Intestinal Farnesoid X Receptor Modulates Duodenal Surface Area but Does Not Control Glucose Absorption in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
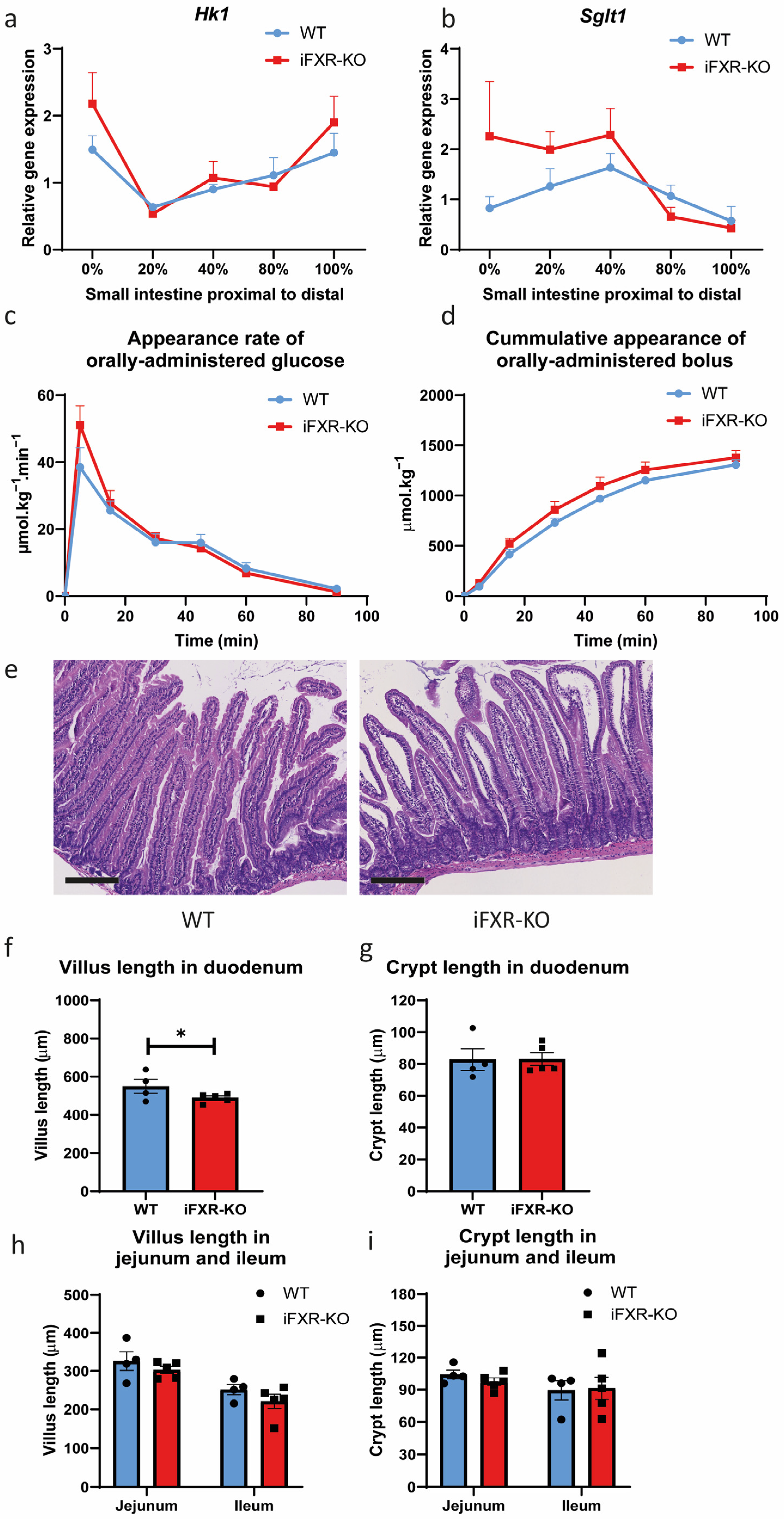
2.1. FXR Deficiency in Intestine Does Not Lead to Delayed Glucose Absorption
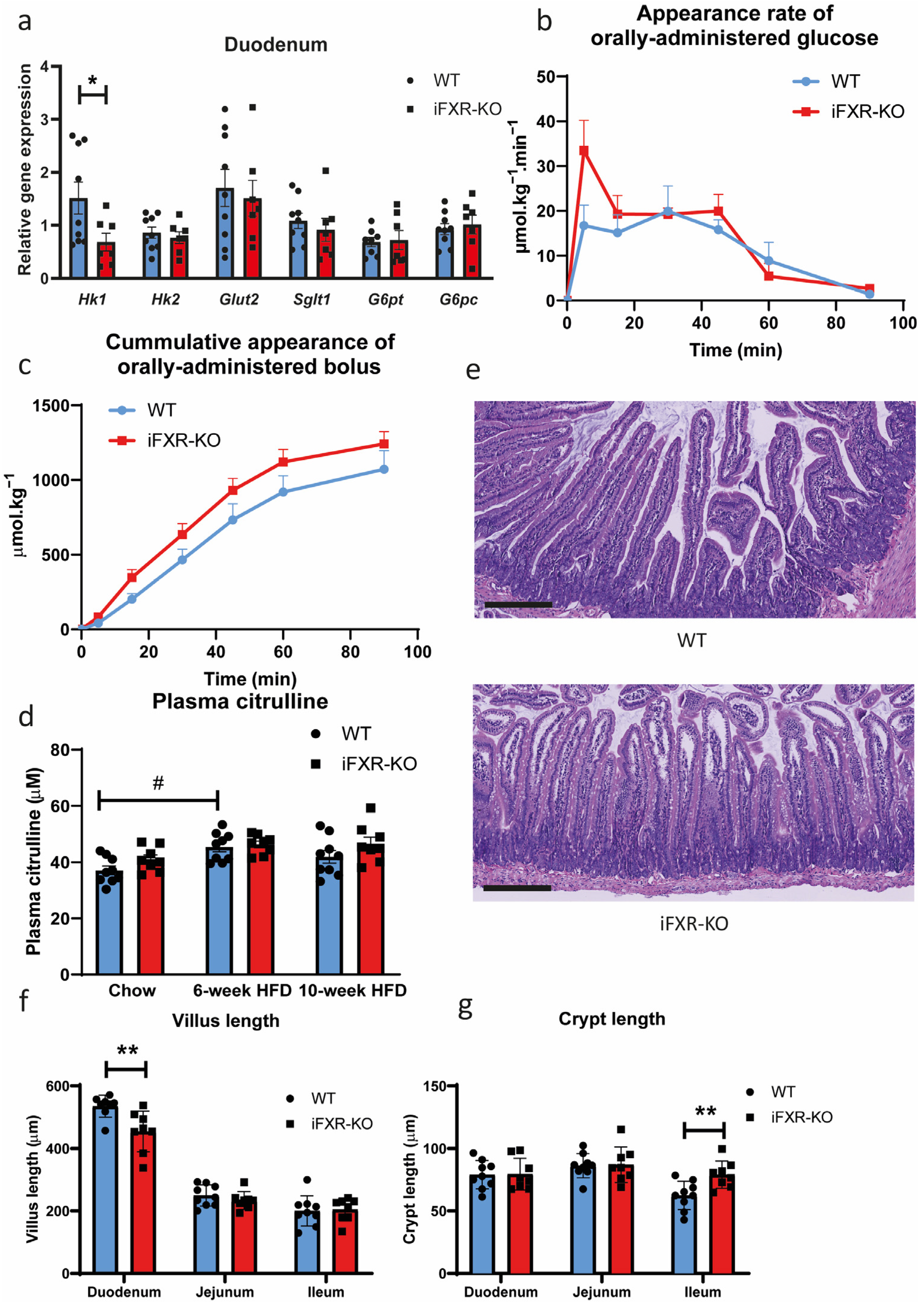
2.2. Long-Term HFD Exposure Does Not Affect Glucose Absorption in iFXR-KO Mice
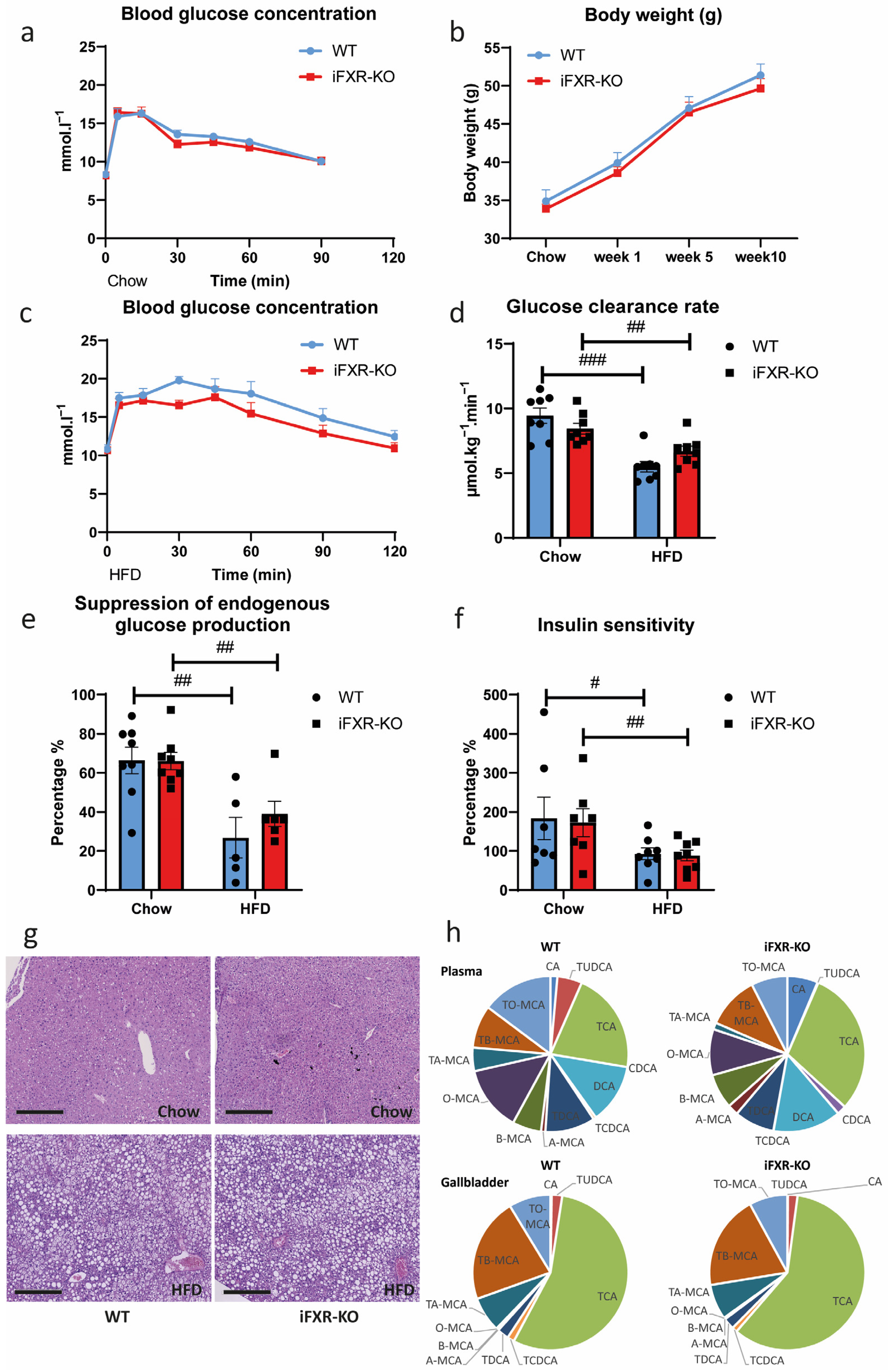
2.3. Long-Term HFD Exposure Perturbs Whole-Body Glucose Metabolism to the Same Extend in Wild-Type and iFXR-KO Mice
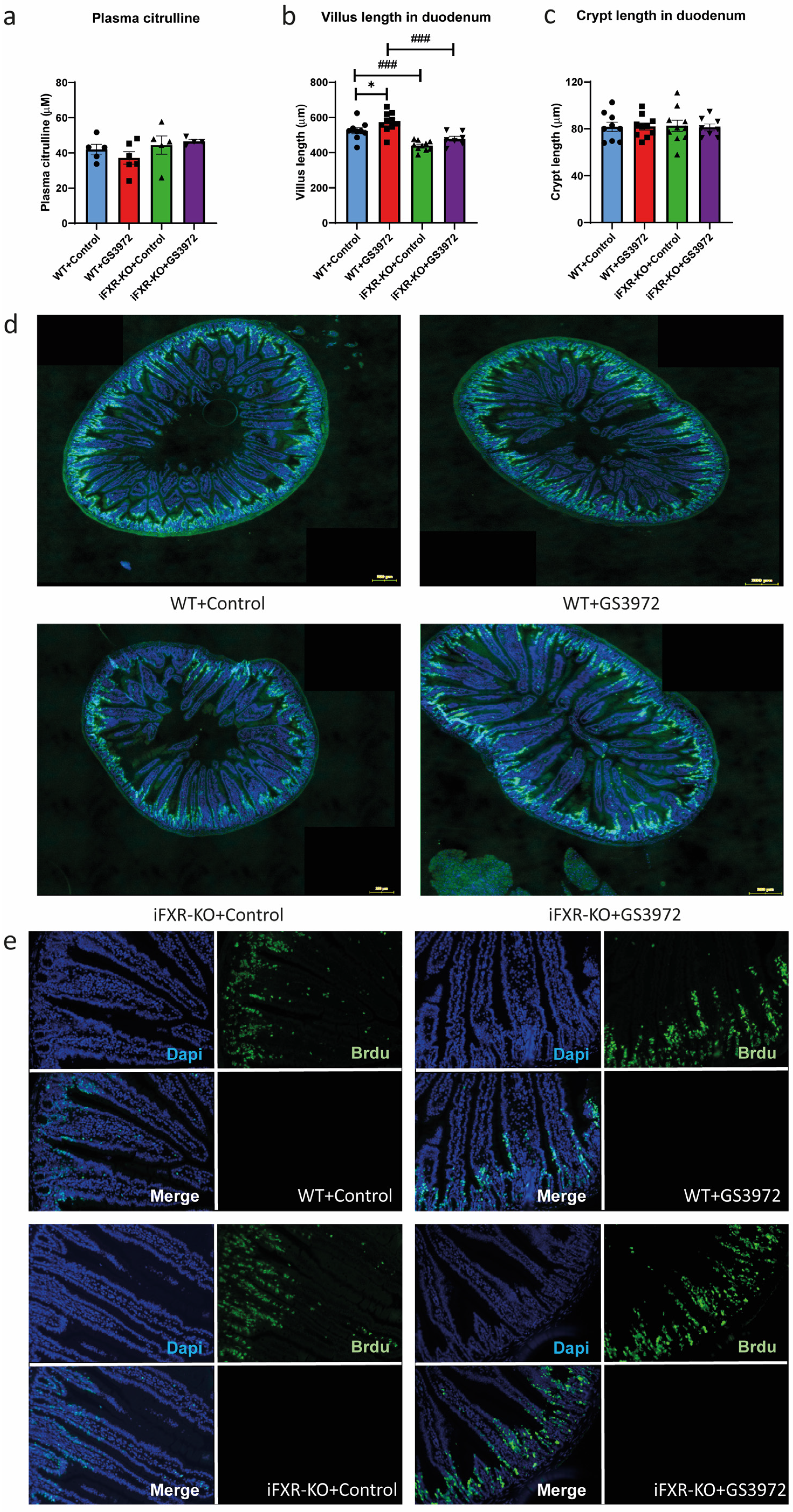
2.4. Activation of FXR by GS3972 Does Not Alter Glucose Absorption in Wild-Type Mice
2.5. Activation of FXR by GS3972 Increases Villus Length in Duodenum
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mice
4.2. Glucose Absorption Test
4.3. Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry
4.4. Tracer Kinetics
4.5. Histology
4.6. Fluorescence Staining
4.7. Plasma Citrulline Measurement
4.8. Real-Time Quantitative Reverse Transcription-PCR
4.9. Bile Acid Profile in Plasma and Gallbladder
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuipers, F.; Bloks, V.W.; Groen, A.K. Beyond intestinal soap—Bile acids in metabolic control. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Grundy, S.M. Cholestyramine Therapy for Dyslipidemia in Non–Insulin-dependent Diabetes Mellitus: A Short-Term, Double-Blind, Crossover Trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 1994, 121, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.; Sonne, D.P.; Mikkelsen, K.H.; Gluud, L.L.; Vilsbøll, T.; Knop, F.K. Bile acid sequestrants for glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review with meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2017, 31, 918–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brønden, A.; Albér, A.; Rohde, U.; Gasbjerg, L.S.; Rehfeld, J.F.; Holst, J.J.; Vilsbøll, T.; Knop, F.K. The bile acid-sequestering resin sevelamer eliminates the acuteGLP-1 stimulatory effect of endogenously released bile acids in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prawitt, J.; Abdelkarim, M.; Stroeve, J.H.M.; Popescu, I.; Duez, H.; Velagapudi, V.R.; Dumont, J.; Bouchaert, E.; van Dijk, T.H.; Lucas, A.; et al. Farnesoid X Receptor Deficiency Improves Glucose Homeostasis in Mouse Models of Obesity. Diabetes 2011, 60, 1861–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez-Talavera, O.; Tailleux, A.; Lefebvre, P.; Staels, B. Bile Acid Control of Metabolism and Inflammation in Obesity, Type 2 Diabetes, Dyslipidemia, and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1679–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pockros, P.J.; Fuchs, M.; Freilich, B.; Schiff, E.; Kohli, A.; Lawitz, E.J.; Hellstern, P.A.; Owens-Grillo, J.; Van Biene, C.; Shringarpure, R.; et al. CONTROL: A randomized phase 2 study of obeticholic acid and atorvastatin on lipoproteins in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis patients. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 2082–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, K.; Harrison, S.A.; Elkhashab, M.; Trotter, J.F.; Herring, R.; Rojter, S.E.; Kayali, Z.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Greenbloom, S.; Jayakumar, S.; et al. Cilofexor, a Nonsteroidal FXR Agonist, in Patients with Noncirrhotic NASH: A Phase 2 Randomized Controlled Trial. Hepatology 2020, 72, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traussnigg, S.; Halilbasic, E.; Hofer, H.; Munda, P.; Stojakovic, T.; Fauler, G.; Kashofer, K.; Krssak, M.; Wolzt, M.; Trauner, M. Open-label phase II study evaluating safety and efficacy of the non-steroidal farnesoid X receptor agonist PX-104 in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2021, 133, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudaliar, S.; Henry, R.R.; Sanyal, A.J.; Morrow, L.; Marschall, H.; Kipnes, M.; Adorini, L.; Sciacca, C.I.; Clopton, P.; Castelloe, E.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the Farnesoid X Receptor Agonist Obeticholic Acid in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, K.K.; Tremaroli, V.; Clemmensen, C.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Myronovych, A.; Karns, R.; Wilson-Pérez, H.E.; Sandoval, D.A.; Kohli, R.; Bäckhed, F.; et al. FXR is a molecular target for the effects of vertical sleeve gastrectomy. Nature 2014, 509, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Zhang, E.; Yang, Q.; Jin, L.; Sousa, K.M.; Dong, B.; Wang, Y.; Tu, J.; Ma, X.; Tian, J.; et al. Vertical sleeve gastrectomy confers metabolic improvements by reducing intestinal bile acids and lipid absorption in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2019388118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzini, G.S.; Khoraki, J.; Dozmorov, M.; Browning, M.G.; Wijesinghe, D.; Wolfe, L.; Gurski, R.R.; Campos, G.M. Concomitant PPARα and FXR Activation as a Putative Mechanism of NASH Improvement after Gastric Bypass Surgery: A GEO Datasets Analysis. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2019, 23, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Suh, J.M.; Reilly, S.M.; Yu, E.; Osborn, O.; Lackey, D.; Yoshihara, E.; Perino, A.; Jacinto, S.; Lukasheva, Y.; et al. Intestinal FXR agonism promotes adipose tissue browning and reduces obesity and insulin resistance. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, M.; Houten, S.M.; Mataki, C.; Christoffolete, M.A.; Kim, B.W.; Sato, H.; Messaddeq, N.; Harney, J.W.; Ezaki, O.; Kodama, T.; et al. Bile acids induce energy expenditure by promoting intracellular thyroid hormone activation. Nature 2006, 439, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cariou, B.; van Harmelen, K.; Duran-Sandoval, D.; van Dijk, T.H.; Grefhorst, A.; Abdelkarim, M.; Caron, S.; Torpier, G.; Fruchart, J.-C.; Gonzalez, F.J.; et al. The Farnesoid X Receptor Modulates Adiposity and Peripheral Insulin Sensitivity in Mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 11039–11049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, H.; Kolodziejczyk, A.A.; Halstuch, D.; Elinav, E. Bile acids in glucose metabolism in health and disease. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 215, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, T.; Moschetta, A.; Lee, Y.-K.; Peng, L.; Zhao, G.; Downes, M.; Yu, R.T.; Shelton, J.M.; Richardson, J.A.; Repa, J.J.; et al. Regulation of antibacterial defense in the small intestine by the nuclear bile acid receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 3920–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Boer, J.F.; Schonewille, M.; Boesjes, M.; Wolters, H.; Bloks, V.W.; Bos, T.; van Dijk, T.H.; Jurdzinski, A.; Boverhof, R.; Wolters, J.C.; et al. Intestinal Farnesoid X Receptor Controls Transintestinal Cholesterol Excretion in Mice. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1126–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, P.; Xie, C.; Nichols, R.G.; Ferrell, J.M.; Boehme, S.; Krausz, K.W.; Patterson, A.D.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Chiang, J.Y.L. Intestine farnesoid X receptor agonist and the gut microbiota activate G-protein bile acid receptor-1 signaling to improve metabolism. Hepatology 2018, 68, 1574–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Jiang, C.; Krausz, K.W.; Li, Y.; Albert, I.; Hao, H.; Fabre, K.M.; Mitchell, J.B.; Patterson, A.D.; Gonzalez, F.J. Microbiome remodelling leads to inhibition of intestinal farnesoid X receptor signalling and decreased obesity. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Xie, C.; Lv, Y.; Li, J.; Krausz, K.W.; Shi, J.; Brocker, C.N.; Desai, D.; Amin, S.G.; Bisson, W.H.; et al. Intestine-selective farnesoid X receptor inhibition improves obesity-related metabolic dysfunction. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 10166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabelsi, M.-S.; Daoudi, M.; Prawitt, J.; Ducastel, S.; Touche, V.; Sayin, S.I.; Perino, A.; Brighton, C.A.; Sebti, Y.; Kluza, J.; et al. Farnesoid X receptor inhibits glucagon-like peptide-1 production by enteroendocrine L cells. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceulemans, L.J.; Verbeke, L.; Decuypere, J.-P.; Farré, R.; De Hertogh, G.; Lenaerts, K.; Jochmans, I.; Monbaliu, D.; Nevens, F.; Tack, J.; et al. Farnesoid X Receptor Activation Attenuates Intestinal Ischemia Reperfusion Injury in Rats. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadaleta, R.M.; Van Erpecum, K.J.; Oldenburg, B.; Willemsen, E.C.L.; Renooij, W.; Murzilli, S.; Klomp, L.W.J.; Siersema, P.D.; Schipper, M.E.I.; Danese, S.; et al. Farnesoid X receptor activation inhibits inflammation and preserves the intestinal barrier in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2011, 60, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osswald, C.; Baumgarten, K.; Stümpel, F.; Gorboulev, V.; Akimjanova, M.; Knobeloch, K.-P.; Horak, I.; Kluge, R.; Joost, H.-G.; Koepsell, H. Mice without the Regulator Gene Rsc1A1 Exhibit Increased Na +-d-Glucose Cotransport in Small Intestine and Develop Obesity. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.Q.; Debreceni, T.L.; Bambrick, J.E.; Chia, B.; Wishart, J.; Deane, A.M.; Rayner, C.K.; Horowitz, M.; Young, R.L. Accelerated Intestinal Glucose Absorption in Morbidly Obese Humans: Relationship to Glucose Transporters, Incretin Hormones, and Glycemia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 968–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baud, G.; Daoudi, M.; Hubert, T.; Raverdy, V.; Pigeyre, M.; Hervieux, E.; Devienne, M.; Ghunaim, M.; Bonner, C.; Quenon, A.; et al. Bile Diversion in Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Modulates Sodium-Dependent Glucose Intestinal Uptake. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijk, T.H.; Grefhorst, A.; Oosterveer, M.H.; Bloks, V.W.; Staels, B.; Reijngoud, D.-J.; Kuipers, F. An Increased Flux through the Glucose 6-Phosphate Pool in Enterocytes Delays Glucose Absorption in Fxr–/– Mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 10315–10323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.; Ahn, S.-H.; Inagaki, T.; Choi, M.; Ito, S.; Guo, G.L.; Kliewer, S.A.; Gonzalez, F.J. Differential regulation of bile acid homeostasis by the farnesoid X receptor in liver and intestine. J. Lipid Res. 2007, 48, 2664–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stott, N.L.; Marino, J.S. High Fat Rodent Models of Type 2 Diabetes: From Rodent to Human. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Xie, C.; Li, F.; Zhang, L.; Nichols, R.G.; Krausz, K.W.; Cai, J.; Qi, Y.; Fang, Z.-Z.; Takahashi, S.; et al. Intestinal farnesoid X receptor signaling promotes nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 386–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, N.; Kowalski, G.M.; Leslie, S.J.; Risis, S.; Yang, C.; Lee-Young, R.S.; Babb, J.R.; Meikle, P.J.; Lancaster, G.I.; Henstridge, D.C.; et al. Distinct patterns of tissue-specific lipid accumulation during the induction of insulin resistance in mice by high-fat feeding. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 1638–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouries, J.; Brescia, P.; Silvestri, A.; Spadoni, I.; Sorribas, M.; Wiest, R.; Mileti, E.; Galbiati, M.; Invernizzi, P.; Adorini, L.; et al. Microbiota-driven gut vascular barrier disruption is a prerequisite for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis development. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 1216–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Wang, M.; Gu, W.; Chen, L. Intestine-specific FXR agonists as potential therapeutic agents for colorectal cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 186, 114430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Kong, B.; Zhang, M.; Rizzolo, D.; Armstrong, L.E.; Schumacher, J.D.; Chow, M.D.; Lee, Y.-H.; Joseph, L.B.; Stofan, M.; et al. Enhanced alcoholic liver disease in mice with intestine-specific farnesoid X receptor deficiency. Lab. Investig. 2020, 100, 1158–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, C.; McLean, M.H.; Durum, S.K. Cytokine Tuning of Intestinal Epithelial Function. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadaleta, R.M.; Oldenburg, B.; Willemsen, E.C.; Spit, M.; Murzilli, S.; Salvatore, L.; Klomp, L.W.; Siersema, P.D.; van Erpecum, K.J.; van Mil, S.W. Activation of bile salt nuclear receptor FXR is repressed by pro-inflammatory cytokines activating NF-κB signaling in the intestine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Mol. Basis Dis. 2011, 1812, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thazhath, S.S.; Wu, T.; Young, R.L.; Horowitz, M.; Rayner, C.K. Glucose absorption in small intestinal diseases. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 8, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kok, T.; Hulzebos, C.V.; Wolters, H.; Havinga, R.; Agellon, L.B.; Stellaard, F.; Shan, B.; Schwarz, M.; Kuipers, F. Enterohepatic Circulation of Bile Salts in Farnesoid X Receptor-deficient Mice: Efficient Intestinal Bile Salt Absorption in the Absence of Ileal Bile Acid-Binding Protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 41930–41937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Houten, S.M.; Wang, L.; Moschetta, A.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Heyman, R.A.; Moore, D.D.; Auwerx, J. Bile acids lower triglyceride levels via a pathway involving FXR, SHP, and SREBP-1c. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 1408–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinal, C.J.; Tohkin, M.; Miyata, M.; Ward, J.M.; Lambert, G.; Gonzalez, F.J. Targeted Disruption of the Nuclear Receptor FXR/BAR Impairs Bile Acid and Lipid Homeostasis. Cell 2000, 102, 731–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijssennagger, N.; van Rooijen, K.S.; Magnúsdóttir, S.; Pittol, J.M.R.; Willemsen, E.C.L.; de Zoete, M.R.; Baars, M.J.D.; Stege, P.B.; Colliva, C.; Pellicciari, R.; et al. Ablation of liver Fxr results in an increased colonic mucus barrier in mice. JHEP Rep. 2021, 3, 100344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Xuan, Z.; Song, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, Z.; Song, G.; Zhu, X.; Xie, H.; Zheng, S.; Song, P. A novel role for farnesoid X receptor in the bile acid-mediated intestinal glucose homeostasis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 12848–12861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rider, A.K.; Schedl, H.P.; Nokes, G.; Shining, S. Small Intestinal Glucose Transport: Proximal-Distal Kinetic Gradients. J. Gen. Physiol. 1967, 50, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellett, G.L.; Brot-Laroche, E.; Mace, O.J.; Leturque, A. Sugar Absorption in the Intestine: The Role of GLUT2. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2008, 28, 35–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stümpel, F.; Burcelin, R.; Jungermann, K.; Thorens, B. Normal kinetics of intestinal glucose absorption in the absence of GLUT2: Evidence for a transport pathway requiring glucose phosphorylation and transfer into the endoplasmic reticulum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 11330–11335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santer, R.; Hillebrand, G.; Steinmann, B.; Schaub, J. Intestinal glucose transport: Evidence for a membrane traffic–based pathway in humans. Gastroenterology 2003, 124, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisielinski, K.; Willis, S.; Prescher, A.; Klosterhalfen, B.; Schumpelick, V. A simple new method to calculate small intestine absorptive surface in the rat. Clin. Exp. Med. 2002, 2, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, V.; Catalá-Gregori, P.; Hernandez, F.; Megias, M.D.; Madrid, J. Effect of Formic Acid and Plant Extracts on Growth, Nutrient Digestibility, Intestine Mucosa Morphology, and Meat Yield of Broilers. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2007, 16, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, A.; Beraldi, E.J.; Ferreira, P.E.B.; Bazotte, R.B.; Buttow, N.C. Intestinal and neuronal myenteric adaptations in the small intestine induced by a high-fat diet in mice. BMC Gastroenterol. 2015, 15, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Davis, E.A.; Dailey, M.J. Obesity, independent of diet, drives lasting effects on intestinal epithelial stem cell proliferation in mice. Exp. Biol. Med. 2018, 243, 826–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casteleyn, C.; Rekecki, A.; Van Der Aa, A.; Simoens, P.; Van den Broeck, W. Surface area assessment of the murine intestinal tract as a prerequisite for oral dose translation from mouse to man. Lab. Anim. 2010, 44, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrebee, C.B.; Dawson, P.A. Metabolic effects of intestinal absorption and enterohepatic cycling of bile acids. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2015, 5, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbeke, L.; Farre, R.; Verbinnen, B.; Covens, K.; Vanuytsel, T.; Verhaegen, J.; Komuta, M.; Roskams, T.; Chatterjee, S.; Annaert, P.; et al. The FXR Agonist Obeticholic Acid Prevents Gut Barrier Dysfunction and Bacterial Translocation in Cholestatic Rats. Am. J. Pathol. 2015, 185, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojancevic, M.; Stankov, K.; Mikov, M. The Impact of Farnesoid X Receptor Activation on Intestinal Permeability in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Can. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 26, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijmeijer, R.M.; Gadaleta, R.M.; van Mil, S.W.C.; van Bodegraven, A.A.; Crusius, J.B.A.; Dijkstra, G.; Hommes, D.W.; de Jong, D.J.; Stokkers, P.C.F.; Verspaget, H.W.; et al. Farnesoid X Receptor (FXR) Activation and FXR Genetic Variation in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashiyama, H.; Kinoshita, M.; Asano, S. Immunolocalization of farnesoid X receptor (FXR) in mouse tissues using tissue microarray. Acta Histochem. 2008, 110, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heppert, J.K.; Davison, J.M.; Kelly, C.; Mercado, G.P.; Lickwar, C.R.; Rawls, J.F. Transcriptional programmes underlying cellular identity and microbial responsiveness in the intestinal epithelium. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashima, S.; Gold, D.; Hartenstein, V. Stem cells and lineages of the intestine: A developmental and evolutionary perspective. Dev. Genes Evol. 2013, 223, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Chen, L.; Su, H.; Yang, X.; He, H.; Liu, F.; Zheng, J.; Ling, M.; et al. Hyodeoxycholic acid (HDCA) suppresses intestinal epithelial cell proliferation through FXR-PI3K/AKT pathway, accompanied by alteration of bile acids metabolism profiles induced by gut bacteria. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 7103–7117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossa, A.Y.; Escobar, O.; Golden, J.; Frey, M.R.; Ford, H.R.; Gayer, C.P. Bile acids regulate intestinal cell proliferation by modulating EGFR and FXR signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2016, 310, G81–G92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maran, R.R.; Thomas, A.; Roth, M.; Sheng, Z.; Esterly, N.; Pinson, D.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ganapathy, V.; Gonzalez, F.J.; et al. Farnesoid X Receptor Deficiency in Mice Leads to Increased Intestinal Epithelial Cell Proliferation and Tumor Development. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009, 328, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, F.; Xing, X.; Yuan, G.; Schäfer, C.; Rauser, S.; Walch, A.; Röcken, C.; Ebeling, M.; Wright, M.B.; Schmid, R.M.; et al. Farnesoid X receptor protects human and murine gastric epithelial cells against inflammation-induced damage. Biochem. J. 2011, 438, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, A.; Foley, E. Hexokinase 1 blocks apoptotic signals at the mitochondria. Cell. Signal. 2013, 25, 2685–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, A.; Foley, E. A functional RNAi screen identifies hexokinase 1 as a modifier of type II apoptosis. Cell. Signal. 2010, 22, 1330–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.K.; Chang, H.-W.; Yan, D.; Lee, K.M.; Ucmak, D.; Wong, K.; Abrouk, M.; Farahnik, B.; Nakamura, M.; Zhu, T.H.; et al. Influence of diet on the gut microbiome and implications for human health. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Marcos, J.A.; Perez-Jimenez, F.; Camargo, A. The role of diet and intestinal microbiota in the development of metabolic syndrome. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 70, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madison, B.B.; Dunbar, L.; Qiao, X.T.; Braunstein, K.; Braunstein, E.; Gumucio, D.L. cis Elements of the Villin Gene Control Expression in Restricted Domains of the Vertical (Crypt) and Horizontal (Duodenum, Cecum) Axes of the Intestine. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 33275–33283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijk, T.H.; Laskewitz, A.J.; Grefhorst, A.; Boer, T.S.; Bloks, V.W.; Kuipers, F.; Groen, A.K.; Reijngoud, D.J. A Novel Approach to Monitor Glucose Metabolism Using Stable Isotopically Labelled Glucose in Longitudinal Studies in Mice. Lab. Anim. 2013, 47, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.G. Application of the Wagner-Nelson absorption method to the two-compartment open model. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm. 1974, 2, 469–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehart, H.; Clevers, H. Tales from the crypt: New insights into intestinal stem cells. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fijlstra, M.; Rings, E.H.H.M.; Verkade, H.J.; van Dijk, T.H.; Kamps, W.A.; Tissing, W.J.E. Lactose maldigestion during methotrexate-induced gastrointestinal mucositis in a rat model. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2011, 300, G283–G291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Ferreira, A.R.; Wardill, H.R.; Havinga, R.; Tissing, W.; Harmsen, H.J. Prophylactic Treatment with Vitamins C and B2 for Methotrexate-Induced Gastrointestinal Mucositis. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boer, J.F.; Verkade, E.; Mulder, N.L.; De Vries, H.D.; Huijkman, N.; Koehorst, M.; Boer, T.; Wolters, J.C.; Bloks, V.W.; Van De Sluis, B.; et al. A Human-like Bile Acid Pool Induced by Deletion of Hepatic Cyp2c70 Modulates Effects of FXR Activation in Mice. J. Lipid Res. 2020, 61, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; van Dijk, T.H.; Koehorst, M.; Havinga, R.; de Boer, J.F.; Kuipers, F.; van Zutphen, T. Intestinal Farnesoid X Receptor Modulates Duodenal Surface Area but Does Not Control Glucose Absorption in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24044132
Yang J, van Dijk TH, Koehorst M, Havinga R, de Boer JF, Kuipers F, van Zutphen T. Intestinal Farnesoid X Receptor Modulates Duodenal Surface Area but Does Not Control Glucose Absorption in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(4):4132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24044132
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jiufang, Theo H. van Dijk, Martijn Koehorst, Rick Havinga, Jan Freark de Boer, Folkert Kuipers, and Tim van Zutphen. 2023. "Intestinal Farnesoid X Receptor Modulates Duodenal Surface Area but Does Not Control Glucose Absorption in Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 4: 4132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24044132
APA StyleYang, J., van Dijk, T. H., Koehorst, M., Havinga, R., de Boer, J. F., Kuipers, F., & van Zutphen, T. (2023). Intestinal Farnesoid X Receptor Modulates Duodenal Surface Area but Does Not Control Glucose Absorption in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(4), 4132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24044132





