Functional Role of NOXA in Hypoxia-Mediated PD-L1 Inhibitor Response in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
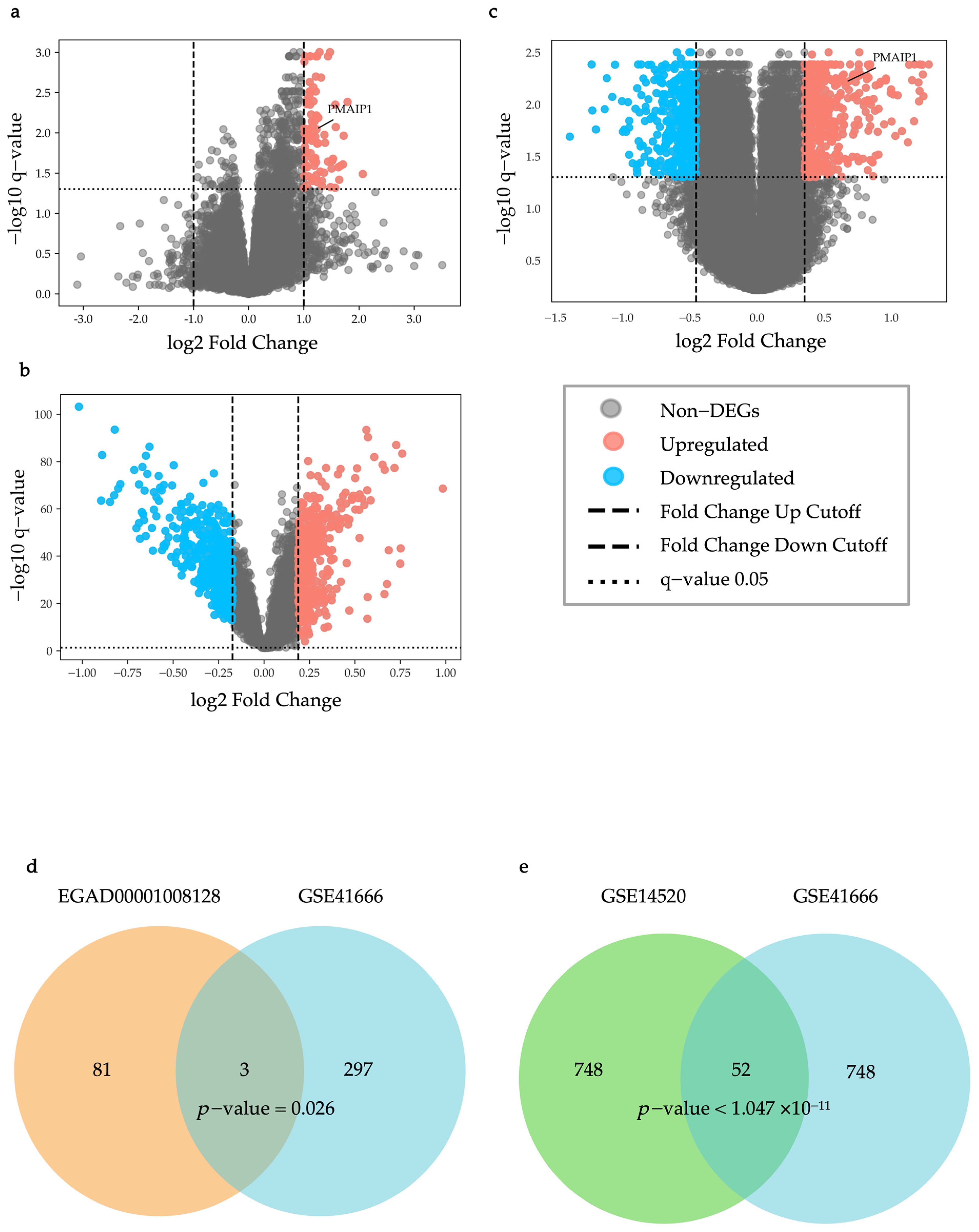
2.1. Identification of IRH and HRH Genes from Public Dataset
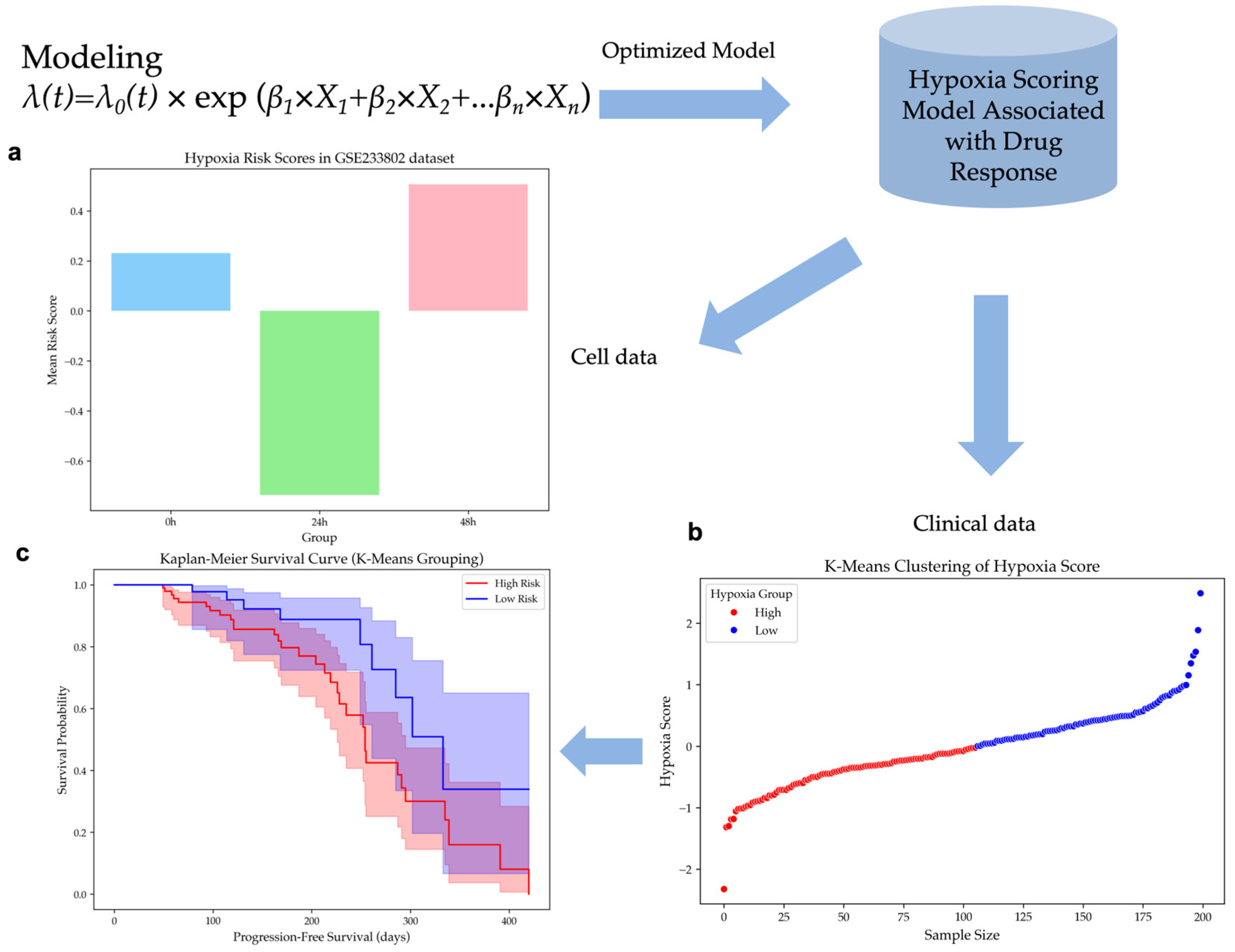
2.2. Construction of a Hypoxia Risk Scoring Model for HCC
2.3. Validation of the Hypoxia Risk Scoring Model in Independent Datasets
2.3.1. Hypoxia Risk Scores Reflect Hypoxia Levels in Cell Line Dataset
2.3.2. Hypoxia Risk Stratification Predicts Survival Outcomes in HCC Patients
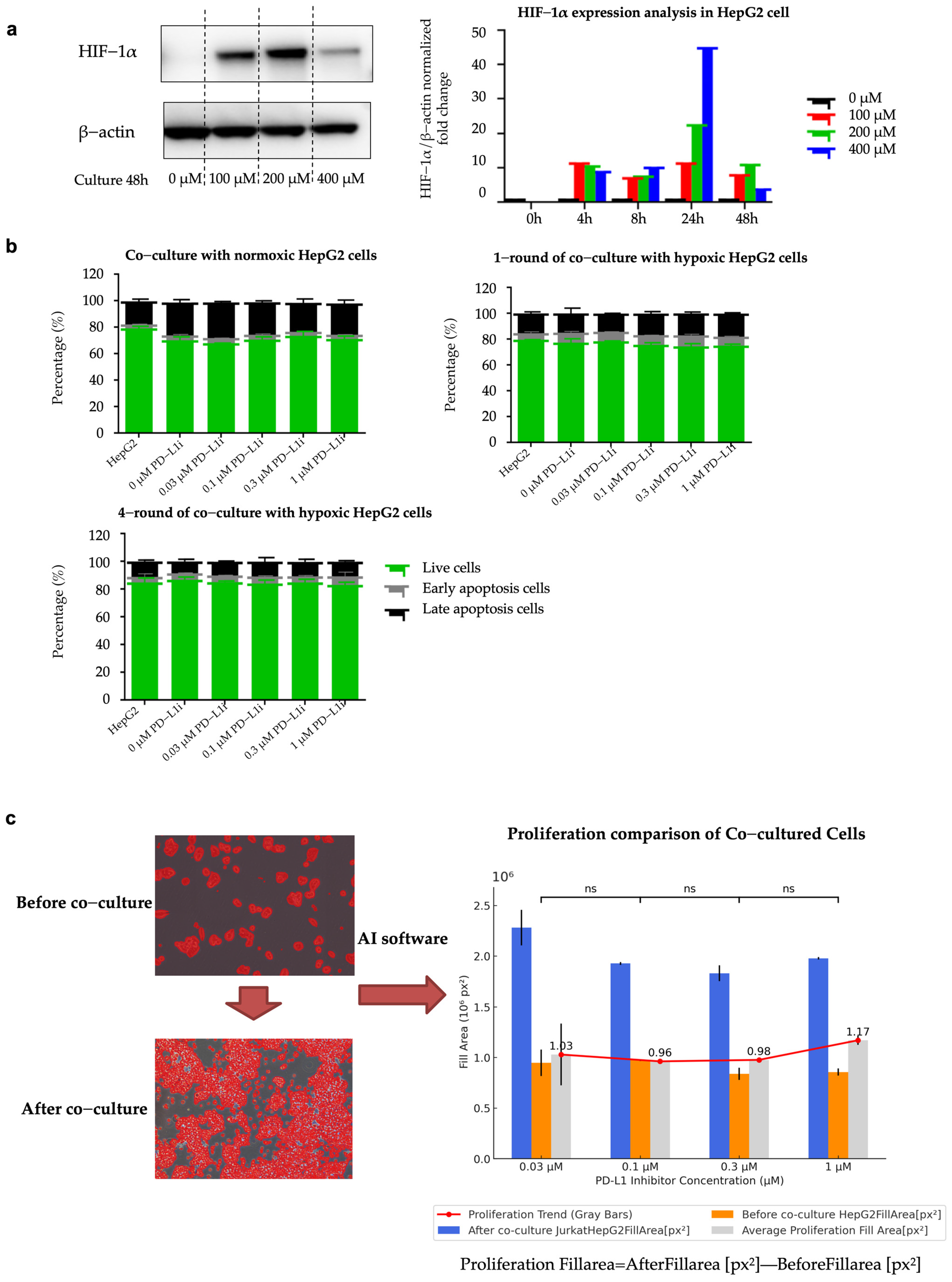
2.4. Establishment of Hypoxia-Induced Resistant HepG2 Cell Line (HepG2-R)
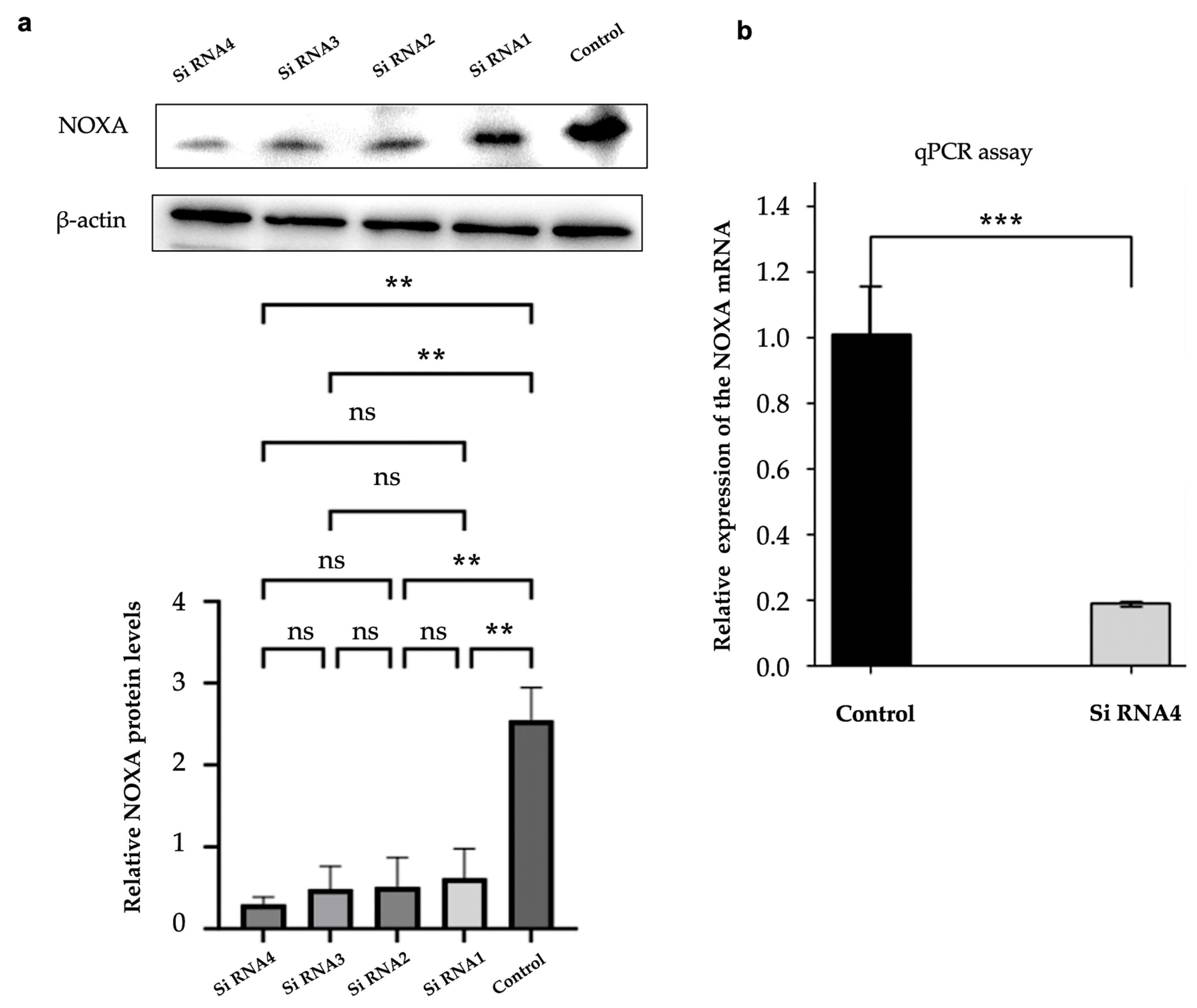
2.5. Efficient Knockdown of NOXA Expression in HepG2-R Cell Line
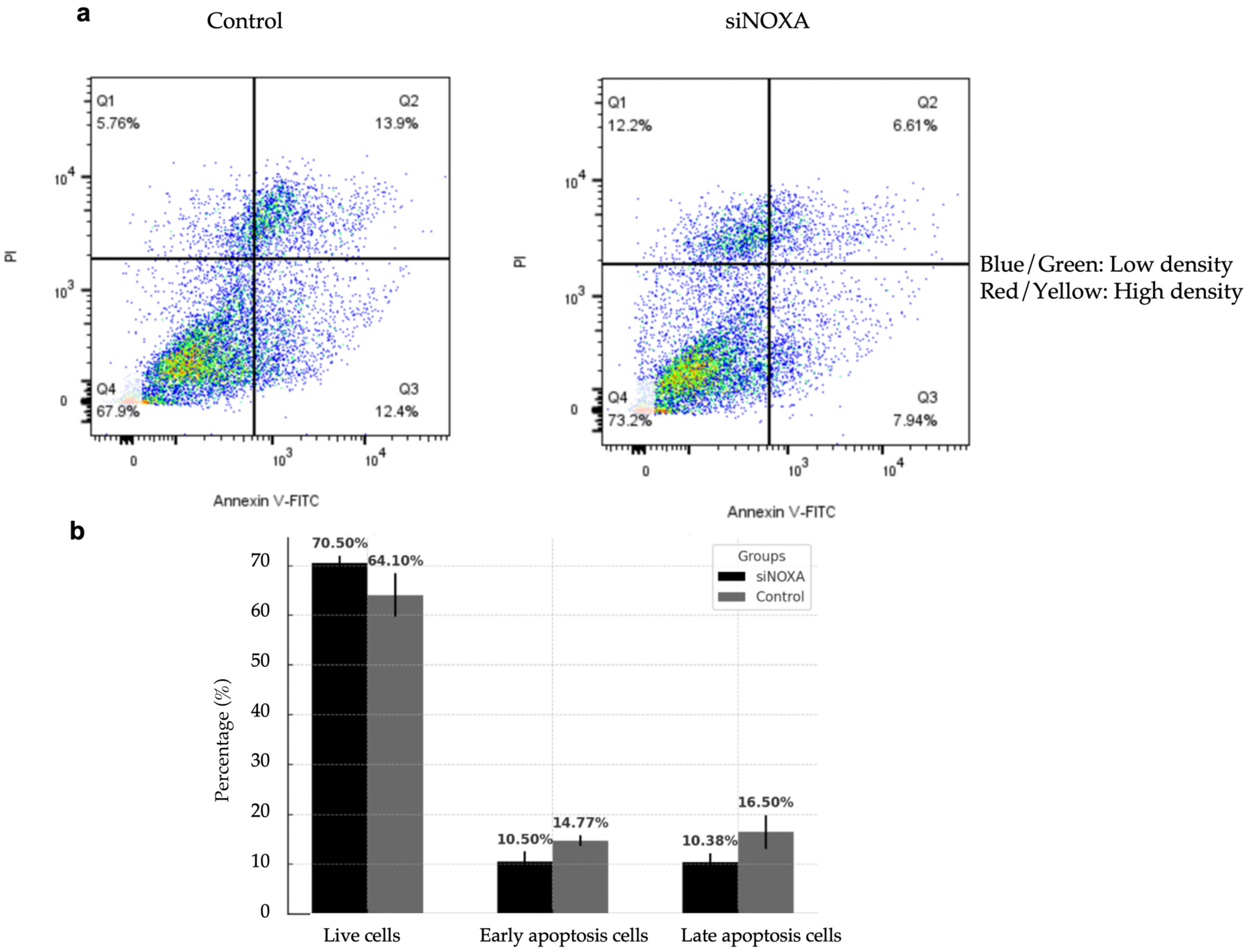
2.6. NOXA Knockdown Reduces Apoptosis in HepG2-R Cell Line
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
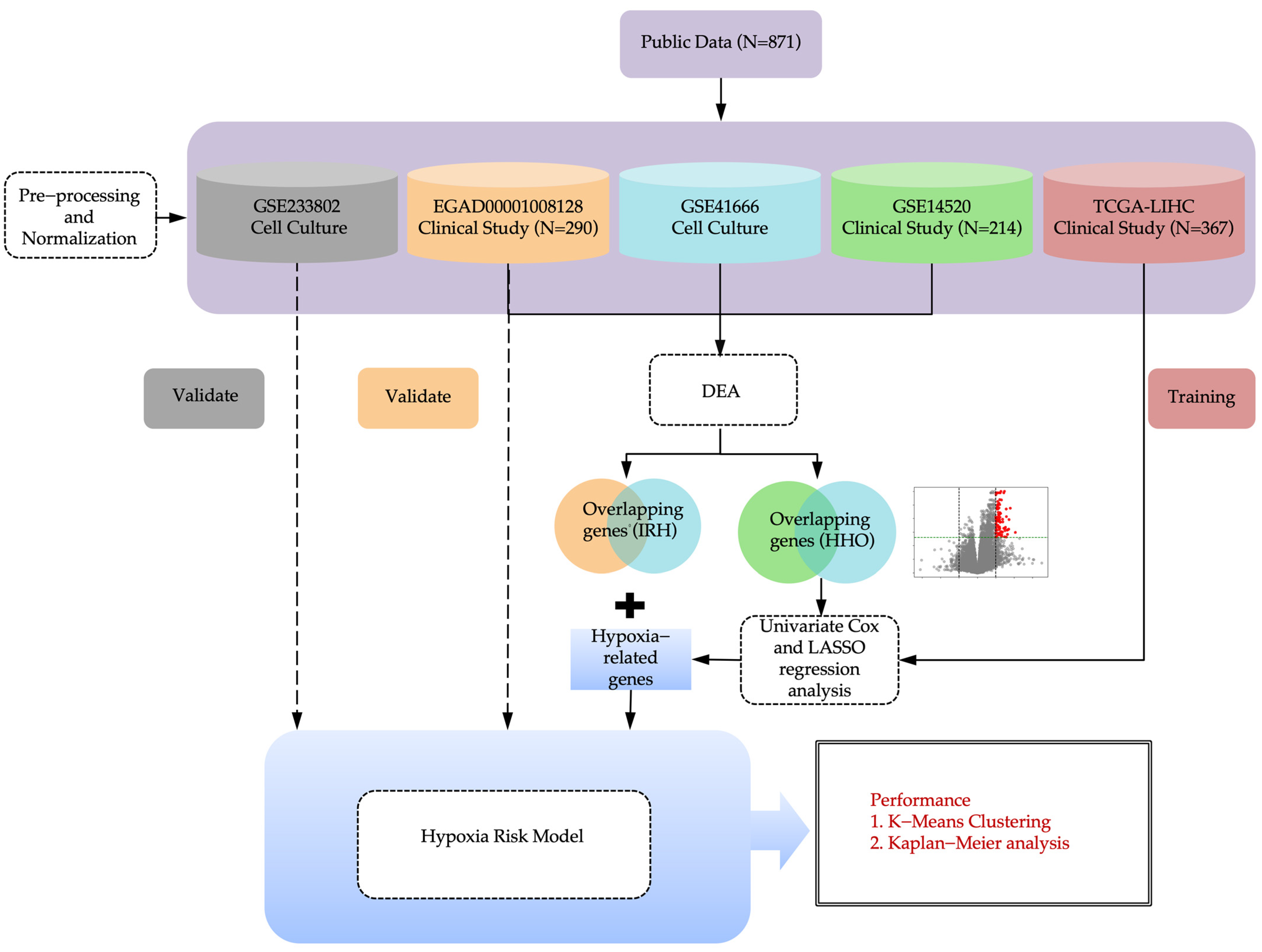
4.1. Study Design
4.2. Data Collection and Preprocessing
4.2.1. Clinical Datasets
4.2.2. Cell Culture Datasets
4.2.3. Pre-Processing of RNA Sequencing Raw Data
4.2.4. Normalizing the Data of Gene Expression
4.3. Selection of Genomic Features
4.3.1. Differential Expression Analysis
4.3.2. Enrichment Analysis
4.4. Hypoxia Risk Score Model Development
4.5. Model Validation
4.5.1. Calculation of Hypoxia Score
4.5.2. K-Means Clustering of Hypoxia Score
4.5.3. Survival Analysis Using Kaplan–Meier Curves
4.6. Cell Experiment
4.6.1. Cell Lines and Culture
4.6.2. Establishment of Co-Culture System
4.6.3. NOXA Gene Knockdown in Hypoxia-Resistant Cells
4.6.4. Western Blot Analysis
4.6.5. RT-qPCR Analysis
4.6.6. Apoptosis Assay
4.6.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calderon-Martinez, E.; Landazuri-Navas, S.; Vilchez, E.; Cantu-Hernandez, R.; Mosquera-Moscoso, J.; Encalada, S.; Al Lami, Z.; Zevallos-Delgado, C.; Cinicola, J. Prognostic Scores and Survival Rates by Etiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2023, 15, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leowattana, W.; Leowattana, T.; Leowattana, P. Systemic treatment for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 29, 1551–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, M.Y.; Chan, L.L.; Chan, S.L. Drug Treatment for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: First-Line and Beyond. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 5489–5507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Liu, D.; Li, L. PD-1/PD-L1 pathway: Current researches in cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 727–742. [Google Scholar]
- Emami Nejad, A.; Najafgholian, S.; Rostami, A.; Sistani, A.; Shojaeifar, S.; Esparvarinha, M.; Nedaeinia, R.; Haghjooy Javanmard, S.; Taherian, M.; Ahmadlou, M.; et al. The role of hypoxia in the tumor microenvironment and development of cancer stem cell: A novel approach to developing treatment. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciepla, J.; Smolarczyk, R. Tumor hypoxia unveiled: Insights into microenvironment, detection tools and emerging therapies. Clin. Exp. Med. 2024, 24, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, L.R.; Micha, D.; Brandenburg, M.; Simpson, K.L.; Morrow, C.J.; Denneny, O.; Hodgkinson, C.; Yunus, Z.; Dempsey, C.; Roberts, D.; et al. Hypoxic human cancer cells are sensitized to BH-3 mimetic-induced apoptosis via downregulation of the Bcl-2 protein Mcl-1. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 1075–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Ahn, H.J.; Ryu, J.H.; Suk, K.; Park, J.H. BH3-only protein Noxa is a mediator of hypoxic cell death induced by hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Chen, X.; Jiang, Y.; Chan, L.W.C. Kolmogorov–Arnold Network Model Integrated with Hypoxia Risk for Predicting PD-L1 Inhibitor Responses in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, B.; Li, L.; Wang, G.; Li, Y.; Fu, R.; Ming, Y.; Ni, R.; Wang, J.; Ye, G.; et al. The Immunostimulative Effect and Mechanisms of a Novel Mouse Anti-Human PD-1 Monoclonal Antibody on Jurkat Lymphocytic Cells Cocultured with Hepatoma Cells. Oncol. Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 12225–12241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, K.N.; Rao, S.; Roth, B.; Bryan, T.; Fernando, D.M.; Dayyani, F.; Imagawa, D.; Abi-Jaoudeh, N. Targeting Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1alpha for the Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Lou, T. Hypoxia inducible factors in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 46691–46703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, M.; Das, P.K. Hypoxia: Intriguing Feature in Cancer Cell Biology. ChemMedChem 2024, 19, e202300551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Han, F.; Du, Y.; Shi, H.; Zhou, W. Hypoxic microenvironment in cancer: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiacheng, D.; Jiayue, C.; Ying, G.; Shaohua, W.; Wenhui, L.; Xinyu, H. Research progress and challenges of the PD-1/PD-L1 axis in gliomas. Cell Biosci. 2024, 14, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandopadhyay, S.; Patranabis, S. Mechanisms of HIF-driven immunosuppression in tumour microenvironment. J. Egypt Natl. Cancer Inst. 2023, 35, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, S.N.; Chen, L.; Dewson, G.; Wei, A.; Naik, E.; Fletcher, J.I.; Adams, J.M.; Huang, D.C. Proapoptotic Bak is sequestered by Mcl-1 and Bcl-xL, but not Bcl-2, until displaced by BH3-only proteins. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 1294–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greaves, G.; Milani, M.; Butterworth, M.; Carter, R.J.; Byrne, D.P.; Eyers, P.A.; Luo, X.; Cohen, G.M.; Varadarajan, S. BH3-only proteins are dispensable for apoptosis induced by pharmacological inhibition of both MCL-1 and BCL-X(L). Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 1037–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juin, P.; Geneste, O.; Gautier, F.; Depil, S.; Campone, M. Decoding and unlocking the BCL-2 dependency of cancer cells. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doffo, J.; Bamopoulos, S.A.; Kose, H.; Orben, F.; Zang, C.; Pons, M.; den Dekker, A.T.; Brouwer, R.W.W.; Baluapuri, A.; Habringer, S.; et al. NOXA expression drives synthetic lethality to RUNX1 inhibition in pancreatic cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2105691119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Chen, D.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Tong, C.; Wei, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Han, W. Identification of NOXA as a pivotal regulator of resistance to CAR T-cell therapy in B-cell malignancies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumont, A.; Lohard, S.; Maillet, L.; Juin, P.P.; Barillé-Nion, S. Noxa the BCL-2 Family Member behind the Scenes in Cancer Treatment. J. Cell. Signal. 2020, 1, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, A.; Gautier, F.; Batard, Q.; Guette, C.; Guillonneau, F.; Campone, M.; Juin, P.; Barillé-Nion, S. NOXA/MCL-1 axis determines cell-death decision between apoptosis and pyroptosis and the inflammatory secretome of breast cancer cells treated with anti-mitotics. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Zheng, J.Y.; Ren, S.N.; Yin, W.; Xia, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.L. A comprehensive workflow for optimizing RNA-seq data analysis. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.X.; Abbas, A.R.; de Galarreta, M.R.; Guan, Y.; Lu, S.; Koeppen, H.; Zhang, W.; Hsu, C.H.; He, A.R.; Ryoo, B.Y.; et al. Molecular correlates of clinical response and resistance to atezolizumab in combination with bevacizumab in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1599–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Yang, S.; Tai, W.C.S.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Cho, W.C.S.; Chan, L.W.C.; Wong, S.C.C. Bioinformatics Identification of Regulatory Genes and Mechanism Related to Hypoxia-Induced PD-L1 Inhibitor Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Chan, L.W.C. Hypoxia-related genes and PD-L1 inhibitor resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. JCO Glob. Oncol. 2023, 9, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene | Forward Primer (5-3′) | Reverse Primer (5-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| NOXA | CAGAGCTGGAAGTCGAGTGTGC | TGCAGTCAGGTTCCTGAGCAGA |
| β-Actin | AGGATTCCTATGTGGGCGAC | ATAGCACAGCCTGGATAGCAA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, M.; Lan, T.; Chen, X.; Chen, R.; Ding, X.; Tai, W.C.-S.; Wong, S.C.-C.; Chan, L.W.-C. Functional Role of NOXA in Hypoxia-Mediated PD-L1 Inhibitor Response in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4766. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104766
Huang M, Lan T, Chen X, Chen R, Ding X, Tai WC-S, Wong SC-C, Chan LW-C. Functional Role of NOXA in Hypoxia-Mediated PD-L1 Inhibitor Response in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4766. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104766
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Mohan, Tian Lan, Xinyue Chen, Rong Chen, Xin Ding, William Chi-Shing Tai, Sze Chuen-Cesar Wong, and Lawrence Wing-Chi Chan. 2025. "Functional Role of NOXA in Hypoxia-Mediated PD-L1 Inhibitor Response in Hepatocellular Carcinoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4766. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104766
APA StyleHuang, M., Lan, T., Chen, X., Chen, R., Ding, X., Tai, W. C.-S., Wong, S. C.-C., & Chan, L. W.-C. (2025). Functional Role of NOXA in Hypoxia-Mediated PD-L1 Inhibitor Response in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4766. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104766







