Role of Epiregulin on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Hepatocarcinogenesis as a Mediator via EGFR Signaling in the Cancer Microenvironment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
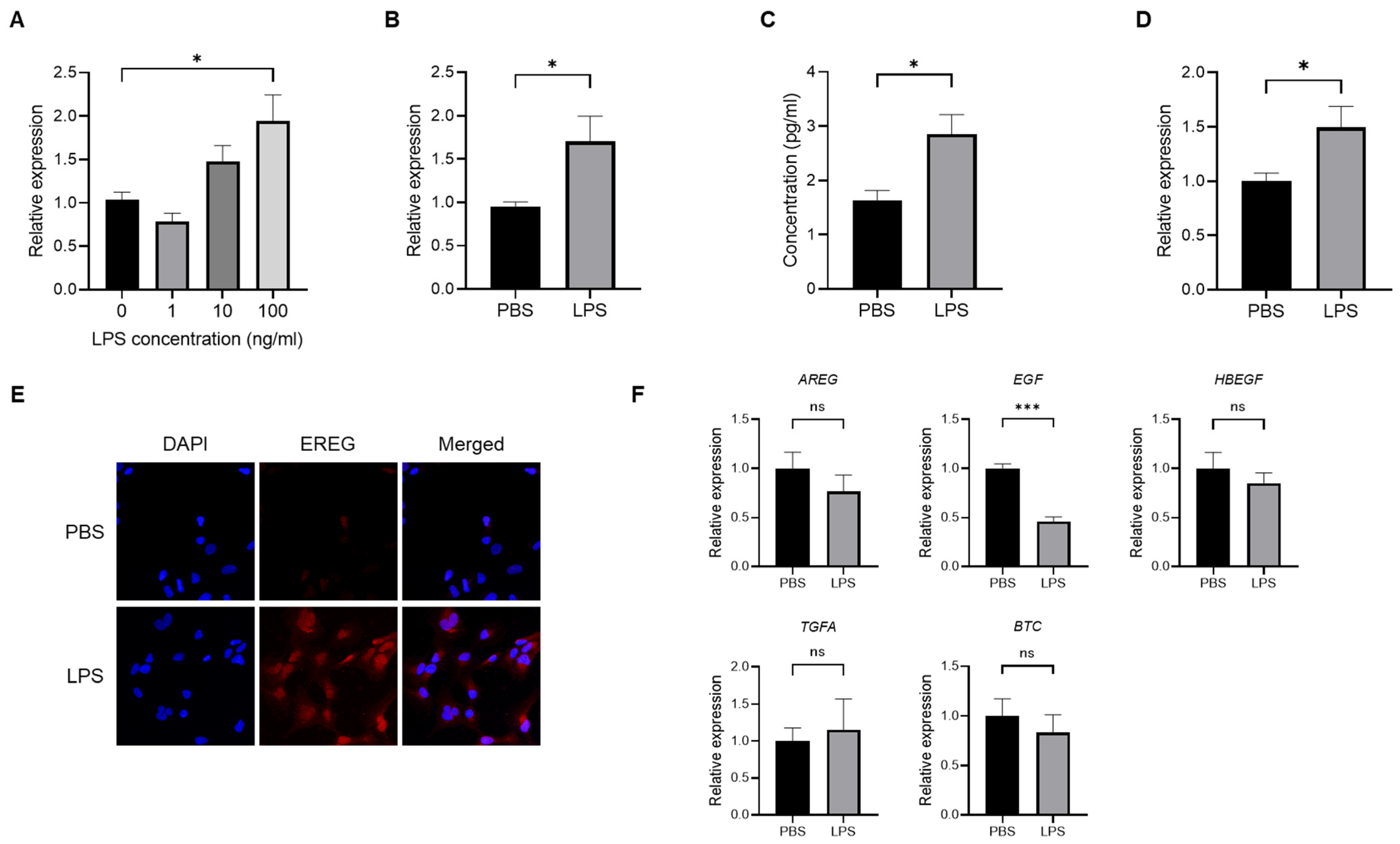
2.1. LPS Induces the Production of EREG from LX-2 Cells In Vitro
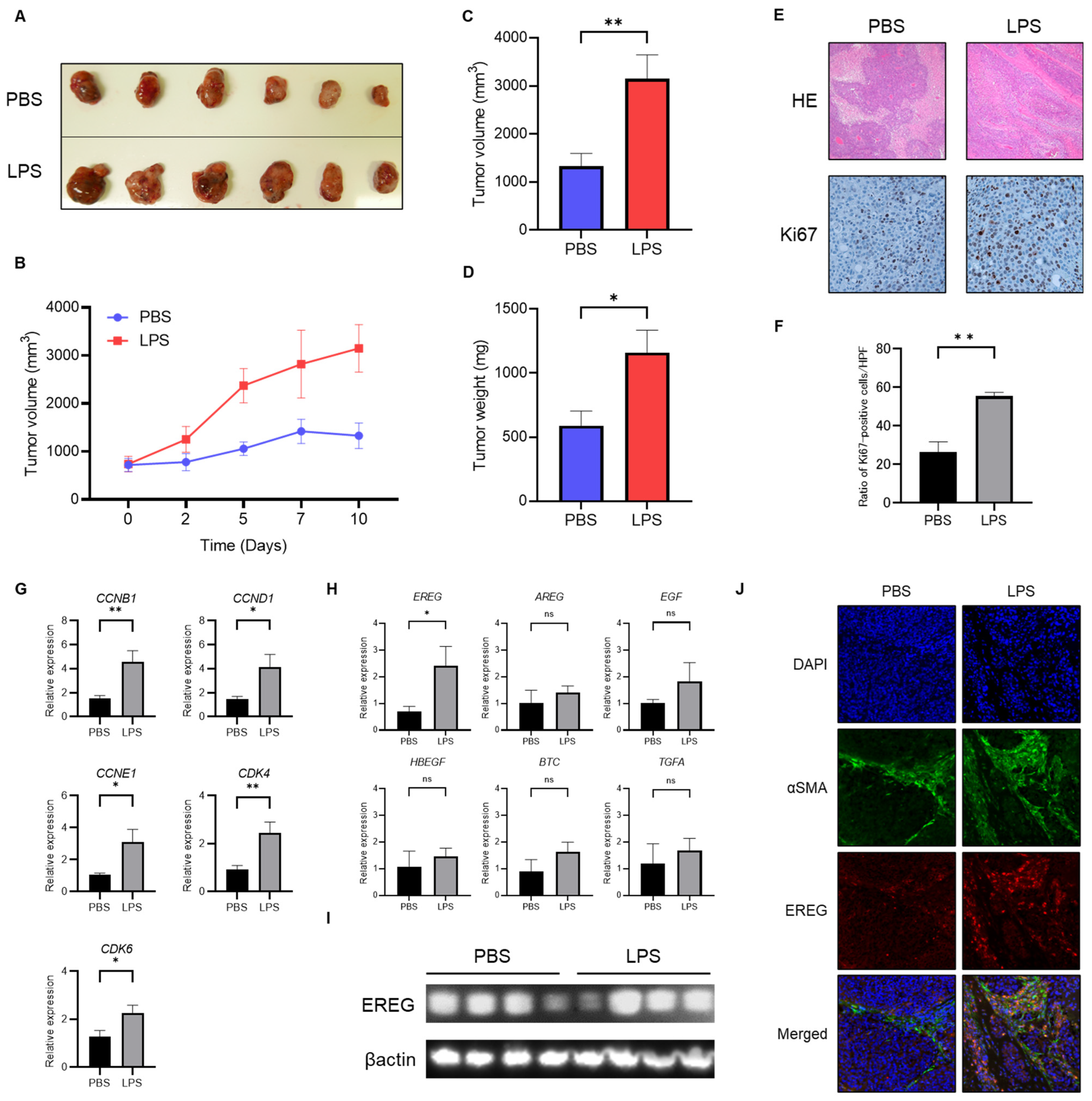
2.2. Administration with LPS Accelerates the Development of Huh7/LX-2 Xenografted Tumors In Vivo
2.3. EREG Promoted Cell Proliferation, and Migration/Invasion Activity of Liver Cancer Cells Expressing EGFR In Vitro
2.4. EREG Drives the Cell Migration and Invasion Activity of Liver Cancer Cells with EGFR
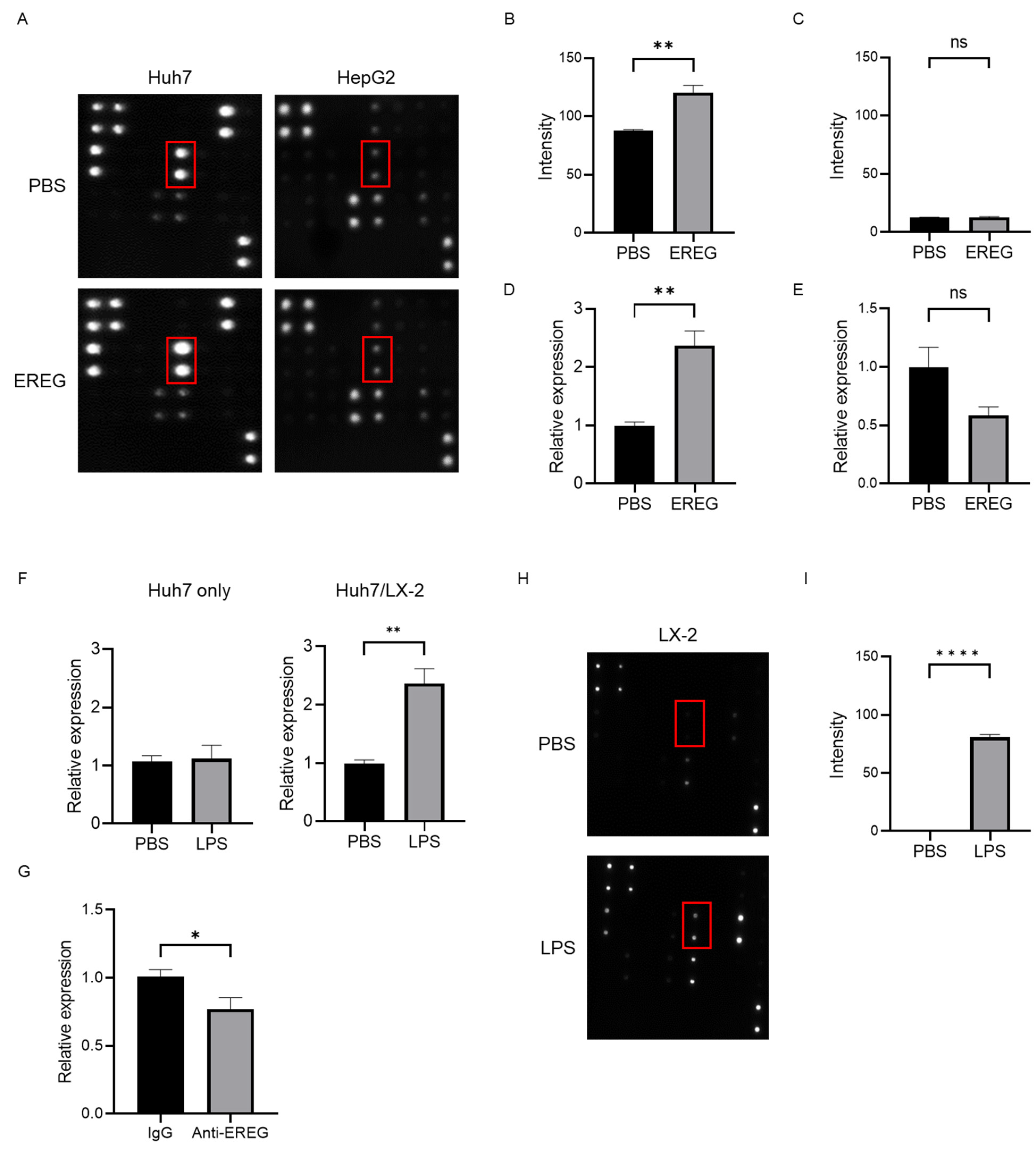
2.5. EREG Promotes the Production of Interleukin 8 (IL-8) from Cancer Cells through the Expression of EGFR
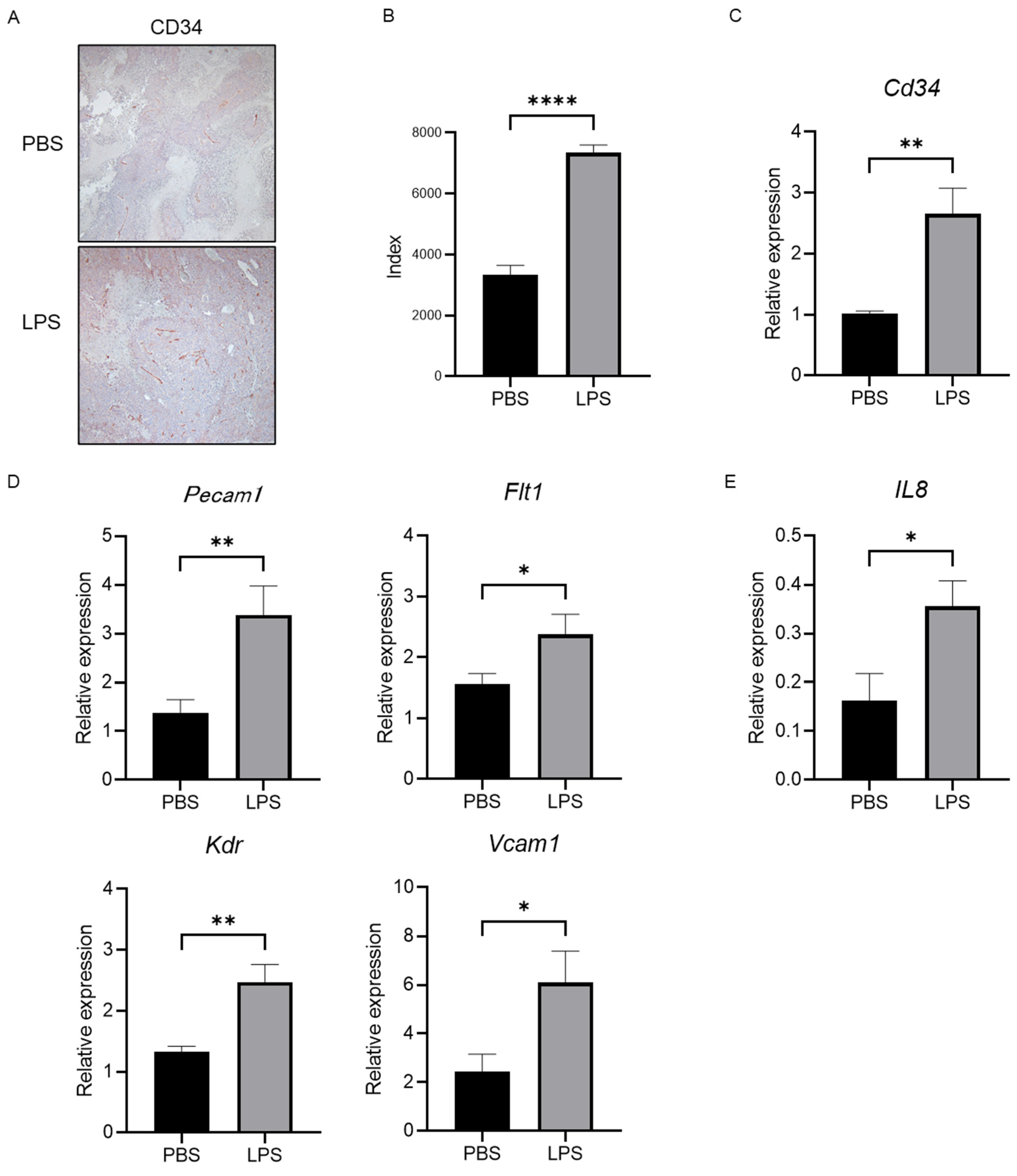
2.6. Elevation of IL-8 Is Closely Linked to the Progression of Neovascularization in Tumor Tissue
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Mouse Model
4.2. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
4.3. Cell Proliferation Assay
4.4. Cell Migration/Invasion Assays
4.5. RNA Isolation and Real-Time Quantitative PCR
4.6. Western Blotting
4.7. Detection of Angiogenesis Proteins
4.8. ELISA Measurement
4.9. Immunohistochemistry/Immunofluorescence Staining
4.10. Immunocytochemistry Staining
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Llovet, J.M.; Kelley, R.K.; Villanueva, A.; Singal, A.G.; Pikarsky, E.; Roayaie, S.; Lencioni, R.; Koike, K.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Finn, R.S. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulik, L.; El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 477–491.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGlynn, K.A.; Petrick, J.L.; London, W.T. Global epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: An emphasis on demographic and regional variability. Clin. Liver Dis. 2015, 19, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.D.; Hainaut, P.; Gores, G.J.; Amadou, A.; Plymoth, A.; Roberts, L.R. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: Trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riordan, S.M.; Williams, R. The intestinal flora and bacterial infection in cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2006, 45, 744–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, S.; Zhou, Z.; Lin, N. Lipopolysaccharide promotes angiogenesis in mice model of HCC by stimulating hepatic stellate cell activation via TLR4 pathway. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2017, 49, 1029–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yu, L.X.; Yan, H.X.; Liu, Q.; Yang, W.; Wu, H.P.; Dong, W.; Tang, L.; Lin, Y.; He, Y.Q.; Zou, S.S.; et al. Endotoxin accumulation prevents carcinogen-induced apoptosis and promotes liver tumorigenesis in rodents. Hepatology 2010, 52, 1322–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dapito, D.H.; Mencin, A.; Gwak, G.Y.; Pradere, J.P.; Jang, M.K.; Mederacke, I.; Caviglia, J.M.; Khiabanian, H.; Adeyemi, A.; Bataller, R.; et al. Promotion of hepatocellular carcinoma by the intestinal microbiota and TLR4. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 504–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riese, D.J.; Cullum, R.L. Epiregulin: Roles in normal physiology and cancer. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 28, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyoda, H.; Komurasaki, T.; Uchida, D.; Takayama, Y.; Isobe, T.; Okuyama, T.; Hanada, K. Epiregulin: A novel epidermal growth factor with mitogenic activity for rat primary hepatocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 7495–7500. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tomita, K.; Haga, H.; Mizuno, K.; Katsumi, T.; Sato, C.; Okumoto, K.; Nishise, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Saito, T.; Ueno, Y. Epiregulin promotes the emergence and proliferation of adult liver progenitor cells. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2014, 307, G50–G57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Ye, D.; Xu, D.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Yu, W.; Wang, Y.; He, Y.; Hu, J.; et al. Autocrine epiregulin activates EGFR pathway for lung metastasis via EMT in salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 25251–25263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastore, S.; Mascia, F.; Mariani, V.; Girolomoni, G. The epidermal growth factor receptor system in skin repair and inflammation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 1365–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, D.; Fukata, M.; Hernandez, Y.G.; Sotolongo, J.P.; Goo, T.; Maki, J.; Hayes, L.A.; Ungaro, R.C.; Chen, A.; Breglio, K.J.; et al. Toll-like receptor 4 differentially regulates epidermal growth factor-related growth factors in response to intestinal mucosal injury. Lab. Investig. 2010, 90, 1295–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuramochi, H.; Nakajima, G.; Kaneko, Y.; Nakamura, A.; Inoue, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Hayashi, K. Amphiregulin and Epiregulin mRNA expression in primary colorectal cancer and corresponding liver metastases. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirasawa, S.; Sugiyama, S.; Baba, I.; Inokuchi, J.; Sekine, S.; Ogino, K.; Kawamura, Y.; Dohi, T.; Fujimoto, M.; Sasazuki, T. Dermatitis due to epiregulin deficiency and a critical role of epiregulin in immune-related responses of keratinocyte and macrophage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13921–13926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, G.P.; Nguyen, D.X.; Chianget, A.C.; Bos, P.D.; Kim, J.Y.; Nadal, C. Mediators of vascular remodelling co-opted for sequential steps in lung metastasis. Nature 2007, 446, 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Iwanaga, K.; Choi, K.C.; Wislez, M.; Raso, M.G.; Wei, W.; Wistuba, I.I.; Kurie, J.M. Intratumoral epiregulin is a marker of advanced disease in non-small cell lung cancer patients and confers invasive properties on EGFR-mutant cells. Cancer Prev. Res. 2008, 1, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, K.; Li, S.L.; Gan, Y.H.; Wang, C.Y.; Yu, G.Y. Epiregulin promotes migration and invasion of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma cell line SACC-83 through activation of ERK and Akt. Oral Oncol. 2009, 45, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, N.; Araki, K.; Kuwano, H.; Shirabe, K. Cancer-associated fibroblasts in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 6841–6850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, G.C.; Candido, S.; Cervello, M.; Nicolosi, D.; Raiti, F.; Travali, S.; Spandidos, D.A.; Libra, M. The tumor microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 40, 1733–1747. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Chen, W.; Leng, S.; Padilla, M.T.; Saxton, B.; Hutt, J.; Tessema, M.; Kato, K.; Kim, K.C.; A Belinsky, S.; et al. Muc1 knockout potentiates murine lung carcinogenesis involving an epiregulin-mediated EGFR activation feedback loop. Carcinogenesis 2017, 38, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neufert, C.; Becker, C.; Tureci, O.; Waldner, M.J.; Backert, I.; Floh, K.; Atreya, I.; Leppkes, M.; Jefremow, A.; Vieth, M.; et al. Tumor fibroblast-derived epiregulin promotes growth of colitis-associated neoplasms through ERK. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1428–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Shi, Y.; Lv, Y.; Yuan, S.; Ramirez, C.F.A.; Lieftink, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Dias, M.H.; et al. EGFR activation limits the response of liver cancer to lenvatinib. Nature 2021, 595, 730–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, U.E.; Friedman, S.L. Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2011, 25, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, Z.; Fan, M.; Tu, B.; Tang, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Yuan, M.; Bai, J.; Huo, S.; et al. The Lin28b/Wnt5a axis drives pancreas cancer through crosstalk between cancer associated fibroblasts and tumor epithelium. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makino, Y.; Hikita, H.; Kodama, T.; Shigekawa, M.; Yamada, R.; Sakamori, R.; Eguchi, H.; Morii, E.; Yokoi, H.; Mukoyama, M.; et al. CTGF mediates tumor-stroma interactions between hepatoma cells and hepatic stellate cells to accelerate HCC progression. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 4902–4914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Jin, Y.; Marchetti, M.; Lewis, M.R.; Hammouda, O.T.; Edgar, B.A. EGFR signaling activates intestinal stem cells by promoting mitochondrial biogenesis and beta-oxidation. Curr. Biol. 2022, 32, 3704–3719.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciardiello, F.; Tortora, G. EGFR antagonists in cancer treatment. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1160–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; He, H.-W.; Sun, H.-X.; Ren, K.-H.; Shao, R.-G. Dual knockdown of N-ras and epiregulin synergistically suppressed the growth of human hepatoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 387, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagahara, T.; Shiraha, H.; Sawahara, H.; Uchida, D.; Takeuchi, Y.; Iwamuro, M.; Kataoka, J.; Horiguchi, S.; Kuwaki, T.; Onishi, H. Hepatic stellate cells promote upregulation of epithelial cell adhesion molecule and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatic cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 1169–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Donato, M.; Di Zazzo, E.; Salvati, A.; Sorrentino, C.; Giurato, G.; Fiore, D.; Proto, M.C.; Rienzo, M.; Casamassimi, A.; Gazzerro, P. RIZ2 at the crossroad of the EGF/EGFR signaling in colorectal cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Yeat, N.Y.; Wang, Y.T.; Lin, S.Y.; Kuo, I.Y.; Wu, K.P.; Wang, W.J.; Wang, W.C.; Su, W.C.; Wang, Y.C. PTPN23 ubiquitination by WDR4 suppresses EGFR and c-MET degradation to define a lung cancer therapeutic target. Cell. Death Dis. 2023, 14, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Cai, E.; Zheng, M.; Liu, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, S. TSPAN8 regulates EGFR/AKT pathway to enhance metastasis in gastric cancer. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 7955–7965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhong, X.; Liu, Q. Effect of LGR4/EGFR signaling on cell growth and cancer stem cell-like characteristics in liver cancer. Cytokine 2023, 165, 156185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Pan, J.; Yu, L.; Liu, H.; Shu, X.; Sun, L.; Lou, J.; Yang, Z.; Ran, Y. Tumor endothelial cells promote metastasis and cancer stem cell-like phenotype through elevated Epiregulin in esophageal cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 6, 2277–2288. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bormann, F.; Stinzing, S.; Tierling, S.; Morkel, M.; Markelova, M.R.; Walter, J.; Weichert, W.; Roßner, F.; Kuhn, N.; Perner, J. Epigenetic regulation of Amphiregulin and Epiregulin in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, D.S.; Cheng, X.; Pawlowski, J.E.; Wallace, A.R.; Ferrer, P.; Molloy, C.J. Epiregulin is a potent vascular smooth muscle cell-derived mitogen induced by angiotensin II, endothelin-1, and thrombin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 1633–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mise, M.; Arii, S.; Higashituji, H.; Furutani, M.; Niwano, M.; Harada, T.; Ishigami, S.; Toda, Y.; Nakayama, H. Clinical significance of vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor gene expression in liver tumor. Hepatology 1996, 23, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoong, K.F.; Afford, S.C.; Jones, R.; Aujla, P.; Qin, S.; Price, K.; Hubscher, S.G.; Adams, D.H. Expression and function of CXC and CC chemokines in human malignant liver tumors: A role for human monokine induced by gamma-interferon in lymphocyte recruitment to hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 1999, 30, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparmann, A.; Bar-Sagi, D. Ras-induced interleukin-8 expression plays a critical role in tumor growth and angiogenesis. Cancer Cell 2004, 6, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Xu, X.; Wang, L.; Zhu, B.; Wang, X.; Xia, J. The role of EGF-EGFR signalling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma inflammatory microenvironment. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2014, 18, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.J.; Li, Y.B.; Yang, L.X.; Cheng, H.J.; Liu, X.; Chen, H. Roles of the CXCL8-CXCR1/2 Axis in the Tumor Microenvironment and Immunotherapy. Molecules 2021, 27, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Qi, F.; Zhao, F.; Li, G.; Shao, S.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, L.; Feng, Y. Cancer-associated fibroblasts enhance tumor-associated macrophages enrichment and suppress NK cells function in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.W.; Yang, L.Q.; Zhao, F.; Chen, C.W.; Xu, L.H.; Fu, J.; Li, S.L.; Ge, X.Y. Epiregulin promotes lung metastasis of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma. Theranostics 2017, 7, 3700–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omi, K.; Matsuo, Y.; Ueda, G.; Aoyama, Y.; Kato, T.; Hayashi, Y.; Imafuji, H.; Saito, K.; Tsuboi, K.; Morimoto, M. Escin inhibits angiogenesis by suppressing interleukin-8 and vascular endothelial growth factor production by blocking nuclear factor-kappaB activation in pancreatic cancer cell lines. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 45, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, S.; Chen, Y.; Gong, Y.; Li, Z.; Xie, R.; Lin, Y.; Zou, B.; Li, J.; Zeng, L. Predictive value of intratumour inflammatory cytokine mRNA levels of hepatocellular carcinoma patients and activation of two distinct pathways govern IL-8 induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human hepatic cancer cell lines. Cytokine 2019, 119, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, H.; Czigany, Z.; Lurje, I.; Reichelt, S.; Bednarsch, J.; Strnad, P.; Trautwein, C.; Roderburg, C.; Tacke, F.; Gaisa, N.T. Impact of angiogenesis- and hypoxia-associated polymorphisms on tumor recurrence in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing surgical resection. Cancers 2020, 12, 3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitagawa, K.; Moriya, K.; Kaji, K.; Saikawa, S.; Sato, S.; Nishimura, N.; Namisaki, T.; Akahane, T.; Mitoro, A.; Yoshiji, H. Atorvastatin augments gemcitabine-mediated anti-cancer effects by inhibiting Yes-associated protein in human cholangiocarcinoma cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Human | Forward | Reverse | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| CDK1 | TTGGATTCTATCCCTCCTGG | CTGGAGTTGAGTAACGAGCTGA | NM_001786.5 |
| CDK2 | TGGTACCGAGCTCCTGAAAT | GAATCTCCAGGGAATAGGGC | NM_052827.4 |
| CYCLINA1 | CCGTGGAGTCTGAAGCAATG | CTCCTGTACTGCCCATTTGC | NM_001413923.1 |
| CYCLINB1 | GAACCTGAGCCAGAACCTGA | ACAGGTCTTCTTCTGCAGGG | NM_031966.4 |
| CYCLIND1 | CCGTCCATGCGGAAGATC | ATGGCCAGCGGGAAGAC | NM_053056.3 |
| CYCLINE1 | CGCTGATGAAGATGCACACA | ACAGAAGAGAACGTGGAGCA | NM_001322262.2 |
| CDK4 | CCCACACAAGCGAATCTCTG | ACCCTCCATAGCCTCAGAGA | NM_000075.4 |
| CDK6 | AGGCATTTTGGGAACTGTTG | TCCCATCCACTTCAAAGGAG | NM_001145306.2 |
| EREG | ACTGGTGTCCGATGTGAACA | TTCAGACTTGCGGCAACTCT | NM_001432.3 |
| EGF | CAGGGAAGATGACCACCACT | CAGTTCCCACCACTTCAGGT | NM_001963.6 |
| HBEGF | TGGGAACTCACTTTCCCTTG | CAGCTCCAATGTTCCCTGTT | NM_001945.3 |
| 18S rRNA | AAACGGCTACCACATCCAAG | CCTCCAATGGATCCTCGTTA | NR_003286.4 |
| TGFA | AATCCATCAGCAGGGATCTG | GATTTGGCCTGAAATGCCTA | NM_003236.4 |
| AREG | TGGATTGGACCTCAATGACA | AGCCAGGTATTTGTGGTTCG | NM_001657.3 |
| BTC | GCTCATTCATGCCCTTTCTC | AATTTCGAGAGCCACCATTG | NM_001316963.2 |
| IL-8 | TAGCAAAATTGAGGCCAAGG | AAACCAAGGCACAGTGGAAC | NM_000584.4 |
| Mouse | Forward | Reverse | Accession Number |
| 18s rrna | CGCGGTTCTATTTTGTTGGT | AGTCGGCATCGTTTATGGTC | NR_003278.3 |
| Cd34 | GGGTAGCTCTCTGCCTGATG | TCTCTGAGATGGCTGGTGTG | NM_133654.4 |
| Flt1 | TCACTCAGCGCATGGCAATA | CTCTCCTTCCGTCGGCATTT | NM_001159920.2 |
| Kdr | CAAGTGGCTAAGGGCATGGA | ATTTCAAAGGGAGGCGAGCA | NM_002253.4 |
| Pcam1 | GACGTGCAGTACACGGAAGT | GGAGCCTTCCGTTCTAGAGTAT | NM_000442.5 |
| Angiogenic Factors Listed in the Array-Membrane | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Posi | Posi | Nega | Nega | Angiogenin | EGF | ENA-78 | bFGF |
| Posi | Posi | Nega | Nega | Angiogenin | EGF | ENA-78 | bFGF |
| GRO | IFN-γ | IGF-1 | IL-6 | IL-8 | Leptin | MCP-1 | PDGF-BB |
| GRO | IFN-γ | IGF-1 | IL-6 | IL-8 | Leptin | MCP-1 | PDGF-BB |
| PIGF | RANTES | TGF-β1 | TIMP-1 | TIMP-2 | Thrombo- poietin | VEGF-A | VEGF-D |
| PIGF | RANTES | TGF-β1 | TIMP-1 | TIMP-2 | Thrombo- poietin | VEGF-A | VEGF-D |
| Blank | Blank | Blank | Blank | Blank | Blank | Nega | Posi |
| Blank | Blank | Blank | Blank | Blank | Blank | Nega | Posi |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kubo, T.; Nishimura, N.; Kaji, K.; Tomooka, F.; Shibamoto, A.; Iwai, S.; Suzuki, J.; Kawaratani, H.; Namisaki, T.; Akahane, T.; et al. Role of Epiregulin on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Hepatocarcinogenesis as a Mediator via EGFR Signaling in the Cancer Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4405. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084405
Kubo T, Nishimura N, Kaji K, Tomooka F, Shibamoto A, Iwai S, Suzuki J, Kawaratani H, Namisaki T, Akahane T, et al. Role of Epiregulin on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Hepatocarcinogenesis as a Mediator via EGFR Signaling in the Cancer Microenvironment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(8):4405. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084405
Chicago/Turabian StyleKubo, Takahiro, Norihisa Nishimura, Kosuke Kaji, Fumimasa Tomooka, Akihiko Shibamoto, Satoshi Iwai, Junya Suzuki, Hideto Kawaratani, Tadashi Namisaki, Takemi Akahane, and et al. 2024. "Role of Epiregulin on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Hepatocarcinogenesis as a Mediator via EGFR Signaling in the Cancer Microenvironment" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 8: 4405. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084405
APA StyleKubo, T., Nishimura, N., Kaji, K., Tomooka, F., Shibamoto, A., Iwai, S., Suzuki, J., Kawaratani, H., Namisaki, T., Akahane, T., & Yoshiji, H. (2024). Role of Epiregulin on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Hepatocarcinogenesis as a Mediator via EGFR Signaling in the Cancer Microenvironment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(8), 4405. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25084405





