Sex Differences in Antennal Transcriptome of Hyphantria cunea and Analysis of Odorant Receptor Expression Profiles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Quality Control
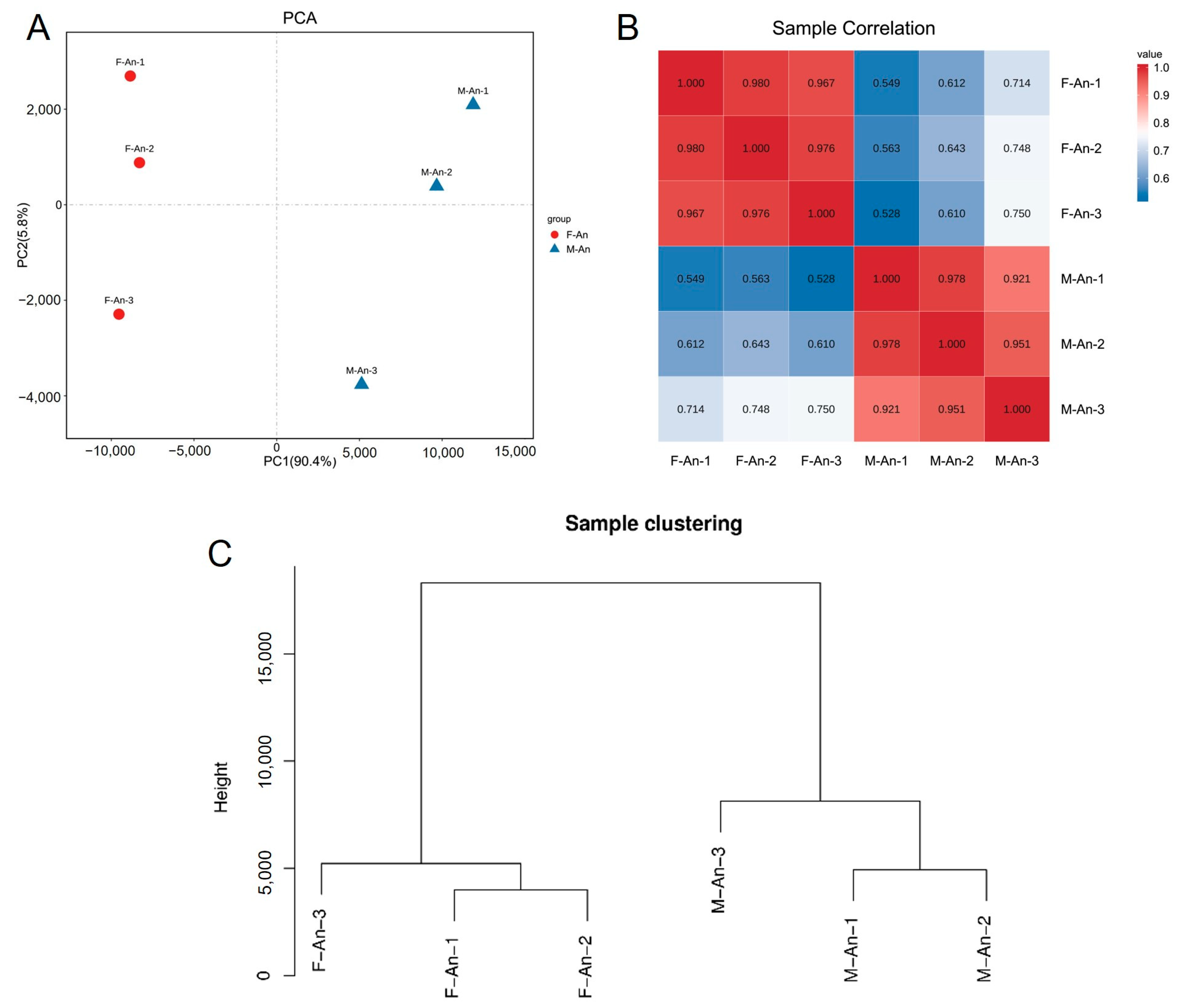
2.2. Sample Relationship Analysis
2.3. Analysis of Annotation Results
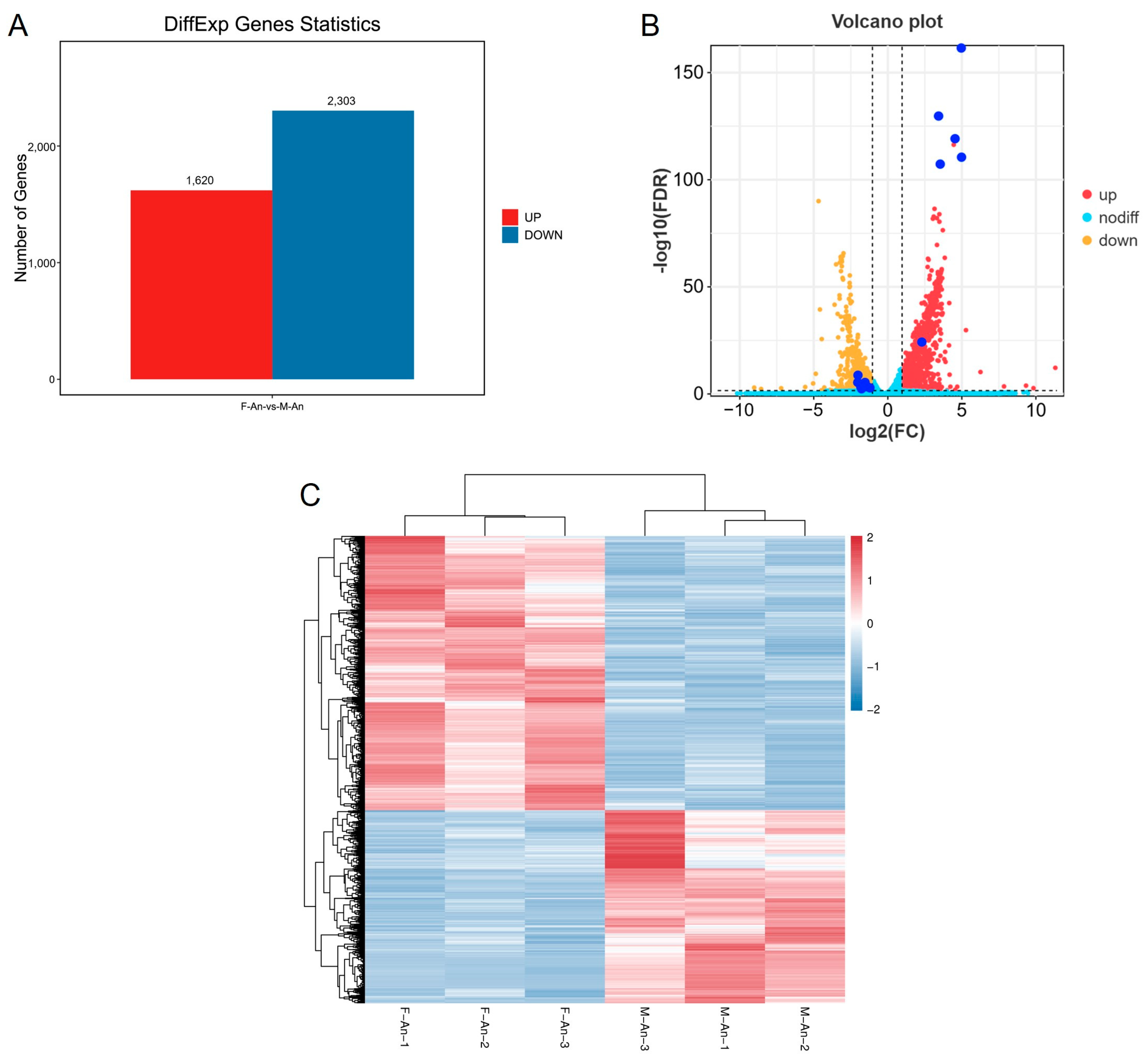
2.4. Overall Statistics of Differential Genes
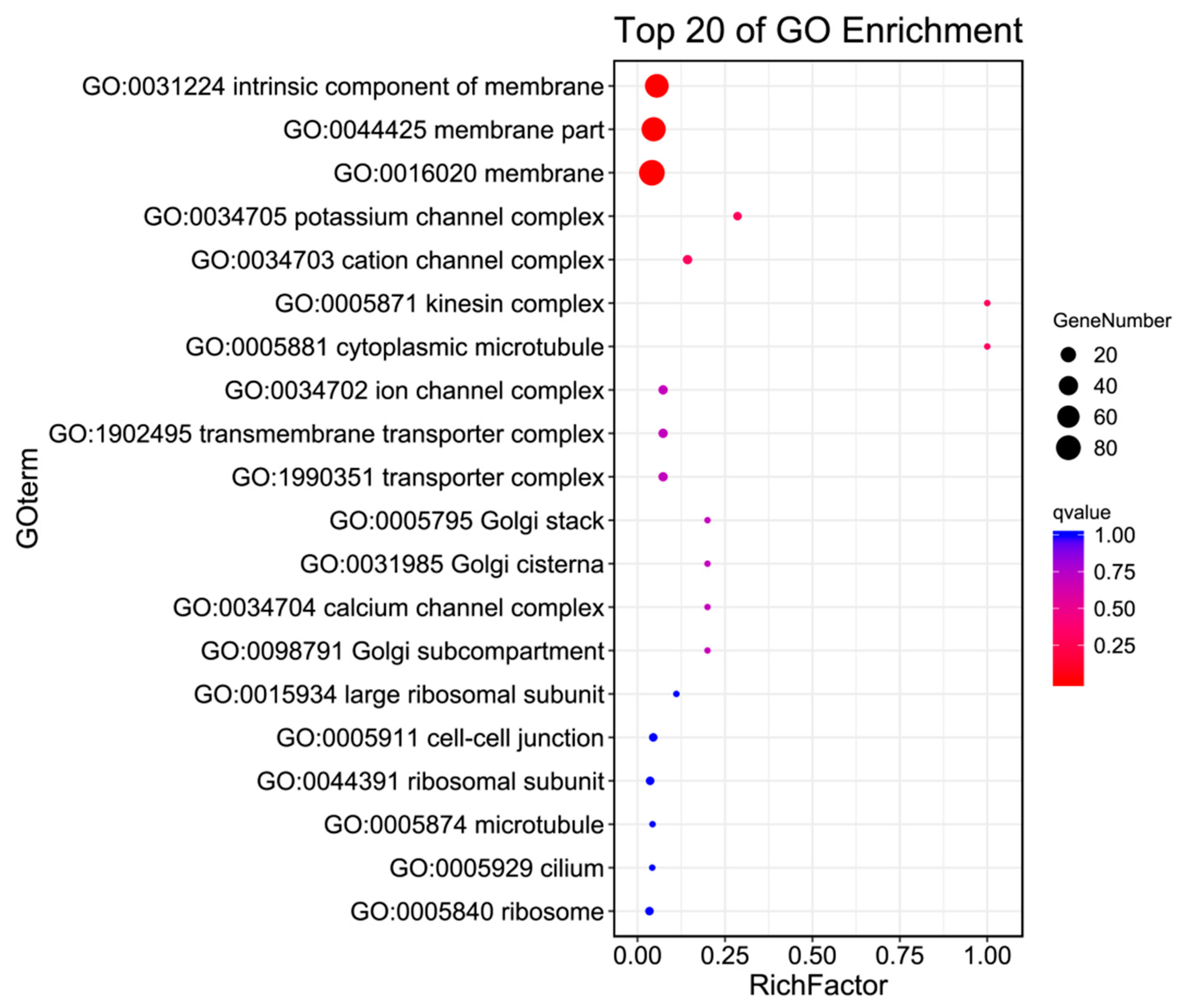
2.5. GO Enrichment
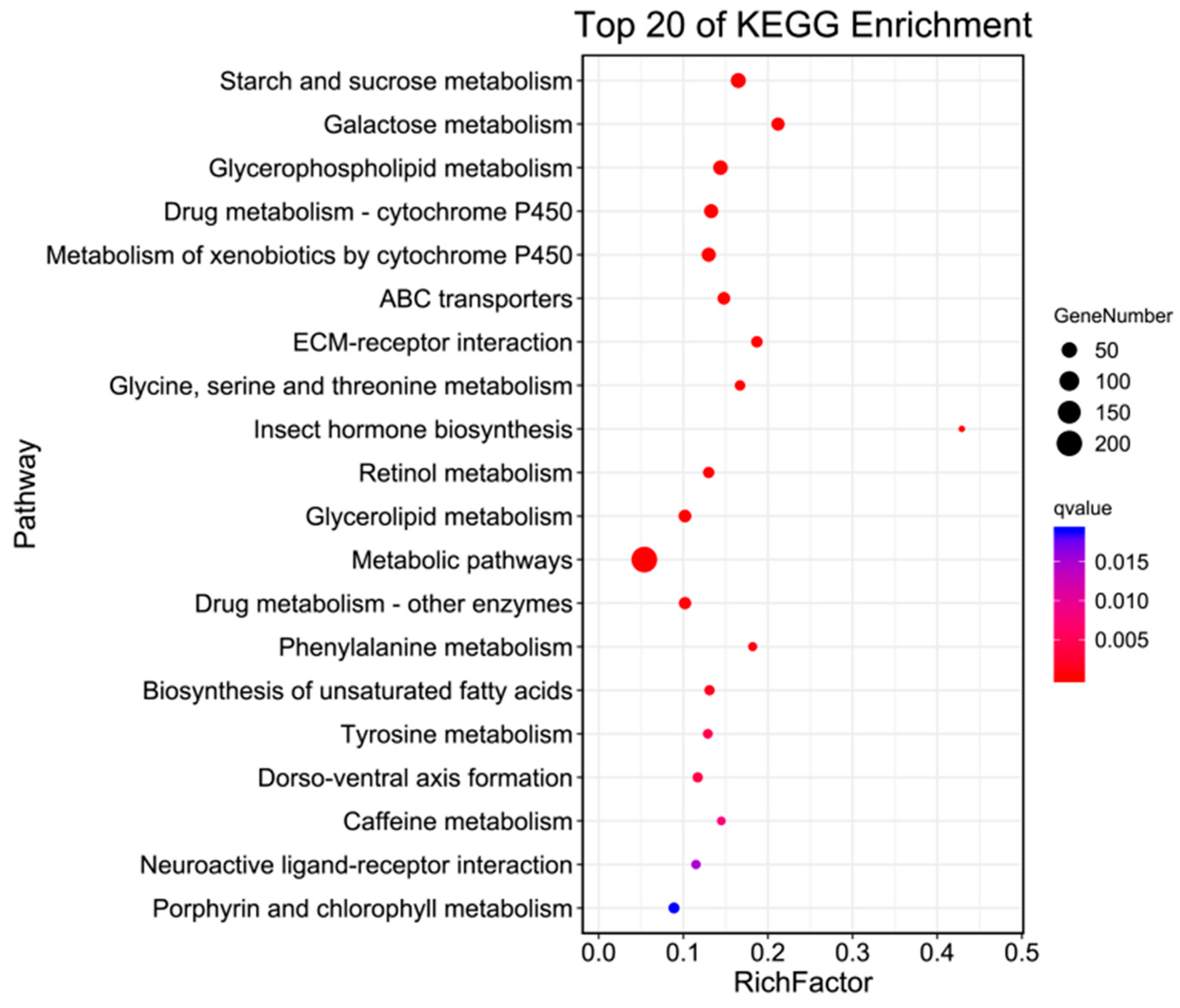
2.6. KO Enrichment
2.7. Identification of Candidate Olfactory-Related Genes
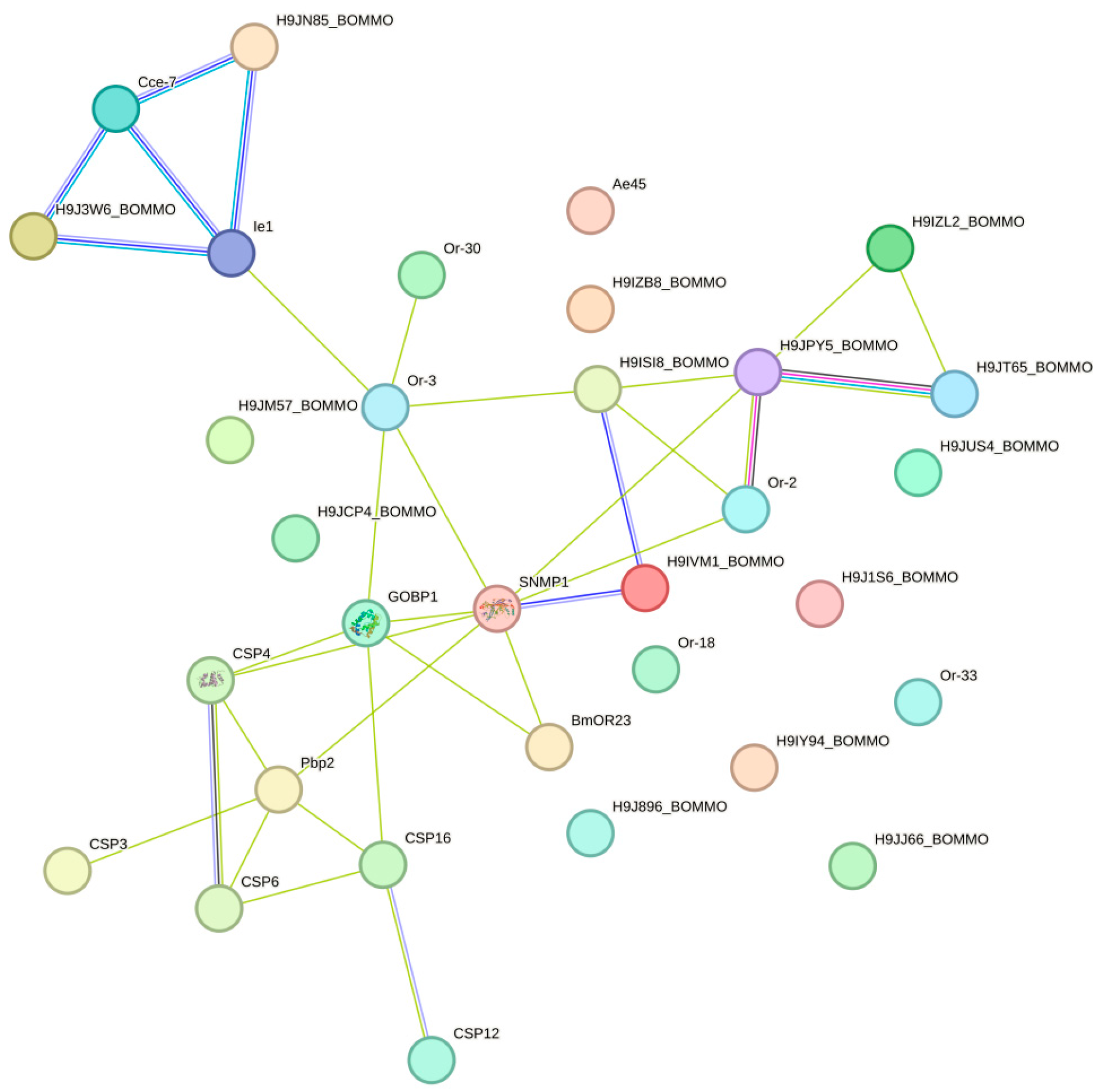
2.8. Protein–Protein Interaction Network Analysis
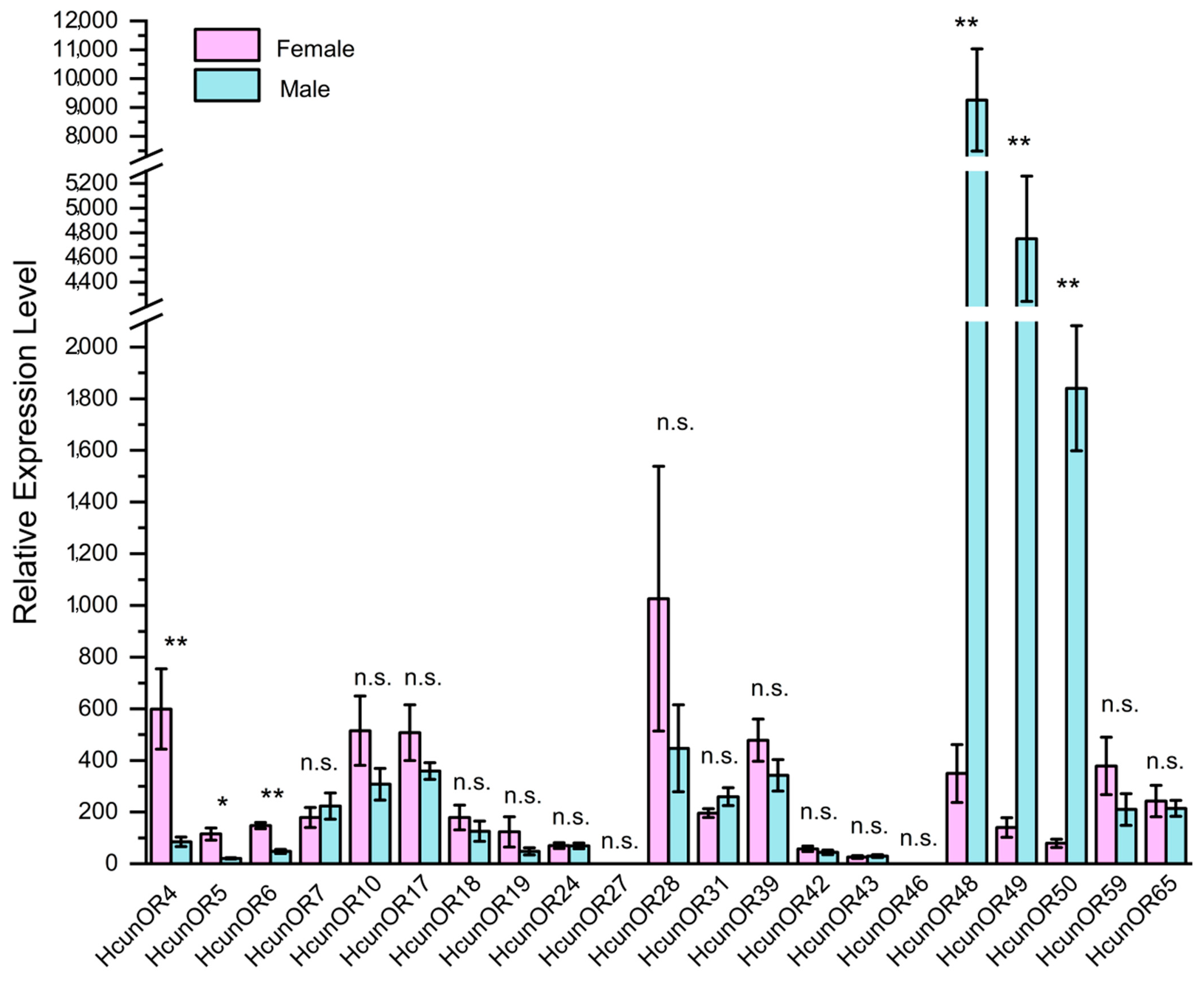
2.9. Expression Levels of HcunOR Genes by RT-qPCR
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Insect Rearing and Tissue Collection
4.2. RNA Extraction and cDNA Library Construction
4.3. Data Quality Control
4.4. Annotation
4.5. Expression Statistics and Differential Expression Analysis
4.6. GO and KO Enrichment Analysis
4.7. Protein–Protein Interaction Network
4.8. RT-qPCR Validation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ha, T.S.; Smith, D.P. Recent insights into insect olfactory receptors and odorant-binding proteins. Insects 2022, 13, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.C.; Berg, B.G.; Wang, G. Recent advances in insect olfaction: Characterization of neural circuits from sensory input to motor output. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2023, 5, 1282499. [Google Scholar]
- Suh, E.; Bohbot, J.; Zwiebel, L.J. Peripheral olfactory signaling in insects. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2014, 1, 86–92. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Lin, K.; Wang, G. Functional specificity of sex pheromone receptors in the cotton bollworm Helicoverpa armigera. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62094. [Google Scholar]
- Du, L.X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, G.R. Molecular mechanisms of signal transduction in the peripheral olfactory system of insects. Sci. Sin. Vitae 2016, 46, 573–583. [Google Scholar]
- Dikmen, F.; Dabak, T.; Özgişi, B.D.; Özenirler, Ç.; Kuralay, S.C.; Çay, S.B.; Çınar, Y.U.; Obut, O.; Balcı, M.A.; Akbaba, P.; et al. Transcriptome-wide analysis uncovers regulatory elements of the antennal transcriptome repertoire of bumblebee at different life stages. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2024, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.J.; Wang, H.X.; Yan, Z.G.; Zhang, M.Z.; Wei, C.H.; Qin, X.C.; Ji, W.R.; Falabella, P.; Du, Y.L. Antennal transcriptome and differential expression of olfactory genes in the yellow peach moth, Conogethes punctiferalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). Sci. Rep. 2016, 1, 29067. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, L.; Li, T.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Yan, S.; Jiang, D. Identification and potential application of key insecticidal metabolites in Tilia amurensis, a low-preference host of Hyphantria cunea. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2024, 199, 105796. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Li, Z.; Hao, D. Spatiotemporal patterns of five small heat shock protein genes in Hyphantria cunea in response to thermal stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.W.; Kang, K.; Jiang, S.C.; Zhang, Y.N.; Wang, T.T.; Zhang, J.; Sun, L.; Yang, Y.Q.; Huang, C.C.; Jiang, L.Y.; et al. Analysis of the antennal transcriptome and insights into olfactory genes in Hyphantria cunea (Drury). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164729. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Purba, E.R.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Q.H.; Dong, S.L.; Zhang, Y.N.; He, P.; Mang, D.; Zhang, L. Functional differentiation of two general-odorant binding proteins in Hyphantria cunea (Drury) (Lepidoptera: Erebidae). Pest Manag. Sci. 2023, 79, 3312–3325. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.Q.; Mang, D.Z.; Liao, H.; Ye, J.; Qian, J.L.; Dong, S.L.; Zhang, Y.N.; He, P.; Zhang, Q.H.; Purba, E.R.; et al. Functional disparity of three pheromone-binding proteins to different sex pheromone components in Hyphantria cunea (Drury). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 55–66. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W.C.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Q.M.; Qin, G.X.; Wang, G.R.; Jiang, D.; Yan, S.C. An odorant receptor-derived peptide biosensor for monitoring the occurrence of Hyphantria cunea larvae by recognizing herbivore-induced plant volatile. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 381, 133432. [Google Scholar]
- Kiyota, R.; Arakawa, M.; Yamakawa, R.; Yasmin, A.; Ando, T. Biosynthetic pathways of the sex pheromone components and substrate selectivity of the oxidation enzymes working in pheromone glands of the fall webworm, Hyphantria cunea. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 41, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, S.; Hull, J.J.; Ohnishi, A.; Moto, K.; Fónagy, A. Molecular mechanisms underlying sex pheromone production in the silkmoth, Bombyx mori: Characterization of the molecular components involved in bombykol biosynthesis. J. Insect Physiol. 2007, 53, 752–759. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.J.; Guo, H.; Di, C.; Yu, S.; Zhu, L.; Huang, L.Q.; Wang, C.Z. Sequence similarity and functional comparisons of pheromone receptor orthologs in two closely related Helicoverpa species. Insect. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 48, 63–74. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Z.; Sun, L.; Li, Y.; Quan, L.; Zhang, H.; Yan, W.; Yue, Q.; Qiu, G. Antennal transcriptome analysis of the chemosensory gene families in Carposina sasakii (Lepidoptera: Carposinidae). BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 544. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, R.F.; Doucet, D.; Bowman, S.; Bouwer, M.C.; Allison, J.D. Prediction of a conserved pheromone receptor lineage from antennal transcriptomes of the pine sawyer genus Monochamus (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). J. Comp. Physiol. A 2022, 208, 615–625. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.C.; Tan, H.L.; Chen, Z.; Meng, L.Z.; Wang, W.B.; Fan, S.C. Assembly and characterization of the transcriptome and development of SSR markers in forsythia suspensa based on RNA-Seq technology. Sci. Sin. (Vitae) 2015, 45, 301–310. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Fu, L.B.; Cheng, B.; Sun, S.H. Morphological Characteristics of Antennal Sensilla in Hyphantria cunea (Drury) (Lepidoptera: Erebidae). Trans. Am. Entomol. Soc. 2019, 145, 421–434. [Google Scholar]
- Kanaujia, S.; Kaissling, K.E. Interactions of pheromone with moth antennae: Adsorption, desorption and transport. J. Insect Physiol. 1985, 31, 71–81. [Google Scholar]
- Pophof, B. Pheromone-binding proteins contribute to the activation of olfactory receptor neurons in the silkmoths Antheraea polyphemus and Bombyx mori. Chem. Senses 2004, 29, 117–125. [Google Scholar]
- Laughlin, J.D.; Ha, T.S.; Jones, D.N. Activation of pheromone-sensitive neurons is mediated by conformational activation of pheromone-binding protein. Cell 2008, 133, 1255–1265. [Google Scholar]
- Long, Y.Q.; Luo, Z.W.; Wang, X.S.; Long, L.X.; Yu, X.S.; Li, J.L.; Qu, H.; Wang, Y.G.; Chen, L.B. Analysis of the antennal transcriptome and olfactory-related genes in the Agriophara rhombata. J. Tea Sci. 2021, 41, 553–563. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Feng, K.; Mei, R.; Li, W.; Tang, F. Analysis of the antennal transcriptome and identification of tissue-specific expression of olfactory-related genes in Micromelalopha troglodyte (Lepidoptera: Notodontidae). J. Insect Sci. 2022, 22, 8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.H.; Zhang, M.Q.; Feng, Q.L.; Cui, Y.; Xiang, H. Comparison of olfactory and gustatory genes between Spodoptera frugiperda and Spodoptera litura. J. Environ. Entomol. 2019, 41, 937–94631. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Anderson, A. Carbon dioxide receptor genes in cotton bollworm Helicoverpa armigera. Sci. Nat. 2015, 102, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Pregitzer, P.; Greschista, M.; Breer, H.; Krieger, J. The sensory neurone membrane protein SNMP1 contributes to the sensitivity of a pheromone detection system. Insect Mol. Biol. 2014, 23, 733–742. [Google Scholar]
- Ishida, Y.; Leal, W.S. Chiral discrimination of the Japanese beetle sex pheromone and a behavioral antagonist by a pheromone-degrading enzyme. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9076–9080. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.T.; Huang, L.Q.; Dong, J.F.; Wang, C.Z. A moth odorant receptor highly expressed in the ovipositor is involved in detecting host-plant volatiles. Elife 2020, 9, e53706. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.Q.; Luo, Z.X.; Cai, X.M.; Bian, L.; Xin, Z.J.; Liu, Y.; Chu, B.; Chen, Z.M. Chemosensory gene families in Ectropis grisescens and candidates for detection of Type-II Sex pheromones. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 953. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.Q.; Cai, X.M.; Luo, Z.X.; Bian, L.; Xin, Z.J.; Chu, B.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.M. Comparison of olfactory genes in two Ectropis Species: Emphasis on candidates involved in the detection of Type-II sex pheromones. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1602. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Du, Y. Identification and Differential Expression of a Candidate Sex Pheromone Receptor in Natural Populations of Spodoptera litura. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131407. [Google Scholar]
- Yuvaraj, J.K.; Jordan, M.D.; Zhang, D.D.; Andersson, M.N.; Löfstedt, C.; Newcomb, R.D.; Corcoran, J.A. Sex pheromone receptors of the light brown apple moth, Epiphyas postvittana, support a second major pheromone receptor clade within the Lepidoptera. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2022, 141, 103708. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357. [Google Scholar]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G.M.; Antonescu, C.M.; Chang, T.C.; Mendell, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 290–295. [Google Scholar]
- Pertea, M.; Kim, D.; Pertea, G.M.; Leek, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. Transcript-level expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with HISAT, StringTie and Ballgown. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 1650. [Google Scholar]
- Conesa, A.; Götz, S.; García-Gómez, J.M.; Terol, J.; Talón, M.; Robles, M. Blast2GO: A universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3674–3676. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNAseq data with DESeq2. Genomebiology 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tao, R.; Li, H.; Sun, Y.H.; Yu, X.H.; Zhu, H.; Hao, D.J. Identification and screening of internal references genes of Hyphantria cunea (Lepidoptera: Arctiidae). Sci. Silvae Sin. 2019, 55, 111–120. [Google Scholar]
| Sample | Clean Reads (%) | Clean Bases (bp) | Q20 (%) | Q30 (%) | N (%) | GC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F-An-1 | 37,805,884 (99.65%) | 5,685,746,323 | 97.90% | 93.49% | 0.00% | 42.59% |
| F-An-2 | 36,204,050 (99.67%) | 5,430,451,779 | 97.88% | 93.41% | 0.00% | 42.01% |
| F-An-3 | 35,361,300 (99.64%) | 5,303,989,239 | 97.80% | 93.26% | 0.00% | 42.08% |
| M-An-1 | 35,108,044 (99.69%) | 5,266,066,509 | 97.81% | 93.30% | 0.00% | 42.54% |
| M-An-2 | 38,852,812 (99.62%) | 5,827,771,407 | 98.00% | 93.78% | 0.00% | 42.45% |
| M-An-3 | 33,361,348 (99.66%) | 5,004,070,064 | 97.75% | 93.20% | 0.00% | 42.02% |
| Database | Unigene/s | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Annotated in NR | 41,271 | 82.28% |
| Annotated in Swiss-Prot | 31,169 | 62.14% |
| Annotated in KOG | 28,779 | 57.38% |
| Annotated in KEGG | 21,591 | 43.05% |
| Annotated in GO | 8287 | 16.52% |
| Not annotated in any database | 8871 | 17.69% |
| Annotated in at least one database | 41,287 | 82.31% |
| GO Term (Level 1) | GO ID (Level 2) | GO Term (Level 2) | Differential Genes(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biological Process | GO:0051179 | localization | 122 |
| GO:0022414 | reproductive process | 2 | |
| GO:0032501 | multicellular organismal process | 26 | |
| GO:0000003 | reproduction | 2 | |
| GO:0040007 | growth | 1 | |
| GO:0044699 | single-organism process | 144 | |
| GO:0040011 | locomotion | 2 | |
| GO:0048519 | negative regulation of biological process | 7 | |
| GO:0023052 | signaling | 23 | |
| GO:0002376 | immune system process | 1 | |
| GO:0032502 | developmental process | 14 | |
| GO:0048518 | positive regulation of biological process | 4 | |
| GO:0051704 | multi-organism process | 3 | |
| GO:0065007 | biological regulation | 54 | |
| GO:0071840 | cellular component organization or biogenesis | 19 | |
| GO:0050789 | regulation of biological process | 46 | |
| GO:0050896 | response to stimulus | 28 | |
| GO:0009987 | cellular process | 137 | |
| GO:0008152 | metabolic process | 124 | |
| Molecular Function | GO:0005215 | transporter activity | 42 |
| GO:0001071 | nucleic acid binding transcription factor activity | 12 | |
| GO:0060089 | molecular transducer activity | 15 | |
| GO:0009055 | electron carrier activity | 1 | |
| GO:0016209 | antioxidant activity | 2 | |
| GO:0004871 | signal transducer activity | 6 | |
| GO:0098772 | molecular function regulator | 5 | |
| GO:0003824 | catalytic activity | 151 | |
| GO:0005198 | structural molecule activity | 2 | |
| GO:0005488 | binding | 124 | |
| Cellular Component | GO:0044425 | membrane part | 75 |
| GO:0016020 | membrane | 88 | |
| GO:0031012 | extracellular matrix | 1 | |
| GO:0099512 | supramolecular fiber | 1 | |
| GO:0030054 | cell junction | 2 | |
| GO:0044421 | extracellular region part | 1 | |
| GO:0005576 | extracellular region | 1 | |
| GO:0032991 | macromolecular complex | 25 | |
| GO:0044422 | organelle part | 12 | |
| GO:0043226 | organelle | 35 | |
| GO:0005623 | cell | 52 | |
| GO:0044464 | cell part | 52 |
| KEGG A Class | Metabolic Pathway | Differential Genes(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Metabolism | Amino acid metabolism | 82 |
| Carbohydrate metabolism | 157 | |
| Biosynthesis of other secondary metabolites | 9 | |
| Energy metabolism | 16 | |
| Global and overview maps | 390 | |
| Glycan biosynthesis and metabolism | 11 | |
| Lipid metabolism | 101 | |
| Metabolism of cofactors and vitamins | 50 | |
| Metabolism of other amino acids | 28 | |
| Metabolism of terpenoids and polyketides | 7 | |
| Nucleotide metabolism | 25 | |
| Xenobiotics biodegradation and metabolism | 101 | |
| Organismal Systems | Sensory system | 2 |
| Immune system | 1 | |
| Environmental adaptation | 8 | |
| Development | 14 | |
| Circulatory system | 1 | |
| Aging | 14 | |
| Genetic Information Processing | Translation | 21 |
| Transcription | 9 | |
| Replication and repair | 2 | |
| Folding, sorting and degradation | 23 | |
| Environmental Information Processing | Signaling molecules and interaction | 31 |
| Signal transduction | 69 | |
| Membrane transport | 27 | |
| Cellular Processes | Transport and catabolism | 55 |
| Cellular community—eukaryotes | 1 | |
| Cell motility | 1 |
| Olfactory-Related Genes | Number of Genes | Proportion |
|---|---|---|
| Odorant receptor (OR) genes | 26 | 11.76% |
| Odorant binding protein (OBP) genes | 77 | 34.84% |
| Gustatory receptor (GR) genes | 3 | 1.36% |
| Ionotropic receptor (IR) genes | 40 | 18.10% |
| Chemosensory protein (CSP) genes | 46 | 20.81% |
| Sensory neuron membrane protein (SNMP) genes | 11 | 4.98% |
| Odorant degrading enzyme (ODE) genes | 18 | 8.14% |
| Gene-ID | Accession Number | FPKM Value (Mean ± SE) | Whether Differential | Significance in qPCR | ORF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F-An | M-An | |||||
| HcunOR28 | PQ100433 | 2.06 ± 0.42 | 1.41 ± 0.37 | No | n.s. | 414 aa |
| HcunOR7 | PQ100434 | 0.42 ± 0.05 | 0.53 ± 0.10 | No | n.s. | 395 aa |
| HcunOR19 | PQ100435 | 3.81 ± 0.35 | 1.48 ± 0.37 | Yes | n.s. | 252 aa |
| HcunOR59 | PQ100436 | 13.56 ± 2.47 | 17.25 ± 3.58 | No | n.s. | 416 aa |
| HcunOR27 | PQ100437 | 5.53 ± 0.44 | 1.96 ± 0.34 | Yes | n.s. | 419 aa |
| HcunOR42 | PQ100438 | 0.68 ± 0.19 | 0.42 ± 0.17 | No | n.s. | 444 aa |
| HcunOR65 | PQ100439 | 5.30 ± 0.42 | 3.00 ± 0.25 | No | n.s. | 226 aa |
| HcunOR61 | PQ100440 | 5.02 ± 0.52 | 2.23 ± 0.29 | Yes | - | 396 aa |
| HcunOR49 | PQ100441 | 4.65 ± 0.51 | 149.07 ± 13.50 | Yes | ** | 404 aa |
| HcunOR48 | PQ100442 | 1.01 ± 0.04 | 32.72 ± 2.75 | Yes | ** | 405 aa |
| HcunOR50 | PQ100443 | 3.00 ± 0.29 | 71.85 ± 7.29 | Yes | ** | 396 aa |
| HcunOR6 | PQ100444 | 1.58 ± 0.17 | 0.83 ± 0.18 | No | ** | 382 aa |
| HcunOR1 | PQ100445 | 2.39 ± 0.09 | 0.70 ± 0.19 | Yes | - | 157 aa |
| HcunOR10 | PQ100446 | 7.61 ± 0.83 | 5.00 ± 0.55 | No | n.s. | 390 aa |
| HcunOR39 | PQ100447 | 4.76 ± 0.30 | 6.86 ± 1.67 | No | n.s. | 386 aa |
| HcunOR46 | PQ100448 | 19.45 ± 3.58 | 10.20 ± 0.93 | No | n.s. | 424 aa |
| HcunOR31 | PQ100449 | 3.92 ± 1.29 | 5.90 ± 2.93 | No | n.s. | 395 aa |
| HcunOR24 | PQ100450 | 18.04 ± 2.21 | 12.23 ± 1.88 | No | n.s. | 399 aa |
| HcunOR17 | PQ100451 | 15.18 ± 1.91 | 3.86 ± 0.74 | Yes | n.s. | 405 aa |
| HcunOR5 | PQ100452 | 5.64 ± 1.23 | 1.42 ± 0.14 | Yes | * | 377 aa |
| HcunOR4 | PQ100453 | 1.23 ± 0.29 | 0.37 ± 0.10 | Yes | ** | 288 aa |
| HcunOR3 | PQ100454 | 7.71 ± 0.56 | 92.16 ± 7.79 | Yes | - | 430 aa |
| HcunOR2 | PQ100455 | 15.33 ± 0.21 | 169.69 ± 11.46 | Yes | - | 422 aa |
| HcunORCO | PQ100456 | 6.68 ± 1.00 | 33.73 ± 5.99 | Yes | - | 473 aa |
| HcunOR18 | PQ100457 | 18.27 ± 3.14 | 18.20 ± 0.67 | No | n.s. | 398 aa |
| HcunOR43 | PQ100458 | 1.70 ± 0.31 | 1.72 ± 0.53 | No | n.s. | 397 aa |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, W.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Yan, S. Sex Differences in Antennal Transcriptome of Hyphantria cunea and Analysis of Odorant Receptor Expression Profiles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25169070
Ma W, Li Y, Yang L, Yan S. Sex Differences in Antennal Transcriptome of Hyphantria cunea and Analysis of Odorant Receptor Expression Profiles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(16):9070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25169070
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Weichao, Yaning Li, Lina Yang, and Shanchun Yan. 2024. "Sex Differences in Antennal Transcriptome of Hyphantria cunea and Analysis of Odorant Receptor Expression Profiles" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 16: 9070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25169070
APA StyleMa, W., Li, Y., Yang, L., & Yan, S. (2024). Sex Differences in Antennal Transcriptome of Hyphantria cunea and Analysis of Odorant Receptor Expression Profiles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(16), 9070. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25169070




