DC-SIGN of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) Mediates Immune Functions against Aeromonas hydrophila through Collaboration with the TLR Signaling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
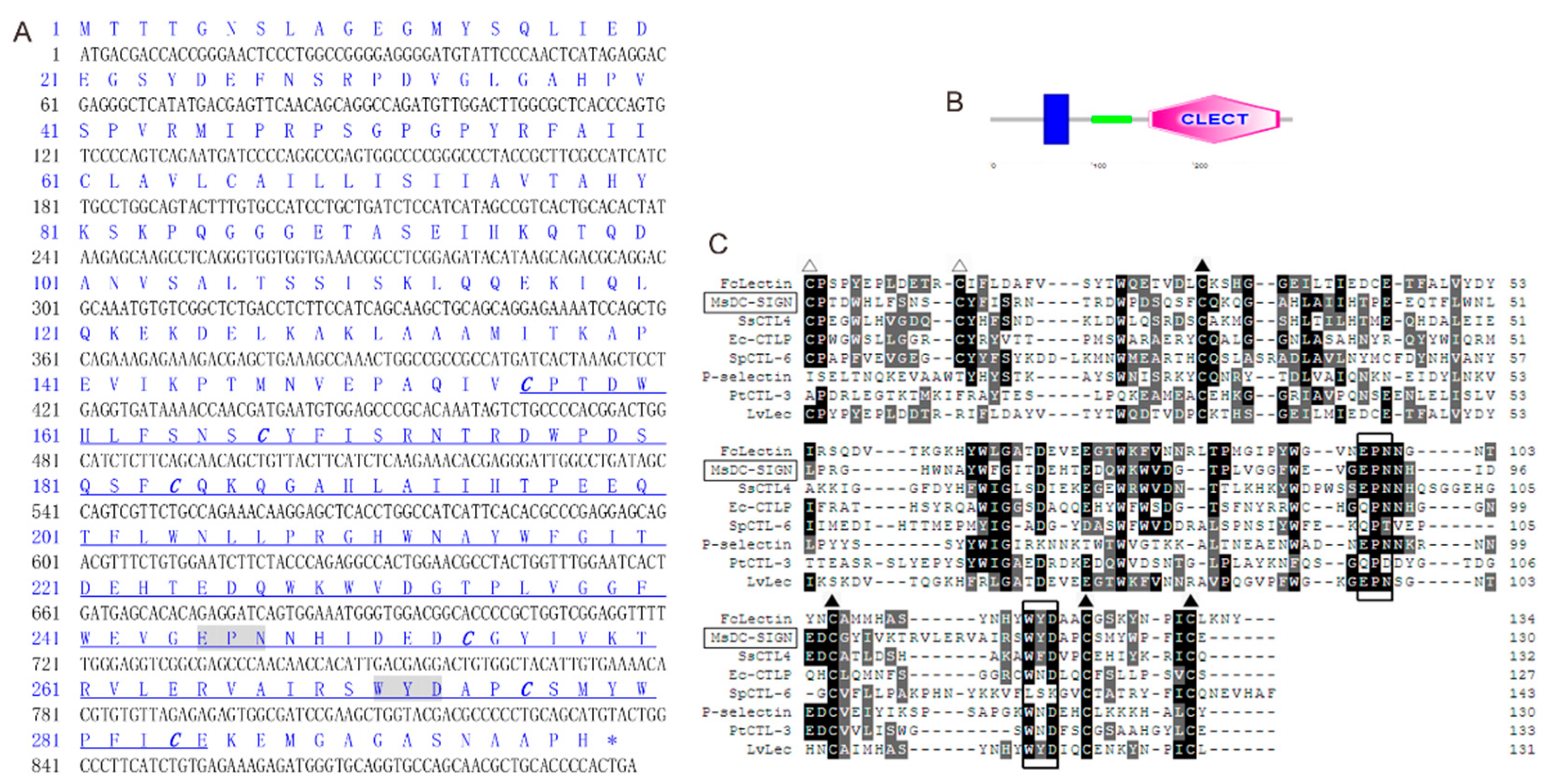
2.1. Sequence Characters and Multiple Alignments of MsDC-SIGN
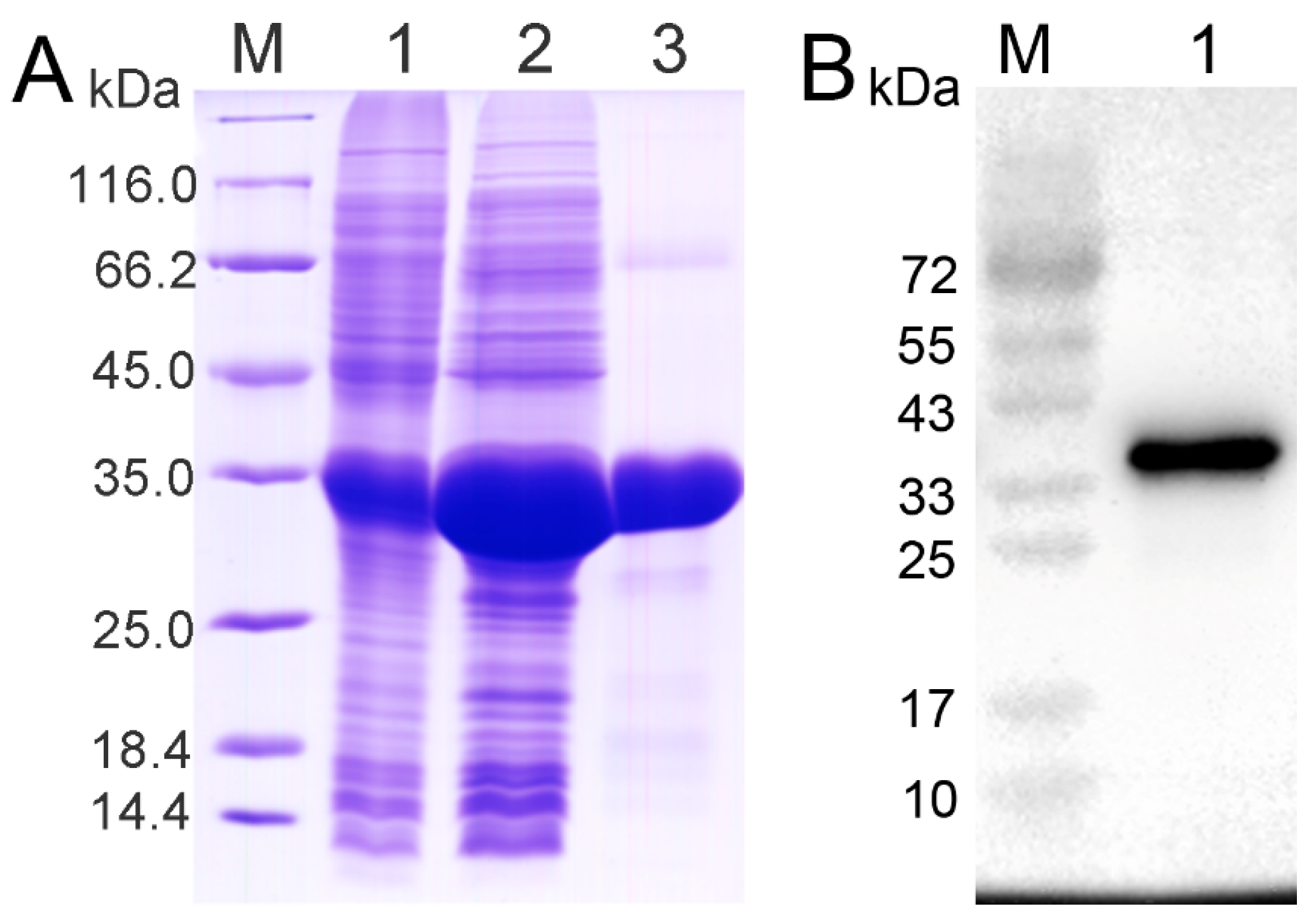
2.2. Recombinant Protein of CRD
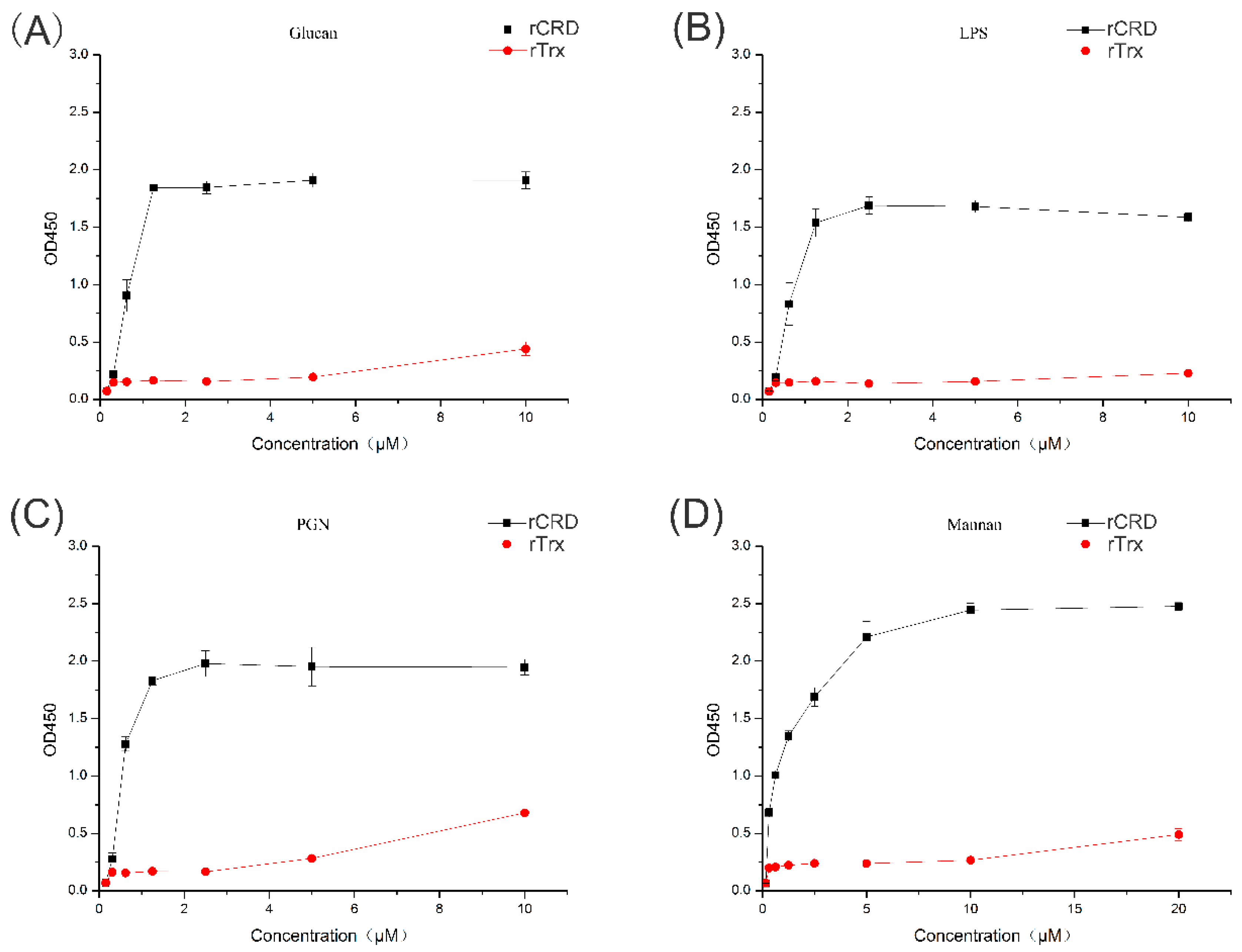
2.3. PAMP Binding Activity of MsDC-SIGN
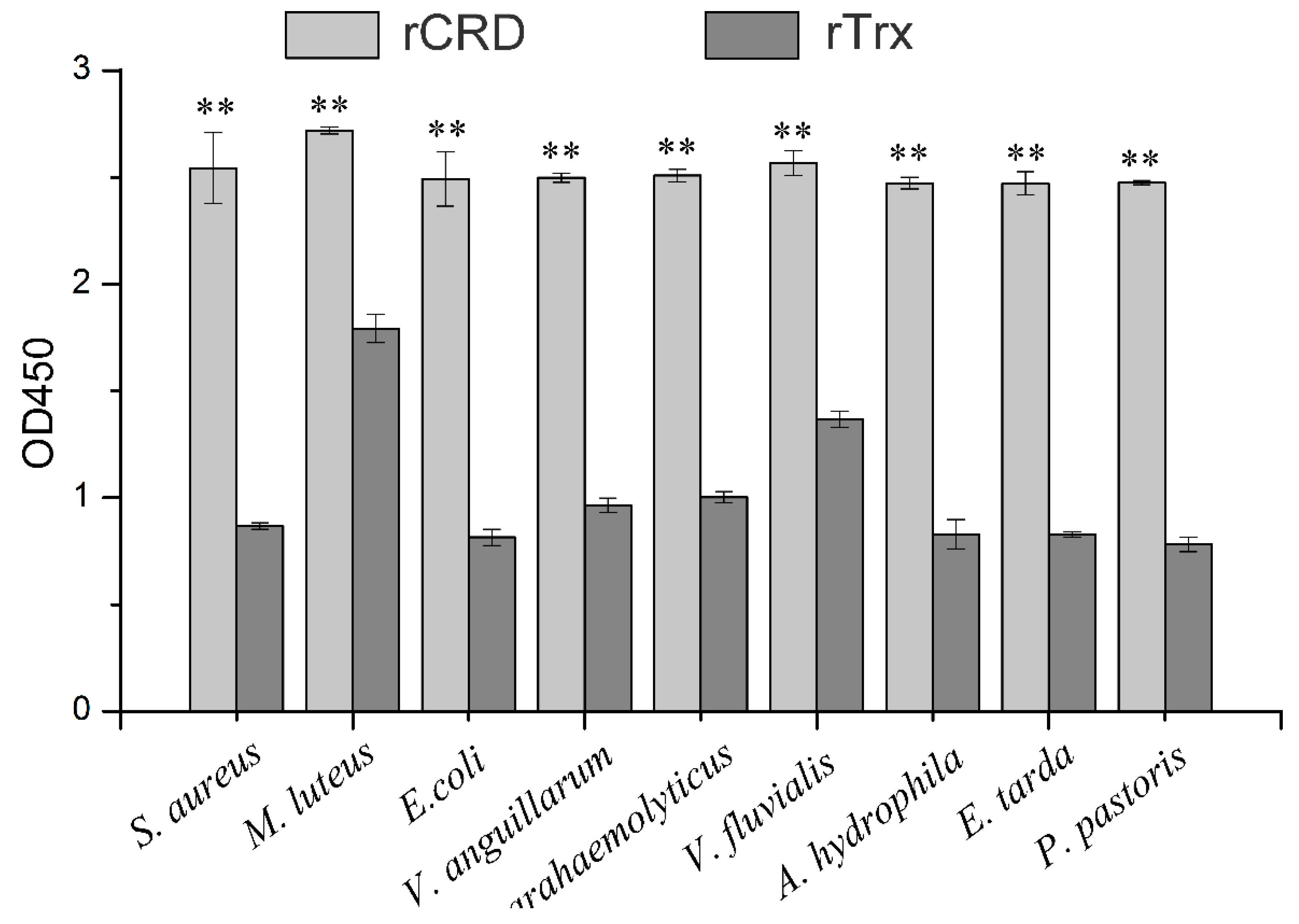
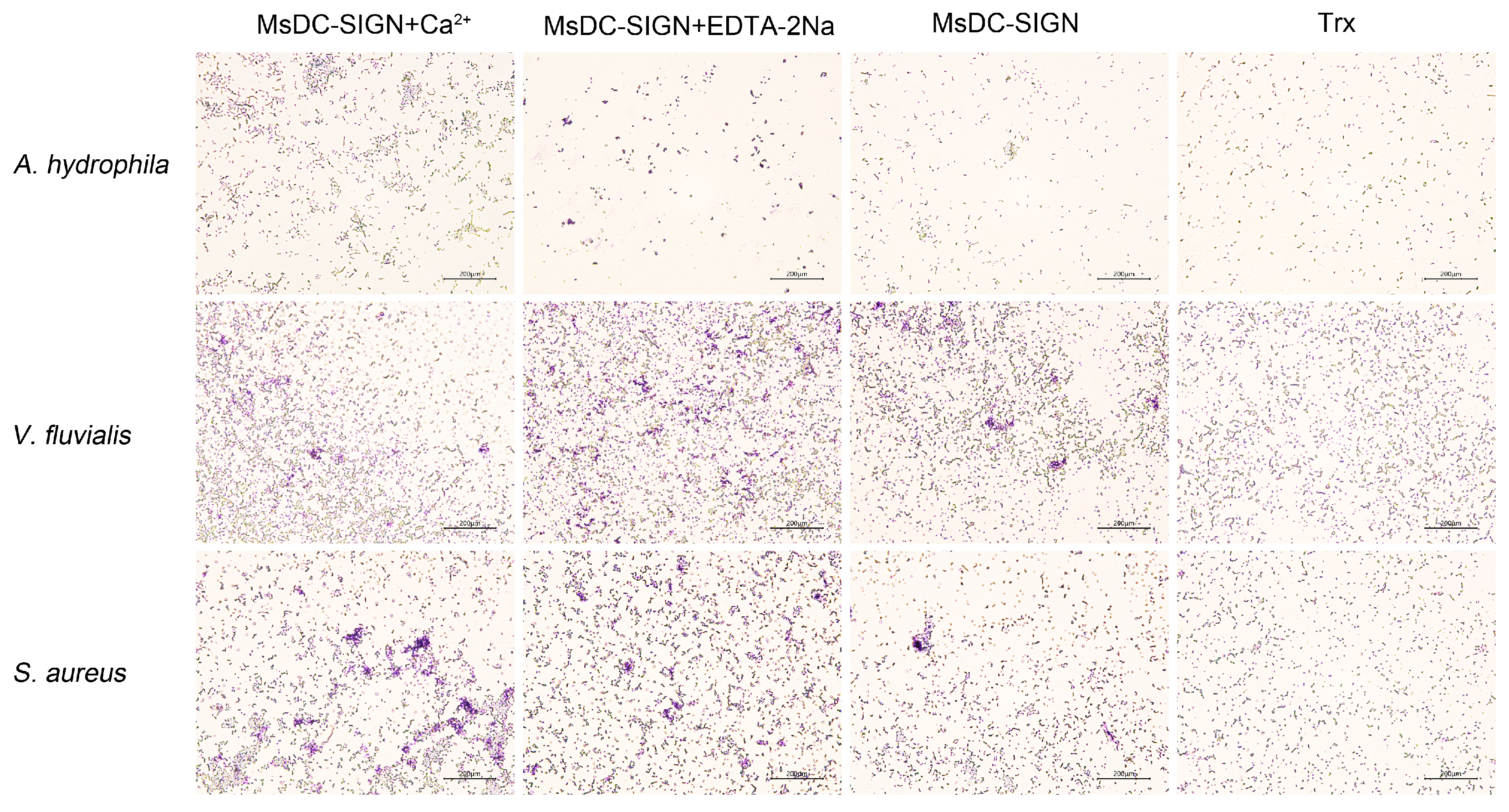
2.4. Microbe-Binding Activity of rCRD
2.5. Microbial Binding Activity of rCRD
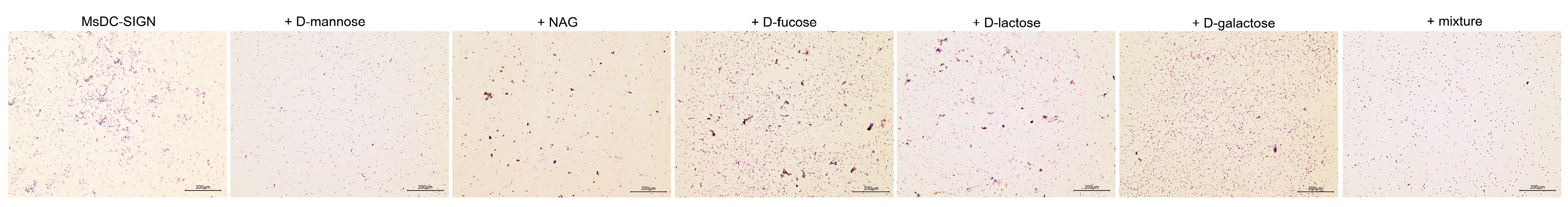
2.6. Carbohydrate-Binding Specificity of rCRD
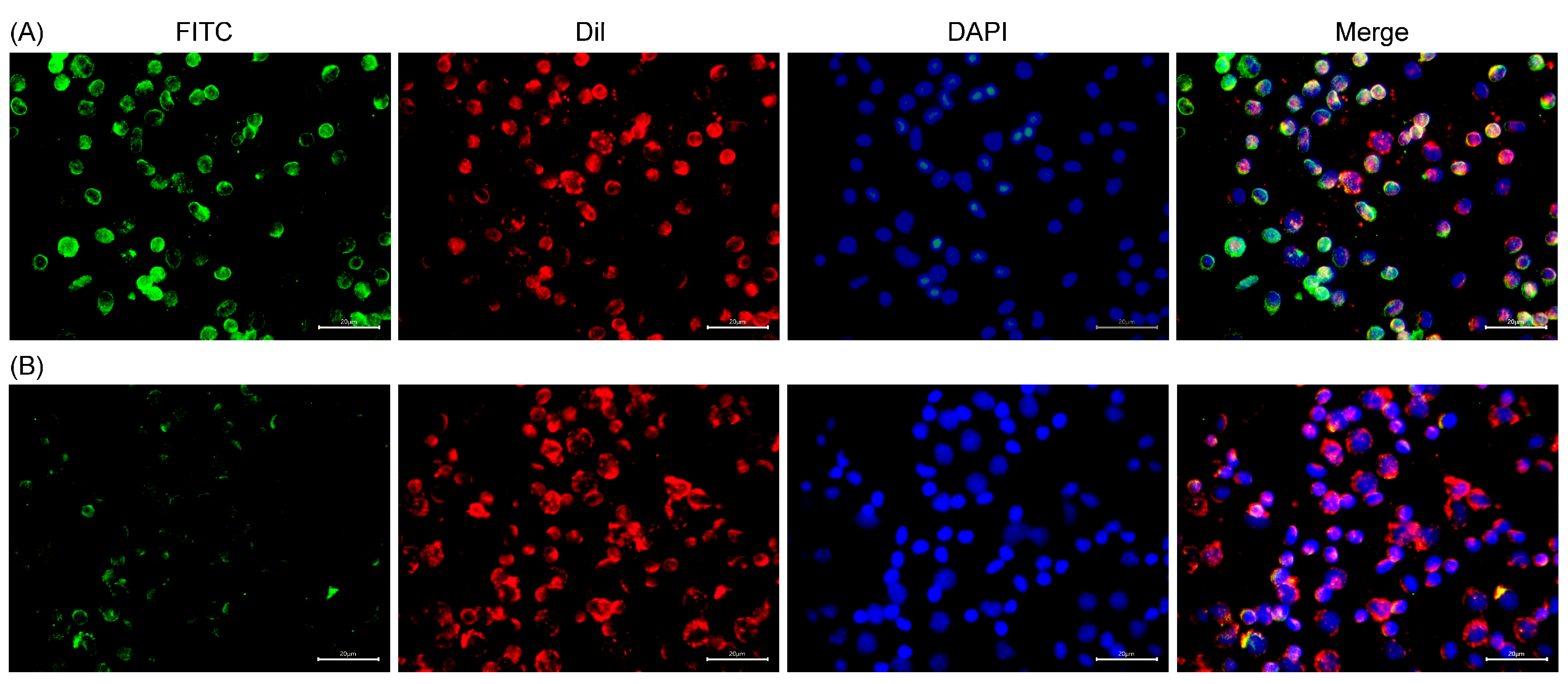
2.7. Subcellular Localization of MsDC-SIGN
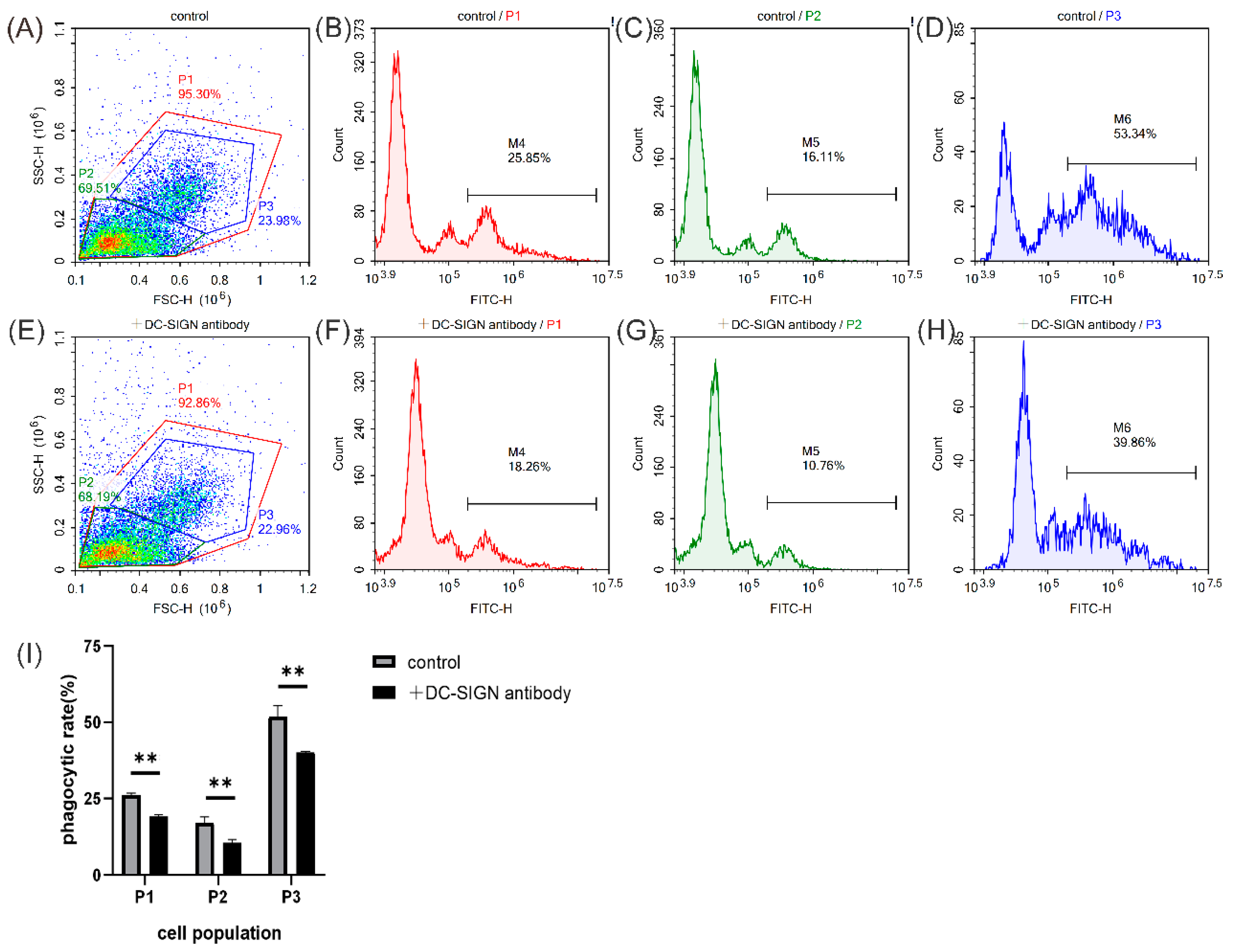
2.8. Phagocytosis Enhancement Activity of MsDC-SIGN
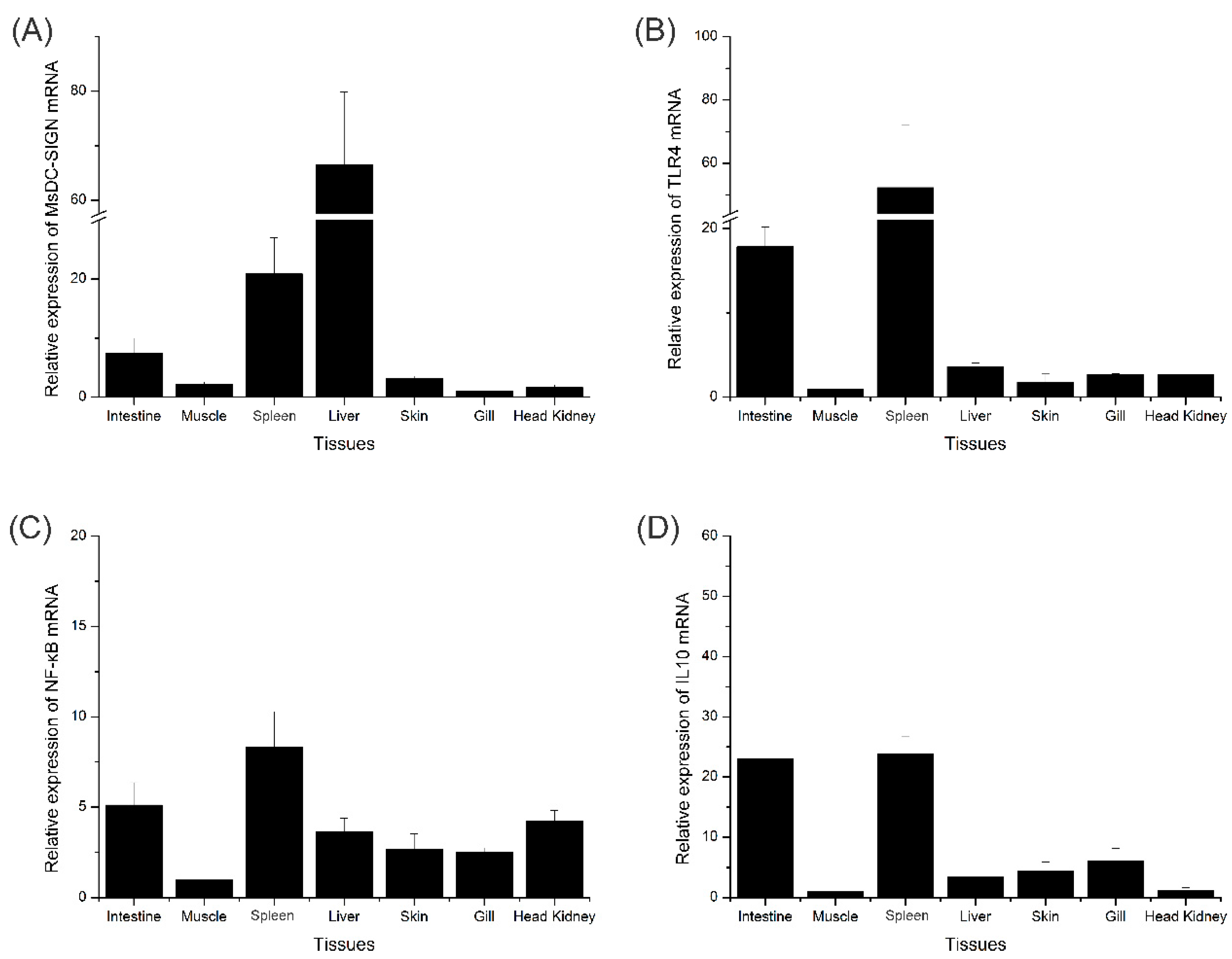
2.9. Tissue Distribution of Key Genes in MsDC-SIGN and TLR Signaling Pathways
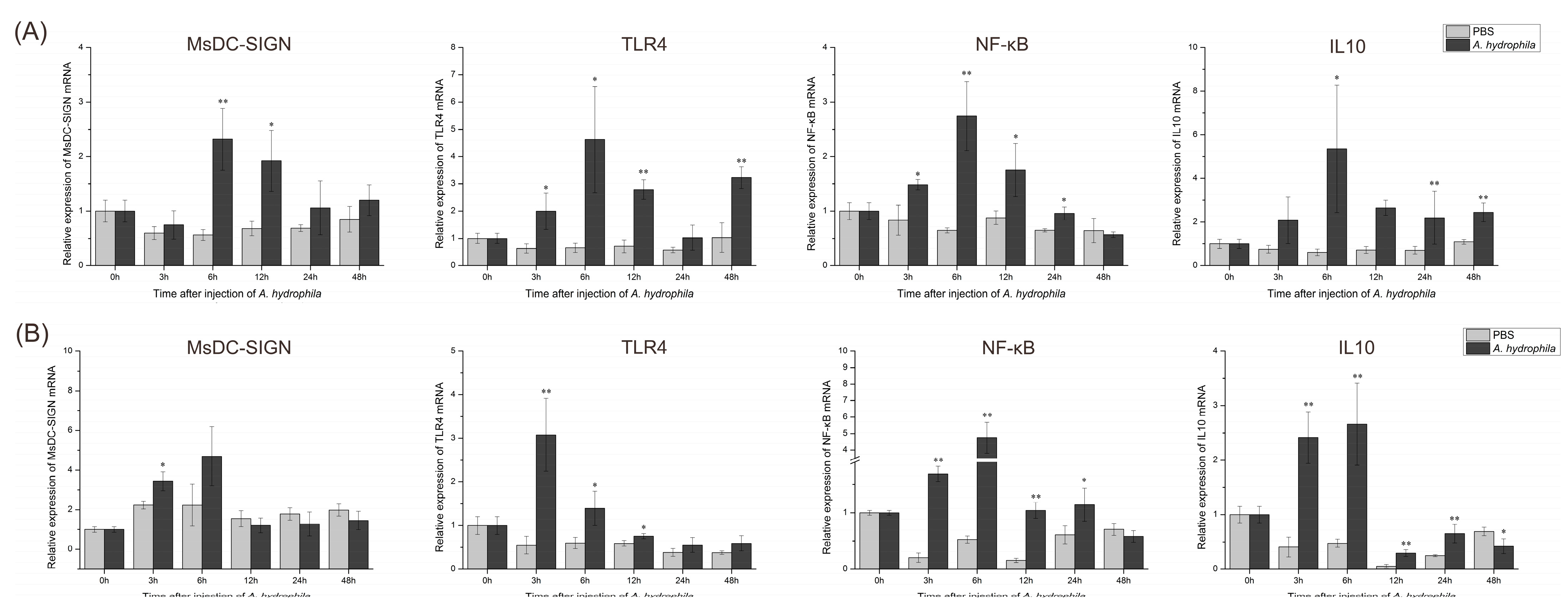
2.10. Expression Patterns of Key Genes in M. salmoides’ C-Type Lectin MsDC-SIGN and TLR Signaling Pathways after Bacterial Stimulation
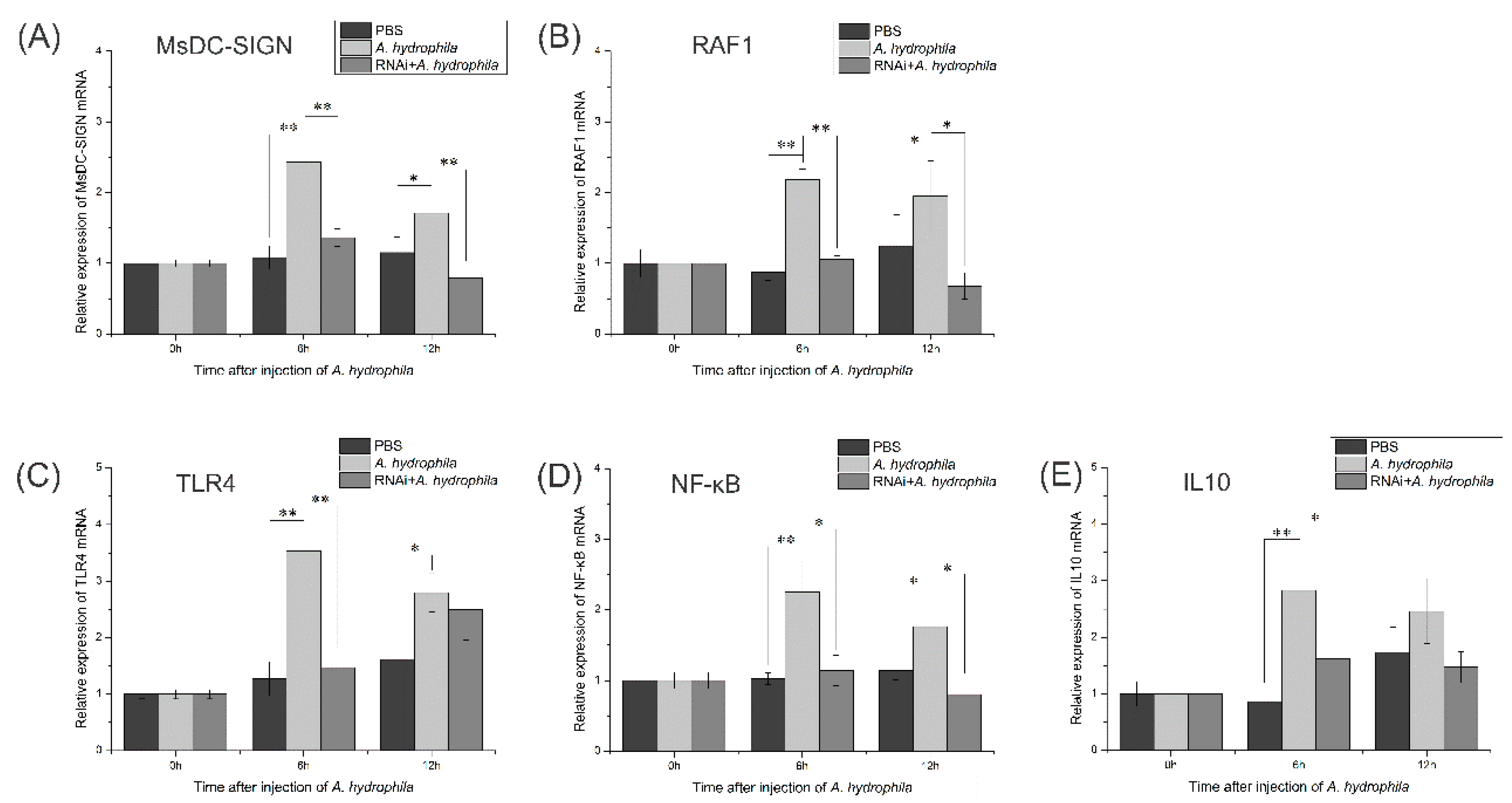
2.11. Expression Patterns of Key Genes in M. salmoides’ TLR Signaling Pathway after RNA Interference with MsDC-SIGN Gene
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. M. salmoides and Microbes
3.2. Cloning and Sequence Analysis of Full-Length cDNA
3.3. Expression and Purification of rCRD
3.4. The PAMP Binding Assay
3.5. Microbe Binding Assay
3.6. Microbial Agglutination and Ca2+-Dependent Assay
3.7. Carbohydrate-Binding Specificity Assay
3.8. Preparation and Western Blot Identification of rCRD Polyclonal Antibody
3.9. Immunofluorescence Analysis of the Subcellular Localization of MsDC-SIGN
3.10. Phagocytosis Assay of Leukocytes
3.11. RNA Isolation and cDNA Synthesis
3.12. Tissue Distribution of Key Genes in MsDC-SIGN and TLR Signaling Pathways
3.13. Expression Patterns of Key Genes in M. salmoides’ C-Type Lectin MsDC-SIGN and TLR Signaling Pathway after Bacterial Stimulation
3.14. Expression Patterns of Key Genes in M. salmoides’ TLR Signaling Pathway after RNA Interference with MsDC-SIGN Gene
3.15. Data Statistics and Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Drickamer, K. Evolution of Ca2+-dependent animal lectins. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 1993, 45, 207–232. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Drickamer, K. C-type lectin-like domains. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1999, 9, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soilleux, E.J.; Morris, L.S.; Leslie, G.; Chehimi, J.; Luo, Q.; Levroney, E.; Trowsdale, J.; Montaner, L.J.; Doms, R.W.; Weissman, D.; et al. Constitutive and induced expression of DC-SIGN on dendritic cell and macrophage subpopulations in situ and in vitro. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2002, 71, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svajger, U.; Anderluh, M.; Jeras, M.; Obermajer, N. C-type lectin DC-SIGN: An adhesion, signalling and antigen-uptake molecule that guides dendritic cells in immunity. Cell. Signal. 2010, 22, 1397–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Navarro, M.; Rojo, J. Targeting DC-SIGN with carbohydrate multivalent systems. Drug News Perspect. 2010, 23, 557–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, A.-F.; Xiang, L.-X.; Wang, Q.-L.; Dong, W.-R.; Gong, Y.-F.; Shao, J.-Z. The DC-SIGN of Zebrafish: Insights into the Existence of a CD209 Homologue in a Lower Vertebrate and Its Involvement in Adaptive Immunity. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 7398–7410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojeda, N.; Salazar, C.; Cardenas, C.; Marshall, S.H. Expression of DC-SIGN-like C-Type Lectin Receptors in Salmo salar. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2020, 113, 103806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Wang, G.-H.; Su, Y.-L.; Zhang, M.; Hu, Y.-H. Black rockfish C-type lectin, SsCTL4: A pattern recognition receptor that promotes bactericidal activity and virus escape from host immune defense. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 79, 340–350. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, N.; Regar, H.; Verma, V.K.; Prusty, D.; Mishra, A.; Prajapati, V.K. Receptor-ligand based molecular interaction to discover adjuvant for immune cell TLRs to develop next-generation vaccine. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 152, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKiel, L.A.; Woodhouse, K.A.; Fitzpatrick, L.E. A macrophage reporter cell assay to examine Toll-like receptor-mediated nf-kb/ap-1 signaling on adsorbed protein layers on polymeric surfaces. Jove-J. Vis. Exp. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boltana, S.; Roher, N.; Goetz, F.W.; MacKenzie, S.A. PAMPs, PRRs and the genomics of gram negative bacterial recognition in fish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, D.; Li, F.; Wang, M.; Huan, M.; Zhang, H.; Song, L. A novel C-type lectin from crab Eriocheir sinensis functions as pattern recognition receptor enhancing cellular encapsulation. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 34, 832–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Ye, C.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, Y.; Chen, W.; Pan, J. Evaluation of the β-barrel outer membrane protein VP1243 as a candidate antigen for a cross-protective vaccine against Vibrio infections. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 147, 104419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, T.; Wang, X.; Ren, X.; Ye, T.; Li, G. Oncolytic vaccinia virus expressing aphrocallistes vastus lectin as a cancer therapeutic agent. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.C.; Gao, Y.J.; Cui, L.Z.; Wu, L.Q.; Yang, X.Y.; Chen, J. Anguilla japonica lectin 1 delivery through adenovirus vector induces apoptotic cancer cell death through interaction with PRMT5. J. Gene Med. 2016, 18, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Feng, C.; Zhou, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, J. Impacts of Ser/Thr protein kinase stk1 on the proteome, twitching motility, and competitive advantage in pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 738690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Ye, T.; Jin, M.; Wang, W.; Hui, K.M.; Ren, Q. Three members of Ras GTPase superfamily are response to white spot syndrome virus challenge in Marsupenaeus japonicus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 55, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCTMethod. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambi, A.; Koopman, M.; Figdor, C.G. How C-type lectins detect pathogens. Cell. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, W.I.; Taylor, M.E.; Drickamer, K. The C-type lectin superfamily in the immune system. Immunol. Rev. 1998, 163, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, K.; Weiss, I.M.; Andre, S.; Gabius, H.J.; Fritz, M. The amino-acid sequence of the abalone (Haliotis laevigata) nacre protein perlucin. Detection of a functional C-type lectin domain with galactose/mannose specificity. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 5257–5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appelmelk, B.J.; van Die, I.; van Vliet, S.J.; Vandenbroucke-Grauls, C.M.J.E.; Geijtenbeek, T.B.H.; van Kooyk, Y. Cutting edge: Carbohydrate profiling identifies new pathogens that interact with dendritic cell-specific ICAM-3-grabbing nonintegrin on dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 1635–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iobst, S.T.; Wormald, M.R.; Weis, W.I.; Dwek, R.A.; Drickamer, K. Binding of sugar ligands to Ca2+-dependent animal lectins. I. Analysis of mannose binding by site-directed mutagenesis and NMR. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 15505–15511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geijtenbeek, T.B.; Torensma, R.; van Vliet, S.J.; van Duijnhoven, G.C.; Adema, G.J.; van Kooyk, Y.; Figdor, C.G. Identification of DC-SIGN, a novel dendritic cell-specific ICAM-3 receptor that supports primary immune responses. Cell 2000, 100, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Kong, X.; Zhao, X.; Pei, C.; Li, L. A C-type lectin, Nattectin-like protein (CaNTC) in Qihe crucian carp Carassius auratus: Binding ability with LPS, PGN and various bacteria, and agglutinating activity against bacteria. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 67, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turville, S.; Wilkinson, J.; Cameron, P.; Dable, J.; Cunningham, A.L. The role of dendritic cell C-type lectin receptors in HIV pathogenesis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2003, 74, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Huang, M.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Qiu, L.; Song, L. CfLec-3 from scallop: An entrance to non-self recognition mechanism of invertebrate C-type lectin. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Skurnik, M.; Zhang, S.-S.; Schwartz, O.; Kalyanasundaram, R.; Bulgheresi, S.; He, J.J.; Klena, J.D.; Hinnebusch, B.J.; Chen, T. Human dendritic cell-specific intercellular adhesion molecule-grabbing nonintegrin (CD209) is a receptor for Yersinia pestis that promotes phagocytosis by dendritic cells. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 2070–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Sun, L. Tongue Sole CD209: A pattern-recognition receptor that binds a broad range of microbes and promotes phagocytosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whyte, S.K. The innate immune response of finfish—A review of current knowledge. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2007, 23, 1127–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, A.; Amemiya, C.T. Phylogeny of lower vertebrates and their immunological structures. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2000, 248, 67–107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zapata, A.; Diez, B.; Cejalvo, T.; Frias, C.G.-D.; Cortes, A. Ontogeny of the immune system of fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2006, 20, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, B. The extrathymic T-cell differentiation in the murine gut. Immunol. Rev. 2007, 215, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medzhitov, R.; Janeway, C.A., Jr. Innate immunity: The virtues of a nonclonal system of recognition. Cell 1997, 91, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.P.; Chen, K.; Xi, B.W.; Xie, J.; Bing, X.W. Protective effects of paeonol against lipopolysaccharide-induced liver oxidative stress and inflammation in gibel carp (Carassius auratus gibelio). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C-Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 257, 109339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gringhuis, S.I.; den Dunnen, J.; Litjens, M.; Hof, B.V.H.; van Kooyk, Y.; Geijtenbeek, T.B.H. C-type lectin DC-SIGN modulates toll-like receptor signaling via Raf-1 kinase-dependent acetylation of transcription factor NF-κB. Immunity 2007, 26, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Primer Name | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|
| β-actin-F | CCACCACAGCCGAGAGGGAA |
| β-actin-R | TCATGGTGGATGGGGCCAGG |
| MsDC-SIGN-F | ACGCCTACTGGTTTGGAATCAC |
| MsDC-SIGN-R | ATGTAGCCACAGTCCTCGTCAAT |
| RAF1-F | TCTACCTCCCAAACCAGCA |
| RAF1-R | CAGTGTTCCAATCCATCCG |
| IL10-F | AAGCCAGCAGCATCATTACCACT |
| IL10-R | AGAACCAGGACGGACAGGAGG |
| TLR4-F | TGATGCTTCTTGCTGGCTGC |
| TLR4-R | CAATCACCTTTCGGCTTTTATGG |
| NF-κB2-F | TGGCTGCCGAAACCGCT |
| NF-κB2-R | GCTGGACGAGGACACGCTG |
| Gene Name | Sequence | |
|---|---|---|
| Sense (5’–3’) | Antisense (5’–3’) | |
| MsDC-SIGN-siRNA | GUUUCUGUGGAAUCUUCUACC | UAGAAGAUUCCACAGAAACGU |
| NC | UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT | ACGUGACACGUUCGGAGAATT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, M.; Liu, J.; Yuan, Z.; Xu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yang, S.; Fei, H. DC-SIGN of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) Mediates Immune Functions against Aeromonas hydrophila through Collaboration with the TLR Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5013. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25095013
Huang M, Liu J, Yuan Z, Xu Y, Guo Y, Yang S, Fei H. DC-SIGN of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) Mediates Immune Functions against Aeromonas hydrophila through Collaboration with the TLR Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(9):5013. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25095013
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Mengmeng, Jingwen Liu, Zhenzhen Yuan, Youxing Xu, Yang Guo, Shun Yang, and Hui Fei. 2024. "DC-SIGN of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) Mediates Immune Functions against Aeromonas hydrophila through Collaboration with the TLR Signaling Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 9: 5013. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25095013
APA StyleHuang, M., Liu, J., Yuan, Z., Xu, Y., Guo, Y., Yang, S., & Fei, H. (2024). DC-SIGN of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) Mediates Immune Functions against Aeromonas hydrophila through Collaboration with the TLR Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(9), 5013. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25095013




