Human Colonoid–Myofibroblast Coculture for Study of Apical Na+/H+ Exchangers of the Lower Cryptal Neck Region
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
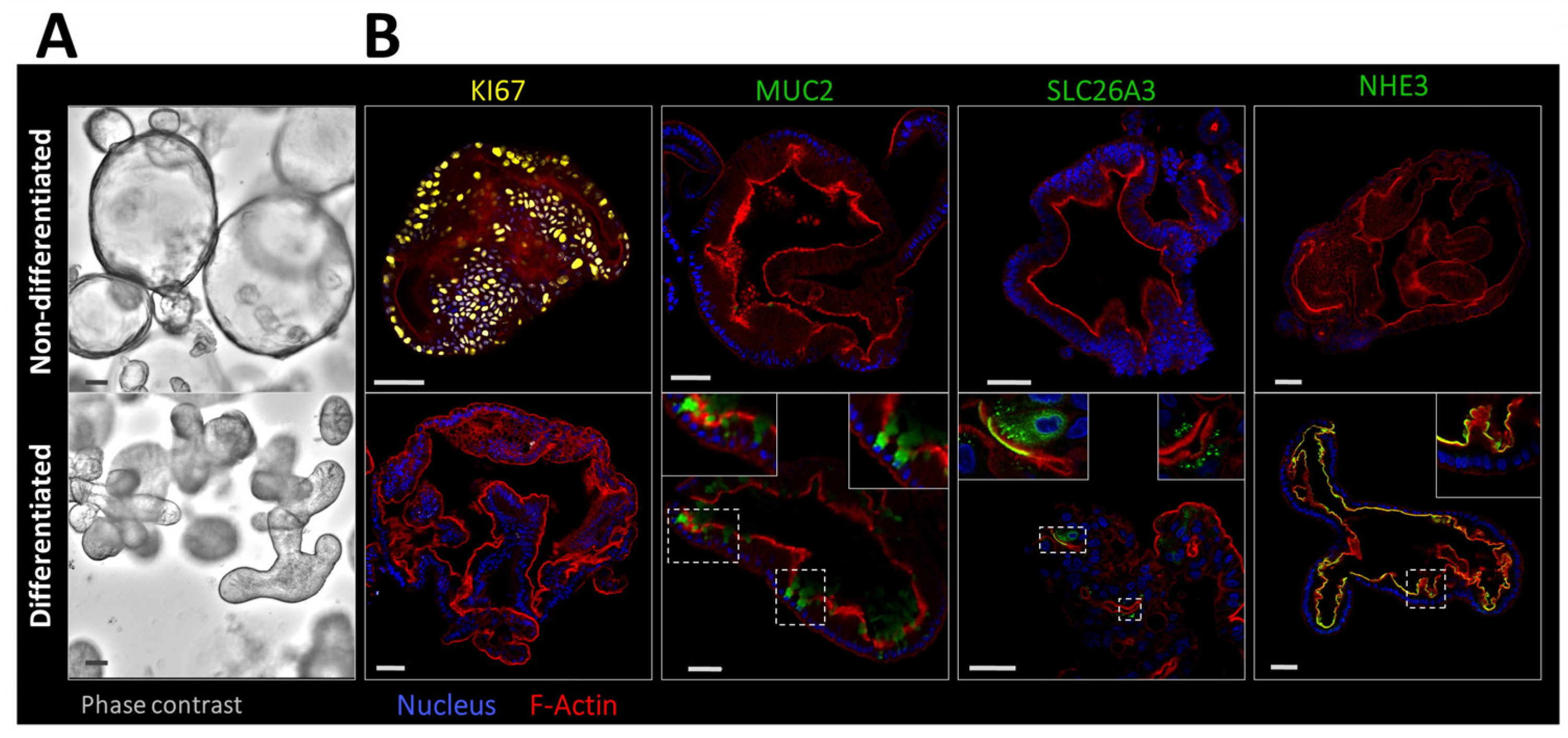
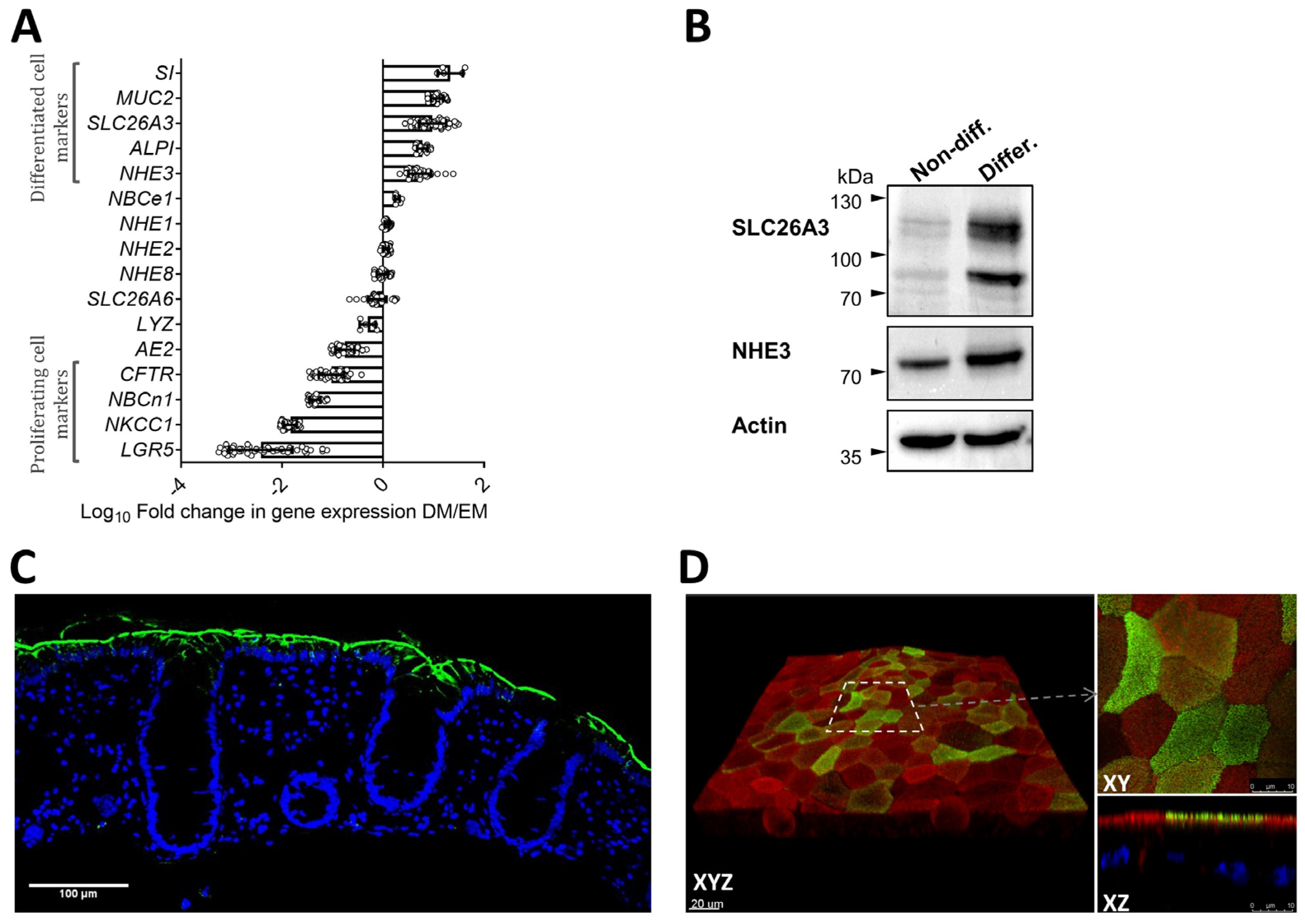
2.1. Morphological Features and Expression Profile of Differentiation Markers and Ion Transporters in Nondifferentiated and Differentiated 3D Human Colonoids
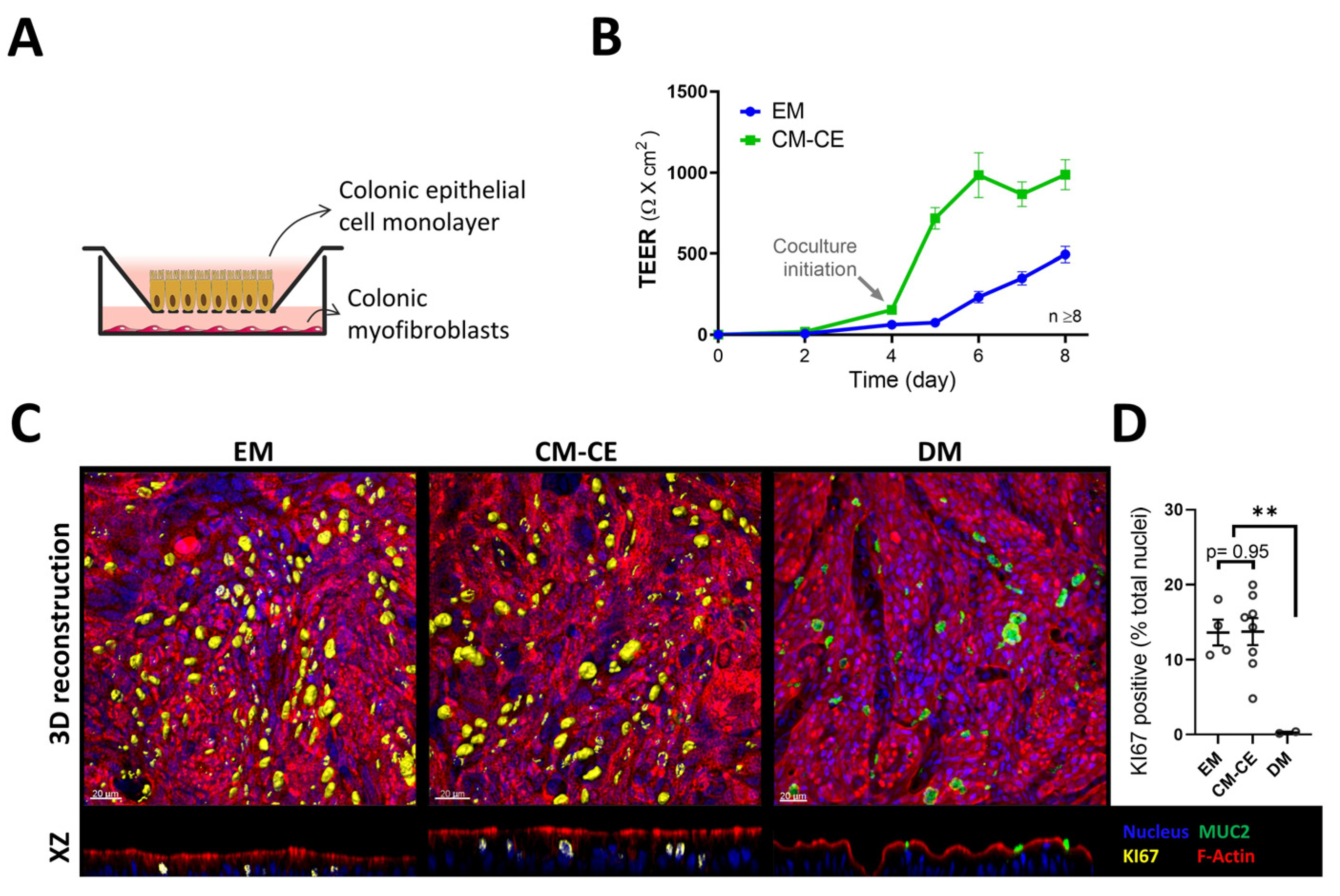
2.2. Modeling of Two-Dimensional Organoid Monolayers with Myofibroblast Coculture
2.3. Expression Changes in Tight Junctional Components during Monolayer Differentiation
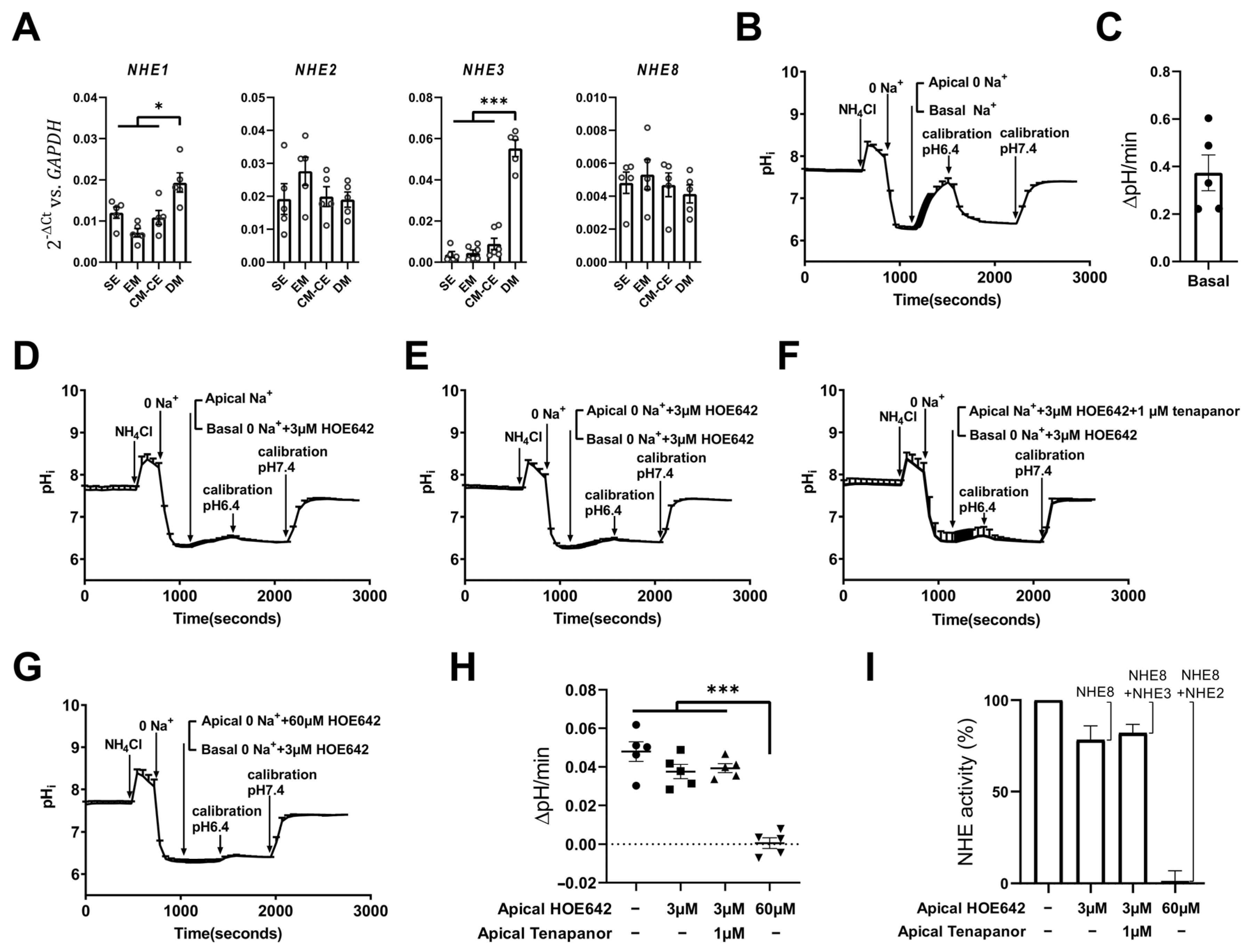
2.4. Expression and Fluorometric Characterization of Apical Na+/H+ (NHE) Exchange in CM-CE Monolayers
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Human Colonoid and Myofibroblast Cultures
4.2. Fluorometric Measurements in CM-CE Monolayers
4.3. Immunofluorescence Imaging of Colonoids
4.4. Immunohistochemical Analysis of Human Colonic Biopsies
4.5. RT-qPCR Analysis
4.6. SDS-PAGE and Western Blot
4.7. Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zachos, N.C.; Tse, M.; Donowitz, M. Molecular physiology of intestinal Na+/H+ exchange. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2005, 67, 411–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Ghishan, F.K.; Kiela, P.R. SLC9 Gene Family: Function, Expression, and Regulation. Compr. Physiol. 2018, 8, 555–583. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nikolovska, K.; Seidler, U.E.; Stock, C. The Role of Plasma Membrane Sodium/Hydrogen Exchangers in Gastrointestinal Functions: Proliferation and Differentiation, Fluid/Electrolyte Transport and Barrier Integrity. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 899286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.P.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Johansson, M.E.V.; Xu, H.; Ghishan, F.K. Loss of NHE8 expression impairs intestinal mucosal integrity. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2015, 309, G855–G864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, C.A.; Laubitz, D.; Ohland, C.L.; Midura-Kiela, M.T.; Patil, K.; Besselsen, D.G.; Jamwal, D.R.; Jobin, C.; Ghishan, F.K.; Kiela, P.R. Microbial dysbiosis associated with impaired intestinal Na+/H+ exchange accelerates and exacerbates colitis in ex-germ free mice. Mucosal Immunol. 2018, 11, 1329–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolovska, K.; Cao, L.; Hensel, I.; Di Stefano, G.; Seidler, A.E.; Zhou, K.Y.; Qian, J.J.; Singh, A.K.; Riederer, B.; Seidler, U. Sodium/hydrogen-exchanger-2 modulates colonocyte lineage differentiation. Acta Physiol. 2022, 234, e13774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Seidler, A.; Zhou, K.; Yuan, Z.; Yeruva, S.; Amiri, M.; Yun, C.C.; Nikolovska, K.; Seidler, U. Expression, Localization and Functional Activity of the Major Na(+)/H(+) Exchange Isoforms Expressed in the Intestinal Cell Line Caco-2BBe. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 52, 1017–1038. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Li, J.; Chen, H.; Ghishan, F.K. NHE8 Deficiency Promotes Colitis-Associated Cancer in Mice via Expansion of Lgr5-Expressing Cells. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 7, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.Y.; Amiri, M.; Salari, A.; Yu, Y.; Xu, H.; Seidler, U.; Nikolovska, K. Functional characterization of the sodium/hydrogen exchanger 8 and its role in proliferation of colonic epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2021, 321, C471–C488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.; Mboya, I.B.; Mwambi, H.; Elbashir, M.K.; Omolo, B. Predictors of colorectal cancer survival using cox regression and random survival forests models based on gene expression data. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0261625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretzschmar, K.; Clevers, H. Organoids: Modeling Development and the Stem Cell Niche in a Dish. Dev. Cell 2016, 38, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Stange, D.E.; Ferrante, M.; Vries, R.G.J.; van Es, J.H.; van den Brink, S.; van Houdt, W.J.; Pronk, A.; van Gorp, J.; Siersema, P.D.; et al. Long-term Expansion of Epithelial Organoids From Human Colon, Adenoma, Adenocarcinoma, and Barrett’s Epithelium. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1762–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukonin, I.; Serra, D.; Meylan, L.C.; Volkmann, K.; Baaten, J.; Zhao, R.; Meeusen, S.; Colman, K.; Maurer, F.; Stadler, M.B.; et al. Phenotypic landscape of intestinal organoid regeneration. Nature 2020, 586, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameen, N.; Alexis, J.; Salas, P. Cellular localization of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator in mouse intestinal tract. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2000, 114, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linley, J.; Loganathan, A.; Kopanati, S.; Sandle, G.I.; Hunter, M. Evidence that two distinct crypt cell types secrete chloride and potassium in human colon. Gut 2014, 63, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakab, R.L.; Collaco, A.M.; Ameen, N.A. Physiological relevance of cell-specific distribution patterns of CFTR, NKCC1, NBCe1, and NHE3 along the crypt-villus axis in the intestine. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2011, 300, G82–G98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Juric, M.; Li, J.H.; Riederer, B.; Yeruva, S.; Singh, A.K.; Zheng, L.F.; Glage, S.; Kollias, G.; Dudeja, P.; et al. Loss of downregulated in adenoma (DRA) impairs mucosal HCO3-secretion in murine ileocolonic inflammation. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2012, 18, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, C.; Lytle, C. Segregation of Na/H exchanger-3 and Cl/HCO3 exchanger SLC26A3 (DRA) in rodent cecum and colon. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2010, 299, G358–G367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Jiang, W.; Furth, E.E.; Wen, X.; Katz, J.P.; Sellon, R.K.; Silberg, D.G.; Antalis, T.M.; Schweinfest, C.W.; Wu, G.D. Intestinal inflammation reduces expression of DRA, a transporter responsible for congenital chloride diarrhea. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 275, G1445–G1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeruva, S.; Farkas, K.; Hubricht, J.; Rode, K.; Riederer, B.; Bachmann, O.; Cinar, A.; Rakonczay, Z.; Molnar, T.; Nagy, F.; et al. Preserved Na+/H+ Exchanger Isoform 3 Expression and Localization, But Decreased NHE3 Function Indicate Regulatory Sodium Transport Defect in Ulcerative Colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2010, 16, 1149–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Tse, C.-M.; Avula, L.R.; Singh, V.; Foulke-Abel, J.; de Jonge, H.R.; Donowitz, M. Molecular Basis and Differentiation-Associated Alterations of Anion Secretion in Human Duodenal Enteroid Monolayers. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 5, 591–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tse, C.-M.; Yin, J.; Singh, V.; Sarker, R.; Lin, R.; Verkman, A.S.; Turner, J.R.; Donowitz, M. cAMP Stimulates SLC26A3 Activity in Human Colon by a CFTR-Dependent Mechanism That Does Not Require CFTR Activity. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 7, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zomer-van Ommen, D.D.; de Poel, E.; Kruisselbrink, E.; Oppelaar, H.; Vonk, A.M.; Janssens, H.M.; van der Ent, C.K.; Hagemeijer, M.C.; Beekman, J.M. Comparison of ex vivo and in vitro intestinal cystic fibrosis models to measure CFTR-dependent ion channel activity. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2018, 17, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- In, J.; Foulke-Abel, J.; Zachos, N.C.; Hansen, A.M.; Kaper, J.B.; Bernstein, H.D.; Halushka, M.; Blutt, S.; Estes, M.K.; Donowitz, M.; et al. Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli reduce mucus and intermicrovillar bridges in human stem cell-derived colonoids. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 2, 48–62.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, K.E. Positive and negative regulation of chloride secretion in T84 cells. Am. J. Physiol. 1993, 265, C859–C868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, D.W.; Adegboyega, P.A.; Di Mari, J.F.; Mifflin, R.C. Epithelial cells and their neighbors I. Role of intestinal myofibroblasts in development, repair, and cancer. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2005, 289, G2–G7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greicius, G.; Kabiri, Z.; Sigmundsson, K.; Liang, C.; Bunte, R.; Singh, M.K.; Virshup, D.M. PDGFR alpha(+) pericryptal stromal cells are the critical source of Wnts and RSPO3 for murine intestinal stem cells in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E3173–E3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastula, A.; Middelhoff, M.; Brandtner, A.; Tobiasch, M.; Hohl, B.; Nuber, A.H.; Demir, I.E.; Neupert, S.; Kollmann, P.; Mazzuoli-Weber, G.; et al. Three-Dimensional Gastrointestinal Organoid Culture in Combination with Nerves or Fibroblasts: A Method to Characterize the Gastrointestinal Stem Cell Niche. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 3710836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpus, O.N.; Westendorp, B.F.; Vermeulen, J.L.M.; Meisner, S.; Koster, J.; Muncan, V.; Wildenberg, M.E.; van den Brink, G.R. Colonic CD90+Crypt Fibroblasts Secrete Semaphorins to Support Epithelial Growth. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 3698–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirokawa, Y.; Yip, K.H.Y.; Tan, C.W.; Burgess, A.W. Colonic myofibroblast cell line stimulates colonoid formation. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2014, 306, G547–G556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, H.Y.K.; Tan, C.W.; Hirokawa, Y.; Burgess, A.W. Colon organoid formation and cryptogenesis are stimulated by growth factors secreted from myofibroblasts. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- In, J.G.; Foulke-Abel, J.; Clarke, E.; Kovbasnjuk, O. Human Colonoid Monolayers to Study Interactions Between Pathogens, Commensals, and Host Intestinal Epithelium. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 146, e59357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, S.C.; Weber, G.J.; van Sambeek, D.M.; Soares, J.W.; Racicot, K.; Breault, D.T. Intestinal enteroids recapitulate the effects of short-chain fatty acids on the intestinal epithelium. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amasheh, S.; Meiri, N.; Gitter, A.H.; Schoneberg, T.; Mankertz, J.; Schulzke, J.D.; Fromm, M. Claudin-2 expression induces cation-selective channels in tight junctions of epithelial cells. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 4969–4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muto, S.; Hata, M.; Taniguchi, J.; Tsuruoka, S.; Moriwaki, K.; Saitou, M.; Furuse, K.; Sasaki, H.; Fujimura, A.; Imai, M.; et al. Claudin-2-deficient mice are defective in the leaky and cation-selective paracellular permeability properties of renal proximal tubules. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 8011–8016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzza, M.S.; Netzel-Arnett, S.; Shea-Donohue, T.; Zhao, A.P.; Lin, C.Y.; List, K.; Szabo, R.; Fasano, A.; Bugge, T.H.; Antalis, T.M. Membrane-anchored serine protease matriptase regulates epithelial barrier formation and permeability in the intestine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4200–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Mumm, J.B.; Herbst, R.; Kolbeck, R.; Wang, Y. IL-22 Increases Permeability of Intestinal Epithelial Tight Junctions by Enhancing Claudin-2 Expression. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 3316–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavet, M.E.; Akhter, S.; Murtazina, R.; De Medina, F.S.; Tse, C.M.; Donowitz, M. Half-lives of plasma membrane Na+/H+ exchangers NHE1-3: Plasma membrane NHE2 has a rapid rate of degradation. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2001, 281, C2039–C2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, M. Regulation of active ion transport in the small intestine. Ciba Found. Symp. 1976, 42, 109–127. [Google Scholar]
- Welsh, M.J.; Smith, P.L.; Fromm, M.; Frizzell, R.A. Crypts are the site of intestinal fluid and electrolyte secretion. Science 1982, 218, 1219–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallback, D.A.; Jodal, M.; Sjoqvist, A.; Lundgren, O. Evidence for cholera secretion emanating from the crypts—A study of villus tissue osmolality and fluid and electrolyte transport in the small-intestine of the cat. Gastroenterology 1982, 83, 1051–1056. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Turnberg, L.A.; Bieberdorf, F.A.; Morawski, S.G.; Fordtran, J.S. Interrelationships of chloride, bicarbonate, sodium, and hydrogen transport in the human ileum. J. Clin. Investig. 1970, 49, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knickelbein, R.G.; Aronson, P.S.; Dobbins, J.W. Membrane distribution of sodium hydrogen and chloride bicarbonate exchangers in crypt and villus cell-membranes from rabbit ileum. J. Clin. Investig. 1988, 82, 2158–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, E.S.; Budinger, M.E.; Hayslett, J.P.; Binder, H.J. Ion-transport in proximal colon of the rat—Sodium depletion stimulates neutral sodium-chloride absorption. J. Clin. Investig. 1986, 77, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, H.J.; Foster, E.S.; Budinger, M.E.; Hayslett, J.P. Mechanism of electroneutral sodium-chloride absorption in distal colon of the rat. Gastroenterology 1987, 93, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldfarb, D.S.; Egnor, R.W.; Charney, A.N. Effects of acid-base variables on ion-transport in rat colon. J. Clin. Investig. 1988, 81, 1903–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donowitz, M. Small intestinal and colonic linked sodium-chloride absorption—New understanding of distribution and regulation. Gastroenterology 1987, 93, 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Binder, H.J.; Boron, W.F.; Geibel, J.P. Fluid absorption in isolated-perfused colonic crypts. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 96, 2373–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, V.M.; Geibel, J.; Binder, H.J. Chloride-dependent Na-H exchange. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 11051–11054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, C.M.; Ma, A.I.; Yang, V.W.; Watson, A.J.; Levine, S.; Montrose, M.H.; Potter, J.; Sardet, C.; Pouyssegur, J.; Donowitz, M. Molecular cloning and expression of a cDNA encoding the rabbit ileal villus cell basolateral membrane Na+/H+ exchanger. Embo J. 1991, 10, 1957–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlowski, J.; Kandasamy, R.A.; Shull, G.E. Molecular cloning of putative members of the Na/H exchanger gene family. cDNA cloning, deduced amino acid sequence, and mRNA tissue expression of the rat Na/H exchanger NHE-1 and two structurally related proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 9331–9339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Chen, R.; Ghishan, F.K. Subcloning, localization, and expression of the rat intestinal sodium-hydrogen exchanger isoform 8. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2005, 289, G36–G41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultheis, P.J.; Clarke, L.L.; Meneton, P.; Miller, M.L.; Soleimani, M.; Gawenis, L.R.; Riddle, T.M.; Duffy, J.J.; Doetschman, T.; Wang, T.; et al. Renal and intestinal absorptive defects in mice lacking the NHE3 Na+/H+ exchanger. Nat. Genet. 1998, 19, 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.X.; Thomas, L.; Tahmasbi, M.; Valdez, A.; Rieg, J.A.D.; Fenton, R.A.; Rieg, T. An inducible intestinal epithelial cell-specific NHE3 knockout mouse model mimicking congenital sodium diarrhea. Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardazzi, C.; Sheikh, I.A.; Xu, H.; Ghishan, F.K. The Physiological Function and Potential Role of the Ubiquitous Na+/H+ Exchanger Isoform 8 (NHE8): An Overview Data. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabiri, Z.; Greicius, G.; Madan, B.; Biechele, S.; Zhong, Z.D.; Zaribafzadeh, H.; Aliyev, J.; Wu, Y.H.; Bunte, R.; Williams, B.O.; et al. Stroma provides an intestinal stem cell niche in the absence of epithelial Wnts. Development 2014, 141, 2206–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altay, G.; Larranaga, E.; Tosi, S.; Barriga, F.M.; Batlle, E.; Fernandez-Majada, V.; Martinez, E. Self-organized intestinal epithelial monolayers in crypt and villus-like domains show effective barrier function. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, R.; Gunzel, D.; Krug, S.M.; Schulzke, J.D.; Fromm, M.; Yu, A.S.L. Claudin-2-mediated cation and water transport share a common pore. Acta Physiol. 2017, 219, 521–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuda, S.; Furuse, M. Claudin-2 knockout by TALEN-mediated gene targeting in MDCK cells: Claudin-2 independently determines the leaky property of tight junctions in MDCK cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, W.; Albus, U.; Counillon, L.; Gögelein, H.; Lang, H.J.; Linz, W.; Weichert, A.; Schölkens, B.A. Protective effects of HOE642, a selective sodium-hydrogen exchange subtype 1 inhibitor, on cardiac ischaemia and reperfusion. Cardiovasc. Res. 1995, 29, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paehler Vor der Nolte, A.; Chodisetti, G.; Yuan, Z.; Busch, F.; Riederer, B.; Luo, M.; Yu, Y.; Menon, M.B.; Schneider, A.; Stripecke, R.; et al. Na(+) /H(+) exchanger NHE1 and NHE2 have opposite effects on migration velocity in rat gastric surface cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 232, 1669–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, N.; Tanaka, S.; Teko, Y.; Mitsui, K.; Kanazawa, H. Four Na+/H+ exchanger isoforms are distributed to Golgi and post-Golgi compartments and are involved in organelle pH regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 1561–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, S.P.; Bright, N.A.; Luzio, J.P.; Bowers, K. The Sodium/Proton Exchanger NHE8 Regulates Late Endosomal Morphology and Function. Mol. Biol. Cell 2010, 21, 3540–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberheide, K.; Puchkov, D.; Jentsch, T.J. Loss of the Na+/H+ exchanger NHE8 causes male infertility in mice by disrupting acrosome formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 10845–10854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.F.; Dong, J.; Tackett, L.; Meyer, J.W.; Shull, G.E.; Montrose, M.H. NHE2 is the main apical NHE in mouse colonic crypts but an alternative Na+-dependent acid extrusion mechanism is upregulated in NHE2-null mice. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2006, 291, G689–G699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmann, O.; Riederer, B.; Rossmann, H.; Groos, S.; Schultheis, P.J.; Shull, G.E.; Gregor, M.; Manns, M.P.; Seidler, U. The Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 2 is the predominant NHE isoform in murine colonic crypts and its lack causes NHE3 upregulation. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2004, 287, G125–G133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.H.; Shull, G.E.; Orlowski, J. Functional properties of the rat Na/H exchanger NHE-2 isoform expressed in Na/H exchanger-deficient Chinese hamster ovary cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 25536–25541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapus, A.; Grinstein, S.; Wasan, S.; Kandasamy, R.; Orlowski, J. Functional characterization of three isoforms of the Na+/H+ exchanger stably expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. ATP dependence, osmotic sensitivity, and role in cell proliferation. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 23544–23552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, O.; Wuchner, K.; Rossmann, H.; Leipziger, J.; Osikowska, B.; Colledge, W.H.; Ratcliff, R.; Evans, M.J.; Gregor, M.; Seidler, U. Expression and regulation of the Na+-K+-2Cl(-) cotransporter NKCC1 in the normal and CFTR-deficient murine colon. J. Physiol.-Lond. 2003, 549, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, N.M.; Liu, J.H.; Stein, S.R.; Stefanski, C.D.; Strubberg, A.M.; Clarke, L.L. Cellular chloride and bicarbonate retention alters intracellular pH regulation in Cftr KO crypt epithelium. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2016, 310, G70–G80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demaurex, N.; Grinstein, S. Na+/H+ antiport: Modulation by ATP and role in cell volume regulation. J. Exp. Biol. 1994, 196, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krndija, D.; El Marjou, F.; Guirao, B.; Richon, S.; Leroy, O.; Bellaiche, Y.; Hannezo, E.; Matic Vignjevic, D. Active cell migration is critical for steady-state epithelial turnover in the gut. Science 2019, 365, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, H.; Nie, W.X.; Edwards, R.A.; Yoo, J. Isolation of Primary Myofibroblasts from Mouse and Human Colon Tissue. Jove-J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 6, 50611. [Google Scholar]
- Dekkers, J.F.; Alieva, M.; Wellens, L.M.; Ariese, H.C.R.; Jamieson, P.R.; Vonk, A.M.; Amatngalim, G.D.; Hu, H.L.; Oost, K.C.; Snippert, H.J.G.; et al. High-resolution 3D imaging of fixed and cleared organoids. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 1756–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salari, A.; Zhou, K.; Nikolovska, K.; Seidler, U.; Amiri, M. Human Colonoid–Myofibroblast Coculture for Study of Apical Na+/H+ Exchangers of the Lower Cryptal Neck Region. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054266
Salari A, Zhou K, Nikolovska K, Seidler U, Amiri M. Human Colonoid–Myofibroblast Coculture for Study of Apical Na+/H+ Exchangers of the Lower Cryptal Neck Region. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(5):4266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054266
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalari, Azam, Kunyan Zhou, Katerina Nikolovska, Ursula Seidler, and Mahdi Amiri. 2023. "Human Colonoid–Myofibroblast Coculture for Study of Apical Na+/H+ Exchangers of the Lower Cryptal Neck Region" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 5: 4266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054266
APA StyleSalari, A., Zhou, K., Nikolovska, K., Seidler, U., & Amiri, M. (2023). Human Colonoid–Myofibroblast Coculture for Study of Apical Na+/H+ Exchangers of the Lower Cryptal Neck Region. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(5), 4266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054266






