Zebrafish Model in Illuminating the Complexities of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorders: A Unique Research Tool
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Zebrafish as an Emerging Model Organism in PTSD Research
3. Pathophysiology of PTSD
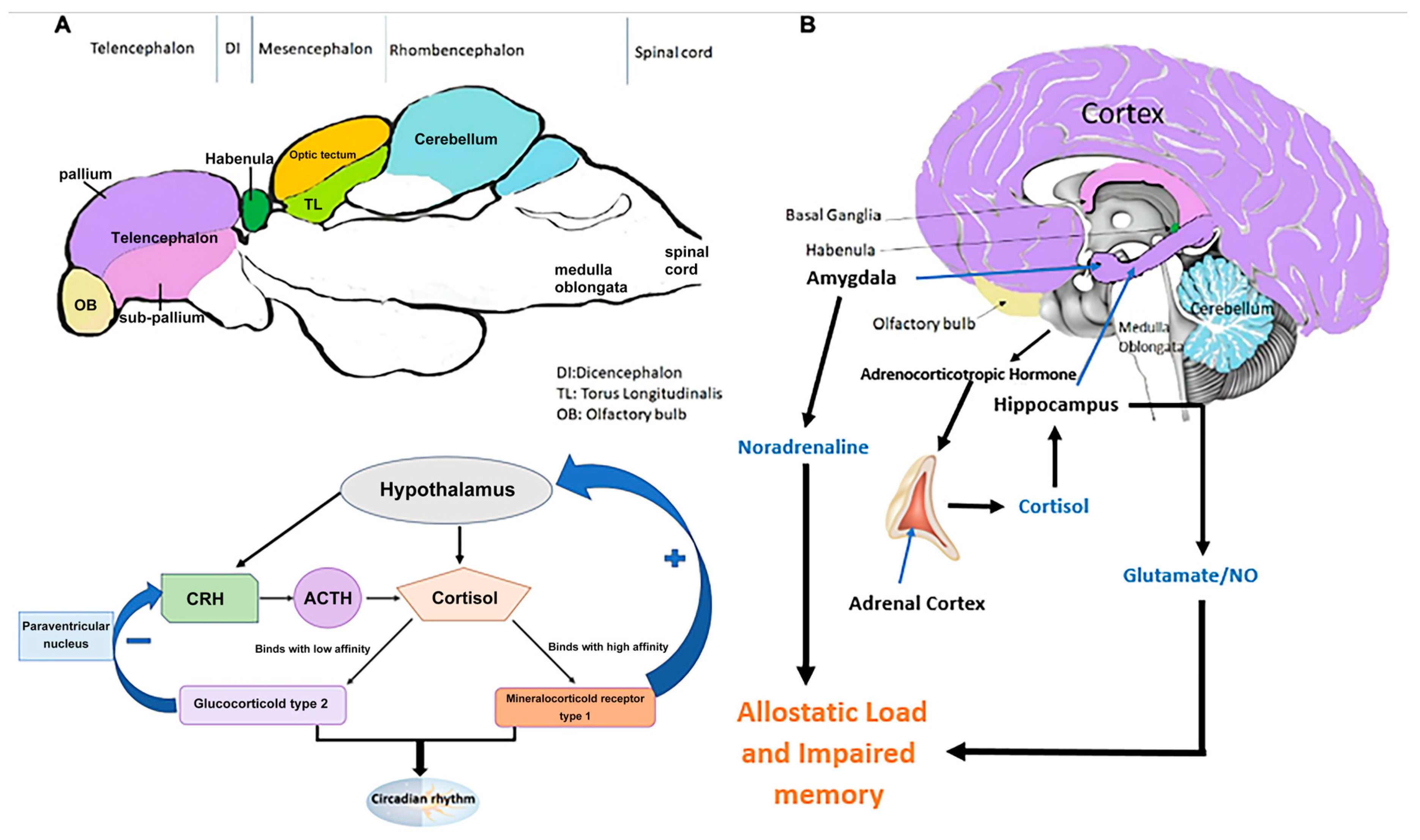
4. Neuroanatomical and Neurochemical Insights from Zebrafish PTSD Studies
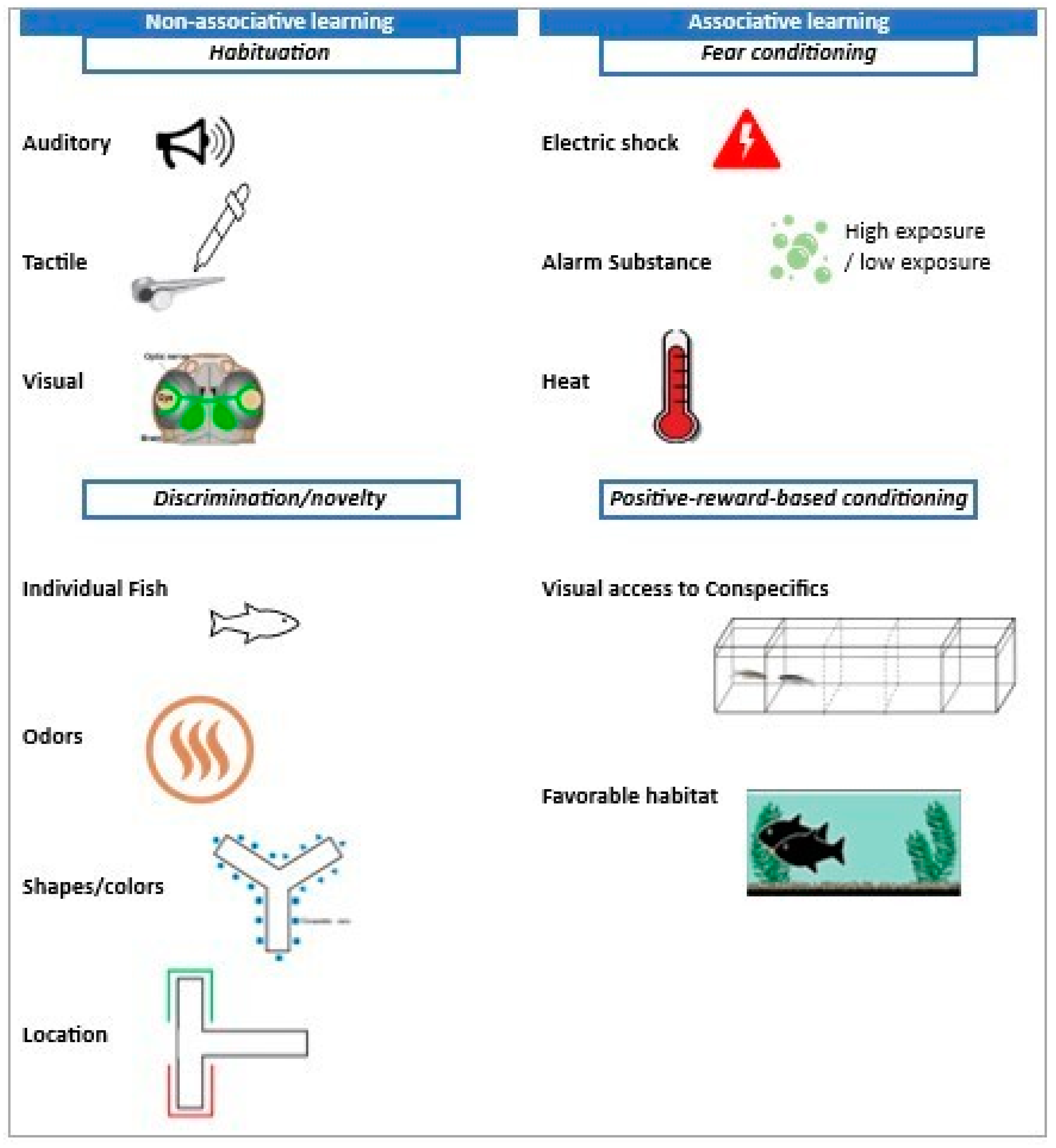
5. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) in Zebrafish: Learning Paradigms and Behavioral Aspects
5.1. Fear and Anxiety
5.2. Associative Learning
5.3. Time-Dependent Sensitization (TDS)
6. Genetic and Molecular Mechanisms Underlying PTSD-like Responses in Zebrafish
7. Pharmacological and Therapeutic Interventions in Zebrafish PTSD Models
8. Zebrafish in PTSD Research: Validation, Advantages, Limitations, and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Loots, H. Development and Validation of a Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Model in Zebrafish; North West University: St, Potchefstroom, South Africa, 2021; Volume 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick, H.A.; Heller, G.M. Post-traumatic stress disorder: Theory and treatment update. Int. J. Psychiatry Med. 2014, 47, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comer, S.D.; Cahill, C.M. Fentanyl: Receptor pharmacology, abuse potential, and implications for treatment. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 106, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, K.; Clark, M.D.; Torroja, C.F.; Torrance, J.; Berthelot, C.; Muffato, M.; Collins, J.E.; Humphray, S.; McLaren, K.; Matthews, L.; et al. The zebrafish reference genome sequence and its relationship to the human genome. Nature 2013, 496, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klee, E.W.; Schneider, H.; Clark, K.J.; Cousin, M.A.; Ebbert, J.O.; Hooten, W.M.; Karpyak, V.M.; Warner, D.O.; Ekker, S.C. Zebrafish: A model for the study of addiction genetics. Hum. Genet. 2012, 131, 977–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederriter, A.R.; Davis, E.E.; Golzio, C.; Oh, E.C.; Tsai, I.-C.; Katsanis, N. In vivo modeling of the morbid human genome using Danio rerio. JoVE (J. Vis. Exp.) 2013, 78, e50338. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S. Linking genes to brain, behavior and neurological diseases: What can we learn from zebrafish? Genes Brain Behav. 2004, 3, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernier, P.; Kyzar, E.J.; Maximino, C.; Tierney, K.; Gebhardt, M.; Lange, M.; Jesuthasan, S.; Stewart, A.M.; Neuhauss, S.C.; Robinson, K. Time to recognize zebrafish ‘affective’ behavior. Behaviour 2012, 149, 1019–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caramillo, E.M.; Khan, K.M.; Collier, A.D.; Echevarria, D.J. Modeling PTSD in the zebrafish: Are we there yet? Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 276, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, D.; Hu, G.; Liu, Z.; Yan, D.; Serikuly, N.; Alpyshov, E.T.; Demin, K.A.; Strekalova, T. Delayed behavioral and genomic responses to acute combined stress in zebrafish, potentially relevant to PTSD and other stress-related disorders: Focus on neuroglia, neuroinflammation, apoptosis and epigenetic modulation. Behav. Brain Res. 2020, 389, 112644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, F.; Fang, Y.; Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Qu, L.; Yang, Q.; Wu, W.; Jin, L.; Sun, D. Advances in Zebrafish as a Comprehensive Model of Mental Disorders. Depress. Anxiety 2023, 2023, 6663141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K.J.; Boczek, N.J.; Ekker, S.C. Stressing zebrafish for behavioral genetics. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 22, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Abreu, M.S.; Demin, K.A.; Giacomini, A.; Amstislavskaya, T.G.; Strekalova, T.; Maslov, G.O.; Kositsin, Y.; Petersen, E.V.; Kalueff, A.V. Understanding how stress responses and stress-related behaviors have evolved in zebrafish and mammals. Neurobiol. Stress. 2021, 15, 100405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bambino, K.; Chu, J. Zebrafish in Toxicology and Environmental Health. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2017, 124, 331–367. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fontana, B.D.; Müller, T.E.; Cleal, M.; De Abreu, M.S.; Norton, W.H.; Demin, K.A.; Amstislavskaya, T.G.; Petersen, E.V.; Kalueff, A.V.; Parker, M.O. Using zebrafish (Danio rerio) models to understand the critical role of social interactions in mental health and wellbeing. Progress. Neurobiol. 2022, 208, 101993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golla, A.; Østby, H.; Kermen, F. Chronic unpredictable stress induces anxiety-like behaviors in young zebrafish. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levraud, J.P.; Rawls, J.F.; Clatworthy, A.E. Using zebrafish to understand reciprocal interactions between the nervous and immune systems and the microbial world. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henríquez Martínez, A.; Ávila, L.C.; Pulido, M.A.; Ardila, Y.A.; Akle, V.; Bloch, N.I. Age-Dependent Effects of Chronic Stress on Zebrafish Behavior and Regeneration. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 856778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graves, C.L.; Norloff, E.; Thompson, D.; Kosyk, O.; Sang, Y.; Chen, A.; Zannas, A.S.; Wallet, S.M. Chronic early life stress alters the neuroimmune profile and functioning of the developing zebrafish gut. Brain Behav. Immun.-Health 2023, 31, 100655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, J.; Oliveri, A.; Levin, E.D. Zebrafish model systems for developmental neurobehavioral toxicology. Birth Defects Res. C Embryo Today 2013, 99, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.K.; Nazar, F.H.; Makpol, S.; Teoh, S.L. Zebrafish: A Pharmacological Model for Learning and Memory Research. Molecules 2022, 27, 7374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.X.M.; Ang, R.J.W.; Wee, C.L. Larval Zebrafish as a Model for Mechanistic Discovery in Mental Health. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 900213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximino, C.; Marques de Brito, T.; Dias, C.A.; Gouveia, A., Jr.; Morato, S. Scototaxis as anxiety-like behavior in fish. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, T.; Wullimann, M. Atlas of Early Zebrafish Brain Development: A Tool for Molecular Neurogenetics; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- MacRae, C.A.; Peterson, R.T. Zebrafish as tools for drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraldez, A.J.; Mishima, Y.; Rihel, J.; Grocock, R.J.; Van Dongen, S.; Inoue, K.; Enright, A.J.; Schier, A.F. Zebrafish MiR-430 promotes deadenylation and clearance of maternal mRNAs. Science 2006, 312, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasevicius, A.; Ekker, S.C. Effective targeted gene ‘knockdown’in zebrafish. Nat. Genet. 2000, 26, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasevicius, A.; Ekker, S.C. The zebrafish as a novel system for functional genomics and therapeutic development applications. Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther. 2001, 3, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bedell, V.M.; Wang, Y.; Campbell, J.M.; Poshusta, T.L.; Starker, C.G.; Krug II, R.G.; Tan, W.; Penheiter, S.G.; Ma, A.C.; Leung, A.Y. In vivo genome editing using a high-efficiency TALEN system. Nature 2012, 491, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerlai, R. High-throughput behavioral screens: The first step towards finding genes involved in vertebrate brain function using zebrafish. Molecules 2010, 15, 2609–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, J.P.; McKlveen, J.M.; Ghosal, S.; Kopp, B.; Wulsin, A.; Makinson, R.; Scheimann, J.; Myers, B. Regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical stress response. Compr. Physiol. 2016, 6, 603. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dunlop, B.W.; Wong, A. The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in PTSD: Pathophysiology and treatment interventions. Progress. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 89, 361–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidi, J.; Lucente, M.; Sonino, N.; Fava, G.A. Allostatic load and its impact on health: A systematic review. Psychother. Psychosom. 2021, 90, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, M.C.; Rao, U. Psychobiology of PTSD in the acute aftermath of trauma: Integrating research on coping, HPA function and sympathetic nervous system activity. Asian J. Psychiatry 2013, 6, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oosthuizen, F.; Wegener, G.; Harvey, B.H. Nitric oxide as inflammatory mediator in post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD): Evidence from an animal model. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2005, 1, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löhr, H.; Hammerschmidt, M. Zebrafish in endocrine systems: Recent advances and implications for human disease. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2011, 73, 183–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnon, S.A.; Wagner, A.D. Acute stress and episodic memory retrieval: Neurobiological mechanisms and behavioral consequences. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2016, 1369, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piato, Â.L.; Capiotti, K.M.; Tamborski, A.R.; Oses, J.P.; Barcellos, L.J.; Bogo, M.R.; Lara, D.R.; Vianna, M.R.; Bonan, C.D. Unpredictable chronic stress model in zebrafish (Danio rerio): Behavioral and physiological responses. Progress. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 35, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaikwad, S.; Stewart, A.; Hart, P.; Wong, K.; Piet, V.; Cachat, J.; Kalueff, A.V. Acute stress disrupts performance of zebrafish in the cued and spatial memory tests: The utility of fish models to study stress–memory interplay. Behav. Process. 2011, 87, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, A.; Banerjee, M.; Upadhya, A.; Bagwe-Parab, S.; Kaur, G. The Brilliance of the Zebrafish Model: Perception on Behavior and Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 861155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leventhal, H.; Bodnar-Deren, S.; Breland, J.Y.; Hash-Converse, J.; Phillips, L.A.; Leventhal, E.A.; Cameron, L.D. Modeling Health and Illness Behavior: The Approach of the Commonsense Model, 1st ed.; Psychology Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012; p. 984. [Google Scholar]
- de Abreu, M.S.; Costa, F.; Giacomini, A.; Demin, K.A.; Zabegalov, K.N.; Maslov, G.O.; Kositsyn, Y.M.; Petersen, E.V.; Strekalova, T.; Rosemberg, D.B.; et al. Towards Modeling Anhedonia and Its Treatment in Zebrafish. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2022, 25, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosili, P.; Mkhize, B.C.; Ngubane, P.; Sibiya, N.; Khathi, A. The dysregulation of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis in diet-induced prediabetic male Sprague Dawley rats. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 17, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinds, J.A.; Sanchez, E.R. The Role of the Hypothalamus–Pituitary–Adrenal (HPA) Axis in Test-Induced Anxiety: Assessments, Physiological Responses, and Molecular Details. Stresses 2022, 2, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, B.B.; Schoonheim, P.J.; Ziv, L.; Voelker, L.; Baier, H.; Gahtan, E. A zebrafish model of glucocorticoid resistance shows serotonergic modulation of the stress response. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalueff, A.V.; Stewart, A.M.; Gerlai, R. Zebrafish as an emerging model for studying complex brain disorders. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 35, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, N.; Wang, D.-T.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, Y. Early developmental stage glucocorticoid exposure causes DNA methylation and behavioral defects in adult zebrafish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 256, 109301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.R.; Zhang, Y.; Rao, Y.B.; Chen, X.; Lou, H.F.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, H.Y.; Fang, P.; Hu, L.W. The changes in, and relationship between, plasma nitric oxide and corticotropin-releasing hormone in patients with major depressive disorder. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2018, 45, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGowan, P.O.; Sasaki, A.; D’alessio, A.C.; Dymov, S.; Labonté, B.; Szyf, M.; Turecki, G.; Meaney, M.J. Epigenetic regulation of the glucocorticoid receptor in human brain associates with childhood abuse. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radtke, K.M.; Ruf, M.; Gunter, H.M.; Dohrmann, K.; Schauer, M.; Meyer, A.; Elbert, T. Transgenerational impact of intimate partner violence on methylation in the promoter of the glucocorticoid receptor. Transl. Psychiatry 2011, 1, e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A.M.; Yang, E.; Nguyen, M.; Kalueff, A.V. Developing zebrafish models relevant to PTSD and other trauma-and stressor-related disorders. Progress. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 55, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankiewicz, A.M.; Swiergiel, A.H.; Lisowski, P. Epigenetics of stress adaptations in the brain. Brain Res. Bull. 2013, 98, 76–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaser, R.; Gerlai, R. Behavioral phenotyping in zebrafish: Comparison of three behavioral quantification methods. Behav. Res. Methods 2006, 38, 456–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenney, J.W. Associative and nonassociative learning in adult zebrafish. In Behavioral and Neural Genetics of Zebrafish; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 187–204. [Google Scholar]
- Reemst, K.; Shahin, H.; Shahar, O.D. Learning and memory formation in zebrafish: Protein dynamics and molecular tools. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1120984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sison, M.; Gerlai, R. Associative learning in zebrafish (Danio rerio) in the plus maze. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 207, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bystritsky, A.; Khalsa, S.S.; Cameron, M.E.; Schiffman, J. Current diagnosis and treatment of anxiety disorders. Pharm. Ther. 2013, 38, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Panula, P.; Chen, Y.-C.; Priyadarshini, M.; Kudo, H.; Semenova, S.; Sundvik, M.; Sallinen, V. The comparative neuroanatomy and neurochemistry of zebrafish CNS systems of relevance to human neuropsychiatric diseases. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 40, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlidis, M.; Theodoridi, A.; Tsalafouta, A. Neuroendocrine regulation of the stress response in adult zebrafish, Danio rerio. Progress. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 60, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, L.K.; Jeyabalan, S.; Wong, L.S.; Sekar, M.; Logeshwari, B.; Umamaheswari, S.; Premkumar, S.; Sekar, R.T.; Begum, M.Y.; Gan, S.H. Baicalein prevents stress-induced anxiety behaviors in zebrafish model. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenbergen, P.J.; Richardson, M.K.; Champagne, D.L. The use of the zebrafish model in stress research. Progress. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 35, 1432–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, E.D.; Bencan, Z.; Cerutti, D.T. Anxiolytic effects of nicotine in zebrafish. Physiol. Behav. 2007, 90, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcellos, L.J.G.; Ritter, F.; Kreutz, L.C.; Quevedo, R.M.; da Silva, L.B.; Bedin, A.C.; Finco, J.; Cericato, L. Whole-body cortisol increases after direct and visual contact with a predator in zebrafish, Danio rerio. Aquaculture 2007, 272, 774–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaser, R.; Chadwick, L.; McGinnis, G. Behavioral measures of anxiety in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 208, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abreu, M.S.; Giacomini, A.C.; Kalueff, A.V.; Barcellos, L.J. The smell of “anxiety”: Behavioral modulation by experimental anosmia in zebrafish. Physiol. Behav. 2016, 157, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assad, N.; Luz, W.L.; Santos-Silva, M.; Carvalho, T.; Moraes, S.; Picanço-Diniz, D.L.W.; Bahia, C.P.; Oliveira Batista, E.d.J.; da Conceição Passos, A.; Oliveira, K.R.H.M. Acute restraint stress evokes anxiety-like behavior mediated by telencephalic inactivation and gabaergic dysfunction in zebrafish brains. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Han, X.; Wang, J.; Sun, J. Baicalin may have a therapeutic effect in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Med. Hypotheses 2015, 85, 761–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiozaki, K.; Kawabe, M.; Karasuyama, K.; Kurachi, T.; Hayashi, A.; Ataka, K.; Iwai, H.; Takeno, H.; Hayasaka, O.; Kotani, T. Neuropeptide Y deficiency induces anxiety-like behaviours in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichmann, F.; Holzer, P. Neuropeptide Y: A stressful review. Neuropeptides 2016, 55, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlai, R. Associative learning in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Methods Cell Biol. 2011, 101, 249–270. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Imari, L.; Gerlai, R. Sight of conspecifics as reward in associative learning in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Behav. Brain Res. 2008, 189, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerlai, R. Learning and memory in zebrafish (Danio rerio). In Methods in Cell Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 134, pp. 551–586. [Google Scholar]
- Gerlai, R. Zebrafish and relational memory: Could a simple fish be useful for the analysis of biological mechanisms of complex vertebrate learning? Behav. Process. 2017, 141, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tulving, E. What is episodic memory? Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 1993, 2, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, T.J.; Myggland, A.; Duperreault, E.; May, Z.; Gallup, J.; Powell, R.A.; Schalomon, M.; Digweed, S.M. Episodic-like memory in zebrafish. Anim. Cogn. 2016, 19, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, R.-H.; Kim, W.; Lee, C.-J. NMDA receptor-dependent long-term potentiation in the telencephalon of the zebrafish. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 370, 248–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antelman, S.M.; Soares, J.C.; Gershon, S. Time-dependent sensitization—Possible implications for clinical psychopharmacology. Behav. Pharmacol. 1997, 8, 505–514, Discussion 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, M.G.; do Carmo Silva, R.X.; dos Santos Silva, S.d.N.; dos Santos Rodrigues, L.d.S.; Oliveira, K.R.H.M.; Batista, E.d.J.O.; Maximino, C.; Herculano, A.M. Time-dependent sensitization of stress responses in zebrafish: A putative model for post-traumatic stress disorder. Behav. Process. 2016, 128, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, B.H.; Oosthuizen, F.; Brand, L.; Wegener, G.; Stein, D.J. Stress–restress evokes sustained iNOS activity and altered GABA levels and NMDA receptors in rat hippocampus. Psychopharmacology 2004, 175, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uys, J.D.; Stein, D.J.; Daniels, W.M.; Harvey, B.H. Animal models of anxiety disorders. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2003, 5, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, L.D.; Muir, K.E.; Perrot, T.S. Stress responses of adolescent male and female rats exposed repeatedly to cat odor stimuli, and long-term enhancement of adult defensive behaviors. Dev. Psychobiol. 2013, 55, 551–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, B.H.; Naciti, C.; Brand, L.; Stein, D.J. Endocrine, cognitive and hippocampal/cortical 5HT1A/2A receptor changes evoked by a time-dependent sensitisation (TDS) stress model in rats. Brain Res. 2003, 983, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, S.K.; Singh, N.; Garabadu, D.; Krishnamurthy, S. A novel stress re-stress model: Modification of re-stressor cue induces long-lasting post-traumatic stress disorder-like symptoms in rats. Int. J. Neurosci. 2020, 130, 941–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisieski, M.J.; Eagle, A.L.; Conti, A.C.; Liberzon, I.; Perrine, S.A. Single-prolonged stress: A review of two decades of progress in a rodent model of post-traumatic stress disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canzian, J.; Fontana, B.D.; Quadros, V.A.; Müller, T.E.; Duarte, T.; Rosemberg, D.B. Single pentylenetetrazole exposure increases aggression in adult zebrafish at different time intervals. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 692, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, V.P.; Poss, K.D. New regulators of vertebrate appendage regeneration. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2008, 18, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanouraki, E.; Mylonas, C.; Papandroulakis, N.; Pavlidis, M. Species specificity in the magnitude and duration of the acute stress response in Mediterranean marine fish in culture. General. Comp. Endocrinol. 2011, 173, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlidis, M.; Digka, N.; Theodoridi, A.; Campo, A.; Barsakis, K.; Skouradakis, G.; Samaras, A.; Tsalafouta, A. Husbandry of zebrafish, Danio rerio, and the cortisol stress response. Zebrafish 2013, 10, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwama, G.K.; Pickering, A.; Sumpter, J.; Schreck, C. Fish Stress and Health in Aquaculture; Society for Experimental Biology Seminar Series; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997; p. 278. ISBN 0 521 55518 3. [Google Scholar]
- Tort, L.; Pavlidis, M.A.; Woo, N.Y.S. Stress and welfare in sparid fishes. Sparidae 2011, 75–94. [Google Scholar]
- Fuzzen, M.L.; Van Der Kraak, G.; Bernier, N.J. Stirring up new ideas about the regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-interrenal axis in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Zebrafish 2010, 7, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendelaar Bonga, S.E. The stress response in fish. Physiol. Rev. 1997, 77, 591–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coste, S.C.; Murray, S.E.; Stenzel-Poore, M.P. Gene targeted animals with alterations in corticotropin pathways: New insights into allostatic control. Tech. Behav. Neural Sci. 2005, 15, 51–74. [Google Scholar]
- Holsboer, F. The corticosteroid receptor hypothesis of depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 2000, 23, 477–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’connor, T.; O’halloran, D.; Shanahan, F. The stress response and the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis: From molecule to melancholia. QJM 2000, 93, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsop, D.; Vijayan, M.M. Development of the corticosteroid stress axis and receptor expression in zebrafish. Am. J. Physiol. -Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2008, 294, R711–R719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaaf, M.; Chatzopoulou, A.; Spaink, H. The zebrafish as a model system for glucocorticoid receptor research. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2009, 153, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolte, E.H.; de Mazon, A.F.; Leon-Koosterziel, K.M.; Jesiak, M.; Bury, N.; Sturm, A.; Savelkoul, H.F.; Verburg-van Kemenade, B.; Flik, G. Corticosteroid receptors involved in stress regulation in common carp, Cyprinus carpio. J. Endocrinol. 2008, 198, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terova, G.; Gornati, R.; Rimoldi, S.; Bernardini, G.; Saroglia, M. Quantification of a glucocorticoid receptor in sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax, L.) reared at high stocking density. Gene 2005, 357, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazzana, M.; Vizzini, A.; Sanfratello, M.A.; Celi, M.; Salerno, G.; Parrinello, N. Differential expression of two glucocorticoid receptors in seabass (teleost fish) head kidney after exogeneous cortisol inoculation. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2010, 157, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teles, M.; Tridico, R.; Callol, A.; Fierro-Castro, C.; Tort, L. Differential expression of the corticosteroid receptors GR1, GR2 and MR in rainbow trout organs with slow release cortisol implants. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2013, 164, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taliaz, D.; Loya, A.; Gersner, R.; Haramati, S.; Chen, A.; Zangen, A. Resilience to chronic stress is mediated by hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 4475–4483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goujon, E.; Layé, S.; Parnet, P.; Dantzer, R. Regulation of cytokine gene expression in the central nervous system by glucocorticoids: Mechanisms and functional consequences. Psychoneuroendocrinology 1997, 22, S75–S80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsink, M.; Steenbergen, P.; Vos, J.; Karst, H.; Joels, M.; De Kloet, E.; Datson, N. Acute activation of hippocampal glucocorticoid receptors results in different waves of gene expression throughout time. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2006, 18, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulkin, J.; Gold, P.W.; McEwen, B.S. Induction of corticotropin-releasing hormone gene expression by glucocorticoids: Implication for understanding the states of fear and anxiety and allostatic load. Psychoneuroendocrinology 1998, 23, 219–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte-Herbrüggen, O.; Chourbaji, S.; Ridder, S.; Brandwein, C.; Gass, P.; Hörtnagl, H.; Hellweg, R. Stress-resistant mice overexpressing glucocorticoid receptors display enhanced BDNF in the amygdala and hippocampus with unchanged NGF and serotonergic function. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2006, 31, 1266–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeanneteau, F.D.; Lambert, W.M.; Ismaili, N.; Bath, K.G.; Lee, F.S.; Garabedian, M.J.; Chao, M.V. BDNF and glucocorticoids regulate corticotrophin-releasing hormone (CRH) homeostasis in the hypothalamus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1305–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarty, S.; Reddy, B.R.; Sudhakar, S.R.; Saxena, S.; Das, T.; Meghah, V.; Brahmendra Swamy, C.V.; Kumar, A.; Idris, M.M. Chronic unpredictable stress (CUS)-induced anxiety and related mood disorders in a zebrafish model: Altered brain proteome profile implicates mitochondrial dysfunction. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, R.J.; Bergner, C.L.; Hart, P.C.; Cachat, J.M.; Canavello, P.R.; Elegante, M.F.; Elkhayat, S.I.; Bartels, B.K.; Tien, A.K.; Tien, D.H.; et al. Understanding behavioral and physiological phenotypes of stress and anxiety in zebrafish. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 205, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A.M.; Ullmann, J.F.P.; Norton, W.H.J.; Parker, M.O.; Brennan, C.H.; Gerlai, R.; Kalueff, A.V. Molecular psychiatry of zebrafish. Mol. Psychiatry 2015, 20, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.L.; Liu, M.; Cui, W.; Yang, L.; Zhang, C.N. Quercetin affects shoaling and anxiety behaviors in zebrafish: Involvement of neuroinflammation and neuron apoptosis. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2020, 105, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Meijer, A.H.; Schaaf, M.J.M. Modeling Inflammation in Zebrafish for the Development of Anti-inflammatory Drugs. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 620984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximino, C.; da Silva, A.W.; Araújo, J.; Lima, M.G.; Miranda, V.; Puty, B.; Benzecry, R.; Picanço-Diniz, D.L.; Gouveia, A., Jr.; Oliveira, K.R.; et al. Fingerprinting of psychoactive drugs in zebrafish anxiety-like behaviors. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourin, M. Animal models for screening anxiolytic-like drugs: A perspective. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 17, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyzar, E.; Zapolsky, I.; Green, J.; Gaikwad, S.; Pham, M.; Collins, C.; Roth, A.; Stewart, A.M.; St-Pierre, P.; Hirons, B. The Zebrafish Neurophenome Database (ZND): A dynamic open-access resource for zebrafish neurophenotypic data. Zebrafish 2012, 9, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatto, E.; Dadda, M.; Bruzzone, M.; Chiarello, E.; De Russi, G.; Maschio, M.D.; Bisazza, A.; Lucon-Xiccato, T. Environmental enrichment decreases anxiety-like behavior in zebrafish larvae. Dev. Psychobiol. 2022, 64, e22255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcon, M.; Mocelin, R.; Benvenutti, R.; Costa, T.; Herrmann, A.P.; de Oliveira, D.L.; Koakoski, G.; Barcellos, L.J.; Piato, A. Environmental enrichment modulates the response to chronic stress in zebrafish. J. Exp. Biol. 2018, 221, jeb176735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, S.; Amlani, S.; Buske, C.; Chatterjee, D.; Gerlai, R. Developmental social isolation affects adult behavior, social interaction, and dopamine metabolite levels in zebrafish. Dev. Psychobiol. 2018, 60, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreosti, E.; Lopes, G.; Kampff, A.R.; Wilson, S.W. Development of social behavior in young zebrafish. Front. Neural Circuits 2015, 9, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anichtchik, O.V.; Kaslin, J.; Peitsaro, N.; Scheinin, M.; Panula, P. Neurochemical and behavioural changes in zebrafish Danio rerio after systemic administration of 6-hydroxydopamine and 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine. J. Neurochem. 2004, 88, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.S.; Dai, M.Z.; Zhu, C.X.; Huang, Y.F.; Liu, J.; Zhang, C.D.; Xie, F.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.Q.; et al. Validation, Optimization, and Application of the Zebrafish Developmental Toxicity Assay for Pharmaceuticals Under the ICH S5(R3) Guideline. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 721130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patton, E.E.; Tobin, D.M. Spotlight on zebrafish: The next wave of translational research. Dis. Model. Mech. 2019, 12, dmm039370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen-Civil, A.I.S.; Sawale, R.A.; Vanwalleghem, G.C. Zebrafish (Danio rerio) as a translational model for neuro-immune interactions in the enteric nervous system in autism spectrum disorders. Brain Behav. Immun. 2023, 112, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, J.B.; Westerfield, M. Zebrafish models in translational research: Tipping the scales toward advancements in human health. Dis. Models Mech. 2014, 7, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, C.; Ijaz, S.; Hoffman, E.J. Zebrafish models of neurodevelopmental disorders: Past, present, and future. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachowicz, J.; Niedziałek, K.; Rostkowska, E.; Szopa, A.; Świąder, K.; Szponar, J.; Serefko, A. Zebrafish as an Animal Model for Testing Agents with Antidepressant Potential. Life 2021, 11, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, M.O.; Brock, A.J.; Walton, R.T.; Brennan, C.H. The role of zebrafish (Danio rerio) in dissecting the genetics and neural circuits of executive function. Front. Neural Circuits 2013, 7, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, K.M.; Collier, A.D.; Meshalkina, D.A.; Kysil, E.V.; Khatsko, S.L.; Kolesnikova, T.; Morzherin, Y.Y.; Warnick, J.E.; Kalueff, A.V.; Echevarria, D.J. Zebrafish models in neuropsychopharmacology and CNS drug discovery. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 1925–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Key Points | Relevance in PTSD Research |
|---|---|
| Behavioral Similarities | Zebrafish exhibit fear responses, anxiety-like behaviors, and stress-related responses, making them suitable for studying the impact of traumatic experiences on behavior [23]. |
| Genetic Similarities | Zebrafish share many genetic homologies with humans, allowing researchers to investigate genes associated with PTSD and their impact on the zebrafish model [4]. |
| Neural Circuitry | Zebrafish have a relatively simple and well-characterized nervous system, aiding in understanding neurobiological underpinnings of stress and anxiety responses relevant to PTSD [24]. |
| High-Throughput Screening | The transparency of zebrafish embryos allows for high-throughput drug screening, facilitating the identification of potential compounds or interventions for PTSD treatment [25]. |
| Genetic Manipulation | Various genetic manipulation techniques in zebrafish, such as morpholino knockdowns and CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing, enable researchers to study the roles of specific genes in PTSD-like behaviors and stress responses [11,26,27,28,29]. |
| Environmental Factors | Zebrafish’s adaptability to different stress paradigms allows researchers to induce stress and trauma in controlled laboratory settings to study their effects on behavior and physiology [30]. |
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Rapid Development Zebrafish exhibit rapid development, enabling the study of PTSD-related changes in a short timeframe. | Behavioral Complexity Zebrafish behavior may not fully capture the complexity of human PTSD symptoms. Thus, zebrafish behavioral responses may not perfectly mirror human emotions and experiences. |
| Large Sample Size The species allows for studies with substantial sample sizes, enhancing statistical robustness. | Ethical Considerations Large-scale breeding for high sample sizes may raise ethical concerns. |
| Low Cost Zebrafish maintenance costs are lower compared to larger vertebrate models. | Limited Adult Relevance PTSD typically manifests in mature organisms, limiting the relevance of observations in transparent larvae. |
| Juvenile Manifestation Symptoms may manifest in the juvenile stage, providing an early window for observation. | Brain Structure Differences Differences in brain complexity and structures may hinder direct translation to human conditions. |
| Genetic Similarities Significant genetic homology with humans facilitates the exploration of PTSD-related genes. | Limited Predictive Validity Zebrafish models may have limited predictive validity for drug responses in more complex mammalian systems. |
| Transparent Larvae Transparent larvae enable real-time observation of molecular and cellular changes. | Environmental Sensitivity Susceptibility to stressors may vary, making standardization challenging. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Zoubi, R.M.; Abu-Hijleh, H.; Zarour, A.; Zakaria, Z.Z.; Yassin, A.; Al-Ansari, A.A.; Al-Asmakh, M.; Bawadi, H. Zebrafish Model in Illuminating the Complexities of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorders: A Unique Research Tool. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25094895
Al-Zoubi RM, Abu-Hijleh H, Zarour A, Zakaria ZZ, Yassin A, Al-Ansari AA, Al-Asmakh M, Bawadi H. Zebrafish Model in Illuminating the Complexities of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorders: A Unique Research Tool. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(9):4895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25094895
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Zoubi, Raed M., Haya Abu-Hijleh, Ahmad Zarour, Zain Z. Zakaria, Aksam Yassin, Abdulla A. Al-Ansari, Maha Al-Asmakh, and Hiba Bawadi. 2024. "Zebrafish Model in Illuminating the Complexities of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorders: A Unique Research Tool" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 9: 4895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25094895
APA StyleAl-Zoubi, R. M., Abu-Hijleh, H., Zarour, A., Zakaria, Z. Z., Yassin, A., Al-Ansari, A. A., Al-Asmakh, M., & Bawadi, H. (2024). Zebrafish Model in Illuminating the Complexities of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorders: A Unique Research Tool. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(9), 4895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25094895






