Trace Element Deficiency in Axial Spondyloarthritis and Psoriatic Arthritis in Relation to Markers of Inflammation and Remission
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of the Study Cohort
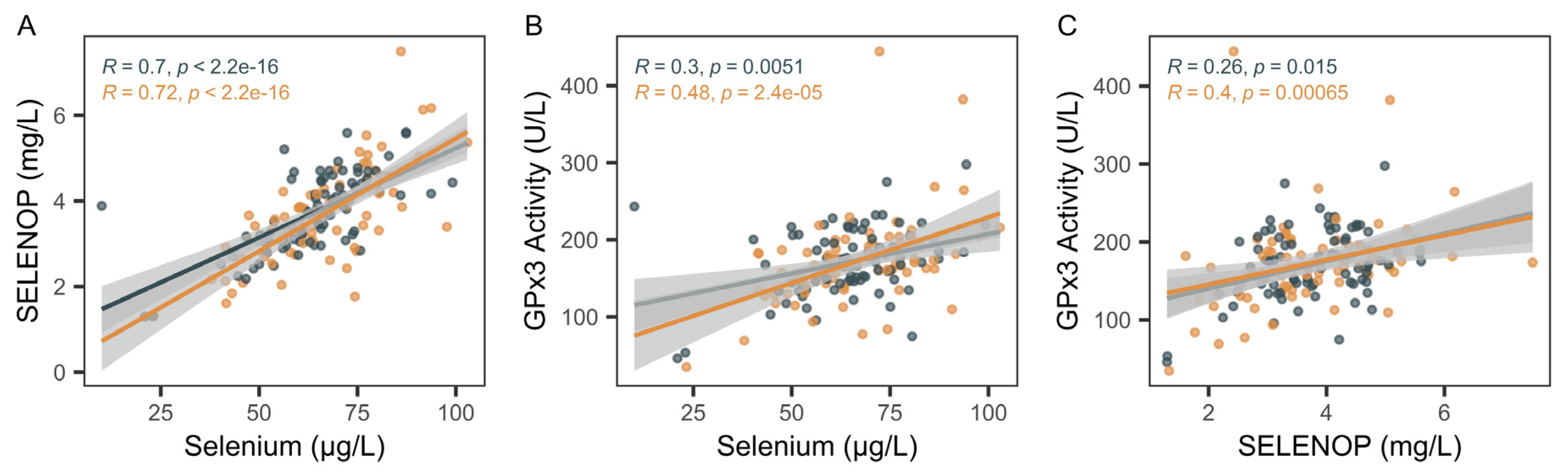
2.2. Biomarkers of Selenium Status
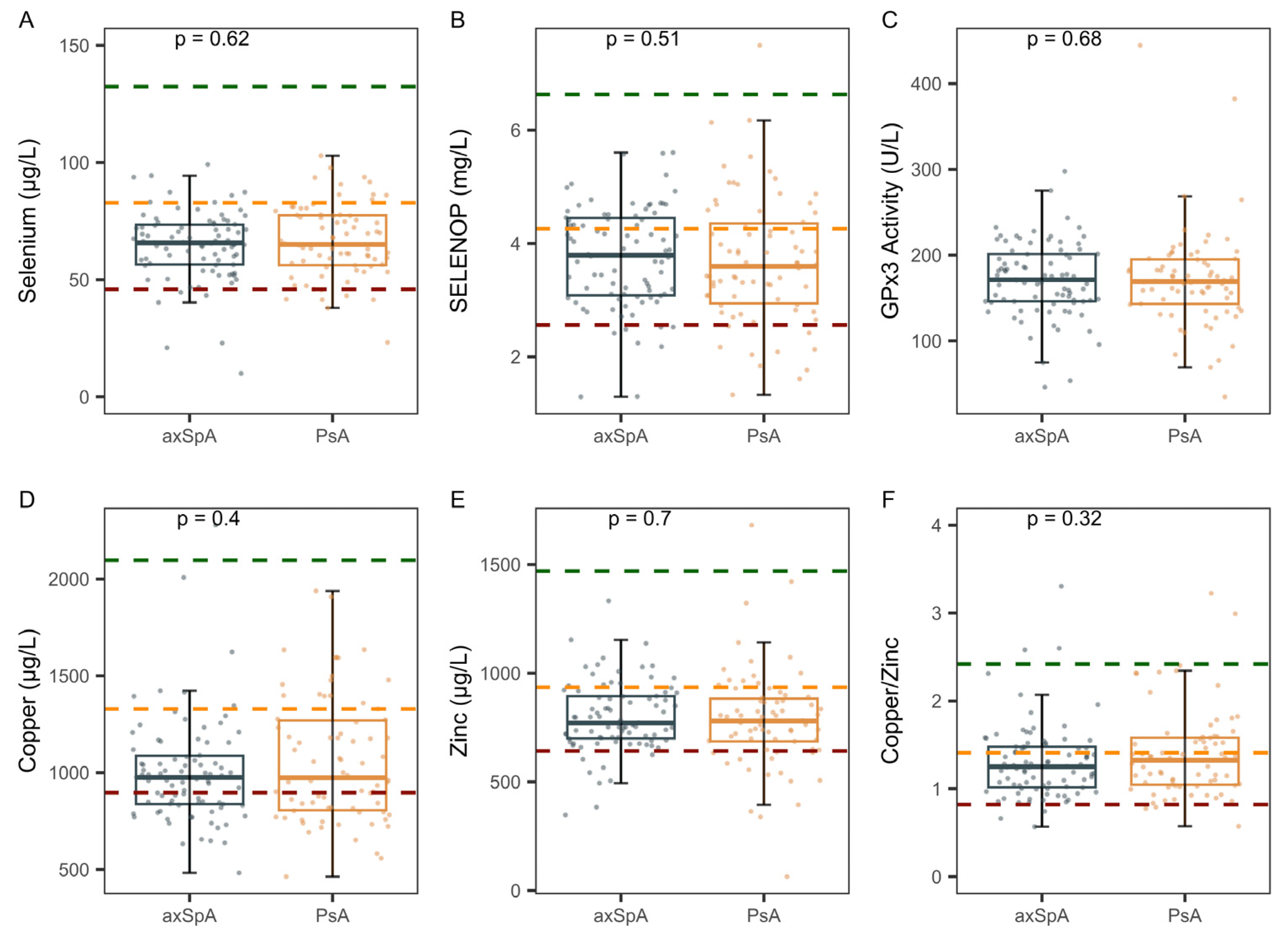
2.3. Comparison of Trace Element Status in axSpA Versus PsA
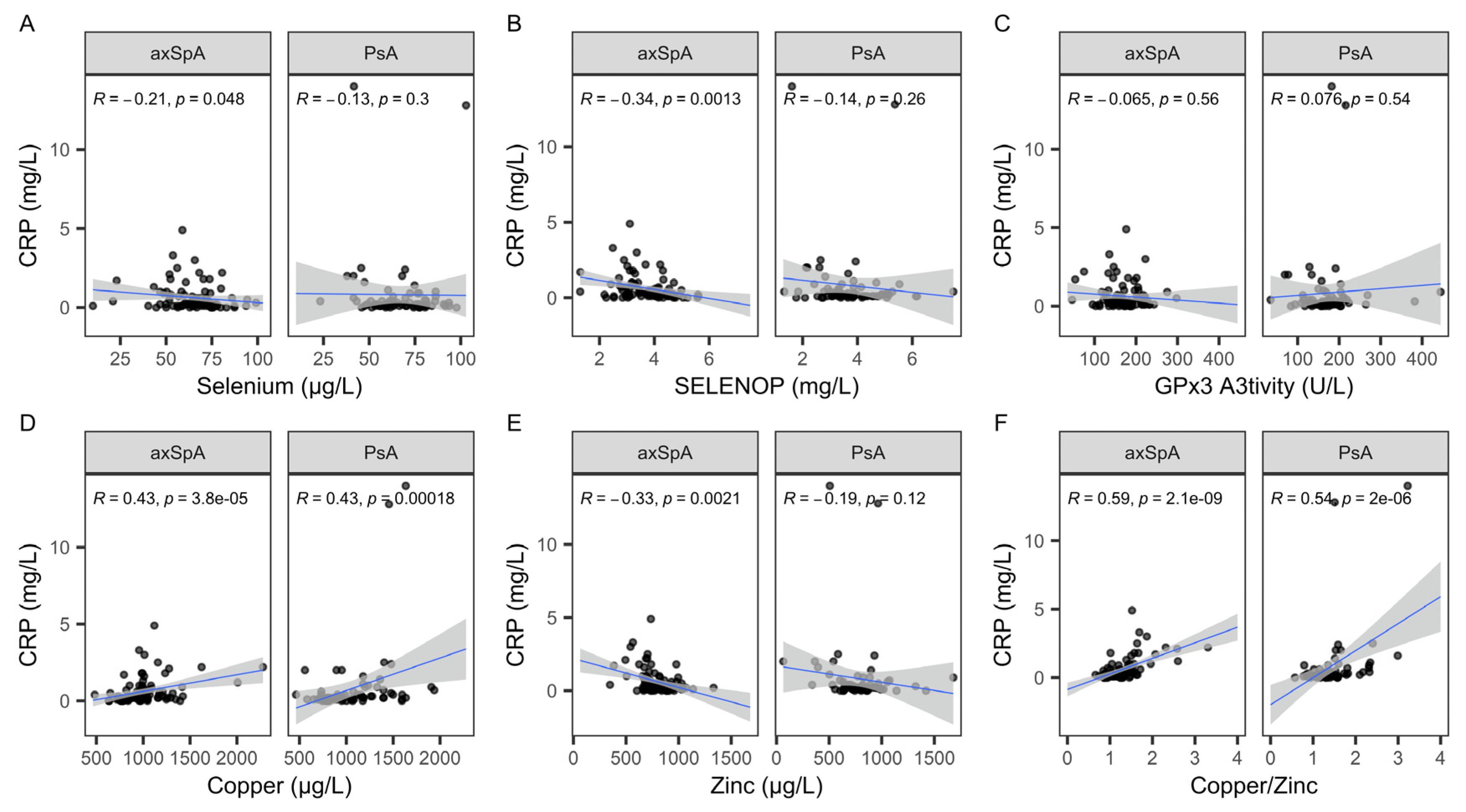
2.4. Analysis of Trace Element Status with Regard to C-Reactive Protein
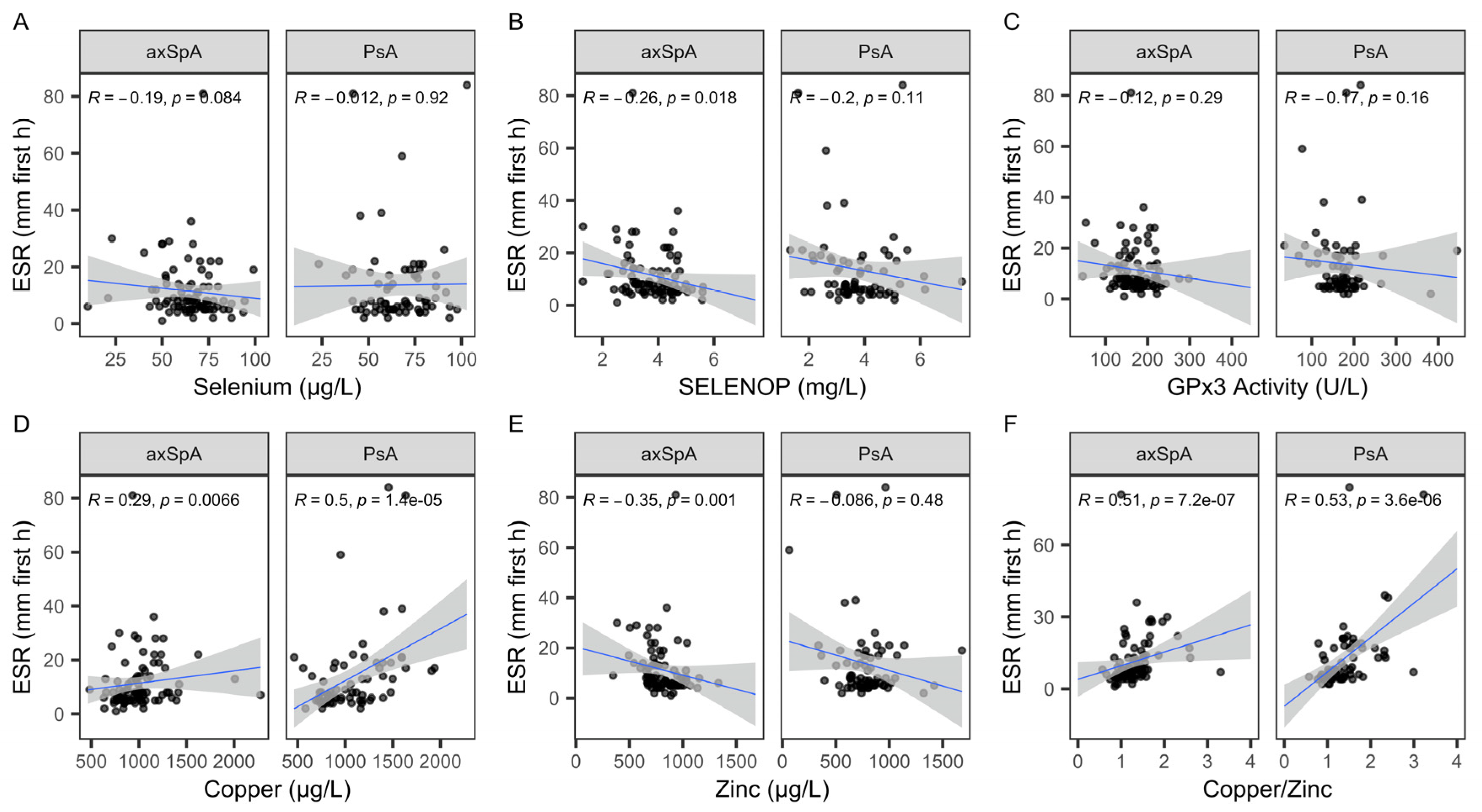
2.5. Associations of TE Status with Regards to Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate
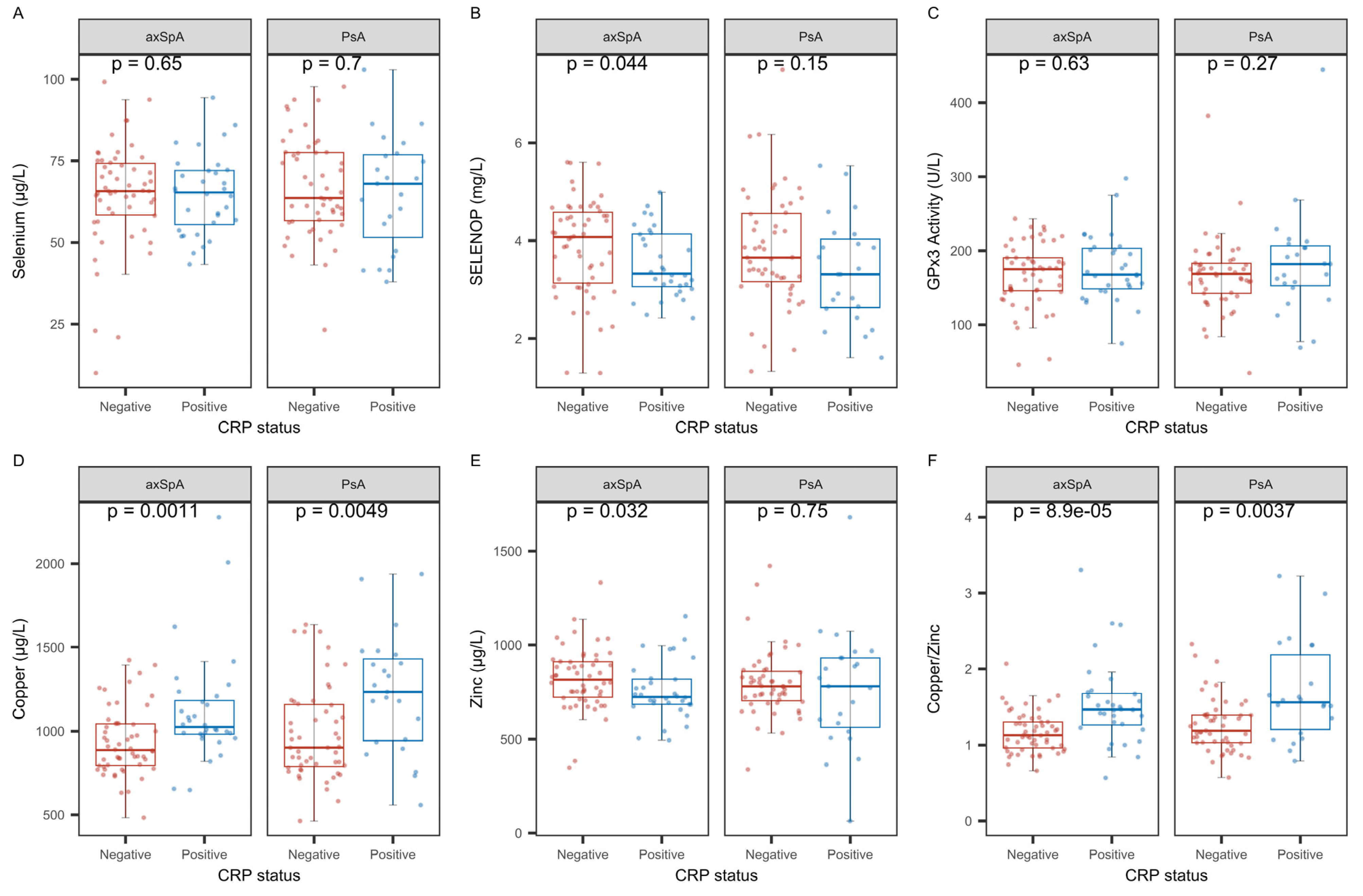
2.6. Associations of SELENOP Sufficiency with Regard to C-Reactive Protein
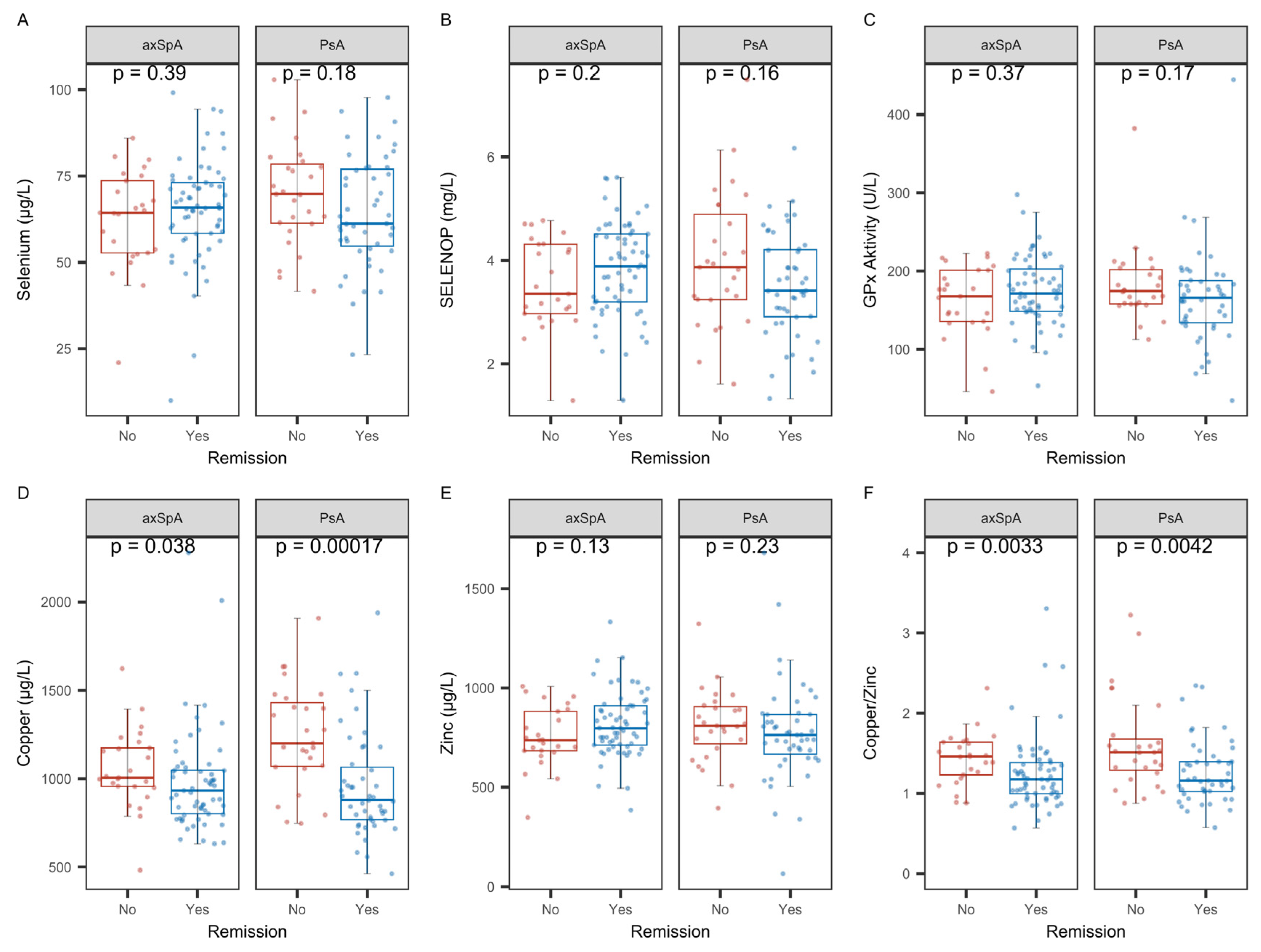
2.7. Analysis of Biomarkers of TE Status with Regard to Remission
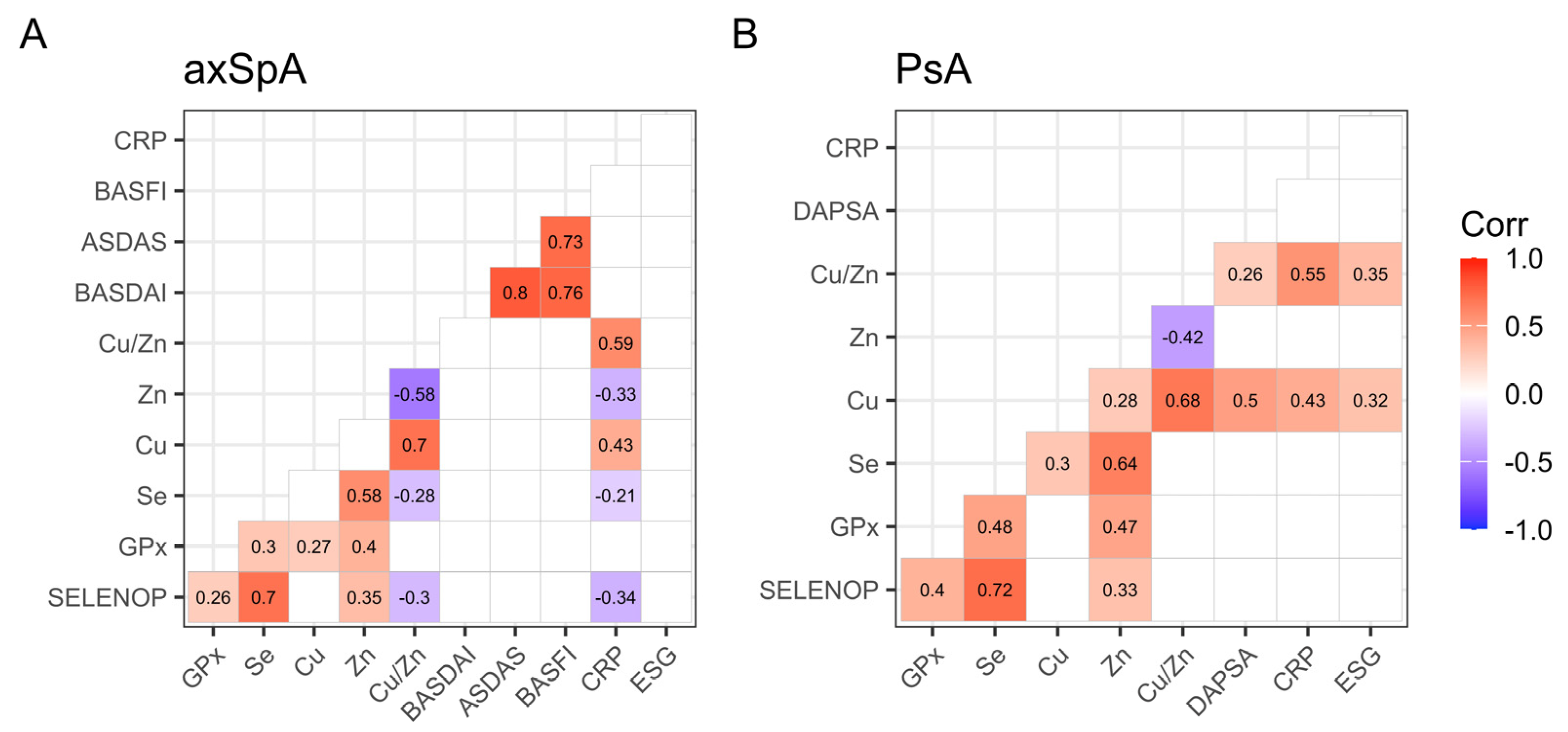
2.8. Overview of the Interactions of Trace Elements and Disease Parameters
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Trace Element Status Assessment
4.3. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Se | selenium |
| Cu | copper |
| Zn | zinc |
| TE | trace element(s) |
| axSpA | axial spondyloarthritis |
| PsA | psoriatic arthritis |
| TXRF | total reflection X-ray fluorescence |
| SELENOP | selenoprotein P |
| GPx3 | extracellular glutathione peroxidase |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| ESR | erythrocyte sedimentation rate |
| SIJ | sacroiliac joints |
| r-axSpA | classic ankylosing spondylitis |
| nr-axSpA | non-radiographic ankylosing spondylitis |
| iRMD | rheumatic musculoskeletal disease(s) |
| GPx1 | cellular glutathione peroxidase |
| GPx4 | phospholipid-hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase |
| EPIC | European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition |
| BASDAI | Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Index |
| DAPSA | Disease Activity in Psoriatic Arthritis |
| LORE cohort | Long-Term Observation of Patients Diagnosed with a Chronic Inflammatory Disease from the Rheumatic Form Group cohort |
References
- Navarro-Compán, V.; Sepriano, A.; Capelusnik, D.; Baraliakos, X. Axial spondyloarthritis. Lancet 2025, 405, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudwaleit, M.; van der Heijde, D.; Landewé, R.; Listing, J.; Akkoc, N.; Brandt, J.; Braun, J.; Chou, C.T.; Collantes-Estevez, E.; Dougados, M.; et al. The development of Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (part II): Validation and final selection. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mease, P.J.; Gladman, D.D.; Papp, K.A.; Khraishi, M.M.; Thaçi, D.; Behrens, F.; Northington, R.; Fuiman, J.; Bananis, E.; Boggs, R.; et al. Prevalence of rheumatologist-diagnosed psoriatic arthritis in patients with psoriasis in European/North American dermatology clinics. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2013, 69, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanassiou, L.; Kostoglou-Athanassiou, I.; Koutsilieris, M.; Shoenfeld, Y. Vitamin D and Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Hoffmann, P.R. Selenoproteins as regulators of T cell proliferation, differentiation, and metabolism. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 115, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flohé, L.; Toppo, S.; Orian, L. The glutathione peroxidase family: Discoveries and mechanism. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 187, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhrle, J. Selenium, Iodine and Iron-Essential Trace Elements for Thyroid Hormone Synthesis and Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, C.; Li, S.; Cui, L.; Zhao, J.; Liao, L. Selenium and thyroid diseases. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1133000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schomburg, L. Selenium Deficiency Due to Diet, Pregnancy, Severe Illness, or COVID-19-A Preventable Trigger for Autoimmune Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turrubiates-Hernández, F.J.; Márquez-Sandoval, Y.F.; González-Estevez, G.; Reyes-Castillo, Z.; Muñoz-Valle, J.F. The Relevance of Selenium Status in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Conrad, M. Ferroptosis: When metabolism meets cell death. Physiol. Rev. 2025, 105, 651–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, W.; Liao, S.; Wang, D.; Liu, P.; Zeng, H. The role of ferroptosis in osteoarthritis: Progress and prospects. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2024, 733, 150683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, L.; Yang, X.; Cai, G.; Fan, D.; Xia, Q.; Liu, L.; Hu, Y.; Ding, N.; Xu, S.; Wang, L.; et al. Serum Levels of Copper and Zinc in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Meta-analysis. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2015, 168, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, C.; Sun, Y.; Francis, M.; Ryu, M.S.; Grider, A.; Ye, K. Genetically predicted circulating levels of copper and zinc are associated with osteoarthritis but not with rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2021, 29, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoli, A.; Altomonte, L.; Caricchio, R.; Galossi, A.; Mirone, L.; Ruffini, M.P.; Magaró, M. Serum zinc and copper in active rheumatoid arthritis: Correlation with interleukin 1 beta and tumour necrosis factor alpha. Clin. Rheumatol. 1998, 17, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grammatikopoulou, M.G.; Marakis, G.; Gkiouras, K.; Athanatou, D.; Maraki, M.I.; Bogdanos, D.P. Fly Me to the Immune: Immunonutrition in Rheumatic Diseases. Mediterr. J. Rheumatol. 2023, 34, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, D.J.; Fedirko, V.; Jenab, M.; Schomburg, L.; Méplan, C.; Freisling, H.; Bueno-de-Mesquita, H.B.; Hybsier, S.; Becker, N.P.; Czuban, M.; et al. Selenium status is associated with colorectal cancer risk in the European prospective investigation of cancer and nutrition cohort. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 1149–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honkanen, V.; Konttinen, Y.T.; Sorsa, T.; Hukkanen, M.; Kemppinen, P.; Santavirta, S.; Saari, H.; Westermarck, T. Serum zinc, copper and selenium in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Trace Elem. Electrolytes Health Dis. 1991, 5, 261–263. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstein, E.D.; Caldwell, J.R. Trace elements in the treatment of rheumatic conditions. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 1999, 25, 929–935, viii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, X.; Fan, D.; Xia, Q.; Wang, M.; Pan, F. Common trace metals in rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2019, 56, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, L.; Samson Chillon, T.; Seemann, P.; Ohrndorf, S.; Ochwadt, R.; Becker, W.; Schomburg, L.; Hoff, P. Serum selenium, selenoprotein P and glutathione peroxidase 3 in rheumatoid, psoriatic, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, and osteoarthritis. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2024, 135, 109776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, M.; Chutia, H.; Changkakati, R. Serum Copper as a Marker of Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2015, 9, BC09–BC011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, A.A.; Wood, B.; Baron, D.N. Serum copper: A marker of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Clin. Pathol. 1983, 36, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiginger, P.; Kolarz, G.; Willvonseder, R. Copper in ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 1978, 7, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayson, M.I.; Davis, P.; Whicher, J.T.; Walters, G. Serum copper and caeruloplasmin in ankylosing spondylitis, systemic sclerosis, and morphea. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1975, 35, 443–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackler, J.; Wisniewska, M.; Greifenstein-Wiehe, L.; Minich, W.B.; Cremer, M.; Bührer, C.; Schomburg, L. Copper and selenium status as biomarkers of neonatal infections. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2020, 58, 126437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grammer, T.B.; Kleber, M.E.; Silbernagel, G.; Pilz, S.; Scharnagl, H.; Lerchbaum, E.; Tomaschitz, A.; Koenig, W.; März, W. Copper, ceruloplasmin, and long-term cardiovascular and total mortality (the Ludwigshafen Risk and Cardiovascular Health Study). Free Radic. Res. 2014, 48, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, T.; Liu, Z. The Effect of Methotrexate on Serum Levels of Trace/Mineral Elements in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 4498–4503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Deng, Y.; Ma, Y.; Shao, M.; Ni, M.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X.; Xu, S.; Chen, Y.; Xu, S.; et al. Common mineral nutrients in ankylosing spondylitis: A 2-sample Mendelian randomization study. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 25, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Su, Y.; Xu, K.; Wan, X.; Xie, J.; Liu, L.; Yang, Z.; Xu, P. Iron, copper, zinc and magnesium on rheumatoid arthritis: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2024, 34, 2776–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hangarter, W.; Lubke, A. Therapy of rheumatic diseases with a copper-sodium salicylate complex compound (permalon). Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 1952, 77, 870–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aaseth, J.; Haugen, M.; Forre, O. Rheumatoid arthritis and metal compounds--perspectives on the role of oxygen radical detoxification. Analyst 1998, 123, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzini, M.; Girelli, D.; Olivieri, O.; Guarini, P.; Stanzial, A.M.; Frigo, A.; Milanino, R.; Bambara, L.M.; Corrocher, R. Fatty acids and antioxidant micronutrients in psoriatic arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 1995, 22, 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, N.; Han, F.; Lin, X.; Tang, C.; Ye, J.; Cai, X. The Association Between Serum Selenium Levels with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 172, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, E.; Vallvé, J.C.; Linares, V.; Paredes, S.; Ibarretxe, D.; Bellés, M. Serum Levels of Trace Elements (Magnesium, Iron, Zinc, Selenium, and Strontium) are Differentially Associated with Surrogate Markers of Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulander, E.; Zverkova Sandström, T.; Beckman Rehnman, J.; Law, L.; Söderberg, S.; Forsblad-d’Elia, H. Patients with radiographic axial spondylarthritis have an impaired dietary intake-a cross-sectional study with matched controls from northern Sweden. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2023, 25, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defi, I.R.; Yamazaki, C.; Kameo, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Nakazawa, M.; Shinya, Y.; Sato, N.; Wada, N.; Shirakura, K.; Koyama, H. Acute phase response of selenium status and glutathione peroxidase activity in blood plasma before and after total knee arthroplasty surgery. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2011, 144, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichol, C.; Herdman, J.; Sattar, N.; O’Dwyer, P.J.; St, J.O.R.D.; Littlejohn, D.; Fell, G. Changes in the concentrations of plasma selenium and selenoproteins after minor elective surgery: Further evidence for a negative acute phase response? Clin. Chem. 1998, 44, 1764–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreher, I.; Jakobs, T.C.; Köhrle, J. Cloning and characterization of the human selenoprotein P promoter. Response of selenoprotein P expression to cytokines in liver cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 29364–29371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renko, K.; Hofmann, P.J.; Stoedter, M.; Hollenbach, B.; Behrends, T.; Köhrle, J.; Schweizer, U.; Schomburg, L. Down-regulation of the hepatic selenoprotein biosynthesis machinery impairs selenium metabolism during the acute phase response in mice. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 1758–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martitz, J.; Becker, N.P.; Renko, K.; Stoedter, M.; Hybsier, S.; Schomburg, L. Gene-specific regulation of hepatic seleno-protein expression by interleukin-6. Metallomics 2015, 7, 1515–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamani, B.; Taghvaee, F.; Akbari, H.; Mohtashamian, A.; Sharifi, N. Effects of Selenium Supplementation on the Indices of Disease Activity, Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2024, 202, 1457–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deyab, G.; Hokstad, I.; Aaseth, J.; Småstuen, M.C.; Whist, J.E.; Agewall, S.; Lyberg, T.; Tveiten, D.; Hjeltnes, G.; Zibara, K.; et al. Effect of anti-rheumatic treatment on selenium levels in inflammatory arthritis. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2018, 49, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaëlsson, G.; Berne, B.; Carlmark, B.; Strand, A. Selenium in whole blood and plasma is decreased in patients with moderate and severe psoriasis. Acta Derm. Venereol. 1989, 69, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Y.; Li, C.; Huang, Y.; Wu, C.; Li, F.; Zhang, X.; Xia, D. Exploring the causal associations of micronutrients on urate levels and the risk of gout: A Mendelian randomization study. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 43, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wei, X.; Qin, F.; Yuan, Z.; Mo, C.; Kang, Y.; Huang, C.; Jiang, J.; Ye, L. Assessing causal association of circulating micronutrients and systemic lupus erythematosus susceptibility: A Mendelian randomization study. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1359697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurnham, D.I.; Northrop-Clewes, C.A. Inflammation and biomarkers of micronutrient status. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2016, 19, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, R.A.; Sun, Q.; Hackler, J.; Seelig, J.; Seibert, L.; Cherkezov, A.; Minich, W.B.; Seemann, P.; Diegmann, J.; Pilz, M.; et al. Prediction of survival odds in COVID-19 by zinc, age and selenoprotein P as composite biomarker. Redox Biol. 2021, 38, 101764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burk, R.F.; Hill, K.E. Regulation of Selenium Metabolism and Transport. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2015, 35, 109–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisniewska, M.; Cremer, M.; Wiehe, L.; Becker, N.P.; Rijntjes, E.; Martitz, J.; Renko, K.; Bührer, C.; Schomburg, L. Copper to Zinc Ratio as Disease Biomarker in Neonates with Early-Onset Congenital Infections. Nutrients 2017, 9, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, Y.; Demircan, K.; Vallon-Christersson, J.; Malmberg, M.; Saal, L.H.; Rydén, L.; Borg, Å.; Schomburg, L.; Sandsveden, M.; Manjer, J. Serum copper, zinc and copper/zinc ratio in relation to survival after breast cancer diagnosis: A prospective multicenter cohort study. Redox Biol. 2023, 63, 102728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuszczak, M.; Kiljańczyk, A.; Marciniak, W.; Derkacz, R.; Stempa, K.; Baszuk, P.; Bryśkiewicz, M.; Cybulski, C.; Dębniak, T.; Gronwald, J.; et al. Antioxidant Properties of Zinc and Copper-Blood Zinc-to Copper-Ratio as a Marker of Cancer Risk BRCA1 Mutation Carriers. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Silvestro, R.A.; Marten, J.; Skehan, M. Effects of copper supplementation on ceruloplasmin and copper-zinc superoxide dismutase in free-living rheumatoid arthritis patients. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 1992, 11, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennie, K.L.; Hughes, J.; Lang, R.; Jebb, S.A. Nutritional management of rheumatoid arthritis: A review of the evidence. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2003, 16, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraliakos, X.; Szumski, A.; Koenig, A.S.; Jones, H. The role of C-reactive protein as a predictor of treatment response in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2019, 48, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalili, C.; Ghanbari, A.; Roshankhah, S.; Salahshoor, M.R. Toxic Effects of Methotrexate on Rat Kidney Recovered by Crocin as a Consequence of Antioxidant Activity and Lipid Peroxidation Prevention. Iran. Biomed. J. 2020, 24, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Oltra, E.; Dijck-Brouwer, D.A.J.; Chillon, T.S.; Seemann, P.; Asaad, S.; Demircan, K.; Espejo-Oltra, J.A.; Sánchez-Fito, T.; Martín-Martínez, E.; et al. Autoantibodies to selenoprotein P in chronic fatigue syndrome suggest selenium transport impairment and acquired resistance to thyroid hormone. Redox Biol. 2023, 65, 102796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, K.; Liu, G.; Wu, T.; Du, L. Selenium for preventing Kashin-Beck osteoarthropathy in children: A meta-analysis. Osteoarhritis Cartil. 2009, 17, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirong, Y.; Huiyun, P.; Zhongzhe, Y.; Birong, D.; Weimin, L.; Ming, Y.; Yi, S. Sodium selenite for treatment of Kashin-Beck disease in children: A systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2012, 20, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Liao, Y.; Yue, J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Deng, C.; Chen, L. Effects of five types of selenium supplementation for treatment of Kashin-Beck disease in children: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e017883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raisbeck, M.F. Selenosis. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2000, 16, 465–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, J.; Olsen, A.K. Selenium—A scoping review for Nordic Nutrition Recommendations 2023. Food Nutr. Res. 2023, 28, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macfarlane, G.J.; MacDonald, R.I.R.; Pathan, E.; Siebert, S.; Gaffney, K.; Choy, E.; Packham, J.; Martin, K.R.; Haywood, K.; Sengupta, R.; et al. Influence of co-morbid fibromyalgia on disease activity measures and response to tumour necrosis factor inhibitors in axial spondyloarthritis: Results from a UK national register. Rheumatology 2018, 57, 1982–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, F.; Clauw, D.J.; Fitzcharles, M.A.; Goldenberg, D.L.; Häuser, W.; Katz, R.L.; Mease, P.J.; Russell, A.S.; Russell, I.J.; Walitt, B. 2016 Revisions to the 2010/2011 fibromyalgia diagnostic criteria. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2016, 46, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukas, C.; Landewé, R.; Sieper, J.; Dougados, M.; Davis, J.; Braun, J.; van der Linden, S.; van der Heijde, D. Development of an ASAS-endorsed disease activity score (ASDAS) in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demircan, K.; Bengtsson, Y.; Sun, Q.; Brange, A.; Vallon-Christersson, J.; Rijntjes, E.; Malmberg, M.; Saal, L.H.; Rydén, L.; Borg, Å.; et al. Serum selenium, selenoprotein P and glutathione peroxidase 3 as predictors of mortality and recurrence following breast cancer diagnosis: A multicentre cohort study. Redox Biol. 2021, 47, 102145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demircan, K.; Jensen, R.C.; Chillon, T.S.; Jensen, T.K.; Sun, Q.; Bonnema, S.J.; Hackler, J.; Korevaar, T.I.M.; Glintborg, D.; Schomburg, L.; et al. Serum selenium, selenoprotein P, and glutathione peroxidase 3 during early and late pregnancy in association with gestational diabetes mellitus: Prospective Odense Child Cohort. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 118, 1224–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaad, S.; Chillon, T.S.; Filipowicz, D.; Wilms, B.; Strenge, F.; Szczepanek-Parulska, E.; Minich, W.B.; Meyhöfer, S.M.; Marquardt, J.U.; Mittag, J.; et al. Serum CD5L as potential biomarker of thyroid hormone status during pregnancy. Bio-Factors 2024, 51, e2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristic | axSpA n = 84 | PsA n = 76 |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 43.0 (21.3) | 52.5 (23.0) |
| (Missing) | 0 | 2 |
| Sex | ||
| Female | 24 (29%) | 44 (58%) |
| Weight | 85.0 (21.8) | 89.0 (28.0) |
| (Missing) | 48 | 53 |
| CRP Status | ||
| Positive, >0.5 mg/dL | 32 (38%) | 23 (30%) |
| ESR Status | ||
| Positive, >20 mm/h | 14 (17%) | 16 (21%) |
| 1Median (IQR); n (%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gröber, U.; Tsiami, S.; Chillon, T.S.; Rousis, E.; Kisters, K.; Karmeli, S.; Kiltz, U.; Schomburg, L.; Baraliakos, X. Trace Element Deficiency in Axial Spondyloarthritis and Psoriatic Arthritis in Relation to Markers of Inflammation and Remission. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4924. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104924
Gröber U, Tsiami S, Chillon TS, Rousis E, Kisters K, Karmeli S, Kiltz U, Schomburg L, Baraliakos X. Trace Element Deficiency in Axial Spondyloarthritis and Psoriatic Arthritis in Relation to Markers of Inflammation and Remission. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4924. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104924
Chicago/Turabian StyleGröber, Uwe, Styliani Tsiami, Thilo Samson Chillon, Evangelos Rousis, Klaus Kisters, Sophia Karmeli, Uta Kiltz, Lutz Schomburg, and Xenofon Baraliakos. 2025. "Trace Element Deficiency in Axial Spondyloarthritis and Psoriatic Arthritis in Relation to Markers of Inflammation and Remission" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4924. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104924
APA StyleGröber, U., Tsiami, S., Chillon, T. S., Rousis, E., Kisters, K., Karmeli, S., Kiltz, U., Schomburg, L., & Baraliakos, X. (2025). Trace Element Deficiency in Axial Spondyloarthritis and Psoriatic Arthritis in Relation to Markers of Inflammation and Remission. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4924. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104924







