Altered Differential Expression of Genes and microRNAs Related to Adhesion and Apoptosis Pathways in Patients with Different Phenotypes of Endometriosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
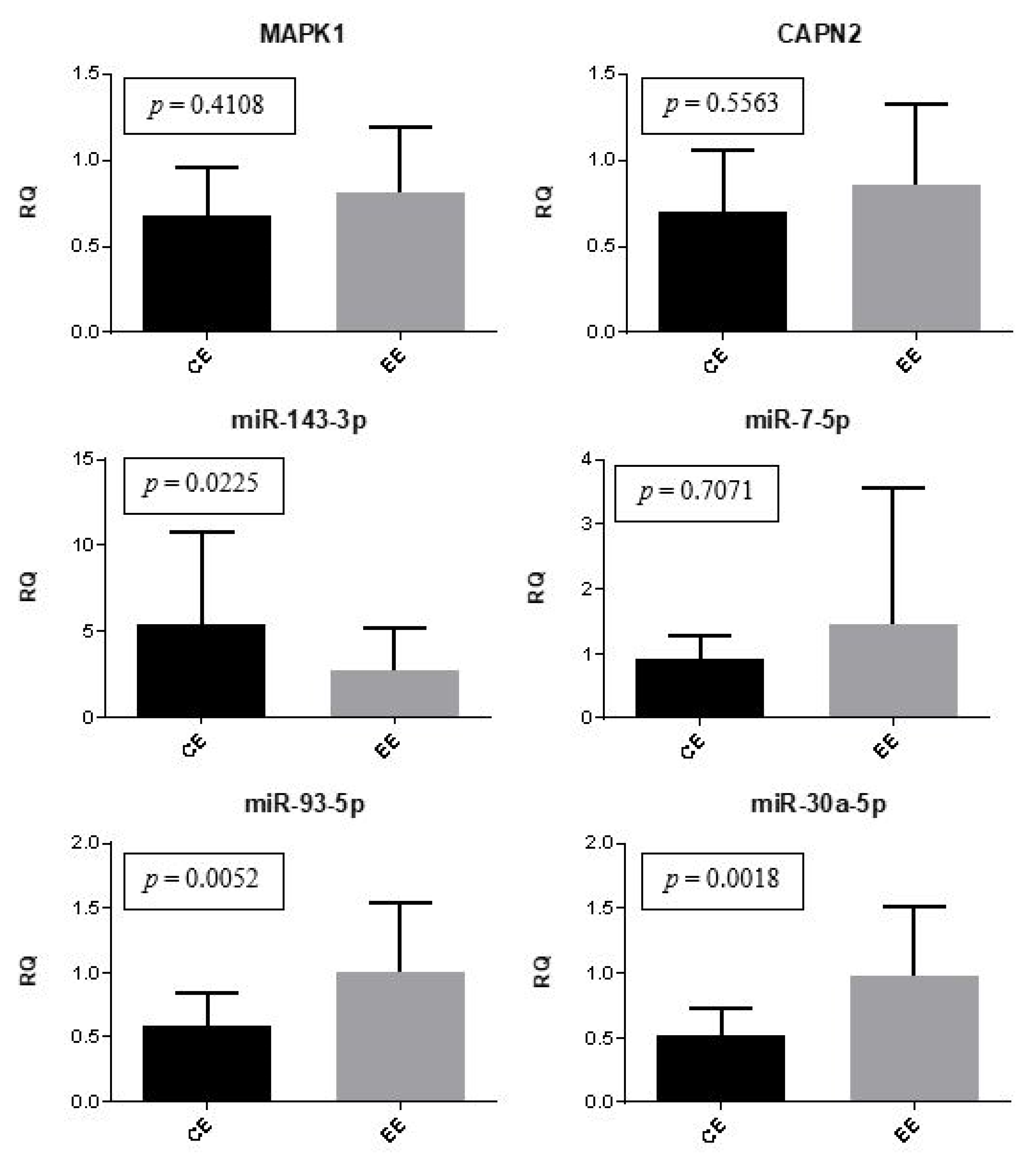
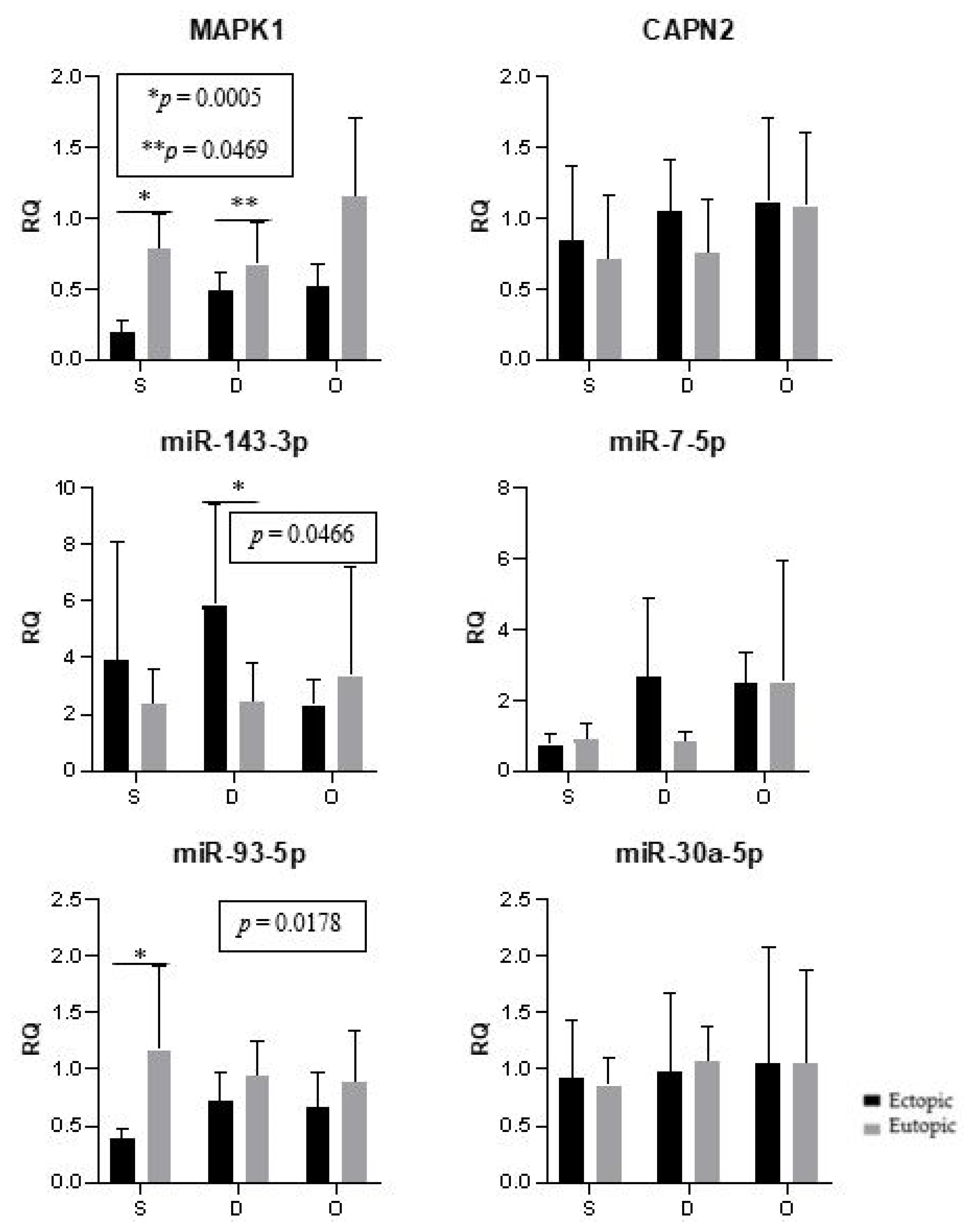
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Methods and Materials
4.1. Sample Collection
4.2. Extraction of Tissue RNA
4.3. Synthesis of Complementary DNA (cDNA)
4.4. RQ-PCR
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zondervan, K.T.; Becker, C.M.; Koga, K.; Missmer, S.A.; Taylor, R.N.; Viganò, P. Endometriosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berker, B.; Seval, M. Problems with the diagnosis of endometriosis. Women’s Health 2015, 11, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Rosa, V.L.; Barra, F.; Chiofalo, B.; Platania, A.; Di Guardo, F.; Conway, F.; Di Angelo Antonio, S.; Lin, L.T. An overview on the relationship between endometriosis and infertility: The impact on sexuality and psychological well-being. J. Psychosom. Obs. Gynaecol. 2020, 41, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Škegro, B.; Bjedov, S.; Mikuš, M.; Mustač, F.; Lešin, J.; Matijević, V.; Ćorić, M.; Elveđi Gašparović, V.; Medić, F.; Sokol Karadjole, V. Endometriosis, pain and mental health. Psychiatr. Danub. 2021, 33, 632–636. [Google Scholar]
- Colette, S.; Defrère, S.; Van Kerk, O.; Van Langendonckt, A.; Dolmans, M.M.; Donnez, J. Differential expression of steroidogenic enzymes according to endometriosis type. Fertil. Steril. 2013, 100, 1642–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcone, T.; Flyckt, R. Clinical Management of Endometriosis. Obs. Gynecol. 2018, 131, 557–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Hu, C.; Ye, C.; Wu, R. Risk factors for coexisting deep endometriosis for patients with recurrent ovarian endometrioma. Front. Surg. 2022, 9, 963686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosti, C.; Pinzauti, S.; Santulli, P.; Chapron, C.; Petraglia, F. Pathogenetic Mechanisms of Deep Infiltrating Endometriosis. Reprod. Sci. 2015, 22, 1053–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siristatidis, C.; Nissotakis, C.; Chrelias, C.; Iacovidou, H.; Salamalekis, E. Immunological factors and their role in the genesis and development of endometriosis. J. Obs. Gynaecol. Res. 2006, 32, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetvicka, V.; Kralickova, M. Immunological aspects of endometriosis: A review. Ann. Transl. Med. 2015, 3, 153. [Google Scholar]
- Gurates, B.; Bulun, S.E. Endometriosis: The ultimate hormonal disease. Semin. Reprod. Med. 2003, 21, 125–134. [Google Scholar]
- Nothnick, W.; Alali, Z. Recent advances in the understanding of endometriosis: The role of inflammatory mediators in disease pathogenesis and treatment. F1000Research 2016, 5, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witz, C.A. Cell adhesion molecules and endometriosis. Semin. Reprod. Med. 2003, 21, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rodgers, W.H.; Matrisian, L.M.; Giudice, L.C.; Dsupin, B.; Cannon, P.; Svitek, C.; Gorstein, F.; Osteen, K.G. Patterns of matrix metalloproteinase expression in cycling endometrium imply differential functions and regulation by steroid hormones. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 94, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dmowski, W.P.; Ding, J.; Shen, J.; Rana, N.; Fernandez, B.B.; Braun, D.P. Apoptosis in endometrial glandular and stromal cells in women with and without endometriosis. Hum. Reprod. 2001, 16, 1802–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djokovic, D.; Calhaz-Jorge, C. Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target in endometriosis. Acta Med. Port. 2014, 27, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Abreu, L.G.; Romão, G.S.; Dos Reis, R.M.; Ferriani, R.A.; De Sá, M.F.; De Moura, M.D. Reduced aromatase activity in granulosa cells of women with endometriosis undergoing assisted reproduction techniques. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2006, 22, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.W. Epigenetics of endometriosis. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2009, 15, 587–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernet-Tomás Mdel, M.; Pérez-Ares, C.T.; Verdú, N.; Fernández-Figueras, M.T.; Molinero, J.L.; Carreras, R. The depolarized expression of the alpha-6 integrin subunit in the endometria of women with endometriosis. J. Soc. Gynecol. Investig. 2006, 13, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, S.M. MicroRNAs as oncogenes. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2006, 16, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlsson Teague, E.M.; Van der Hoek, K.H.; Van der Hoek, M.B.; Perry, N.; Wagaarachchi, P.; Robertson, S.A.; Print, C.G.; Hull, L.M. MicroRNA-regulated pathways associated with endometriosis. Mol. Endocrinol. 2009, 23, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burney, R.O.; Hamilton, A.E.; Aghajanova, L.; Vo, K.C.; Nezhat, C.N.; Lessey, B.A.; Giudice, L.C. MicroRNA expression profiling of eutopic secretory endometrium in women with versus without endometriosis. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2009, 15, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghajanova, L.; Giudice, L.C. Molecular evidence for differences in endometrium in severe versus mild endometriosis. Reprod. Sci. 2011, 18, 229–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braza-Boïls, A.; Marí-Alexandre, J.; Gilabert, J.; Sánchez-Izquierdo, D.; España, F.; Estellés, A.; Gilabert-Estellés, J. MicroRNA expression profile in endometriosis: Its relation to angiogenesis and fibrinolytic factors. Hum. Reprod. 2014, 29, 978–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toloubeydokhti, T.; Bukulmez, O.; Chegini, N. Potential regulatory functions of microRNAs in the ovary. Semin. Reprod. Med. 2008, 26, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, S.Z.; Yang, Y.; Lang, J.; Sun, P.; Leng, J. Plasma miR-17-5p, miR-20a and miR-22 are down-regulated in women with endometriosis. Hum. Reprod. 2013, 28, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.T.; Zhao, Y.N.; Han, B.W.; Hong, S.J.; Chen, Y.Q. Circulating microRNAs identified in a genome-wide serum microRNA expression analysis as noninvasive biomarkers for endometriosis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Mutlu, L.; Grechukhina, O.; Taylor, H.S. Circulating microRNAs as potential biomarkers for endometriosis. Fertil. Steril. 2015, 103, 1252–1260.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nothnick, W.B.; Al-Hendy, A.; Lue, J.R. Circulating Micro-RNAs as Diagnostic Biomarkers for Endometriosis: Privation and Promise. J. Minim. Invasive Gynecol. 2015, 22, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekker, K.; Saare, M.; Roost, A.M.; Kaart, T.; Sõritsa, D.; Karro, H.; Sõritsa, A.; Simón, C.; Salumets, A.; Peters, M. Circulating miR-200-family micro-RNAs have altered plasma levels in patients with endometriosis and vary with blood collection time. Fertil. Steril. 2015, 104, 938–946.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, S.M.; Creighton, C.J.; Han, D.Y.; Zariff, A.; Anderson, M.L.; Gunaratne, P.H.; Matzuk, M.M. Functional microRNA involved in endometriosis. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 25, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fassbender, A.; Burney, R.O.; O, D.F.; D’Hooghe, T.; Giudice, L. Update on Biomarkers for the Detection of Endometriosis. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 130854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panir, K.; Schjenken, J.E.; Robertson, S.A.; Hull, M.L. Non-coding RNAs in endometriosis: A narrative review. Hum. Reprod. Update 2018, 24, 497–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Xu, H.; Kuang, Y. Systematic enrichment analysis of microRNA expression profiling studies in endometriosis. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2015, 18, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.D.; Chen, Q.H.; Chen, Q.X. The action of p38 MAP kinase and its inhibitors on endometriosis. Yao Xue Xue Bao 2010, 45, 548–554. [Google Scholar]
- Santulli, P.; Marcellin, L.; Tosti, C.; Chouzenoux, S.; Cerles, O.; Borghese, B.; Batteux, F.; Chapron, C. MAP kinases and the inflammatory signaling cascade as targets for the treatment of endometriosis? Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2015, 19, 1465–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yotova, I.Y.; Quan, P.; Leditznig, N.; Beer, U.; Wenzl, R.; Tschugguel, W. Abnormal activation of Ras/Raf/MAPK and RhoA/ROCKII signalling pathways in eutopic endometrial stromal cells of patients with endometriosis. Hum. Reprod. 2011, 26, 885–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Chen, L.; Yang, S.; Han, J.; Zhai, D.; Ni, J.; Yu, C.; Cai, Z. Puerarin suppresses proliferation of endometriotic stromal cells partly via the MAPK signaling pathway induced by 17ß-estradiol-BSA. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Cao, J.; Liu, Q.; Zou, Y.; Li, H.; Yin, T. MAPK/ERK signal pathway involved expression of COX-2 and VEGF by IL-1β induced in human endometriosis stromal cells in vitro. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2013, 6, 2129–2136. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.Q.; Shao, J.; Meng, Y.H.; Mei, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Chang, K.K.; Wang, X.Q.; Zhu, X.Y.; et al. NME1 suppression promotes growth, adhesion and implantation of endometrial stromal cells via Akt and MAPK/Erk1/2 signal pathways in the endometriotic milieu. Hum. Reprod. 2013, 28, 2822–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Zhou, W.; Chen, S.; Shi, Y.; Su, L.; Zhu, M.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Q. Lipoxin A4 suppresses the development of endometriosis in an ALX receptor-dependent manner via the p38 MAPK pathway. Br. J. Pharm. 2014, 171, 4927–4940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Jin, A.; Huang, W.; Tsang, L.L.; Cai, Z.; Zhou, X.; Chen, H.; Chan, H.C. Up-regulation of Bcl-2 by CD147 Through ERK Activation Results in Abnormal Cell Survival in Human Endometriosis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, E955–E963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngô, C.; Nicco, C.; Leconte, M.; Chéreau, C.; Arkwright, S.; Vacher-Lavenu, M.C.; Weill, B.; Chapron, C.; Batteux, F. Protein kinase inhibitors can control the progression of endometriosis in vitro and in vivo. J. Pathol. 2010, 222, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshino, O.; Osuga, Y.; Hirota, Y.; Koga, K.; Hirata, T.; Harada, M.; Morimoto, C.; Yano, T.; Nishii, O.; Tsutsumi, O.; et al. Possible pathophysiological roles of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) in endometriosis. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2004, 52, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Chen, P.; Liu, W. Down regulation of MiR-93 contributes to endometriosis through targeting MMP3 and VEGFA. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 1706–1717. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.; Shen, H.; Xu, J.; Zhao, S.; Yao, S.; Jiang, N. MiR-143-3p suppresses the progression of ovarian cancer. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 866–874. [Google Scholar]
- Song, B.; Tang, Y.J.; Zhang, W.G.; Wan, C.C.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.J. MiR-143 regulates proliferation and apoptosis of myelocytic leukemia cell HL-60 via modulating ERK1. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 3333–3341. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, L.; Zhang, D.; Shi, H.; Bian, Y.; Guo, R. MiR-143 inhibits endometrial cancer cell proliferation and metastasis by targeting MAPK1. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 84384–84395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, L.; DeVine, A.; Sierra, L.J.; Brown, A.G.; Elovitz, M.A. miR-143 and miR-145 disrupt the cervical epithelial barrier through dysregulation of cell adhesion, apoptosis and proliferation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yu, X.; Guo, X.; Tian, Z.; Su, M.; Long, Y.; Huang, C.; Zhou, F.; Liu, M.; Wu, X.; et al. miR-143 is downregulated in cervical cancer and promotes apoptosis and inhibits tumor formation by targeting Bcl-2. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 5, 753–760. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, B.; Xue, X.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, J.; Xu, C.Y.; Duan, P. The differential expression of microRNA-143,145 in endometriosis. Iran. J. Reprod. Med. 2014, 12, 555–560. [Google Scholar]
- Cosar, E.; Mamillapalli, R.; Ersoy, G.S.; Cho, S.; Seifer, B.; Taylor, H.S. Serum microRNAs as diagnostic markers of endometriosis: A comprehensive array-based analysis. Fertil. Steril. 2016, 106, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Hu, T.; Hu, P.; Qi, C.; Qian, L. miR-143-3p inhibits endometriotic stromal cell proliferation and invasion by inactivating autophagy in endometriosis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filigheddu, N.; Gregnanin, I.; Porporato, P.E.; Surico, D.; Perego, B.; Galli, L.; Patrignani, C.; Graziani, A.; Surico, N. Differential expression of microRNAs between eutopic and ectopic endometrium in ovarian endometriosis. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 2010, 369549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, B.; Fang, M.; Guo, F.; Cui, M. Identification of microRNAs and target genes involved in serous ovarian carcinoma and their influence on survival. Eur. J. Gynaecol. Oncol. 2014, 35, 655–661. [Google Scholar]
- Chein, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fang, X.; Hu, X. Evidence for calpains in cancer metastasis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 8233–8240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penna, I.; Du, H.; Ferriani, R.; Taylor, H.S. Calpain5 expression is decreased in endometriosis and regulated by HOXA10 in human endometrial cells. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2008, 14, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Jin, X.; Zhu, L.; Shen, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Hu, Y.; Yan, G.; et al. CAPN 7 promotes the migration and invasion of human endometrial stromal cell by regulating matrix metalloproteinase 2 activity. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2013, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.Y.; Zhan, Y.S.; Huang, J.; Chen, Y.X. MicroRNA-7 suppresses human colon cancer invasion and proliferation by targeting the expression of focal adhesion kinase. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Carlo, C.; Bonifacio, M.; Tommaselli, G.A.; Bifulco, G.; Guerra, G.; Nappi, C. Metalloproteinases, vascular endothelial growth factor, and angiopoietin 1 and 2 in eutopic and ectopic endometrium. Fertil. Steril. 2009, 91, 2315–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, X.; Zhou, L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, J. MicroRNA-7 inhibits metastasis and invasion through targeting focal adhesion kinase in cervical cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, P.; Chen, Z.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Tang, H. MicroRNA-7 downregulates XIAP expression to suppress cell growth and promote apoptosis in cervical cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 2247–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Liu, C.; Zhao, C.; Zhai, L.; Lv, S. Downregulation of β3 integrin by miR-30a-5p modulates cell adhesion and invasion by interrupting Erk/Ets-1 network in triple-negative breast cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haikalis, M.E.; Wessels, J.M.; Leyland, N.A.; Agarwal, S.K.; Foster, W.G. MicroRNA expression pattern differs depending on endometriosis lesion type. Biol. Reprod. 2018, 98, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saare, T.M.; Rekker, K.; Laisk-Podar, T.; Sõritsa, D.; Roost, A.M.; Simm, J.; Velthut-Meikas, A.; Samuel, K.; Metsalu, T.; Karro, H.; et al. High-Throughput Sequencing Approach Uncovers the miRNome of Peritoneal Endometriotic Lesions and Adjacent Healthy. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malysheva, O.V.; Kopteva, O.S.; Krylova, Y.S.; Molotkov, A.S.; Osinovskaya, N.S.; Shved, N.Y.; Yarmolinskaya, M.I.; Baranov, V.S. Expression of Protein Markers of Adipogenesis in Endometriotic Lesions. Cell Tissue Biol. 2020, 14, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toor, K.; Wessels, J.M.; Agarwal, S.K.; Leyland, N.; Foster, W.G. Clinical markers of endometriosis: Have we been too quick to judge? Med. Hypotheses 2014, 82, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| D | O | S | C | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parity | Nulligravida | 6 | 5 | 5 | 1 | 0.1099 |
| GxPx | 4 | 5 | 5 | 9 | ||
| Medication | Present | 6 | 6 | 8 | 3 | 0.1566 |
| Absent | 4 | 4 | 2 | 7 | ||
| Other diseases | Present | 3 | 7 | 7 | 3 | 0.0937 |
| Absent | 7 | 3 | 3 | 7 | ||
| Mean age | 35.3 | 36.1 | 33.2 | 31.2 | 0.1870 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antonio, L.G.L.; Meola, J.; Rosa-e-Silva, A.C.J.d.S.; Nogueira, A.A.; Candido dos Reis, F.J.; Poli-Neto, O.B.; Rosa-e-Silva, J.C. Altered Differential Expression of Genes and microRNAs Related to Adhesion and Apoptosis Pathways in Patients with Different Phenotypes of Endometriosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4434. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054434
Antonio LGL, Meola J, Rosa-e-Silva ACJdS, Nogueira AA, Candido dos Reis FJ, Poli-Neto OB, Rosa-e-Silva JC. Altered Differential Expression of Genes and microRNAs Related to Adhesion and Apoptosis Pathways in Patients with Different Phenotypes of Endometriosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(5):4434. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054434
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntonio, Luana Grupioni Lourenço, Juliana Meola, Ana Carolina Japur de Sá Rosa-e-Silva, Antonio Alberto Nogueira, Francisco José Candido dos Reis, Omero Benedicto Poli-Neto, and Julio César Rosa-e-Silva. 2023. "Altered Differential Expression of Genes and microRNAs Related to Adhesion and Apoptosis Pathways in Patients with Different Phenotypes of Endometriosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 5: 4434. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054434
APA StyleAntonio, L. G. L., Meola, J., Rosa-e-Silva, A. C. J. d. S., Nogueira, A. A., Candido dos Reis, F. J., Poli-Neto, O. B., & Rosa-e-Silva, J. C. (2023). Altered Differential Expression of Genes and microRNAs Related to Adhesion and Apoptosis Pathways in Patients with Different Phenotypes of Endometriosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(5), 4434. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054434






