Fetal Brain-Derived Exosomal miRNAs from Maternal Blood: Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers for Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASDs)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Prenatal EtOH Exposure Was Associated with Reduced miRNA Levels in Fetal Brain but Increased miRNA Levels in Maternal Serum during Development
- NPCs: neural progenitor cells
- ELAVL3/4: embryonic lethal abnormal vision-like 3/4;
- EZH2: enhancer of zeste 2 polycomb repressive complex 2 subunit;
- MSI1: Musashi1
- PTBP1/2: polypyrimidine tract binding protein 1/2
- REST: RE1 Silencing Transcription Factor
- SCP1: CTD small phosphatase 1 (also known as CTDSP1)
- ZFP36: ZFP36 ring finger protein;
- ZFP36L1: ZFP36 ring finger protein like 1
- Sox9: SRY-Box Transcription Factor 9
- NOVA1: NOVA Alternative Splicing Regulator 1, Neuro-Oncological Ventral Antigen 1 N NOVA Alternative Splic1
- Rbfox1: RNA Binding Fox-1 Homolog 1
- Phf6: X-linked syndromic intellectual disability gene
- PCM1: pericentriolar material 1
- AMPARs: AMPA-type glutamate receptors
- CREB: cAMP response element binding protein
- MeCP2: methyl CpG-binding protein 2
- Cdh5: vascular endothelial cadherin (VE-cadherin)
- FMRP: fragile X mental retardation protein
2.2. EtOH Exposure Was Associated with Changes in Expression of Array miRNAs
2.3. EtOH Exposure Was Associated with Reduced miR-9 and miR-132 in FB-Es
2.4. miR-9 Expression in FB-Es
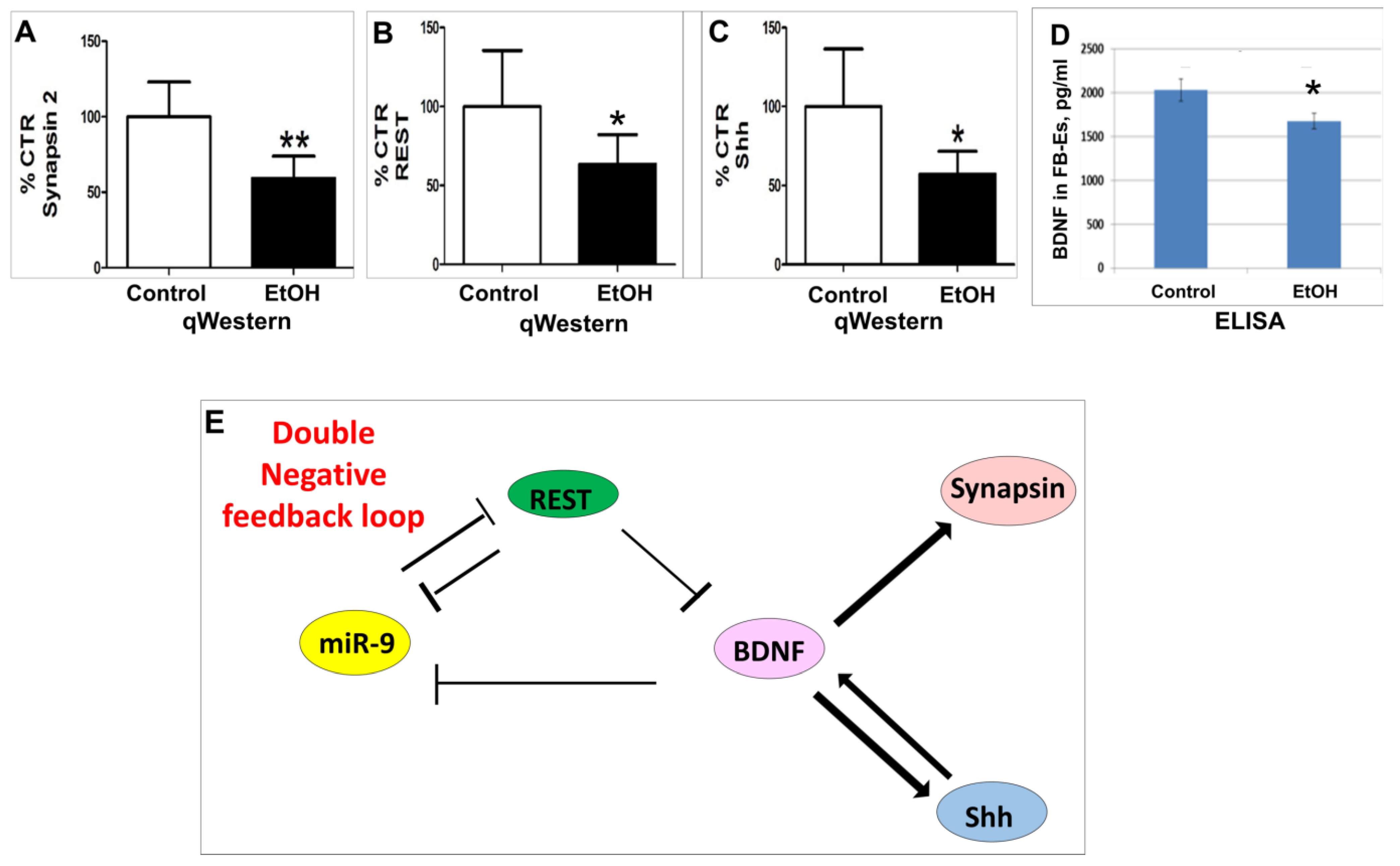
2.5. miRNA-9 Targets in a Double Negative Feedback Loop Pathway
2.6. Reductions in FB-E miR-9 Levels in Fetuses Exposed to EtOH Correlate with Reductions in Eye Diameter in Fetuses Exposed to EtOH in a Larger Population
3. Discussion
3.1. MicroRNAs as Indicators of Alcohol-Associated Fetal Pathology
3.2. FB-Es as Non-Invasive Tools to Assess Potential Molecular Biomarkers
3.3. The Association between Exposure to EtOH and Reduced Fetal miRNA Expression Probably Is Due to a Direct Effect of EtOH on Fetal Brain
3.4. Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Clinical Samples
4.2. RNA Preparation
4.3. miRNA Preparation and Real-Time qRT-PCR
4.4. Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR)
4.5. Primers (IDT Inc., Coralville, IA, USA)
4.6. ELISA Quantification of Exosomal Proteins
4.7. Quantitative Western Blots
4.8. Isolation of Fetal Brain-Derived Exosomes (FB-Es) from Maternal Serum and ELISA Quantification of Exosomal Proteins
4.9. Statistical Analysis
4.10. Ethics: Human Subjects
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BDNF | brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| ddPCR | digital droplet polymerase chain reaction |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| EtOH | ethanol, alcohol |
| FAS | fetal alcohol syndrome |
| FASD | fetal alcohol spectrum disorders |
| FB-Es | fetal brain-derived exosomes |
| GA | gestation age |
| miR-9 | microRNA-9 |
| qRT-PCR | quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction |
| REST | restrictive element-1 silencing transcription factor |
| Shh | Sonic hedgehog protein |
| SNORD | small nucleolar RNA D |
| SRY | sex-determining region of the Y chromosome |
References
- Popova, S.; Charness, M.E.; Burd, L.; Crawford, A.; Hoyme, H.E.; Mukherjee RA, S.; Riley, E.P.; Elliott, E.J. Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2023, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, P.A.; Baete, A.; Russo, J.; Elliott, A.J.; Blankenship, J.; Kalberg, W.O.; Buckley, D.; Brooks, M.; Hasken, J.; Abdul-Rahman, O.; et al. Prevalence and characteristics of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Pediatrics 2014, 134, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyme, H.E.; Kalberg, W.O.; Elliott, A.J.; Blankenship, J.; Buckley, D.; Marais, A.S.; Manning, M.A.; Robinson, L.K.; Adam, M.P.; Abdul-Rahman, O.; et al. Updated Clinical Guidelines for Diagnosing Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders. Pediatrics 2016, 138, e20154256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaraman, S.; Schafer, J.J.; Tseng, A.M.; Wertelecki, W.; Yevtushok, L.; Zymak-Zakutnya, N.; Chambers, C.D.; Miranda, R.C. Plasma miRNA Profiles in Pregnant Women Predict Infant Out- 946 comes following Prenatal Alcohol Exposure. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahnke, A.H.; Salem, N.A.; Tseng, A.M.; Chung, D.D.; Miranda, R.C. Nonprotein-coding 952 RNAs in Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2018, 157, 299–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; He, Z.; Wang, J. MicroRNA-124: A Key Player in Microglia-Mediated Inflammation in Neurological Diseases. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 771898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.F.; Gao, J.; Liu, C.M. The Role of Non-Coding RNAs in Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lungu, G.; Stoica, G.; Ambrus, A. MicroRNA profiling and the role of microRNA-132 in neurodegeneration using a rat model. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 553, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Mateos, E.M.; Engel, T.; Merino-Serrais, P.; Fernaud-Espinosa, I.; Rodriguez-Alvarez, N.; Reynolds, J.; Reschke, C.R.; Conroy, R.M.; McKiernan, R.C.; deFelipe, J.; et al. Antagomirs targeting microRNA-134 increase hippocampal pyramidal neuron spine volume in vivo and protect against pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. Brain Struct. Funct. 2015, 220, 2387–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Li, C.Y.; Wang, L.J.; Xia, Y.; Feng, C.A.; Peng, Y.F.; Han, Y.B.; Fan, Y.; Ba, Y.C. MicroRNA-138 Regulates Spinal Cord Development by Activating the Shh in Fetal Rats. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2022, 57, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Wang, M.; Gao, X.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhao, N.; Ding, C.; Ma, Z.; Wang, Y. miR-9-5p promotes myogenic differentiation via the Dlx3/Myf5 axis. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghibaudi, M.; Boido, M.; Vercelli, A. Functional integration of complex miRNA networks in central and peripheral lesion and axonal regeneration. Prog. Neurobiol. 2017, 158, 69–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, J.; Huang, W.; Han, B.; Wang, Q.; Qi, C.; Wang, M.; Liu, F. miR-106b-5p Inhibits IRF1/IFN-β Signaling to Promote M2 Macrophage Polarization of Glioblastoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 7479–7492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Piccus, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yang, H.; Jarrell, H.; Ding, Y.; Teng, Z.; Tchernichovski, O.; Li, X. miR-9 regulates basal ganglia-dependent developmental vocal learning and adult vocal performance in songbirds. Elife 2018, 7, e29087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bludau, A.; Schwartz, U.; Zeitler, D.M.; Royer, M.; Meister, G.; Neumann, I.D.; Menon, R. Functional involvement of septal miR-132 in extinction and oxytocin-mediated reversal of social fear. Mol. Psychiatry 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Ai, R.; Tian, Y.; Mi, N.; Cheng, L.; Qian, N.; Zhu, X. Study on the Mechanism of Action of MicroRNA-140-5p in the Treatment of Autism by Regulating the Nuclear Factor Kappa B Signaling Pathway. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 83, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, W.; Zheng, Y. Recent Progress on Relevant microRNAs in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.L.; Xing, A.Y.; Bai, H.; Wu, L. miRNA-148b-3p Influences Glucose Metabolism of Offspring with Maternal Cholestasis by Regulating GLUT1 Expression in Placental Trophoblast Cells. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban J. Sichuan Univ. (Med. Sci. Ed.) 2019, 50, 328–333. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ran, J.; Zhang, L.; Yao, M.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L. miR-15a-5p inhibits metastasis and lipid metabolism by suppressing histone acetylation in lung cancer. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 161, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokawa, R.; Yoshino, Y.; Funahashi, Y.; Horiuchi, F.; Iga, J.I.; Ueno, S.I. MiR-15b-5p Expression in the Peripheral Blood: A Potential Diagnostic Biomarker of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Brain Sci. 2022, 13, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonacci, A.; Bagnato, G.; Pandolfo, G.; Billeci, L.; Sansone, F.; Conte, R.; Gangemi, S. MicroRNA Cross-Involvement in Autism Spectrum Disorders and Atopic Dermatitis: A Literature Review. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Lin, Y.; Sun, Z.; Yuan, X.; Chen, L.; Shen, B. Knowledge-Guided Bioinformatics Model for Identifying Autism Spectrum Disorder Diagnostic MicroRNA Biomarkers. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cava, C.; Manna, I.; Gambardella, A.; Bertoli, G.; Castiglioni, I. Potential Role of miRNAs as Theranostic Biomarkers of Epilepsy. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 13, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Pula, T.; Tews, D.; Amri, E.Z.; Debatin, K.M.; Wabitsch, M.; Fischer-Posovszky, P.; Roos, J. microRNA-27a-3p but Not -5p Is a Crucial Mediator of Human Adipogenesis. Cells 2021, 10, 3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasu, M.; Anitha, A.; Thanseem, I.; Suzuki, K.; Yamada, K.; Takahashi, T.; Wakuda, T.; Iwata, K.; Tsujii, M.; Sugiyama, T.; et al. Serum microRNA profiles in children with autism. Mol. Autism 2014, 5, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lu, T.; Li, X.; Jiang, M.; Jia, M.; Liu, J.; Zhang, D.; Li, J.; Wang, L. Altered Expression of Brain-specific Autism-Associated miRNAs in the Han Chinese Population. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 865881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Yuan, X.; Xu, N.; Zhao, S.; Hou, L.; Yang, L.; Zhang, N. miR-431-5p regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis in fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis by targeting XIAP. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honorato-Mauer, J.; Xavier, G.; Ota, V.K.; Chehimi, S.N.; Mafra, F.; Cuóco, C.; Ito, L.T.; Ormond, R.; Asprino, P.F.; Oliveira, A.; et al. Alterations in microRNA of extracellular vesicles associated with major depression, attention-deficit/hyperactivity and anxiety disorders in adolescents. Transl. Psychiatry 2023, 13, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujitani, M.; Zhang, S.; Fujiki, R.; Fujihara, Y.; Yamashita, T. A chromosome 16p13.11 microduplication causes hyperactivity through dysregulation of miR-484/protocadherin-19 signaling. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Tan, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z. Decoding microRNAs in autism spectrum disorder. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2022, 30, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuzziello, N.; Craig, F.; Simone, M.; Consiglio, A.; Licciulli, F.; Margari, L.; Grillo, G.; Liuni, S.; Liguori, M. Integrated Analysis of microRNA and mRNA Expression Profiles: An Attempt to Disentangle the Complex Interaction Network in Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kim, W.; Lee, K.H. The role of microRNAs in the molecular link between circadian rhythm and autism spectrum disorder. Anim. Cells Syst. 2023, 27, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Hou, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, G.; Cao, P.; Chen, W.; Hu, L.; Gan, D. miR-93-5p promotes insulin resistance to regulate type 2 diabetes progression in HepG2 cells by targeting HGF. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansur, F.A.; Raman, N.F.A.; Rahman, H.A.; Mohd Manzor, N.F. Mechanism of Autism Spectrum Disorder and The Involvement of microRNA. Malays. J. Sci. Health Technol. 2021, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, N.; Boyer, F.; Jaouen, F.; Belzeaux, R.; Gascon, E. Social Isolation and Enrichment Induce Unique miRNA Signatures in the Prefrontal Cortex and Behavioral Changes in Mice. iScience 2020, 23, 101790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Feng, T.; Lu, G.; Wang, S.; Song, J.; Xia, P.; et al. Biological Functions of Let-7e-5p in Promoting the Differentiation of MC3T3-E1 Cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 671170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Zhang, K.; Han, X.; Su, C.; Zhao, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, G.; Zhang, L.; Hu, W. Extracellular Vesicle-Derived miR-105-5p Promotes Malignant Phenotypes of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Targeting SPARCL1 via FAK/AKT Signaling Pathway. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 819699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, W.; He, J.; Huang, C.; Chen, L.; Tao, D.; Wu, X.; Wang, M.; Luo, G.; Xiao, X.; Zeng, F.; et al. miR-106b-5p targets tumor suppressor gene SETD2 to inactive its function in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 4066–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beveridge, N.J.; Gardiner, E.; Carroll, A.P.; Tooney, P.A.; Cairns, M.J. Schizophrenia is associated with an increase in cortical microRNA biogenesis. Mol. Psychiatry 2010, 15, 1176–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Qu, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Tian, H.L.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, G.Y. MicroRNA-126-3p/-5p Overexpression Attenuates Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption in a Mouse Model of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion. Stroke 2020, 51, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budi, H.S.; Younus, L.A.; Lafta, M.H.; Parveen, S.; Mohammad, H.J.; Al-Qaim, Z.H.; Jawad, M.A.; Parra, R.M.R.; Mustafa, Y.F.; Alhachami, F.R.; et al. The role of miR-128 in cancer development, prevention, drug resistance, and immunotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2023, 12, 1067974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.S.; Zhang, Y.N.; Li, C.; Yang, Z.Y.; Liu, Z.H.; Zhan, T.Z.; Xu, J.; Xia, C.M. MiR-130a-3p Alleviates Liver Fibrosis by Suppressing HSCs Activation and Skewing Macrophage to Ly6Clo Phenotype. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 696069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daswani, R.; Gilardi, C.; Soutschek, M.; Nanda, P.; Weiss, K.; Bicker, S.; Fiore, R.; Dieterich, C.; Germain, P.L.; Winterer, J.; et al. MicroRNA-138 controls hippocampal interneuron function and short-term memory in mice. Elife 2022, 11, e74056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Xie, G.; Yin, Y.; Zhao, E.; Tao, K.; Li, R. MicroRNA-152 regulates immune response via targeting B7-H1 in gastric carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 28125–28134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissman, R.; Diamond, E.L.; Haroche, J.; Durham, B.H.; Cohen, F.; Buthorn, J.; Amoura, Z.; Emile, J.F.; Mazor, R.D.; Shomron, N.; et al. MicroRNA-15a-5p acts as a tumor suppressor in histiocytosis by mediating CXCL10-ERK-LIN28a-let-7 axis. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1139–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyileten, C.; Sharif, L.; Wicik, Z.; Jakubik, D.; Jarosz-Popek, J.; Soplinska, A.; Postula, M.; Czlonkowska, A.; Kaplon-Cieslicka, A.; Mirowska-Guzel, D. The Relation of the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor with MicroRNAs in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Ischemic Stroke. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 329–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saba, R.; Störchel, P.H.; Aksoy-Aksel, A.; Kepura, F.; Lippi, G.; Plant, T.D.; Schratt, G.M. Dopamine-regulated microRNA MiR-181a controls GluA2 surface expression in hippocampal neurons. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 32, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Yao, J.; Xie, H.; Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Wei, K.; Ji, Y.; Liu, L. MicroRNA-195-5p Downregulation Inhibits Endothelial Mesenchymal Transition and Myocardial Fibrosis in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy by Targeting Smad7 and Inhibiting Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1-Smads-Snail Pathway. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 709123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzhanov, I.; Sintakova, K.; Romanyuk, N. The Role of miR-20 in Health and Disease of the Central Nervous System. Cells 2022, 11, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, C.; Luan, L.; Li, J.; Yang, L. MiR-212-3p improves rat functional recovery and inhibits neurocyte apoptosis in spinal cord injury models via PTEN downregulation-mediated activation of AKT/mTOR pathway. Brain Res. 2021, 1768, 147576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladejo, A.O.; Li, Y.; Imam, B.H.; Ma, X.; Shen, W.; Wu, X.; Jiang, W.; Yang, J.; Lv, Y.; Ding, X.; et al. MicroRNA miR-24-3p Mediates the Negative Regulation of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Endometrial Inflammatory Response by Targeting TNF Receptor-Associated Factor 6 (TRAF6). J. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 15, 807–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Zheng, S.; Duan, N.; Li, X.; Wen, J. MicroRNA-26b-5p alleviates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats via inhibiting the N-myc/PTEN axis by downregulating KLF10 expression. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2021, 40, 1250–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harati, R.; Hammad, S.; Tlili, A.; Mahfood, M.; Mabondzo, A.; Hamoudi, R. miR-27a-3p regulates expression of intercellular junctions at the brain endothelium and controls the endothelial barrier permeability. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camkurt, M.A. Blood microRNA dysregulation in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2015, 25, S112. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, M.; Ye, L.; Chen, C.; She, J.; Song, Y. MiR-29b-3p promotes particulate matter-induced inflammatory responses by regulating the C1QTNF6/AMPK pathway. Aging 2020, 12, 1141–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Cai, M.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, L.; Guo, R. miR-29c-3p inhibits autophagy and cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer by regulating FOXP1/ATG14 pathway. Cell Cycle 2020, 19, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.N.; Hong, Y.; Ma, Z.L.; Pang, R.P.; Lei, Q.Q.; Lv, X.F.; Zhou, J.G.; Huang, H.; Zhang, T.T. MiR-302a Limits Vascular Inflammation by Suppressing Nuclear Factor-κ B Pathway in Endothelial Cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 682574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasukawa, K.; Kinoshita, D.; Yaku, K.; Nakagawa, T.; Koshiba, T. The microRNAs miR-302b and miR-372 regulate mitochondrial metabolism via the SLC25A12 transporter, which controls MAVS-mediated antiviral innate immunity. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 444–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Salvador, A.M.; Li, G.; Valkov, N.; Ziegler, O.; Yeri, A.; Xiao, C.Y.; Meechoovet, B.; Alsop, E.; Rodosthenous, R.S.; et al. Mir-30d Regulates Cardiac Remodeling by Intracellular and Paracrine Signaling. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, e1–e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Shi, H.; Ren, F.; Feng, W.; Cao, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, Z.; Ji, P.; Zhang, M. MicroRNA-338-3p suppresses ovarian cancer cells growth and metastasis: Implication of Wnt/catenin beta and MEK/ERK signaling pathways. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, C.E.; Deng, L.; Orafidiya, F.; Yuan, W.; Lorentzen, M.P.G.S.; Cyran, O.W.; Varela-Carver, A.; Constantin, T.A.; Leach, D.A.; Dobbs, F.M.; et al. A non-coding RNA balancing act: miR-346-induced DNA damage is limited by the long non-coding RNA NORAD in prostate cancer. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Zhou, Y.; Ran, Q.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ju, J.; Yang, T.; Zhang, W.; Yu, X.; He, S. MicroRNA-381-3p Functions as a Dual Suppressor of Apoptosis and Necroptosis and Promotes Proliferation of Renal Cancer Cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Zhu, L.; Xu, J.; Lu, B.; Yang, Y.; Liu, F.; Wang, Z. MicroRNA-409-3p functions as a tumor suppressor in human lung adenocarcinoma by targeting c-Met. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 34, 1273–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Zuo, M.; Pei, Z.; Xie, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, M.; Kuang, D. MicroRNA-455-5p Contributes to Cholangiocarcinoma Growth and Mediates Galangin’s Anti-Tumor Effects. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 4710–4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Shuang, T.; Gao, Y.; Lu, F.; Zhang, J.; He, W.; Qu, L.; Chen, B.; Hao, Q. Targeted delivery of exosomal miR-484 reprograms tumor vasculature for chemotherapy sensitization. Cancer Lett. 2022, 530, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Wu, H.; Wang, R.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, T.; Zhang, G.; Liu, C.; Liu, J. MicroRNA-485-5p suppresses the proliferation, migration and invasion of small cell lung cancer cells by targeting flotillin-2. Bioengineered 2019, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; He, M.; Jiang, Q.; Yan, Y.; Guan, S.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Z.; Chen, Q.; Sun, M.; Yao, W.; et al. MiR-487a Promotes TGF-β1-induced EMT, the Migration and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cells by Directly Targeting MAGI2. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 12, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Zheng, W.; Sun, Y.; Xu, T. microRNA-489 negatively modulates RIG-I signaling pathway via targeting TRAF6 in miiuy croaker after poly(I:C) stimulation. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2021, 113, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravegnini, G.; De Leo, A.; Coada, C.; Gorini, F.; de Biase, D.; Ceccarelli, C.; Dondi, G.; Tesei, M.; De Crescenzo, E.; Santini, D.; et al. Identification of miR-499a-5p as a Potential Novel Biomarker for Risk Stratification in Endometrial Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 757678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, B.; Hu, Q. Exosomal miR-512-3p derived from mesenchymal stem cells inhibits oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced vascular endothelial cells dysfunction via regulating Keap1. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Lu, H.; Wang, H.; Shi, X.; Shao, X.; Li, Y.X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.L. miR-518b Enhances Human Trophoblast Cell Proliferation Through Targeting Rap1b and Activating Ras-MAPK Signal. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augenlicht, A.; Saiselet, M.; Decaussin-Petrucci, M.; Andry, G.; Dumont, J.E.; Maenhaut, C. MiR-7-5p inhibits thyroid cell proliferation by targeting the EGFR/MAPK and IRS2/PI3K signaling pathways. Oncotarget 2021, 12, 1587–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, J.; Zhang, H.; Dong, H.; Tong, X. miR-9-3p inhibits glioma cell proliferation and apoptosis by directly targeting FOXG1. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 2007–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, C.; Chen, L.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; An, Z.; Lin, C.; Han, H. MicroRNA miR-92a-3p regulates breast cancer cell proliferation and metastasis via regulating B-cell translocation gene 2 (BTG2). Bioengineered 2021, 12, 2033–2044. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya, P.; Biswas, A.; Biswas, S.C. Brain-enriched miR-128: Reduced in exosomes from Parkinson’s patient plasma, improves synaptic integrity, and prevents 6-OHDA mediated neuronal apoptosis. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2023, 16, 1037903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, H.S.; Lee, S.; Lee, H.J.; Min, J.W.; Iwatsubo, T.; Teunissen, C.E.; Cho, H.J.; Ryu, J.H. Targeting MicroRNA-485-3p Blocks Alzheimer’s Disease Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Han, E.; Choi, Y.C.; Kee, H.; Jeong, Y.; Yoon, J.; Baek, K. Inhibition of cell proliferation and migration by miR-509-3p that targets CDK2, Rac1, and PIK3C2A. Mol. Cells 2014, 37, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regis, S.; Dondero, A.; Spaggiari, G.M.; Serra, M.; Caliendo, F.; Bottino, C.; Castriconi, R. miR-24-3p down-regulates the expression of the apoptotic factors FasL and BIM in human natural killer cells. Cell. Signal. 2022, 98, 110415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Lin, Y.; Ren, X.; Xie, T.; Lin, J.; Wu, S.; Ye, Q. Let-7b-5p inhibits breast cancer cell growth and metastasis via repression of hexokinase 2-mediated aerobic glycolysis. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.H.; Li, C.; Cao, L.; Zhang, C.H.; Zhang, Z.H. Cucurbitacin B regulates lung cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis via inhibiting the IL-6/STAT3 pathway through the lncRNA XIST/miR-let-7c axis. Pharm. Biol. 2022, 60, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.N.; Ren, C.C.; Yang, L.; Nai, M.M.; Xu, Y.M.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Y. MicroRNA let 7d 5p rescues ovarian cancer cell apoptosis and restores chemosensitivity by regulating the p53 signaling pathway via HMGA1. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 1771–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Lin, G.; Yao, Y.; Chen, J.; Shui, H.; Yang, Q.; Wang, X.; Weng, X.; Sun, L.; Chen, F.; et al. MicroRNA hsa-let-7e-5p as a potential prognosis marker for rectal carcinoma with liver metastases. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 6913–6924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yang, R.; Chen, J.; Qi, E.; Zhou, S.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Q.; Chen, R.; Fang, X. Let-7i-5p Regulation of Cell Morphology and Migration Through Distinct Signaling Pathways in Normal and Pathogenic Urethral Fibroblasts. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, P.; Huang, S.; Han, X.; Zhang, C.; Yang, L.; Xiao, W.; Fu, J.; Li, H.; Zhou, Y. Exosomal miR-101-3p and miR-423-5p inhibit medulloblastoma tumorigenesis through targeting FOXP4 and EZH2. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagar, S.K. miR-106b as an emerging therapeutic target in cancer. Genes Dis. 2021, 9, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahonen, M.A.; Haridas, P.A.N.; Mysore, R.; Wabitsch, M.; Fischer-Posovszky, P.; Olkkonen, V.M. miR-107 inhibits CDK6 expression, differentiation, and lipid storage in human adipocytes. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2019, 479, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, C.; Liu, X.; Guo, Y.; Fo, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhou, J.; Yang, B. MiR-128-3p inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration by repressing FOXO4/MMP9 signaling pathway. Mol. Med. 2020, 26, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, N.; Nouri-Vaskeh, M.; Hasanpour Segherlou, Z.; Baghbanzadeh, A.; Halimi, M.; Rezaee, H.; Baradaran, B. Diagnos-tic, prognostic, and therapeutic significance of miR-139-5p in cancers. Life Sci. 2020, 256, 117865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, F.; Wei, M.; Qiu, Y.; Ma, C.; Shen, L.; Huang, Y. Chronic constriction injury-induced microRNA-146a-5p alle-viates neuropathic pain through suppression of IRAK1/TRAF6 signaling pathway. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurel, O.M.; Torrisi, S.A.; Barbagallo, C.; Purrello, M.; Salomone, S.; Drago, F.; Ragusa, M.; Leggio, G.M. Dysregulation of miR-15a-5p, miR-497a-5p and miR-511-5p Is Associated with Modulation of BDNF and FKBP5 in Brain Areas of PTSD-Related Susceptible and Resilient Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Di Wang, X. miR-150-5p represses TP53 tumor suppressor gene to promote proliferation of colon adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Xia, Y.; Lv, J.; Wang, W.; Xuan, Z.; Chen, C.; Jiang, T.; Fang, L.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; et al. miR-151a-3p-rich small extracel-lular vesicles derived from gastric cancer accelerate liver metastasis via initiating a hepatic stemness-enhancing niche. Oncogene 2021, 40, 6180–6194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, F.; Lei, Q.; Zhang, T.; Li, K.; Guo, J.; Hong, Y.; Bu, G.; Lv, X.; et al. MicroRNA-181a-5p and microRNA-181a-3p cooperatively restrict vascular inflammation and atherosclerosis. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Cai, W.; Xu, Y.; Zuo, W. Down-regulation of miR-19b-3p enhances IGF-1 expression to induce osteoblast differentia-tion and improve osteoporosis. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2022, 68, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Hu, J.; Sun, F.; Bian, H.; Tang, B.; Fang, X. MicroRNA-20a-5p suppresses tumor angiogenesis of non-small cell lung cancer through RRM2-mediated PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2021, 476, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorur, A.; Bayraktar, R.; Ivan, C.; Mokhlis, H.A.; Bayraktar, E.; Kahraman, N.; Karakas, D.; Karamil, S.; Kabil, N.N.; Kan-likilicer, P.; et al. ncRNA therapy with miRNA-22-3p suppresses the growth of triple-negative breast cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2021, 23, 930–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liang, J.; Chen, N. The Potential Role of miRNA-Regulated Autophagy in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.; Pan, H.; Sun, D.; Xu, H.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Li, L.; Wang, T. miR-26b-5p Inhibits the Proliferation, Migration and Invasion of Human Papillary Thyroid Cancer in a β-Catenin-Dependent Manner. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 1593–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duwe, L.; Munoz-Garrido, P.; Lewinska, M.; Lafuente-Barquero, J.; Satriano, L.; Høgdall, D.; Taranta, A.; Nielsen, B.S.; Ghazal, A.; Matter, M.S.; et al. MicroRNA-27a-3p targets FoxO signalling to induce tumour-like phenotypes in bile duct cells. J. Hepatol. 2023, 78, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Yang, H.; Ma, X.; Wu, G. Strand-specific miR-28-3p and miR-28-5p have differential effects on nasopharyngeal cancer cells proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Zhong, D.; Wang, C.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, G. MiR-298 Exacerbates Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Following Ischemic Stroke by Targeting Act1. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 48, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Han, X.; Hu, W.; Su, C.; He, B. miR-29a-3p inhibits the malignant characteristics of non-small cell lung cancer cells by reducing the activity of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2022, 24, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Yun, H.J.; Elkin, K.; Guo, Y.; Ding, Y.; Li, G. MicroRNA-29b Suppresses Inflammation and Protects Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity in Ischemic Stroke. Mediat. Inflamm. 2022, 2022, 1755416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghehchian, N.; Lotfi, M.; Zangouei, A.S.; Akhlaghipour, I.; Moghbeli, M. MicroRNAs as the critical regulators of Forkhead box protein family during gynecological and breast tumor progression and metastasis. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, Y.-T.; Tang, J.-Y.; Shiau, J.-P.; Yen, C.-Y.; Chang, F.-R.; Yang, K.-H.; Hou, M.-F.; Farooqi, A.A.; Chang, H.-W. Modu-lating Effects of Cancer-Derived Exosomal miRNAs and Exosomal Processing by Natural Products. Cancers 2023, 15, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Yin, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Li, H.; Dai, B.; Fan, J.; He, M.; Nie, X.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, D.W.; et al. miR-320a induces pancreatic β cells dysfunction in diabetes by inhibiting MafF. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2021, 26, 444–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.C.; Hsi, E.; Hu, C.Y.; Chou, W.W.; Liang, C.L.; Juo, S.H. MicroRNA-328 may influence myopia development by me-diating the PAX6 gene. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 2732–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Cai, J.; Cai, X.H.; Chen, L. miR-346 regulates osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesen-chymal stem cells by targeting the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72266. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Liao, Y.; Tang, L. MicroRNA-34 family: A potential tumor suppressor and therapeutic candidate in cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xue, Y.; Ma, J.; Shao, L.; Wang, D.; Zheng, J.; Liu, X.; Yang, C.; He, Q.; Ruan, X.; et al. SNHG1 promotes malignant bio-logical behaviors of glioma cells via microRNA-154-5p/miR-376b-3p- FOXP2- KDM5B participating positive feedback loop. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Su, Z.; Hu, W.; Yuan, X.; Yu, T.; Yang, J.; Xiao, X.; Zheng, S.; Lin, B. miR-433 Inhibits Glioblastoma Progression by Suppressing the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway Through Direct Targeting of ERBB4. OMICS J. Integr. Biol. 2023, 27, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Dai, C.; Yu, X.; Yin, X.B.; Zhou, F. microRNA-485-5p inhibits the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through blocking the WBP2/Wnt signaling pathway. Cell. Signal. 2020, 66, 109466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, H.; He, Z.; Xie, D.; Ni, J.; Lin, X. MicroRNA-488-3p inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis by targeting ZBTB2 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 18702–18713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Xu, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, X. miR-511-3p promotes hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome by activating hedgehog pathway via targeting Ptch1. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2021, 321, G344–G354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; He, L.; Yue, Q.; Lu, J.; Kang, N.; Xu, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H. MiR-9-5p promotes MSC migration by activating β-catenin signaling pathway. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2017, 313, C80–C93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Feng, X.; Liu, H.; Tong, R.; Wu, J.; Li, C.; Yu, H.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Chen, J.; et al. High-metastatic cancer cells derived exosomal miR92a-3p promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of low-metastatic cancer cells by regulating PTEN/Akt pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2020, 39, 6529–6543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Xiao, R.; Wang, X.; Xiong, Y.; Duan, Z.; Li, D.; Kan, Q. MiR-93-5p regulates tumorigenesis and tumor immunity by targeting PD-L1/CCND1 in breast cancer. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Shi, X.; Li, J.; Jia, Y. MicroRNA-98-5p inhibits human mesangial cell proliferation and TNF-α and IL-6 secretion by targeting BTB and CNC homology 1. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajares, M.J.; Alemany-Cosme, E.; Goñi, S.; Bandres, E.; Palanca-Ballester, C.; Sandoval, J. Epigenetic Regulation of mi-croRNAs in Cancer: Shortening the Distance from Bench to Bedside. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, L.; Zhang, T.; Liu, W.; Chen, Y. Inhibition of miR-128 Abates Aβ-Mediated Cytotoxicity by Targeting PPAR-γ via NF-κB Inactivation in Primary Mouse Cortical Neurons and Neuro2a Cells. Yonsei Med. J. 2018, 59, 1096–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Wei, S.; Luo, M.; Tang, Z.; Lin, Q.; Wang, X.; Luo, M.; He, Y.; Wang, C.; Wei, D.; et al. MiR-139-5p has an antide-pressant-like effect by targeting phosphodiesterase 4D to activate the cAMP/PKA/CREB signaling pathway. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Zheng, R.; Shao, G. Mechanisms and application strategies of miRNA-146a regulating inflammation and fibrosis at molecular and cellular levels (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2023, 51, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wu, L.; Sun, Q.; Yang, Q.; Xue, J.; Shi, M.; Tang, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Q. MicroRNA-191 blocking the translocation of GLUT4 is involved in arsenite-induced hepatic insulin resistance through inhibiting the IRS1/AKT pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 215, 112130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Han, Z.; An, Z.; Li, Y.; Xie, X.; Zhou, J.; He, S.; Lv, Y.; He, M.; Qu, H.; et al. The miR-203a Regulatory Network Affects the Proliferation of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia K562 Cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 616711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.A.; Gao, L.F.; Zhang, Z.G.; Xiang, D.K. Down-regulation of miR-320 exerts protective effects on myocardial I-R injury via facilitating Nrf2 expression. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 1730–1741. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Song, R.; Wu, J.; Wang, W.; Chen, X.; Yin, J. MicroRNA-337 regulates the PI3K/AKT and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways to inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma progression by targeting high-mobility group AT-hook 2. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 8, 405–421. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, W.; Yang, X.; Yang, H.; Lv, M.; Sun, X.; Zhou, B. Correction: Exosomal miR-338-3p suppresses non-small-cell lung can-cer cells metastasis by inhibiting CHL1 through the MAPK signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.R.; Shi, M.M.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, X.L.; Wei, L.B.; Qin, X.J. MicroRNA-339-5p inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced rat mesangial cells by regulating the Syk/Ras/c-Fos pathway. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2022, 395, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, L.; Lv, Z.; Li, Q.; Gong, W.; Wu, H. MicroRNA-342-3p Inhibits the Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Osteosarcoma Cells by Targeting Astrocyte-Elevated Gene-1 (AEG-1). Oncol. Res. 2017, 25, 1505–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, H.; Chu, S.; Liu, X.; Qu, X.; Li, J.; Liu, D.; Li, H. miR-124-3p promotes BMSC osteogenesis via suppressing the GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling pathway in diabetic osteoporosis rats. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol.-Anim. 2020, 56, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Li, H.F.; Pan, Q.; Jin, H.L.; Yang, M.; Wang, R.R.; Wang, Q.Y.; Zhang, J.P. MiR-132-3p Modulates MEKK3-Dependent NF-κB and p38/JNK Signaling Pathways to Alleviate Spinal Cord Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Hindering M1 Polariza-tion of Macrophages. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 570451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, Y.J.; Ren, Q.H.; Bi, L. miR-135b-5p regulates human mesenchymal stem cell osteogenic differentiation by facilitating the Hippo signaling pathway. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2017, 10, 7767–7775. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Chu, X.; Wang, P.; Ma, X.; Wei, C.; Sun, C.; Yang, J.; Li, Y. MicroRNA-29a-3p Reduces TNFα-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction by Targeting Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor 1. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 18, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, H.; Zhong, X.S.; Xiao, Y.; Sun, Z.; Shen, Y.; Zhao, K.; Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Niu, Q.; Liu, M.; et al. Exosomal miR-29b of Gut Origin in Patients With Ulcerative Colitis Suppresses Heart Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 759689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zuo, X.; Han, J.; Dai, Q.; Xu, H.; Liu, Y.; Cui, S. MiR-9-5p inhibits mitochondrial damage and oxidative stress in AD cell models by targeting GSK-3β. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2020, 84, 2273–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, S.E.; Lim, C.S.; Kim, J.I.; Seo, D.; Chun, H.; Yu, N.K.; Lee, J.; Kang, S.J.; Ko, H.G.; Choi, J.H.; et al. The Brain-Enriched MicroRNA miR-9-3p Regulates Synaptic Plasticity and Memory. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 8641–8652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.C.; Zheng, J.Y.; Tang, L.J.; Huang, B.S.; Li, K.; Tao, Y.; Yu, W.; Zhu, R.L.; Li, S.; Li, L.X. MiR-133b Promotes neurite out-growth by targeting RhoA expression. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 35, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Bai, Q.; Wang, C.; Meng, Q.; Gu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xu, W.; Han, Y.; Qin, Y.; Jia, S.; et al. miR-433 Inhibits Neuronal Growth and Promotes Autophagy in Mouse Hippocampal HT-22 Cell Line. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 11, 536913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-de Frutos, M.; Galán-Chilet, I.; Goedeke, L.; Kim, B.; Pardo-Marqués, V.; Pérez-García, A.; Herrero, J.I.; Fernán-dez-Hernando, C.; Kim, J.; Ramírez, C.M. MicroRNA 7 Impairs Insulin Signaling and Regulates Aβ Levels through Post-transcriptional Regulation of the Insulin Receptor Substrate 2, Insulin Receptor, Insulin-Degrading Enzyme, and Liver X Re-ceptor Pathway. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2019, 39, e00170-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Yang, C.; Gao, A.; Sun, M.; Lv, D. MiR-101: An Important Regulator of Gene Expression and Tumor Ecosystem. Cancers 2022, 14, 5861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-hasso IK, Q.; Al-Derzi, A.R.; Abbas AA, H.; Gorial, F.I.; Alnuimi, A.S. Role of circulating miRNA-130b-3p and TGF-β 1cytokine in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Gene Rep. 2022, 26, 101476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, A. miR-19b-3p relieves intervertebral disc degeneration through modulating PTEN/PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Aging 2021, 13, 22459–22473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, A.M.; Mahnke, A.H.; Wells, A.B.; Salem, N.A.; Allan, A.M.; Roberts, V.H.; Newman, N.; Walter, N.A.; Kroenke, C.D.; Grant, K.A.; et al. Maternal circulating miRNAs that predict infant FASD outcomes influence placental maturation. Life Sci. Alliance 2019, 2, e201800252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, R.C. MicroRNAs and ethanol toxicity. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2014, 115, 245–284. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mahnke, A.H.; Sideridis, G.D.; Salem, N.A.; Tseng, A.M.; Carter, R.C.; Dodge, N.C.; Rathod, A.B.; Molteno, C.D.; Meintjes, E.M.; Jacobson, S.W.; et al. Infant circulating MicroRNAs as biomarkers of effect in fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirle, N.T.; Sheu-Gruttadauria, J.; MacRae, I.J. Gene regulation. Structural basis for microRNA targeting. Science 2014, 346, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetzl, L.; Darbinian, N.; Merabova, N. Noninvasive assessment of fetal central nervous system insult: Potential application to Prenatal Diagnosis. Prenat. Diagn. 2019, 39, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbinian, N.; Darbinyan, A.; Merabova, N.; Bajwa, A.; Tatevosian, G.; Martirosyan, D.; Zhao, H.; Selzer, M.E.; Goetzl, L. Ethanol-mediated alterations in oligodendrocyte differentiation in the developing brain. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 148, 105181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbinian, N.; Darbinyan, A.; Sinard, J.; Tatevosian, G.; Merabova, N.; D’Amico, F.; Khader, T.; Bajwa, A.; Martirosyan, D.; Gawlinski, A.K.; et al. Molecular Markers in Maternal Blood Exosomes Allow Early Detection of Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbinian, N.; Merabova, N.; Tatevosian, G.; Morrison, M.; Darbinyan, A.; Zhao, H.; Goetzl, L.; Selzer, M.E. Biomarkers of Affective Dysregulation Associated with In Utero Exposure to EtOH. Cells 2024, 13, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visvanathan, J.; Lee, S.; Lee, B.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, S.K. The microRNA miR-124 antagonizes the anti-neural REST/SCP1 pathway during embryonic CNS development. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 744–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conaco, C.; Otto, S.; Han, J.J.; Mandel, G.; Otto, S.; Han, J.J.; Mandel, G.; Han, J.J.; Mandel, G.; Mandel, G. Reciprocal actions of REST and a microRNA promote neuronal identity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2422–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.C.; Pastrana, E.; Tavazoie, M.; Doetsch, F. miR-124 regulates adult neurogenesis in the subventricular zone stem cell niche. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, B.C.; Power, E.M.; Mc Dermott, K.W. Developmentally regulated expression of Sox9 and microRNAs 124 128 and 23 in neuroepithelial stem cells in the developing spinal cord. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2011, 29, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åkerblom, M.; Sachdeva, R.; Barde, I.; Verp, S.; Gentner, B.; Trono, D.; Jakobsson, J. MicroRNA-124 is a subventricular zone neuronal fate determinant. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 8879–8889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makeyev, E.V.; Zhang, J.; Carrasco, M.A.; Maniatis, T. The microRNA miR-124 promotes neuronal differentiation by triggering brain-specific alternative pre-mRNA splicing. Mol. Cell 2007, 27, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Qian, H.; Hu, J.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, X.; Karakhanyan, A.; Pang, Z.; Fu, X.D. Sequential regulatory loops as key gatekeepers for neuronal reprogramming in human cells. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Ouyang, K.; Huang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Ouyang, H.; Li, H.; Wang, G.; Wu, Q.; Wei, C.; Bi, Y.; et al. Direct conversion of fibroblasts to neurons by reprogramming PTB-regulated MicroRNA circuits. Cell 2013, 152, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, W.; Li, W.; Hoque, M.; Li, Z.; Tian, B.; Makeyev, E.V. A post-transcriptional mechanism pacing expression of neural genes with precursor cell differentiation status. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadimitriou, E.; Koutsoudaki, P.N.; Thanou, I.; Karagkouni, D.; Karamitros, T.; Chroni-Tzartou, D.; Gaitanou, M.; Gkemisis, C.; Margariti, M.; Xingi, E.; et al. A miR-124-mediated post-transcriptional mechanism controlling the cell fate switch of astrocytes to induced neurons. Stem Cell Rep. 2023, 18, 915–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epple, R.; Krüger, D.; Berulava, T.; Brehm, G.; Ninov, M.; Islam, R.; Köster, S.; Fischer, A. The Coding and Small Non-coding Hippocampal Synaptic RNAome. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 2940–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.L. microRNAs and Fragile X Syndrome. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 888, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Edbauer, D.; Neilson, J.R.; Foster, K.A.; Wang, C.-F.; Seeburg, D.P.; Batterton, M.N.; Tada, T.; Dolan, B.M.; Sharp, P.A.; Sheng, M. Regulation of Synaptic Structure and Function by FMRP-Associated MicroRNAs miR-125b and miR-132. Neuron 2010, 65, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vo, D.T.; Qiao, M.; Smith, A.D.; Burns, S.C.; Brenner, A.J.; Penalva, L.O.F. The oncogenic RNA-binding protein Musashi1 is regulated by tumor suppressor miRNAs. RNA Biol. 2011, 8, 817–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, M.C.T.; Tegge, A.N.; Correa, B.R.; Mahesula, S.; Kohnke, L.Q.; Qiao, M.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Kokovay, E.; Penalva, L.O.F. MiR-124, -128, and -137 orchestrate neural differentiation by acting on overlapping gene sets containing a highly connected transcription factor network. Stem Cells 2016, 34, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Kim, P.J.; Chen, Z.; Lokman, H.; Qiu, L.; Zhang, K.; Rozen, S.G.; Tan, E.K.; Je, H.S.; Zeng, L. MiRNA-128 regulates the proliferation and neurogenesis of neural precursors by targeting PCM1 in the developing cortex. Elife 2016, 5, e11324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzoni, E.; Booker, S.A.; Parthasarathy, S.; Rehfeld, F.; Grosser, S.; Srivatsa, S.; Fuchs, H.; Tarabykin, V.; Vida, I.; Wulczyn, F.G. miR-128 regulates neuronal migration, outgrowth and intrinsic excitability via the intellectual disability gene Phf6. Elife 2015, 4, e04263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Ye, P.; Murai, K.; Lang, M.F.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Li, W.; Fu, C.; Yin, J.; Wang, A.; et al. miR-137 forms a regulatory loop with nuclear receptor TLX and LSD1 in neural stem cells. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olde Loohuis, N.F.; Ba, W.; Stoerchel, P.H.; Kos, A.; Jager, A.; Schratt, G.; Martens, G.J.; van Bokhoven, H.; Nadif Kasri, N.; Aschrafi, A. MicroRNA-137 Controls AMPA-Receptor-Mediated Transmission and mGluR-Dependent LTD. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 1876–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmohsen, K.; Hutchison, E.R.; Lee, E.K.; Kuwano, Y.; Kim, M.M.; Masuda, K.; Srikantan, S.; Subaran, S.S.; Marasa, B.S.; Mattson, M.P.; et al. miR-375 inhibits differentiation of neurites by lowering HuD levels. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 30, 4197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magill, S.T.; Cambronne, X.A.; Luikart, B.W.; Lioy, D.T.; Leighton, B.H.; Westbrook, G.L.; Mandel, G.; Goodman, R.H. microRNA-132 regulates dendritic growth and arborization of newborn neurons in the adult hippocampus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 20382–20387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, M.L.; Preitner, N.; Quan, J.; Flanagan, J.G. MicroRNA-132 is enriched in developing axons, locally regulates Rasa1 mRNA, and promotes axon extension. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marler, K.J.; Suetterlin, P.; Dopplapudi, A.; Rubikaite, A.; Adnan, J.; Maiorano, N.A.; Lowe, A.S.; Thompson, I.D.; Pathania, M.; Bordey, A.; et al. BDNF promotes axon branching of retinal ganglion cells via miRNA-132 and p250GAP. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 969–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luikart, B.W.; Bensen, A.L.; Washburn, E.K.; Perederiy, J.V.; Su, K.G.; Li, Y.; Kernie, S.G.; Parada, L.F.; Westbrook, G.L. miR-132 mediates the integration of newborn neurons into the adult dentate gyrus. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayman, G.A.; Davare, M.; Ando, H.; Fortin, D.; Varlamova, O.; Cheng, H.Y.; Marks, D.; Obrietan, K.; Soderling, T.R.; Goodman, R.H.; et al. An activity-regulated microRNA controls dendritic plasticity by down-regulating p250GAP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9093–9098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellios, N.; Sugihara, H.; Castro, J.; Banerjee, A.; Le, C.; Kumar, A.; Crawford, B.; Strathmann, J.; Tropea, D.; Levine, S.S.; et al. miR-132, an experience-dependent microRNA, is essential for visual cortex plasticity. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 1240–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tognini, P.; Putignano, E.; Coatti, A.; Pizzorusso, T. Experience-dependent expression of miR-132 regulates ocular dominance plasticity. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 1237–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, S.; Majeti, B.K.; Acevedo, L.M.; Murphy, E.A.; Mukthavaram, R.; Scheppke, L.; Huang, M.; Shields, D.J.; Lindquist, J.N.; Lapinski, P.E.; et al. MicroRNA-132-mediated loss of p120RasGAP activates the endothelium to facilitate pathological angiogenesis. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, M.E.; Lioy, D.T.; Ma, L.; Impey, S.; Mandel, G.; Goodman, R.H. Homeostatic regulation of MeCP2 expression by a CREB-induced microRNA. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 1513–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagos, D.; Pollara, G.; Henderson, S.; Gratrix, F.; Fabani, M.; Milne, R.S.; Gotch, F.; Boshoff, C. miR-132 regulates antiviral innate immunity through suppression of the p300 transcriptional co-activator. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Du, X.F.; Li, J.; Zi, H.X.; Bu, J.W.; Yan, Y.; Han, H.; Du, J.L. Neurons secrete miR-132-containing exosomes to regulate brain vascular integrity. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 882–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walgrave, H.; Penning, A.; Tosoni, G.; Snoeck, S.; Davie, K.; Davis, E.; Wolfs, L.; Sierksma, A.; Mars, M.; Bu, T.; et al. microRNA-132 regulates gene expression programs involved in microglial homeostasis. iScience 2023, 26, 106829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dajas-Bailador, F.; Bonev, B.; Garcez, P.; Stanley, P.; Guillemot, F.; Papalopulu, N. microRNA-9 regulates axon extension and branching by targeting Map1b in mouse cortical neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 697–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, R.J., Jr.; Chang, S.; Etchberger, J.F.; Ortiz, C.O.; Hobert, O. MicroRNAs acting in a double-negative feedback loop to control a neuronal cell fate decision. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 12449–12454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Zhou, P.; Liu, Z. Functional characteristics of a double negative feedback loop mediated by microRNAs. Cogn. Neurodyn. 2013, 7, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radhakrishnan, B.; Alwin Prem Anand, A. Role of miRNA-9 in Brain Development. J. Exp. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 101–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuva-Aydemir, Y.; Simkin, A.; Gascon, E.; Gao, F.B. MicroRNA-9: Functional evolution of a conserved small regulatory RNA. RNA Biol. 2011, 8, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, A.N.; Xing, Y.; Harper, S.Q.; Jones, L.; Davidson, B.L. The bifunctional microRNA miR-9/miR-9* regulates REST and CoREST and is downregulated in Huntington’s disease. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 14341–14346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, A.; Conn, R. Eye abnormalities in fetal alcohol syndrome. Ulst. Med. J. 2009, 78, 164–165. [Google Scholar]
- Strömland, K. Visual impairment and ocular abnormalities in children with fetal alcohol syndrome. Addict. Biol. 2004, 9, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, D.; Barone, S. Critical periods of vulnerability for the developing nervous system: Evidence from humans and animal models. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108 (Suppl. S3), 511–533. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miranda, R.C. MicroRNAs and Fetal Brain Development: Implications for Ethanol Teratology during the Second Trimester Period of Neurogenesis. Front. Genet. 2012, 3, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Carreon, S.; Qiang, M. Chronic intermittent ethanol exposure and its removal induce a different miRNA expression pattern in primary cortical neuronal cultures. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2012, 36, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Q.; Yang, R.; Pei, X.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, S.F.; Li, Y. Ethanol exposure induces differential microRNA and target gene expression and teratogenic effects which can be suppressed by folic acid supplementation. Hum. Reprod. 2009, 24, 562–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sathyan, P.; Golden, H.B.; Miranda, R.C. Competing interactions between micro-RNAs determine neural progenitor survival and proliferation after ethanol exposure: Evidence from an ex vivo model of the fetal cerebral cortical neuroepithelium. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 8546–8557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrzykowski, A.Z.; Friesen, R.M.; Martin, G.E.; Puig, S.I.; Nowak, C.L.; Wynne, P.M.; Siegelmann, H.T.; Treistman, S.N. Posttranscriptional regulation of BK channel splice variant stability by miR-9 underlies neuroadaptation to alcohol. Neuron 2008, 59, 274–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaraman, S.; Winzer-Serhan, U.H.; Miranda, R.C. Opposing actions of ethanol and nicotine on microRNAs are mediated by nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in fetal cerebral cortical-derived neural progenitor cells. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2012, 36, 1669–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tal, T.L.; Franzosa, J.A.; Tilton, S.C.; Philbrick, K.A.; Iwaniec, U.T.; Turner, R.T.; Waters, K.M.; Tanguay, R.L. MicroRNAs control neurobehavioral development and function in zebrafish. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 1452–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukes, K.; Tripp, T.; Petersen, J.; Robinson, F.; Odendaal, H.; Elliott, A.; Willinger, M.; Hereld, D.; Raffo, C.; Kinney, H.C.; et al. A modified Timeline Followback assessment to capture alcohol exposure in pregnant women: Application in the Safe Passage Study. Alcohol 2017, 62, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

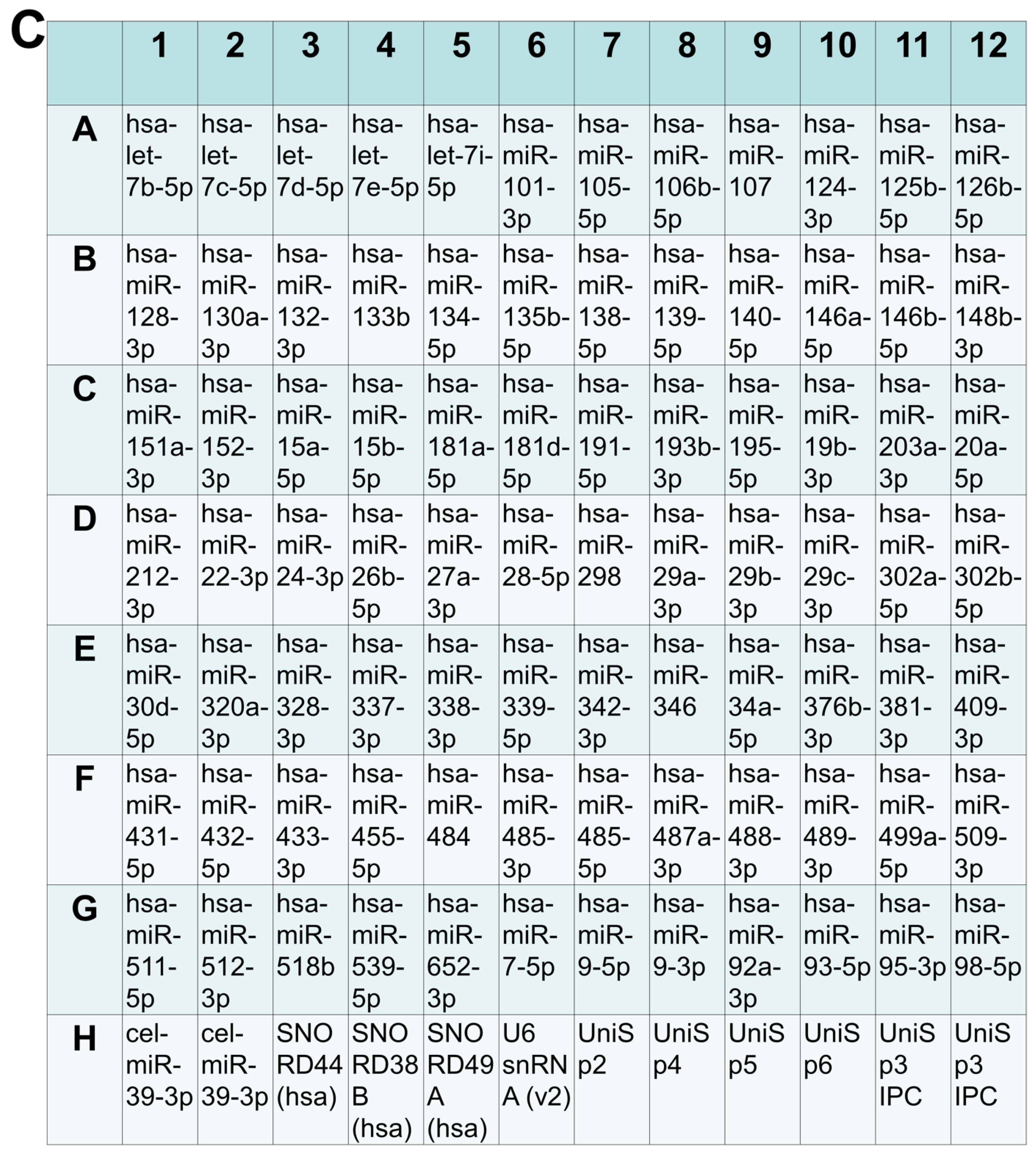
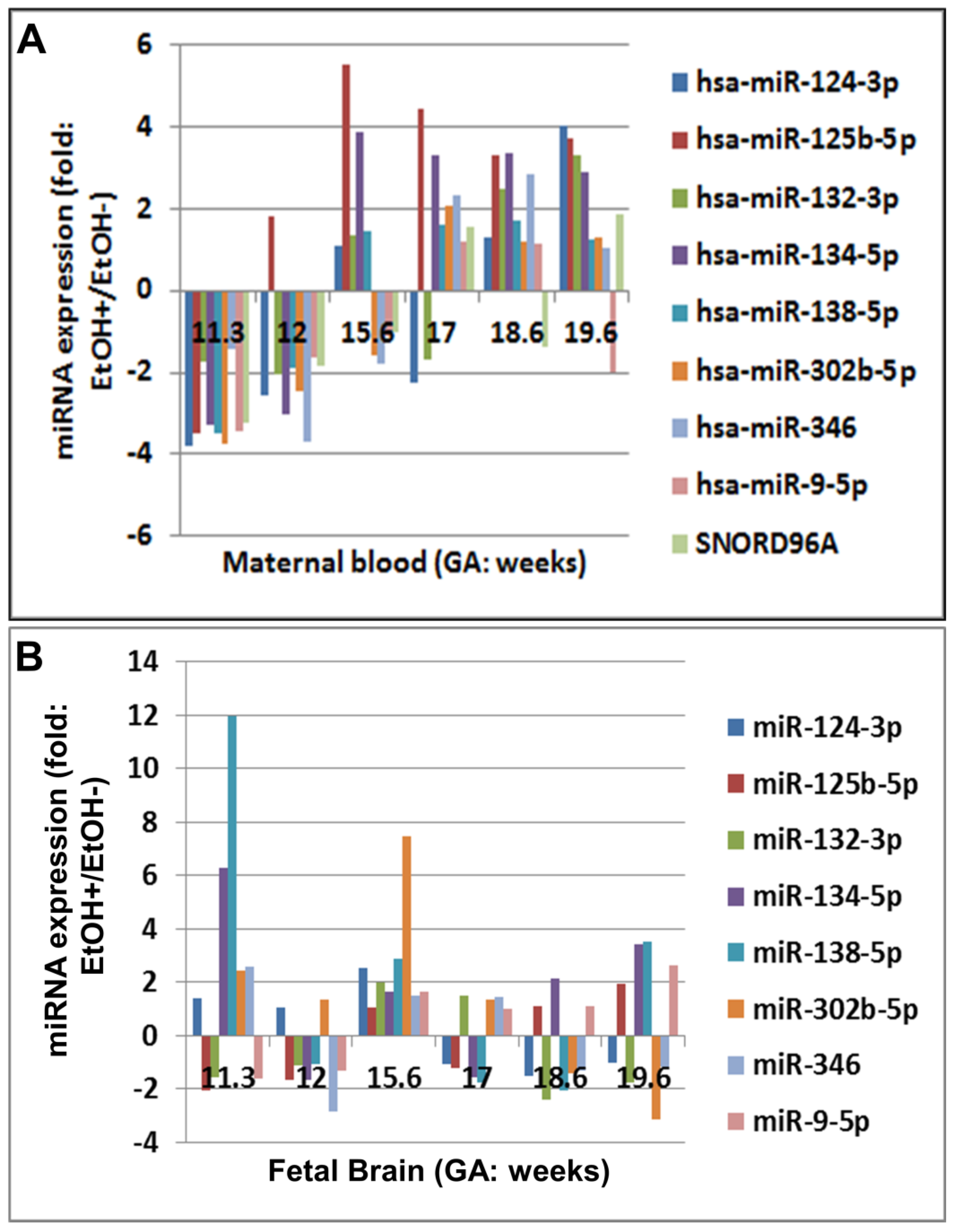
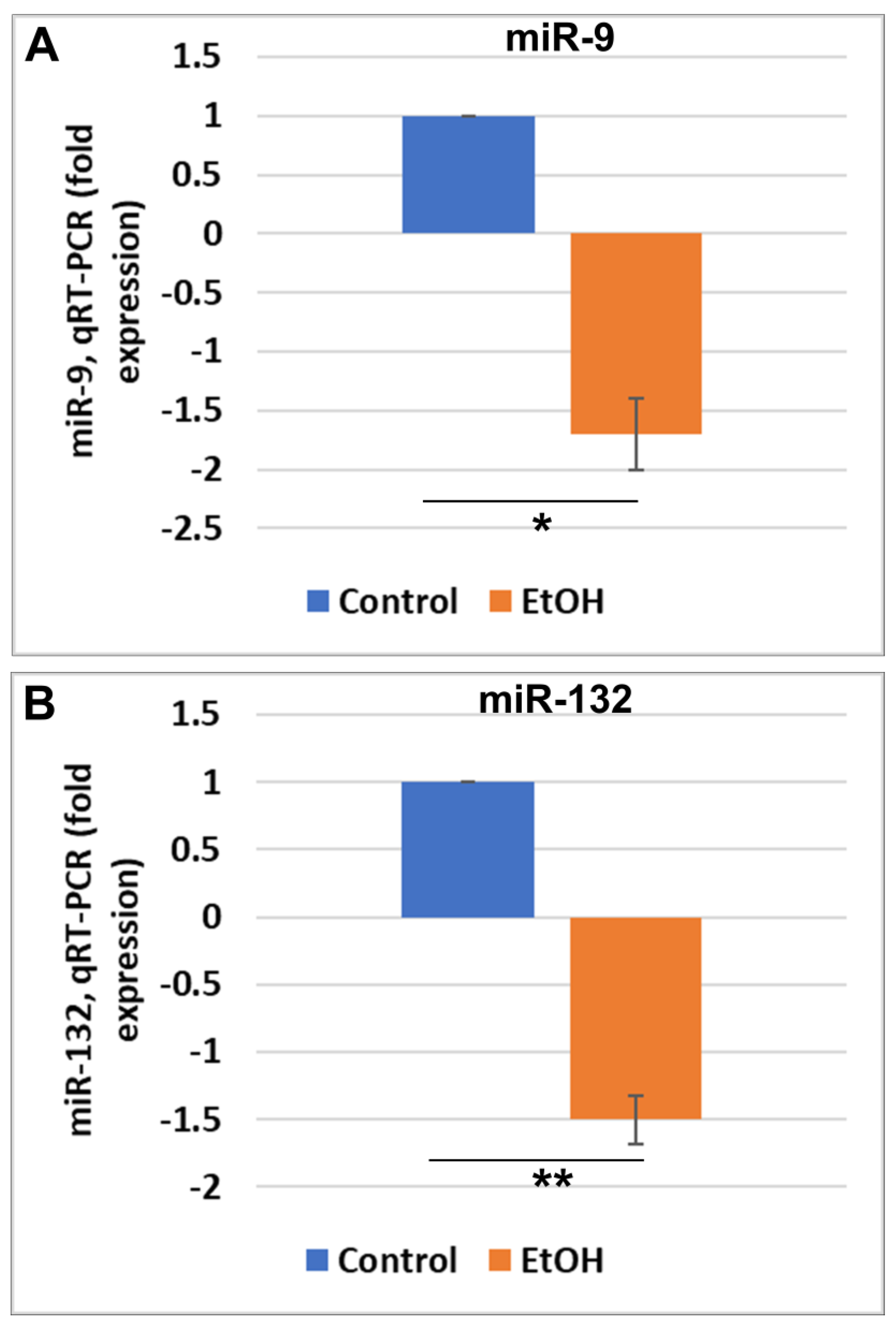
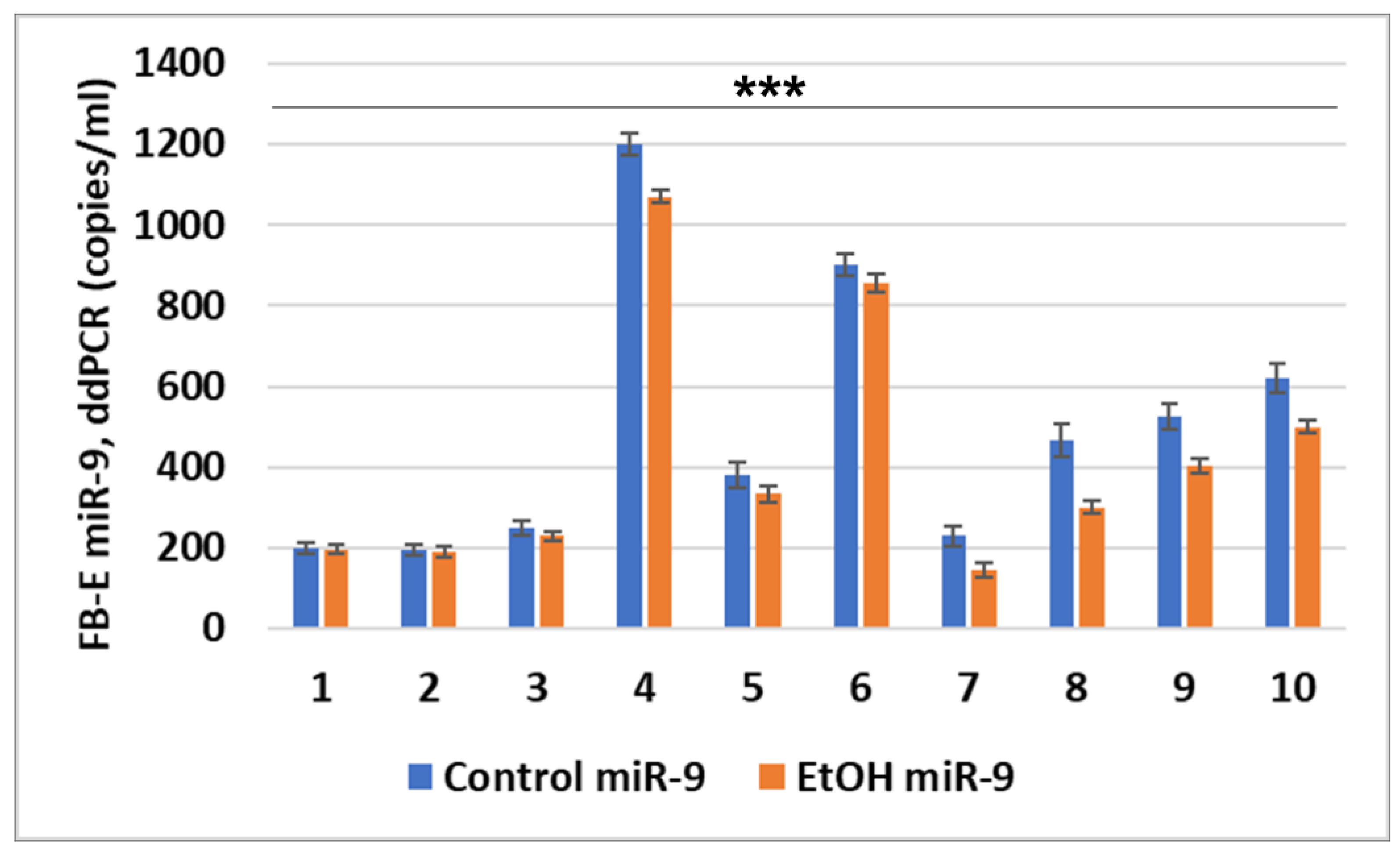

| EtOH-Consuming Subjects (n = 40) | Control Subjects (No EtOH, n = 40) | |
|---|---|---|
| Maternal Age (years ± SD) | 26.17 ± 2.15 | 22.34 ± 1.70 |
| Gestational Age (weeks ± SD) | 15.47 ± 1.33 | 15.16 ± 1.42 |
| Race: White vs. Black (%) | 50 vs. 50 | 50 vs. 50 |
| Fetal Sex (male vs. female, %) | 50 vs. 50 | 50 vs. 50 |
| miRNAs in Neurological Development and Disease |
|---|
| Development: miR-124-3p, miR-125b-5p, miR-132-3p, miR-134, miR-138-5p, miR-9-5p. |
| Autistic Disorders: miR-106b-5p, miR-128, miR-132-3p, miR-140-5p, miR-146b-5p, miR-148b-3p, miR-15a-5p, miR-15b-5p, miR-181d, miR-193b-3p, miR-212-3p, miR-27a-3p, miR-320a, miR-381-3p, miR-431-5p, miR-432-5p, miR-484, miR-539-5p, miR-652-3p, miR-7-5p, miR-93-5p, miR-95. |
| Schizophrenia: let-7d-5p, let-7e-5p, miR-105-5p, miR-106b-5p, miR-107, miR-126-5p, miR-128, miR-130a-3p, miR-138-5p, miR-152, miR-15a-5p, miR-15b-5p, miR-181a-5p, miR-195-5p, miR-20a-5p, miR-212-3p, miR-24-3p, miR-26b-5p, miR-27a-3p, miR-29a-3p, miR-29b-3p, miR-29c-3p, miR-302a-5p, miR-302b-5p, miR-30d-5p, miR-338-3p, miR-346, miR-381-3p, miR-409-3p, miR-455-5p, miR-484, miR-485-5p, miR-487a, miR-489, miR-499a-5p, miR-512-3p, miR-518b, miR-7-5p, miR-9-3p, miR-92a-3p. |
| Anxiety Disorder: miR-128, miR-485-3p, miR-509-3p. |
| Tourette’s Syndrome: miR-24-3p. |
| Prion Diseases: let-7b-5p, miR-128, miR-139-5p, miR-146a-5p, miR-191-5p, miR-203a, miR-320a, miR-337-3p, miR-338-3p, miR-339-5p, miR-342-3p. |
| Huntington’s Disease: miR-124-3p, miR-132-3p, miR-135b-5p, miR-29a-3p, miR-29b-3p, miR-9-5p, miR-9-3p. |
| Parkinson’s Disease: miR-133b, miR-433, miR-7-5p. |
| Spinocerebellar Ataxia 1: miR-101-3p, miR-130a-3p, miR-19b-3p. |
| miRNA | Target Molecule/Interaction | Effect | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR-124 | SCP1 | Stimulation of neurogenesis, neuronal differentiation During CNS development, timely down-regulation of SCP1 stimulates neurogenesis, and miR-124 contributes to this process by down-regulating SCP1 expression. | [152] |
| Nonneuronal cells including neural progenitors: REST/SCP1 transcriptionally represses expression of miR-124 and other neuronal genes. | [153] | ||
| Neurogenesis: miR-124 expression is derepressed, miR-124 post-transcriptionally suppresses multiple anti-neural factors including SCP1, resulting in further inhibition of the anti-neural pathway by REST/SCP1. | [154] | ||
| miR-124 mediated repression of Sox9 associated with progression along the SVZ stem cell lineage to neurons (miR-124 is a neuronal fate determinant in the subventricular zone). | [155] | ||
| Sox9 | Neuronal differentiation as a result of interplay between miR-124, PTBP1, and SCP1/REST | [156] | |
| [157] | |||
| De-repression of neuronal specific transcripts, including neurogenic RBPs Nova1, Rbfox1 and the nElavls | [158] | ||
| Stimulation of neurogenesis | |||
| Ptbp1 | [159] | ||
| Zfp36l1 | [160] | ||
| Ezh2 (a negative regulator of neurogenesis) | [161] | ||
| microRNA-124-5p | Member of the synaptic microRNAome–regulators of the synaptic mRNA pool | [162] | |
| miR-125a miR-125b | FMRP | Interaction with FMRP: regulation of the signal transduction of metabolic glutamate receptors (mGluR1) and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDAR) and neuronal development | [163] |
| [164] | |||
| miR-128 (critical role in cortical neurogenesis) | MSI1 | Commitment of NSPC to the neuronal lineage | [165] |
| [166] | |||
| PCM1 | Reduced NPC proliferation, stimulation of NPC differentiation into neurons | [167] | |
| Phf6 | Cortical lamination: migration of neurons through the cortex, termination of upper neuron migration | [168] | |
| miR-137 | MSI1 | Commitment of NSPC to the neuronal lineage | [165] |
| [166] | |||
| Neuronal differentiation and increased migration of progenitors into the cortical plate | [169] | ||
| GluA1 subunit of AMPARs | Synaptic efficacy and mGluR-dependent synaptic plasticity | [170] | |
| miR-9 | Zfp36 Ezh2 | De-repression of neuronal specific transcripts, including neurogenic RBPs Nova1, Rbfox1 and the nElavls; Stimulation of neurogenesis | [160] |
| miR-375 | Elavl4 | miR-375 is downregulated during the late stages of cortical development. The decrease of miR-375 leads to the de-repression of ELAVL4, with subsequent enhancement of neurite outgrowth in developing neurons | [171] |
| miR-132 | p250GAP; | Regulation of dendritic growth and arborization of newborn neurons in the adult hippocampus (CREB-mediated signaling) | [172] |
| A positive regulation of developing axon extension | [173] | ||
| mRNA for the Ras GTPase activator Rasa1; | Synaptic structure and function | [174] | |
| FMRP | [175] | ||
| Visual cortex plasticity | [164] | ||
| MeCP2 | |||
| Brain vascular integrity | [176] | ||
| Cdh5 | [177] | ||
| [178] | |||
| [179] | |||
| [180] | |||
| [181] | |||
| Microglial homeostasis | [182] |
| miRNA | Targets | Some Important Roles |
|---|---|---|
| 138 | ARHGEF3, ROCK2, VIM, SIRT, ETC. | Precursor expressed in all tissues; mature miRNA only expressed in the brain. DNA Damage repair, and possibly sleep regulation. |
| 26b | EPHA2, CDK6, CCNE1, ETC. | Neural Differentiation, and gene expression. |
| 125b | IGF2, IL6R, E2F2, MAPK14, ETC. | Immune response, Osteoblast differentiation, and Neuroblastoma. |
| 509 | NTRK3, CFTR, ETC. | Cell proliferation and migration. |
| 134 | VEGFA, ABCC1, FOXM1, ETC. | Brain-specific, memory formation, and overexpressed in Schizophrenia. |
| 132 | SIRT, CDKN1A, CCNA2, ETC. | Neurogenesis, regulation of Inflammation in the brain and in the body, and Angiogenesis. |
| 9 | REST, NFKB1, SIRT1, VIM, ETC. | Neural Differentiation. |
| 485 | NTRK3, NFYB, ETC. | Synaptic formation regulation, and systemic iron balance. |
| 128 | RELN, TGFBR1, TP53, ETC. | Neuronal Migration, outgrowth, and excitability. |
| 124 | EFNB1, CDK4, CDK6, VIM, ROCK2, NR3C1, IT6B1, SLC16A1, ETC. | Neural Differentiation. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Darbinian, N.; Hampe, M.; Martirosyan, D.; Bajwa, A.; Darbinyan, A.; Merabova, N.; Tatevosian, G.; Goetzl, L.; Amini, S.; Selzer, M.E. Fetal Brain-Derived Exosomal miRNAs from Maternal Blood: Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers for Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASDs). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5826. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115826
Darbinian N, Hampe M, Martirosyan D, Bajwa A, Darbinyan A, Merabova N, Tatevosian G, Goetzl L, Amini S, Selzer ME. Fetal Brain-Derived Exosomal miRNAs from Maternal Blood: Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers for Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASDs). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(11):5826. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115826
Chicago/Turabian StyleDarbinian, Nune, Monica Hampe, Diana Martirosyan, Ahsun Bajwa, Armine Darbinyan, Nana Merabova, Gabriel Tatevosian, Laura Goetzl, Shohreh Amini, and Michael E. Selzer. 2024. "Fetal Brain-Derived Exosomal miRNAs from Maternal Blood: Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers for Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASDs)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 11: 5826. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115826
APA StyleDarbinian, N., Hampe, M., Martirosyan, D., Bajwa, A., Darbinyan, A., Merabova, N., Tatevosian, G., Goetzl, L., Amini, S., & Selzer, M. E. (2024). Fetal Brain-Derived Exosomal miRNAs from Maternal Blood: Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers for Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASDs). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(11), 5826. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25115826





