Systematic Review of IL-1, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, IL-15, and IL-18 Gene Polymorphisms and Meta-Analysis of IL-6 Variant and Its Association with Overweight and Obesity Risk in Men
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Search Strategies
2.4. Study Selection and Data Extraction
2.5. Risk-of-Bias Assessment
2.6. Data Synthesis and Meta-Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
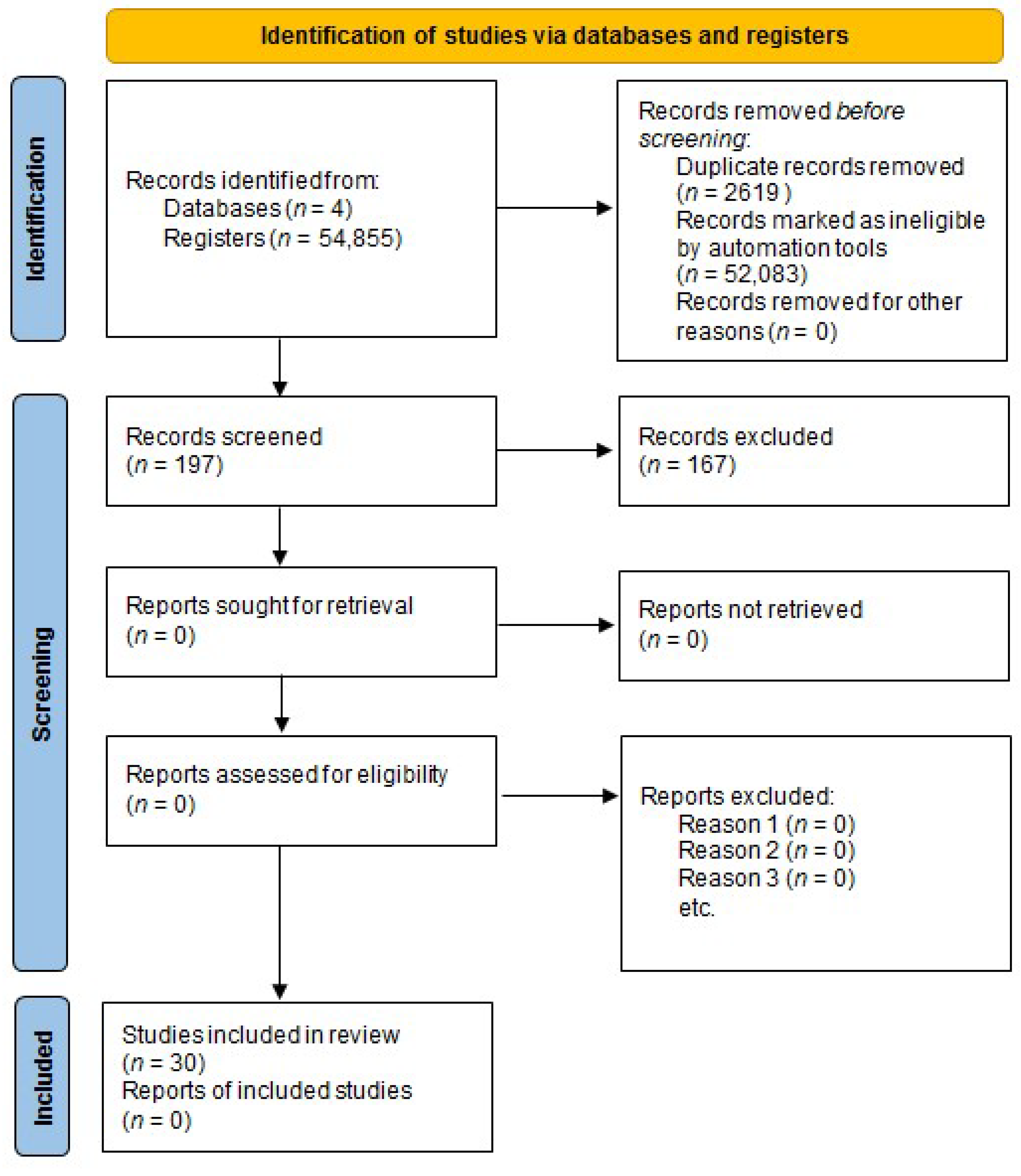
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
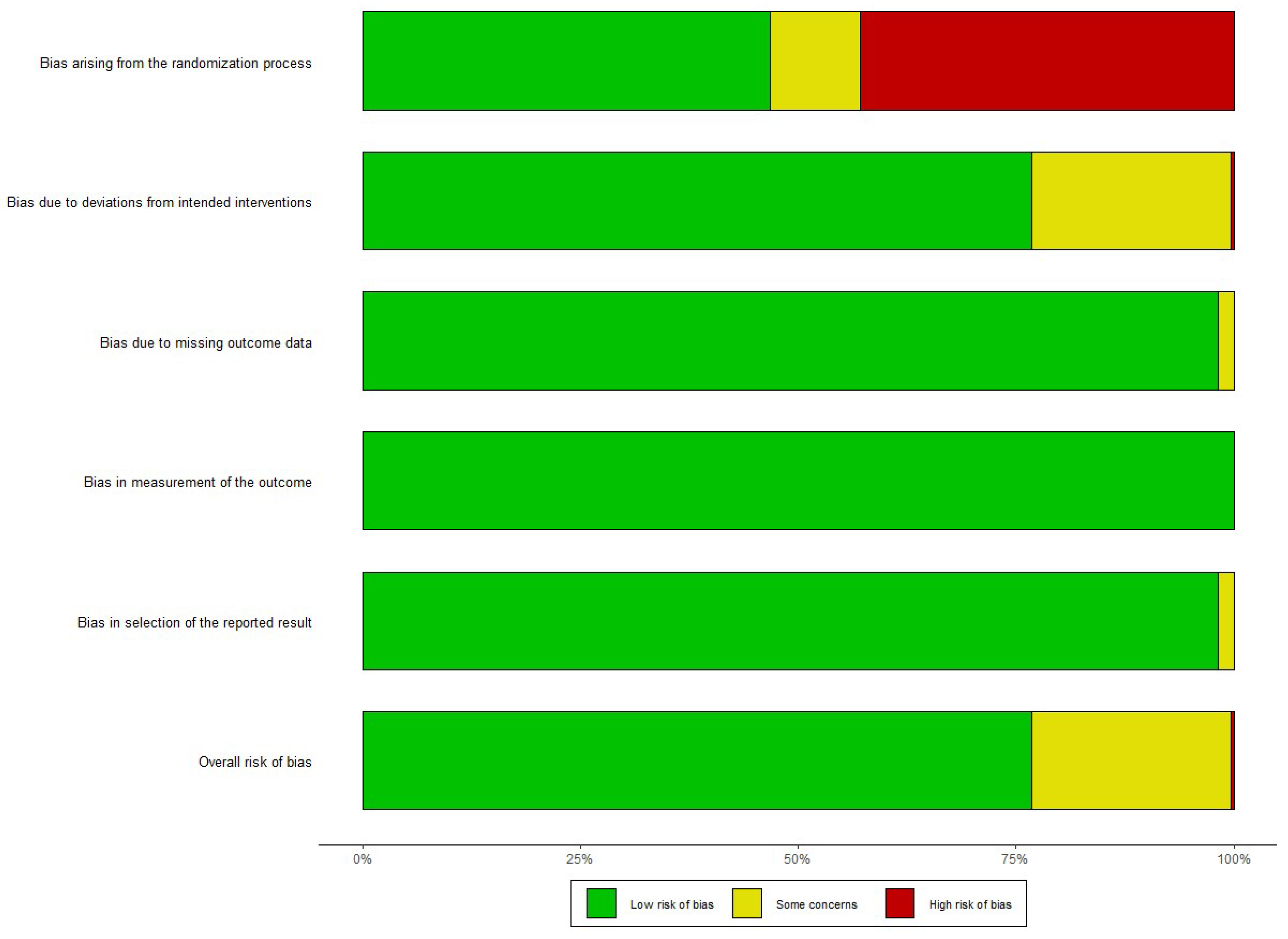
3.3. Risk of Bias
3.4. Review
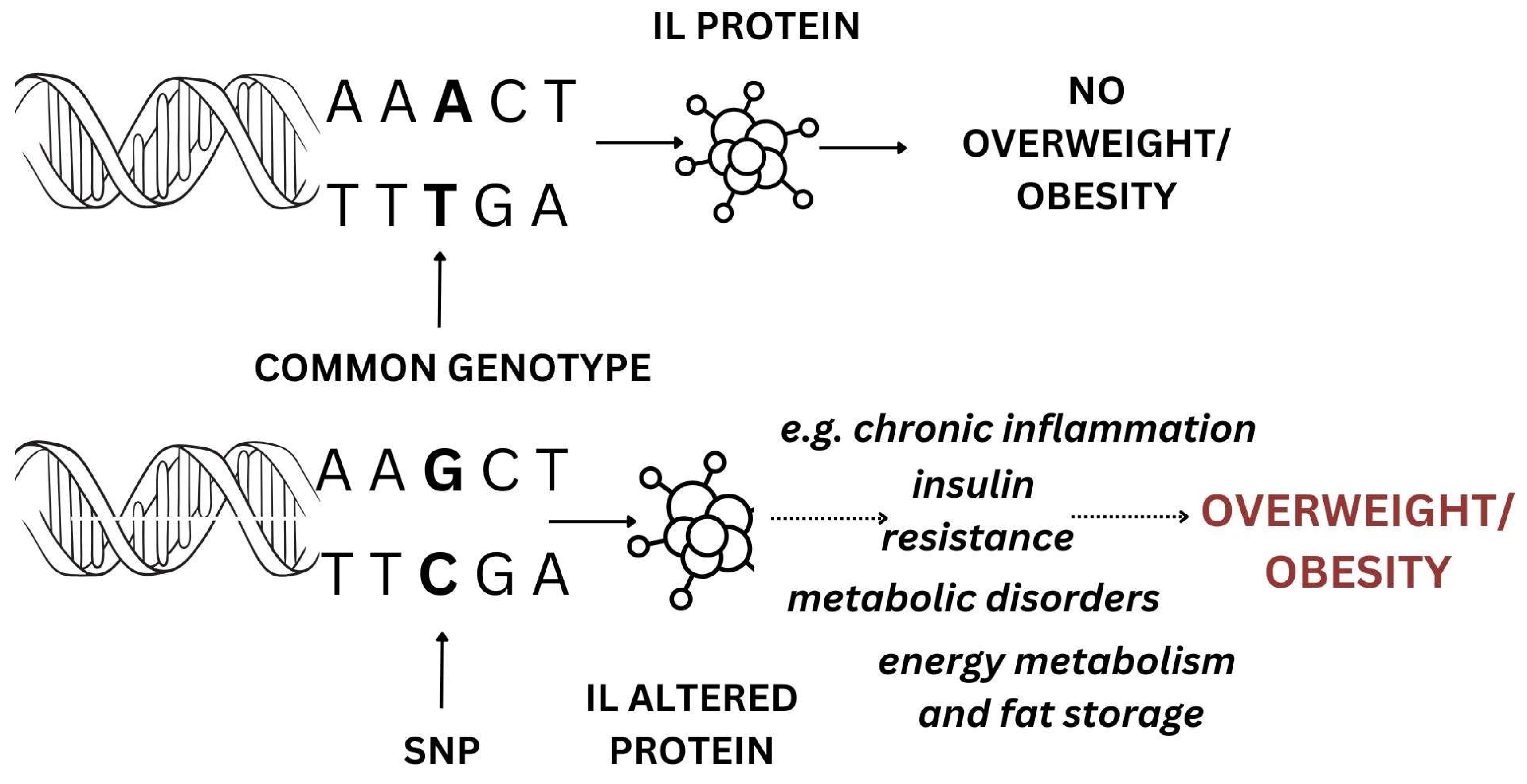
3.4.1. IL Gene Polymorphisms and Overweight/Obesity
3.4.2. IL-1 Gene Complex Polymorphisms
3.4.3. IL-4 Gene Polymorphisms
3.4.4. IL-6 Gene Polymorphisms
3.4.5. IL-10 Gene Polymorphisms
3.4.6. IL-15 Gene Polymorphisms
3.4.7. IL-18 Gene Polymorphisms
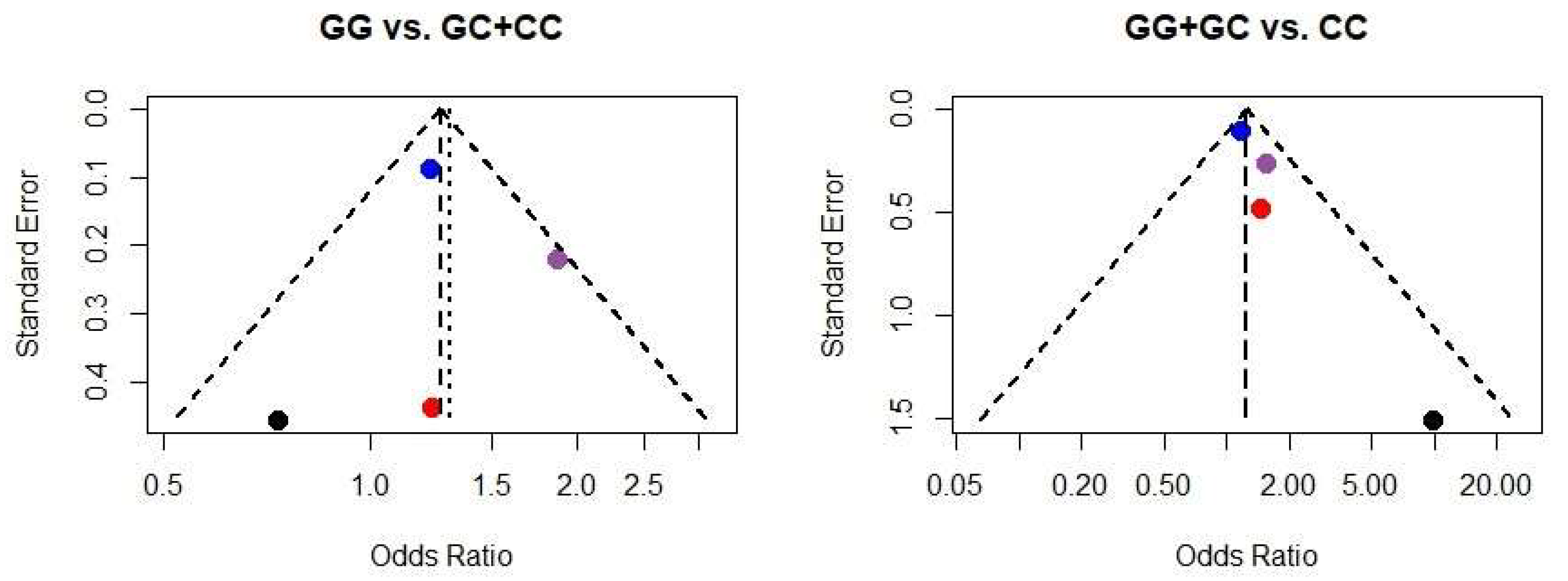
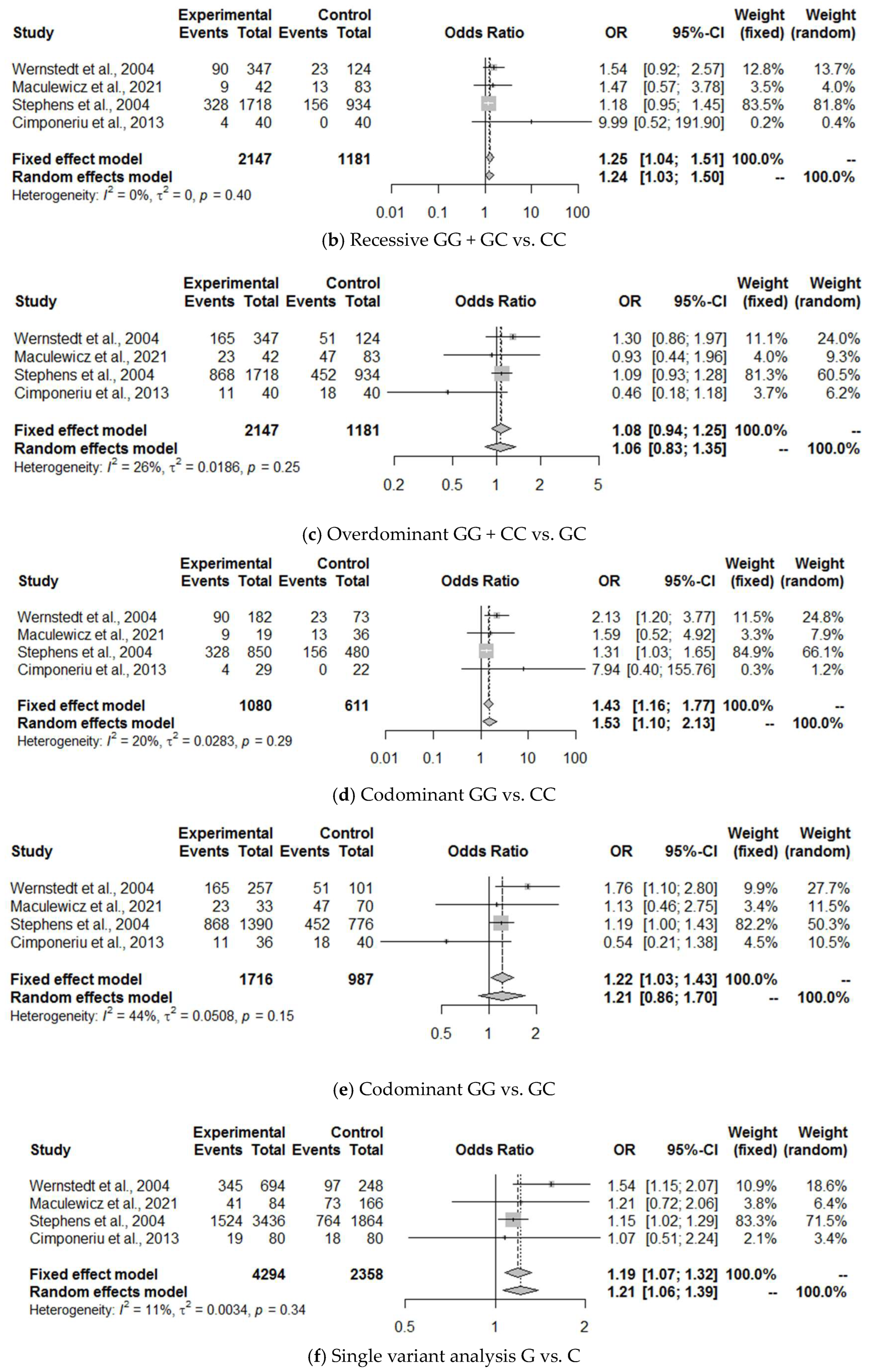
3.5. Meta-Analysis
3.6. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight. 2023. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 7 November 2023).
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration. Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: A pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128·9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet 2017, 390, 2627–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchard, C. Genetics of Obesity: What We Have Learned Over Decades of Research. Obesity 2021, 29, 802–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, M.; Sharifi, F.; Shahriari, S.; Khoshnevisan, K.; Larijani, B.; Amoli, M.M. Association of interleukin-6 polymorphisms with obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cytokine 2019, 123, 154769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kwon, Y.D.; Hong, S.H.; Jeong, H.J.; Kim, H.M.; Um, J.Y. Interleukin-1 beta gene polymorphism and traditional constitution in obese women. Int. J. Neurosci. 2008, 118, 793–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpelli, D.; Cardellini, M.; Andreozzi, F.; Laratta, E.; Hribal, M.L.; Marini, M.A.; Tassi, V.; Lauro, R.; Perticone, F.; Sesti, G. Variants of the interleukin-10 promoter gene are associated with obesity and insulin resistance but not type 2 diabetes in Caucasian Italian subjects. Diabetes 2006, 55, 1529–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeks, K.A.C.; Bentley, A.R.; Gouveia, M.H.; Chen, G.; Zhou, J.; Lei, L.; Adeyemo, A.A.; Doumatey, A.P.; Rotimi, C.N. Genome-wide analyses of multiple obesity-related cytokines and hormones informs biology of cardiometabolic traits. Gen. Med. 2021, 13, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppack, S.W. Pro-inflammatory cytokines and adipose tissue. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2001, 60, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kern, L.; Mittenbühler, M.J.; Vesting, A.J.; Ostermann, A.L.; Wunderlich, C.M.; Wunderlich, F.T. Obesity-induced TNFα and IL-6 signaling: The missing link between obesity and inflammation- driven liver and colorectal cancers. Cancers 2019, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbe-Bürger, A.; Egyed, A.; Olt, S.; Stingl, G.; Klubal, R.; Mann, U.; Rappersberger, K.; Rot, A. Overexpression of IL-4 alters the homeostasis in the skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2002, 118, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorrilla, E.P.; Sanchez-Alavez, M.; Sugama, S.; Brennan, M.; Fernandez, R.; Bartfai, T.; Conti, B. Interleukin-18 controls energy homeostasis by suppressing appetite and feed efficiency. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11097–11102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, L.S.; Anderson, B.G. Interleukin-15, IL-15 receptor-alpha, and obesity: Concordance of laboratory animal and human genetic studies. J. Obes. 2011, 2011, 456347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, D.; Richard, J.E.; Maric, I.; Porteiro, B.; Häring, M.; Kooijman, S.; Musovic, S.; Eerola, K.; López-Ferreras, L.; Peris, E. Parabrachial Interleukin-6 Reduces Body Weight and Food Intake and Increases Thermogenesis to Regulate Energy Metabolism. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 3011–3026.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyrzak, B.; Wisniewska, A.; Majcher, A.; Popko, K.; Wasik, M.; Demkow, U. Association between metabolic disturbances and G-174C polymorphism of interleukin-6 gene in obese children. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2009, 14 (Suppl. 4), 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, G.; Skonieczna-Żydecka, K.; Madlani, A.; Ogonowski, J.; Grochans, E.; Pierzak-Sominka, J.; Brodowski, J.; Karakiewicz, B. Association between depression, parameters of adiposity and genetic polymorphisms of pro-inflammatory cytokines: IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-2 and IL-6 in subjects over 55 years old. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2016, 63, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loos, R.J.F.; Yeo, G.S.H. The genetics of obesity: From discovery to biology. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2022, 23, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The prisma 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Altman, D.G.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Jüni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savović, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A.C.; et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, J. What is heterogeneity and is it important? BMJ 2007, 334, 94–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Gupta, V.; Singh, A.K.; Tiwari, S.; Agrawal, S.; Natu, S.; Agrawal, C.; Negi, M.; Pant, A. Interleukin-6 G-174C gene polymorphism and serum resistin levels in North Indian women: Potential risk of metabolic syndrome. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2010, 30, 1445–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oana, M.C.; Claudia, B.; Carmen, D.; Maria, P.A.; Septimiu, V.; Claudiu, M. The role of IL-6 572 C/G, 190 C/T, and 174 G/C gene polymorphisms in children’s obesity. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2014, 173, 1285–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, J.W.; Hurel, S.J.; Cooper, J.A.; Acharya, J.; Miller, G.J.; Humphries, S.E. A common functional variant in the interleukin-6 gene is associated with increased body mass index in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2004, 82, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maculewicz, E.; Antkowiak, B.; Antkowiak, O.; Mastalerz, A.; Białek, A.; Cywińska, A.; Borecka, A.; Humińska-Lisowska, K.; Garbacz, A.; Lorenz, K.; et al. IL-6 Polymorphisms Are Not Related to Obesity Parameters in Physically Active Young Men. Genes 2021, 12, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyenechea, E.; Parra, D.; Martínez, J.A. Impact of interleukin 6 -174G>C polymorphism on obesity-related metabolic disorders in people with excess in body weight. Metabolism 2007, 56, 1643–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klipstein-Grobusch, K.; Möhlig, M.; Spranger, J.; Hoffmann, K.; Rodrigues, F.U.S.; Sharma, A.M.; Klaus, S.; Pfeiffer, A.F.H.; Boeing, H. Interleukin-6 g.-174G>C promoter polymorphism is associated with obesity in the EPIC-potsdam study. Obesity 2006, 14, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozen, W.; Gebregziabher, M.; Conti, D.V.; Berg, D.J.V.D.; Coetzee, G.A.; Wang, S.S.; Rothman, N.; Bernstein, L.; Hartge, P.; Morhbacher, A.; et al. Interleukin-6-related genotypes, body mass index, and risk of multiple myeloma and plasmacytoma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2006, 15, 2285–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimponeriu, D.; Serafinceanu, C.; Apostol, P.; Toma, M.; Stavarachi, M.; Radu, I.; Craciun, A.; Spandole, S.; Nicolae, P.; Rusu, L.; et al. Potential association of obesity with IL6 G-174C polymorphism and TTV infections. Cent. Eur. J. Biol. 2013, 8, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, Y.H.; Rose, C.S.; Urhammer, S.A.; Kristiansen, O.P.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T.; Borch-Johnsen, K.; Jorgensen, T.; Hansen, T.; Pedersen, O.; Glümer, C.; et al. Variations of the interleukin-6 promoter are associated with features of the metabolic syndrome in Caucasian Danes. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Renzo, L.; Gloria-Bottini, F.; Saccucci, P.; Bigioni, M.; Abenavoli, L.; Gasbarrini, G.; De Lorenzo, A. Role of interleukin-15 receptor alpha polymorphisms in normal weight obese syndrome. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2009, 22, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponasenko, A.; Sinitsky, M.; Minina, V.; Vesnina, A.; Khutornaya, M.; Prosekov, A.; Barbarash, O. Immune Response and Lipid Metabolism Gene Polymorphisms Are Associated with the Risk of Obesity in Middle-Aged and Elderly Patients. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.L.; Cho, S.O.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, S.-H.; Chung, W.-S.; Chung, S.-H.; Ko, S.-G.; Jeong, C.-H.; Kim, S.-J.; Hong, S.-H.; et al. Association of interleukin-18 gene polymorphism with body mass index in women. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2012, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, L.M.; Kaye, E.K.; Wang, H.-Y.; Rogus, J.; Doucette-Stamm, L.; Kornman, K.; Garcia, R.I. Influence of Obesity on Periodontitis Progression Is Conditional on Interleukin-1 Inflammatory Genetic Variation. J. Periodontol. 2017, 88, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wernstedt, I.; Eriksson, A.L.; Berndtsson, A.; Hoffstedt, J.; Skrtic, S.; Hedner, T.; Hultén, L.M.; Wiklund, O.; Ohlsson, C.; Jansson, J.-O. A common polymorphism in the interleukin-6 gene promoter is associated with overweight. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2004, 28, 1272–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mărginean, C.; MǍrginean, C.O.; BǍnescu, C.; Meliţ, L.; Tripon, F.; Iancu, M. Impact of demographic, genetic, and bioimpedance factors on gestational weight gain and birth weight in a Romanian population: A cross-sectional study in mothers and their newborns: The Monebo study (STROBE-compliant article). Medicine 2016, 95, e4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panoulas, V.F.; Stavropoulos-Kalinoglou, A.; Metsios, G.S.; Smith, J.P.; Milionis, H.J.; Douglas, K.M.; Nightingale, P.; Kitas, G.D. Association of interleukin-6 (IL-6)-174G/C gene polymorphism with cardiovascular disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: The role of obesity and smoking. Atherosclerosis 2009, 204, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeta-Lopez, K.; Duran, J.; Elizondo, D.; Gonzales, E.; Rentfro, A.; Schwarzbach, A.E.; Nair, S. Association of interleukin-6 polymorphisms with obesity or metabolic traits in young Mexican-Americans. Obes. Sci. Pr. 2018, 4, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Miyaki, K.; Araki, J.; Zhang, L.; Omae, K.; Muramatsu, M. The interaction between the interleukin 6 receptor gene genotype and dietary energy intake on abdominal obesity in Japanese men. Metabolism 2007, 56, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthier, M.T.; Paradis, A.M.; Tchernof, A.; Bergeron, J.; Prud’homme, D.; Després, J.-P.; Vohl, M.C. The interleukin 6 -174G/C polymorphism is associated with indices of obesity in men. J. Hum. Genet. 2003, 48, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolford, J.K.; Colligan, P.B.; Gruber, J.D.; Bogardus, C. Variants in the interleukin 6 receptor gene are associated with obesity in Pima Indians. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2003, 80, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strandberg, L.; Lorentzon, M.; Hellqvist, Å.; Nilsson, S.; Wallenius, V.; Ohlsson, C.; Jansson, J.-O. Interleukin-1 system gene polymorphisms are associated with fat mass in young men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 2749–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strandberg, L.; Mellström, D.; Ljunggren, Ö.; Grundberg, E.; Karlsson, M.K.; Holmberg, A.H.; Orwoll, E.S.; Eriksson, A.L.; Svedberg, J.; Bengtsson, M.; et al. IL6 and IL1B polymorphisms are associated with fat mass in older men: The MrOS study Sweden. Obesity 2008, 16, 710–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manica-Cattani, M.F.; Bittencourt, L.; Rocha, M.I.U.; Algarve, T.; Bodanese, L.; Rech, R.; Machado, M.; Santos, G.; Gottlieb, M.; Schwanke, C.; et al. Association between interleukin-1 beta polymorphism (+3953) and obesity. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2010, 314, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maculewicz, E.; Antkowiak, B.; Antkowiak, O.; Borecka, A.; Mastalerz, A.; Leońska-Duniec, A.; Humińska-Lisowska, K.; Michałowska-Sawczyn, M.; Garbacz, A.; Lorenz, K.; et al. The interactions between interleukin-1 family genes: IL1A, IL1B, IL1RN, and obesity parameters. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, E.; Yang, S.H.; Yoo, K.I.; Chung, I.-S.; Lee, M.-Y.; Bae, J.-H.; Seo, J.-C.; Chung, J.-H.; Shin, D.-H. Interleukin 4 receptor is associated with an increase in body mass index in Koreans. Life Sci. 2008, 82, 1040–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maculewicz, E.; Dzitkowska-Zabielska, M.; Antkowiak, B.; Antkowiak, O.; Mastalerz, A.; Garbacz, A.; Massidda, M.; Bojarczuk, A.; Dziuda, Ł.; Cięszczyk, P. Association of Interleukin Genes IL10 and IL10RB with Parameters of Overweight in Military Students. Genes 2022, 13, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maculewicz, E.; Mastalerz, A.; Antkowiak, B.; Antkowiak, O.; Garbacz, A.; Szarska, E.; Rusin, P.; Cywińska, A.; Białek, A.; Cięszczyk, P. The effect of IL10 gene polymorphism on obesity parameters in highly physically active young men. Biol. Sport. 2022, 39, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Barquero, V.; De Marco, G.; Martínez-Hervas, S.; Adam-Felici, V.; Pérez-Soriano, C.; Gonzalez-Albert, V.; Rojo, G.; Ascaso, J.F.; Real, J.T.; Garcia-Garcia, A.B.; et al. Are IL18RAP gene polymorphisms associated with body mass regulation? BMJ Open 2017, 7, e017875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, A.P.; Gillett, R. How to do a meta-analysis. Br. J. Math. Stat. Psychol. 2010, 63 Pt 3, 665–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcaterra, V.; De Amici, M.; Klersy, C.; Torre, C.; Brizzi, V.; Scaglia, F.; Albanesi, M.; Albertini, R.; Allais, B.; Larizza, D. Adiponectin, IL-10 and Metabolic Syndrome in Obese Children and Adolescents. Acta Biomed. 2009, 80, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Esposito, K.; Pontillo, A.; Giugliano, F.; Giugliano, G.; Marfella, R.; Nicoletti, G.; Giugliano, D. Association of low interleukin-10 levels with the metabolic syndrome in obese women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 1055–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Renzo, L.; Del Gobbo, V.; Bigioni, M.; Premrov, M.G.; Cianci, R.; De Lorenzo, A. Body composition analyses in normal weight obese women. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2006, 10, 191–196. [Google Scholar]
- De Lorenzo, A.; Martinoli, R.; Vaia, F.; Di Renzo, L. Normal weight obese (NWO) women: An evaluation of a candidate new syndrome. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2006, 16, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Ji, Y.; Kersten, S.; Qi, L. Mechanisms of inflammatory responses in obese adipose tissue. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2012, 32, 261–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature 2006, 444, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastard, J.-P.; Maachi, M.; Lagathu, C.; Kim, M.J.; Caron, M.; Vidal, H.; Capeau, J.; Feve, B. Recent advances in the relationship between obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2006, 17, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Baat, A.; Trinh, B.; Ellingsgaard, H.; Donath, M.Y. Physiological role of cytokines in the regulation of mammalian metabolism. Trends Immunol. 2023, 44, 613–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedemann, S.J.; Trimigliozzi, K.; Dror, E.; Meier, D.T.; Molina-Tijeras, J.A.; Rachid, L.; Le Foll, C.; Magnan, C.; Schulze, F.; Stawiski, M.; et al. The cephalic phase of insulin release is modulated by IL-1β. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 991–1003.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, M.C.; Wernstedt, I.; Berndtsson, A.; Enge, M.; Bell, M.; Hultgren, O.; Horn, M.; Ahrén, B.; Enerback, S.; Ohlsson, C.; et al. Mature-onset obesity in interleukin-1 receptor I knockout mice. Diabetes 2006, 55, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuki, T.; Horai, R.; Sudo, K.; Iwakura, Y. IL-1 plays an important role in lipid metabolism by regulating insulin levels under physiological conditions. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, A.J.; Kraakman, M.J.; Kammoun, H.L.; Dragoljevic, D.; Lee, M.K.S.; Lawlor, K.E.; Wentworth, J.M.; Vasanthakumar, A.; Gerlic, M.; Whitehead, L.W.; et al. IL-18 Production from the NLRP1 Inflammasome Prevents Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netea, M.G.; Joosten, L.A.B. The NLRP1-IL18 Connection: A Stab in the Back of Obesity-Induced Inflammation. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 6–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michurina, S.; Agareva, M.; Zubkova, E.; Menshikov, M.; Stafeev, I.; Parfyonova, Y. IL-4 activates the futile triacylglyceride cycle for glucose utilization in white adipocytes. Biochem. J. 2024, 481, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajuwon, K.M.; Spurlock, M.E. Direct regulation of lipolysis by interleukin-15 in primary pig adipocytes. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2004, 287, R608–R611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barra, N.G.; Reid, S.; MacKenzie, R.; Werstuck, G.; Trigatti, B.L.; Richards, C.; Holloway, A.C.; Ashkar, A.A. Interleukin-15 contributes to the regulation of murine adipose tissue and human adipocytes. Obesity 2010, 18, 1601–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furmanczyk, P.S.; Quinn, L.B.S. Interleukin-15 increases myosin accretion in human skeletal myogenic cultures. Cell Biol. Int. 2003, 27, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pistilli, E.E.; Bogdanovich, S.; Garton, F.; Yang, N.; Gulbin, J.P.; Conner, J.D.; Anderson, B.G.; Quinn, L.S.; North, K.; Ahima, R.S.; et al. Loss of IL-15 receptor α alters the endurance, fatigability, and metabolic characteristics of mouse fast skeletal muscles. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 3120–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanemi, A.; St-Amand, J. Interleukin-6 as a “metabolic hormone”. Cytokine 2018, 112, 32–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, B.; Peletier, M.; Simonsen, C.; Plomgaard, P.; Karstoft, K.; Pedersen, B.K.; van Hall, G.; Ellingsgaard, H. Blocking endogenous IL-6 impairs mobilization of free fatty acids during rest and exercise in lean and obese men. Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Febbraio, M.A.; Hiscock, N.; Sacchetti, M.; Fischer, C.P.; Pedersen, B.K. Interleukin-6 is a novel factor mediating glucose homeostasis during skeletal muscle contraction. Diabetes 2004, 53, 1643–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellingsgaard, H.; Hauselmann, I.; Schuler, B.; Habib, A.M.; Baggio, L.L.; Meier, D.T.; Eppler, E.; Bouzakri, K.; Wueest, S.; Muller, Y.D.; et al. Interleukin-6 enhances insulin secretion by increasing glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion from L cells and alpha cells. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hall, G.; Steensberg, A.; Sacchetti, M.; Fischer, C.; Keller, C.; Schjerling, P.; Hiscock, N.; Møller, K.; Saltin, B.; Febbraio, M.A.; et al. Interleukin-6 stimulates lipolysis and fat oxidation in humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 3005–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, E.W.; Carey, A.L.; Sacchetti, M.; Steinberg, G.R.; Macaulay, S.L.; Febbraio, M.A.; Pedersen, B.K. Acute IL-6 treatment increases fatty acid turnover in elderly humans in vivo and in tissue culture in vitro. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 288, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallenius, K.; Wallenius, V.; Sunter, D.; Dickson, S.L.; Jansson, J.O. Intracerebroventricular interleukin-6 treatment decreases body fat in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 293, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, R.H.; Lehrskov, L.L.; Wedell-Neergaard, A.S.; Legaard, G.E.; Ried-Larsen, M.; Karstoft, K.; Krogh-Madsen, R.; Pedersen, B.K.; Ellingsgaard, H.; Rosenmeier, J.B. Aerobic exercise induces cardiac fat loss and alters cardiac muscle mass through an interleukin-6 receptor-dependent mechanism. Circulation 2019, 140, 1684–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunschede, S.; Kubant, R.; Akilen, R.; Thomas, S.; Anderson, G.H. Decreased appetite after high-intensity exercise correlates with increased plasma interleukin-6 in normal-weight and overweight/obese boys. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2017, 1, e000398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornath, D.P.D.; McKie, G.L.; McCarthy, S.F.; Vanderheyden, L.W.; Howe, G.J.; Medeiros, P.J.; Hazell, T.J. Interleukin-6 is not involved in appetite regulation following moderate-intensity exercise in males with normal weight and obesity. Obesity 2023, 31, 2315–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roytblat, L.; Rachinsky, M.; Fisher, A.; Greemberg, L.; Shapira, Y.; Douvdevani, A.; Gelman, S. Raised interleukin-6 levels in obese patients. Obes. Res. 2000, 8, 673–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sindhu, S.; Thomas, R.; Shihab, P.; Sriraman, D.; Behbehani, K.; Ahmad, R. Obesity is a positive modulator of IL-6R and IL-6 expression in the subcutaneous adipose tissue: Significance for metabolic inflammation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziccardi, P.; Nappo, F.; Giugliano, G.; Esposito, K.; Marfella, R.; Cioffi, M.; D’andrea, F.; Molinari, A.M.; Giugliano, D. Reduction of inflammatory cytokine concentrations and improvement of endothelial functions in obese women after weight loss over one year. Circulation 2002, 105, 804–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruun, J.M.; Verdich, C.; Toubro, S.; Astrup, A.; Richelsen, B. Association between measures of insulin sensitivity and circulating levels of interleukin-8, interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Effect of weight loss in obese men. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2003, 148, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koc, G.; Doran, T.; Uygur, M.M.; Kirac, D. Obesity is associated with IL-6 gene polymorphisms rs1800795 and rs1800796 but not SOCS3 rs4969170. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 2041–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubaszek, A.; Pihlajamäki, J.; Punnonen, K.; Karhapää, P.; Vauhkonen, I.; Laakso, M. The C-174G promoter polymorphism of the IL-6 gene affects energy expenditure and insulin sensitivity. Diabetes 2003, 52, 558–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isshiki, H.; Akira, S.; Tanabe, O.; Nakajima, T.; Shimamoto, T.; Hirano, T.; Kishimoto, T. Constitutive and interleukin-1 (IL-1)-inducible factors interact with the IL-1-responsive element in the IL-6 gene. Mol. Cell Biol. 1990, 10, 2757–2764. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


| Interleukin Gene | Polymorphism (rs) | Author | Population | Cohort (Sex, Sample Size) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-6 | 1800795, 1800796 | Wernstedt et al., 2004 [33] | Caucasian | 355 males, 204 females |
| IL-6 | 1800795 | Gupta et al., 2010 [20] | Caucasian | 370 females |
| IL-6 | 1800795, 1800796 | Mărginean et al., 2016 [34] | Caucasian | 309 females and 309 newborns of unknown sex |
| IL-6 | 1800795, 1800796 | Oana et al., 2014 [21] | Caucasian | 114 males, 98 females |
| IL-6 | 1800795 | Panoulas et al., 2009 [35] | Caucasian | 270 males, 535 females |
| IL-6 | 1800795 | Stephens et al., 2004 [22] | Caucasian | 2652 males |
| IL-6 | 1800797, 1800796, 1800795 | Boeta-Lopez et al., 2018 [36] | Mexican Americans | 146 males, 291 females |
| IL-6 | 1800795, 1800796, 13306435 | Maculewicz et al., 2021 [23] | Caucasian | 125 males |
| IL-6 | 1800795 | Goyenechea et al., 2007 [24] | Caucasian | 54 males, 52 females |
| IL-6 | 1800795 | Klipstein-Grobusch et al., 2006 [25] | Caucasian | 334 males, 334 females |
| IL-6 | 1800795, 1800797, 1800796 | Cozen et al., 2006 [26] | non-Latino White (White), African American, Latino White (Latino), Asian/other | 218 males, 170 females |
| IL-6 | 8192284 | Song et al., 2007 [37] | Asian | 321 males, 37 females |
| IL-6 | 1800795 | Berthier et al., 2003 [38] | French-Canadian | 270 males |
| IL-6 | 1800795 | Cimponeriu et al., 2013 [27] | Caucasian | 80 males, 220 females |
| IL-6 | 2228145, 2229238, 4845623 | Wolford et al., 2003 [39] | Pima Indian | 1813 males, 1920 females |
| IL-6 | 1800795, 1800797, 1800796 | Hamid et al., 2005 [28] | Caucasian | 3919 males, 3640 females |
| IL-1 | 1143634 | Strandberget al., 2006 [40] | Caucasian | 1068 males |
| IL-1 | 1143634 | Strandberg et al., 2008 [41] | Caucasian | 3014 males |
| IL-1 | 1143634 | Lee et al., 2008 [5] | Asian | 181 females |
| IL-1 | 1143634 | Manica-Cattani et al., 2010 [42] | Caucasian | 880 participants of an unknown number of males and females |
| IL-1 | 16944, 1143623, 4848306, 1143633, 17561, 1143634 | Wilkins et al., 2017 [32] | 288 White and 4 Black | 292 males |
| IL-1 | 1800587,1143634, 2234677 | Maculewicz et al., 2022 [43] | Caucasian | 101 males |
| IL-10 | 1518111, 1878672, 3024496, 3024498, 3024505 | Ha et al., 2008 [44] | Asian | 446 males, 421 females |
| IL-10 | 1800896, 1800871, 1800872 | Maculewicz et al., 2022 [45] | Caucasian | 139 males |
| IL-10 | 1800896, 1800871, 1800872 | Scarpelli et al., 2006 [6] | Caucasian | 759 males, 923 females |
| IL-10 | 1518111, 1878672, 3024496, 3024498, 3024505 | Maculewicz et al., 2022 [46] | Caucasian | 131 males |
| IL-15 | 3136617, 3136618, 2296135 | Di Renzo et al., 2009 [29] | Caucasian | 108 females |
| IL-18 | 187238 | Ponasenko et al., 2022 [30] | Caucasian | 319 males, 241 females |
| IL-18 | 1946518, 187238 | Kim et al., 2012 [31] | Asian | 101 males and 170 females; 409 controls of unknown sex |
| IL-18 | 7559479, 2293225, 2272127 | Martínez-Barquero et al., 2017 [47] | Caucasian | 966 males, 1006 females |
| Interleukin Gene | Polymorphism (rs) | Author | Age | Body Composition Assessment | Additional Information |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-6 | 1800795, 1800796 | Wernstedt et al., 2004 [33] | 56.8 ± 0.31 | normal weight, overweight | healthy, and with hypertension, diabetes not excluded |
| IL-6 | 1800795 | Gupta et al., 2010 [20] | obese: 29.12 ± 6.51, non-obese: 28.04 ± 5.86 | non-obese, obese | obese group had significantly higher values for blood glucose, CRP-HOMA-IR |
| IL-6 | 1800795, 1800796 | Mărginean et al., 2016 [34] | 29.20 ± 5.44 | normal weight, overweight, obesity | 0.60% diabetics, 4.50% gestational arterial hypertension |
| IL-6 | 1800795, 1800796 | Oana et al., 2014 [21] | obese: 9.61 ± 3.9, non-obese: 10.67 ± 4.54 | normal weight, obesity | control patients with normal nutritional status, and obese patients |
| IL-6 | 1800795 | Panoulas et al., 2009 [35] | RA patients: 61.3 ± 12.1, controls: 50.1 ± 15.7 | overweight, obesity | cardiovascular diseases, RA, smoking |
| IL-6 | 1800795 | Stephens et al., 2004 [22] | obese: 64.4 (10.4), non-obese: 69.2 (10.8) | normal weight, overweight, obesity | metabolic syndrome including elevated systolic and diastolic blood pressure, triglycerides, total cholesterol: HDL-cholesterol ratio, CRP, and lower HDL |
| IL-6 | 1800797, 1800796, 1800795 | Boeta-Lopez et al., 2018 [36] | 17 ± 8.26 | normal weight, overweight, obesity | HDL, HOMA-IR, LDL |
| IL-6 | 1800795, 1800796, 13306435 | Maculewicz et al., 2021 [23] | CONBMI 21.87 ± 1.57, OVERBMI 21.98 ± 1.79, CONFat 21.92 ± 1.79, OVERFat 21.84 ± 1.87 | normal weight, overweight, obesity | physical activity |
| IL-6 | 1800795 | Goyenechea et al., 2007 [24] | median (IQR): 34 (25–43) | obesity | metabolic disorders, such as hypertension, atherogenic dyslipidemia, and insulin resistance evaluated by the homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance index |
| IL-6 | 1800795 | Klipstein- Grobusch et al., 2006 [25] | obese: 53.9 ± 7.3, non-obese: 53.8 ± 7.3 | normal weight, obesity | high blood pressure, smoking status, prevalence of T2DM, and myocardial infarction |
| IL-6 | 1800795, 1800797, 1800796 | Cozen et al., 2006 [26] | median age = 61 | normal weight, overweight, obesity | risk of multiple myeloma and plasmacytoma |
| IL-6 | 8192284 | Song et al., 2007 [37] | 46.1 ± 11.5 | normal weight, overweight, obesity | dietary interactions |
| IL-6 | 1800795 | Berthier et al., 2003 [38] | GG genotype: 41.83 ± 7.39, GC genotype: 42.64 ± 7.89, CC genotype: 43.64 ± 8.77 | obesity | body fat distribution (waist circumference, subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue), and metabolic responses (plasma glucose and insulin levels during an oral glucose tolerance test) |
| IL-6 | 1800795 | Cimponeriu et al., 2013 [27] | obese: 43.13 ± 12.20, non-obese: 44.21 ± 11.95 | normal weight, overweight, obesity | viral infections (TTV), hypertensive status (resting blood pressure exceeding 130/85 mm Hg or subject under antihypertensive treatment), smoking(more than five cigarettes per day for at least one year), and drinking (at least five units of alcohol per day for at least one year) |
| IL-6 | 2228145, 2229238, 4845623 | Wolford et al., 2003 [39] | NA | normal weight, overweight, obesity | T2DM |
| IL-6 | 1800795, 1800797, 1800796 | Hamid et al., 2005 [28] | 57 ± 11 | obesity | Inter99 cohort without metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetic patients |
| IL-1 | 1143634 | Strandberg et al., 2006 [40] | 18.9 ± 0.6 | obesity | Gothenburg Osteoporosis and Obesity Determinants (GOOD) study group |
| IL-1 | 1143634 | Strandberg et al., 2008 [41] | 69–81 | overweight | the Swedish part of the Osteoporotic Fractures in Men (MrOS) multicenter study |
| IL-1 | 1143634 | Lee et al., 2008 [5] | 18–62 | normal weight, overweight, and obesity | divided into three BMI groups |
| IL-1 | 1143634 | Manica-Cattani et al., 2010 [42] | 18–92 | normal weight, overweight, and obesity | divided into three BMI groups |
| IL-1 | 16944, 1143623, 4848306, 1143633, 17561, 1143634 | Wilkins et al., 2017 [32] | 29–64 | obesity | the study group from the Veterans Affairs Dental Longitudinal Study (DLS), free of chronic medical conditions at the start of the study |
| IL-1 | 1800587,1143634, 2234677 | Maculewicz et al., 2022 [43] | OVERBMI 21.8 ± 1.64, CONBMI 21.9 ± 1.61, OVERFat 21.4 ± 1.6, CONFat 21.9 ± 1.6 | normal weight, overweight | two control and two study groups based on two criteria: BMI and fat percentage, healthy, physical activity |
| IL-10 | 1518111, 1878672, 3024496, 3024498, 3024505 | Ha et al., 2008 [44] | 43.75 years ±12.73 | normal weight, moderately obese, and obesity | divided into three BMI groups |
| IL-10 | 1800896, 1800871, 1800872 | Maculewicz et al., 2022 [45] | CONBMI 22.02 ± 1.86, OVERBMI 22.63 ± 2.36, CONFMI 22.10 ± 1.92, OVERFMI 24.10 ± 2.95, CONFat 22.13 ± 1.89, OVERFat 2.83 ± 2.78 | normal weight, overweight | three control and three study groups based on two criteria: BMI and fat percentage, healthy |
| IL-10 | 1800896, 1800871, 1800872 | Scarpelli et al., 2006 [6] | 47 ± 14 nondiabetics, 61 ± 11 diabetics | normal weight, overweight, and obesity | non-diabetic control, patients with T2DM |
| IL-10 | 1518111, 1878672, 3024496, 3024498, 3024505 | Maculewicz et al., 2022 [46] | OVERBMI 22.6 ± 2.5, CONBMI 22.3 ± 2.1 OVERFat 22.30 ± 2.3 CONFat 22.4 ± 2.2 | normal weight, overweight | two control and two study groups based on two criteria: BMI and fat percentage, healthy, physical activity |
| IL-15 | 3136617, 3136618, 2296135 | Di Renzo et al., 2009 [29] | 20–45 | non-obese, normal weight obese, preobese-obese | three groups based on body composition (non-obese, normal weight obese, preobese-obese), healthy, physical activity |
| IL-18 | 187238 | Ponasenko et al., 2022 [30] | ≤60 and >60 | non-obese, obese | two groups based on body composition (non-obese, obese), healthy |
| IL-18 | 1946518, 187238 | Kim et al., 2012 [31] | moderately overweight 28.9 ± 11.2, severely overweight 31.3 ± 10.54, obese 33.1 ± 12.9 | moderately overweight, severely overweight, and obese | three groups based on BMI, healthy |
| IL-18 | 7559479, 2293225, 2272127 | Martínez-Barquero et al., 2017 [47] | VALCAR 46.4 ± 14.9, Hortega 54.4 ± 19.3 | non-obese, obese | VALCAR and Hortega groups (at cardiovascular risk) |
| Publication Reference | Random Sequence Generation | Allocation Concealment | Blinding of Participants and Personnel | Blinding of Outcome Assessment | Incomplete Outcome Data | Selective Reporting | Other Bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| e.g., [reference number] | Criteria for a judgement of ‘Low risk’ of bias. e.g., low | Criteria for a judgement of ‘Low risk’ of bias. e.g., low | Criteria for a judgement of ‘Low risk’ of bias. e.g., low | Criteria for a judgement of ‘Low risk’ of bias. e.g., low | Criteria for a judgement of ‘Low risk’ of bias. e.g., low | Criteria for a judgement of ‘Low risk’ of bias. e.g., low | Criteria for a judgement of ‘Low risk’ of bias. e.g., low |
| Criteria for the judgement of ‘High risk’ of bias. e.g., low | Criteria for the judgement of ‘High risk’ of bias. e.g., low | Criteria for the judgement of ‘High risk’ of bias. e.g., low | Criteria for the judgement of ‘High risk’ of bias. e.g., low | Criteria for the judgement of ‘High risk’ of bias. e.g., low | Criteria for the judgement of ‘High risk’ of bias. e.g., low | Criteria for the judgement of ‘High risk’ of bias. e.g., low | |
| Criteria for the judgement of ‘High risk’ of bias. e.g., low | Criteria for the judgement of ‘High risk’ of bias. e.g., low | Criteria for the judgement of ‘High risk’ of bias. e.g., low | Criteria for the judgement of ‘High risk’ of bias. e.g., low | Criteria for the judgement of ‘High risk’ of bias. e.g., low | Criteria for the judgement of ‘High risk’ of bias. e.g., low | Criteria for the judgement of ‘High risk’ of bias. e.g., low |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bojarczuk, A.; Garbacz, A.; Żekanowski, C.; Borzemska, B.; Cięszczyk, P.; Maculewicz, E. Systematic Review of IL-1, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, IL-15, and IL-18 Gene Polymorphisms and Meta-Analysis of IL-6 Variant and Its Association with Overweight and Obesity Risk in Men. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13501. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413501
Bojarczuk A, Garbacz A, Żekanowski C, Borzemska B, Cięszczyk P, Maculewicz E. Systematic Review of IL-1, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, IL-15, and IL-18 Gene Polymorphisms and Meta-Analysis of IL-6 Variant and Its Association with Overweight and Obesity Risk in Men. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(24):13501. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413501
Chicago/Turabian StyleBojarczuk, Aleksandra, Aleksandra Garbacz, Cezary Żekanowski, Beata Borzemska, Paweł Cięszczyk, and Ewelina Maculewicz. 2024. "Systematic Review of IL-1, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, IL-15, and IL-18 Gene Polymorphisms and Meta-Analysis of IL-6 Variant and Its Association with Overweight and Obesity Risk in Men" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 24: 13501. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413501
APA StyleBojarczuk, A., Garbacz, A., Żekanowski, C., Borzemska, B., Cięszczyk, P., & Maculewicz, E. (2024). Systematic Review of IL-1, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, IL-15, and IL-18 Gene Polymorphisms and Meta-Analysis of IL-6 Variant and Its Association with Overweight and Obesity Risk in Men. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(24), 13501. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413501









