Strategic Optimization of the Middle Domain IIIA in RBP-Albumin IIIA-IB Fusion Protein to Enhance Productivity and Thermostability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
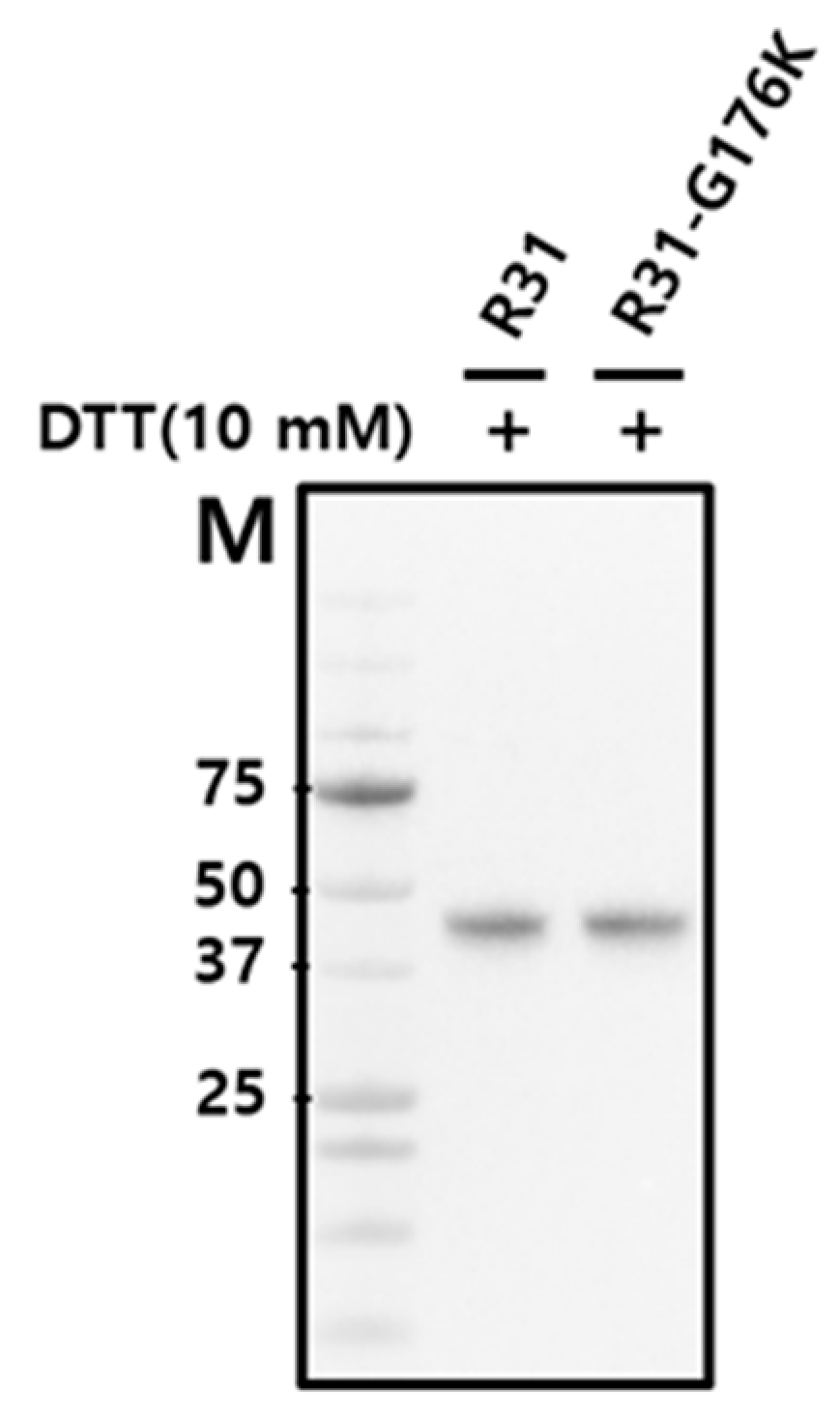
2.1. The Productivity of the Fusion Protein R31 Needs to Be Enhanced
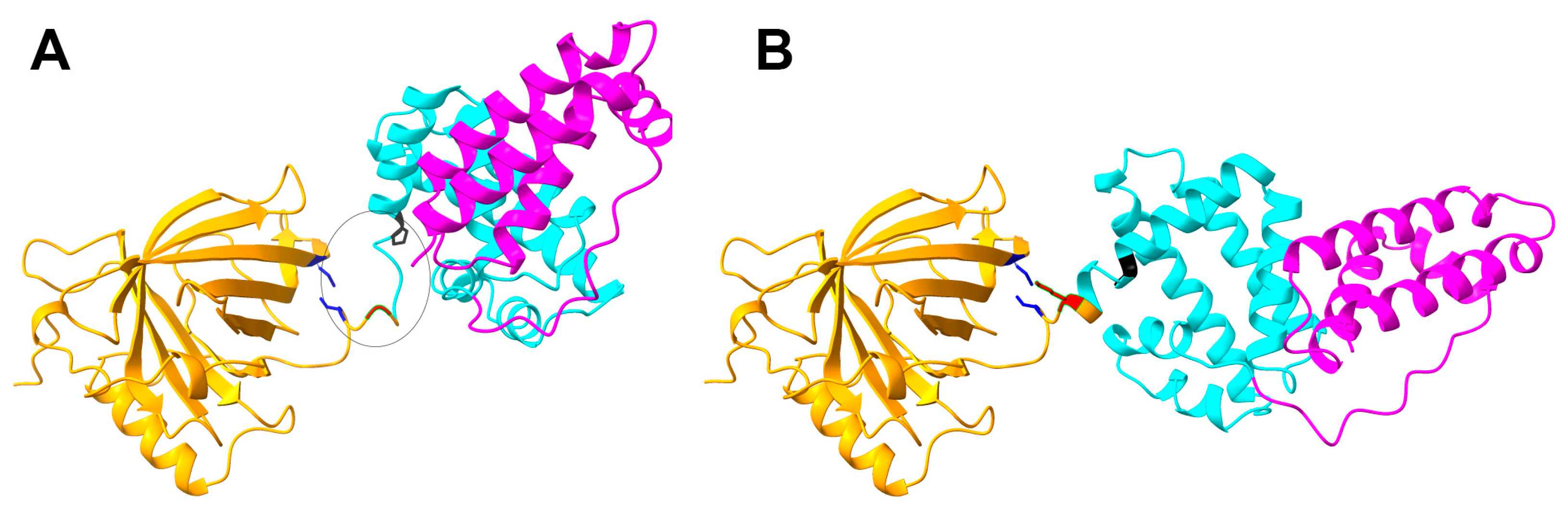
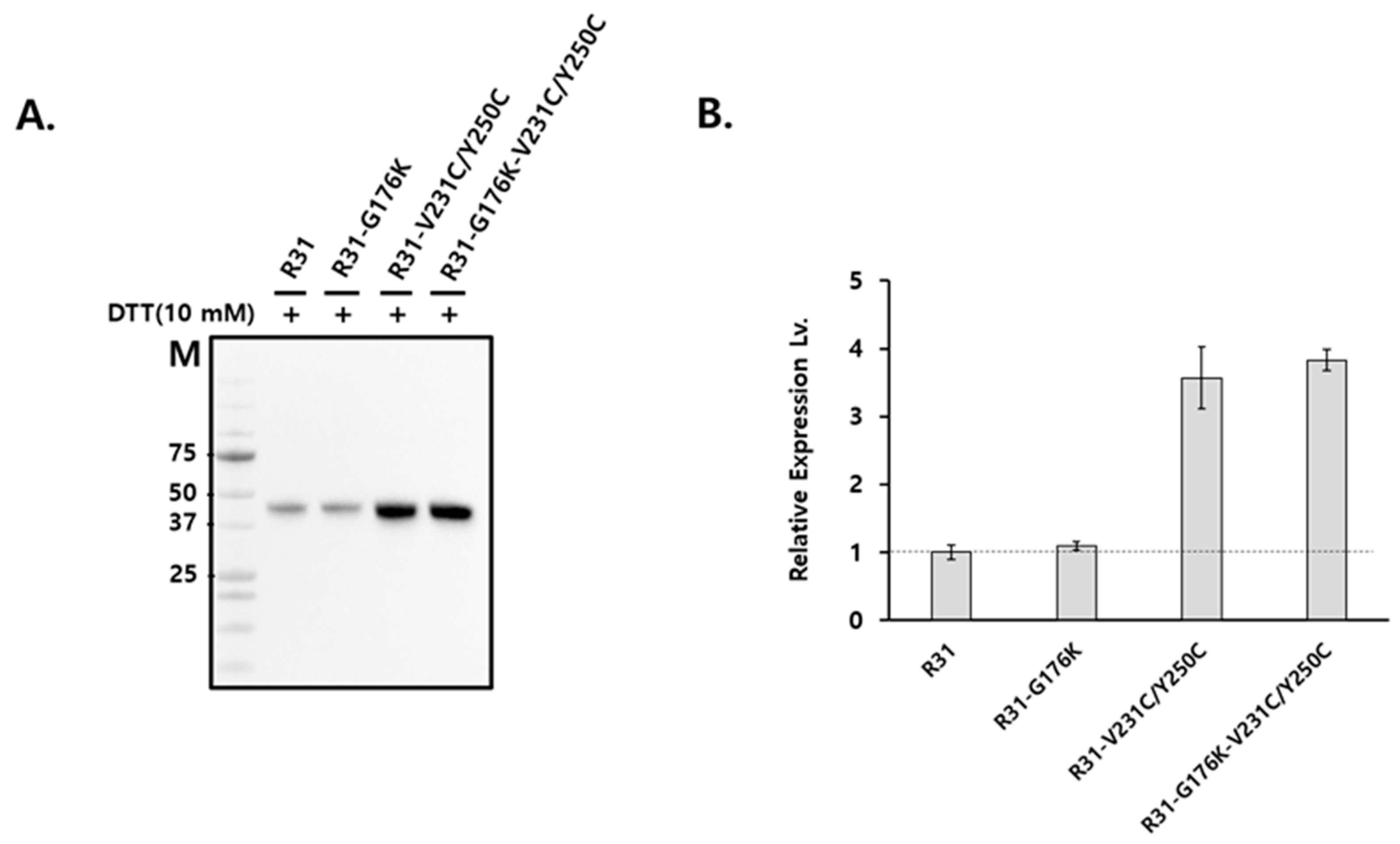
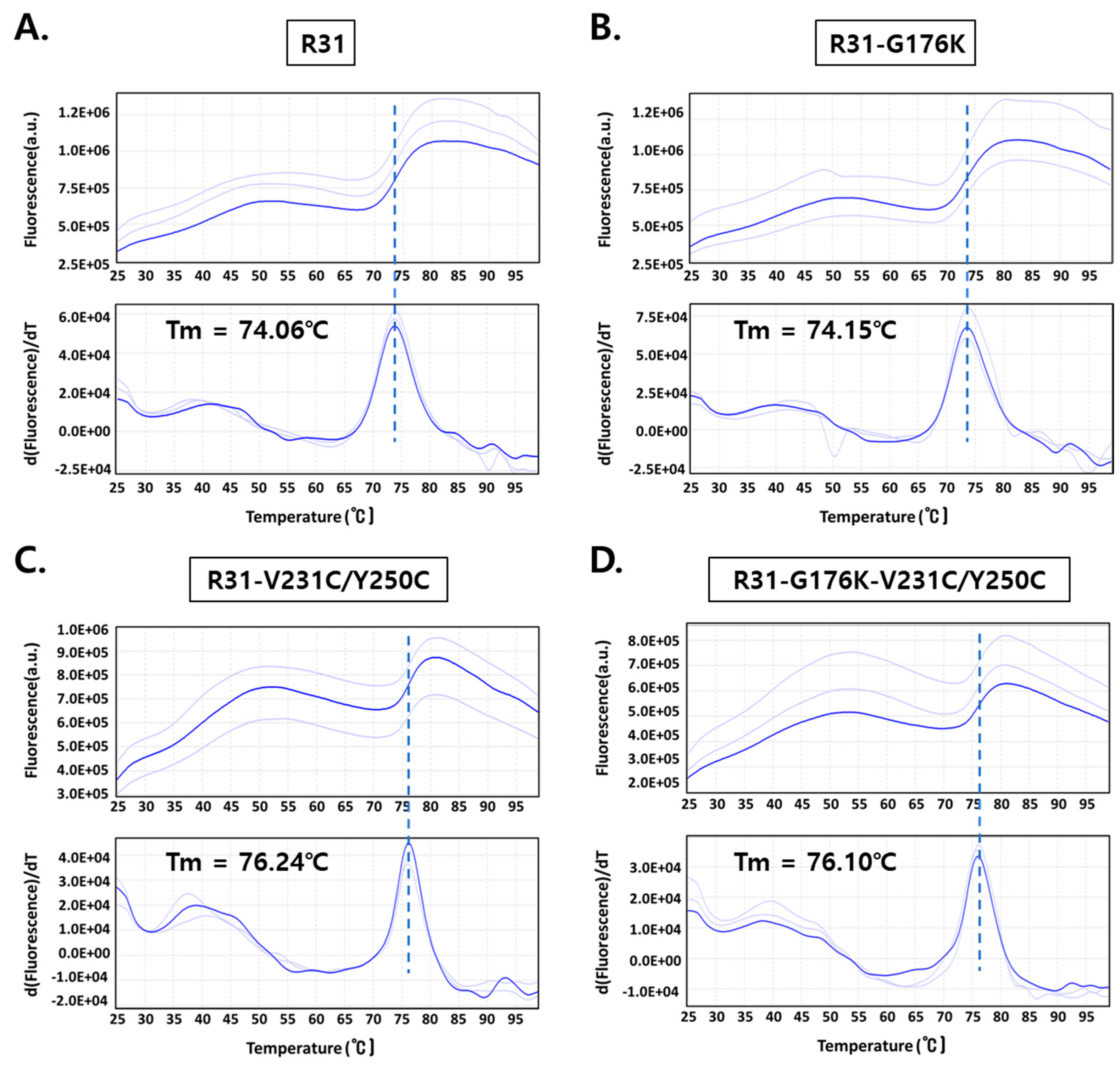
2.2. The Productivity of R31 Was Improved by Incorporating an Additional Disulfide Bond, V231C/Y250C
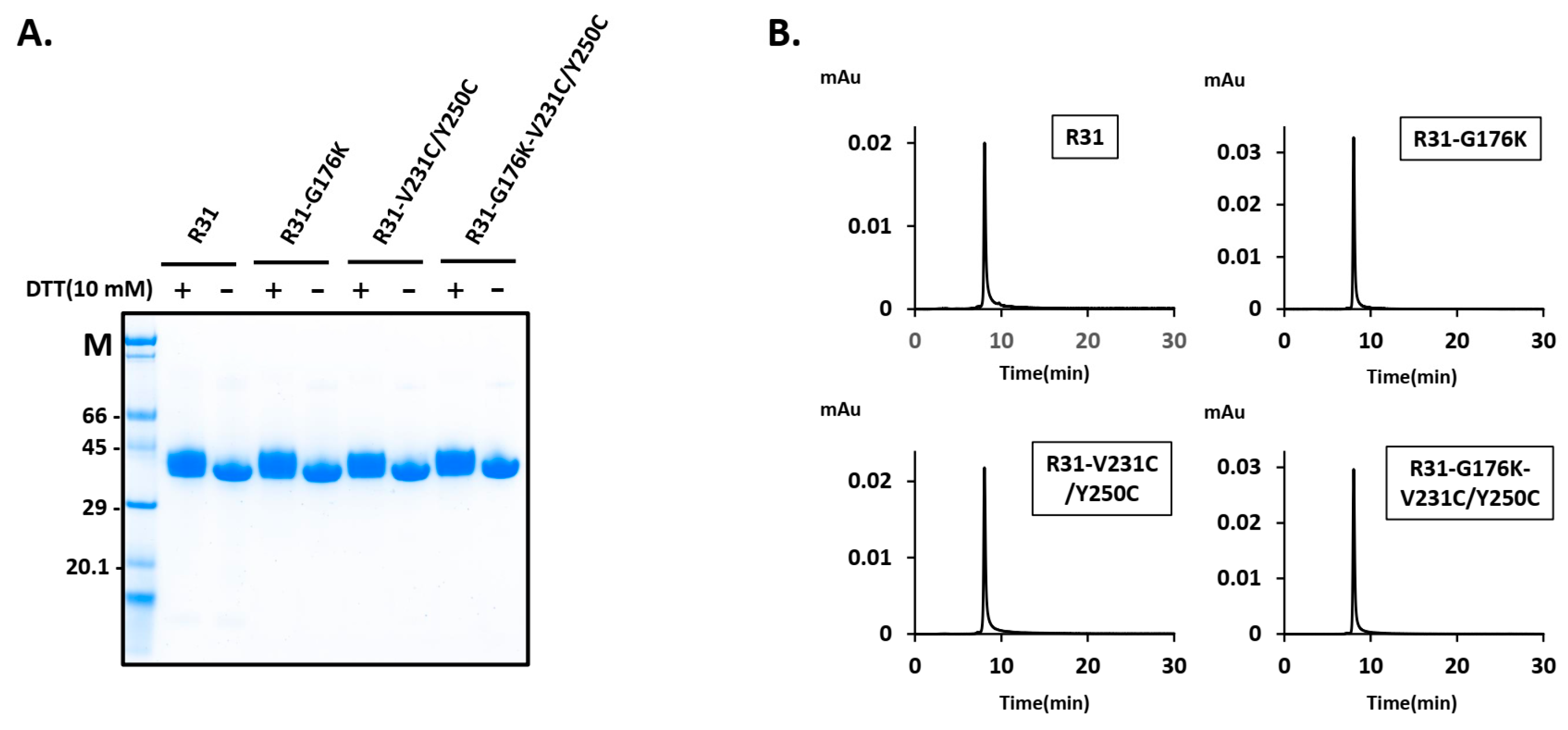
2.3. The Fusion Protein R31-G176K-V231C/Y250C Exhibited Improved Productivity and Thermal Stability
2.4. The Fusion Protein R31-G176K-V231C/Y250C Showed Increased Anti-Fibrotic Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Expression and Purification of Fusion Proteins
4.3. SDS-PAGE and Western Blot Analysis
4.4. Computational Analysis of Residue Interactions
4.5. Protein Thermal Shift (PTS) Assay
4.6. Isolation of Mouse Hepatic Stellate Cells (HSCs)
4.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, M.; Zhou, S.; Lu, Y.; Cui, H.; Racanelli, A.C.; Zhang, L.; Ye, T.; Ding, B.; et al. Targeting fibrosis, mechanisms and cilinical trials. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiskirchen, R.; Weiskirchen, S.; Tacke, F. Organ and tissue fibrosis: Molecular signals, cellular mechanisms and translational implications. Mol. Asp. Med. 2019, 65, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamm, D.R.; McCommis, K.S. Hepatic stellate cells in physiology and pathology. J. Physiol. 2022, 600, 1825–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchida, T.; Friedman, S.L. Mechanisms of hepatic stellate cell activation. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roehlen, N.; Crouchet, E.; Baumert, T.F. Liver Fibrosis: Mechanistic Concepts and Therapeutic Perspectives. Cells 2020, 9, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkan, M. The role of pancreatic stellate cells in pancreatic cancer. Pancreatol. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Pancreatol. 2013, 13, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.J.; Mandal, C.; Ghee, J.Y.; Yoo, J.A.; Lee, M.J.; Kang, Y.S.; Hyun, Y.Y.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, H.W.; Han, S.Y.; et al. Inhibition of Renal Stellate Cell Activation Reduces Renal Fibrosis. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry, S.; Mandelkow, H.; Brick, P.; Franks, N. Crystal structure of human serum albumin complexed with fatty acid reveals an asymmetric distribution of binding sites. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1998, 5, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Yoo, W.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.; Lee, H.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, D.U.; Oh, J. Formation of vitamin A lipid droplets in pancreatic stellate cells requires albumin. Gut 2009, 58, 1382–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Kim, J.; Choi, S.Y.; Lee, B.; Lee, J.E.; Park, H.; Moon, J.W.; Park, S.H.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, H.S.; et al. Albumin inhibits the nuclear translocation of Smad3 via interleukin-1beta signaling in hepatic stellate cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Jeong, H.; Park, S.; Yoo, W.; Choi, S.; Choi, K.; Lee, M.G.; Lee, M.; Cha, D.; Kim, Y.S.; et al. Fusion protein of retinol-binding protein and albumin domain III reduces liver fibrosis. EMBO Mol. Med. 2015, 7, 819–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, R.; Yu, J.; Honda, J.; Hu, J.; Whitelegge, J.; Ping, P.; Wiita, P.; Bok, D.; Sun, H. A membrane receptor for retinol binding protein mediates cellular uptake of vitamin A. Science 2007, 315, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi, S.B.; Samanta, D. Engineering protein-based therapeutics through structural and chemical design. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zaro, J.L.; Shen, W.C. Fusion protein linkers: Property, design and functionality. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1357–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellas, N.; Liu, J.; Botham, R.C.; Huisman, G.W. Adapting protein sequences for optimized therapeutic efficacy. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2021, 64, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Kwon, S.; Choi, S.Y.; Kim, B.; Oh, J. Optimizing the Amino Acid Sequence Enhances the Productivity and Bioefficacy of the RBP-Albumin Fusion Protein. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, S.L. Hepatic stellate cells: Protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 125–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, M.C.; Owen, S.C. Therapeutic Fusion Proteins. AAPS J. 2023, 26, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, V.; McShan, A.C. The power and pitfalls of AlphaFold2 for structure prediction beyond rigid globular proteins. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2024, 20, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, H.; Kim, P. Artificial intelligence in fusion protein three-dimensional structure prediction: Review and perspective. Clin. Transl. Med. 2024, 14, e1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, R.; Ueda, H.; Kitayama, A.; Kamiya, N.; Nagamune, T. Design of the linkers which effectively separate domains of a bifunctional fusion protein. Protein Eng. 2001, 14, 529–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, R.A.; Heringa, J. An analysis of protein domain linkers: Their classification and role in protein folding. Protein Eng. 2002, 15, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.K.; Menon, D.V.; Patel, D.H.; Dave, G. Linkers: A synergistic way for the synthesis of chimeric proteins. Protein Expr. Purif. 2022, 191, 106012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassa, A.; Dey, A.K.; Sarkar, P.; Labranche, C.; Go, E.P.; Clark, D.F.; Sun, Y.; Nandi, A.; Hartog, K.; Desaire, H.; et al. Stabilizing exposure of conserved epitopes by structure guided insertion of disulfide bond in HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Ahmed, S.; Cheng, G.; Chen, T.; Wang, Y.; Peng, D.; Yuan, Z. Analysis of the stability and affinity of BlaR-CTD protein to β-lactam antibiotics based on docking and mutagenesis studies. J. Biol. Eng. 2019, 13, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Chuenchor, W.; Jiang, J.; Cheng, J.; Li, Y.; Fang, K.; Huang, M.; Smith, P.; Xiao, T.S. Design of an expression system to enhance MBP-mediated crystallization. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.H.; You, C.Z.; Jiang, H.L.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, H.E.; Cheng, X. AlphaFold2 versus experimental structures: Evaluation on G protein-coupled receptors. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2023, 44, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramoff, M.D.; Magalhaes, P.J.; Ram, S.J. Imaging processing with ImageJ. Biophotonics Int. 2004, 11, 36–42. [Google Scholar]
- Schrödinger, LLC. Schrödinger Release 2024-2: Prime; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Mederacke, I.; Dapito, D.H.; Affo, S.; Uchinami, H.; Schwabe, R.F. High-yield and high-purity isolation of hepatic stellate cells from normal and fibrotic mouse livers. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Fusion Proteins | Productivity 1 (mg L−1) |
|---|---|
| R31 | 36.52 (±23.64) |
| R31-G176K | 31.22 (±24.35) |
| R31-V231/Y250C | 115.80 (±8.20) |
| R31-G176K-V231/Y250C | 135.92 (±19.54) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sohn, M.; Kim, S.; Jeong, H.J.; Ko, I.Y.; Moon, J.W.; Lee, D.; Oh, J. Strategic Optimization of the Middle Domain IIIA in RBP-Albumin IIIA-IB Fusion Protein to Enhance Productivity and Thermostability. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010137
Sohn M, Kim S, Jeong HJ, Ko IY, Moon JW, Lee D, Oh J. Strategic Optimization of the Middle Domain IIIA in RBP-Albumin IIIA-IB Fusion Protein to Enhance Productivity and Thermostability. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(1):137. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010137
Chicago/Turabian StyleSohn, Myungho, Sanggil Kim, Hyeon Ju Jeong, In Young Ko, Ji Wook Moon, Dowon Lee, and Junseo Oh. 2025. "Strategic Optimization of the Middle Domain IIIA in RBP-Albumin IIIA-IB Fusion Protein to Enhance Productivity and Thermostability" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 1: 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010137
APA StyleSohn, M., Kim, S., Jeong, H. J., Ko, I. Y., Moon, J. W., Lee, D., & Oh, J. (2025). Strategic Optimization of the Middle Domain IIIA in RBP-Albumin IIIA-IB Fusion Protein to Enhance Productivity and Thermostability. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(1), 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010137






