Characterization and Functional Analysis of a Novel Fungal Immunomodulatory Protein Gene from Ganoderma leucocontextum in B16-F10 Mouse Melanoma Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
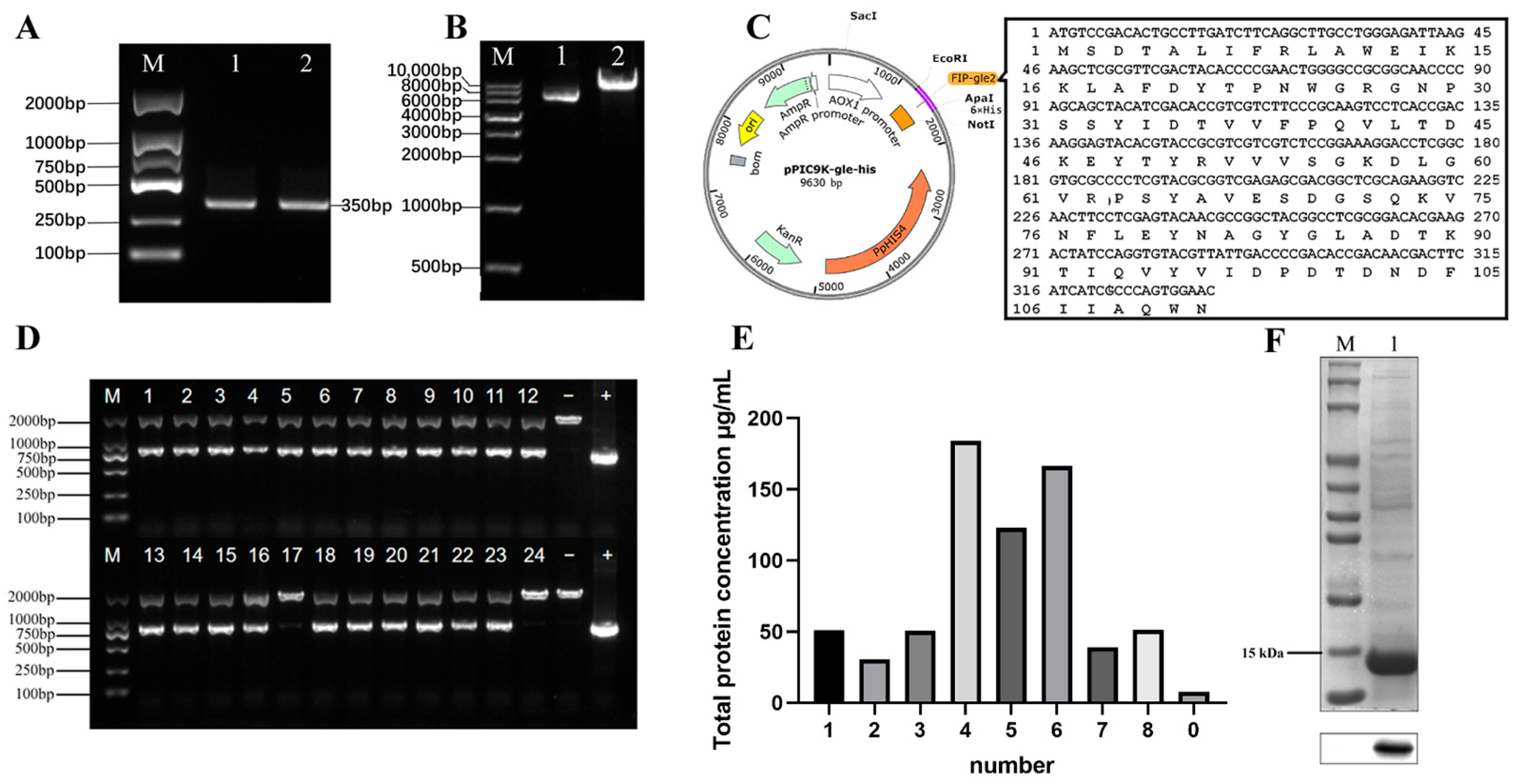
2.1. Bioinformatics Analysis of FIP-gle2 Gene
2.2. Expression and Purification of rFIP-gle2
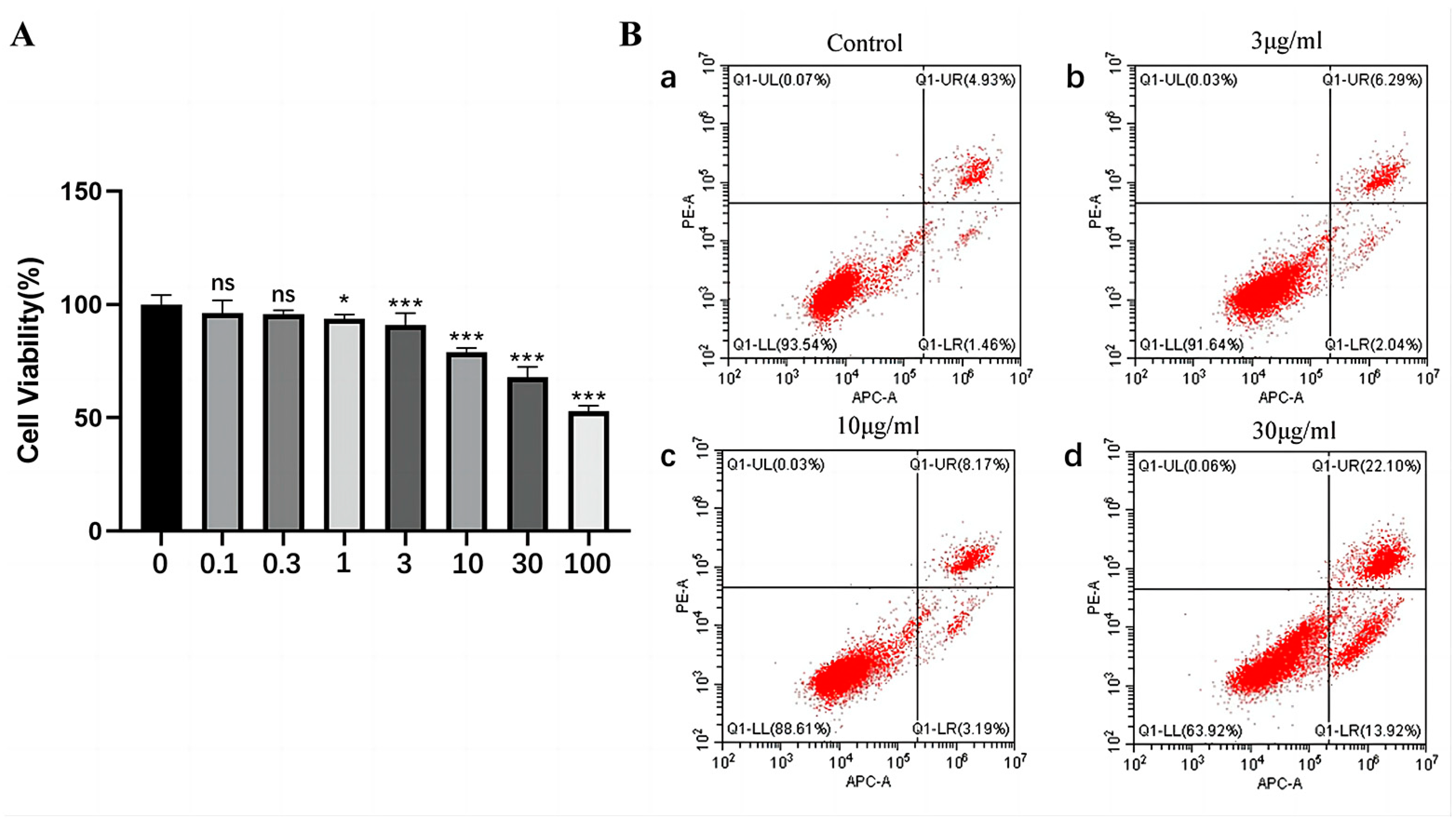
2.3. The Effect of rFIP-gle2 on Cell Viability and Cell Apoptosis
2.4. The Effect of rFIP-gle2 on Melanin Synthesis
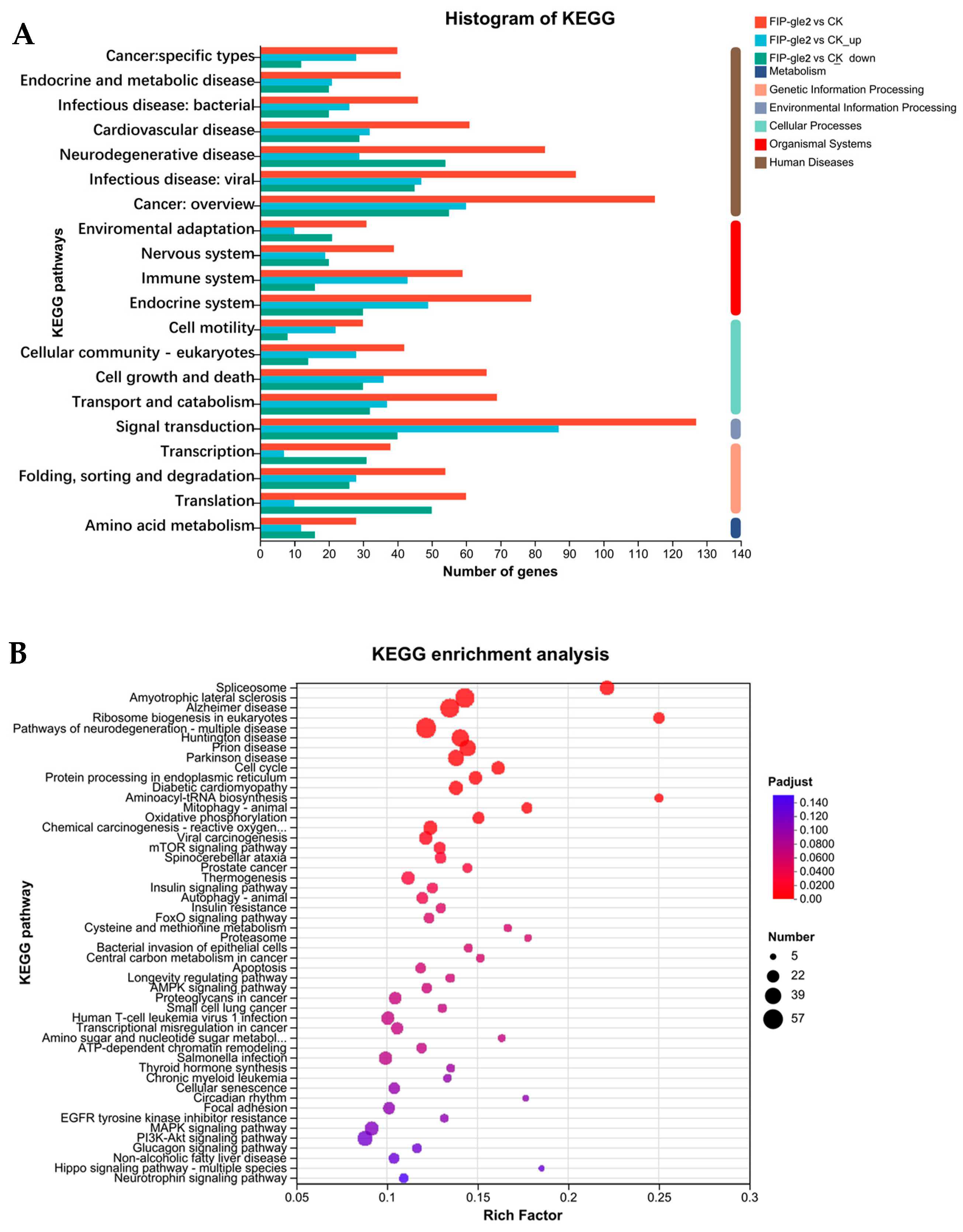
2.5. RNA-Seq Analysis
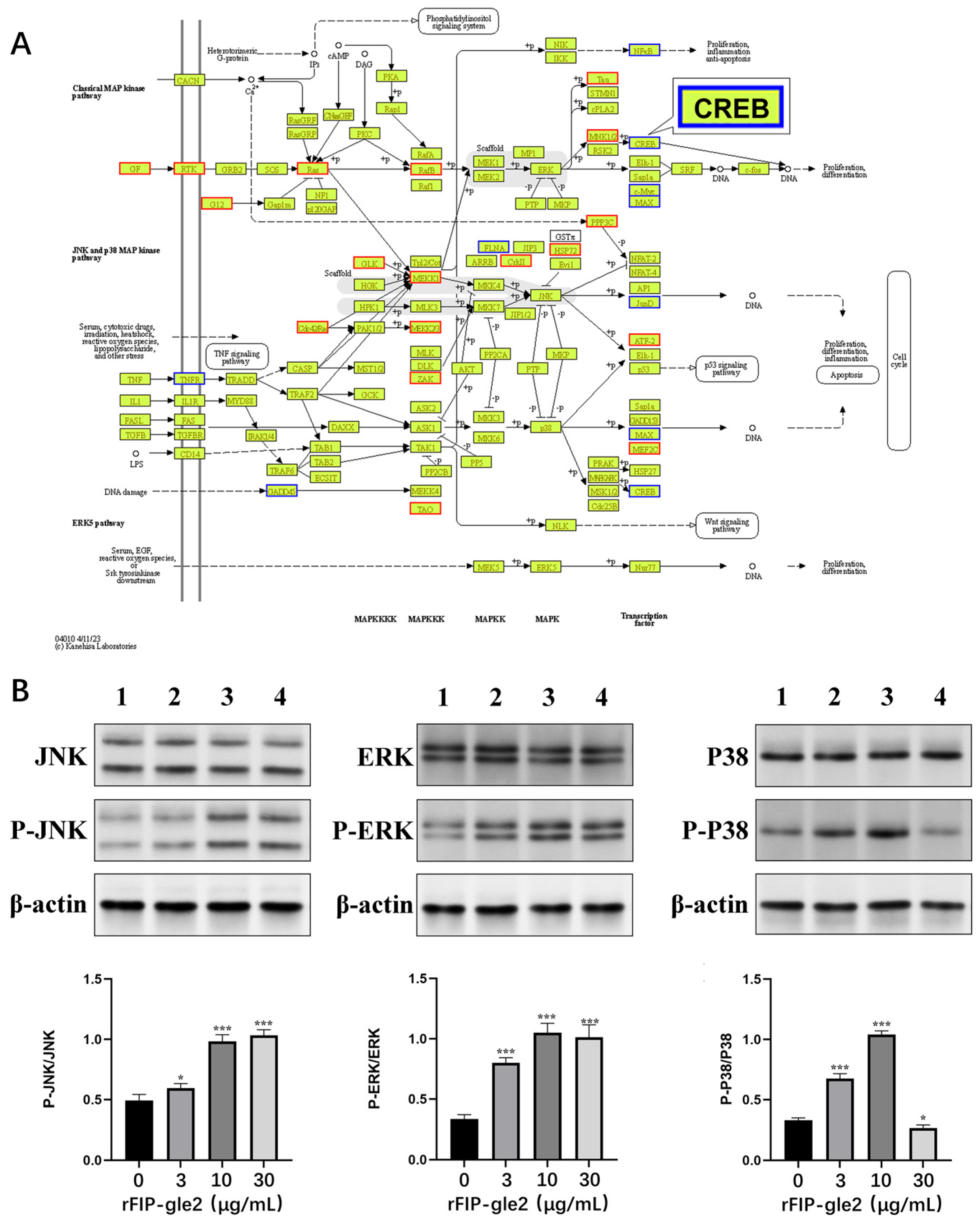
2.6. rFIP-gle2 Regulates the MAPK Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cloning and Bioinformatics Analysis of FIP-gle2 Gene
4.3. Expression and Purification of FIP-gle2
4.4. Cell Culture
4.5. Cell Viability Assay
4.6. Cell Apoptosis Assay
4.7. Determination of Tyrosinase Activity
4.8. Determination of Melanin Content
4.9. RT-qPCR Analysis
4.10. RNA-Seq Analysis
4.11. Western Blot
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, T.; Hu, H.; Deng, W.; Wu, S.; Wang, D.; Tsering, T. Ganoderma leucocontextum, a new member of the G. lucidum complex from southwestern China. Mycoscience 2015, 56, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Qi, J.; Ho, C.T.; Li, B.; Mu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, H.; Mo, W.; Chen, Z.; Xie, Y. Structural characterization and immunomodulatory activity of a water-soluble polysaccharide from Ganoderma leucocontextum fruiting bodies. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 249, 116874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Chen, H.; Li, Z.; Dong, Z.; Bai, X.; Zhou, Z.; Feng, T.; Liu, J. Leucocontextins A-R, lanostane-type triterpenoids from Ganoderma leucocontextum. Fitoterapia 2016, 109, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luangharn, T.; Mortimer, P.E.; Karunarathna, S.C.; Hyde, K.D.; Xu, J. Domestication of Ganoderma leucocontextum, G. resinaceum, and G. gibbosum collected from Yunnan province, China. Biosci. Biotechnol. Res. Asia 2020, 17, 7–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Shang, L.; Luo, X.; Sun, D. Research progress on artificial cultivation and active components of Ganoderma leucocontextum. Edible Fungi China 2020, 39, 1–4. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Peng, G.; Xiong, C.; Zeng, X.; Jin, Y.; Huang, W. Exploring nutrient profiles, phytochemical composition, and the antiproliferative activity of Ganoderma lucidum and Ganoderma leucocontextum: A comprehensive comparative study. Foods 2024, 13, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Qi, J.; Ho, C.T.; Li, B.; Xie, Y.; Chen, S.; Hu, H.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Q. Purification, physicochemical properties, and antioxidant activities of two low-molecular-weight polysaccharides from Ganoderma leucocontextum fruiting bodies. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Wang, K.; Kuang, S.; Cao, R.; Bao, L.; Liu, R.; Liu, H.; Sun, C. The natural compound GL22, isolated from Ganoderma mushrooms, suppresses tumor growth by altering lipid metabolism and triggering cell death. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zeng, R.; Qi, J.; Ho, C.-T.; Li, B.; Chen, Z.; Chen, S.; Xiao, C.; Hu, H.; Cai, M.J. Immunoregulatory activity of a low-molecular-weight heteropolysaccharide from Ganoderma leucocontextum fruiting bodies in vitro and in vivo. Food Chem. X 2022, 14, 100321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejike, U.C.; Chan, C.J.; Okechukwu, P.N.; Lim, R.L. New advances and potentials of fungal immunomodulatory proteins for therapeutic purposes. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2020, 40, 1172–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, A.; Ahmed, S. Optimization, purification and characterization of laccase from Ganoderma leucocontextum along with its phylogenetic relationship. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Bastiaan-Net, S.; Wichers, H.J. Current understanding of the structure and function of fungal immunomodulatory proteins. Front Nutr. 2020, 7, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Jiang, Z.; Sun, L.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, F.; Xin, F. Characterization of a new fungal immunomodulatory protein, FIP-dsq2 from Dichomitus squalens. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 246, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Chen, H.; Bai, Y.; Li, S.; Liang, G.; Fan, T.; Gao, N.; Wu, X.; Li, H.; Chen, G.; et al. Ganoderma immunomodulatory proteins: Mushrooming functional FIPs. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 2367–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.Z.; Zheng, Y.Z.; Zhou, X.W. Fungal immunomodulatory proteins: Characteristic, potential antitumor activities and their molecular mechanisms. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Hsu, C.; Tang, S.; Huang, Y.; Lin, J.; Ko, J. Fungal immunomodulatory protein from Flammulina velutipes induces interferon-gamma production through p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 2721–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Chang, Y.; He, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhou, X. Immunomodulatory activity of Ganoderma lucidum immunomodulatory protein 20via PI3K/Akt and MAPK signaling pathways in RAW264.7 cells. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 23337–23348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Bao, D.; Bing, W.; Li, Y.; Chen, H. Characterization, recombinant production, and bioactivity of a novel immunomodulatory protein from Hypsizygus marmoreus. Molecules 2023, 28, 4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Li, S.; Sun, L.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Wen, B.; Sun, L.; Fang, X.; Chai, Y.; Cao, H.; et al. Fungal immunomodulatory protein from Nectria haematococca suppresses growth of human lung adenocarcinoma by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Hsiao, Y.; Sheu, G.; Chang, J.; Wang, P.; Wu, M.; Shieh, G.; Hsu, C.; Ko, J. Nuclear translocation of telomerase reverse transcriptase and calcium signaling in repression of telomerase activity in human lung cancer cells by fungal immunomodulatory protein from Ganoderma tsugae. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 74, 1541–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Lin, T.; Hsu, H.; Sheu, F.; Ho, C.; Chen, E. Ling Zhi-8 mediates p53-dependent growth arrest of lung cancer cells proliferation via the ribosomal protein S7-MDM2-p53 pathway. Carcinogenesis 2011, 32, 1890–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Guan, S.; Duan, Z.; Han, X.; Zhang, X.; Fan, W.; Li, H.; Chen, L.; Ma, H.; Liu, H.; et al. Molecular cloning, codon-optimized gene expression, and bioactivity assessment of two novel fungal immunomodulatory proteins from Ganoderma applanatum in Pichia. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 5483–5494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Liao, Y.; Yang, S.; Jin, T.; Yu, B.; Zhao, K.; Sai, Y.; Lin, C.; Song, Y.; Ma, H.; et al. Identification of a novel Ganoderma FIP gene from Ganoderma capense and its functional expression in Pichia pastoris. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 40, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaan-Net, S.; Chanput, W.; Hertz, A.; Zwittink, R.D.; Mes, J.J.; Wichers, H.J. Biochemical and functional characterization of recombinant fungal immunomodulatory proteins (rFIPs). Int. Immunopharmacol. 2013, 15, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Mello, S.A.; Finlay, G.J.; Baguley, B.C.; Askarian-Amiri, M.E. Signaling pathways in melanogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Chen, X.; Mao, P.; Jin, M.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, X. N-Glycosylated Ganoderma lucidum immunomodulatory protein improved anti-inflammatory activity via inhibition of the p38 MAPK pathway. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 3393–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J.Y.; Jin, M.Y.; Mao, P.W.; Zhou, X.W. Evaluating the application potential of a recombinant Ganoderma protein as bioactive ingredients in cosmetics. Molecules 2023, 28, 3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, T.; Feng, X.; Yang, N.; Zhou, H. Signaling pathway of MAPK/ERK in cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, senescence and apoptosis. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 2015, 35, 600–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakis, J.M.; Avruch, J. Mammalian MAPK signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation: A 10-year update. Physiol. Rev. 2012, 92, 689–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaloni, D.; Diepstraten, S.; Strasser, A.; Kelly, G. BCL-2 protein family: Attractive targets for cancer therapy. Apoptosis 2023, 28, 20–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Zhao, M.; Zhong, J.; Ma, Y.; Deng, G.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Yuan, X.; Huang, C. NAIF1 is down-regulated in gastric cancer and promotes apoptosis through the caspase-9 pathway in human MKN45 cells. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 25, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kashyap, D.; Garg, V.; Goel, N. Intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of apoptosis: Role in cancer development and prognosis. Adv. Protein. Chem. Struct. Biol. 2021, 125, 73–120. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, J.; Tang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hu, H. Inhibition of fatty acid synthase (FASN) affects the proliferation and apoptosis of HepG2 hepatoma carcinoma cells via the β-catenin/C-myc signaling pathway. Ann. Hepatol. 2020, 19, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanasekaran, D.; Reddy, E. JNK signaling in apoptosis. Oncogene 2008, 27, 6245–6251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, S.; Won, K.; Moon, H.; Yoo, H.; Hong, A.; Song, Y.; Chang, S. Novel regulation of melanogenesis by adiponectin via the AMPK/CRTC pathway. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2017, 30, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Hong, A.R.; Kim, Y.H.; Yoo, H.; Kang, S.W.; Chang, S.E.; Song, Y. JNK suppresses melanogenesis by interfering with CREB-regulated transcription coactivator 3-dependent MITF expression. Theranostics 2020, 10, 4017–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Lee, W.J.; Chang, S.E.; Lee, G.Y. Hesperidin, a popular antioxidant inhibits melanogenesis via Erk1/2 mediated MITF degradation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 18384–18395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molagoda, I.; Karunarathne, W.; Park, S.; Choi, Y.; Park, E.; Jin, C.; Yu, H.; Jo, W.; Lee, K.; Kim, G. GSK-3β-Targeting fisetin promotes melanogenesis in B16F10 melanoma cells and Zebrafish larvae through β-Catenin activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngeow, K.; Friedrichsen, H.; Li, L.; Zeng, Z.; Andrews, S.; Volpon, L.; Brunsdon, H.; Berridge, G.; Picaud, S.; Fischer, R.; et al. BRAF/MAPK and GSK3 signaling converges to control MITF nuclear export. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E8668–E8677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaled, M.; Larribere, L.; Bille, K.; Aberdam, E.; Ortonne, J.; Ballotti, R.; Bertolotto, C. Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta is activated by cAMP and plays an active role in the regulation of melanogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 33690–33697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santarpia, L.; Lippman, S.; El-Naggar, A. Targeting the MAPK-RAS-RAF signaling pathway in cancer therapy. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 2012, 16, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; He, X.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Xing, W.; Liu, W.; Ren, C.; Han, X.; Guo, B. Celastrol inhibits mouse B16-F10 melanoma cell survival by regulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and repressing HIF-1α expression. Discov. Oncol. 2024, 15, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, X.J.; Zou, J.; Zou, T.; Shang, H.; Sun, L.Y. A newly authenticated compound from traditional Chinese medicine decoction induces melanogenesis in B16-F10 cells by increasing tyrosinase activity. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 8485670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| FIPs | Homology Compared to FIP-gle2 | Resource | Number of Amino Acids (aa) | Molecular Weight (kDa) | Theoretical pI | Gene ID/Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FIP-gle2 | — | G. leucocontextum | 111 | 12.60 | 4.48 | — |
| FIP-gle1 | 93.69% | G. leucocontextum | 112 | 12.64 | 4.73 | KAI1793471.1 |
| FIP-glu1 (LZ-8) | 82.88% | G. lucidum | 111 | 13.1 | 4.84 | AAA33350.1 |
| FIP-glu2 (LZ-9) | 94.59% | G. lucidum | 111 | 12.40 | 4.55 | [24] |
| FIP-gca | 87.39% | G. capense | 111 | 12.41 | 4.44 | UOF75531.1 |
| FIP-gmi | 85.59% | G. microsporum | 111 | 12.40 | 4.58 | 3KCW (PDB) |
| FIP-gre | 83.78% | G. resinaceum | 111 | 12.46 | 5.14 | AUB29452.1 |
| FIP-gja | 83.78% | G. japonicum | 111 | 12.48 | 4.62 | AAX98241.1 |
| FIP-gte | 82.88% | G. tenue | 111 | 12.52 | 4.84 | UOF75530.1 |
| FIP-gbo | 82.73% | G. boninense | 110 | 12.33 | 4.62 | KT124392.1 |
| FIP-gat | 81.98% | G. atrum | 111 | 12.45 | 4.80 | AJD79556.1 |
| FIP-gam | 78.50% | G. amboinense | 107 | 11.98 | 4.48 | [13] |
| FIP-gap1 | 77.48% | G. applanatum | 113 | 12.74 | 4.93 | AEP68179.1 |
| FIP-cru | 76.58% | C. rutilus | 113 | 12.65 | 4.93 | AKU37620.1 |
| FIP-gap2 | 69.37% | G. applanatum | 113 | 12.52 | 4.86 | ART88472.1 |
| FIP-fve | 62.16% | F. velutipes | 114 | 12.73 | 6.17 | ADB24832.1 |
| Gene | Forward Primer (5′→3′) | Reverse Primer (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| LZ8 | TACGTAGAATTCATGTCCGACACTGCCTTGATCTTCAG | ATGATGGGGCCCGTTCCACTGGGCGATGATGAAGTCG |
| Gle | GGCTGAAGCTTACGTAGAATTCATGTCCGACACTGCCTTGATCTTCAG | TGATGGTGATGGTGGGGCCCGTTCCACTGGGCGATGATGAAGTCG |
| AOX1 | GACTGGTTCCAATTGACAAGC | GGC AAATGGCATTCTGACAT |
| MITF | CAAATGGCAAATACGTTACCCG | CTCCCTTTTTATGTTGGGAAGGT |
| TYR | CACCATGCTTTTGTGGACAG | GGCTTCTGGGTAAACTTCCAA |
| TRP-1 | CTGTGGATTATTGGGATGA | GTGAGCCACCACTTTGAG |
| TRP-2 | GCTGATTAGTCGGAACTCGA | GGTTGGCAGTTTCTCATTATTT |
| GAPDH | TATGTCGTGGAGTCTACTGGT | GAGTTGTCATATTTCTCGTGG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Jin, M.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, X. Characterization and Functional Analysis of a Novel Fungal Immunomodulatory Protein Gene from Ganoderma leucocontextum in B16-F10 Mouse Melanoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5063. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115063
Yang J, Jin M, Zhang L, Wu Y, Zhou X. Characterization and Functional Analysis of a Novel Fungal Immunomodulatory Protein Gene from Ganoderma leucocontextum in B16-F10 Mouse Melanoma Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5063. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115063
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jiayi, Mengyuan Jin, Lida Zhang, Yingying Wu, and Xuanwei Zhou. 2025. "Characterization and Functional Analysis of a Novel Fungal Immunomodulatory Protein Gene from Ganoderma leucocontextum in B16-F10 Mouse Melanoma Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5063. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115063
APA StyleYang, J., Jin, M., Zhang, L., Wu, Y., & Zhou, X. (2025). Characterization and Functional Analysis of a Novel Fungal Immunomodulatory Protein Gene from Ganoderma leucocontextum in B16-F10 Mouse Melanoma Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5063. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115063







