Opioid-Induced Regulation of Cortical Circular-Grin2b_011731 Is Associated with Regulation of circGrin2b Sponge Target miR-26b-3p
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
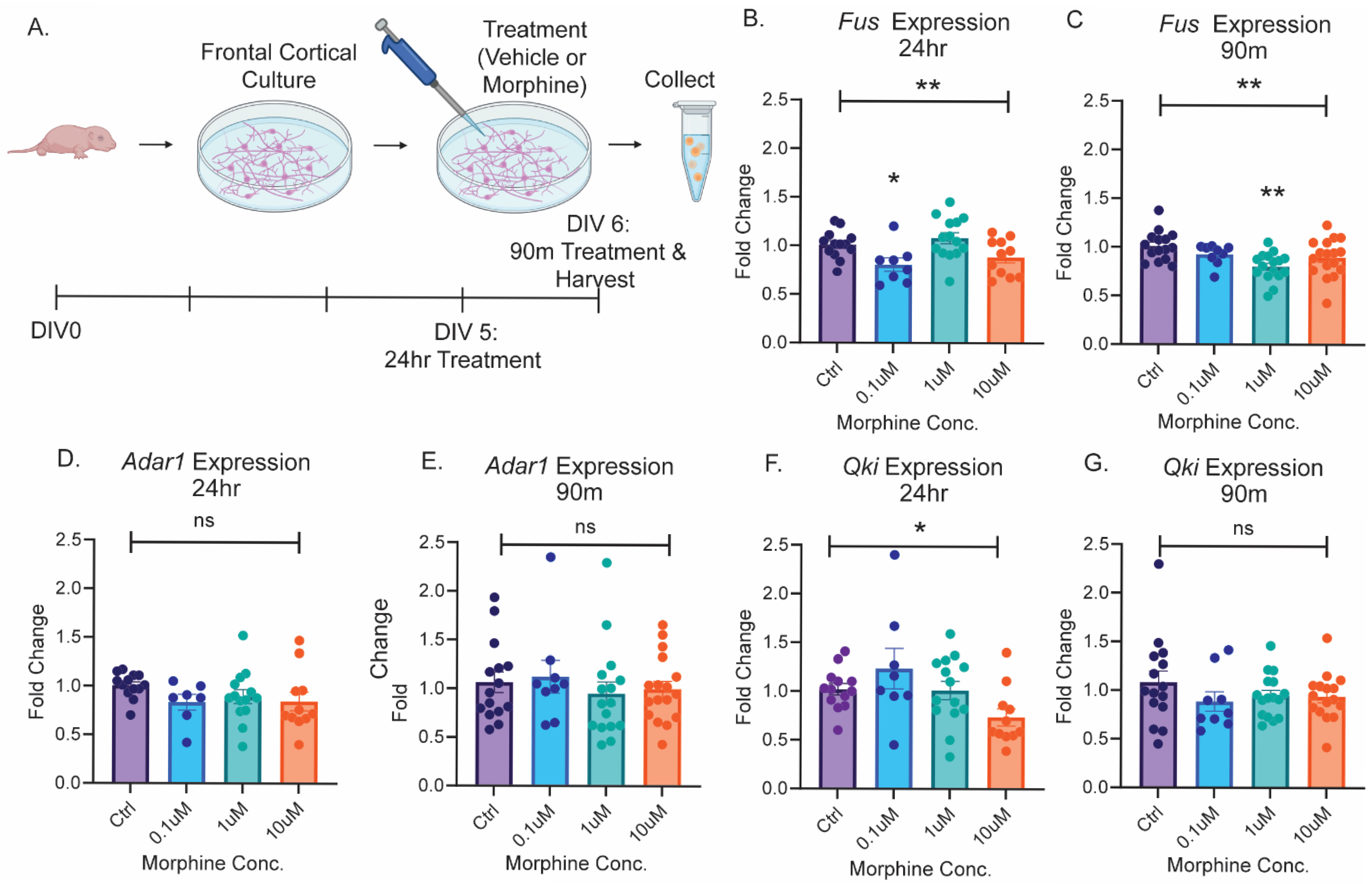
2.1. The Splicing Enzyme Fus Is Regulated by Opioid Exposure
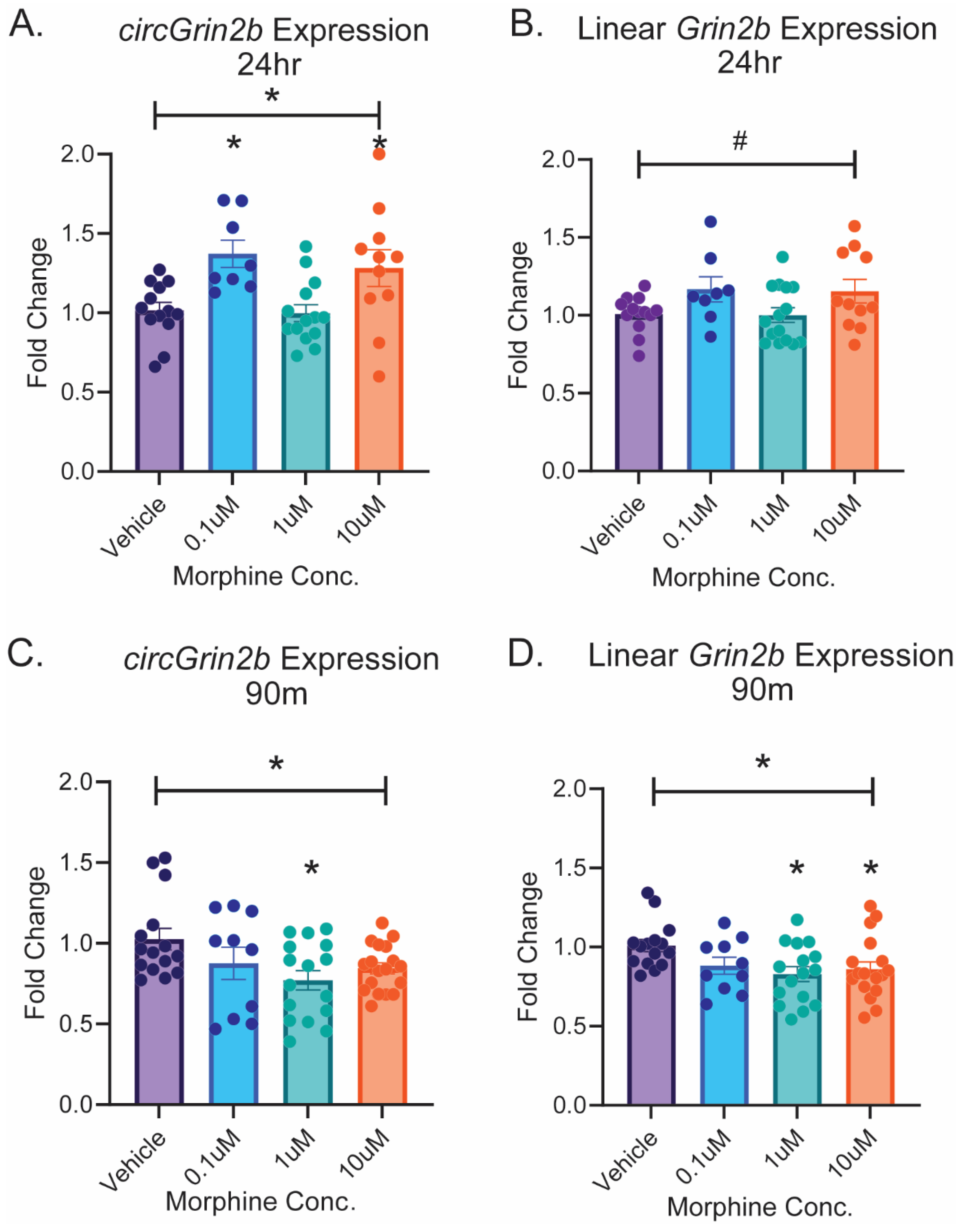
2.2. Opioid-Induced Regulation of circGrin2b In Vitro Corresponds to Regulation of Putative circRNA Biogenesis Enzyme Fus
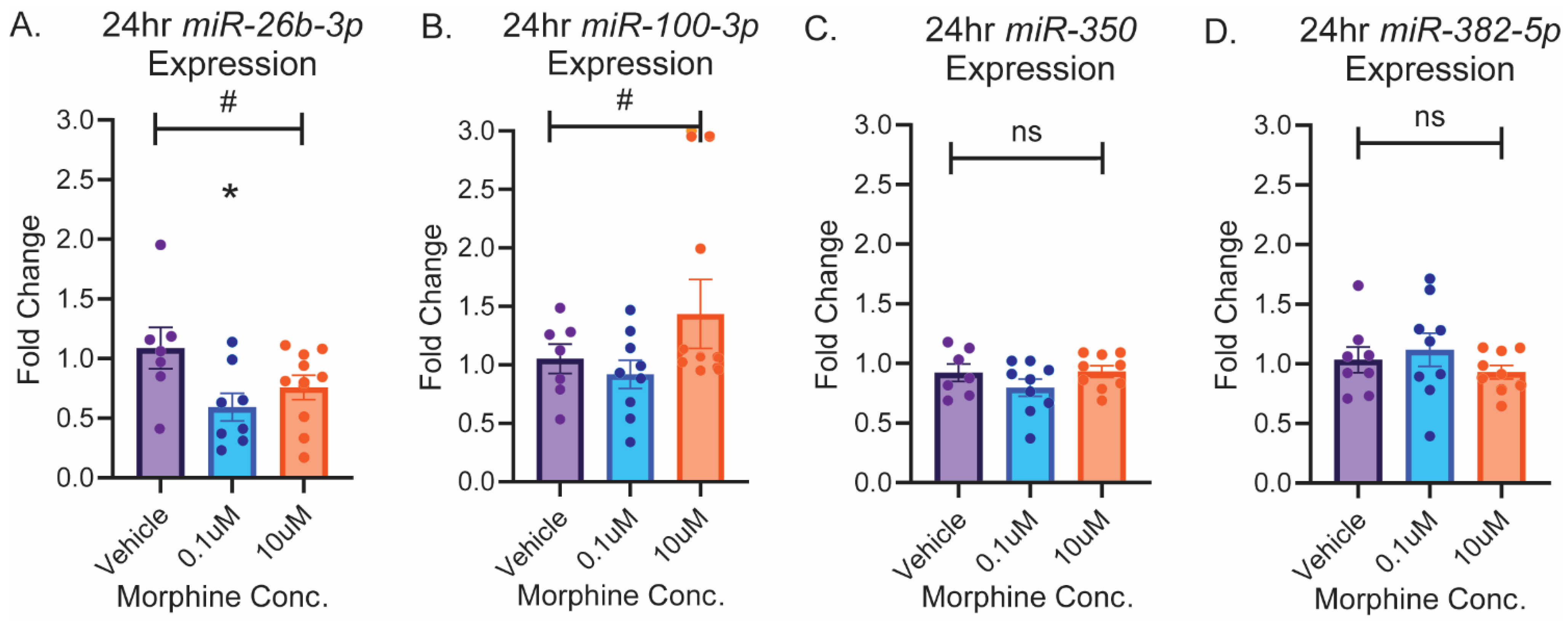
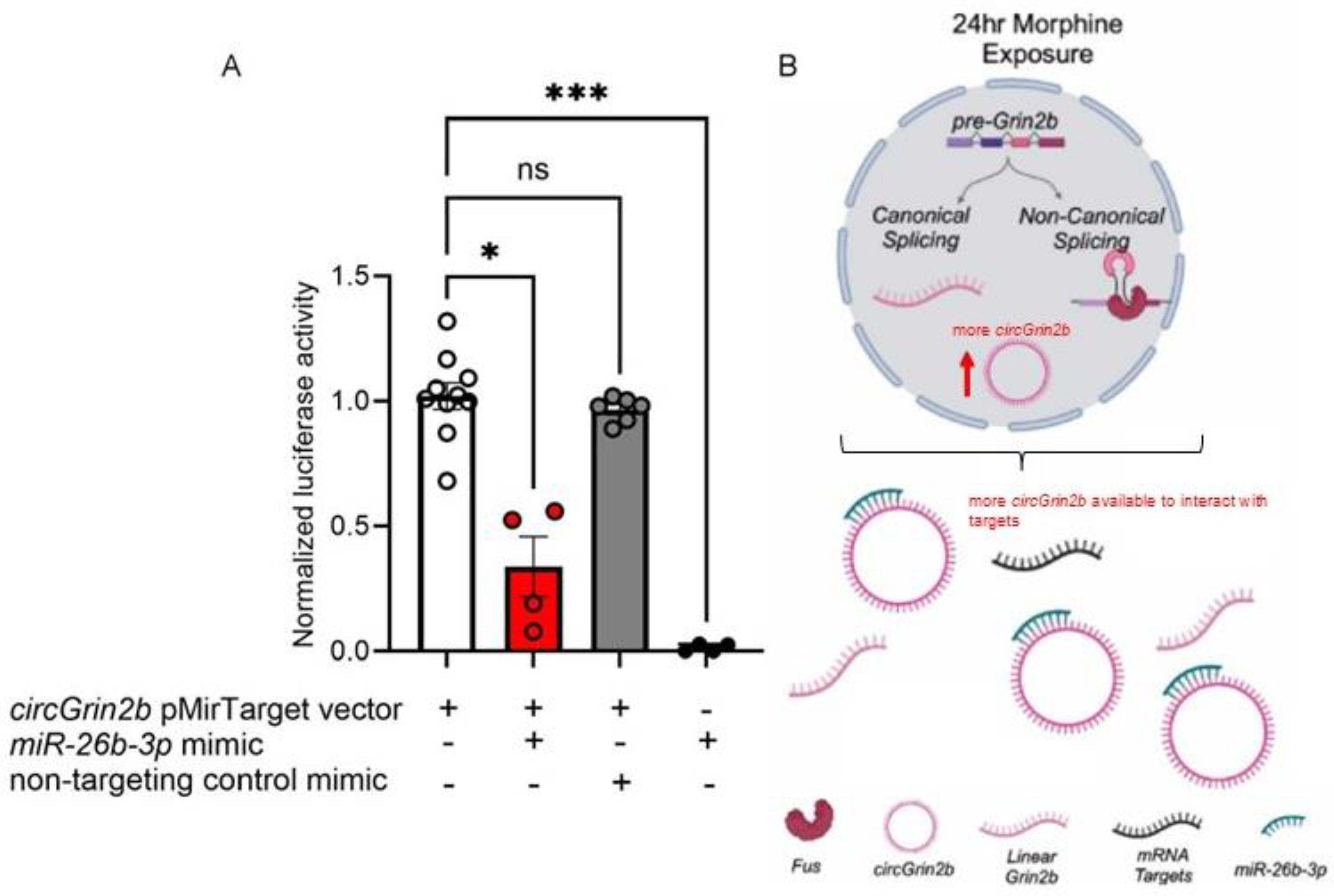
2.3. circGrin2b Sponges miR-26b-3p
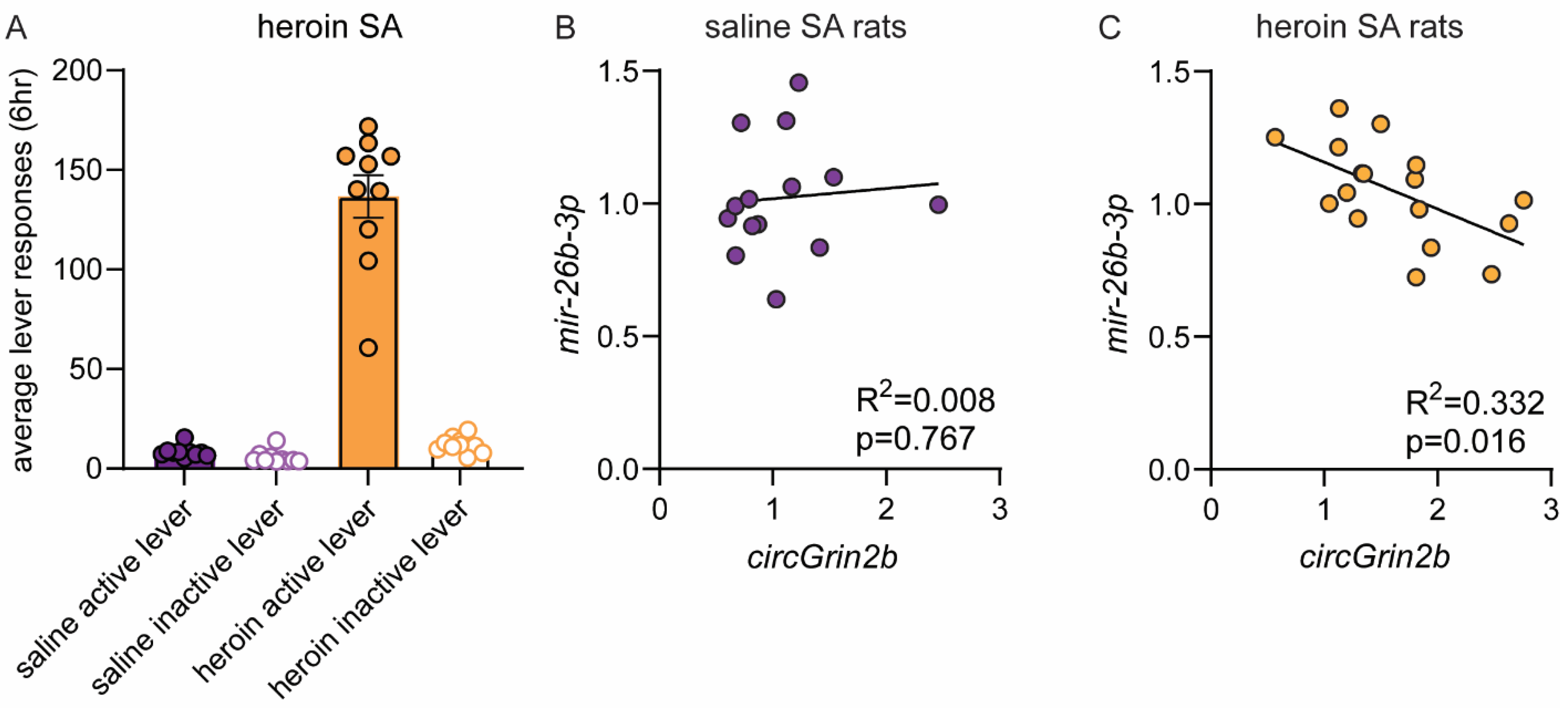
2.4. OFC circGrin2b Levels Are Negatively Correlated with miR-26b-3p Expression Following Heroin SA
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Reagents
4.3. Primary Frontal Cortex Cultures
4.4. RNA Extraction
4.5. Gene Expression Assays
4.6. circRNA Primer Validation
4.7. Luciferase Reporter Assay
4.8. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmad, F.B.; Cisewski, J.A.; Rossen, L.M.; Sutton, P. National Center for Health Statistics. 2022. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nvss/vsrr/drug-overdose-data.htm (accessed on 4 September 2024).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Multiple Cause of Death Files, National Center for Health Statistics. 1999–2019. Available online: https://wonder.cdc.gov/ (accessed on 27 September 2021).
- Hedegaard, H.; Miniño, A.M.; Warner, M. Co-involvement of opioids in drug overdose deaths involving cocaine and psychostimulants. NCHS Data Briefs 2021, 406, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Volkow, N.D.; Morales, M. The Brain on Drugs: From Reward to Addiction. Cell 2015, 162, 712–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, B.P.; Barry, J.; Keenan, E.; Ducray, K. Lapse and relapse following inpatient treatment of opiate dependence. Ir. Med. J. 2010, 103, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grella, C.E.; Lovinger, K. 30-year trajectories of heroin and other drug use among men and women sampled from methadone treatment in California. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2011, 118, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalana, H.; Kundal, T.; Gupta, V.; Malhari, A.S. Predictors of Relapse after Inpatient Opioid Detoxification during 1-Year Follow-Up. J. Addict. 2016, 2016, 7620860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, H.B.; Brown, R.M.; Short, J.L.; Lawrence, A.J. Investigation of the neuroanatomical substrates of reward seeking following protracted abstinence in mice. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 2427–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, M.; Wang, E.; Shen, Y.; Wang, J. Cue-elicited craving in heroin addicts at different abstinent time: An fMRI pilot study. Subst. Use Misuse 2012, 47, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, M.J. Cellular neuroadaptations to chronic opioids: Tolerance, withdrawal and addiction. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 154, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradin, V.B.; Baldacchino, A.; Balfour, D.; Matthews, K.; Steele, J.D. Abnormal brain activity during a reward and loss task in opiate-dependent patients receiving methadone maintenance therapy. Neuropsychopharmacology 2014, 39, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauer, J.A.; Malenka, R.C. Synaptic plasticity and addiction. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 844–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruyer, A.; Chioma, V.C.; Kalivas, P.W. The Opioid-Addicted Tetrapartite Synapse. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 87, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.; Moussawi, K.; Zhou, W.; Toda, S.; Kalivas, P.W. Heroin relapse requires long-term potentiation-like plasticity mediated by NMDA2b-containing receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 19407–19412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, J.; Strang, J. Medication Treatment of Opioid Use Disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 87, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, X.; Vlatkovic, I.; Babic, A.; Will, T.; Epstein, I.; Tushev, G.; Akbalik, G.; Wang, M.; Glock, C.; Quedenau, C.; et al. Neural circular RNAs are derived from synaptic genes and regulated by development and plasticity. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, S.P.; Salzman, J. Circular RNAs: Analysis, expression and potential functions. Development 2016, 143, 1838–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, L.S.; Andersen, M.S.; Stagsted, L.V.W.; Ebbesen, K.K.; Hansen, T.B.; Kjems, J. The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 675–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.L. The Biogenesis, Functions, and Challenges of Circular RNAs. Mol. Cell 2018, 71, 428–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Huang, W.; Mu, Y.; Li, Y.; Ouyang, H. CircNf1-mediated CXCL12 expression in the spinal cord contributes to morphine analgesic tolerance. Brain Behav. Immun. 2023, 107, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowski, K.R.; Floris, G.; Gillespie, A.; Daws, S.E. Orbitofrontal intronic circular RNA from Nrxn3 mediates reward learning and motivation for reward. Prog. Neurobiol. 2023, 232, 102546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafez, A.K.; Zimmerman, A.J.; Papageorgiou, G.; Chandrasekaran, J.; Amoah, S.K.; Lin, R.; Lozano, E.; Pierotti, C.; Dell’Orco, M.; Hartley, B.J.; et al. A bidirectional competitive interaction between circHomer1 and Homer1b within the orbitofrontal cortex regulates reversal learning. Cell Rep. 2022, 38, 110282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Tan, L.; Wang, X. Circular HDAC9/microRNA-138/Sirtuin-1 Pathway Mediates Synaptic and Amyloid Precursor Protein Processing Deficits in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurosci. Bull. 2019, 35, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piwecka, M.; Glažar, P.; Hernandez-Miranda, L.R.; Memczak, S.; Wolf, S.A.; Rybak-Wolf, A.; Filipchyk, A.; Klironomos, F.; Cerda Jara, C.A.; Fenske, P.; et al. Loss of a mammalian circular RNA locus causes miRNA deregulation and affects brain function. Science 2017, 357, eaam8526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Q.; Xie, B.; Galaj, E.; Yu, H.; Li, X.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wen, D.; Ma, C. CircTmeff-1 in the nucleus accumbens regulates the reconsolidation of cocaine-associated memory. Brain Res. Bull. 2022, 185, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Du, L.; Bai, Y.; Han, B.; He, C.; Gong, L.; Huang, R.; Shen, L.; Chao, J.; Liu, P.; et al. CircDYM ameliorates depressive-like behavior by targeting miR-9 to regulate microglial activation via HSP90 ubiquitination. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 25, 1175–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, A.J.; Hafez, A.K.; Amoah, S.K.; Rodriguez, B.A.; Dell’Orco, M.; Lozano, E.; Hartley, B.J.; Alural, B.; Lalonde, J.; Chander, P.; et al. A psychiatric disease-related circular RNA controls synaptic gene expression and cognition. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 25, 2712–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeck, W.R.; Sharpless, N.E. Detecting and characterizing circular RNAs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeck, W.R.; Sorrentino, J.A.; Wang, K.; Slevin, M.K.; Burd, C.E.; Liu, J.; Marzluff, W.F.; Sharpless, N.E. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA 2013, 19, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragan, C.; Goodall, G.J.; Shirokikh, N.E.; Preiss, T. Insights into the biogenesis and potential functions of exonic circular RNA. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak-Wolf, A.; Stottmeister, C.; Glažar, P.; Jens, M.; Pino, N.; Giusti, S.; Hanan, M.; Behm, M.; Bartok, O.; Ashwal-Fluss, R.; et al. Circular RNAs in the Mammalian Brain Are Highly Abundant, Conserved, and Dynamically Expressed. Mol. Cell 2015, 58, 870–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floris, G.; Gillespie, A.; Zanda, M.T.; Dabrowski, K.R.; Daws, S.E. Heroin Regulates Orbitofrontal Circular RNAs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, P.; Pierotti, C.; Lozano, E.; Amoah, S.K.; Gardiner, A.S.; Caldwell, K.K.; Allan, A.M.; Mellios, N. Prenatal Alcohol Exposure Results in Sex-Specific Alterations in Circular RNA Expression in the Developing Mouse Brain. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 581895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daws, S.E.; Gillespie, A. Circular RNA regulation and function in drug seeking phenotypes. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2023, 125, 103841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, U.; Del-Aguila, J.L.; Li, Z.; Budde, J.P.; Jiang, S.; Hsu, S.; Ibanez, L.; Fernandez, M.V.; Farias, F.; Norton, J.; et al. An atlas of cortical circular RNA expression in Alzheimer disease brains demonstrates clinical and pathological associations. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 1903–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudi, E.; Cairns, M.J. Circular RNAs are temporospatially regulated throughout development and ageing in the rat. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajaczkowski, E.L.; Bredy, T.W. Circular RNAs in the Brain: A Possible Role in Memory? Neuroscientist 2021, 27, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vornholt, E.; Drake, J.; Mamdani, M.; McMichael, G.; Taylor, Z.N.; Bacanu, S.A.; Miles, M.F.; Vladimirov, V.I. Identifying a novel biological mechanism for alcohol addiction associated with circRNA networks acting as potential miRNA sponges. Addict. Biol. 2021, 26, e13071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Meng, S.; Huang, S.; Chang, S.; Shi, J. Identification of Functional CircRNA-miRNA-mRNA Regulatory Network in Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex Neurons of Patients With Cocaine Use Disorder. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 839233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boroujeni, M.E.; Nasrollahi, A.; Boroujeni, P.B.; Fadaeifathabadi, F.; Farhadieh, M.; Tehrani, A.M.; Nakhaei, H.; Sajedian, A.M.; Peirouvi, T.; Aliaghaei, A. Exposure to methamphetamine exacerbates motor activities and alters circular RNA profile of cerebellum. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 144, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Q.; Long, H.; Shao, X.; Gu, H.; Kong, J.; Luo, L.; Liu, B.; Guo, W.; Wang, H.; Tian, J.; et al. Cocaine induces differential circular RNA expression in striatum. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Orco, M.; Elyaderani, A.; Vannan, A.; Sekar, S.; Powell, G.; Liang, W.S.; Neisewander, J.L.; Perrone-Bizzozero, N.I. HuD Regulates mRNA-circRNA-miRNA Networks in the Mouse Striatum Linked to Neuronal Development and Drug Addiction. Biology 2021, 10, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Bu, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Q.; Li, M.; Lu, Z.; Rong, X.; Zheng, D.; et al. Circular RNA expression alteration identifies a novel circulating biomarker in serum exosomal for detection of alcohol dependence. Addict. Biol. 2021, 26, e13031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altshuler, R.D.; Yang, E.S.; Garcia, K.T.; Davis, I.R.; Olaniran, A.; Haile, M.; Razavi, S.; Li, X. Role of orbitofrontal cortex in incubation of oxycodone craving in male rats. Addict. Biol. 2021, 26, e12927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanous, S.; Goldart, E.M.; Theberge, F.R.; Bossert, J.M.; Shaham, Y.; Hope, B.T. Role of orbitofrontal cortex neuronal ensembles in the expression of incubation of heroin craving. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 11600–11609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiner, D.J.; Lofaro, O.M.; Applebey, S.V.; Korah, H.; Venniro, M.; Cifani, C.; Bossert, J.M.; Shaham, Y. Role of Projections between Piriform Cortex and Orbitofrontal Cortex in Relapse to Fentanyl Seeking after Palatable Food Choice-Induced Voluntary Abstinence. J. Neurosci. 2020, 40, 2485–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenbaum, G.; Shaham, Y. The role of orbitofrontal cortex in drug addiction: A review of preclinical studies. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 63, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaLumiere, R.T.; Kalivas, P.W. Glutamate release in the nucleus accumbens core is necessary for heroin seeking. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 3170–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, J.; De Vries, T.J. Glutamate mechanisms underlying opiate memories. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a012088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.Y.; Yu, P.; Guo, C.Y.; Cui, C.L. Effects of ifenprodil on morphine-induced conditioned place preference and spatial learning and memory in rats. Neurochem. Res. 2011, 36, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narita, M.; Aoki, T.; Suzuki, T. Molecular evidence for the involvement of NR2B subunit containing N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in the development of morphine-induced place preference. Neuroscience 2000, 101, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errichelli, L.; Dini Modigliani, S.; Laneve, P.; Colantoni, A.; Legnini, I.; Capauto, D.; Rosa, A.; De Santis, R.; Scarfò, R.; Peruzzi, G.; et al. FUS affects circular RNA expression in murine embryonic stem cell-derived motor neurons. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Yan, P.; Liang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Shen, J.; Zhou, S.; Lin, H.; Liang, X.; Cai, X. Circular RNA expression is suppressed by androgen receptor (AR)-regulated adenosine deaminase that acts on RNA (ADAR1) in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conn, S.J.; Pillman, K.A.; Toubia, J.; Conn, V.M.; Salmanidis, M.; Phillips, C.A.; Roslan, S.; Schreiber, A.W.; Gregory, P.A.; Goodall, G.J. The RNA binding protein quaking regulates formation of circRNAs. Cell 2015, 160, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omata, Y.; Okawa, M.; Haraguchi, M.; Tsuruta, A.; Matsunaga, N.; Koyanagi, S.; Ohdo, S. RNA editing enzyme ADAR1 controls miR-381-3p-mediated expression of multidrug resistance protein MRP4 via regulation of circRNA in human renal cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, C.X.; Xue, W.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Yin, Q.F.; Wei, J.; Yao, R.W.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.L. Coordinated circRNA Biogenesis and Function with NF90/NF110 in Viral Infection. Mol. Cell 2017, 67, 214–227.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshparvar, H.; Sadat-Shirazi, M.S.; Fekri, M.; Khalifeh, S.; Ziaie, A.; Esfahanizadeh, N.; Vousooghi, N.; Zarrindast, M.R. NMDA receptor subunits change in the prefrontal cortex of pure-opioid and multi-drug abusers: A post-mortem study. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 269, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garikipati, V.N.S.; Verma, S.K.; Cheng, Z.; Liang, D.; Truongcao, M.M.; Cimini, M.; Yue, Y.; Huang, G.; Wang, C.; Benedict, C.; et al. Circular RNA CircFndc3b modulates cardiac repair after myocardial infarction via FUS/VEGF-A axis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dill, H.; Linder, B.; Fehr, A.; Fischer, U. Intronic miR-26b controls neuronal differentiation by repressing its host transcript, ctdsp2. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauer, M.; Was, N.; Ziegenhals, T.; Wang, X.; Hafner, M.; Becker, M.; Fischer, U. The miR-26 family regulates neural differentiation-associated microRNAs and mRNAs by directly targeting REST. J. Cell Sci. 2021, 134, jcs257535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stringer, R.L.; Laufer, B.I.; Kleiber, M.L.; Singh, S.M. Reduced expression of brain cannabinoid receptor 1 (Cnr1) is coupled with an increased complementary micro-RNA (miR-26b) in a mouse model of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Clin. Epigenet. 2013, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, T.; Shu, Y.; Qu, Y.; Gao, S.; Zhang, L. miR-26b inhibits total neurite outgrowth, promotes cells apoptosis and downregulates neprilysin in Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 11, 3383–3390. [Google Scholar]
- Caputo, V.; Sinibaldi, L.; Fiorentino, A.; Parisi, C.; Catalanotto, C.; Pasini, A.; Cogoni, C.; Pizzuti, A. Brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression is regulated by microRNAs miR-26a and miR-26b allele-specific binding. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Nagappan, G.; Lu, Y. BDNF and synaptic plasticity, cognitive function, and dysfunction. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2014, 220, 223–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, N.; Wang, R.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, Y.; Gong, J.; Zhuang, S.M. MicroRNA-26b suppresses the NF-κB signaling and enhances the chemosensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting TAK1 and TAB3. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, R.C.; Farh, K.K.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanda, M.T.; Floris, G.; Daws, S.E. Orbitofrontal cortex microRNAs support long-lasting heroin seeking behavior in male rats. Transl. Psychiatry 2023, 13, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, A.; Mayberry, H.L.; Wimmer, M.E.; Daws, S.E. microRNA expression levels in the nucleus accumbens correlate with morphine-taking but not morphine-seeking behaviour in male rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2022, 55, 1742–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanda, M.T.; Saikali, L.; Morris, P.; Daws, S.E. MicroRNA-mediated translational pathways are regulated in the orbitofrontal cortex and peripheral blood samples during acute abstinence from heroin self-administration. Adv. Drug Alcohol Res. 2023, 3, 11668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rom, S.; Dykstra, H.; Zuluaga-Ramirez, V.; Reichenbach, N.L.; Persidsky, Y. miR-98 and let-7g* protect the blood-brain barrier under neuroinflammatory conditions. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2015, 35, 1957–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gillespie, A.; Daws, S.E. Opioid-Induced Regulation of Cortical Circular-Grin2b_011731 Is Associated with Regulation of circGrin2b Sponge Target miR-26b-3p. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5010. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115010
Gillespie A, Daws SE. Opioid-Induced Regulation of Cortical Circular-Grin2b_011731 Is Associated with Regulation of circGrin2b Sponge Target miR-26b-3p. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5010. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115010
Chicago/Turabian StyleGillespie, Aria, and Stephanie E. Daws. 2025. "Opioid-Induced Regulation of Cortical Circular-Grin2b_011731 Is Associated with Regulation of circGrin2b Sponge Target miR-26b-3p" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5010. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115010
APA StyleGillespie, A., & Daws, S. E. (2025). Opioid-Induced Regulation of Cortical Circular-Grin2b_011731 Is Associated with Regulation of circGrin2b Sponge Target miR-26b-3p. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5010. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115010




