The Influence of Environmental Exposure to Heavy Metals on the Occurrence of Selected Elements in the Maxillary Bone
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klotz, K.; Göen, T. Human Biomonitoring of Lead Exposure. Met. Ions Life Sci. 2017, 17, 99–121. Available online: https://books/9783110434330/9783110434330-006/9783110434330-006.xml (accessed on 27 October 2022). [CrossRef]
- Pounds, J.G.; Long, G.J.; Rosen, J.F. Cellular and Molecular Toxicity of Lead in Bone. Environ. Health Perspect. 1991, 91, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, E.H.; Andersen, N.L.; Møller, A.; Petersen, A.; Mortensen, G.K.; Petersen, J. Monitoring the Content and Intake of Trace Elements from Food in Denmark. Food. Addit. Contam. 2002, 19, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, W.; Hoogewerff, J.; Latkoczy, C.; Almirall, J.R. Application of Laser Ablation (LA-ICP-SF-MS) for the Elemental Analysis of Bone and Teeth Samples for Discrimination Purposes. Forensic Sci. Int. 2010, 195, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.J.H.; Gutierrez, C.; Ogunseitan, O.A. Metallic Burden of Deciduous Teeth and Childhood Behavioral Deficits. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 6771–6787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leventouri, T.; Antonakos, A.; Kyriacou, A.; Venturelli, R.; Liarokapis, E.; Perdikatsis, V. Crystal Structure Studies of Human Dental Apatite as a Function of Age. Int. J. Biomater. 2009, 2009, e698547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, A.; Bauer, J.A.; Austin, C.; Downs, T.J.; Tripodis, Y.; Heiger-Bernays, W.; White, R.F.; Arora, M.; Claus Henn, B. Multiple Metals in Children’s Deciduous Teeth: Results from a Community-Initiated Pilot Study. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2022, 32, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, T.J.; Dirks, W.; Roberts, N.M.W.; Patel, J.G.; Hodgson, S.; Pless-Mulloli, T.; Walton, P.; Parrish, R.R. Tracing Fetal and Childhood Exposure to Lead Using Isotope Analysis of Deciduous Teeth. Environ. Res. 2016, 146, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, J.A.; Claus Henn, B.; Austin, C.; Zoni, S.; Fedrighi, C.; Cagna, G.; Placidi, D.; White, R.F.; Yang, Q.; Coull, B.A.; et al. Manganese in Teeth and Neurobehavior: Sex-Specific Windows of Susceptibility. Environ. Int. 2017, 108, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulson, B.L. Tooth Analyses of Sources and Intensity of Lead Exposure in Children. Environ. Health Perspect. 1996, 104, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malara, P.; Fischer, A.; Malara, B. Selected Toxic and Essential Heavy Metals in Impacted Teeth and the Surrounding Mandibular Bones of People Exposed to Heavy Metals in the Environment. J. Occup. Med. Toxicol. 2016, 11, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shashikiran, N.D.; Subba Reddy, V.V.; Hiremath, M.C. Estimation of Trace Elements in Sound and Carious Enamel of Primary and Permanent Teeth by Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry: An in Vitro Study. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2007, 18, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malara, P.; Kwapulinski, J.; Malara, B. Do the Levels of Selected Metals Differ Significantly between the Roots of Carious and Non-Carious Teeth? Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 369, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malara, P.; Kwapuliński, J. Determination of Chromium in Human Premolar Teeth by Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Chem. Anal. 2005, 50, 481–486. [Google Scholar]
- Pye, K. Isotope and Trace Element Analysis of Human Teeth and Bones for Forensic Purposes. In Forensic Geoscience: Principles, Techniques and Applications; Pye, K., Croft, D.J., Eds.; Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2004; Volume 232, pp. 215–236. ISBN 978-1-86239-161-1. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui, J.A.; Partridge, N.C. Physiological Bone Remodeling: Systemic Regulation and Growth Factor Involvement. Physiology 2016, 31, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, E.F. Cellular Mechanisms of Bone Remodeling. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2010, 11, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florencio-Silva, R.; Sasso, G.R.d.S.; Sasso-Cerri, E.; Simões, M.J.; Cerri, P.S. Biology of Bone Tissue: Structure, Function, and Factors That Influence Bone Cells. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 421746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahidi, G.; Rux, C.; Sherk, V.D.; Heveran, C.M. Lacunar-Canalicular Bone Remodeling: Impacts on Bone Quality and Tools for Assessment. Bone 2021, 143, 115663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teitelbaum, S.L. Bone Resorption by Osteoclasts. Science 2000, 289, 1504–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kołodziejska, B.; Stępień, N.; Kolmas, J. The Influence of Strontium on Bone Tissue Metabolism and Its Application in Osteoporosis Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treece, G.; Gee, A. Cortical Bone Mapping: Measurement and Statistical Analysis of Localised Skeletal Changes. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2018, 16, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malara, P.; Kwapuliński, J.; Malara, B. The Influence of Lead on Occurrence of Some Essential Elements in Teeth. Acta Toxicol. 2004, 12, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Kwapulinski, J.; Brodziak, B.; Bogunia, M. Relative Changes of Elements in Human Osseous Tissue. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2003, 70, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roczniak, W.; Brodziak-Dopierała, B.; Cipora, E.; Mitko, K.; Jakóbik-Kolon, A.; Konieczny, M.; Babuśka-Roczniak, M. The Content of Structural and Trace Elements in the Knee Joint Tissues. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gang, N.; JiaMin, C.; Ye, W.; FuPing, X.; HuanHuan, L.; LiSong, L. Comparing the Efficacy of Sinus Irrigation with Traditional Caldwell-Luc Procedure Following Odontogenic Cyst Surgery Involving the Maxillary Sinus. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohar, M.S.; Niazi, S.A.; Niazi, S.B. Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery as a Primary Modality of Treatment for Primary and Recurrent Nasal Polyposis. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 33, 380–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, J.P.; Hicks, M.D.; Grayson, J.W.; Woodworth, B.A.; Cho, D.-Y. Endoscopic Management of Maxillary Sinus Diseases of Dentoalveolar Origin. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 32, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aukštakalnis, R.; Simonavičiūtė, R.; Simuntis, R. Treatment Options for Odontogenic Maxillary Sinusitis: A Review. Stomatologija 2018, 20, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Rezende, N.C.; Pinheiro-Neto, C.D.; Leonel, L.C.P.C.; Van Gompel, J.J.; Peris-Celda, M.; Choby, G. Three-Hundred and Sixty Degrees of Surgical Approaches to the Maxillary Sinus. World J. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck. Surg. 2022, 8, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astolfi, M.L.; Pietris, G.; Mazzei, C.; Marconi, E.; Canepari, S. Element Levels and Predictors of Exposure in the Hair of Ethiopian Children. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaurock-Busch, E.; Amin, O.R.; Dessoki, H.H.; Rabah, T. Toxic Metals and Essential Elements in Hair and Severity of Symptoms among Children with Autism. Maedica 2012, 7, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salcedo-Bellido, I.; Gutiérrez-González, E.; García-Esquinas, E.; Fernández de Larrea-Baz, N.; Navas-Acien, A.; Téllez-Plaza, M.; Pastor-Barriuso, R.; Lope, V.; Gómez-Ariza, J.L.; García-Barrera, T.; et al. Toxic Metals in Toenails as Biomarkers of Exposure: A Review. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 111028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karatela, S.; Coomarasamy, C.; Paterson, J.; Ward, N.I. Household Smoking Status and Heavy Metal Concentrations in Toenails of Children. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, M.K.; Hsu, L.; Claus Henn, B.; Margolis, A.; Austin, C.; Svensson, K.; Schnaas, L.; Gennings, C.; Hu, H.; Wright, R.; et al. Dentine Biomarkers of Prenatal and Early Childhood Exposure to Manganese, Zinc and Lead and Childhood Behavior. Environ. Int. 2018, 121, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodziak-Dopierała, B.; Kwapuliński, J.; Sobczyk, K.; Kowol, J. The Occurrence of Nickel and Other Elements in Tissues of the Hip Joint. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, B. Contents and Relationship of Elements in Human Hair for a Non-Industrialised Population in Poland. Sci. Total Environ. 1998, 209, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, B.; Chmielnicka, J. Relationship of Lead and Cadmium to Essential Elements in Hair, Teeth, and Nails of Environmentally Exposed People. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2000, 46, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Guerrero, J.C.; Jiménez-Farfán, M.D.; Belmont, R.; Ledesma-Montes, C.; Baez, A. Lead Levels in Primary Teeth of Children Living in Mexico City. Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2004, 14, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunier, R.B.; Arora, M.; Jerrett, M.; Bradman, A.; Harley, K.G.; Mora, A.M.; Kogut, K.; Hubbard, A.; Austin, C.; Holland, N.; et al. Manganese in Teeth and Neurodevelopment in Young Mexican-American Children. Environ. Res. 2015, 142, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciosek, Ż.; Kot, K.; Kosik-Bogacka, D.; Łanocha-Arendarczyk, N.; Rotter, I. The Effects of Calcium, Magnesium, Phosphorus, Fluoride, and Lead on Bone Tissue. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Baaij, J.H.F.; Hoenderop, J.G.J.; Bindels, R.J.M. Magnesium in Man: Implications for Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couce, M.L.; Saenz de Pipaon, M. Bone Mineralization and Calcium Phosphorus Metabolism. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erikson, K.M.; Aschner, M. Manganese: Its Role in Disease and Health. Met. Ions Life Sci. 2019, 19, 253–266. Available online: https://books/9783110527872/9783110527872-016/9783110527872-016.xml (accessed on 27 October 2022). [CrossRef]
- Murshed, M. Mechanism of Bone Mineralization. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a031229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Yang, F.; Ling, M.; Fan, Y. Association between Bone Trace Elements and Osteoporosis in Older Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study. Adv. Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 14, 1759720X221125984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Partridge, N.C. Parathyroid Hormone Signaling in Bone and Kidney. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2009, 18, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntoumanis, N.; Ng, J.Y.Y.; Prestwich, A.; Quested, E.; Hancox, J.E.; Thøgersen-Ntoumani, C.; Deci, E.L.; Ryan, R.M.; Lonsdale, C.; Williams, G.C. A Meta-Analysis of Self-Determination Theory-Informed Intervention Studies in the Health Domain: Effects on Motivation, Health Behavior, Physical, and Psychological Health. Health Psychol. Rev. 2021, 15, 214–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Buhr, E.; Tannen, A. Parental Health Literacy and Health Knowledge, Behaviours and Outcomes in Children: A Cross-Sectional Survey. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inspekcja Ochrony Środowiska. Available online: Http://Powietrze.Gios.Gov.Pl (accessed on 9 September 2022).
- Szczygiel, A.; Pillich, A.; Straszak, K. (Eds.) Estimation of the Air Quality in Silesian Voivodiship in Years 2002–2006 (in Polish: Ocena Jakości Powietrza w Województwie Śląskim w Latach 2002–2006); Wojewódzki Inspektorat Ochrony Środowiska w Katowicach: Katowice, Poland, 2007.
- Bajor, R.; Sosnowska, M.; Tyczyński, A. Atmospheric Pollution in Silesian Voivodiship in Years 2000–2001; Epidemiological Department in Katowice: Katowice, Poland, 2002. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Polak, J.; Bartoszek, M.; Ządło, M.; Kos, A.; Sułkowski, W.W. The Spectroscopic Studies of Humic Acid Extracted from Sediment Collected at Different Seasons. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 1548–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Toral, M.A.; Porter, A.; Schock, M.R. Detection and Evaluation of Elevated Lead Release from Service Lines: A Field Study. Environ. Sci Technol. 2013, 47, 9300–9307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levallois, P.; Barn, P.; Valcke, M.; Gauvin, D.; Kosatsky, T. Public Health Consequences of Lead in Drinking Water. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2018, 5, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, F.; Facio, A.; Villanueva, E.; Pérez, M.L.; Tojo, R.; Gil, A. The Association of Tooth Lead Content with Dental Health Factors. Sci. Total Environ. 1996, 192, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
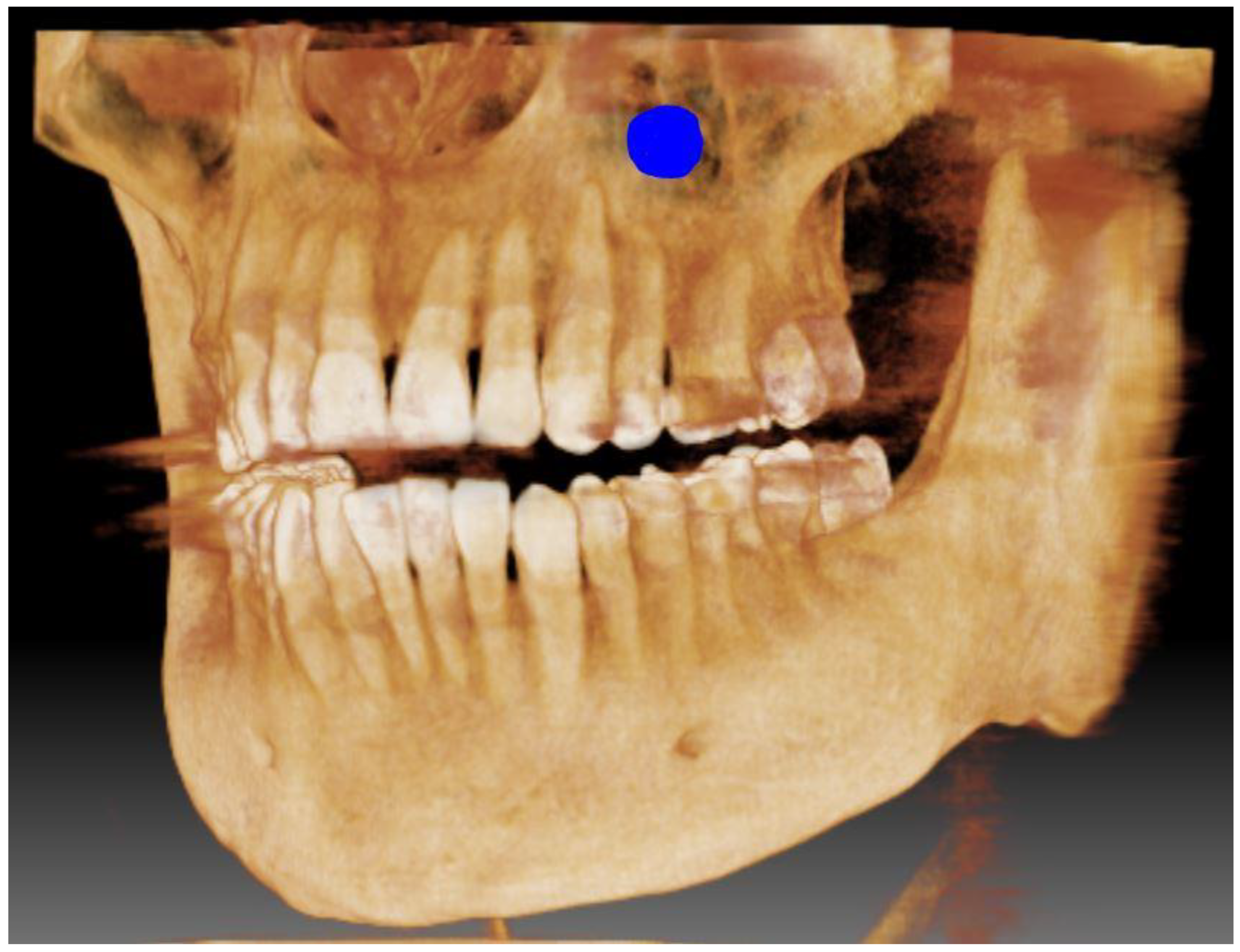
| Samples from People Living in Bielsko-Biala (n = 64) | Samples from People Living in Katowice (n = 62) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element | Mean ± SD | Min–Max | 95% Limit of Confidence | Mean ± SD | Min–Max | 95% Limit of Confidence | p-Level * |
| Pb | 3.26 ± 2.42 | 1.24–7.13 | 2.65–4.95 | 7.66 ± 2.79 | 2.12–14.92 | 6.22–9.12 | <0.001 a |
| Cd | 0.74 ± 0.38 | 0.12–1.86 | 0.42–1.12 | 1.12 ± 0.08 | 0.11–2.87 | 0.98–1.62 | 0.007 a |
| Fe | 21.54 ± 11.44 | 5.66–49.12 | 15.44–28.16 | 18.22 ± 10.74 | 3.12–46.79 | 14.27–21.98 | 0.652 |
| Mn | 1.76 ± 1.11 | 0.14–3.87 | 1.12–2.47 | 4.87 ± 2.22 | 0.27–8.12 | 3.12–5.54 | <0.001 a |
| Cr | 1.82 ± 1.62 | 0.22–4.12 | 1.16–2.53 | 3.96 ± 4.12 | 0.14–15.69 | 2.56–5.78 | 0.022 a |
| Cu | 7.12 ± 4.08 | 1.66–14.29 | 5.14–10.11 | 14.27 ± 7.72 | 4.12–30.16 | 11.77–16.87 | <0.001 a |
| Zn | 149.12 ± 44.29 | 63.27–278.66 | 98.52–211.44 | 246.13 ± 108.92 | 82.45–412.87 | 187.45–301.24 | <0.001 a |
| Element | Women (n = 42) Median | Men (n = 22) Median | U-Value | p-Level * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | 4.12 | 3.06 | 92 | 0.326 |
| Cd | 0.81 | 0.69 | 87 | 0.388 |
| Fe | 19.18 | 26.32 | 98 | 0.422 |
| Mn | 1.94 | 1.52 | 79 | 0.343 |
| Cr | 2.02 | 1.66 | 84 | 0.254 |
| Cu | 8.11 | 5.89 | 88 | 0.366 |
| Zn | 152.75 | 144.54 | 103 | 0.720 |
| Element | Women (n = 39) Median | Men (n = 23) Median | U-Value | p-Level * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | 8.94 | 6.82 | 96 | 0.226 |
| Cd | 1.33 | 1.08 | 101 | 0.824 |
| Fe | 16.89 | 21.24 | 98 | 0.351 |
| Mn | 5.69 | 3.86 | 54 | 0.022 a |
| Cr | 6.62 | 1.54 | 51 | 0.008 a |
| Cu | 18.42 | 9.06 | 48 | 0.048 |
| Zn | 273.12 | 202.33 | 78 | 0.062 |
| Element | 0–7 km (n = 38) Median | 7–14 km (n = 26) Median | U-Value | p-Level * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | 2.98 | 3.42 | 112 | 0.122 |
| Cd | 0.72 | 0.81 | 92 | 0.336 |
| Fe | 22.78 | 19.84 | 84 | 0.082 |
| Mn | 1.62 | 1.84 | 102 | 0.523 |
| Cr | 1.66 | 1.89 | 113 | 0.425 |
| Cu | 7.28 | 6.92 | 99 | 0.226 |
| Zn | 167.23 | 131.26 | 113 | 0.092 |
| Element | 0–7 km (n = 41) Median | 7–14 km (n = 21) Median | U-Value | p-Level * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | 7.92 | 7.24 | 101 | 0.229 |
| Cd | 1.64 | 0.97 | 89 | 0.663 |
| Fe | 16.37 | 19.44 | 92 | 0.811 |
| Mn | 4.12 | 5.29 | 76 | 0.219 |
| Cr | 3.62 | 4.12 | 91 | 0.118 |
| Cu | 13.22 | 15.01 | 78 | 0.328 |
| Zn | 231.22 | 278.19 | 81 | 0.691 |
| Educational Level | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element | Primary (n = 8) Median | Vocational (n = 24) Median | Secondary (n = 15) Median | Higher (n = 17) Median | H-Value | p-Level * |
| Pb | 3.44 | 3.12 | 3.98 | 2.98 | 1.924 | 0.892 |
| Cd | 0.82 | 0.65 | 0.72 | 0.77 | 3.882 | 0.587 |
| Fe | 22.65 | 28.54 | 21.56 | 18.74 | 4.341 | 0.645 |
| Mn | 1.66 | 1.94 | 1.22 | 1.12 | 3.226 | 0.447 |
| Cr | 1.64 | 2.02 | 1.93 | 1.77 | 2.998 | 0.682 |
| Cu | 6.89 | 8.99 | 6.12 | 7.01 | 3.882 | 0.221 |
| Zn | 162.66 | 127.55 | 140.29 | 152.89 | 2.669 | 0.442 |
| Educational Level | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element | Primary (n = 11) Median | Vocational (n = 29) Median | Secondary (n = 14) Median | Higher (n = 8) Median | H-Value | p-Level * |
| Pb | 8.12 | 8.44 | 7.12 | 6.82 | 4.101 | 0.367 |
| Cd | 1.42 | 1.62 | 0.88 | 1.01 | 2.522 | 0.622 |
| Fe | 17.77 | 16.22 | 17.98 | 19.43 | 3.112 | 0.882 |
| Mn | 4.92 | 5.11 | 3.78 | 4.91 | 2.117 | 0.229 |
| Cr | 4.12 | 3.11 | 3.87 | 4.22 | 1.119 | 0.691 |
| Cu | 12.29 | 17.24 | 14.29 | 14.87 | 3.972 | 0.711 |
| Zn | 188.11 | 192.88 | 297.12 | 289.14 | 4.008 | 0.311 |
| Year | Pb in PM 10 [µg/m3] | Cd in PM 10 [ng/m3] | PM 10 [µg/m3] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2006 | Bielsko-Biala | 0.027 | 0.7 | 35.7 |
| Katowice | 0.062 | 1.8 | 58.4 | |
| 2011 | Bielsko-Biala | 0.023 | 0.9 | 43.3 |
| Katowice | 0.051 | 1.9 | 49.9 | |
| 2016 | Bielsko-Biala | 0.026 | 1.0 | 35.8 |
| Katowice | 0.060 | 1.8 | 38.6 | |
| 2021 | Bielsko-Biala | 0.006 | 0.3 | 25.6 |
| Katowice | 0.015 | 0.4 | 32.2 |
| Element | Certified Value | Experimental Value |
|---|---|---|
| Pb | 1.335 ± 0.014 | 1.483 ± 0.024 |
| Cd | 0.011 a | 0.013 ± 0.010 |
| Fe | 99 ± 8 | 112 ± 14 |
| Mn | 1.16 a | 1.32 ± 0.36 |
| Cr | 0.03 b | 0.03 ± 0.010 |
| Cu | 0.8 a | 0.91 ± 0.07 |
| Zn | 147 ± 16 | 141 ± 12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malara, P.; Misiołek, M.; Fischer, A.; Malara, B. The Influence of Environmental Exposure to Heavy Metals on the Occurrence of Selected Elements in the Maxillary Bone. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032552
Malara P, Misiołek M, Fischer A, Malara B. The Influence of Environmental Exposure to Heavy Metals on the Occurrence of Selected Elements in the Maxillary Bone. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(3):2552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032552
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalara, Piotr, Maciej Misiołek, Agnieszka Fischer, and Beata Malara. 2023. "The Influence of Environmental Exposure to Heavy Metals on the Occurrence of Selected Elements in the Maxillary Bone" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 3: 2552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032552
APA StyleMalara, P., Misiołek, M., Fischer, A., & Malara, B. (2023). The Influence of Environmental Exposure to Heavy Metals on the Occurrence of Selected Elements in the Maxillary Bone. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(3), 2552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032552









