The Role of AP2/ERF Transcription Factors in Plant Responses to Biotic Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
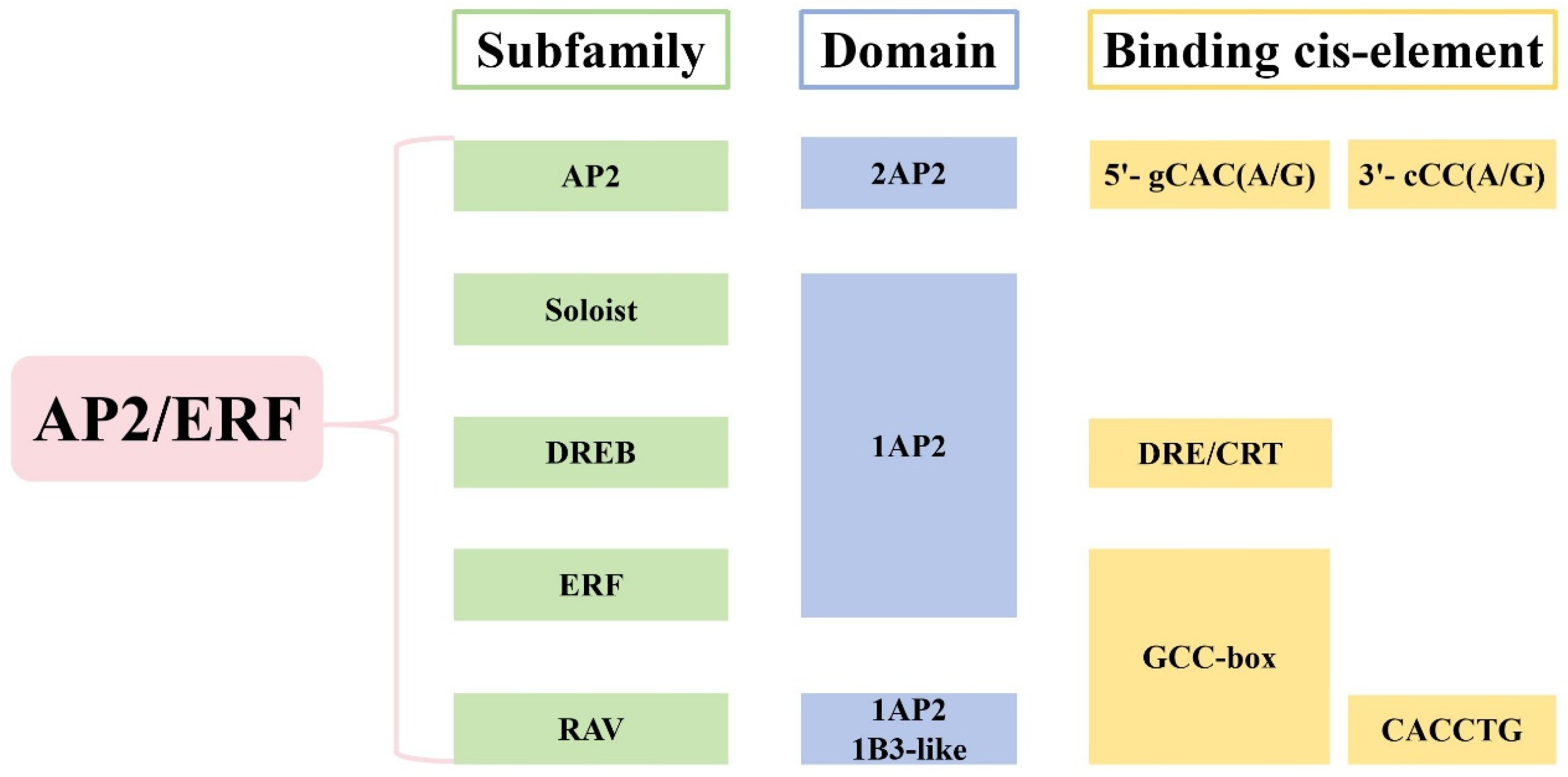
2. The Structure and Classification of AP2/ERF TFs
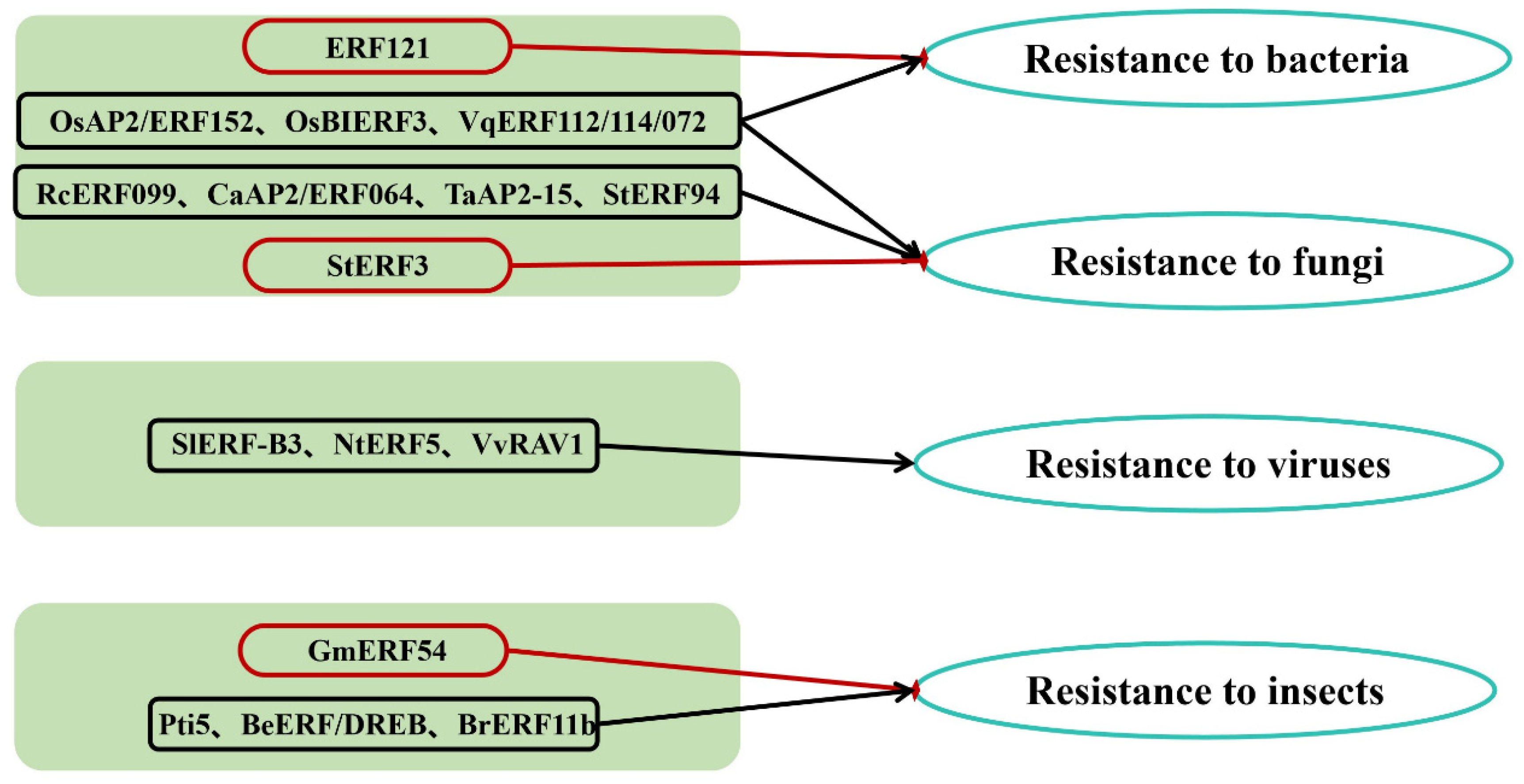
3. The Distribution and Quantity of AP2/ERF TFs Involved in Responses to Biotic Stresses
3.1. Bacterial Diseases
3.2. Fungal Diseases
3.3. Viral Diseases
3.4. Insect Pests
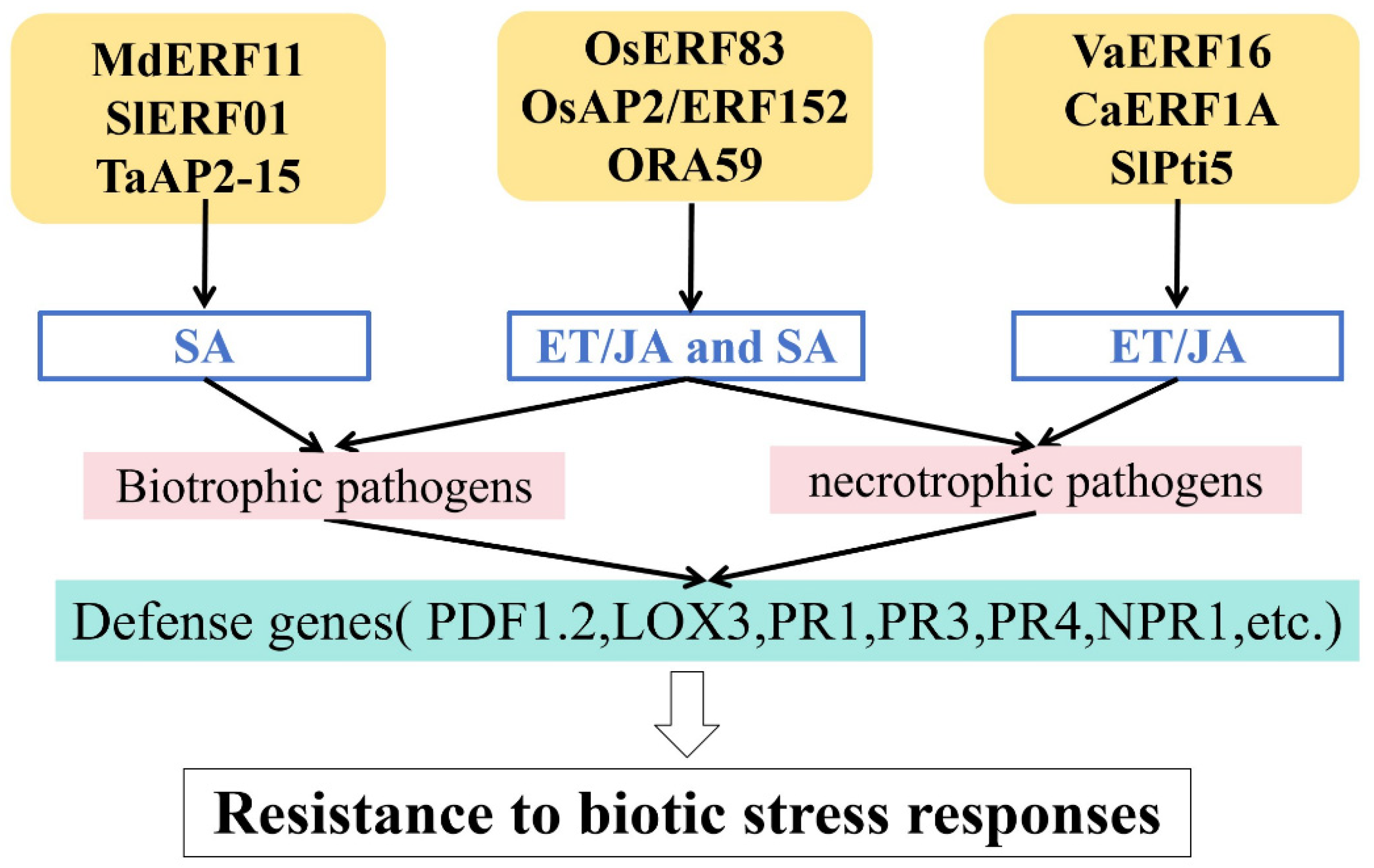
4. Regulation of Hormones in Responses to Biotic Stress
4.1. SA-Mediated Regulation
4.2. ET/JA-Mediated Regulation
4.3. ET/JA- and SA-Mediated Regulation
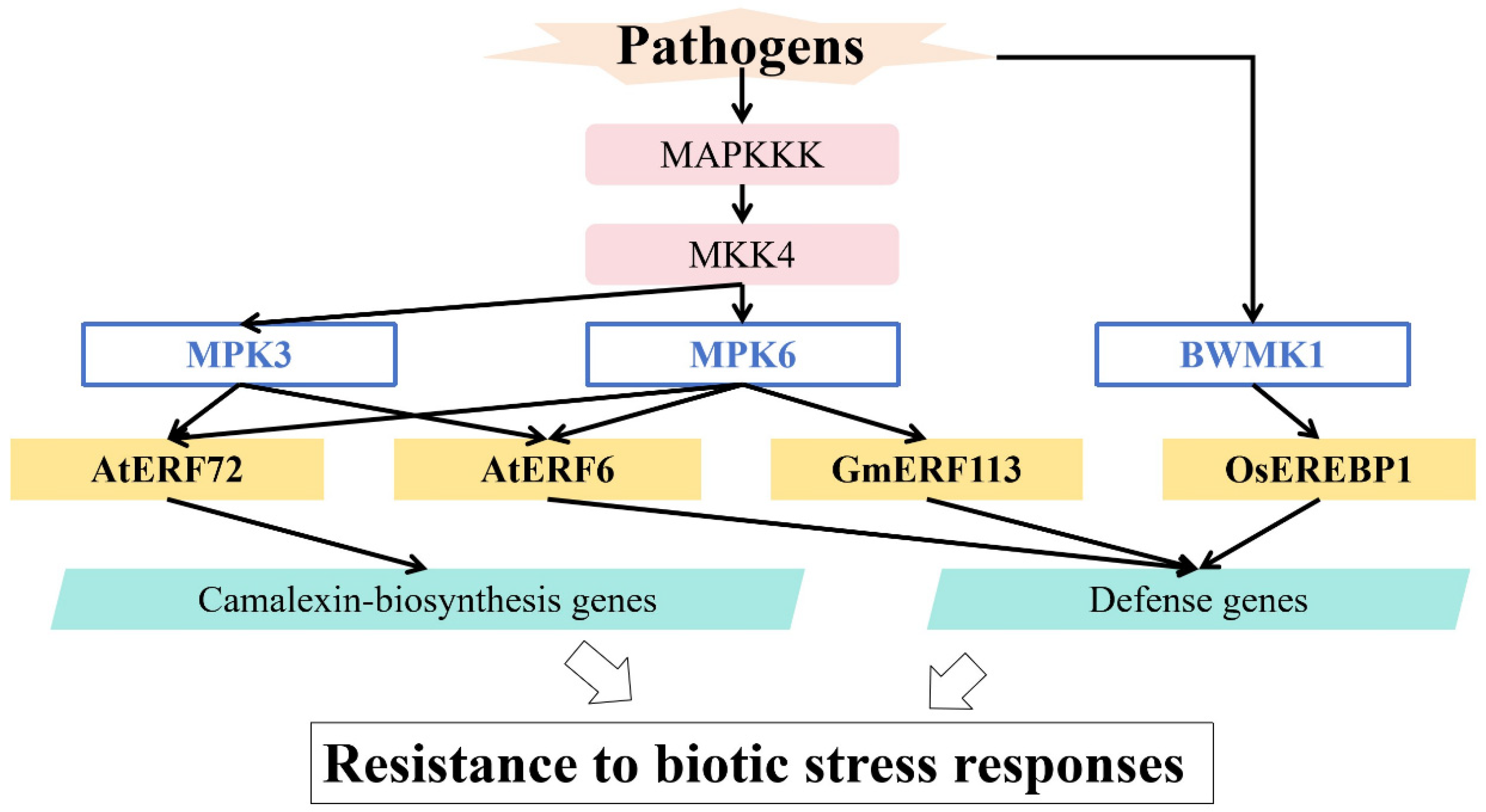
5. Regulation of MAPK in Responses to Biotic Stress
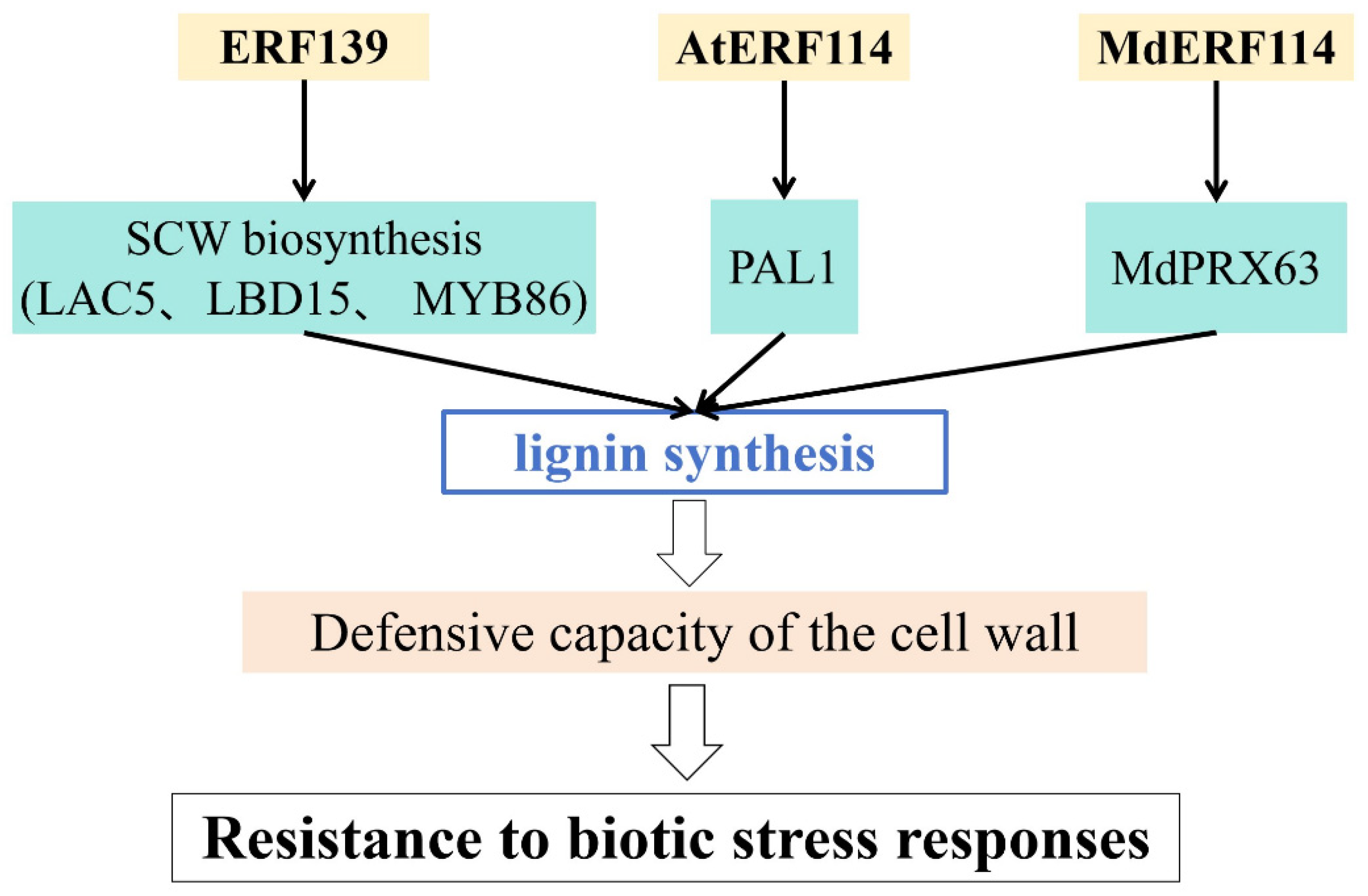
6. Regulation of Cell Wall in Responses to Biotic Stress
7. Epigenetic Regulation of the AP2/ERF TF Family in Plant Growth and Development
8. Challenges and Future Directions for AP2/ERF TFs
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Badis, G.; Berger, M.F.; Philippakis, A.A.; Talukder, S.; Gehrke, A.R.; Jaeger, S.A.; Chan, E.T.; Metzler, G.; Vedenko, A.; Chen, X.; et al. Diversity and complexity in DNA recognition by transcription factors. Science 2009, 324, 1720–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Ding, C.; Hu, H.; Dong, G.; Zhang, G.; Qian, Q.; Ren, D. Molecular Events of Rice AP2/ERF Transcription Factors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakuma, Y.; Liu, Q.; Dubouzet, J.G.; Abe, H.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. DNA-binding specificity of the ERF/AP2 domain of Arabidopsis DREBs, transcription factors involved in dehydration- and cold-inducible gene expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 290, 998–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Hu, L.; Jiang, W. Understanding AP2/ERF transcription factor responses and tolerance to various abiotic stresses in plants: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, K.; Hou, X.-L.; Xing, G.-M.; Liu, J.-X.; Duan, A.-Q.; Xu, Z.-S.; Li, M.-Y.; Zhuang, J.; Xiong, A.-S. Advances in AP2/ERF super-family transcription factors in plant. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2020, 40, 750–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, R.C.; Betzner, A.S.; Huttner, E.; Oakes, M.P.; Tucker, W.Q.; Gerentes, D.; Perez, P.; Smyth, D.R. AINTEGUMENTA, an APETALA2-like gene of Arabidopsis with pleiotropic roles in ovule development and floral organ growth. Plant Cell 1996, 8, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aukerman, M.J.; Sakai, H. Regulation of flowering time and floral organ identity by a MicroRNA and its APETALA2-like target genes. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 2730–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizek, B.A.; Eaddy, M. AINTEGUMENTA-LIKE6 regulates cellular differentiation in flowers. Plant Mol. Biol. 2012, 78, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Guo, M.; Yang, F.; Duncan, K.; Jackson, D.; Rafalski, A.; Wang, S.; Li, B. Mutations in an AP2 transcription factor-like gene affect internode length and leaf shape in maize. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moose, S.P.; Sisco, P.H. Glossy15, an APETALA2-like gene from maize that regulates leaf epidermal cell identity. Genes Dev. 1996, 10, 3018–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuck, G.; Meeley, R.B.; Hake, S. The control of maize spikelet meristem fate by the APETALA2-like gene indeterminate spikelet1. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutilier, K.; Offringa, R.; Sharma, V.K.; Kieft, H.; Ouellet, T.; Zhang, L.; Hattori, J.; Liu, C.M.; van Lammeren, A.A.; Miki, B.L.; et al. Ectopic expression of BABY BOOM triggers a conversion from vegetative to embryonic growth. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 1737–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Yu, X.; Cao, B.; Peng, L.; Gao, Y.; Feng, T.; Li, H.; Ren, Z. LkAP2L2, an AP2/ERF transcription factor gene of Larix kaempferi, with pleiotropic roles in plant branch and seed development. Russ. J. Genet. 2017, 53, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinshi, H.; Usami, S.; Ohme-Takagi, M. Identification of an ethylene-responsive region in the promoter of a tobacco class I chitinase gene. Plant Mol. Biol. 1995, 27, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.; Munné-Bosch, S. Ethylene Response Factors: A Key Regulatory Hub in Hormone and Stress Signaling. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubouzet, J.G.; Sakuma, Y.; Ito, Y.; Kasuga, M.; Dubouzet, E.G.; Miura, S.; Seki, M.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. OsDREB genes in rice, Oryza sativa L., encode transcription activators that function in drought-, high-salt- and cold-responsive gene expression. Plant J. 2003, 33, 751–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; He, R.J.; Xie, Q.L.; Zhao, X.H.; Deng, X.M.; He, J.B.; Song, L.; He, J.; Marchant, A.; Chen, X.Y.; et al. ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR 74 (ERF74) plays an essential role in controlling a respiratory burst oxidase homolog D (RbohD)-dependent mechanism in response to different stresses in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2017, 213, 1667–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banno, H.; Ikeda, Y.; Niu, Q.W.; Chua, N.H. Overexpression of Arabidopsis ESR1 induces initiation of shoot regeneration. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 2609–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Fits, L.; Memelink, J. ORCA3, a jasmonate-responsive transcriptional regulator of plant primary and secondary metabolism. Science 2000, 289, 295–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Huang, Z.; Ge, F.; Liu, D.; Lu, R.; Chen, C. An AP2/ERF family transcription factor PnERF1 raised the biosynthesis of saponins in Panax notoginseng. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2017, 36, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.X.; Li, J.X.; Yang, C.Q.; Hu, W.L.; Wang, L.J.; Chen, X.Y. The jasmonate-responsive AP2/ERF transcription factors AaERF1 and AaERF2 positively regulate artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua L. Mol. Plant 2012, 5, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; Shinozaki, K. A novel cis-acting element in an Arabidopsis gene is involved in responsiveness to drought, low-temperature, or high-salt stress. Plant Cell 1994, 6, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomashow, M.F. Plant Cold Acclimation: Freezing Tolerance Genes and Regulatory Mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 1999, 50, 571–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, H.R.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Lee, U.; Song, I.J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Nam, H.G.; Lim, P.O. The RAV1 transcription factor positively regulates leaf senescence in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 3947–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, K.H.; Lee, S.C.; Jung, H.W.; Hong, J.K.; Hwang, B.K. Expression and functional roles of the pepper pathogen-induced transcription factor RAV1 in bacterial disease resistance, and drought and salt stress tolerance. Plant Mol. Biol. 2006, 61, 897–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, J.M.; Stepanova, A.N.; Solano, R.; Wisman, E.; Ferrari, S.; Ausubel, F.M.; Ecker, J.R. Five components of the ethylene-response pathway identified in a screen for weak ethylene-insensitive mutants in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 2992–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Cheng, X.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, S.; Cheng, B.; Xiang, Y. Genome-wide analysis of cyclins in maize (Zea mays). Genet. Mol. Res. 2010, 9, 1490–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owji, H.; Hajiebrahimi, A.; Seradj, H.; Hemmati, S. Identification and functional prediction of stress responsive AP2/ERF transcription factors in Brassica napus by genome-wide analysis. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2017, 71, 32–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.D.; Yamasaki, K.; Ohme-Takagi, M.; Tateno, M.; Suzuki, M. A novel mode of DNA recognition by a β-sheet revealed by the solution structure of the GCC-box binding domain in complex with DNA. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 5484–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jofuku, K.D.; den Boer, B.G.; Van Montagu, M.; Okamuro, J.K. Control of Arabidopsis flower and seed development by the homeotic gene APETALA2. Plant Cell 1994, 6, 1211–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohme-Takagi, M.; Shinshi, H. Ethylene-inducible DNA binding proteins that interact with an ethylene-responsive element. Plant Cell 1995, 7, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockinger, E.J.; Gilmour, S.J.; Thomashow, M.F. Arabidopsis thaliana CBF1 encodes an AP2 domain-containing transcriptional activator that binds to the C-repeat/DRE, a cis-acting DNA regulatory element that stimulates transcription in response to low temperature and water deficit. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagaya, Y.; Ohmiya, K.; Hattori, T. RAV1, a novel DNA-binding protein, binds to bipartite recognition sequence through two distinct DNA-binding domains uniquely found in higher plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, T.; Suzuki, K.; Fujimura, T.; Shinshi, H. Genome-wide analysis of the ERF gene family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140, 411–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigyo, M.; Ito, M. Analysis of gymnosperm two-AP2-domain-containing genes. Dev. Genes Evol. 2004, 214, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nole-Wilson, S.; Krizek, B.A. DNA binding properties of the Arabidopsis floral development protein AINTEGUMENTA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 4076–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liao, J.; Ling, Q.; Xi, Y.; Qian, Y. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling analysis of maize AP2/ERF superfamily genes reveal essential roles in abiotic stress tolerance. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, D.; Ohme-Takagi, M.; Sarai, A. Unique mode of GCC box recognition by the DNA-binding domain of ethylene-responsive element-binding factor (ERF domain) in plant. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 26857–26861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraudat, J.; Hauge, B.M.; Valon, C.; Smalle, J.; Parcy, F.; Goodman, H.M. Isolation of the Arabidopsis ABI3 gene by positional cloning. Plant Cell 1992, 4, 1251–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riechmann, J.L.; Heard, J.; Martin, G.; Reuber, L.; Jiang, C.; Keddie, J.; Adam, L.; Pineda, O.; Ratcliffe, O.J.; Samaha, R.R.; et al. Arabidopsis transcription factors: Genome-wide comparative analysis among eukaryotes. Science 2000, 290, 2105–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Chen, M.; Chen, X.; Xu, Z.; Guan, S.; Li, L.C.; Li, A.; Guo, J.; Mao, L.; Ma, Y. Phylogeny, gene structures, and expression patterns of the ERF gene family in soybean (Glycine max L.). J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 4095–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.; Guangyuan, H.; Guangxiao, Y.; Hussain, J.; Xu, Y. AP2/ERF Transcription Factor in Rice: Genome-Wide Canvas and Syntenic Relationships between Monocots and Eudicots. Evol. Bioinform. 2012, 8, 321–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Ma, R.; Xu, D.; Bi, H.; Xia, Z.; Peng, H. Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of the AP2 Transcription Factor Gene Family in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.W.; Hong, L.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Jiang, H.Y.; Zhu, S.W.; Fan, J.; Cheng, B.J. A genome-wide analysis of the ERF gene family in sorghum. Genet. Mol. Res. 2013, 12, 2038–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Sun, W.; Ma, Z.; Zheng, T.; Huang, L.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, G.; Tang, Z.; Bu, T.; Li, C.; et al. Genome-wide investigation of the AP2/ERF gene family in tartary buckwheat (Fagopyum Tataricum). BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, F.; Yang, W.; Ci, J.; Ren, X.; Jiang, L.; Yang, W. Maize ethylene response factor ZmERF061 is required for resistance to Exserohilum turcicum. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 630413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reboledo, G.; Agorio, A.; Vignale, L.; Alvarez, A.; Ponce De León, I. The moss-specific transcription factor PpERF24 positively modulates immunity against fungal pathogens in Physcomitrium patens. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 908682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ai, S.; Liu, C.; Ma, F.; Li, C. MdERF114 enhances the resistance of apple roots to Fusarium solani by regulating the transcription of MdPRX63. Plant Physiol. 2023, 192, 2015–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Nolan, T.M.; Jiang, H.; Yin, Y. AP2/ERF transcription factor regulatory networks in hormone and abiotic stress responses in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillai, S.E.; Kumar, C.; Dasgupta, M.; Kumar, B.K.; Vungarala, S.; Patel, H.K.; Sonti, R.V. Ectopic expression of a cell-wall-degrading enzyme-induced OsAP2/ERF152 leads to resistance against bacterial and fungal infection in Arabidopsis. Phytopathology 2020, 110, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlobin, N.; Lebedeva, M.; Monakhova, Y.; Ustinova, V.; Taranov, V. An ERF121 transcription factor from Brassica oleracea is a target for the conserved TAL-effectors from different Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris strains. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2021, 22, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Wang, H.; Gao, Y.; Bi, Y.; Xiong, X.; Yan, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Song, F. ERF transcription factor OsBIERF3 positively contributes to immunity against fungal and bacterial diseases but negatively regulates cold tolerance in rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y. Heterologous expression of Chinese wild grapevine VqERFs in Arabidopsis thaliana enhance resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 and to Botrytis cinerea. Plant Sci. 2020, 293, 110421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Liu, X.; Shu, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Z. Global analysis of the AP2/ERF gene family in rose (Rosa chinensis) genome unveils the role of RcERF099 in Botrytis resistance. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.-H.; Zhang, H.-X.; Ali, M.; Wei, A.-M.; Luo, D.-X.; Gong, Z.-H. The CaAP2/ERF064 regulates dual functions in pepper: Plant cell death and resistance to Phytophthora capsici. Genes 2019, 10, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawku, M.D.; Goher, F.; Islam, M.A.; Guo, J.; He, F.; Bai, X.; Yuan, P.; Kang, Z.; Guo, J. TaAP2-15, an AP2/ERF transcription factor, is positively involved in wheat resistance to Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charfeddine, M.; Samet, M.; Charfeddine, S.; Bouaziz, D.; Gargouri Bouzid, R. Ectopic expression of StERF94 transcription factor in potato plants improved resistance to Fusarium solani infection. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 37, 450–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; He, Q.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, F.; Xie, C. The potato ERF transcription factor StERF3 negatively regulates resistance to Phytophthora infestans and salt tolerance in potato. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 992–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, B.L.; Sun, S.; Xing, G.M.; Wang, F.; Li, M.Y.; Tian, Y.S.; Xiong, A.S. AP2/ERF transcription factors involved in response to tomato yellow leaf curly virus in tomato. Plant Genome 2016, 9, plantgenome2015.2009.0082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, U.; Dröge-Laser, W. Overexpression of NtERF5, a new member of the tobacco ethylene response transcription factor family enhances resistance to tobacco mosaic virus. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2004, 17, 1162–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Zeng, Q.; Huang, W.; Huang, H.; Xie, Y.; Yu, S.; Kan, Q. GLRaV-2 protein p24 suppresses host defenses by interaction with a RAV transcription factor from grapevine. Plant Physiol. 2022, 189, 1848–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Qin, R.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Yu, D.; Wang, H. GmERF54, an ERF Transcription Factor, Negatively Regulates the Resistance of Soybean to the Common Cutworm (Spodoptera litura Fabricius). Agronomy 2023, 13, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Avila, C.A.; Goggin, F.L. The ethylene response factor Pti5 contributes to potato aphid resistance in tomato independent of ethylene signalling. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiong, T.; Zheng, X.-D.; Jun, G.; Ting, Y. Tomato SlPti5 plays a regulative role in the plant immune response against Botrytis cinerea through modulation of ROS system and hormone pathways. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 697–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Gao, H.; Zhu, X.; Li, D. An ERF transcription factor enhances plant resistance to Myzus persicae and Spodoptera litura. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2020, 34, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; Gu, K.D.; Han, P.L.; Yu, J.Q.; Wang, C.K.; Zhang, Q.Y.; You, C.X.; Hu, D.G.; Hao, Y.J. Apple ethylene response factor MdERF11 confers resistance to fungal pathogen Botryosphaeria dothidea. Plant Sci. 2020, 291, 110351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Shen, F.; Wang, H.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, J.; Xu, X.; Li, J. Functional analysis of the SlERF01 gene in disease resistance to S. lycopersici. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Chai, S.; Yin, W.; Gao, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, X. The transcription factors VaERF16 and VaMYB306 interact to enhance resistance of grapevine to Botrytis cinerea infection. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2022, 23, 1415–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, S.U. Functional analysis of hot pepper ethylene responsive factor 1A in plant defense. Plant Signal. Behav. 2022, 17, 2027137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezuka, D.; Kawamata, A.; Kato, H.; Saburi, W.; Mori, H.; Imai, R. The rice ethylene response factor OsERF83 positively regulates disease resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 135, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.J.; Zhang, J.; Lin, Z.; Yu, P.; Lu, M.; Li, N. The AP2/ERF transcription factor ORA59 regulates ethylene-induced phytoalexin synthesis through modulation of an acyltransferase gene expression. J. Cell. Physiol. 2024, 239, e30935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Xu, J.; He, Y.; Yang, K.-Y.; Mordorski, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S. Phosphorylation of an ERF transcription factor by Arabidopsis MPK3/MPK6 regulates plant defense gene induction and fungal resistance. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 1126–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, K.; Tong, G.; Xi, C.; Liu, J.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Ren, D.; Han, S. MPK3/MPK6-mediated phosphorylation of ERF72 positively regulates resistance to Botrytis cinerea through directly and indirectly activating the transcription of camalexin biosynthesis enzymes. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 73, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, Y.H.; Moon, B.C.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, C.Y.; Kim, M.C.; Kim, I.H.; Park, C.Y.; Kim, J.C.; Park, B.O.; Koo, S.C. BWMK1, a rice mitogen-activated protein kinase, locates in the nucleus and mediates pathogenesis-related gene expression by activation of a transcription factor. Plant Physiol. 2003, 132, 1961–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Jiang, L.; Du, B.; Ning, B.; Ding, X.; Zhang, C.; Song, B.; Liu, S.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, Y. GmMKK4-activated GmMPK6 stimulates GmERF113 to trigger resistance to Phytophthora sojae in soybean. Plant J. 2022, 111, 473–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessels, B.; Seyfferth, C.; Escamez, S.; Vain, T.; Antos, K.; Vahala, J.; Delhomme, N.; Kangasjärvi, J.; Eder, M.; Felten, J. An AP 2/ERF transcription factor ERF 139 coordinates xylem cell expansion and secondary cell wall deposition. New Phytol. 2019, 224, 1585–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, J.; Jia, F.; Zeng, H.; Li, G.; Yang, X. Ethylene-responsive factor ERF114 mediates fungal pathogen effector PevD1-induced disease resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2022, 23, 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Z.; Gai, J.; Ji, D.; Ren, Z. A study on leaf-feeding insect species on soyabeans in the Nanjing area. Soybean Sci. 1997, 16, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Luo, C.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, X.; Fu, C.; Yang, Y. Transcriptome-based discovery of AP2/ERF transcription factors and expression profiles under herbivore stress conditions in bamboo (Bambusa emeiensis). J. Plant Biol. 2019, 62, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phukan, U.J.; Jeena, G.S.; Tripathi, V.; Shukla, R.K. Regulation of Apetala2/Ethylene Response Factors in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, L.L.; da Fonseca Dos Santos, R.; Neto, J.P.B.; Guida-Santos, M.; Crovella, S.; Benko-Iseppon, A.M. Transcription factors involved in plant resistance to pathogens. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2017, 18, 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, B.; Zheng, X.-y.; Li, J.; Yang, M.; Dong, X.; He, G.; An, C.; Deng, X.W. Salicylic acid biosynthesis is enhanced and contributes to increased biotrophic pathogen resistance in Arabidopsis hybrids. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, M.-Z.; Bastías, D.A.; Christensen, M.J.; Zhong, R.; Nan, Z.-B.; Zhang, X.-X. The plant salicylic acid signalling pathway regulates the infection of a biotrophic pathogen in grasses associated with an Epichloë endophyte. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Han, X.; Feng, D.; Yuan, D.; Huang, L.-J. Signaling crosstalk between salicylic acid and ethylene/jasmonate in plant defense: Do we understand what they are whispering? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, L.; Xiang, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yu, D. The transcription factor WRKY75 positively regulates jasmonate-mediated plant defense to necrotrophic fungal pathogens. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 1473–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Su, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, S. Conveying endogenous and exogenous signals: MAPK cascades in plant growth and defense. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2018, 45, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, S. Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in plant signaling. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2022, 64, 301–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miedes, E.; Vanholme, R.; Boerjan, W.; Molina, A. The role of the secondary cell wall in plant resistance to pathogens. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Liu, R.; Pang, J.; Ren, B.; Zhou, H.; Wang, G.; Wang, E.; Liu, J. Poaceae-specific cell wall-derived oligosaccharides activate plant immunity via OsCERK1 during Magnaporthe oryzae infection in rice. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesarino, I. Structural features and regulation of lignin deposited upon biotic and abiotic stresses. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2019, 56, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanholme, R.; De Meester, B.; Ralph, J.; Boerjan, W. Lignin biosynthesis and its integration into metabolism. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2019, 56, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Ding, Y.; Sun, X.; Xie, S.; Wang, D.; Liu, X.; Su, L.; Wei, W.; Pan, L.; Zhou, D.-X. Histone deacetylase HDA9 negatively regulates salt and drought stress responsiveness in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.-S.; Duan, C.-G. Epigenetic regulation of plant immunity: From chromatin codes to plant disease resistance. Abiotech 2023, 4, 124–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovannoni, J.; Nguyen, C.; Ampofo, B.; Zhong, S.; Fei, Z. The epigenome and transcriptional dynamics of fruit ripening. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2017, 68, 61–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, S.; Zhao, M.; Luo, M.; Yu, C.-W.; Chen, C.-Y.; Tai, R.; Wu, K. Transcriptional repression by histone deacetylases in plants. Mol. Plant 2014, 7, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, L.; Li, J.; He, S.; Zhou, K.; Yang, F.; Huang, M.; Jiang, L.; Li, L. Trichostatin A selectively suppresses the cold-induced transcription of the ZmDREB1 gene in maize. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Su, L.; Hu, B.; Li, L. Expression of AhDREB1, an AP2/ERF transcription factor gene from peanut, is affected by histone acetylation and increases abscisic acid sensitivity and tolerance to osmotic stress in Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.-P.; Agarwal, M.; Ohta, M.; Guo, Y.; Halfter, U.; Wang, P.; Zhu, J.-K. Role of an Arabidopsis AP2/EREBP-type transcriptional repressor in abscisic acid and drought stress responses. The Plant Cell 2005, 17, 2384–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethke, G.; Unthan, T.; Uhrig, J.F.; Pöschl, Y.; Gust, A.A.; Scheel, D.; Lee, J. Flg22 regulates the release of an ethylene response factor substrate from MAP kinase 6 in Arabidopsis thaliana via ethylene signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 8067–8072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizoi, J.; Kanazawa, N.; Kidokoro, S.; Takahashi, F.; Qin, F.; Morimoto, K.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Heat-induced inhibition of phosphorylation of the stress-protective transcription factor DREB2A promotes thermotolerance of Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 902–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, H.; Hellmann, H. Arabidopsis thaliana BTB/POZ-MATH proteins interact with members of the ERF/AP2 transcription factor family. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 6624–6635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, K.; Ohama, N.; Kidokoro, S.; Mizoi, J.; Takahashi, F.; Todaka, D.; Mogami, J.; Sato, H.; Qin, F.; Kim, J.-S. BPM-CUL3 E3 ligase modulates thermotolerance by facilitating negative regulatory domain-mediated degradation of DREB2A in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E8528–E8536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, F.; Sakuma, Y.; Tran, L.-S.P.; Maruyama, K.; Kidokoro, S.; Fujita, Y.; Fujita, M.; Umezawa, T.; Sawano, Y.; Miyazono, K.-i. Arabidopsis DREB2A-interacting proteins function as RING E3 ligases and negatively regulate plant drought stress–responsive gene expression. The Plant Cell 2008, 20, 1693–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.-C.; Hsieh, E.-J.; Chen, J.-H.; Chen, H.-Y.; Lin, T.-P. Arabidopsis RGLG2, functioning as a RING E3 ligase, interacts with AtERF53 and negatively regulates the plant drought stress response. Plant Physiol. 2012, 158, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Gao, H.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, L.; He, S.; Song, B.; Liu, S.; Zhao, M.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y. The BTB/POZ domain protein GmBTB/POZ promotes the ubiquitination and degradation of the soybean AP2/ERF-like transcription factor GmAP2 to regulate the defense response to Phytophthora sojae. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 7891–7908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Species | Gene Name | Subfamily | Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oryza sativa | OsAP2/ERF152 | AP2/ERF | Enhances resistance to bacterial and fungal infections | [50] |
| Brassica oleracea | ERF121 | ERF | Promotes susceptibility to Xanthomonas infections | [51] |
| Oryza sativa | OsBIERF3 | ERF | Enhances resistance to fungal and bacterial pathogens | [52] |
| Vitis quinquangularis | VqERF112/114/072 | ERF | Positively regulates resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv. Tomato DC3000 and Botrytis cinerea | [53] |
| Rose chinensis | RcERF099 | ERF | Positively regulates resistance to Botrytis cinerea infections | [54] |
| Capsicum annuum | CaAP2/ERF064 | AP2/ERF | Enhances resistance to Phytophthora blight in Capsicums | [55] |
| Triticum aestivum | TaAP2-15 | AP2 | Increases susceptibility to Puccinia striiformis f. Sp. Tritici in wheat | [56] |
| Solanum tuberosum | StERF94 | ERF | Inhibits fungal proliferation in cellular tissues | [57] |
| Solanum tuberosum | StERF3 | ERF | Negatively regulates resistance to Phytophthora infestans | [58] |
| Solanum lycopersicum | SlERF-B3 | ERF | Differentially expressed in resistant and susceptible tomato during TYLCV infection | [59] |
| Nicotiana tabacum | NtERF5 | ERF | Enhances resistance to tobacco mosaic virus | [60] |
| Vitis vinifera | VvRAV1 | RAV | Suppresses the host’s defense responses and facilitates the accumulation and infection of glrav-2 | [61] |
| Glycine max | GmERF54 | ERF | Decreases resistance to CCW | [62] |
| Solanum lycopersicum | Pti5 | ERF | Contributes to resistance to potato aphid and Botrytis cinerea in tomato | [63,64] |
| Brassica rapa | BrERF11b | ERF | Enhances plant resistance to chewing insects and sap-sucking insects | [65] |
| Malus × domestica | MdERF11 | ERF | Enhances resistance to gray mold disease in apple trees | [66] |
| Solanum lycopersicum | SlERF01 | ERF | Enhances resistance to Stemphylium lycopersici in tomato | [67] |
| Vitis amurensis | VaERF16 | ERF | Improves resistance to Botrytis cinerea in grape | [68] |
| Capsicum annuum | CaERF1A | ERF | Enhances resistance to necrotrophic fungal pathogens | [69] |
| Oryza sativa | OsERF83 | ERF | Improves resistance to rice blast disease | [70] |
| Arabidopsis thaliana | ORA59 | ERF | Enhances resistance to necrotrophic pathogen infection | [71] |
| Arabidopsis thaliana | AtERF6/72 | ERF | Enhance resistance to Botrytis cinerea | [72,73] |
| Oryza sativa | OsEREBP1 | Enhances disease resistance | [74] | |
| Glycine max | GmERF113 | ERF | Enhances immune responses to Phytophthora sojae | [75] |
| Populus tremula | ERF139 | ERF | Increases lignin synthesis and defensive capacity of cell wall | [76] |
| Arabidopsis thaliana | AtERF114 | ERF | Increases lignin synthesis and defensive capacity of cell wall | [77] |
| Malus × domestica | MdERF114 | ERF | Increases lignin synthesis and defensive capacity of cell wall | [48] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, Z.-L.; Li, A.-M.; Wang, M.; Qin, C.-X.; Pan, Y.-Q.; Liao, F.; Chen, Z.-L.; Zhang, B.-Q.; Cai, W.-G.; Huang, D.-L. The Role of AP2/ERF Transcription Factors in Plant Responses to Biotic Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104921
Su Z-L, Li A-M, Wang M, Qin C-X, Pan Y-Q, Liao F, Chen Z-L, Zhang B-Q, Cai W-G, Huang D-L. The Role of AP2/ERF Transcription Factors in Plant Responses to Biotic Stress. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104921
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Ze-Lin, Ao-Mei Li, Miao Wang, Cui-Xian Qin, You-Qiang Pan, Fen Liao, Zhong-Liang Chen, Bao-Qing Zhang, Wen-Guo Cai, and Dong-Liang Huang. 2025. "The Role of AP2/ERF Transcription Factors in Plant Responses to Biotic Stress" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104921
APA StyleSu, Z.-L., Li, A.-M., Wang, M., Qin, C.-X., Pan, Y.-Q., Liao, F., Chen, Z.-L., Zhang, B.-Q., Cai, W.-G., & Huang, D.-L. (2025). The Role of AP2/ERF Transcription Factors in Plant Responses to Biotic Stress. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4921. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104921






