Spinal Cord Injury and Complications Related to Neuraxial Anaesthesia Procedures: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
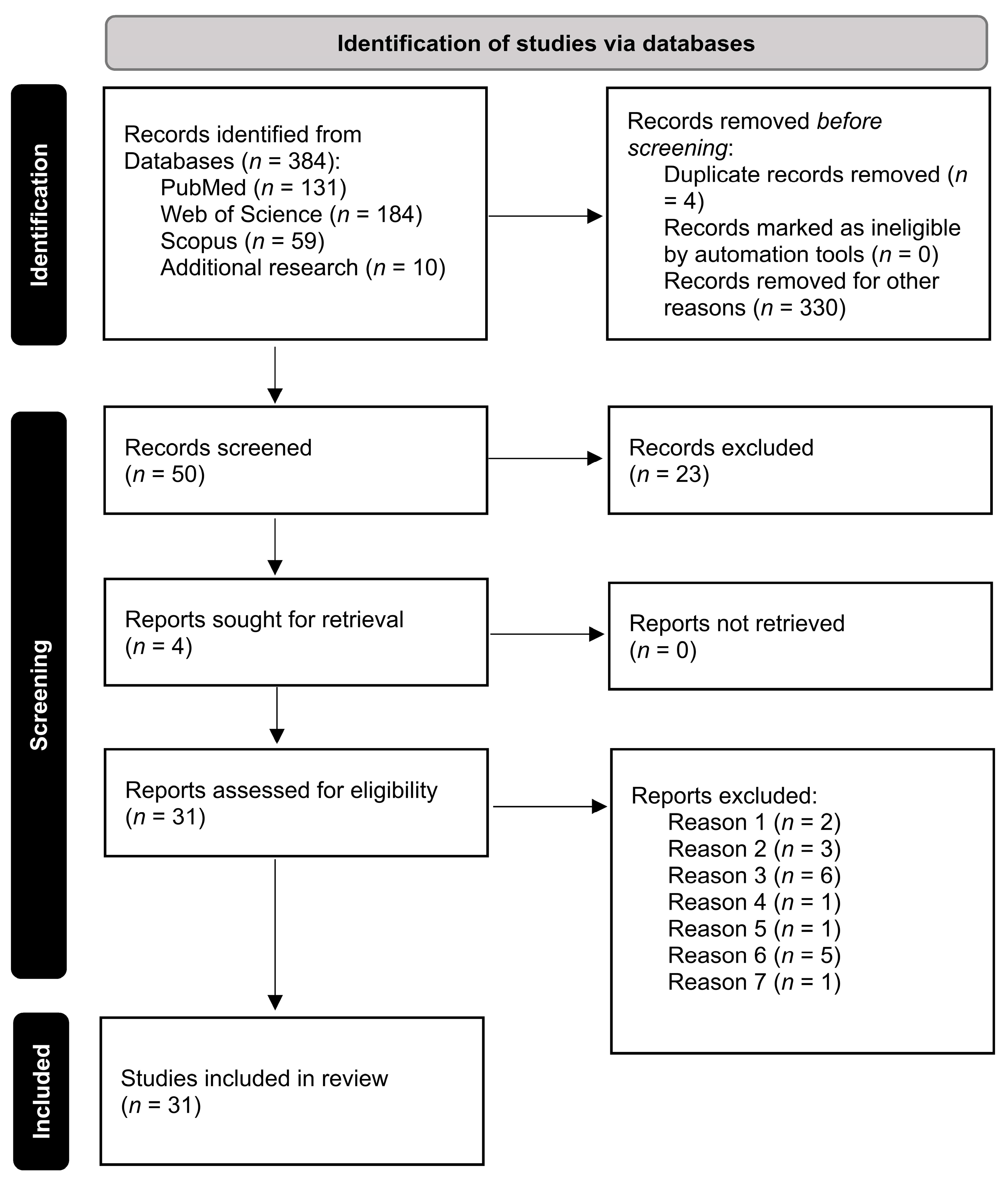
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hewson, D.W.; Bedforth, N.M.; Hardman, J.G. Spinal cord injury arising in anaesthesia practice. Anaesthesia 2018, 73, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotoda, M.; Mochizuki, N.; Matsuoka, T.; Kondoh, D.; Matsukawa, T. Successful epidural anesthesia in a patient with an extremely shallow epidural space: A case report. Anaesth. Pain Intensive Care 2018, 22, 224–226. [Google Scholar]
- Drummond, J.C.; Krane, E.J.; Tomatsu, S.; Theroux, M.C.; Lee, R.R. Paraplegia after epidural-general anesthesia in a Morquio patient with moderate thoracic spinal stenosis. Can. J. Anaesth. 2015, 62, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schildt, E. Low spinal cord injuries following spinal anesthesia. Acta Chir. Scand. 1947, 95, 101–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercauteren, M.; Waets, P.; Pitkanen, M.; Forster, J. Neuraxial techniques in patients with pre-existing back impairment or prior spine interventions: A topical review with special reference to obstetrics. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2011, 55, 910–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, J.M.; Bernards, C.M.; Hadzic, A.; Hebl, J.R.; Hogan, Q.H.; Horlocker, T.T.; Lee, L.A.; Rathmell, J.P.; Sorenson, E.J.; Suresh, S.; et al. ASRA Practice Advisory on Neurologic Complications in Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2008, 33, 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Kishore, K. Complications and controversies of regional anaesthesia: A review. Indian J. Anaesth. 2009, 53, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meyer, M.J.; Krane, E.J.; Goldschneider, K.R.; Klein, N.J. Case report: Neurological complications associated with epidural analgesia in children: A report of 4 cases of ambiguous etiologies. Anesth. Analg. 2012, 115, 1365–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroud, C.C.; Markel, D.; Sidhu, K. Complete paraplegia as a result of regional anesthesia. J. Arthroplast. 2000, 15, 1064–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulow, P.M.; Biering-Sorensen, F. Paraplegia, a severe complication to epidural analgesia. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 1999, 43, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabio, C.; Romualdo, D.; Eugenio, A.F.; Vittoradolfo, T.; Massimiliano, V.A.; Giovanna, R. Thoracic Unilateral Spinal Cord Injury After Spinal Anaesthesia for Total Hip Replacement: Fate or Mistake? Turk. J. Anaesthesiol. Reanim. 2017, 45, 116–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagathan, D.S.; Singh, B.P.; Ghatanatti, S.; Sankhwar, S.N. Spinal cord injury: A rare complication following thoracic epidural anesthesia for percutaneous nephrolithotomy. Acta Anaesthesiol. Taiwanica 2012, 50, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, M.G.; Peixoto, A.R.; Fonseca, S.; Santos, F.; Pinho, C.; Leite, D. Assessment of main complications of regional anesthesia recorded in an acute pain unit in a tertiary care university hospital: A retrospective cohort. Braz. J. Anesthesiol. 2022, 72, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olawin, A.M.; Das, J.M. Spinal Anesthesia. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Gadsden, J.; Warlick, A. Regional anesthesia for the trauma patient: Improving patient outcomes. Local Reg. Anesth. 2015, 8, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.P.; Hauerberg, J.; Schmidt, J.F. Incidence of spinal epidural abscess after epidural analgesia: A national 1-year survey. Anesthesiology 1999, 91, 1928–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makito, K.; Mouri, H.; Matsui, H.; Michihata, N.; Fushimi, K.; Yasunaga, H. Spinal epidural hematoma and abscess after neuraxial anesthesia: A historical cohort study using the Japanese Diagnosis Procedure Combination database. Can. J. Anaesth. 2021, 68, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, F.-P.; Zhang, H.-G.; Zhu, S.-M. Anesthetic considerations for patients with acute cervical spinal cord injury. Neural Regen. Res. 2017, 12, 499–504. [Google Scholar]
- Neal, J.M. Anatomy and pathophysiology of spinal cord injury associated with regional anesthesia and pain medicine. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2008, 33, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horlocker, T.T.; Wedel, D.J.; Benzon, H.; Brown, D.L.; Enneking, F.K.; Heit, J.A.; Mulroy, M.F.; Rosenquist, R.W.; Rowlingson, J.; Tryba, M.; et al. Regional anesthesia in the anticoagulated patient: Defining the risks (the second ASRA Consensus Conference on Neuraxial Anesthesia and Anticoagulation). Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2003, 28, 172–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.X.; Eric Nyam, T.T.; Liu, C.A.; Lee, Y.L.; Kuo, J.R.; Sung, K.C. Spontaneous Spinal Epidural Hematoma After Normal Spontaneous Delivery with Epidural Analgesia: Case Report and Literature Review. World Neurosurg. 2020, 137, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, E.E.; Arendt, K.W.; Jacob, A.K.; Pasternak, J.J. Anesthetic management of parturients with pre-existing paraplegia or tetraplegia: A case series. Int. J. Obstet. Anesth. 2015, 24, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greaves, J.D. Serious spinal cord injury due to haematomyelia caused by spinal anaesthesia in a patient treated with low-dose heparin. Anaesthesia 1997, 52, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, L.; Rodermond, B.; Post, P.; Iborra, S.; Stickeler, E.; Schiefer, J.; Alt, J.P.; Rossaint, R.; Röhl, A. Intramedulläre Injektion bei “tethered cord”. Anaesthesist 2018, 67, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, I.; Alderson, J.; Lydon, M.; Franks, C.I. Cardiovascular effects of spinal subarachnoid anesthesia—A study in patients with chronic spinal-cord injuries. Anaesthesia 1985, 40, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiro, C.J.; Kamdar, B.B. Labor Epidural Analgesia in a Patient with Brown-Sequard Syndrome: A Case Report. A A Pract. 2020, 14, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciliberti, B.J.; Goldpein, J.; Rovenstine, E.A. HYPERTENSION DURING ANESTHESIA IN PATIENTS WITH SPINAL CORD INJURIES. Anesthesiology 1954, 15, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezig, K.; Diar, N.; Benabidallah, D.; Khodja, A.; Saint-Leger, S. Paraplegia and pregnancy: Anaesthesic management. Ann. Fr. D’anesth. Reanim. 2003, 22, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Altman, D.G.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Juni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savovic, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A.; et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; Group, P. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, A. Painless epidural haematoma. Anaesth. Intensive Care 1994, 22, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartos, A.; Breazu, C.M.; Bartos, D.; Mitre, C.I. Accidental Spinal Cord Injury Following an Attempted Thoracic Epidural for acute Pancreatitis Pain Management. Turk. J. Anaesthesiol. Reanim. 2020, 48, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mimata, R.; Higashi, M.; Yasui, M.; Hirai, T.; Yamaura, K. Spinal Epidural Hematoma Following Epidural Catheter Removal in a Patient with Postoperative Urgent Coronary Intervention and Intra-Aortic Balloon Pumping (IABP): A Case Report. Am. J. Case Rep. 2019, 20, 1356–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, M.C.; Tsai, S.K.; Tsou, M.Y.; Lee, H.K.; Guo, W.Y.; Hu, J.S. Paraplegia after delayed detection of inadvertent spinal cord injury during thoracic epidural catheterization in an anesthetized elderly patient. Anesth. Analg. 2004, 99, 580–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoll, A.; Sanchez, M. Epidural hematoma after epidural block: Implications for its use in pain management. Surg. Neurol. 2002, 57, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberg, L.; Harvey, W.R.; Marshall, R.J. Post-operative paraplegia following spinal cord infarction. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2002, 46, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayall, M.F.; Calder, I. Spinal cord injury following an attempted thoracic epidural. Anaesthesia 1999, 54, 990–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabitza, P.; Parrini, M. Slow-onset subdural hematoma, evolving into paraplegia, after attempted spinal anesthesia—A case report. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1998, 69, 650–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barontini, F.; Conti, P.; Marello, G.; Maurri, S. Major neurological sequelae of lumbar epidural anesthesia. Report of three cases. Ital. J. Neurol. Sci. 1996, 17, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nay, P.G.; Milaszkiewicz, R.; Jothilingam, S. Extradural air as a cause of paraplegia following lumbar analgesia. Anaesthesia 1993, 48, 402–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriani, J.; Naragi, M. Paraplegia associated with epidural anesthesia. South Med. J. 1986, 79, 1350–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Zhou, F.; Li, L.; Yin, Q.; Qiu, M.; Zhang, Y. Success with neurotropin in treating pediatric lower extremity pain induced by spinal cord injury after epidural anesthesia. J. Pain Res. 2017, 10, 1391–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harsha, K.J.; Parameswaran, K. Permanent spinal cord injury during lumbar spinal anesthesia: A report of two cases. Neurol. India 2016, 64, 808–811. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Netravathi, M.; Taly, A.B.; Sinha, S.; Bindu, P.S.; Goel, G. Accidental spinal cord injury during spinal anesthesia: A report. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2010, 13, 297–298. [Google Scholar]
- Han, I.S.; Chung, E.Y.; Hahn, Y.J. Spinal epidural hematoma after epidural anesthesia in a patient receiving enoxaparin—A case report. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2010, 59, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, R.; Tietke, M.; Heese, O.; Walter, U. Serious Complications After Epidural Catheter Placement: Two Case Reports. Local Reg. Anesth. 2021, 14, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killeen, T.; Kamat, A.; Walsh, D.; Parker, A.; Aliashkevich, A. Severe adhesive arachnoiditis resulting in progressive paraplegia following obstetric spinal anaesthesia: A case report and review. Anaesthesia 2012, 67, 1386–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, T.; Kato, T.; Kawabata, S.; Enomoto, M.; Tomizawa, S.; Yoshii, T.; Sakaki, K.; Shinomiya, K.; Okawa, A. Adhesive arachnoiditis with extensive syringomyelia and giant arachnoid cyst after spinal and epidural anesthesia: A case report. Spine 2012, 37, E195–E198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Lin, K.; Xie, L.; Wen, H.; Geng, W.; Zhu, S. The Incidence of and Risk Factors for Localized Pain at the Epidural Insertion Site After Epidural Anesthesia: A Prospective Survey of More Than 5000 Cases in Nonobstetric Surgery. Risk Manag. Healthc. Policy 2021, 14, 2171–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer-Bender, A.; Kern, A.; Pollwein, B.; Crispin, A.; Lang, P.M. Incidence and predictors of immediate complications following perioperative non-obstetric epidural punctures. BMC Anesthesiol. 2012, 12, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, T.M.; Counsell, D.; Wildsmith, J.A.; Royal College of Anaesthetists Third National Audit Project. Major complications of central neuraxial block: Report on the Third National Audit Project of the Royal College of Anaesthetists. Br. J. Anaesth. 2009, 102, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moen, V.; Dahlgren, N.; Irestedt, L. Severe neurological complications after central neuraxial blockades in Sweden 1990–1999. Anesthesiology 2004, 101, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breivik, H.; Norum, H.; Fenger-Eriksen, C.; Alahuhta, S.; Vigfusson, G.; Thomas, O.; Lagerkranser, M. Reducing risk of spinal haematoma from spinal and epidural pain procedures. Scand. J. Pain 2018, 18, 129–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupeyrat, A.; Dequire, P.M.; Merouani, A.; Moullier, P.; Eid, G. Subarachnoid hematoma and spinal anesthesia. Ann. Fr. D’anesth. Reanim. 1990, 9, 560–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeAngelis, J. Hazards of subdural and epidural anesthesia during anticoagulant therapy: A case report and review. Anesth. Analg. 1972, 51, 676–679. [Google Scholar]
- Bent, U.; Gniffke, S.; Reinbold, W.D. Epidural hematoma following single-shot epidural-anesthesia. Anaesthesist 1994, 43, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, C.W.; Wall, C.L. Total spinal anesthesia: A rare complication of intrathoracic intercostal nerve block. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1976, 22, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benumof, J.L. Permanent loss of cervical spinal cord function associated with interscalene block performed under general anesthesia. Anesthesiology 2000, 93, 1541–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, J.B. Spinal Cord Injury in a Child After Single-Shot Epidural Anesthesia. Anesth. Analg. 2003, 96, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorenson, E.J. Neurological injuries associated with regional anesthesia. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2008, 33, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Zhou, J. Spinal subdural hematoma and subdural anesthesia following combined spinal-epidural anesthesia: A case report. BMC Anesthesiol. 2021, 21, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Ref | Patients/Age, RF | Type of Anaesthesia and Injury | Possible Reasons/Aetiology/ Consequences | Treatments/Conducts/ Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [3] | 1 CR
| L2–3 epidural + GA | Spinal cord infarction leading to complete paraplegia | Epidural discontinued and catheter removal |
| [8] | 4 paediatric CRs
| Epidural + GA:
|
|
|
| [9] | 2 CRs
|
| Complete paraplegia: one spinal cord compression (hematoma) and one subdural hematoma. A patient died in the decompression surgery | Drug discontinued and catheter removed + urgent decompression of the spinal canal |
| [10] | 4 CRs
|
|
| Same treatment for all cases: epidural abscess evacuation + antibiotic treatment + rehabilitation |
| [11] | 1 CR
| L2–L3 spinal
| Severe subacute axonal sciatic damage and S1 root | Not reported |
| [12] | 1 CR
| T12-L1 epidural
| Permanent paraplegia following percutaneous nephrolithotomy | Monitoring to allow early detection of mismanagement and prevention of further neurologic injury |
| [21] | 1 CR
| L3-4 epidural
| Pain, numbness, paraplegia, areflexia sensory loss and anal tone absent. Deep vein thrombosis | Surgical hematoma treatment and rehabilitation with functional recovery. Pharmacologic therapy to prevent further thrombosis |
| [23] | 1 CR
| Spinal anaesthesia with first attempt believed to be at the L3–4 | Intense pain, paralysis, sensory deficit. Autopsy: extensive haematomyelia | Subarachnoid injection withdrawn and moved to GA |
| [34] | 1 CR
| T11-12 epidural + GA
| Fatigue in legs, loss of sensation, motor paralysis. CT + MRI showed a T9-11 spinal epidural hematoma | Emergency laminectomy and rehabilitation with symptoms slightly improved |
| [35] | 1 CR
| T9-10 epidural + GA
| Numbness, weakness, bowel, and bladder incontinence. Sensory loss below T11 and permanent paraplegia | Little improvement after corticoid and rehabilitation |
| [36] | 1 CR
| C5-C6 epidural steroid block for pain control
| Acute cervical myelopathy with pain, weakness | Hemilaminectomy with a near complete recovery |
| [37] | 1 CR
| T10-11 epidural + GA
| Confusion, pyrexia and tachycardia. Systemic inflammatory response syndrome. L3 flaccid paralysis, areflexia, analgesia and impaired sensation | Epidural catheter removed and rehabilitation |
| [38] | 1 CR
| GA + several tentative of thoracic epidural
| Spinal cord damage due to needle puncture and subsequent haematoma | Surgical dura repair with no improvement (paraplegic) |
| [39] | 1 CR
| 3 attempts of L2-L3 spinal anaesthesia
| Mental confusion, fever, permanent paraplegia | Moved to GA.Antibiotic + antinflammatory + hematoma decompression |
| [40] | 3 CRs
|
|
|
|
| [32] | 1 CR
| L1-2 epidural (paraesthesia)
| Limited sensory and motor function, bowel and bladder incontinent. 10 days later: gangrenous stump and septic shock | Urgent spinal cord decompression + rehabilitation |
| [41] | 1 CR
| L2-4 epidural (4 attempts) + GA
| Prolonged paraesthesia and paresis | Corticoids. Patient with no pain or neurological symptoms |
| [42] | 3 CRs
|
|
|
|
| [43] | 1 CR
| T12–L1 epidural + propofol sedationunexpected needle puncture | Myodynamia improved, but progressive pain persisted that was absent after second treatment | Analgesics and corticoids, then neurotropin. Patient reported gradual pain decrease |
| [44] | 2 CRs
|
|
|
|
| [45] | 1 CR
| L1-2 Spinal anaesthesia + T12–L1 interspace second attempt | Pain, persistent numbness, and weakness of her left lower limb with normal bladder and bowel sensations | Corticoids with gradual improvement |
| [46] | 1 CR
| L4-5 epidural + GA + enoxaparin
| 2nd postoperative day reduced sensation of the right and motor weakness of the left leg | Laminectomy with no improvement in neurologic function |
| [47] | 2 CRs
|
|
|
|
| [33] | 1 CR
| Attempted T11-12 epidural for pain management
| Motor deficit on right lower limb. MRI showed a direct spinal cord injury | Pharmacological treatment and laminectomy with slow recovery |
| [32] | 1 CR
| L3–4 spinal–epidural several attempts
| Left leg sensation and motor function completely recovered 3 h later | Hematoma absorption observation |
| [48] | 1 CR
| L4-5 spinal
| Pain, communicating hydrocephalus and syringomyelia. Rapid, progressive paraplegia and sphincter dysfunction | Unsuccessful laminectomy, external drainage of the syrinx and intravenous steroids |
| [49] | 1 CR
| Combined spinal at L3-4 and epidural at L1-2
| Paraplegia, widespread syringomyelia, massive anterior arachnoid spinal cyst | Shunting of the cyst prevented symptoms progression. Numbness and motor weakness remained |
| Ref | Study/Patients | Type of Anaesthesia | Anaes-SCI | Treatments/Conducts/ Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [13] | Retrospective Study: 10,838 referred to Acute Pain Unit |
| 10.1% with side effects/ complications:
| The Acute Pain Units are fundamental in monitoring, following-up and guiding the treatment of patients with complications |
| [16] | Prospective study: 17,372 epidural catheters |
| 9 cases of epidural abscess:
| Main treatments:
|
| [50] | Prospective study: 5083 surgical inpatients |
| Major complications
| Anaesthesiologist’s skills could be improved to reduce the incidence of Anaes-SCI |
| [51] | Retrospective Study: 7958 non-obstetrical |
|
| Increasing anaesthesiologists’ awareness of patients at higher risk for Anaes-SCI will enhance safety |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pozza, D.H.; Tavares, I.; Cruz, C.D.; Fonseca, S. Spinal Cord Injury and Complications Related to Neuraxial Anaesthesia Procedures: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4665. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054665
Pozza DH, Tavares I, Cruz CD, Fonseca S. Spinal Cord Injury and Complications Related to Neuraxial Anaesthesia Procedures: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(5):4665. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054665
Chicago/Turabian StylePozza, Daniel H., Isaura Tavares, Célia Duarte Cruz, and Sara Fonseca. 2023. "Spinal Cord Injury and Complications Related to Neuraxial Anaesthesia Procedures: A Systematic Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 5: 4665. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054665
APA StylePozza, D. H., Tavares, I., Cruz, C. D., & Fonseca, S. (2023). Spinal Cord Injury and Complications Related to Neuraxial Anaesthesia Procedures: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(5), 4665. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054665







