IgA Antibodies to Bovine Serum Albumin in Adult Patients with Celiac Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
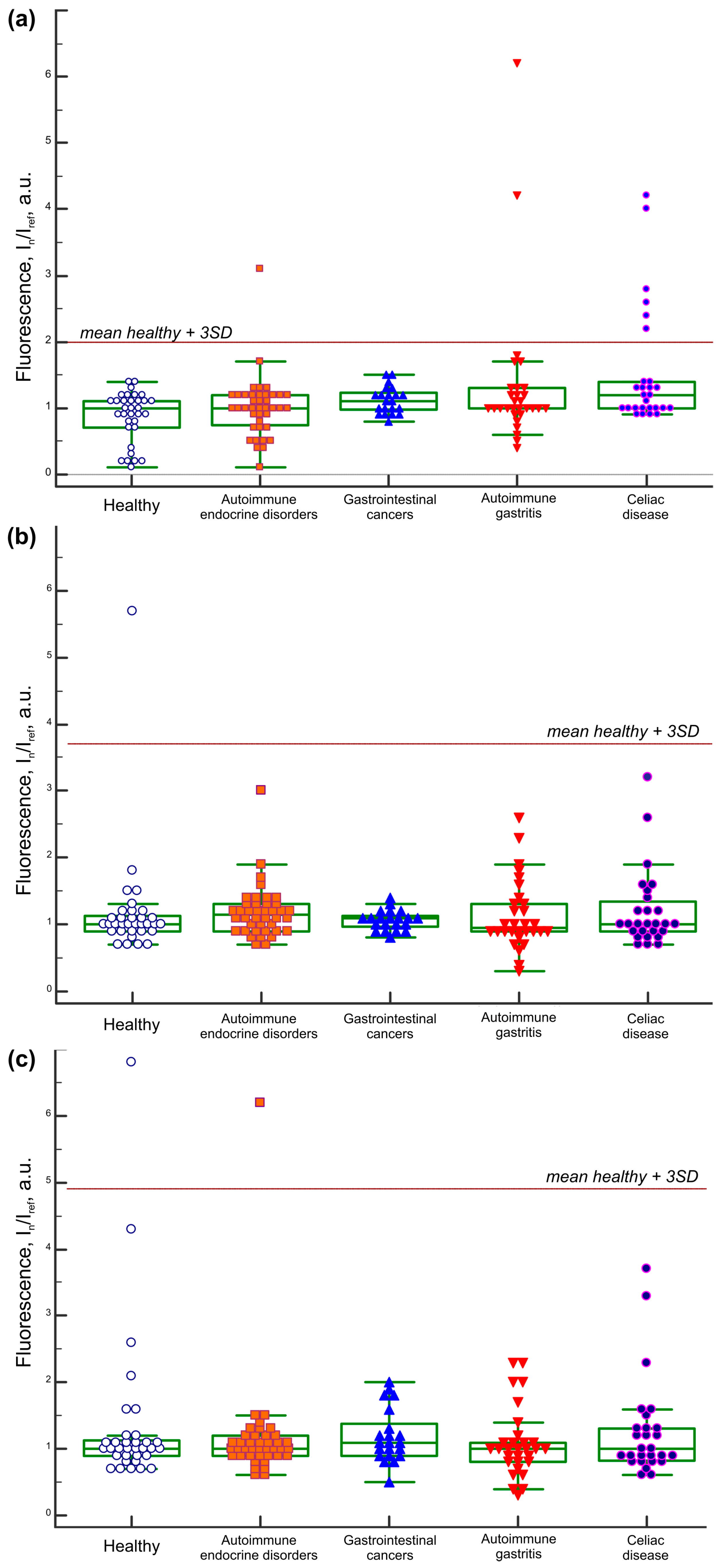
2. Results
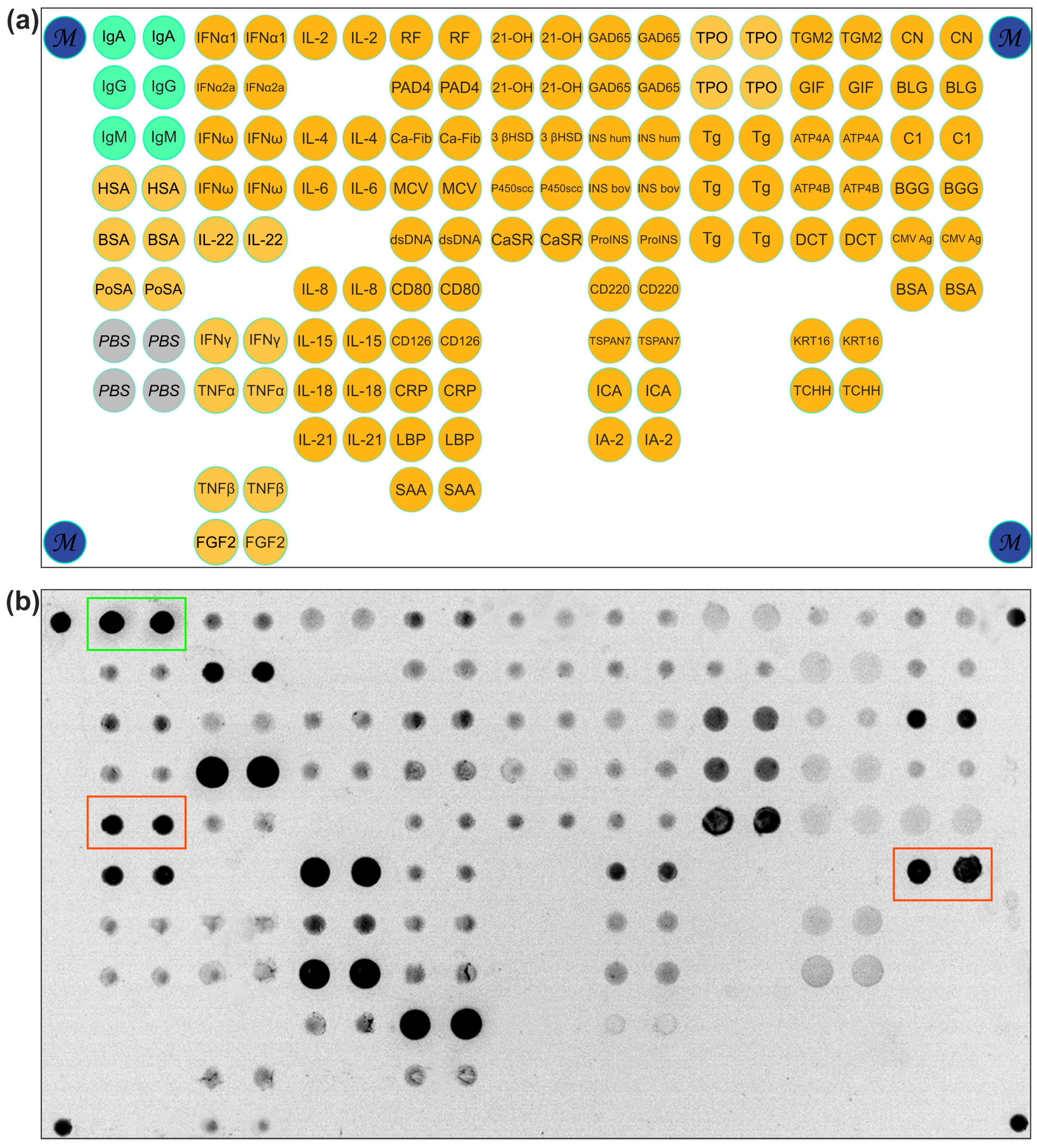
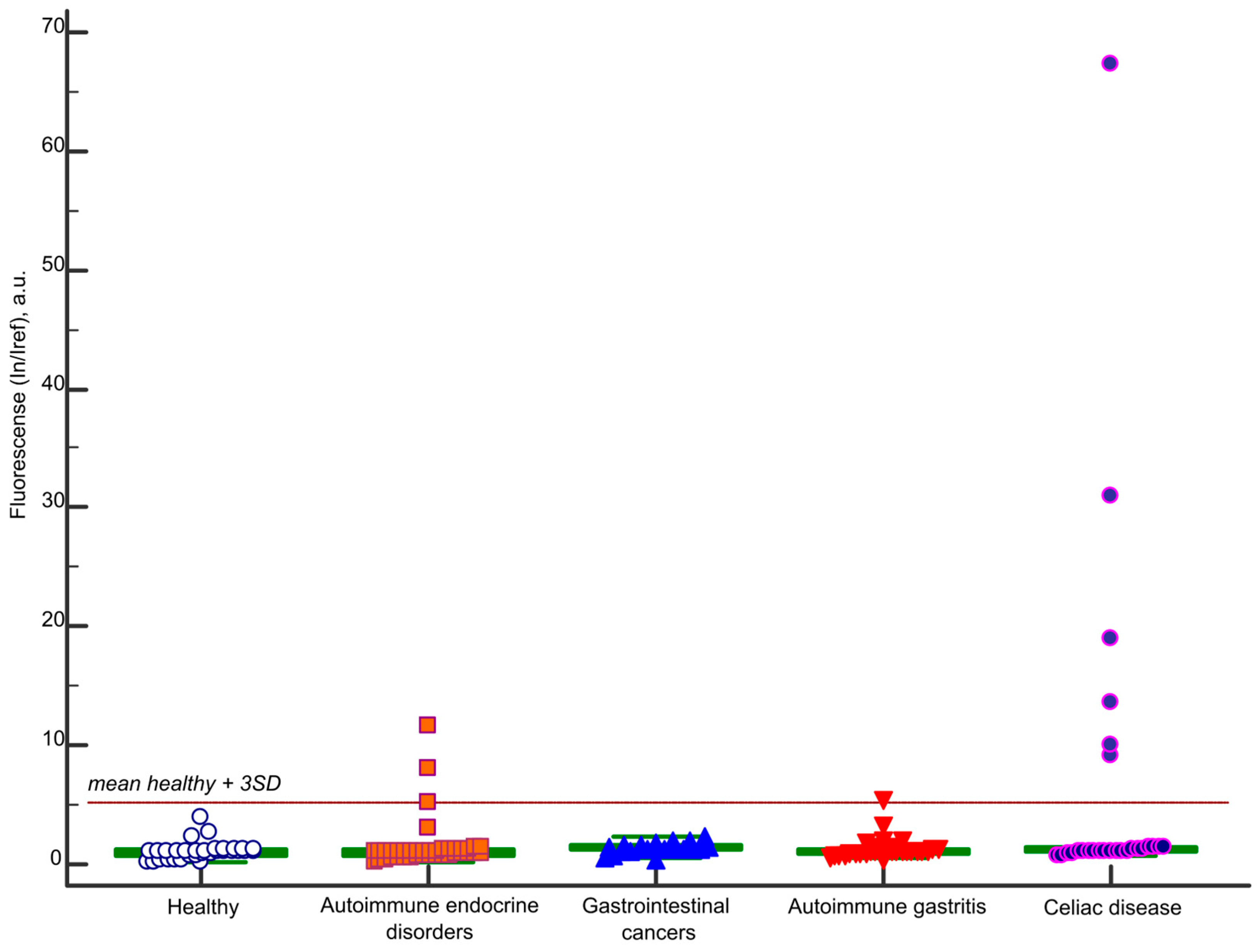
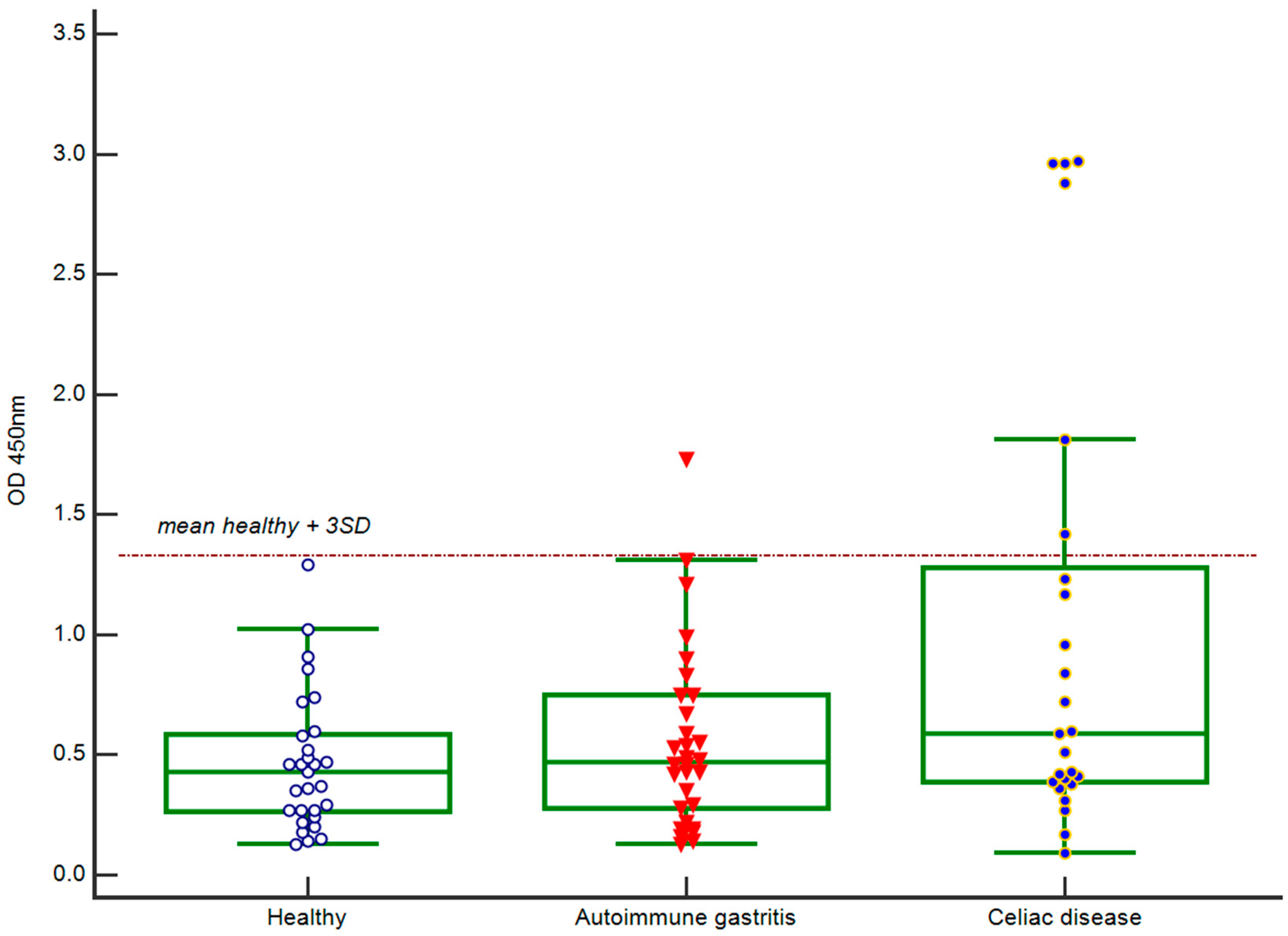
2.1. IgA Antibody Response to BSA
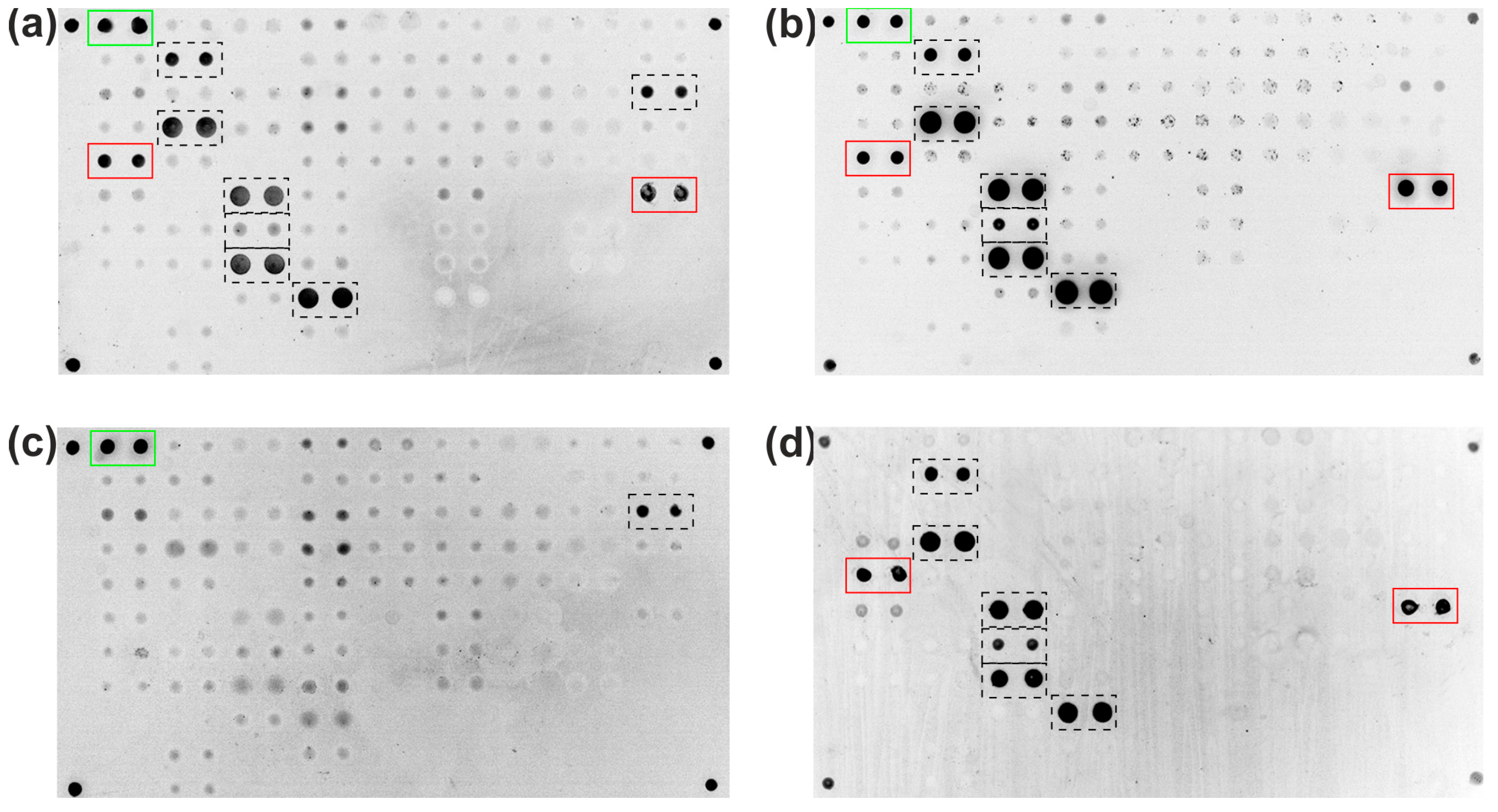
2.2. Analysis of Isolated Serum Antibodies to BSA
2.3. IgA and IgG Antibody Repertoire to Serum Albumins
3. Discussion
- -
- A 19-year-old male (#A093) with T1D and autoimmune thyroiditis;
- -
- A 47-year-old female (#A248) with Addison’s disease and autoimmune thyroiditis;
- -
- A 30-year-old male with T1D, autoimmune thyroiditis, autoimmune alopecia, enamel hypoplasia, and Raynaud’s syndrome (#A347);
- -
- A 45-year-old female (#A162) with Addison’s disease, autoimmune thyroiditis, autoimmune gastritis, and vitiligo.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Microarray Manufacturing
4.3. Detection of Antibodies by Microarrays
4.4. Direct Assay for BSA Detection and Cross-Reactivity Check
4.5. Detection of Antibodies by ELISA
4.5.1. TGM2, Anti-Gliadin, and Total IgA
4.5.2. IgA-BSA
4.6. Isolation of BSA-Specific Antibodies
4.7. BSA Antibody Immunoprecipitation
4.8. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CD | Celiac disease |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| GFD | Gluten-free diet |
| TGM2 | Tissue transglutaminase 2 |
| Ig | Immunoglobulin |
| T1D | Type 1 diabetes mellitus |
| HSA | Human serum albumin |
| PoSA | Porcine serum albumin |
| Cy | Cyanine dyes |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| OD | Optical density |
References
- Dieterich, W.; Ehnis, T.; Bauer, M.; Donner, P.; Volta, U.; Riecken, E.O.; Schuppan, D. Identification of tissue transglutaminase as the autoantigen of celiac disease. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Arora, A.; Strand, T.A.; Leffler, D.A.; Catassi, C.; Green, P.H.; Kelly, C.P.; Ahuja, V.; Makharia, G.K. Global Prevalence of Celiac Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kvamme, J.M.; Sørbye, S.; Florholmen, J.; Halstensen, T.S. Population-based screening for celiac disease reveals that the majority of patients are undiagnosed and improve on a gluten-free diet. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penny, H.A.; Baggus, E.M.R.; Rej, A.; Snowden, J.A.; Sanders, D.S. Non-Responsive Coeliac Disease: A Comprehensive Review from the NHS England National Centre for Refractory Coeliac Disease. Nutrients 2020, 12, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Tapia, A.; Rahim, M.W.; See, J.A.; Lahr, B.D.; Wu, T.-T.; Murray, J.A. Mucosal Recovery and Mortality in Adults with Celiac Disease After Treatment with a Gluten-Free Diet. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 1412–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bykova, S.V.; Sabelnikova, E.A.; Novikov, A.A.; Baulo, E.V.; Khomeriki, S.G.; Parfenov, A.I. Zonulin and I-FABP are markers of enterocyte damage in celiac disease. Ter. Arkh. 2022, 94, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husby, S.; Oxelius, V.-A.; Teisner, B.; Jensenius, J.C.; Svehag, S.-E. Humoral Immunity to Dietary Antigens in Healthy Adults. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 1985, 77, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Shen, J.; Zhao, D.; Qiao, Y.; Xu, A.; Jin, S.; Ran, Z.; Zheng, Q. Serological Investigation of Food Specific Immunoglobulin G Antibodies in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leviatan, S.; Vogl, T.; Klompus, S.; Kalka, I.N.; Weinberger, A.; Segal, E. Allergenic food protein consumption is associated with systemic IgG antibody responses in non-allergic individuals. Immunity 2022, 55, 2454–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siniscalco, E.R.; Williams, A.; Eisenbarth, S.C. All roads lead to IgA: Mapping the many pathways of IgA induction in the gut. Immunol. Rev. 2024, 326, 66–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojdani, A.; Gushgari, L.R.; Vojdani, E. Interaction between food antigens and the immune system: Association with autoimmune disorders. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karjalainen, J.; Martin, J.M.; Knip, M.; Ilonen, J.; Robinson, B.H.; Savilahti, E.; Akerblom, H.K.; Dosch, H.-M. A Bovine Albumin Peptide as a Possible Trigger of Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992, 327, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saukkonen, T.; Savilahti, E.; Dahlquist, G. IgA bovine serum albumin antibodies are increased in newly diagnosed patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, but the increase is not an independent risk factor for diabetes. Acta Pediatr. 1995, 84, 1258–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rønningen, K.S.; Atrazhev, A.; Luo, L.; Luo, C.; Smith, D.K.; Korbutt, G.; Rajotte, R.V.; Elliott, J.F. Anti-BSA Antibodies do not Cross-react with the 69-kDa Islet Cell Autoantigen ICA69. J. Autoimmun. 1998, 11, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niinistö, S.; Cuthbertson, D.; Miettinen, M.E.; Hakola, L.; Nucci, A.; Korhonen, T.E.; Hyöty, H.; Krischer, J.P.; Vaarala, O.; Knip, M.; et al. High Concentrations of Immunoglobulin G Against Cow Milk Proteins and Frequency of Cow Milk Consumption Are Associated With the Development of Islet Autoimmunity and Type 1 Diabetes—The Trial to Reduce Insulin-dependent Diabetes Mellitus (IDDM) in the Gen. J. Nutr. 2024, 154, 2493–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogues, T.; Li, J.; Coburn, J.; Kuter, D.J. IgG antibodies against bovine serum albumin in humans—Their prevalence and response to exposure to bovine serum albumin. J. Immunol. Methods 2005, 300, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, S.L.; Mortimer, G.L.; Kozhakhmetova, A.; Leveret, J.; Newton, R.; Reimand, K.; Shield, J.P.H.; Uibo, R.; Williams, A.J.K.; Gillespie, K.M. Increased levels of anti-BSA antibodies in children with Down syndrome. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1056925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debiec, H.; Lefeu, F.; Kemper, M.J.; Niaudet, P.; Deschênes, G.; Remuzzi, G.; Ulinski, T.; Ronco, P. Early-Childhood Membranous Nephropathy Due to Cationic Bovine Serum Albumin. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2101–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenrick, K.G.; Walker-Smith, S. Immunoglobulins and dietary protein antibodies in childhood coeliac disease. Gut 1970, 11, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Falchuk, K.R.; Isselbacher, K.J. Circulating antibodies to bovine albumin in ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Characterization of the antibody response. Gastroenterology 1976, 70, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, M.; Husby, S.; Larsen, M.L.; Svehag, S.-E. ELISA Analysis of IgA Subclass Antibodies to Dietary Antigens. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 1988, 87, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hvatum, M.; Scott, H.; Brandtzaeg, P. Serum IgG subclass antibodies to a variety of food antigens in patients with coeliac disease. Gut 1992, 33, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rodríguez-Juan, C.; Sala-Silveira, L.; Pérez-Blas, M.; Valeri, A.P.; Aguilera, N.; López-Santalla, M.; Fuertes, A.; Martín-Villa, J.M. Increased levels of bovine serum albumin antibodies in patients with type 1 diabetes and celiac disease-related antibodies. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2003, 37, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilger, C.; Grigioni, F.; De Beaufort, C.; Michel, G.; Freilinger, J.; Hentges, F. Differential binding of IgG and IgA antibodies to antigenic determinants of bovine serum albumin. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2001, 123, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, Y.; Liu, L. Characterization and determination of bovine immunoglobulin G subtypes in milk and dairy products by UPLC-MS. Food Chem. 2022, 390, 133170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wu, Z.; Weng, P. Insights into oat polyphenols constituent against advanced glycation end products mechanism by spectroscopy and molecular interaction. Food Biosci. 2021, 43, 101313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Liu, L.; Farag, M.; Liu, L. The binding mechanism of oat phenolic acid to whey protein and its inhibition mechanism against AGEs as revealed using spectroscopy, chromatography and molecular docking. Food Funct. 2023, 13, 10221–10231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristjánsson, G.; Venge, P.; Hällgren, R. Mucosal reactivity to cow’s milk protein in coeliac disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2007, 147, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berti, C.; Trovato, C.; Bardella, M.T.; Forlani, F. IgA anti-gliadin antibody immunoreactivity to food proteins. Food Agric. Immunol. 2003, 15, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martelli, A.; De Chiara, A.; Corvo, M.; Restani, P.; Fiocchi, A. Beef allergy in children with cow’s milk allergy; cow’s milk allergy in children with beef allergy. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2002, 89, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehring, J.; Schirmbeck, L.A.; Friebus-Kardash, J.; Dubler, D.; Huynh-Do, U.; Chizzolini, C.; Ribi, C.; Trendelenburg, M. Autoantibodies Against Albumin in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.J.K.; Curnock, R.; Reed, C.R.; Easton, P.; Rokni, S.; Bingley, P.J. Anti-BSA antibodies are a major cause of non-specific binding in insulin autoantibody radiobinding assays. J. Immunol. Methods 2010, 362, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroun, M. Bovine serum albumin antibodies as a disease marker for hepatitis E virus infection. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2005, 2005, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöwall, C.; Kastbom, A.; Almroth, G.; Wetterö, J.; Skogh, T. Beware of Antibodies to Dietary Proteins in “Antigen-specific” Immunoassays! Falsely Positive Anticytokine Antibody Tests Due to Reactivity with Bovine Serum Albumin in Rheumatoid Arthritis (The Swedish TIRA Project). J. Rheumatol. 2011, 38, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taubert, R.; Engel, B.; Diestelhorst, J.; Hupa-Breier, K.L.; Behrendt, P.; Baerlecken, N.T.; Sühs, K.; Janik, M.K.; Zachou, K.; Sebode, M.; et al. Quantification of polyreactive immunoglobulin G facilitates the diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology 2022, 75, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, R.; Azegami, T.; Yamaguchi, S.; Hagiwara, A.; Hishikawa, A.; Yoshimoto, N.; Hashiguchi, A.; Hayashi, K. False-positive Serum Antiglomerular Basement Membrane Antibody due to Bovine Serum Albumin-containing Surgical Adhesive: A Case Report. Kidney Med. 2024, 6, 100880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terato, K.; Do, C.T.; Cutler, D.; Waritani, T.; Shionoya, H. Preventing intense false positive and negative reactions attributed to the principle of ELISA to re-investigate antibody studies in autoimmune diseases. J. Immunol. Methods 2014, 407, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moritz, C.P.; Tholance, Y.; Lassablière, F.; Camdessanché, J.P.; Antoine, J.C. Reducing the risk of misdiagnosis of indirect ELISA by normalizing serum-specific background noise: The example of detecting anti-FGFR3 autoantibodies. J. Immunol. Methods 2019, 466, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güven, E.; Duus, K.; Lydolph, M.C.; Jørgensen, C.S.; Laursen, I.; Houen, G. Non-specific binding in solid phase immunoassays for autoantibodies correlates with inflammation markers. J. Immunol. Methods 2014, 403, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savvateeva, E.N.; Yukina, M.Y.; Nuralieva, N.F.; Filippova, M.A.; Gryadunov, D.A.; Troshina, E.A. Multiplex Autoantibody Detection in Patients with Autoimmune Polyglandular Syndromes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parfenov, A.I.; Bykova, S.V.; Sabelnikova, E.A.; Maev, I.V.; Baranov, A.A.; Bakulin, I.G.; Krums, L.M.; Belmer, S.V.; Borovik, T.E.; Zakharova, I.N.; et al. All-Russian Consensus on Diagnosis and Treatment of Celiac Disease in Children and Adults. Ter. Arkhiv 2017, 89, 94–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gryadunov, D.A.; Shaskolskiy, B.L.; Nasedkina, T.V.; Rubina, A.Y.; Zasedatelev, A.S. The EIMB Hydrogel Microarray Technology: Thirty Years Later. Acta Naturae 2018, 10, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lysov, Y.; Barsky, V.; Urasov, D.; Urasov, R.; Cherepanov, A.; Mamaev, D.; Yegorov, Y.; Chudinov, A.; Surzhikov, S.; Rubina, A.; et al. Microarray analyzer based on wide field fluorescent microscopy with laser illumination and a device for speckle suppression. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
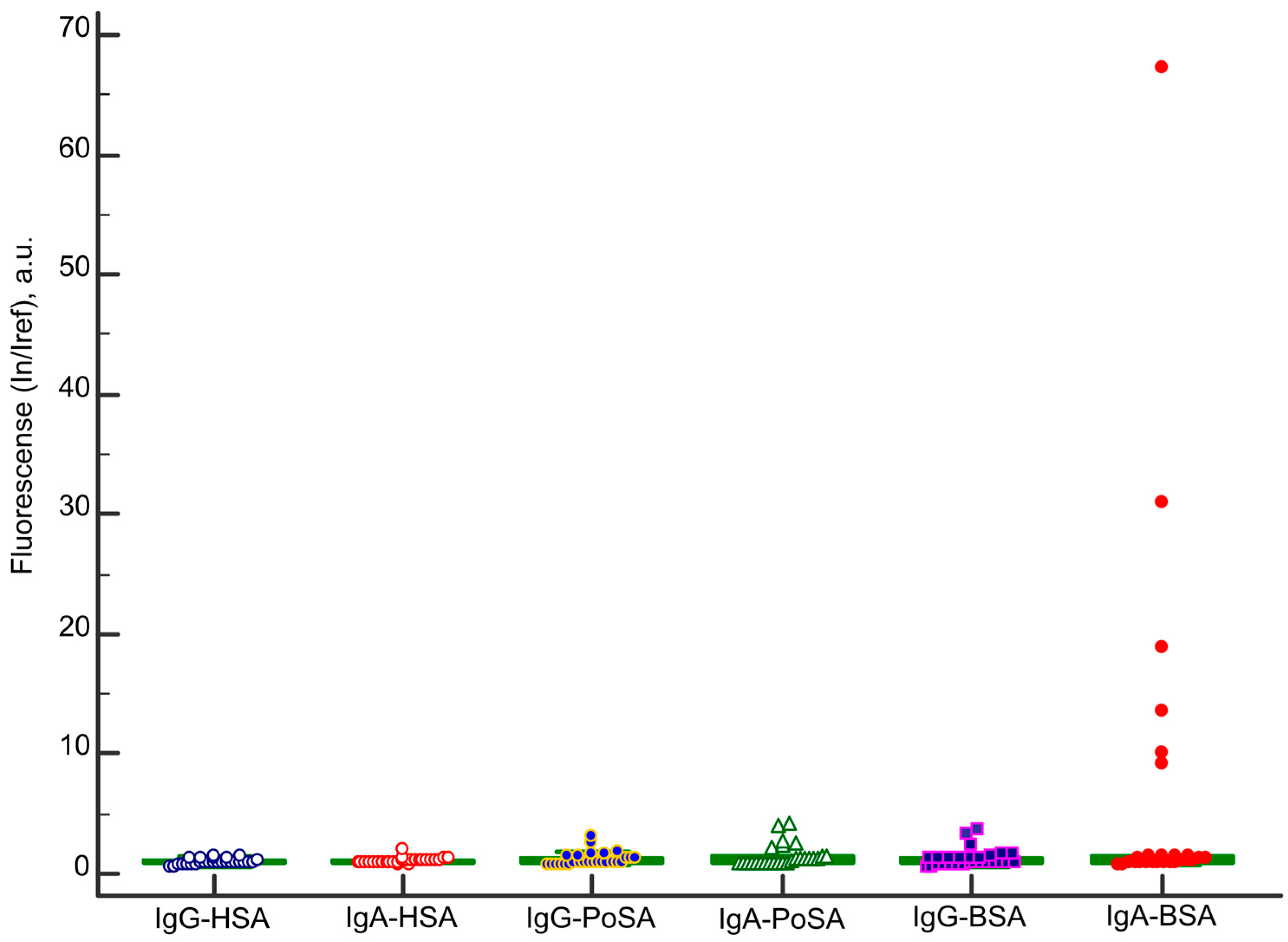
| Sample ID | Age | Gender | Diagnosis | Microarray | ELISA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IgA-BSA, In/Iref, Cut-Off ≥ 5.2 | Other Anti-Albumins Antibodies | IgA-BSA, OD 450 nm, Cut-Off ≥ 1.32 | ||||
| A093 | 19 | m | Type 1 diabetes mellitus, autoimmune thyroiditis | 5.2 | - | 1.46 |
| A248 | 47 | f | Addison’s disease, autoimmune thyroiditis | 8.0 | IgA-PoSA | 2.11 |
| A347 | 30 | m | Type 1 diabetes mellitus, autoimmune thyroiditis, autoimmune alopecia, dental enamel hypoplasia, Raynaud’s syndrome | 11.7 | IgG-BSA | 1.99 |
| A162 | 45 | f | Autoimmune gastritis, Addison’s disease, autoimmune thyroiditis, vitiligo | 5.2 | IgA-PoSA | 1.73 |
| A113 | 18 | m | Celiac disease | 30.9 | IgA-PoSA | 1.81 |
| A268 | 76 | f | Celiac disease | 13.6 | IgA-PoSA | 2.88 |
| A308 | 29 | m | Celiac disease | 9.1 | - | 1.42 |
| A314 | 18 | m | Celiac disease | 18.9 | IgA-PoSA | 2.97 |
| A315 | 30 | m | Celiac disease | 10.0 | IgA-PoSA | 2.96 |
| A321 | 26 | f | Celiac disease | 67.3 | IgG-BSA IgA-PoSA | 2.96 |
| Group | n | Mean Age (Range) | Female, % | Male, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Celiac disease | 27 | 39 (18–76) | 63 | 37 |
| Autoimmune gastritis | 30 | 51.5 (27–86) | 93 | 7 |
| Gastrointestinal cancers | 21 | 61 (31–80) | 44 | 56 |
| Autoimmune endocrine disorders | 39 | 44 (19–81) | 77 | 23 |
| Healthy | 33 | 39 (19–67) | 76 | 24 |
| Total | 150 | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Savvateeva, E.; Yukina, M.; Nuralieva, N.; Bykova, S.; Abramov, I.; Polyakova, V.; Bodunova, N.; Donnikov, M.; Kovalenko, L.; Mazurenko, E.; et al. IgA Antibodies to Bovine Serum Albumin in Adult Patients with Celiac Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4988. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26114988
Savvateeva E, Yukina M, Nuralieva N, Bykova S, Abramov I, Polyakova V, Bodunova N, Donnikov M, Kovalenko L, Mazurenko E, et al. IgA Antibodies to Bovine Serum Albumin in Adult Patients with Celiac Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):4988. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26114988
Chicago/Turabian StyleSavvateeva, Elena, Marina Yukina, Nurana Nuralieva, Svetlana Bykova, Ivan Abramov, Vera Polyakova, Natalia Bodunova, Maxim Donnikov, Lyudmila Kovalenko, Elena Mazurenko, and et al. 2025. "IgA Antibodies to Bovine Serum Albumin in Adult Patients with Celiac Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 4988. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26114988
APA StyleSavvateeva, E., Yukina, M., Nuralieva, N., Bykova, S., Abramov, I., Polyakova, V., Bodunova, N., Donnikov, M., Kovalenko, L., Mazurenko, E., Pavlova, E., Kulagina, E., Troshina, E., & Gryadunov, D. (2025). IgA Antibodies to Bovine Serum Albumin in Adult Patients with Celiac Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 4988. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26114988








