Rapid Reduction of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines with an Oral Topical Composition Comprising Olive Oil, Trimethylglycine and Xylitol: A Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of Participants
2.2. Inflammatory Cytokine Levels in Total Population
2.3. Inflammatory Cytokine Levels in Overweight/Pre-Obesity Subgroup
2.4. Secondary Outcomes
2.5. Adverse Effects and Overall Acceptability of Intervention Composition
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
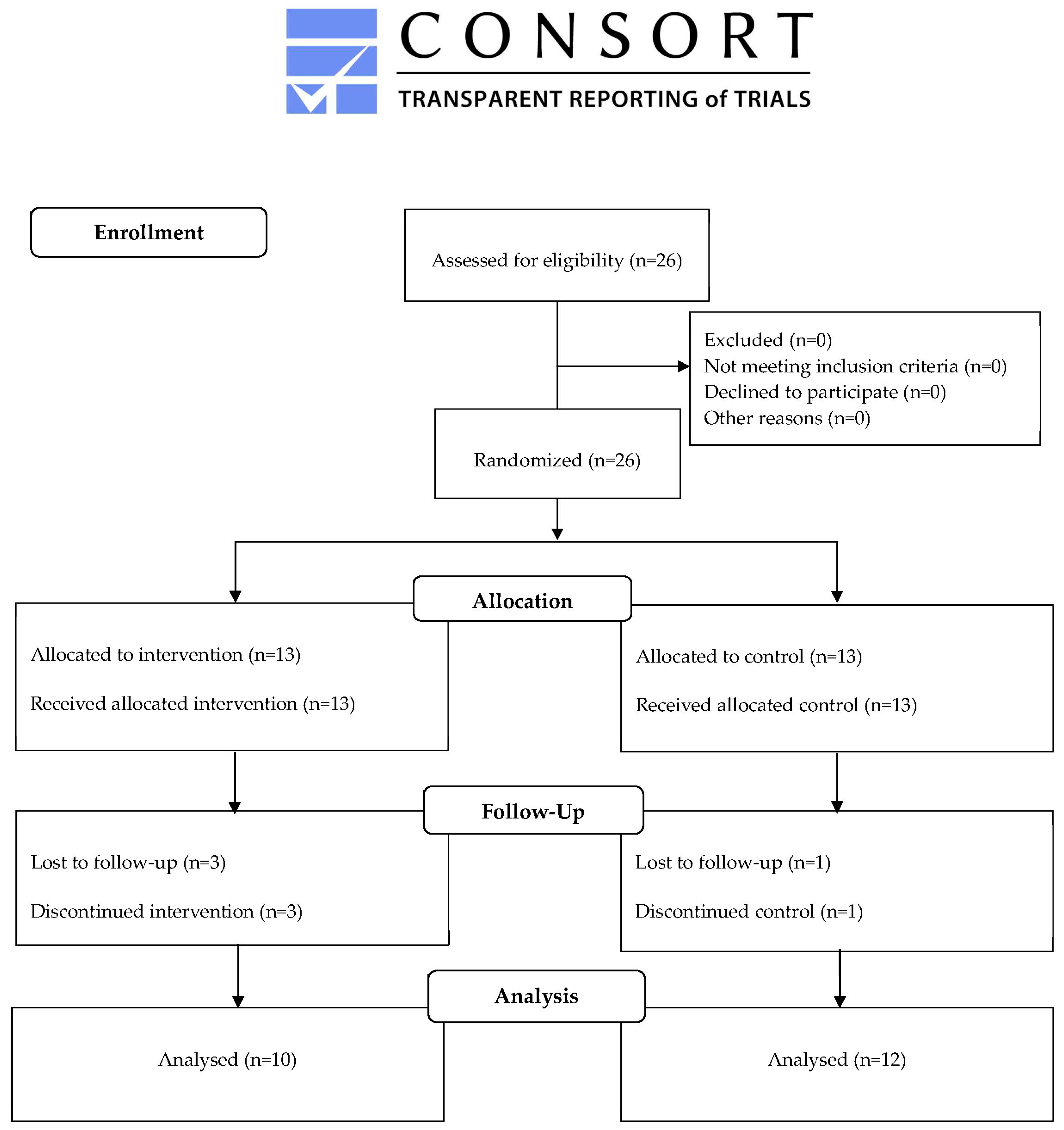
4.1. Study Design and Participants
4.2. Randomization and Masking
4.3. Procedures
- First Visit (T0):
- II.
- Second Visit (T1):
4.4. Outcomes
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMI | body mass index |
| BOP | bleeding on probing |
| CAL | clinical attachment loss |
| CFU | colony forming units |
| CG | control group |
| BPE | basic periodontal examination |
| DMFT | decayed, missing and filled teeth |
| ELISA | enzyme linked immunosorbent assay |
| GLP-1RA | glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists |
| IG | intervention group |
| IL-1β | interleukin-1β |
| IL-4 | interleukin-4 |
| IL-6 | interleukin-6 |
| i-NO | inducible nitric oxide |
| NLRP3 | nucleotide-binding domain and leucine-rich repeat pyrin containing protein-3 |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| qPCR | quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| RCT | randomized controlled trial |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor-α |
| VAS | visual analogue scale |
References
- Burcelin, R. Regulation of Metabolism: A Cross Talk Between Gut Microbiota and Its Human Host. Physiology 2012, 27, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-M.; An, J. Cytokines, Inflammation and Pain. Int. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2007, 45, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gärtner, Y.; Bitar, L.; Zipp, F.; Vogelaar, C.F. Interleukin-4 as a Therapeutic Target. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 242, 108348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Roub, A.; Al Madhoun, A.; Akhter, N.; Thomas, R.; Miranda, L.; Jacob, T.; Al-Ozairi, E.; Al-Mulla, F.; Sindhu, S.; Ahmad, R. IL-1β and TNFα Cooperativity in Regulating IL-6 Expression in Adipocytes Depends on CREB Binding and H3K14 Acetylation. Cells 2021, 10, 3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lê, S.; Laurencin-Dalicieux, S.; Minty, M.; Assoulant-Anduze, J.; Vinel, A.; Yanat, N.; Loubieres, P.; Azalbert, V.; Diemer, S.; Burcelin, R.; et al. Obesity Is Associated with the Severity of Periodontal Inflammation Due to a Specific Signature of Subgingival Microbiota. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajishengallis, G.; Chavakis, T. Inflammatory Memory and Comorbidities. Clin. Transl. Med. 2022, 12, e984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavish, D.C.; Szabo, Y.Z. What Moderates Salivary Markers of Inflammation Reactivity to Stress? A Descriptive Report and Meta-Regression. Stress 2021, 24, 710–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongiovanni, P.; Meroni, M.; Casati, S.; Goldoni, R.; Thomaz, D.V.; Kehr, N.S.; Galimberti, D.; Del Fabbro, M.; Tartaglia, G.M. Salivary Biomarkers: Novel Noninvasive Tools to Diagnose Chronic Inflammation. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2023, 15, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonetti, M.S.; Greenwell, H.; Kornman, K.S. Staging and Grading of Periodontitis: Framework and Proposal of a New Classification and Case Definition. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89, S159–S172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, E.M.; Reis, C.; Manzanares-Céspedes, M.C. Chronic Periodontitis, Inflammatory Cytokines, and Interrelationship with Other Chronic Diseases. Postgrad. Med. 2018, 130, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhol, N.K.; Bhanjadeo, M.M.; Singh, A.K.; Dash, U.C.; Ojha, R.R.; Majhi, S.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Jena, A.B. The Interplay between Cytokines, Inflammation, and Antioxidants: Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Potentials of Various Antioxidants and Anti-Cytokine Compounds. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 178, 117177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, M.C.; Casabona, J.C.; Puntel, M.; Pitossi, F.J. Interleukin-1β and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α: Reliable Targets for Protective Therapies in Parkinson’s Disease? Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2013, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Jin, S.; Sonobe, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Horiuchi, H.; Parajuli, B.; Kawanokuchi, J.; Mizuno, T.; Takeuchi, H.; Suzumura, A. Interleukin-1β Induces Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption by Downregulating Sonic Hedgehog in Astrocytes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Balachandran, Y.L.; Chong, W.P.; Chan, K.W.Y. Roles of Cytokines in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkwill, F. Tumour Necrosis Factor and Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briukhovetska, D.; Dörr, J.; Endres, S.; Libby, P.; Dinarello, C.A.; Kobold, S. Interleukins in Cancer: From Biology to Therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 481–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meduri, G.U.; Kanangat, S.; Stefan, J.; Tolley, E.; Schaberg, D. Cytokines IL-1beta, IL-6, and TNF-Alpha Enhance in Vitro Growth of Bacteria. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 160, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rider, P.; Carmi, Y.; Cohen, I. Biologics for Targeting Inflammatory Cytokines, Clinical Uses, and Limitations. Int. J. Cell Biol. 2016, 2016, 9259646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; Everett, B.M.; Thuren, T.; MacFadyen, J.G.; Chang, W.H.; Ballantyne, C.; Fonseca, F.; Nicolau, J.; Koenig, W.; Anker, S.D.; et al. CANTOS Trial Group. Antiinflammatory Therapy with Canakinumab for Atherosclerotic Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Agurto, A.; Bravo, M.; Magán-Fernandez, A.; López-Toruño, A.; Muñoz, R.; Ferrer, J.; Mesa, F. Randomized Clinical Trial on the Clinical Effects of a Toothpaste Containing Extra Virgin Olive Oil, Xylitol, and Betaine in Gingivitis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Obesity: Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic: Report of a WHO Consultation. 2000. Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/42330 (accessed on 27 November 2024).
- Palmer, R.; Floyd, P. Periodontal Examination and Screening. Br. Dent. J. 2023, 235, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, T.; Ower, P.; Tank, M.; West, N.X.; Walter, C.; Needleman, I.; Hughes, F.J.; Wadia, R.; Milward, M.R.; Hodge, P.J.; et al. Periodontal Diagnosis in the Context of the 2017 Classification System of Periodontal Diseases and Conditions – Implementation in Clinical Practice. Br. Dent. J. 2019, 226, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frodge, B.D.; Ebersole, J.L.; Kryscio, R.J.; Thomas, M.V.; Miller, C.S. Bone Remodeling Biomarkers of Periodontal Disease in Saliva. J. Periodontol. 2008, 79, 1913–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riis, J.L.; Out, D.; Dorn, L.D.; Beal, S.J.; Denson, L.A.; Pabst, S.; Jaedicke, K.; Granger, D.A. Salivary Cytokines in Healthy Adolescent Girls: Intercorrelations, Stability, and Associations with Serum Cytokines, Age, and Pubertal Stage. Dev. Psychobiol. 2014, 56, 797–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, C.S.; King, C.P.; Langub, M.C.; Kryscio, R.J.; Thomas, M.V. Salivary Biomarkers of Existing Periodontal Disease. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2006, 137, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz, M.; Herrera, D.; Kebschull, M.; Chapple, I.; Jepsen, S.; Beglundh, T.; Sculean, A.; Tonetti, M.S. Treatment of Stage I-III Periodontitis-The EFP S3 Level Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2020, 47, 4–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, R.; Yeltiwar, R.K.; Pushpanshu, K. Salivary Interleukin-1β Levels in Patients with Chronic Periodontitis Before and After Periodontal Phase I Therapy and Healthy Controls: A Case-Control Study. J. Periodontol. 2011, 82, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yama, K.; Nishimoto, Y.; Kumagai, K.; Jo, R.; Harada, M.; Maruyama, Y.; Aita, Y.; Fujii, N.; Inokuchi, T.; Kawamata, R.; et al. Dysbiosis of Oral Microbiome Persists after Dental Treatment-Induced Remission of Periodontal Disease and Dental Caries. mSystems 2023, 8, e0068323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbdelMassih, A.; Eid, M.; Gadalla, M.; AbouShadi, N.; Youssef, S.; Ali, B.; AbdelDayem, J.; AbdelFatah, E.; Mahmoud, A.; ElLithey, A.; et al. Is Microbiota a Part of Obesogenic Memory? Insights about the Role of Oral and Gut Microbiota in Re-Obesity. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2023, 47, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballini, A.; Scacco, S.; Boccellino, M.; Santacroce, L.; Arrigoni, R. Microbiota and Obesity: Where Are We Now? Biology 2020, 9, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltiel, A.R.; Olefsky, J.M. Inflammatory Mechanisms Linking Obesity and Metabolic Disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijakowski, K.; Lehmann, A.; Rutkowski, R.; Korybalska, K.; Witowski, J.; Surdacka, A. Poor Oral Hygiene and High Levels of Inflammatory Cytokines in Saliva Predict the Risk of Overweight and Obesity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meduri, G.U. Clinical Review: A Paradigm Shift: The Bidirectional Effect of Inflammation on Bacterial Growth. Clinical Implications for Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Crit. Care 2001, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadkhoda, Z.; Amirzargar, A.; Esmaili, Z.; Vojdanian, M.; Akbari, S. Effect of TNF-α Blockade in Gingival Crevicular Fluid on Periodontal Condition of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Iran. J. Immunol. 2016, 13, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Balci Yuce, H.; Gokturk, O.; Aydemir Turkal, H.; Inanir, A.; Benli, I.; Demir, O. Assessment of Local and Systemic 25-Hydroxy-Vitamin D, RANKL, OPG, and TNF Levels in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Periodontitis. J. Oral Sci. 2017, 59, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulmer, C.; Avenell, A. The Effect of Dietary Weight-Loss Interventions on the Inflammatory Markers Interleukin-6 and TNF-Alpha in Adults with Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Clinical Trials. Obes. Rev. 2025, e13910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarreal-Calderon, J.R.; Cuellar-Tamez, R.; Castillo, E.C.; Luna-Ceron, E.; García-Rivas, G.; Elizondo-Montemayor, L. Metabolic Shift Precedes the Resolution of Inflammation in a Cohort of Patients Undergoing Bariatric and Metabolic Surgery. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachuła, M.; Kosowski, M.; Ryl, S.; Basiak, M.; Okopień, B. Impact of Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists on Biochemical Markers of the Initiation of Atherosclerotic Process. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, K.F.; Altman, D.G.; Moher, D. CONSORT 2010 Statement: Updated Guidelines for Reporting Parallel Group Randomised Trials. BMJ 2010, 340, c332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, H.; Palmer, C.E. Studies on Dental Caries: IX. The Prevalence and Incidence of Dental Caries Experience, Dental Care, and Carious Defects Requiring Treatment in High School Children. Public Health Rep. 1896-1970 1940, 55, 1258–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, T.J.; Drake, R.B.; Naylor, J.E. The Plaque Control Record. J. Periodontol. 1972, 43, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma, L.F.; Gonnelli, F.A.S.; Marcucci, M.; Giordani, A.J.; Dias, R.S.; Segreto, R.A.; Segreto, H.R.C. A Novel Method to Evaluate Salivary Flow Rates of Head and Neck Cancer Patients after Radiotherapy: A Pilot Study. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2018, 84, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.-W.; Kim, H.-K.; Kim, M.-E. Clinical Usefulness of pH Papers in the Measurement of Salivary pH. J. Oral Med. Pain 2015, 40, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Intervention (n = 10) | Control (n = 12) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years old), mean (SD) | 43.8 (16.7) | 53.2 (24.7) | 0.32 |
| Gender, n (%) | |||
| Female | 5 (50%) | 10 (83.3%) | 0.09 |
| Male | 5 (50%) | 2 (16.7%) | |
| Anthropometric parameters, n (%) *# | |||
| Normal weight (BMI ≤ 24.9) | 2 (22.2%) | 4 (33.3%) | 0.66 |
| Overweight/Pre-obesity (25 ≤ BMI ≤ 29.9) | 7 (77.8%) | 8 (66.7%) | |
| Obese (BMI ≥ 30) | 0 | 0 | |
| Basic Periodontal Examination (BPE), n (%) † | |||
| Code 1 | 4 (40%) | 4 (33.3%) | 0.949 |
| Code 2 | 3 (30%) | 4 (33.3%) | |
| Code 3 | 3 (30%) | 4 (33.3%) | |
| DMFT, mean (SD) ‡ | 13.6 (9.2) | 13.8 (6.4) | 0.628 |
| Inflammatory mediators (pg/mL), median (IQR) | |||
| IL-1ß | 263.48 (124.74–563.01) | 294.65 (78.85–513.82) | 0.87 |
| TNF-α | 5.27 (1.20–14.38) | 3.15 (2.40–4.26) | 0.28 |
| IL-4 | 12.53 (7.99–26.37) | 0.25 (0.0–22.01) | 0.09 |
| Total subgingival bacterial load (log cfu/mL), median (IQR) | 5.48 (3.39–6.46) | 4.18 (1.81–5.19) | 0.15 |
| Inflammatory Cytokine Levels (pg/mL) | Intervention (n = 10) | Control (n = 12) | p-Value (Between Groups) | r-Value (Effect Size) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-1 ß | ||||
| T0 | 263.48 (124.74–563.01) | 294.65 (78.85–513.82) | ||
| T1 | 29.14 (0.0–263.22) | 355.77 (110.76–570.96) | ||
| Difference (T1-T0) | −160.06 (−326.29–(54.29)) | 66.17 (−71.40–139.99) | 0.003 | Z = 2.901 r = 0.62 |
| p-value (intra-group) | 0.008 | 0.21 | ||
| TNF-α | ||||
| T0 | 5.27 (1.20–14.38) | 3.15 (2.40–4.26) | ||
| T1 | 2.07 (0.21–5.07) | 7.73 (2.96–28.38) | ||
| Difference (T1-T0) | −3.44 (−9.90–(-1.03)) | 5.00 (0.04–20.97) | 0.001 | Z = 3.23 r = 0.69 |
| p-value (intra-group) | 0.059 | 0.01 | ||
| IL-4 | ||||
| T0 | 12.53 (7.99–26.37) | 0.25 (0.0–22.01) | ||
| T1 | 15.61 (5.05–23.62) | 9.85 (0.0–28.98) | ||
| Difference (T1-T0) | −3.77 (−14.28–10.66) | 3.17 (-0.37–12.27) | 0.203 | Z = 1.321 r = 0.28 |
| p-value (intra-group) | 0.57 | 0.21 |
| Inflammatory Cytokine Levels (pg/mL) | Overweight/Pre-Obesity (n = 15) | p-Value (Between Groups) | r-Value (Effect Size) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intervention (n = 7) | Control (n = 8) | |||
| IL-1 ß | ||||
| T0 | 169.79 (60.00–551.67) | 316.66 (113.86–486.80) | ||
| T1 | 0.00 (0.00–109.14) | 454.41 (145.23–564.74) | ||
| Difference (T1-T0) | −140.06 (−350.18–(−37.18)) | 82.73 (−36.61–210.97) | 0.014 | Z = 2.430 r = 0.63 |
| p-value (intra-group) | 0.028 | 0.208 | ||
| TNF-α | ||||
| T0 | 5.94 (0–26.90) | 2.90 (2.07–4.26) | ||
| T1 | 2.34 (0.24–4.40) | 7.16 (1.96–19.65) | ||
| Difference (T1-T0) | −3.92 (−22.50–0.30) | 3.33 (−0.29–16.17) | 0.029 | Z = 2.199 r = 0.57 |
| p-value (intra-group) | 0.176 | 0.128 | ||
| IL-4 | ||||
| T0 | 9.87 (4.20–25.88) | 0.35 (0.00–21.81) | ||
| T1 | 14.41 (6.73–24.20) | 18.61 (0.00–28.62) | ||
| Difference (T1-T0) | −3.13 (−14.27–20.00) | 5.68 (−4.88–20.60) | 0.613 | Z = 0.579 r = 0.15 |
| p-value (intra-group) | 1.000 | 0.249 | ||
| Total Bacterial Count (log cfu/mL) | Intervention (n = 10) | Control (n = 11) | p-Value (Between Groups) |
|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | 5.48 (3.39–6.46) | 4.18 (1.81–5.19) | |
| T1 | 4.81 (2.51–5.69) | 4.45 (1.98–6.82) | |
| Difference (T1-T0) | −1.20 (−2.10–1.79) | 1.14 (−1.28–2.46) | 0.16 |
| p-value (intra-group) | 0.51 | 0.29 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
López-López, J.; Reuss, J.M.; Vinuesa-Aumedes, T.; Egido-Moreno, S.; Roselló-Llabres, X.; Pereira-Riveros, T.; Reuss, D.; Alonso-Gamo, L.; Rodríguez-Vilaboa, B. Rapid Reduction of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines with an Oral Topical Composition Comprising Olive Oil, Trimethylglycine and Xylitol: A Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4920. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104920
López-López J, Reuss JM, Vinuesa-Aumedes T, Egido-Moreno S, Roselló-Llabres X, Pereira-Riveros T, Reuss D, Alonso-Gamo L, Rodríguez-Vilaboa B. Rapid Reduction of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines with an Oral Topical Composition Comprising Olive Oil, Trimethylglycine and Xylitol: A Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4920. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104920
Chicago/Turabian StyleLópez-López, José, José M. Reuss, Teresa Vinuesa-Aumedes, Sonia Egido-Moreno, Xavier Roselló-Llabres, Tanya Pereira-Riveros, Debora Reuss, Laura Alonso-Gamo, and Beatriz Rodríguez-Vilaboa. 2025. "Rapid Reduction of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines with an Oral Topical Composition Comprising Olive Oil, Trimethylglycine and Xylitol: A Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4920. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104920
APA StyleLópez-López, J., Reuss, J. M., Vinuesa-Aumedes, T., Egido-Moreno, S., Roselló-Llabres, X., Pereira-Riveros, T., Reuss, D., Alonso-Gamo, L., & Rodríguez-Vilaboa, B. (2025). Rapid Reduction of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines with an Oral Topical Composition Comprising Olive Oil, Trimethylglycine and Xylitol: A Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4920. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104920








