Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Developing in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome Is Characterized by Osteopontin Overexpression in the Tumor Stroma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
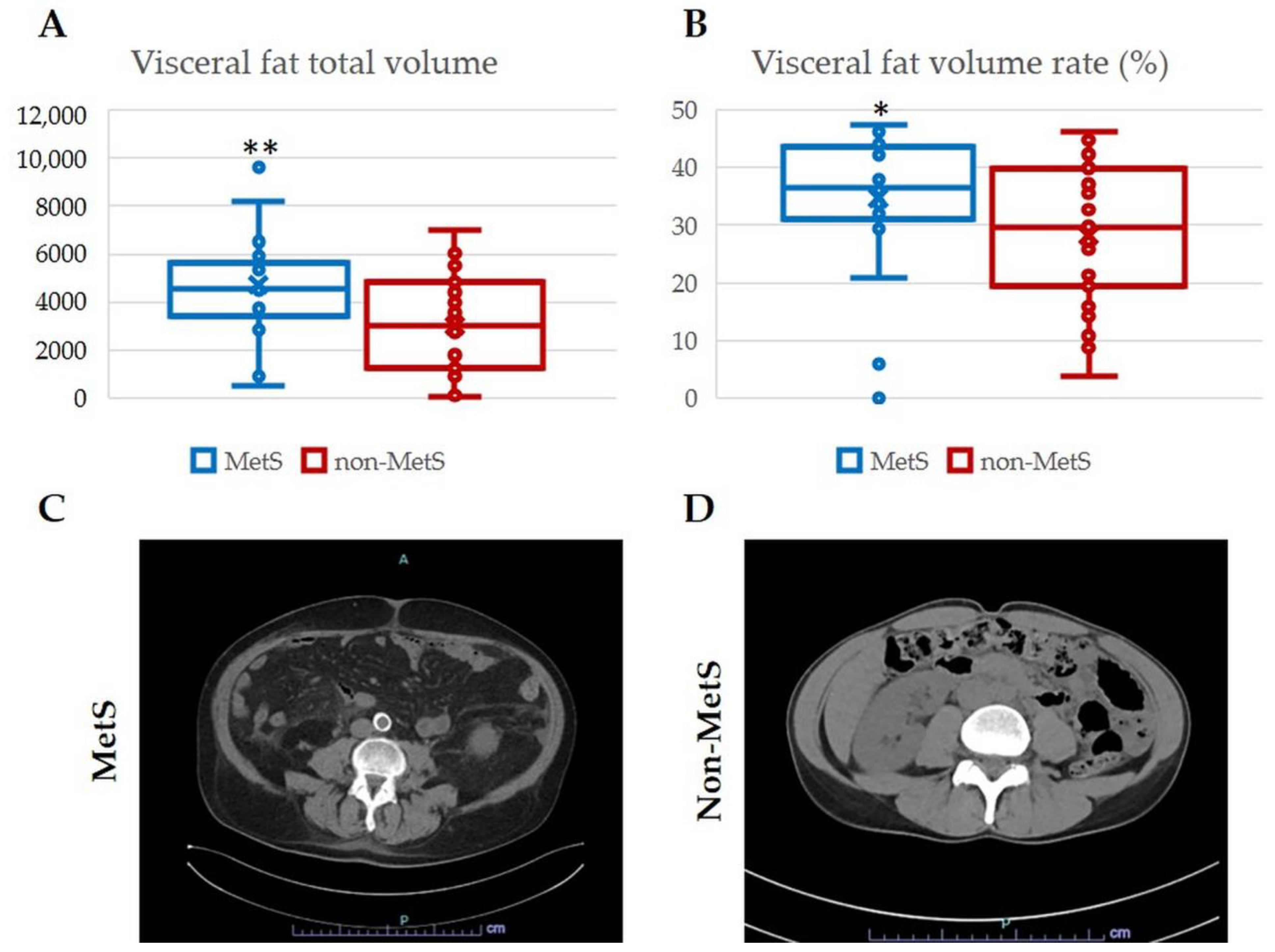
2.1. Demographic and Clinical Features of iCCA Patients with and without MetS
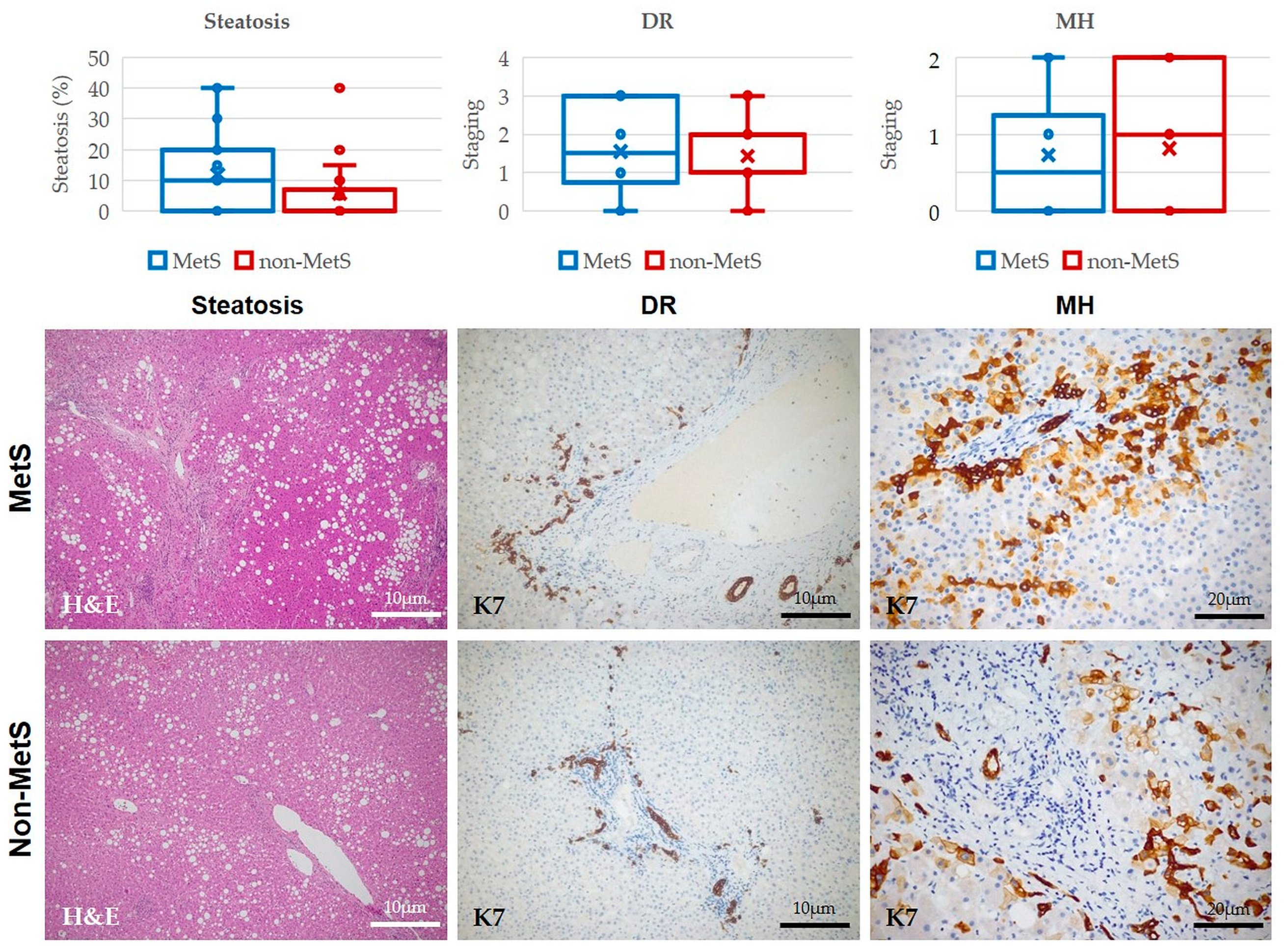
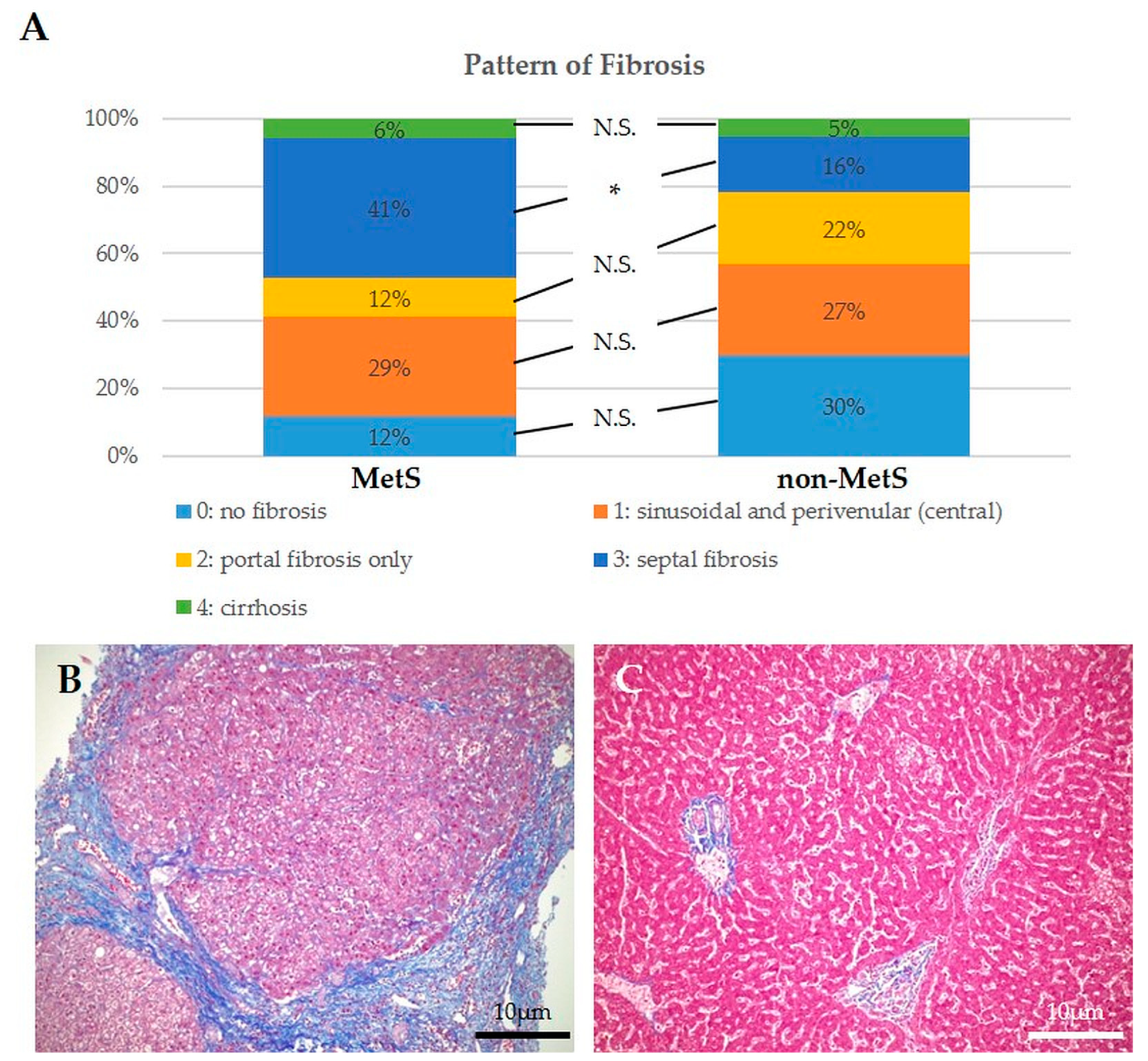
2.2. Histological Analysis of Hepatic Steatosis, DR, MHs, and Fibrosis in Liver Tissue Adjacent to iCCA Showed no Significant Differences between Patients with and without MetS, though Fibrosis Patterns Were Different
2.3. POSTN, TnC, and OPN Expression Were Significantly Increased in Tumor Compared to Peritumor Areas in Both MetS and Non-MetS iCCA; OPN Was More Expressed in MetS iCCA with Respect to Non-MetS iCCA
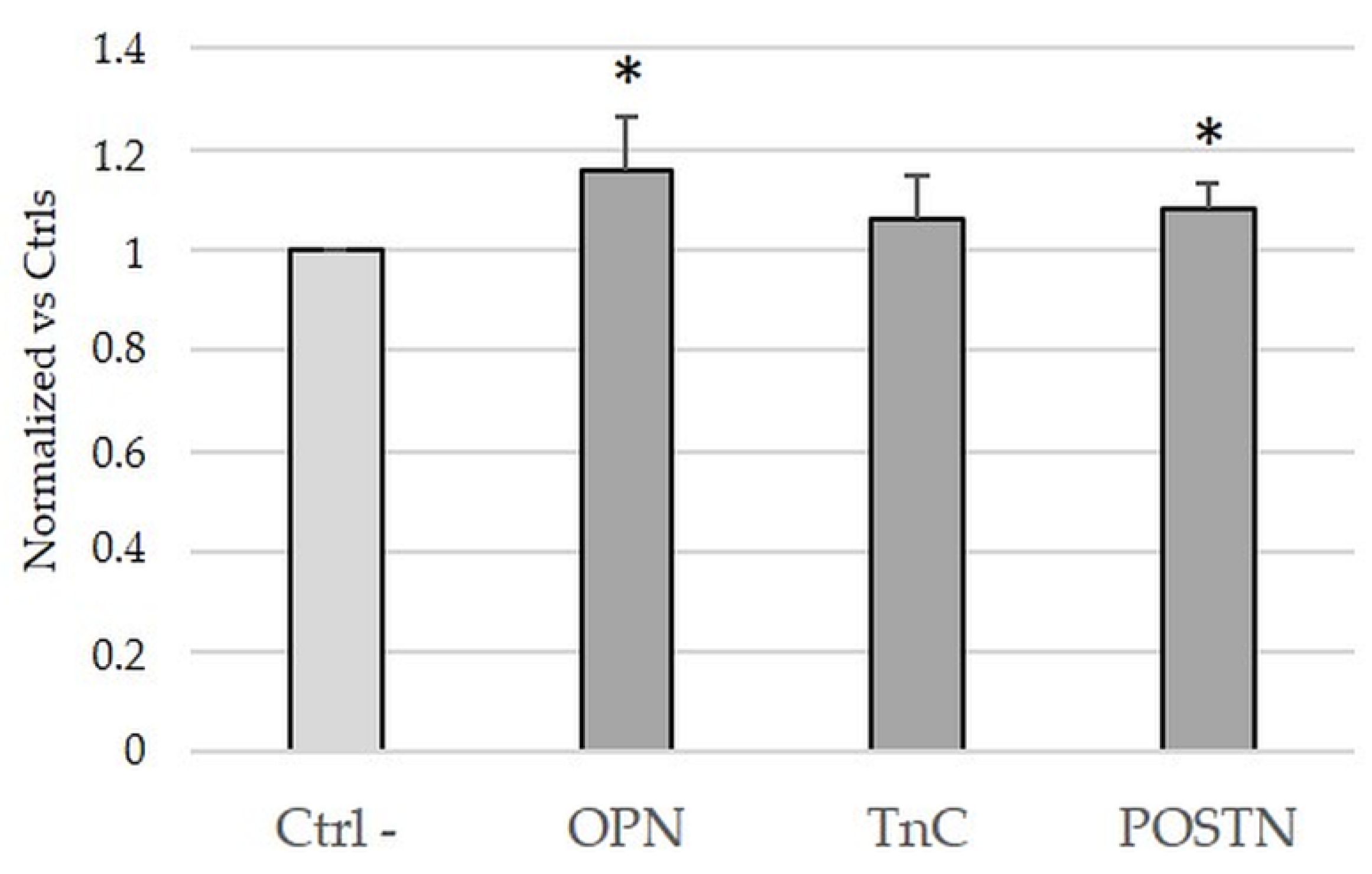
2.4. Treatment with OPN and POSTN but Not with TnC Slightly Sustained Cell Viability in iCCA Cells In Vitro
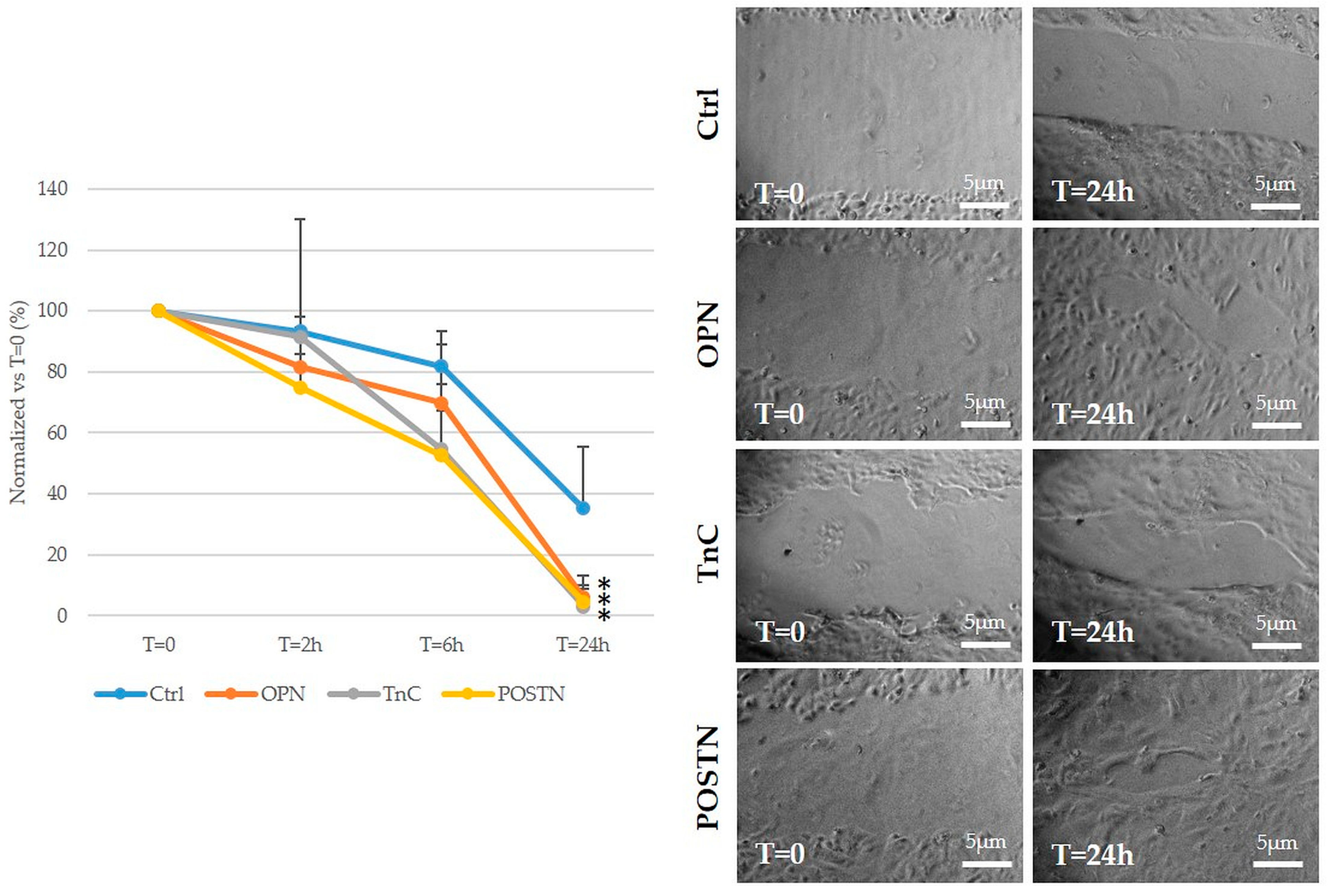
2.5. Treatment with OPN, TnC, and POSTN Potently Stimulated iCCA Cell Motility
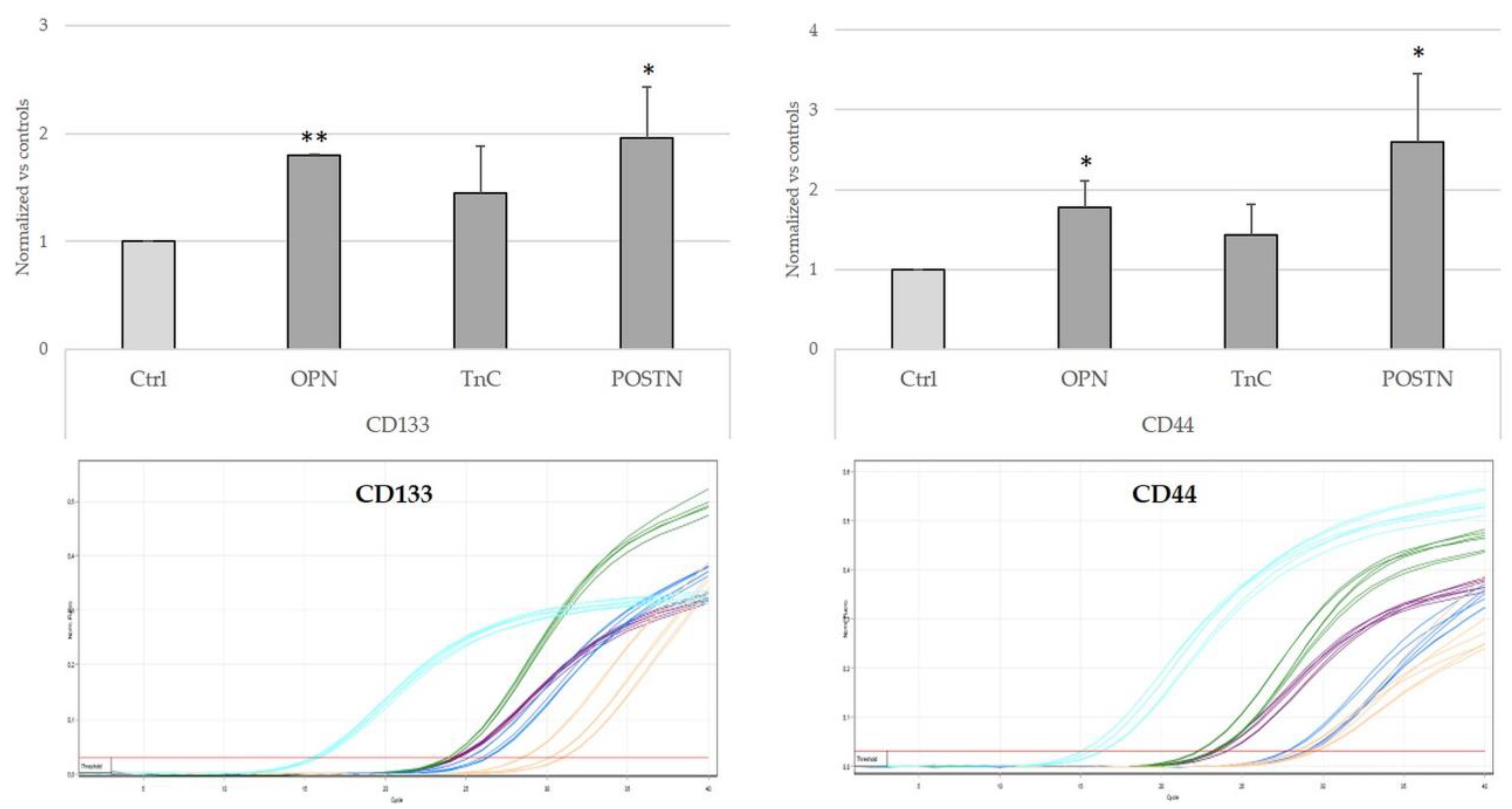
2.6. Treatment with OPN, TnC, and POSTN Induced iCCA Cells to Acquire Cancer-Stem-Cell-like Phenotypic Traits
3. Discussion
4. Methods and Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Banales, J.M.; Marin, J.J.G.; Lamarca, A.; Rodrigues, P.M.; Khan, S.A.; Roberts, L.R.; Cardinale, V.; Carpino, G.; Andersen, J.B.; Braconi, C.; et al. Cholangiocarcinoma 2020: The next horizon in mechanisms and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 557–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyson, G.L.; El-Serag, H.B. Risk factors for cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology 2011, 54, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadamuro, M.; Stecca, T.; Brivio, S.; Mariotti, V.; Fiorotto, R.; Spirli, C.; Strazzabosco, M.; Fabris, L. The deleterious interplay between tumor epithelia and stroma in cholangiocarcinoma. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 1435–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirica, A.E.; Strazzabosco, M.; Cadamuro, M. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Morpho-molecular pathology, tumor reactive microenvironment, and malignant progression. Adv. Cancer Res. 2021, 149, 321–387. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, T. Cholangiocarcinoma--controversies and challenges. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 8, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cillo, U.; Fondevila, C.; Donadon, M.; Gringeri, E.; Mocchegiani, F.; Schlitt, H.J.; Ijzermans, J.N.M.; Vivarelli, M.; Zieniewicz, K.; Olde Damink, S.W.M.; et al. Surgery for cholangiocarcinoma. Liv. Int. 2018, 39, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabris, L.; Cadamuro, M.; Cagnin, S.; Strazzabosco, M.; Gores, G.J. Liver Matrix in Benign and Malignant Biliary Tract Disease. Semin. Liv. Dis. 2020, 40, 282–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannito, S.; Milani, C.; Cappon, A.; Parola, M.; Strazzabosco, M.; Cadamuro, M. Fibroinflammatory Liver Injuries as Preneoplastic Condition in Cholangiopathies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskams, T.A.; Theise, N.D.; Balabaud, C.; Bhagat, G.; Bhathal, P.S.; Bioulac-Sage, P.; Brunt, E.M.; Crawford, J.M.; Crosby, H.A.; Desmet, V.; et al. Nomenclature of the finer branches of the biliary tree: Canals, ductules, and ductular reactions in human livers. Hepatology 2004, 39, 1739–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labib, P.L.; Goodchild, G.; Pereira, S.P. Molecular Pathogenesis of Cholangiocarcinoma. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongjarupong, N.; Assavapongpaiboon, B.; Susantitaphong, P.; Cheungpasitporn, W.; Treeprasertsuk, S.; Rerknimitr, R.; Chaiteerakij, R. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease as a risk factor for cholangiocarcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2017, 17, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease—A global public health perspective. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadamuro, M.; Lasagni, A.; Sarcognato, S.; Guido, M.; Fabris, R.; Strazzabosco, M.; Strain, A.J.; Simioni, P.; Villa, E.; Fabris, L. The Neglected Role of Bile Duct Epithelial Cells in NASH. Semin. Liv. Dis. 2022, 42, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, G.; Du, L.; Chen, Q. Osteopontin, a possible modulator of cancer stem cells and their malignant niche. Oncoimmunology 2013, 2, e24169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhu, X.; Cai, Y.; Fang, X.; Lin, S.; Yuan, L.; et al. Periostin contributes to the acquisition of multipotent stem cell-like properties in human mammary epithelial cells and breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchisello, S.; Di Pino, A.; Scicali, R.; Urbano, F.; Piro, S.; Purrello, F.; Rabuazzo, A.M. Pathophysiological, Molecular and Therapeutic Issues of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: An Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghidini, M.; Ramai, D.; Facciorusso, A.; Singh, J.; Tai, W.; Rijavec, E.; Galassi, B.; Grossi, F.; Indini, A. Metabolic disorders and the risk of cholangiocarcinoma. Exp. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 15, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiseler, M.; Tacke, F. Inflammatory Mechanisms Underlying Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and the Transition to Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, A.R.; Lin, X.Z.; Crawford, J.M. The normal adult human liver biopsy: A quantitative reference standard. Hepatology 1998, 28, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brierley, J.; Gospodarowicz, M.K.; Wittekind, C. TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours, 8th ed.; JohnWiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, J.A. Metabolic Syndrome: A Warning Sign of Liver Fibrosis. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2022, 31, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.S.; Taylor, R.J.; Bayliss, S.; Hagström, H.; Nasr, P.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Ishigami, M.; Toyoda, H.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Peleg, N.; et al. Association Between Fibrosis Stage and Outcomes of Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1611–1625.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Méndez-Gutiérrez, A.; Aguilera, C.M.; Plaza-Díaz, J. Extracellular Matrix Remodeling of Adipose Tissue in Obesity and Metabolic Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahles, F.; Findeisen, H.M.; Bruemmer, D. Osteopontin: A novel regulator at the cross roads of inflammation, obesity and diabetes. Mol. Metab. 2014, 3, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, J.; Miles, P.D.; Ofrecio, J.M.; Neels, J.G.; Yu, J.G.; Resnik, J.L.; Wilkes, J.; Talukdar, S.; Thapar, D.; Johnson, K.; et al. Osteopontin is required for the early onset of high fat diet-induced insulin resistance in mice. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiefer, F.W.; Zeyda, M.; Gollinger, K.; Pfau, B.; Neuhofer, A.; Weichhart, T.; Säemann, M.D.; Geyeregger, R.; Schlederer, M.; Kenner, L.; et al. Neutralization of osteopontin inhibits obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance. Diabetes 2010, 59, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Jeong, S.; Xia, Q.; Kong, X. Role of Osteopontin in Liver Diseases. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 12, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syn, W.K.; Agboola, K.M.; Swiderska, M.; Michelotti, G.A.; Liaskou, E.; Pang, H.; Xie, G.; Philips, G.; Chan, I.S.; Karaca, G.F.; et al. NKT-associated hedgehog and osteopontin drive fibrogenesis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Gut 2012, 61, 1323–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.; Song, K.; Han, C.; Chen, W.; Wang, Y.; Dash, S.; Lim, K.; Wu, T. Inhibition of hedgehog signaling ameliorates hepatic inflammation in mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2016, 63, 1155–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirica, A.E. Matricellular proteins in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Adv. Cancer Res. 2022, 156, 249–281. [Google Scholar]
- Utispan, K.; Sonongbua, J.; Thuwajit, P.; Chau-In, S.; Pairojkul, C.; Wongkham, S.; Thuwajit, C. Periostin activates integrin α5β1 through a PI3K/AKT-dependent pathway in invasion of cholangiocarcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 41, 1110–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Wang, W.; Jia, W.D.; Sun, Q.K.; Huang, M.; Zhou, H.C.; Xia, H.H.; Liu, W.B.; Chen, H.; Sun, S.N.; et al. High preoparative levels of serum periostin are associated with poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy. Eur. J. Surgic. Oncol. 2013, 39, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben, Q.-W.; Zhao, Z.; Ge, S.-F.; Zhou, J.; Yuan, F.; Yuan, Y.-Z. Circulating levels of periostin may help identify patients with more aggressive colorectal cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2009, 34, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hao, C.; Cui, Y.; Owen, S.; Li, W.; Cheng, S.; Jiang, W.G. Human osteopontin: Potential clinical applications in cancer (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 39, 1327–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briones-Orta, M.A.; Avendaño-Vázquez, S.E.; Aparicio-Bautista, D.I.; Coombes, J.D.; Weber, G.F.; Syn, W.K. Osteopontin splice variants and polymorphisms in cancer progression and prognosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2017, 1868, 93–108.A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, R.; Wong, J.P.C.; Kwok, H.F. Osteopontin—A promising biomarker for cancer therapy. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 2173–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiguchi, K.; Matsuda, A.; Yamada, M.; Matsumoto, S.; Sakurazawa, N.; Kawano, Y.; Yamada, T.; Miyashita, M.; Yoshida, H. The utility of serum osteopontin levels for predicting postoperative complications after colorectal cancer surgery. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 27, 1706–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagtegaal, I.D.; Odze, R.D.; Klimstra, D.; Paradis, V.; Rugge, M.; Schirmacher, P.; Washington, K.M.; Carneiro, F.; Cree, I.A.; WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. The 2019 WHO classification of tumours of the digestive system. Histopathology 2020, 76, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuck, A.B.; Hota, C.; Wilson, S.M.; Chambers, A.F. Osteopontin-induced migration of human mammary epithelial cells involves activation of EGF receptor and multiple signal transduction pathways. Oncogene 2003, 22, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paron, I.; Berchtold, S.; Vörös, J.; Shamarla, M.; Erkan, M.; Höfler, H.; Esposito, I. Tenascin-C enhances pancreatic cancer cell growth and motility and affects cell adhesion through activation of the integrin pathway. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| MetS | Non-MetS | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22 | 44 | ||
| BMI > 30 or waist to hip ratio >0.9 (male) or >0.85 (female) (n (%)) | 10/18 (55.56) | 2/43 (4.65) | <0.001 |
| T2DM [n (%)] | 18/22 (81.82) | 13/34 (38.24) | <0.001 |
| Systemic hypertension (n (%)) | 20/22 (90.90) | 13/43 (30.23) | <0.001 |
| Hypertriglyceridemia (n (%)) | 14/19 (73.68) | 6/21 (28.57) | 0.004 |
| Low HDL cholesterol (n (%)) | 6/14 (42.86) | 6/16 (37.50) | 0.775 |
| MetS | Non-MetS | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 22 | 44 | |
| Age | 68.36 | 63.07 | 0.113 |
| Female sex (n (%)) | 7/22 (31.82) | 25/44 (56.82) | 0.057 |
| AFP (ng/mL) | 7.84 | 83.67 | 0.488 |
| CEA (ng/mL) | 11.14 | 11.60 | 1 |
| CA19.9 (U/mL) | 655.01 | 1121.317 | 0.1 |
| CT adjuvant (n (%)) | 5/15 (33.33) | 16/32 (50.00) | 0.294 |
| Deceased (n (%)) | 13/21 (61.90) | 26/43 (60.47) | 0.913 |
| OS (days) | 1152.14 | 937.0732 | 0.29 |
| Recurrence (n (%)) | 8/21 (38.10) | 21/43 (48.84) | 0.426 |
| Relapse-free interval (days) | 869.48 | 613.51 | 0.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cadamuro, M.; Sarcognato, S.; Camerotto, R.; Girardi, N.; Lasagni, A.; Zanus, G.; Cillo, U.; Gringeri, E.; Morana, G.; Strazzabosco, M.; et al. Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Developing in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome Is Characterized by Osteopontin Overexpression in the Tumor Stroma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4748. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054748
Cadamuro M, Sarcognato S, Camerotto R, Girardi N, Lasagni A, Zanus G, Cillo U, Gringeri E, Morana G, Strazzabosco M, et al. Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Developing in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome Is Characterized by Osteopontin Overexpression in the Tumor Stroma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(5):4748. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054748
Chicago/Turabian StyleCadamuro, Massimiliano, Samantha Sarcognato, Riccardo Camerotto, Noemi Girardi, Alberto Lasagni, Giacomo Zanus, Umberto Cillo, Enrico Gringeri, Giovanni Morana, Mario Strazzabosco, and et al. 2023. "Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Developing in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome Is Characterized by Osteopontin Overexpression in the Tumor Stroma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 5: 4748. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054748
APA StyleCadamuro, M., Sarcognato, S., Camerotto, R., Girardi, N., Lasagni, A., Zanus, G., Cillo, U., Gringeri, E., Morana, G., Strazzabosco, M., Campello, E., Simioni, P., Guido, M., & Fabris, L. (2023). Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Developing in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome Is Characterized by Osteopontin Overexpression in the Tumor Stroma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(5), 4748. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054748







