Androgen Receptor Upregulates Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue 1 to Induce NF-κB Activity via Androgen-Dependent and -Independent Pathways in Prostate Carcinoma Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
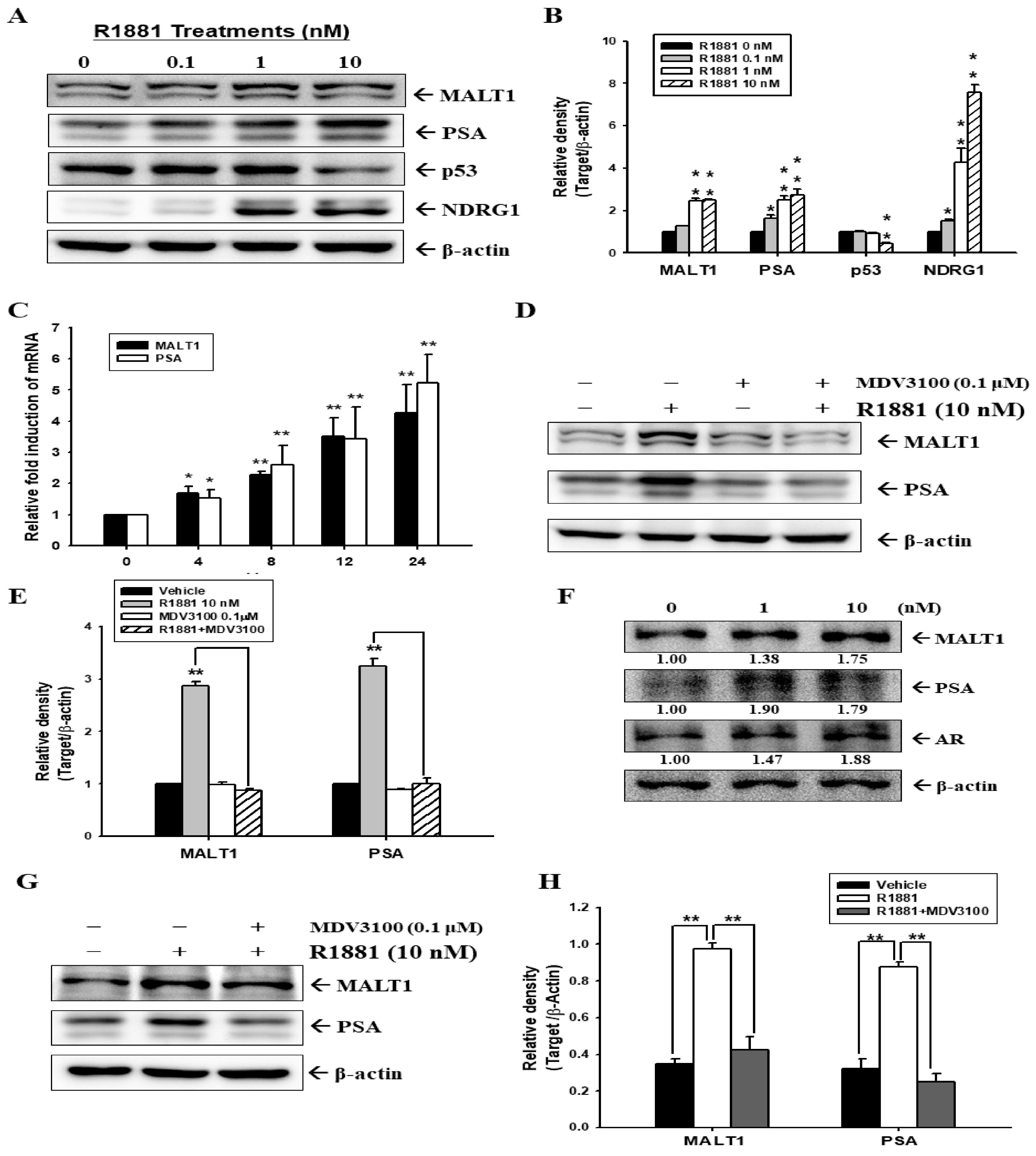
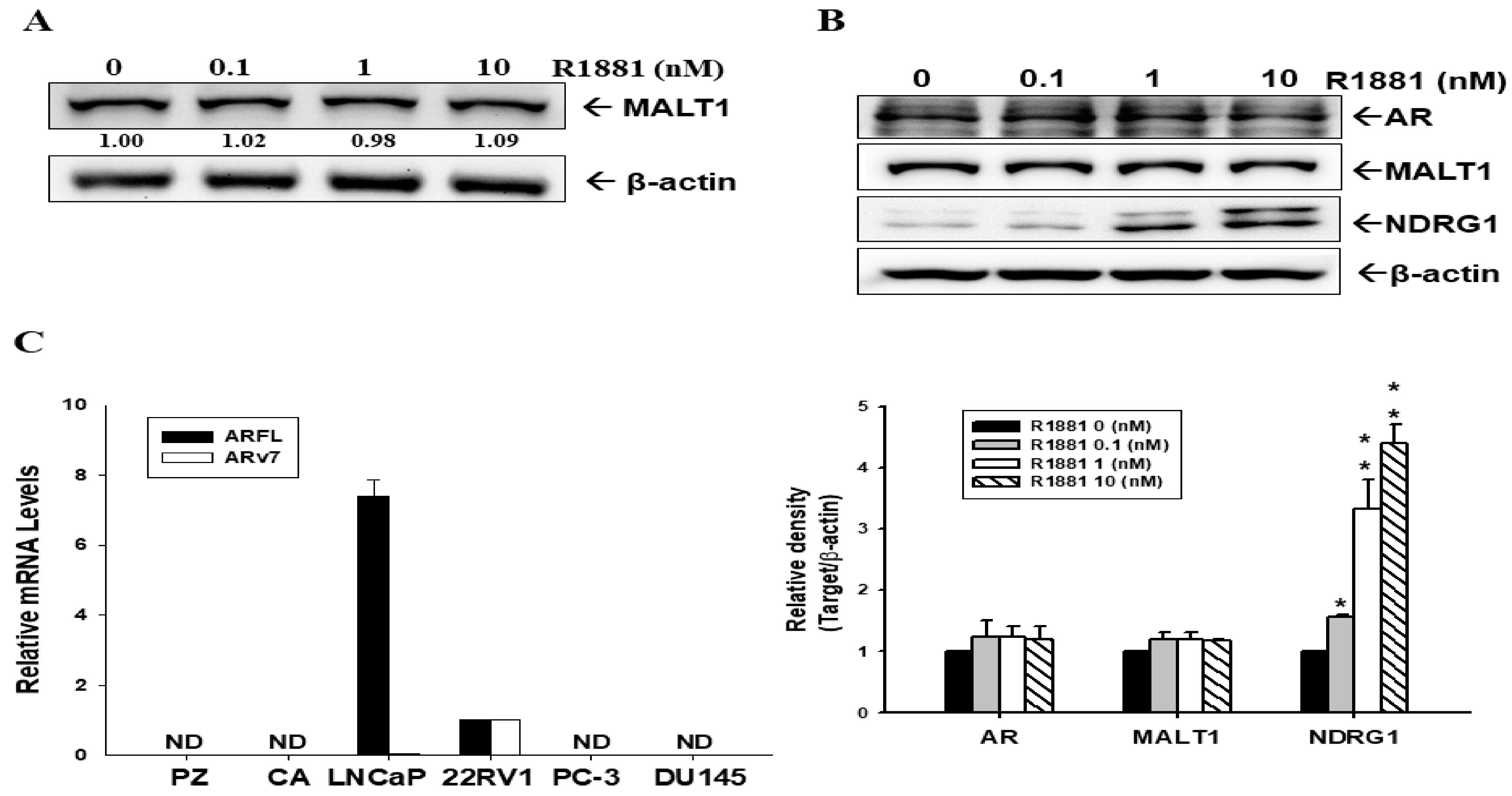
2.1. Androgen Induces MALT1 Expression in LNCaP and 22Rv1 Prostate Cancer Cells
2.2. Androgen Upregulates MALT1 to Promote PSA Expression in LNCaP Cells
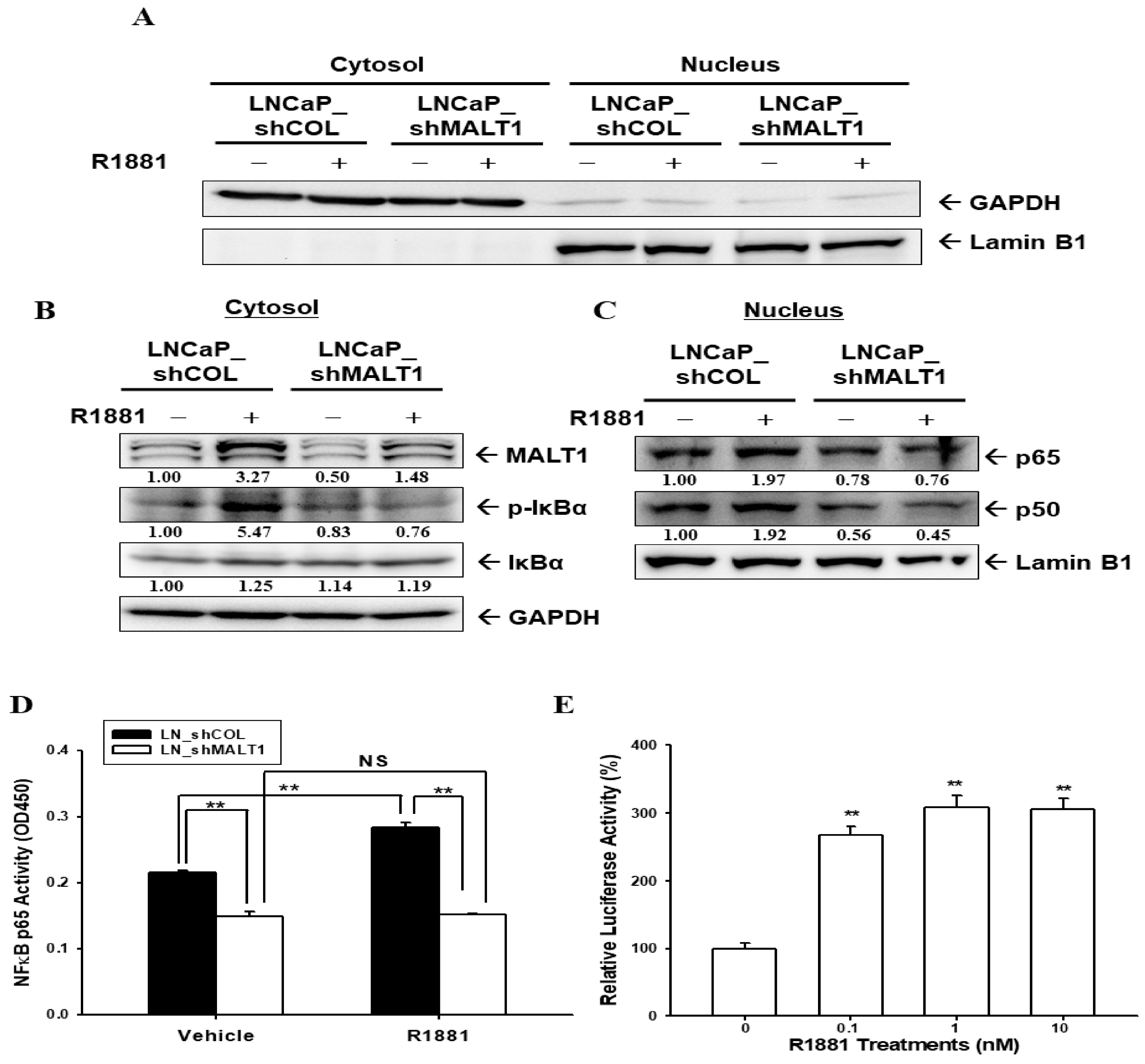
2.3. Androgen Upregulates MALT1 to Promote NF-κB Activation in LNCaP Cells
2.4. Androgen Does Not Induce MALT1 Expression in Ectopic ARFL-Overexpressed PC-3 Cells
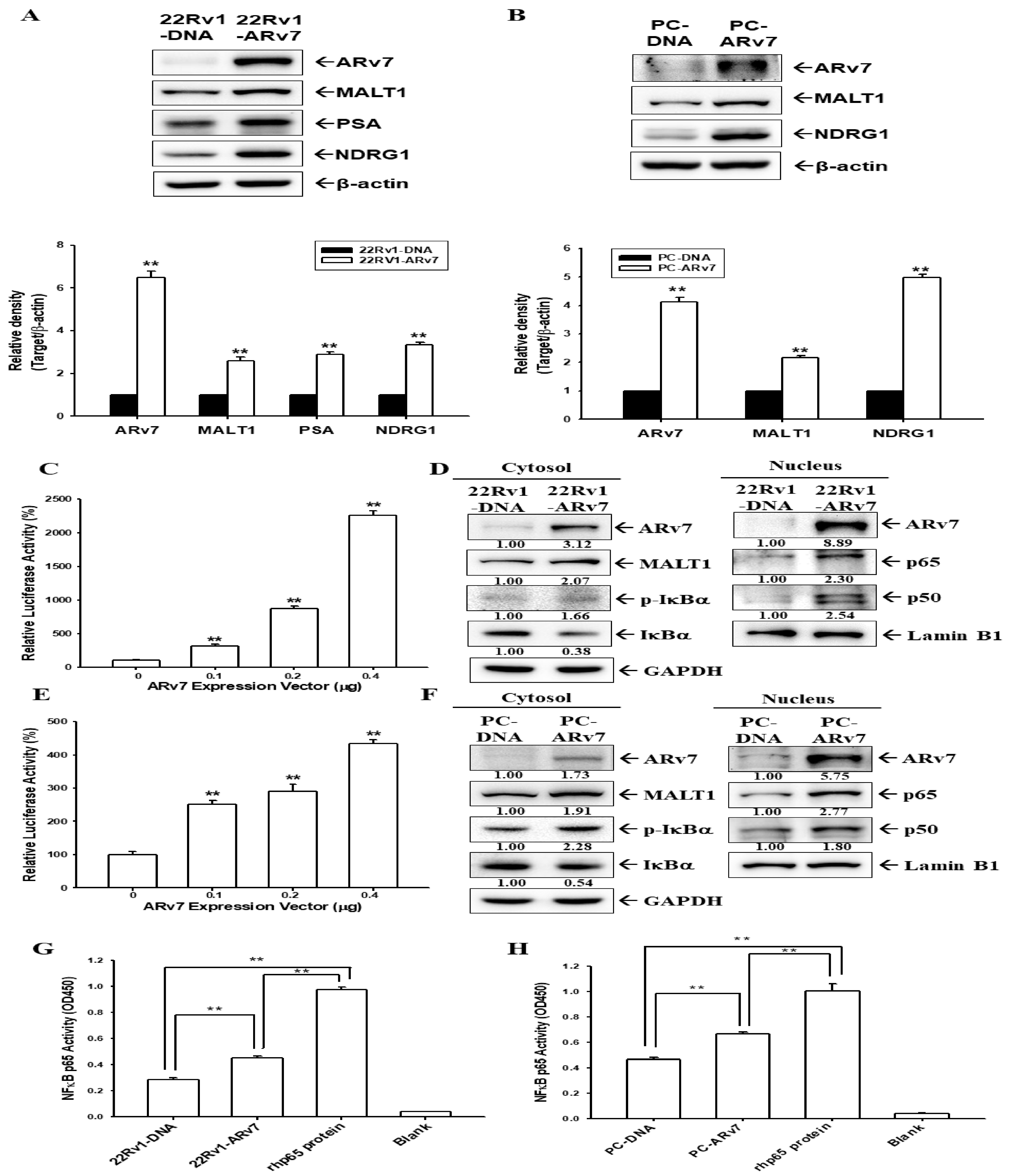
2.5. Ectopic ARv7 Overexpression Enhances MALT1 to Promote NF-κB Activation in PC-3 and 22Rv1 Cells
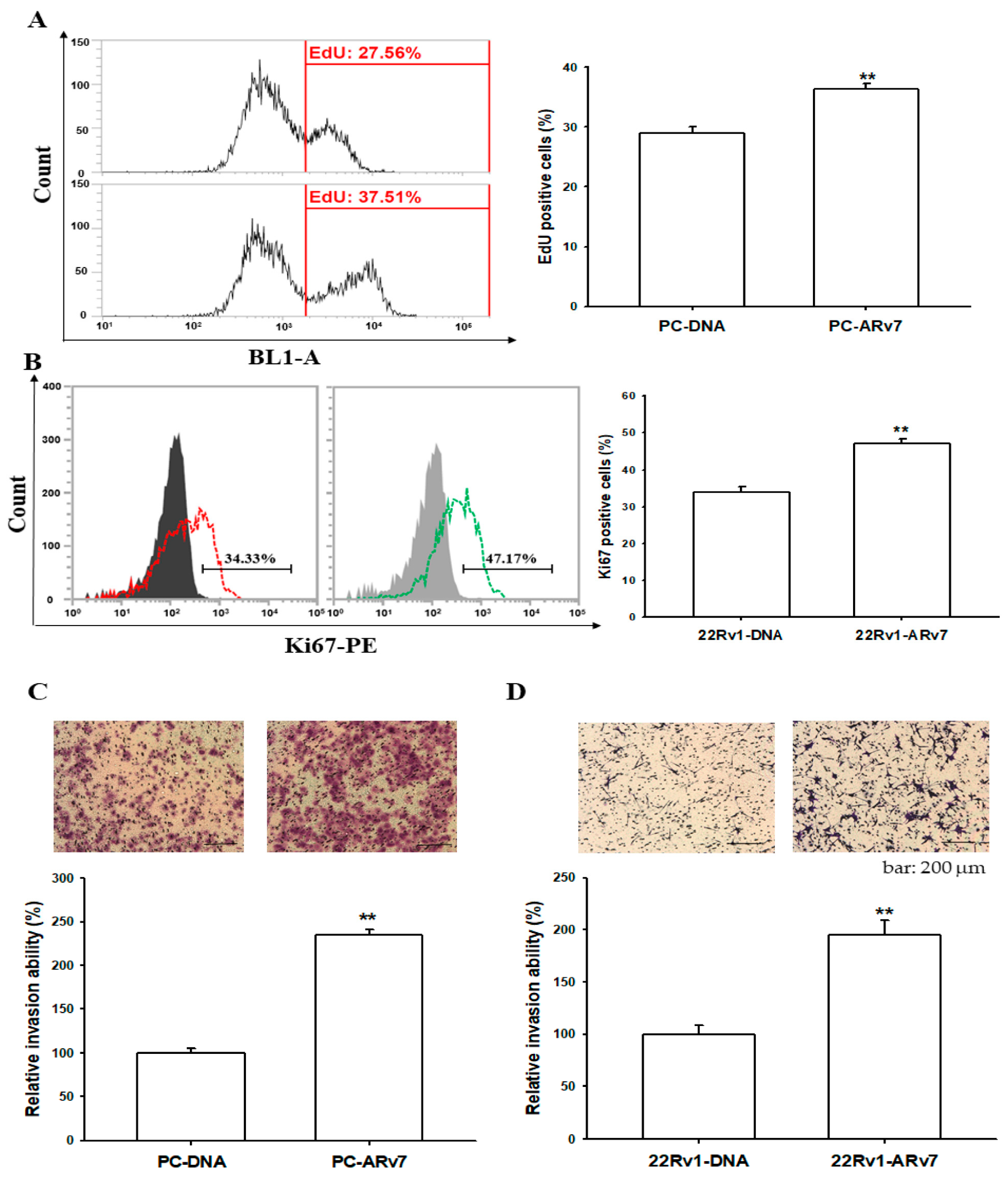
2.6. Ectopic ARv7 Overexpression Promotes Cell Proliferation and Invasion in PC-3 and 22Rv1 Cells
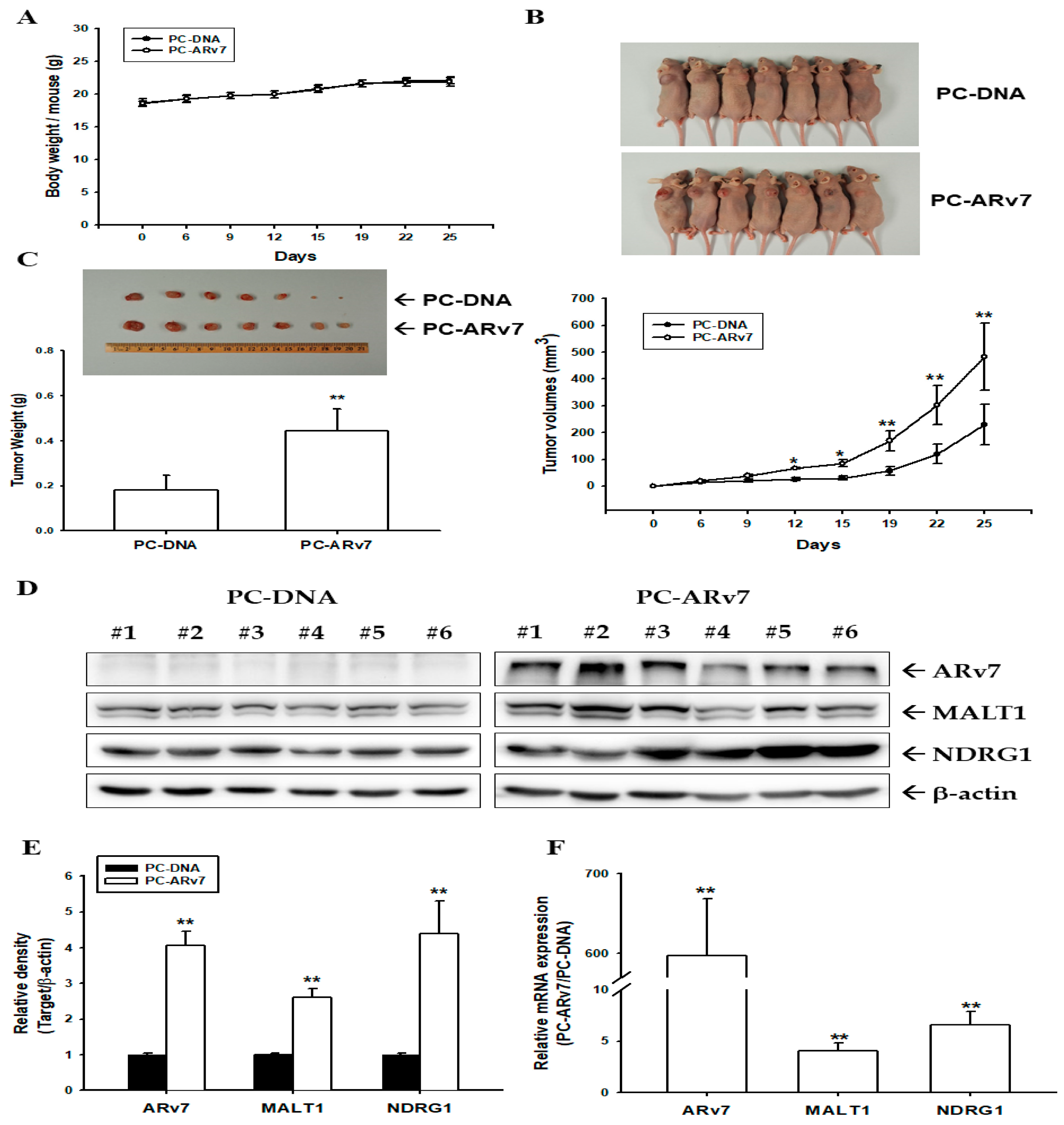
2.7. Ectopic ARv7 Overexpression Enhances Tumor Growth of PC-3 Cells in Xenograft Animal Study
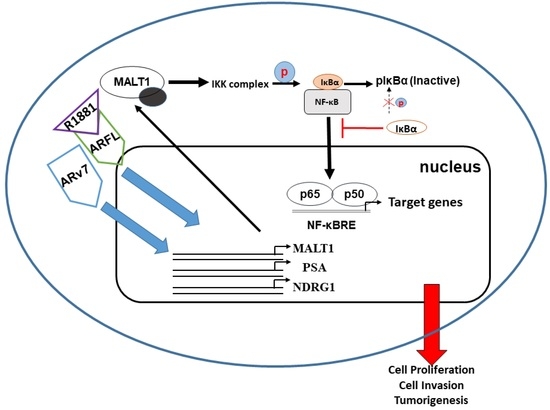
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
4.2. Immunoblot Assays
4.3. Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Quantitative Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
4.4. EdU and Ki67 Flow Cytometry Assay
4.5. Expression Vector Constructs and Stable Transfection
4.6. Gene Knockdown
4.7. Reporter Vector Constructs, Transient Transfection, and Reporter Assay
4.8. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
4.9. Matrigel Invasion Assay
4.10. NF-κB (p65) Transcription Factor Binding Assay
4.11. Xenograft Animal Model
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huggins, C.; Scot, W.W. Bilateral adrenalectomy in prostatic cancer: Clinical features and urinary excretion of 17-ketosteroids and estrogen. Ann. Surg. 1945, 122, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Sena, L.A.; Denmeade, S.R.; Kachhap, S. The testosterone paradox of advanced prostate cancer: Mechanistic insights and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.S.; Kokontis, J.; Liao, S.T. Molecular cloning of human and rat complementary DNA encoding androgen receptors. Science 1988, 240, 324–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Tummel, C.; Beato, M.; Herrlich, P.; Schutz, G.; Umesono, K.; Blumberg, B.; Kastner, P.; Mark, M.; Chambon, P.; et al. The nuclear receptor superfamily: The second decade. Cell 1995, 83, 835–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, C.; Luo, J. Decoding the androgen receptor splice variants. Trans. Androl. Urol. 2013, 2, 178–186. [Google Scholar]
- Ware, K.E.; Garcia-Blanco, M.A.; Armstrong, A.J.; Dehm, S.M. Biologic and clinical significance of androgen receptor variants in castration resistant prostate cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2014, 21, T87–T103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Luo, J. Regulation of androgen receptor variants in prostate cancer. Asia J. Urol. 2020, 7, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, A.; Mollica, V.; Rosellini, M.; Marchetti, A.; Ricci, A.D.; Fiorentino, M.; Battelli, N.; Santoni, M.; Massari, F. Exploring the association between metastatic sites and androgen receptor splice variant 7 (AR-V7) in castration-resistant prostate cancer patients: A meta-analysis of prospective clinical trials. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2021, 222, 153440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonarakis, E.S.; Lu, C.; Wang, H.; Luber, B.; Nakazawa, M.; Roeser, J.C.; Chen, Y.; Mohammad, T.; Chen, Y.; Fedor, H.L.; et al. AR-V7 and resistance to enzalutamide and abiraterone in prostate cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1028–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cato, L.; de Tribolet-Hardy, J.; Lee, I.; Rottenberg, J.T.; Coleman, I.; Melchers, D.; Houtman, R.; Xiao, T.; Li, W.; Uo, T.; et al. ARv7 represses tumor –suppressor genes in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Cell 2019, 35, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basil, P.; Robertson, M.J.; Bingman III, W.E.; Dash, A.; Krause, W.C.; Shafi, A.A.; Piyarathna, B.; Coarfa, C.; Weigel, N.L. Cistrome and transcriptome analysis identifies unique and androgen receptor (AR) and AR-V7 splice variant chromatin binding and transcriptional activities. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, R.; Yi, Y.; Yull, F.E.; Blackwell, T.S.; Clark, P.E.; Koyama, J.; Smith Jr, J.A.; Matusik, R.J. NF-κB gene signature predicts prostate cancer progress. Mol. Cell. Pathobiol. 2014, 74, 2763–2772. [Google Scholar]
- Staal, J.; Beyaert, R. Inflammation and NF-κB signaling in prostate cancer: Mechanisms and clinical implications. Cells 2018, 7, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, R.J.; Lho, Y.; Connelly, L.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X.; Saint Jean, L.; Case, T.C.; Ellwood-Yen, K.; Sawyers, C.L.; Bhowmick, N.A.; et al. The nuclear factor-κB pathway controls the progression of prostate cancer to androgen-independent growth. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 6762–6769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, H.Z.; Yang, T.W.; Zang, W.J.; Wu, S.F. Dehydroepiandrosterone-induced proliferation of prostatic epithelial cell is mediated by NFκB via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. J. Endocrinol. 2010, 204, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suh, J.; Payvandi, F.; Edelstein, L.C.; Amenta, P.S.; Zong, W.X.; Gelinas, C.; Rabson, A.B. Mechanisms of constitutive NF-κB activation in human prostate cancer cells. Prostate 2002, 52, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, N.; Sikka, S.C. Targeting crosstalk between Nrf-2, NF-κB and androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer. Cancers 2018, 10, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Altuwaijri, S.; Deng, F.; Chen, L.; Lai, P.; Bhanot, U.K.; Korets, R.; Wenske, S.; Lilja, H.G.; Chang, C.; et al. NF-κB regulates androgen receptor expression and prostate cancer growth. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 175, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malinen, M.; Niskanen, E.A.; Kaikkonen, M.U.; Palvimo, J.J. Crosstalk between androgen and pro-inflammatory signaling remodel androgen receptor and NF-κB cistrome to reprogram the prostate cancer cells transcriptome. Nucleic Acid Res. 2017, 45, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basilio, J.; Horchreiter, B.; Hoesel, B.; Sheshori, E.; Mussbacher, M.; Hanel, R.; Schmid, J.A. Antagonistic functions of androgen receptor and NF-κB in prostate cancer—Experimental and computational analyses. Cancers 2022, 14, 6164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, D.C.; Strand, D.W.; Lover, H.L.; Franco, O.E.; Jang, A.; Grabowska, M.M.; Miller, N.; Hameed, O.; Clark, P.E.; Fowke, J.H. NF-κB and androgen receptor variant expression correlate with human progression. Prostate 2016, 76, 491–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Young, R.M.; Staudt, L.M. A new “brew” of MALT1 inhibitors. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 706–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Afonina, I.S.; Elton, L.; Carpentier, I.; Beyaert, R. MALT1—A universal soldier: Multiple strategies to ensure NF-κB activation and target gene expression. FEBS J. 2015, 282, 3286–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thome, M. CARMA1, BCL-10 and MALT1 in lymphocyte development and activation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister-Lucas, L.M.; Baens, M.; Lucas, P.C. MALT1 protease: A new therapeutic target in B lymphoma and beyond? Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 6623–6631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ekambaram, P.; Lee, J.L.; Hubel, N.E.; Hu, D.; Yerneni, S.; Campbell, P.G.; Pollock, N.; Klei, L.R.; Concel, V.J.; Delekta, P.C.; et al. The CARMA3-Bcl10-MALT1 signalosome drives NFkappaB activation and promotes aggressiveness in angiotensin II receptor-positive breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 1225–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, D.; Jiang, C.; Ma, Z.; Blonska, M.; You, M.J.; Lin, X. MALT1 is required for EGFR-induced NF-kappaB activation and contributes to EGFR-driven lung cancer progression. Oncogene 2016, 35, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Jin, J.; Degan, S.; Tameze, Y.; Zhang, J.Y. MALT1 promotes melanoma progression through JNK/c-Jun signaling. Oncogenesis 2017, 6, e365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeh, C.N.; Chang, Y.C.; Su, Y.; Hsu, D.S.S.; Cheng, C.T.; Wu, R.C.; Chung, Y.H.; Chiang, K.C.; Yeh, T.S.; Lu, M.L.; et al. Identification of MALT1 as both a prognostic factor and a potential therapeutic target of regorafenib in cholangiocarcinoma patients. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 113444–113459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsui, K.H.; Chang, K.S.; Sung, H.C.; Hsu, S.Y.; Lin, Y.H.; Hou, C.P.; Yang, P.S.; Chen, C.L.; Feng, T.H.; Juang, H.H. Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue 1 is an oncogene inducing cell proliferation, invasion, and tumor growth via the upregulation of NF-κB activity in human prostate carcinoma cells. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, J.J.; Weyrich, M.S.; Durbin, S.; Liu, Y.; Band, H.; Melnikow, J. Prostate-specific antigen-based screening for prostate cancer: Evidence report and systematic review for the US preventive services task force. JAMA 2018, 319, 1914–1931. [Google Scholar]
- Tsui, K.H.; Wu, L.; Chang, P.L.; Hsieh, M.L.; Juang, H.H. Identifying the combination of the transcriptional regulatory sequences on prostate specific antigen and human glandular kallikrein genes. J. Urol. 2004, 172, 2029–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsui, K.H.; Feng, T.H.; Lin, C.M.; Chang, P.L.; Juang, H.H. Curcumin blocks the activation of androgen and interlukin-6 on prostate-specific antigen expression in human prostatic carcinoma cells. J. Androl. 2008, 29, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.D.; Sawyers, C.L. NF-kappa B activates prostate-specific antigen expression and is upregulated in androgen-independent prostate cancer. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 22, 2862–2870. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, K.S.; Tsui, K.H.; Hsu, S.Y.; Sung, H.C.; Lin, Y.H.; Hou, C.P.; Yang, P.S.; Chen, C.L.; Feng, T.H.; Juang, H.H. The antitumor effect of caffeic acid phenethyl ester by downregulating mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue 1 via AR/p53/NF-κB signaling in prostate carcinoma cells. Cancers 2022, 14, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggins, C.; Hodges, C.V. Studies on prostate cancer. I. The effect of castration of estrogen and androgen injection on serum phosphatases in metastatic carcinoma of the prostate. Cancer Res. 1941, 1, 293–297. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, R.; Yamashita, H.; Yu, X.; Wang, J.; Franco, O.E.; Wang, Y.; Hayward, S.W.; Matusik, R.J. inhibitor of NF-kappa B signaling restores responsiveness of castrate-resistant prostate cancer cells to anti-androgen treatment by decreasing androgen receptor-variant expression. Oncogene 2014, 34, 3700–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gasparian, A.V.; Yao, Y.J.; Kowalczyk, D.; Lyakh, L.A.; Karseladze, A.; Slaga, T.J.; Budunova, I.V. The role of IKK in constitutive activation of NF-κB transcription factor in prostate carcinoma cells. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Clarke, P.A.G.; Davis, R.; Mumuni, S.; Kwabi-Addo, B. Sex steroid-induced DNA methylation changes and inflammation response in prostate cancer. Cytokine 2016, 86, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tu, L.C.; Yan, X.; Hood, L.; Lin, B. Proteomics analysis of the interactome of N-myc downstream regulated gene 1 and its interactions with the androgen response program in prostate cancer cells. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2007, 6, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pflueger, D.; Rickman, D.S.; Sboner, A.; Perner, S.; LaFargue, C.J.; Svensson, M.A.; Moss, B.J.; Kitabayashi, N.; Pan, Y.; de la Taille, A.; et al. N-myc downstream regulated gene 1 (NDRG1) is fused to ERG in prostate cancer. Neoplasia 2009, 11, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.; Sun, L.; Hao, T.; Zhang, B.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, S.; Quan, C.; Niu, Y.; et al. Restoration of FKBP51 protein promotes the progression of castration resistant prostate cancer. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, A.; Yang, X.; Sun, F.; Juang, R.; Linn, D.E.; Chen, H.; Chen, H.; Kong, X.; Melamed, J.; Tepper, C.G.; et al. A novel androgen receptor splice variant is up-regulated during prostate cancer progression and promotes androgen depletion-resistant growth. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 2305–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scher, H.J.; Graf, R.P.; Schreiber, N.A.; McLaughlin, B.; Lu, D.; Louw, J.; Danila, D.C.; Dugan, L.; Johnson, A.; Heller, G.; et al. Nuclear-specific AR-V7 protein localization is necessary to guide treatment selection in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Tang, K.; Zhou, H.; Liu, H.; Yang, L.; Guan, W.; Chen, K.; Xu, H.; Ye, Z. Prognostic value of andogen receptor splice variant 7 in the treatment of castration-resistant prostate cancer with next generation androgen receptor signal inhibition: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Urol. Focus 2018, 4, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, M.; Dong, J.; Robertson, M.J.; Basil, P.; Coarfa, C.; Weigel, N.L. Androgen receptor and its splice variant, AR-V7, differentially induce mRNA splicing in prostate cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xie, N.; Gleave, M.E.; Rennie, P.S.; Dong, X. AR-v7 protein expression is upregulated by protein kinase and phosphatase. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 33743–33753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sasaki, T.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Kageyama, T.; Sugino, Y.; Kato, M.; Masui, S.; Nishikawa, K.; Inoue, T. Prostate fibroblasts enhance androgen receptor splice variant 7 expression in prostate cancer. Prostate 2023, 83, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Dunn, T.A.; Wei, S.; Isharwal, S.; Veltri, R.; Humphreys, E.; Han, M.; Partin, A.W.; Vessella, R.L.; Isaacs, W.B.; et al. Ligand-independent androgen receptor variants derived from splicing of cryptic exon signify hormone refractory prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qu, F.; Xie, W.; Nakabayashi, M.; Zhang, H.; Jeong, S.H.; Wang, X.; Komura, K.; Sweeney, C.J.; Sartor, O.; Lee, G.H.M.; et al. Association of AR-V7 and prostate-specific antigen RNA levels in blood with efficacy of abiraterone acetate and enzalutamide treatment in men with prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reddy, V.; Iskander, A.; Hwang, C.; Divine, G.; Menon, M.; Barrack, E.R.; Reddy, G.P.V.; Kim, S.H. Castration-resistant prostate cancer: Androgen receptor inactivation induces telomere DNA damage, and damage response inhibition leads to cell death. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Djusberg, E.; Jernberg, E.; Thysell, E.; Golovelva, I.; Lunberg, P.; Crnalic, S.; Widmark, A.; Bergh, A.; Brattand, M.; Wikstrom, P. High levels of the AR-V7 splice variant and co-amplification of the Golgi protein coding YIPF6 in AR amplified prostate cancer bone metastases. Prostate 2017, 77, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiura, M.; Sato, H.; Okabe, A.; Fukuyo, M.; Mano, Y.; Shinohara, K.I.; Rahmutulla, B.; Higuchi, K.; Maimaiti, M.; Kanesaka, M.; et al. Identification of AR-V7 downstream genes commonly targeted by AR/AR-V7 and specifically targeted by AR-V7 in castration resistant prostate cancer. Trans. Oncol. 2021, 14, 100915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottard, F.; Asmane, I.; Drdmann, E.; Bergerat, J.P.; Kurt, J.E.; Ceraline, J. Constitutively active androgen receptor variants upregulate expression of mesenchymal markers in prostate cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsui, K.H.; Chang, P.L.; Feng, T.H.; Chung, L.C.; Shu, S.Y.; Juang, H.H. Down-regulation of matriptase by overexpression of bikunin attenuates cell invasion in prostate carcinoma cells. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 1977–1984. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, P.A.; Chen, Y.F.; Balbas, M.D.; Wongvipat, J.; Socci, N.D.; Viale, A.; Kim, K.; Sawyers, C.L. Constitutively active androgen receptor splice variants expressed in castration-resistant prostate cancer require full-length androgen receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 16759–16765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsui, K.H.; Feng, T.H.; Chung, L.C.; Chao, C.H.; Chang, P.L.; Juang, H.H. Prostate specific antigen gene expression in androgen insensitive prostate carcinoma subculture cell line. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 1969–1976. [Google Scholar]
- Juang, H.H.; Hsieh, M.L.; Tsui, K.H. Testosterone modulates mitochondrial aconitase in the full-length human androgen receptor-transfected PC-3 prostatic carcinoma cells. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2004, 33, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, K.-S.; Chen, S.-T.; Sung, H.-C.; Hsu, S.-Y.; Lin, W.-Y.; Hou, C.-P.; Lin, Y.-H.; Feng, T.-H.; Tsui, K.-H.; Juang, H.-H. Androgen Receptor Upregulates Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue 1 to Induce NF-κB Activity via Androgen-Dependent and -Independent Pathways in Prostate Carcinoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076245
Chang K-S, Chen S-T, Sung H-C, Hsu S-Y, Lin W-Y, Hou C-P, Lin Y-H, Feng T-H, Tsui K-H, Juang H-H. Androgen Receptor Upregulates Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue 1 to Induce NF-κB Activity via Androgen-Dependent and -Independent Pathways in Prostate Carcinoma Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(7):6245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076245
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Kang-Shuo, Syue-Ting Chen, Hsin-Ching Sung, Shu-Yuan Hsu, Wei-Yin Lin, Chen-Pang Hou, Yu-Hsiang Lin, Tsui-Hsia Feng, Ke-Hung Tsui, and Horng-Heng Juang. 2023. "Androgen Receptor Upregulates Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue 1 to Induce NF-κB Activity via Androgen-Dependent and -Independent Pathways in Prostate Carcinoma Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 7: 6245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076245
APA StyleChang, K.-S., Chen, S.-T., Sung, H.-C., Hsu, S.-Y., Lin, W.-Y., Hou, C.-P., Lin, Y.-H., Feng, T.-H., Tsui, K.-H., & Juang, H.-H. (2023). Androgen Receptor Upregulates Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue 1 to Induce NF-κB Activity via Androgen-Dependent and -Independent Pathways in Prostate Carcinoma Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(7), 6245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076245