Characterization of the First Animal Toxin Acting as an Antagonist on AT1 Receptor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Screening on Angiotensin II Receptors
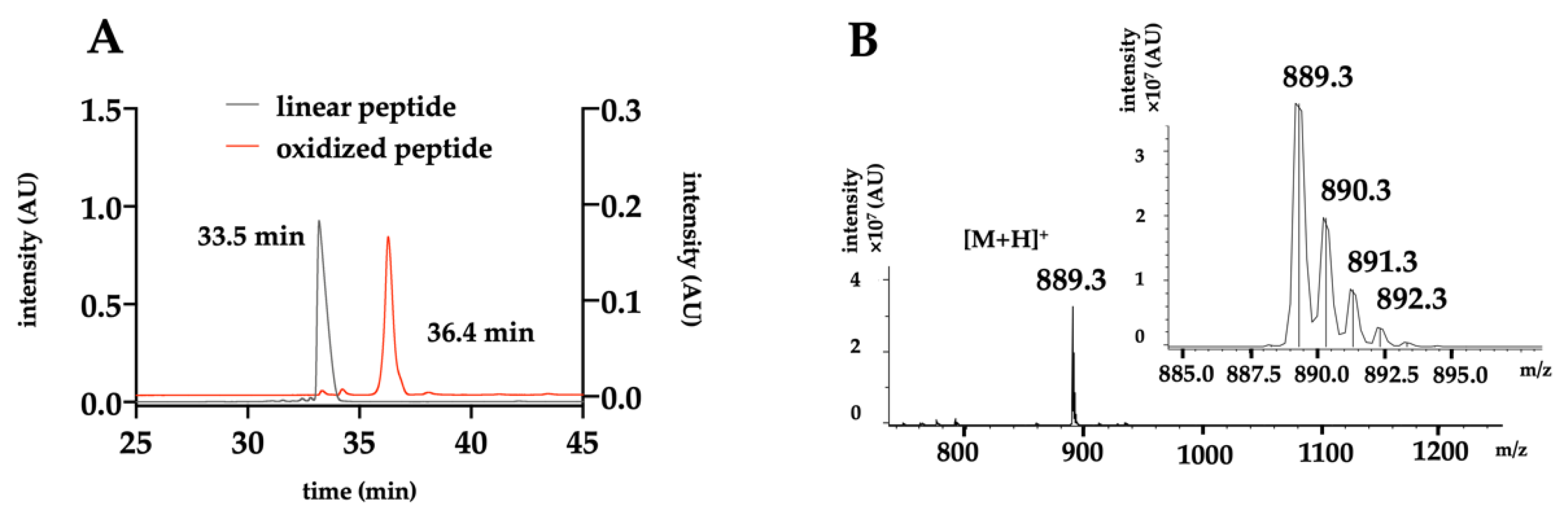
2.2. Chemical Production of the Toxin
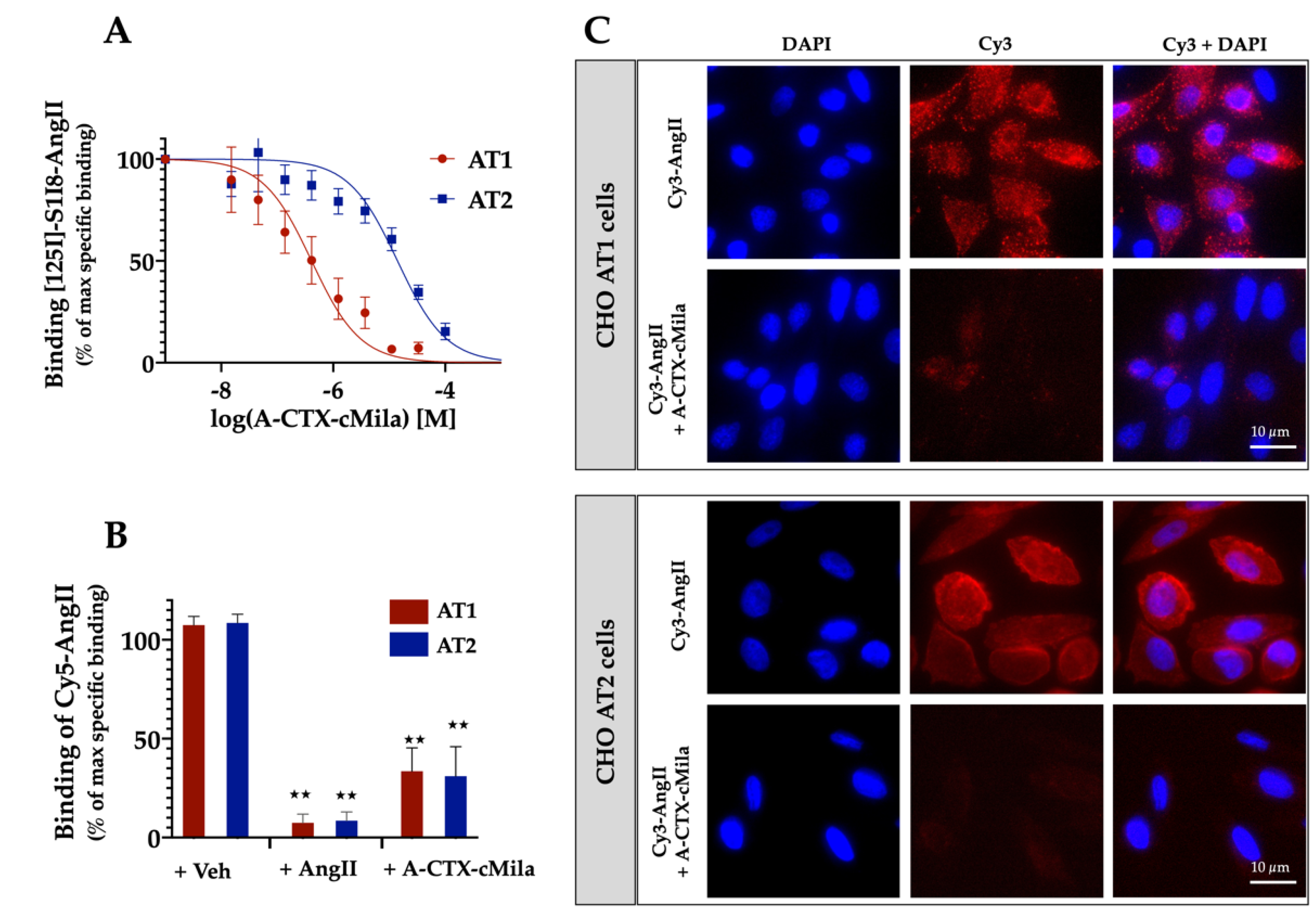
2.3. Binding Properties of A-CTX-cMila on Angiotensin II Receptors
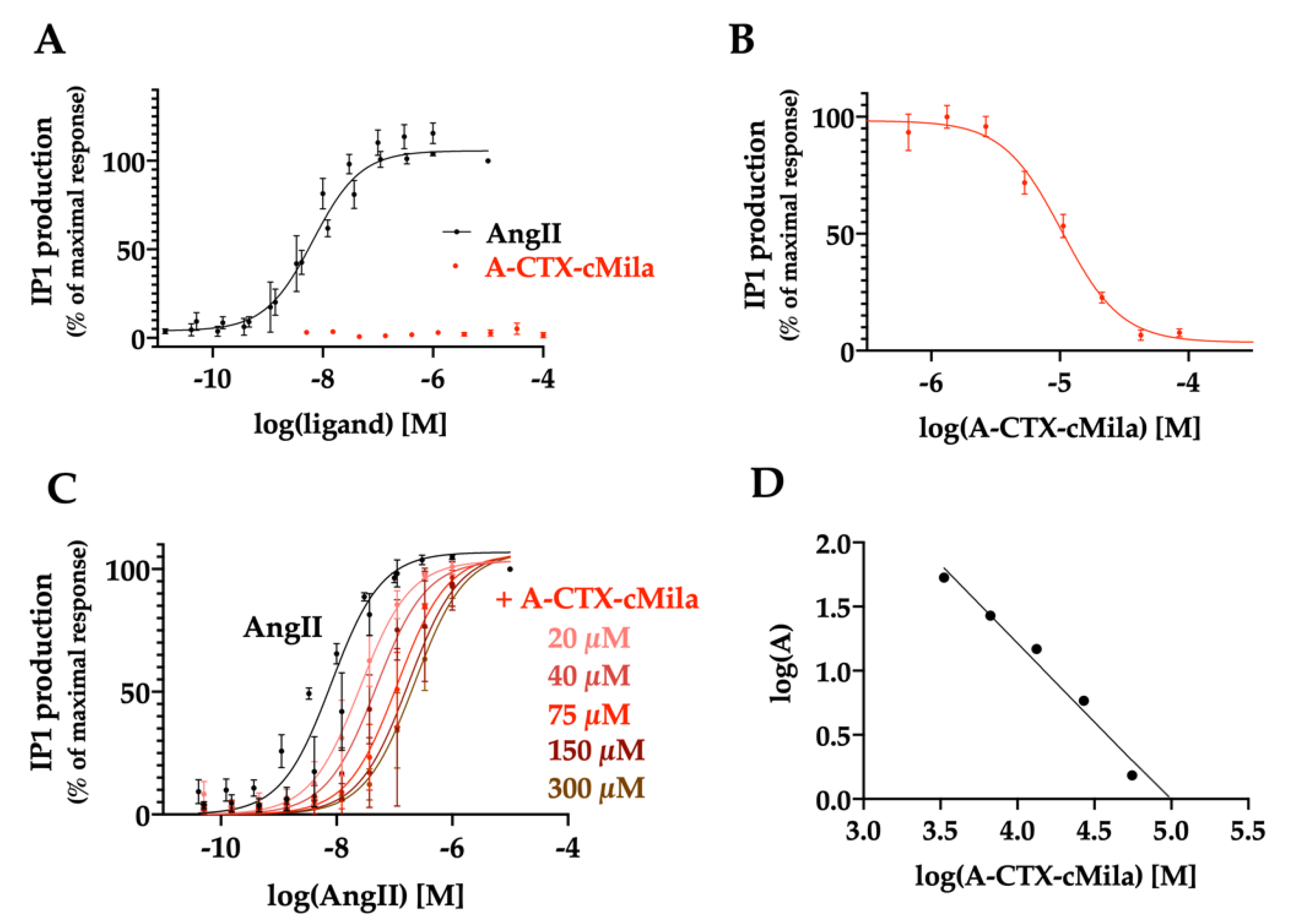
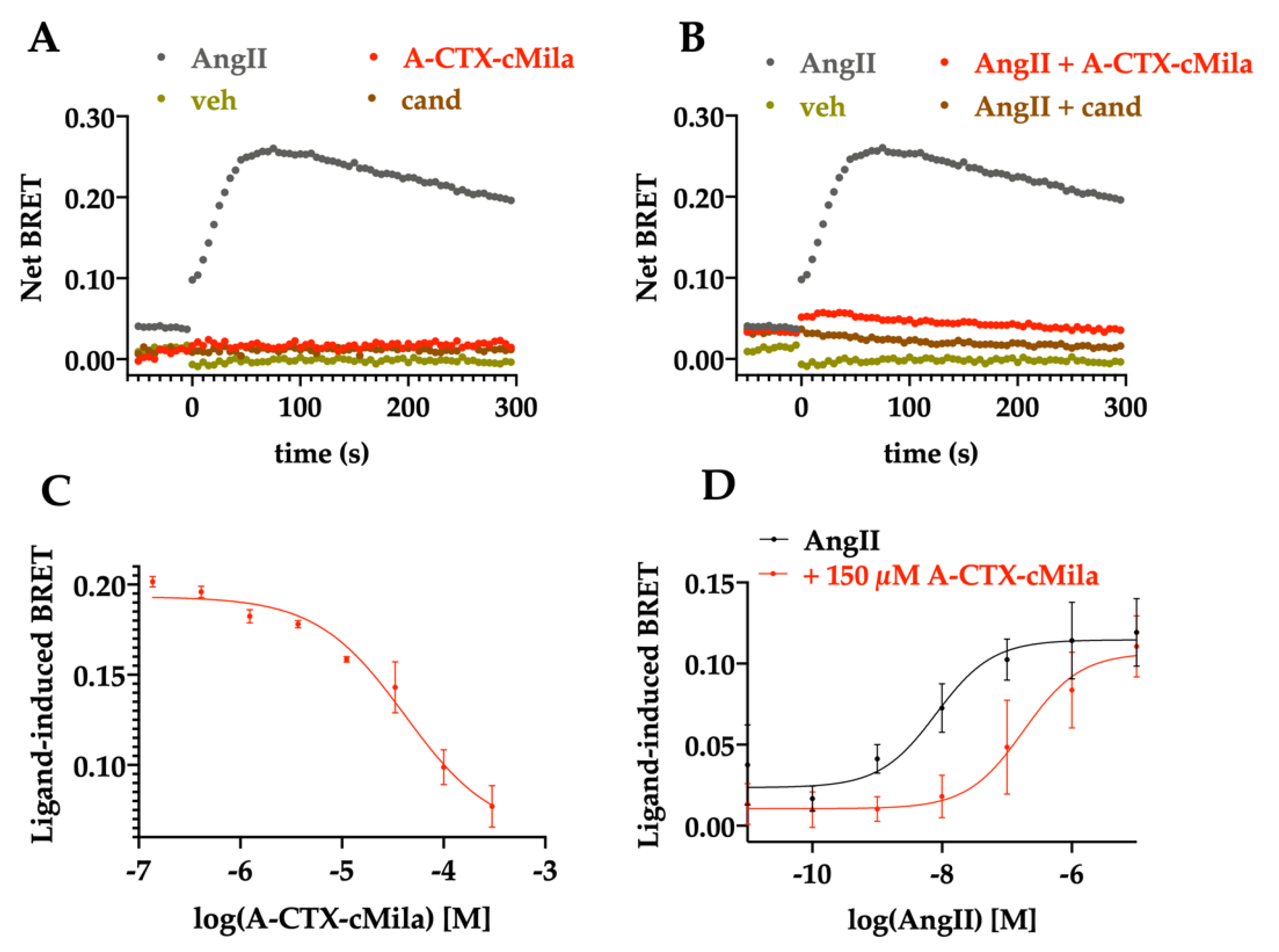
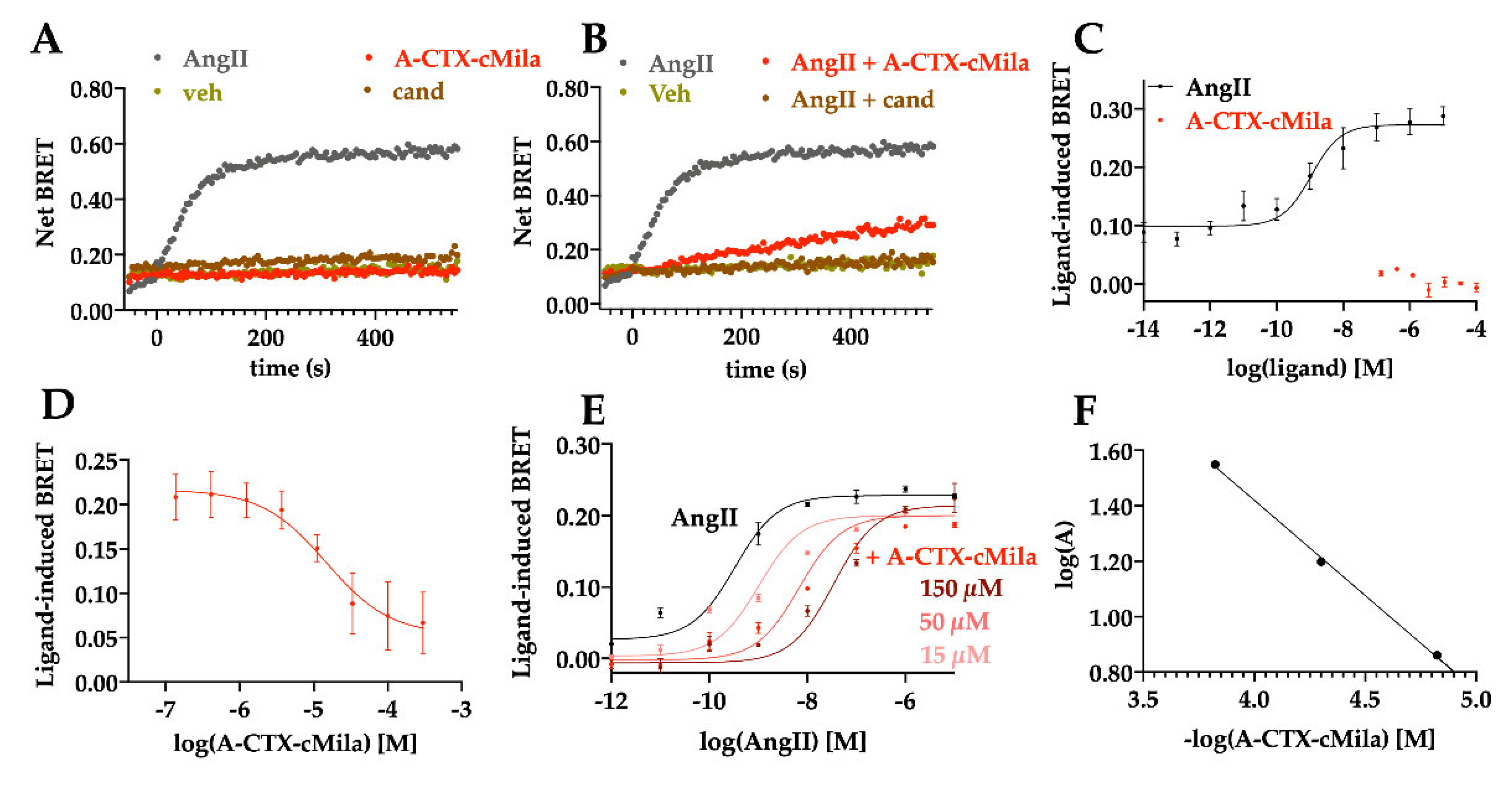
2.4. Pharmacological Characterization of A-CTX-cMila on AT1-Mediated Gαq/PLC Pathway
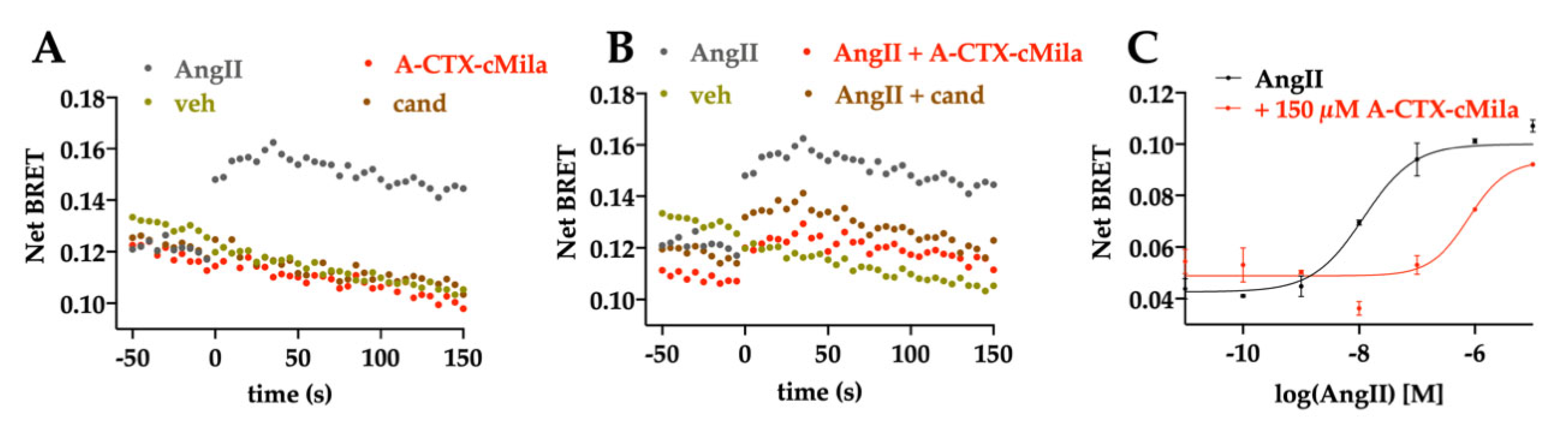
2.5. Pharmacological Characterization of A-CTX-cMila on AT1-Mediated Gαi3 and GαoA Pathways
2.6. Pharmacological Characterization of A-CTX-cMila on AT1-Mediated β-arrestin 2 Recruitment
2.7. Pharmacological Characterization of A-CTX-cMila on AT1-Mediated ERK1/2 Activation
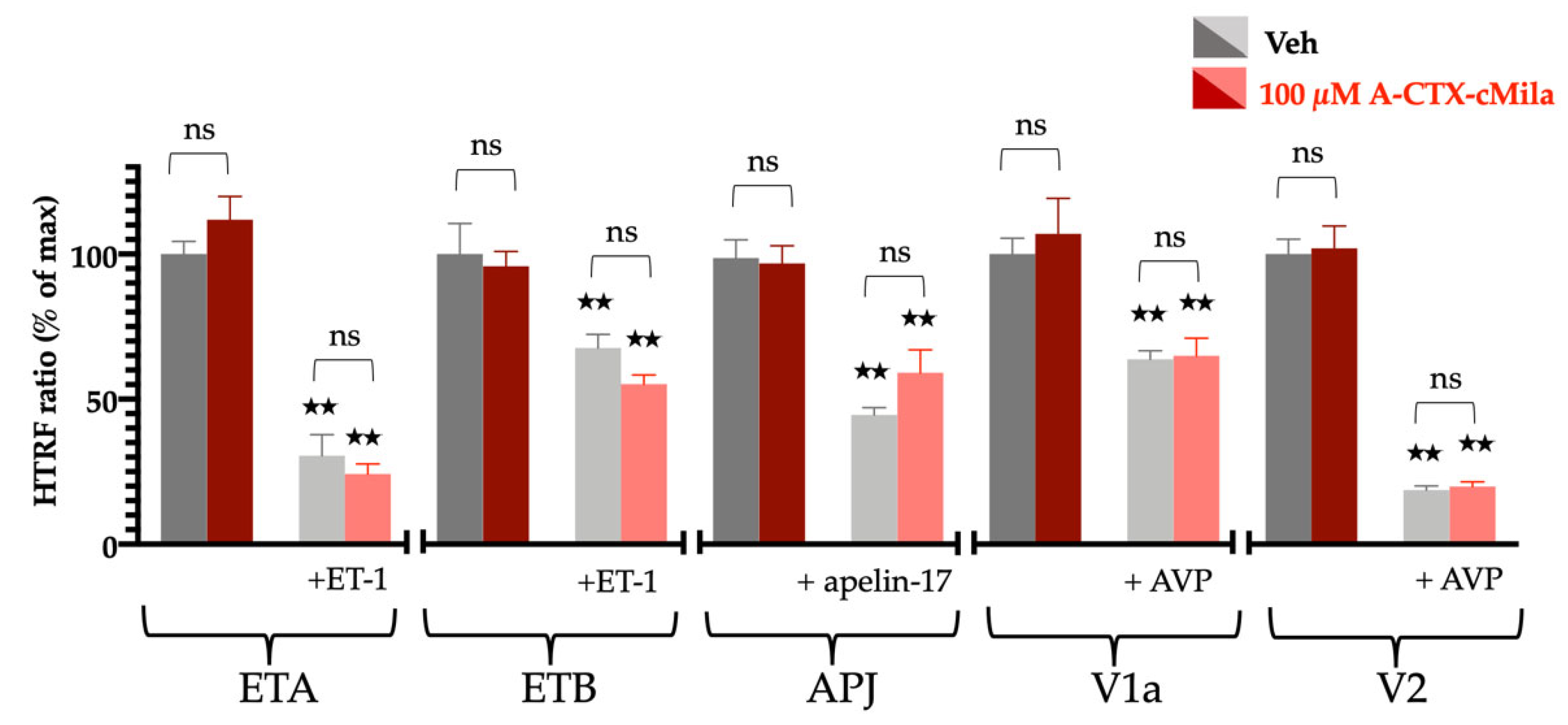
2.8. Selectivity Profile of A-CTX-cMila
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Transfection
4.2. Membrane Preparation
4.3. Radioligand Binding Assays
4.4. Production of A-CTX-cMila
4.5. HPLC Purification and Analysis
4.6. Mass Spectrometry Analysis
4.7. Thermodynamic Oxidation
4.8. Labeling of AngII with Cy3 and Cy5
4.9. Fluorescent-AngII Binding Assays
4.10. Second Messengers Assays
4.10.1. IP1 Assay
4.10.2. cAMP Assay
4.11. β-arrestin 2 Recruitment and Biosensors Assays
4.12. ERK1/2 Activation
4.13. Data Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gilles, N.; Servent, D. The European FP7 Venomics Project. Future Med. Chem. 2014, 6, 1611–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peigneur, S.; Tytgat, J. Toxins in Drug Discovery and Pharmacology. Toxins 2018, 10, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.A.; Day, M.; Heavner, J.E. Ziconotide: An update and review. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2008, 9, 1575–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Baelen, A.-C.; Robin, P.; Kessler, P.; Maïga, A.; Gilles, N.; Servent, D. Structural and Functional Diversity of Animal Toxins Interacting with GPCRs. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 811365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocaranza, M.P.; Riquelme, J.A.; García, L.; Jalil, J.E.; Chiong, M.; Santos, R.A.S.; Lavandero, S. Counter-regulatory renin–angiotensin system in cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, N.E.; Page, I.H. Hypertension produced by constriction of the renal artery in sympathectomized dogs. Am. Heart J. 1937, 14, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuyer, G.; Yates, C.J.; Sturrock, E.D.; Acharya, K.R. Angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE): Structure, biological roles, and molecular basis for chloride ion dependence. Biol. Chem. 2014, 395, 1135–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, I.H.; Helmer, O.M. A crystalline pressor substance (angiotonin) resulting from the reaction between renin and renin-activator. J. Exp. Med. 1940, 71, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottari, S.P.; de Gasparo, M.; Steckelings, U.M.; Levens, N.R. Angiotensin II receptor subtypes: Characterization, signalling mechanisms, and possible physiological implications. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 1993, 14, 123–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukoyama, M.; Nakajima, M.; Horiuchi, M.; Sasamura, H.; Pratt, R.E.; Dzau, V.J. Expression cloning of type 2 angiotensin II receptor reveals a unique class of seven-transmembrane receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 24539–24542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunyady, L.; Catt, K.J. Pleiotropic AT1 Receptor Signaling Pathways Mediating Physiological and Pathogenic Actions of Angiotensin II. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 20, 953–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradis, P.; Dali-Youcef, N.; Paradis, F.W.; Thibault, G.; Nemer, M. Overexpression of angiotensin II type I receptor in cardiomyocytes induces cardiac hypertrophy and remodeling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lijnen, P.J.; Petrov, V.V.; Fagard, R.H. Induction of cardiac fibrosis by transforming growth factor-beta(1). Mol. Genet. Metab. 2000, 71, 418–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bihl, J.C.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Xiao, X.; Ma, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhao, B.; Chen, Y. Angiotensin-(1–7) counteracts the effects of Ang II on vascular smooth muscle cells, vascular remodeling and hemorrhagic stroke: Role of the NFκB inflammatory pathway. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2015, 73, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen Dinh Cat, A.; Montezano, A.C.; Burger, D.; Touyz, R.M. Angiotensin II, NADPH Oxidase, and Redox Signaling in the Vasculature. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 1110–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, T.; Suzuki, C.; Ohnishi, J.; Murakami, K.; Miyazaki, H. Identification of regions in the human angiotensin II receptor type 1 responsible for Gi and Gq coupling by mutagenesis study. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 218, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, S.K.; Lefkowitz, R.J. β-arrestin-mediated receptor trafficking and signal transduction. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 32, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, E.; Ayoub, M.A.; Pellissier, L.P.; Landomiel, F.; Musnier, A.; Tréfier, A.; Gandia, J.; De Pascali, F.; Tahir, S.; Yvinec, R.; et al. β-arrestin signalling and bias in hormone-responsive GPCRs. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2017, 449, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, R.M.; Howell, N.L.; Jin, X.H.; Siragy, H.M. Angiotensin type 2 receptor-mediated hypotension in angiotensin type-1 receptor-blocked rats. Hypertension 2001, 38, 1272–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, R.M.; Padia, S.H. Angiotensin AT2 receptors: Control of renal sodium excretion and blood pressure. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 19, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namsolleck, P.; Recarti, C.; Foulquier, S.; Steckelings, U.M.; Unger, T. AT(2) receptor and tissue injury: Therapeutic implications. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2014, 16, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, B.A.; Howell, N.L.; Gildea, J.J.; Keller, S.R.; Padia, S.H.; Carey, R.M. AT₂ receptor activation induces natriuresis and lowers blood pressure. Circ. Res. 2014, 115, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, T.N.; Saraiva, A.L.L.; Guimarães, R.M.; Luiz, J.P.M.; Pinto, L.G.; de Melo Rodrigues Ávila, V.; Goulart, L.R.; Cunha-Junior, J.P.; McNaughton, P.A.; Cunha, T.M.; et al. Angiotensin type 2 receptor antagonism as a new target to manage gout. Inflammopharmacology 2022, 30, 2399–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehnert, B.; Valero-Esquitino, V.; Schett, G.; Unger, T.; Steckelings, U.M.; Voll, R.E. Angiotensin AT2 Receptor Stimulation Alleviates Collagen-Induced Arthritis by Upregulation of Regulatory T Cell Numbers. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 921488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, O.; Schuh, K.; Brede, M.; Röthlein, N.; Burkard, N.; Hein, L.; Neyses, L. AT2 receptor activation regulates myocardial eNOS expression via the calcineurin-NF-AT pathway. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 283–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Pratt, R.E. The AT2 receptor selectively associates with Gialpha2 and Gialpha3 in the rat fetus. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 15026–15033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.L.; Servant, G.; Baranski, T.J.; Fujita, T.; Iiri, T.; Sheikh, S.P. Functional reconstitution of the angiotensin II type 2 receptor and G(i) activation. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, A.; Holleran, B.J.; Simard, É.; Baillargeon, J.-P.; Lavigne, P.; Leduc, R. Interplay between intracellular loop 1 and helix VIII of the angiotensin II type 2 receptor controls its activation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 168, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hein, L.; Meinel, L.; Pratt, R.E.; Dzau, V.J.; Kobilka, B.K. Intracellular trafficking of angiotensin II and its AT1 and AT2 receptors: Evidence for selective sorting of receptor and ligand. Mol. Endocrinol. 1997, 11, 1266–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Han, G.W.; Batyuk, A.; Ishchenko, A.; White, K.L.; Patel, N.; Sadybekov, A.; Zamlynny, B.; Rudd, M.T.; Hollenstein, K.; et al. Structural basis for selectivity and diversity in angiotensin II receptors. Nature 2017, 544, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipnis, S.R.; Hooper, N.M.; Hyde, R.; Karran, E.; Christie, G.; Turner, A.J. A Human Homolog of Angiotensin-converting Enzyme Cloning and functional expression as a captopril-insensitive carboxypeptidase. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 33238–33243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization Guideline for the Pharmacological Treatment of Hypertension in Adults; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; ISBN 978-92-4-003398-6.
- King, G.F.; Gentz, M.C.; Escoubas, P.; Nicholson, G.M. A rational nomenclature for naming peptide toxins from spiders and other venomous animals. Toxicon 2008, 52, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaas, Q.; Westermann, J.-C.; Craik, D.J. Conopeptide characterization and classifications: An analysis using ConoServer. Toxicon 2010, 55, 1491–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrifield, R.B. Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis. I. The Synthesis of a Tetrapeptide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1963, 85, 2149–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maziarz, M.; Park, J.-C.; Leyme, A.; Marivin, A.; Garcia-Lopez, A.; Patel, P.P.; Garcia-Marcos, M. Revealing the Activity of Trimeric G-proteins in Live Cells with a Versatile Biosensor Design. Cell 2020, 182, 770–785.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couvineau, P.; Llorens-Cortes, C.; Iturrioz, X. Elabela/Toddler and apelin bind differently to the apelin receptor. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 7989–8000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conklin, B.R.; Farfel, Z.; Lustig, K.D.; Julius, D.; Bourne, H.R. Substitution of three amino acids switches receptor specificity of Gq alpha to that of Gi alpha. Nature 1993, 363, 274–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanck, D.A.; Sheets, M.F. Site-3 toxins and cardiac sodium channels. Toxicon 2007, 49, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedro, R.C.A.; Menaldo, D.L.; Costa, T.R.; Zoccal, K.F.; Sartim, M.A.; Santos-Filho, N.A.; Faccioli, L.H.; Sampaio, S.V. Cytotoxic and inflammatory potential of a phospholipase A2 from Bothrops jararaca snake venom. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 24, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducancel, F. The sarafotoxins. Toxicon 2002, 40, 1541–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciolek, J.; Zoukimian, C.; Dhot, J.; Burban, M.; Triquigneaux, M.; Lauzier, B.; Guimbert, C.; Boturyn, D.; Ferron, M.; Ciccone, L.; et al. MT9, a natural peptide from black mamba venom antagonizes the muscarinic type 2 receptor and reverses the M2R-agonist-induced relaxation in rat and human arteries. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 150, 113094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgson, W.C.; Isbister, G.K. The application of toxins and venoms to cardiovascular drug discovery. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2009, 9, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porrello, E.R.; Delbridge, L.M.D.; Thomas, W.G. The angiotensin II type 2 (AT2) receptor: An enigmatic seven transmembrane receptor. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2009, 14, 958–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, S.; Karnik, S.S. Angiotensin II type 1 and type 2 receptors bind angiotensin II through different types of epitope recognition. J. Hypertens. 1999, 17, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamano, Y.; Ohyama, K.; Kikyo, M.; Sano, T.; Nakagomi, Y.; Inoue, Y.; Nakamura, N.; Morishima, I.; Guo, D.F.; Hamakubo, T. Mutagenesis and the molecular modeling of the rat angiotensin II receptor (AT1). J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 14024–14030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noda, K.; Saad, Y.; Karnik, S.S. Interaction of Phe8 of angiotensin II with Lys199 and His256 of AT1 receptor in agonist activation. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 28511–28514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kufareva, I.; Rueda, M.; Katritch, V.; Stevens, R.C.; Abagyan, R. GPCR Dock 2010 participants Status of GPCR modeling and docking as reflected by community-wide GPCR Dock 2010 assessment. Structure 2011, 19, 1108–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Dowd, B.F.; Heiber, M.; Chan, A.; Heng, H.H.; Tsui, L.C.; Kennedy, J.L.; Shi, X.; Petronis, A.; George, S.R.; Nguyen, T. A human gene that shows identity with the gene encoding the angiotensin receptor is located on chromosome 11. Gene 1993, 136, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsault, E.; Llorens-Cortes, C.; Iturrioz, X.; Chun, H.J.; Lesur, O.; Oudit, G.Y.; Auger-Messier, M. The apelinergic system: A perspective on challenges and opportunities in cardiovascular and metabolic disorders. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2019, 1455, 12–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.; Kenward, C.; Rainey, J.K. Apelinergic System Structure and Function. Compr. Physiol. 2017, 8, 407–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, T.; Yanagisawa, M.; Masaki, T. Molecular characterization of endothelin receptors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1992, 13, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, M.; Yanagisawa, M. Endothelin: 30 Years from Discovery to Therapy. Hypertension 2019, 74, 1232–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbach, J.; Goldsmith, S.R. Vasopressin antagonism in heart failure: A review of the hemodynamic studies and major clinical trials. Ther. Adv. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 15, 1753944720977741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, S. Cryo-EM structure of AVP-V2 receptor complex. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2021, 17, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabareesh, V.; Gowd, K.H.; Ramasamy, P.; Sudarslal, S.; Krishnan, K.S.; Sikdar, S.K.; Balaram, P. Characterization of contryphans from Conus loroisii and Conus amadis that target calcium channels. Peptides 2006, 27, 2647–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebbe, E.K.M.; Tytgat, J. In the picture: Disulfide-poor conopeptides, a class of pharmacologically interesting compounds. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 22, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutertre, S.; Croker, D.; Daly, N.L.; Andersson, A.; Muttenthaler, M.; Lumsden, N.G.; Craik, D.J.; Alewood, P.F.; Guillon, G.; Lewis, R.J. Conopressin-T from Conus tulipa reveals an antagonist switch in vasopressin-like peptides. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 7100–7108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giribaldi, J.; Ragnarsson, L.; Pujante, T.; Enjalbal, C.; Wilson, D.; Daly, N.L.; Lewis, R.J.; Dutertre, S. Synthesis, Pharmacological and Structural Characterization of Novel Conopressins from Conus miliaris. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, T.; Oda, T.; Muramatsu, T. Purification and characterization of a dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase from the polychaete Neanthes virens resembling angiotensin I converting enzyme. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2000, 126, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satou, R.; Nakagawa, T.; Ido, H.; Tomomatsu, M.; Suzuki, F.; Nakamura, Y. Angiotensin II and III upregulate body fluid volume of the clam worm Perinereis sp. via angiotensin II receptors in different manners. Peptides 2005, 26, 2452–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynaud, S.; Ciolek, J.; Degueldre, M.; Saez, N.J.; Sequeira, A.F.; Duhoo, Y.; Brás, J.L.A.; Meudal, H.; Cabo Díez, M.; Fernández Pedrosa, V.; et al. A Venomics Approach Coupled to High-Throughput Toxin Production Strategies Identifies the First Venom-Derived Melanocortin Receptor Agonists. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 8250–8264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, T.J.; Alexander, R.W.; Griendling, K.K.; Runge, M.S.; Bernstein, K.E. Isolation of a cDNA encoding the vascular type-1 angiotensin II receptor. Nature 1991, 351, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmugam, S.; Llorens-Cortes, C.; Clauser, E.; Corvol, P.; Gasc, J.M. Expression of angiotensin II AT2 receptor mRNA during development of rat kidney and adrenal gland. Am. J. Physiol. 1995, 268, F922–F930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Van Baelen, A.-C.; Iturrioz, X.; Chaigneau, M.; Kessler, P.; Llorens-Cortes, C.; Servent, D.; Gilles, N.; Robin, P. Characterization of the First Animal Toxin Acting as an Antagonist on AT1 Receptor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2330. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032330
Van Baelen A-C, Iturrioz X, Chaigneau M, Kessler P, Llorens-Cortes C, Servent D, Gilles N, Robin P. Characterization of the First Animal Toxin Acting as an Antagonist on AT1 Receptor. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(3):2330. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032330
Chicago/Turabian StyleVan Baelen, Anne-Cécile, Xavier Iturrioz, Marion Chaigneau, Pascal Kessler, Catherine Llorens-Cortes, Denis Servent, Nicolas Gilles, and Philippe Robin. 2023. "Characterization of the First Animal Toxin Acting as an Antagonist on AT1 Receptor" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 3: 2330. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032330
APA StyleVan Baelen, A.-C., Iturrioz, X., Chaigneau, M., Kessler, P., Llorens-Cortes, C., Servent, D., Gilles, N., & Robin, P. (2023). Characterization of the First Animal Toxin Acting as an Antagonist on AT1 Receptor. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(3), 2330. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032330






