276, 404–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemmens, I.; Van de Ven, W.J.; Kas, K.; Zhang, C.X.; Giraud, S.; Wautot, V.; Buisson, N.; De Witte, K.; Salandre, J.; Lenoir, G.; et al. Identification of the Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 1 (MEN1) Gene. The European Consortium on MEN1. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1997, 6, 1177–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakker, R.V.; Newey, P.J.; Walls, G.V.; Bilezikian, J.; Dralle, H.; Ebeling, P.R.; Melmed, S.; Sakurai, A.; Tonelli, F.; Brandi, M.L. Clinical Practice Guidelines for Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 1 (MEN1). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 2990–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemos, M.C.; Thakker, R.V. Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 1 (MEN1): Analysis of 1336 Mutations Reported in the First Decade Following Identification of the Gene. Hum. Mutat. 2008, 29, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falchetti, A. Genetic Screening for Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Syndrome Type 1 (MEN-1): When and How. F1000 Med. Rep. 2010, 2, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concolino, P.; Costella, A.; Capoluongo, E. Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 1 (MEN1): An Update of 208 New Germline Variants Reported in the Last Nine Years. Cancer Genet. 2016, 209, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donati, S.; Ciuffi, S.; Marini, F.; Palmini, G.; Miglietta, F.; Aurilia, C.; Brandi, M.L. Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 1: The Potential Role of microRNAs in the Management of the Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malan-Müller, S.; Hemmings, S.M.J.; Seedat, S. Big Effects of Small RNAs: A Review of microRNAs in Anxiety. Mol. Neurobiol. 2013, 47, 726–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.; Hayder, H.; Zayed, Y.; Peng, C. Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntzinger, E.; Izaurralde, E. Gene Silencing by microRNAs: Contributions of Translational Repression and mRNA Decay. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ipsaro, J.J.; Joshua-Tor, L. From Guide to Target: Molecular Insights into Eukaryotic RNAi Machinery. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015, 22, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, W.; Shen, J.; Zheng, H.; Fan, W. The Role and Mechanisms of Action of microRNAs in Cancer Drug Resistance. Clin. Epigenetics 2019, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luzi, E.; Marini, F.; Giusti, F.; Galli, G.; Cavalli, L.; Brandi, M.L. The Negative Feedback-Loop between the Oncomir Mir-24-1 and Menin Modulates the Men1 Tumorigenesis by Mimicking the “Knudson’s Second Hit”. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, J.; Maggi, E.C.; Crabtree, J.S. miR-24 Regulates Menin in the Endocrine Pancreas. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 307, E84–E92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzi, E.; Ciuffi, S.; Marini, F.; Mavilia, C.; Galli, G.; Brandi, M.L. Analysis of Differentially Expressed microRNAs in MEN1 Parathyroid Adenomas. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 1743–1753. [Google Scholar]
- Gallo, A.; Tandon, M.; Alevizos, I.; Illei, G.G. The Majority of MicroRNAs Detectable in Serum and Saliva Is Concentrated in Exosomes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.A.; Baxter, D.H.; Zhang, S.; Huang, D.Y.; Huang, K.H.; Lee, M.J.; Galas, D.J.; Wang, K. The microRNA Spectrum in 12 Body Fluids. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 1733–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, T.; Zhu, Q.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Gao, X.; Li, X. Immune-Related microRNAs Are Abundant in Breast Milk Exosomes. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 8, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silveira, J.C.; Veeramachaneni, D.N.R.; Winger, Q.A.; Carnevale, E.M.; Bouma, G.J. Cell-Secreted Vesicles in Equine Ovarian Follicular Fluid Contain miRNAs and Proteins: A Possible New Form of Cell Communication within the Ovarian Follicle. Biol. Reprod. 2012, 86, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vickers, K.C.; Palmisano, B.T.; Shoucri, B.M.; Shamburek, R.D.; Remaley, A.T. MicroRNAs Are Transported in Plasma and Delivered to Recipient Cells by High-Density Lipoproteins. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turchinovich, A.; Weiz, L.; Burwinkel, B. Extracellular miRNAs: The Mystery of Their Origin and Function. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2012, 37, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabet, F.; Vickers, K.C.; Cuesta Torres, L.F.; Wiese, C.B.; Shoucri, B.M.; Lambert, G.; Catherinet, C.; Prado-Lourenco, L.; Levin, M.G.; Thacker, S.; et al. HDL-Transferred microRNA-223 Regulates ICAM-1 Expression in Endothelial Cells. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, P.S.; Parkin, R.K.; Kroh, E.M.; Fritz, B.R.; Wyman, S.K.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Peterson, A.; Noteboom, J.; O’Briant, K.C.; Allen, A.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as Stable Blood-Based Markers for Cancer Detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10513–10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Ba, Y.; Ma, L.; Cai, X.; Yin, Y.; Wang, K.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Guo, X.; et al. Characterization of microRNAs in Serum: A Novel Class of Biomarkers for Diagnosis of Cancer and Other Diseases. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chim, S.S.C.; Shing, T.K.F.; Hung, E.C.W.; Leung, T.-Y.; Lau, T.-K.; Chiu, R.W.K.; Lo, Y.M.D. Detection and Characterization of Placental microRNAs in Maternal Plasma. Clin. Chem. 2008, 54, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrie, C.H.; Gal, S.; Dunlop, H.M.; Pushkaran, B.; Liggins, A.P.; Pulford, K.; Banham, A.H.; Pezzella, F.; Boultwood, J.; Wainscoat, J.S.; et al. Detection of Elevated Levels of Tumour-Associated microRNAs in Serum of Patients with Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 141, 672–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Q.-L.; Hu, C.-W.; Wang, X.-R.; Yin, G.-F.; Shang, J.-X. Association between Downexpression of miR-1301 and Poor Prognosis in Patients with Glioma. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 4298–4303. [Google Scholar]
- Luzi, E.; Marini, F.; Ciuffi, S.; Galli, G.; Brandi, M.L. An Autoregulatory Network between Menin and Pri-miR-24-1 Is Required for the Processing of Its Specific Modulator miR-24-1 in BON1 Cells. Mol. Biosyst. 2016, 12, 1922–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falchetti, A.; Marini, F.; Luzi, E.; Giusti, F.; Cavalli, L.; Cavalli, T.; Brandi, M.L. Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 1 (MEN1): Not Only Inherited Endocrine Tumors. Genet. Med. 2009, 11, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.; Wang, J.; Song, Y.; Zhao, S.; Liu, H.; Tang, D.; Pan, B.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Q. miRNA-24-3p Promotes Cell Proliferation and Inhibits Apoptosis in Human Breast Cancer by Targeting p27Kip1. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Wang, H.; Yao, X.; Zhang, D.; Xie, Y.; Cui, R.; Zhang, X. Circulating MicroRNAs in Cancer: Potential and Challenge. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modlin, I.M.; Drozdov, I.; Alaimo, D.; Callahan, S.; Teixiera, N.; Bodei, L.; Kidd, M. A Multianalyte PCR Blood Test Outperforms Single Analyte ELISAs (Chromogranin A, Pancreastatin, Neurokinin A) for Neuroendocrine Tumor Detection. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2014, 21, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modlin, I.M.; Kidd, M.; Malczewska, A.; Drozdov, I.; Bodei, L.; Matar, S.; Chung, K.-M. The NETest: The Clinical Utility of Multigene Blood Analysis in the Diagnosis and Management of Neuroendocrine Tumors. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 47, 485–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldevilla, B.; Lens-Pardo, A.; Espinosa-Olarte, P.; Carretero-Puche, C.; Molina-Pinelo, S.; Robles, C.; Benavent, M.; Gomez-Izquierdo, L.; Fierro-Fernández, M.; Morales-Burgo, P.; et al. MicroRNA Signature and Integrative Omics Analyses Define Prognostic Clusters and Key Pathways Driving Prognosis in Patients with Neuroendocrine Neoplasms. Mol. Oncol. 2023, 17, 582–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooblall, K.G.; Stokes, V.J.; Shariq, O.A.; English, K.A.; Stevenson, M.; Broxholme, J.; Wright, B.; Lockstone, H.E.; Buck, D.; Grozinsky-Glasberg, S.; et al. miR-3156-5p Is Downregulated in Serum of MEN1 Patients and Regulates Expression of MORF4L2. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2022, 29, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trukhina, D.A.; Mamedova, E.O.; Nikitin, A.G.; Koshkin, P.A.; Belaya, Z.E.; Melnichenko, G.A. Plasma miRNA expression in patients with genetically confirmed multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 syndrome and its phenocopies. Probl. Endokrinol. 2024, 69, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donati, S.; Ciuffi, S.; Brandi, M.L. Human Circulating miRNAs Real-Time qRT-PCR-Based Analysis: An Overview of Endogenous Reference Genes Used for Data Normalization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondal, T.; Jensby Nielsen, S.; Baker, A.; Andreasen, D.; Mouritzen, P.; Wrang Teilum, M.; Dahlsveen, I.K. Assessing Sample and miRNA Profile Quality in Serum and Plasma or Other Biofluids. Methods 2013, 59, S1–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Huang, R.; Meng, X.; Sun, F. Long Non-Coding RNA LINC01207 Promotes Cell Proliferation and Migration but Suppresses Apoptosis and Autophagy in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma by the microRNA-1301-3p/Lactate Dehydrogenase Isoform A Axis. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 7780–7793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Mao, L.; Shi, R.; Wang, W.; Cheng, J. circRNA MYLK Accelerates Cervical Cancer via Up-Regulation of RHEB and Activation of mTOR Signaling. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 3611–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Sun, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, G.; Cui, Y.; Lei, C. CircRNA Circ_0004370 Promotes Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion and Inhibits Cell Apoptosis of Esophageal Cancer via miR-1301-3p/COL1A1 Axis. Open Med. 2021, 16, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Liu, Y.-T.; Wu, C.-P.; Jiang, J.-T.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.-L.; Wang, Q.-Y. Long Non-Coding RNA Linc01433 Promotes Tumorigenesis and Progression in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Sponging miR-1301. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 4785–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Xie, L.; Fu, Y.; Yang, J.; Cui, Y. lncRNA MIAT Promotes Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression by Regulating miR-1301-3p/INCENP Axis and Interacting with SOX2. J. Cell Physiol. 2020, 235, 7933–7944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Zeng, F. NFIB-Mediated lncRNA PVT1 Aggravates Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression via the miR-1301-3p/MBNL1 Axis. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 8675123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, D.-H.; He, X.-M.; Yang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Deng, X.; Cheng, L.; Zhou, X.-Y. miR-1301-3p Suppresses Tumor Growth by Downregulating PCNA in Thyroid Papillary Cancer. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2021, 42, 102920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.-P.; Chen, L.-Y.; Bai, B.; Qi, X.-F.; Liu, J.-N.; Qin, S. Circ_0067934 Promotes the Progression of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Cells through miR-1301-3p/HMGB1 Axis. Neoplasma 2022, 69, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer-Valuck, B.W.; Michalski, J.M.; Contreras, J.A.; Brenneman, R.; Christodouleas, J.P.; Abraham, C.D.; Kim, E.H.; Arora, V.K.; Bullock, A.D.; Carmona, R.; et al. A Propensity Analysis Comparing Definitive Chemo-Radiotherapy for Muscle-Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Bladder vs. Urothelial Carcinoma of the Bladder Using the National Cancer Database. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 15, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, T.; Jiang, K.; Zhang, C.; Xu, X.; Wu, W.; Nie, E.; Yu, T.; Zhou, X.; Bao, Z.; Jin, X.; et al. MicroRNA-1301 Inhibits Proliferation of Human Glioma Cells by Directly Targeting N-Ras. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2017, 7, 982–998. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.; Piao, L.-H.; Sun, G.-C.; Lv, C.-X.; Jing, Y.; Jin, R.-H. Long Non-Coding RNA Plasmacytoma Variant Translocation 1 (PVT1) Promotes Glioblastoma Multiforme Progression via Regulating miR-1301-3p/TMBIM6 Axis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 11658–11665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Chen, K.-C.; Liu, H.-J.E.; Liu, A.-J.; Wang, K.-L.; Shih, C.-M. MicroRNA-1301-Mediated RanGAP1 Downregulation Induces BCR-ABL Nuclear Entrapment to Enhance Imatinib Efficacy in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, T.; Shuang, W.; Ye, D.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Z.; Fang, W.; Xu, H.; Gu, M.; Xu, W.; Guan, C. SNHG16 Promotes Cell Proliferation and Inhibits Cell Apoptosis via Regulation of the miR-1303-p/STARD9 Axis in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cell Signal 2021, 84, 110013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, G. NNT-AS1 Enhances Bladder Cancer Cell Growth by Targeting miR-1301-3p/PODXL Axis and Activating Wnt Pathway. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2020, 39, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hu, K.; Chao, Y. MicroRNA-1301 Inhibits Migration and Invasion of Osteosarcoma Cells by Targeting BCL9. Gene 2018, 679, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Meng, M.; Bao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Gao, B.; Sa, R.; Luo, W. miR-1301/TRIAP1 Axis Participates in Epirubicin-Mediated Anti-Proliferation and Pro-Apoptosis in Osteosarcoma. Yonsei Med. J. 2019, 60, 832–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hu, K.; Chao, Y.; Wang, L. LncRNA SNHG16 Promotes Proliferation, Migration and Invasion of Osteosarcoma Cells by Targeting miR-1301/BCL9 Axis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 114, 108798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, M.; Zhou, F.; Yan, J. Serum miR-1301-3p, miR-335-5p, miR-28-5p, and Their Target B7-H3 May Serve as Novel Biomarkers for Colorectal Cancer. J. BUON 2019, 24, 1120–1127. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Wang, H.; Yuan, D.; Yao, J.; Meng, L.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Dang, C.; Zhu, K. RUNX1-Activated Upregulation of lncRNA RNCR3 Promotes Cell Proliferation, Invasion, and Suppresses Apoptosis in Colorectal Cancer via miR-1301-3p/AKT1 Axis in Vitro and in Vivo. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 22, 1762–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Wang, H.; Yan, B.; Li, T.; Min, L.; Chen, E.; Yang, J. Decreased Level of miR-1301 Promotes Colorectal Cancer Progression via Activation of STAT3 Pathway. Biol. Chem. 2021, 402, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matamala, N.; Vargas, M.T.; González-Cámpora, R.; Miñambres, R.; Arias, J.I.; Menéndez, P.; Andrés-León, E.; Gómez-López, G.; Yanowsky, K.; Calvete-Candenas, J.; et al. Tumor microRNA Expression Profiling Identifies Circulating microRNAs for Early Breast Cancer Detection. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 1098–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, M.; Liaw, C.S.; Ji, S.M.; Tan, H.H.; Wong, C.Y.; Thike, A.A.; Tan, P.H.; Ho, G.H.; Lee, A.S.-G. Identification of Circulating microRNA Signatures for Breast Cancer Detection. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 4477–4487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimaldi, A.M.; Incoronato, M. Clinical Translatability of “Identified” Circulating miRNAs for Diagnosing Breast Cancer: Overview and Update. Cancers 2019, 11, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.-L.; Sun, J.; Lu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cao, H.; Zhang, H.; Calin, G.A. MiR-200 Family and Cancer: From a Meta-Analysis View. Mol. Asp. Med. 2019, 70, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliciano, A.; González, L.; Garcia-Mayea, Y.; Mir, C.; Artola, M.; Barragán, N.; Martín, R.; Altés, A.; Castellvi, J.; Benavente, S.; et al. Five microRNAs in Serum Are Able to Differentiate Breast Cancer Patients From Healthy Individuals. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 586268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, F.; Brandi, M.L. Role of miR-24 in Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 1: A Potential Target for Molecular Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrezk, R.; Hannah-Shmouni, F.; Stratakis, C.A. MEN4 and CDKN1B Mutations: The Latest of the MEN Syndromes. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2017, 24, T195–T208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revia, R.A.; Stephen, Z.R.; Zhang, M. Theranostic Nanoparticles for RNA-Based Cancer Treatment. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 1496–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bašová, P.; Pešta, M.; Sochor, M.; Stopka, T. Prediction Potential of Serum miR-155 and miR-24 for Relapsing Early Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavropoulou, M.P.; Pazaitou-Panayiotou, K.; Yovos, J.G.; Poulios, C.; Anastasilakis, A.D.; Vlachodimitropoulos, D.; Vambakidis, K.; Tsave, O.; Chrisafi, S.; Daskalaki, E.; et al. Circulating and Tissue Expression Profile of MicroRNAs in Primary Hyperparathyroidism Caused by Sporadic Parathyroid Adenomas. JBMR Plus 2021, 5, e10431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Jeong, J.J.; Kim, S.H.; Chung, Y.J.; Song, S.Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Rhee, Y. Differential Expression of miRNA199b-5p as a Novel Biomarker for Sporadic and Hereditary Parathyroid Tumors. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirschner, M.B.; Edelman, J.J.B.; Kao, S.C.-H.; Vallely, M.P.; van Zandwijk, N.; Reid, G. The Impact of Hemolysis on Cell-Free microRNA Biomarkers. Front. Genet. 2013, 4, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, F.; Xiang, G.; Jiang, D.; Pu, X. Identification of Endogenous Controls for Analyzing Serum Exosomal miRNA in Patients with Hepatitis B or Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Dis. Markers 2015, 2015, 893594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Dong, J.; Wang, L.-E.; Ma, H.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, J.; Chen, X.; Dai, J.; Wei, Q.; et al. Serum microRNA Profiling and Breast Cancer Risk: The Use of miR-484/191 as Endogenous Controls. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 828–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, K.; Wang, X.; Ren, G.; Xie, P. Identification of Suitable Plasma-Based Reference Genes for miRNAome Analysis of Major Depressive Disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2014, 163, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| MEN1 Group | HC Group | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 25 | 25 | |
| Gender | 0.23 | ||
| Males | 8 | 12 | |
| Females | 17 | 13 | |
| Age | 0.312 | ||
| Mean | 44.4 | 40.1 | |
| ±SD | 12.12 | 10.25 |
| Patient ID | Age (Years) | Gender | Inherited MEN1 Syndrome | Type of MEN1 Mutation | Age of Onset | 1st Clinical Sign of MEN1 | MEN1 Phenotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 50 | F | Yes | Frameshift | 39 | PHPT | PHPT |
| 2 | 54 | F | Yes | Missense | 28 | Nephrolithiasis | PHPT |
| 3 | 52 | F | Yes | Nonsense | 35 | Insulinoma | PHPT, insulinoma, PRLoma, meningioma, cutaneous lesions |
| 4 | 47 | F | Yes | Frameshift | 19 | PRLoma | PRLoma, PHPT, insulinoma |
| 5 | 46 | F | Yes | Frameshift | 32 | PRLoma | PRLoma, non-functioning NET, adrenal hyperlasia |
| 6 | 39 | F | Yes | Missense | 33 | PHPT | PHPT |
| 7 | 56 | M | Yes | Missense | 37 | Nephrolithiasis | PHPT, non-functioning NET, LI, cutaneous lesions |
| 8 | 38 | M | Yes | Missense | 31 | PHPT | PHPT, PRLoma, cutaneous lesions |
| 9 | 54 | F | Yes | Splicing | 49 | PHPT | PHPT, PA, gastrinoma, lung carcinoid, LI |
| 10 | 52 | M | Yes | Frameshift | 29 | Nephrolithiasis, PHPT | PHPT, gastrinoma, lipoma, cutaneous lesions |
| 11 | 20 | F | Yes | Splicing | 19 | PHPT | PHPT |
| 12 | 14 | M | Yes | Frameshift | / | Asymptomatic | - |
| 13 | 44 | F | Yes | Splicing | 38 | Gastrointestinal disorders | PHPT, PA, gastrinoma, lung carcinoid |
| 14 | 65 | F | Yes | Frameshift | 18 | Nephrolithiasis | PHPT, PRLoma, non-functioning NET |
| 15 | 33 | M | Yes | Nonsense | 15 | PHPT | PHPT |
| 16 | 47 | M | Yes | Nonsense | 40 | Hypoglycemia | PHPT, insulinoma |
| 17 | 36 | F | Yes | Frameshift | 30 | PHPT | PHPT, PRLoma, insulinoma |
| 18 | 35 | M | Yes | Missense | 15 | Renal colic | PHPT, LI, cutaneous lesions |
| 19 | 42 | M | Yes | Missense | 39 | Lipoma of the gluteus | PHPT, non-functioning NET, LI, cutaneous lesions |
| 20 | 48 | F | Yes | Genetic variant in the 5’UTR | 23 | Hyperprolactinemia | PHPT, PRLoma, gastrinoma |
| 21 | 45 | F | Yes | Missense | 22 | PHPT | PHPT, PRLoma, non-functioning NET |
| 22 | 37 | F | No | Splicing | 25 | Hypoglycemic seizures | PHPT, PRLoma, insulinoma |
| 23 | 41 | F | Yes | Missense | 15 | PHPT | PHPT, PRLoma, insulinoma |
| 24 | 70 | F | No | Missense | 58 | PHPT | PHPT, PRLoma, insulinoma, gastrinoma, lung carcinoid, LI |
| 25 | 46 | F | Yes | Frameshift | 20 | Hypoglycemia | PHPT, PRLoma, insulinoma, gastrinoma, lung carcinoid, LI |
| miRNA | Min | Max | Mean | SE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa-miR-23a-3p | 22.5 | 33.3 | 27.23 | 0.40 |
| hsa-miR-93-5p | 25.47 | 40 | 29.99 | 0.66 |
| hsa-miR-191-5p | 20.10 | 40 | 29.7 | 0.82 |
| miRBase ID | Role in the Study | Mature miRNA Sequence | miScript Primer Assay | miRbase Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cel-miR-39-3p | Exogenous spike-in miRNA to evaluate efficiency of RNA extraction and cDNA reverse transcription | UCACCGGGUGUAAAUCAGCUUG | 219610 | MIMAT0000010 |
| hsa-miR-451a | Hemolysis indicator | AAACCGUUACCAUUACUGAGUU | MS0004242 | MIMAT0001631 |
| hsa-miR-23a-3p | Reference miRNA | AUCACAUUGCCAGGGAUUUCC | MS00031633 | MIMAT0000078 |
| hsa-miR-93-5p | Reference miRNA | CAAAGUGCUGUUCGUGCAGGUAG | MS00003346 | MIMAT0000093 |
| hsa-miR-191-5p | Reference miRNA | CAACGGAAUCCCAAAAGCAGCUG | MS00003682 | MIMAT0000440 |
| hsa-miR-24-3p | Tested c-miRNA | UGGCUCAGUUCAGCAGGAACAG | MS00006552 | MIMAT0000080 |
| hsa-miR-1301-3p | Tested c-miRNA | UUGCAGCUGCCUGGGAGUGACUUC | MS00031381 | MIMAT0005797 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Donati, S.; Aurilia, C.; Marini, F.; Giusti, F.; Palmini, G.; Falsetti, I.; Cioppi, F.; Ranaldi, F.; Iantomasi, T.; Moro, A.; et al. Serums miR-24-3p and miR-1301-3p as Potential Biomarkers in MEN1 Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5076. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115076
Donati S, Aurilia C, Marini F, Giusti F, Palmini G, Falsetti I, Cioppi F, Ranaldi F, Iantomasi T, Moro A, et al. Serums miR-24-3p and miR-1301-3p as Potential Biomarkers in MEN1 Syndrome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5076. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115076
Chicago/Turabian StyleDonati, Simone, Cinzia Aurilia, Francesca Marini, Francesca Giusti, Gaia Palmini, Irene Falsetti, Federica Cioppi, Francesco Ranaldi, Teresa Iantomasi, Arcangelo Moro, and et al. 2025. "Serums miR-24-3p and miR-1301-3p as Potential Biomarkers in MEN1 Syndrome" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5076. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115076
APA StyleDonati, S., Aurilia, C., Marini, F., Giusti, F., Palmini, G., Falsetti, I., Cioppi, F., Ranaldi, F., Iantomasi, T., Moro, A., Tonelli, F., & Brandi, M. L. (2025). Serums miR-24-3p and miR-1301-3p as Potential Biomarkers in MEN1 Syndrome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5076. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115076








